Trawl Fishing Fleet Operations Used to Illustrate the Life Cycle of the Southern Brown Shrimp: Insights to Management and Sustainable Fisheries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
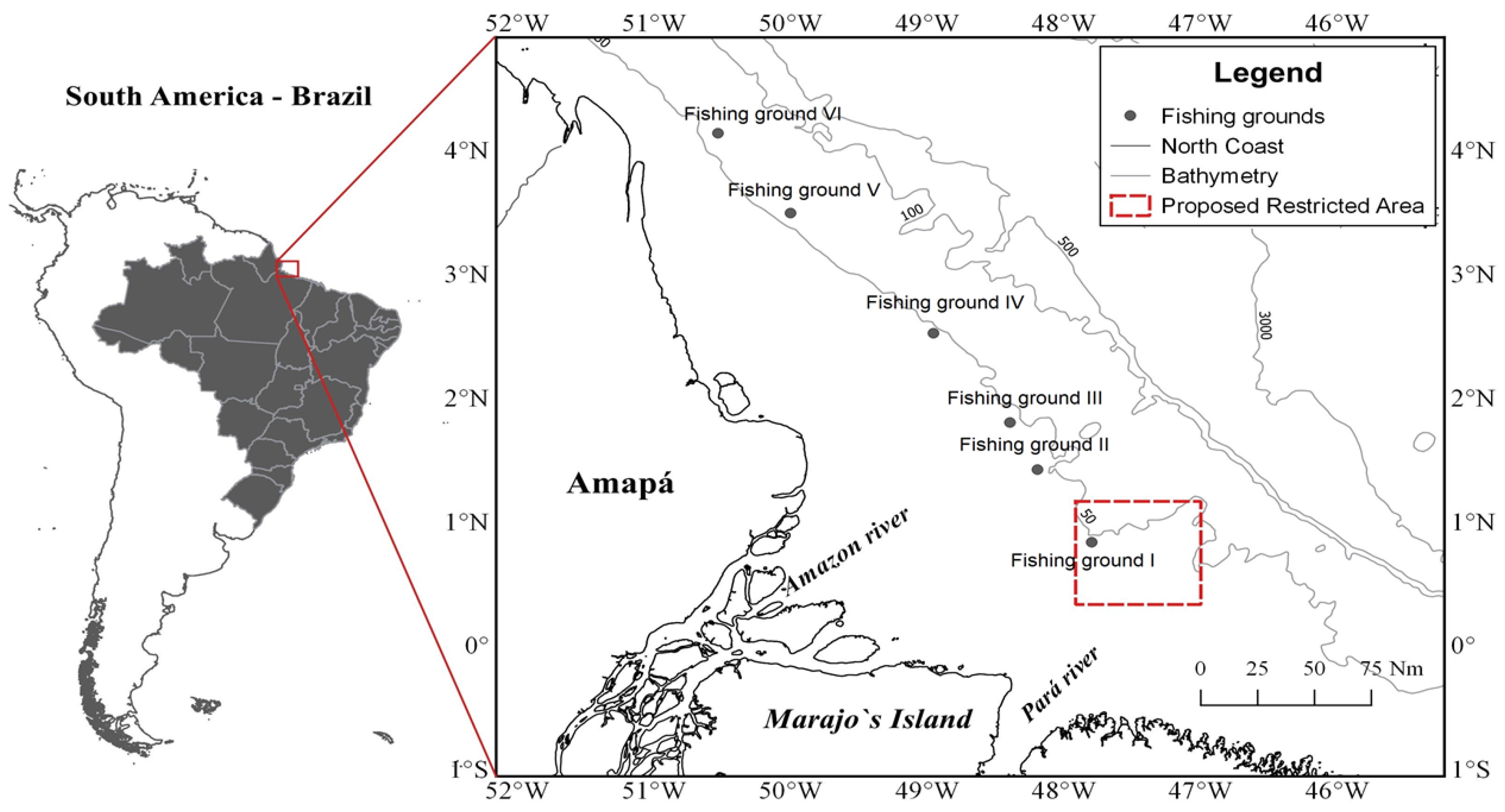
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Shrimp Data
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Total Length Mean
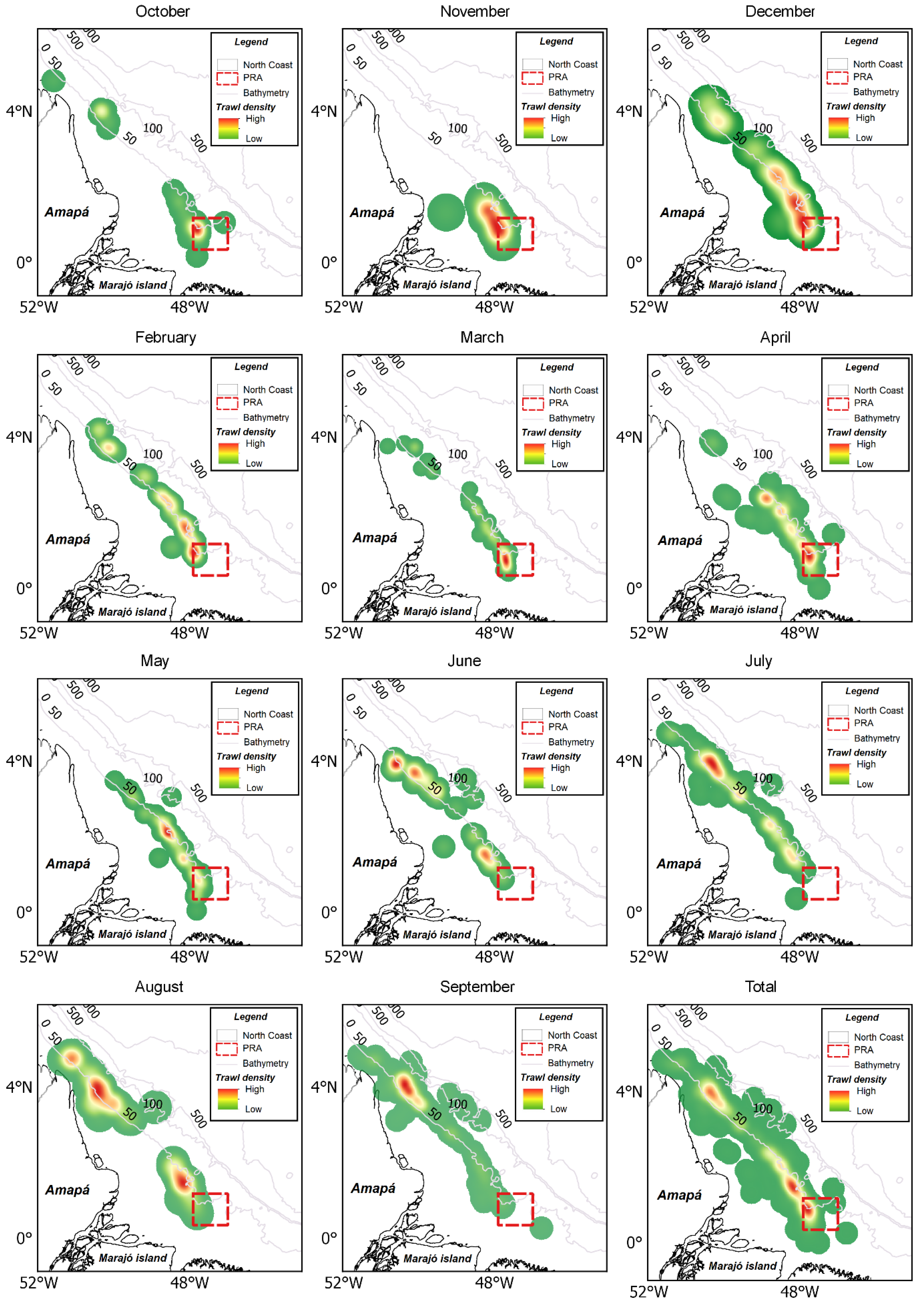
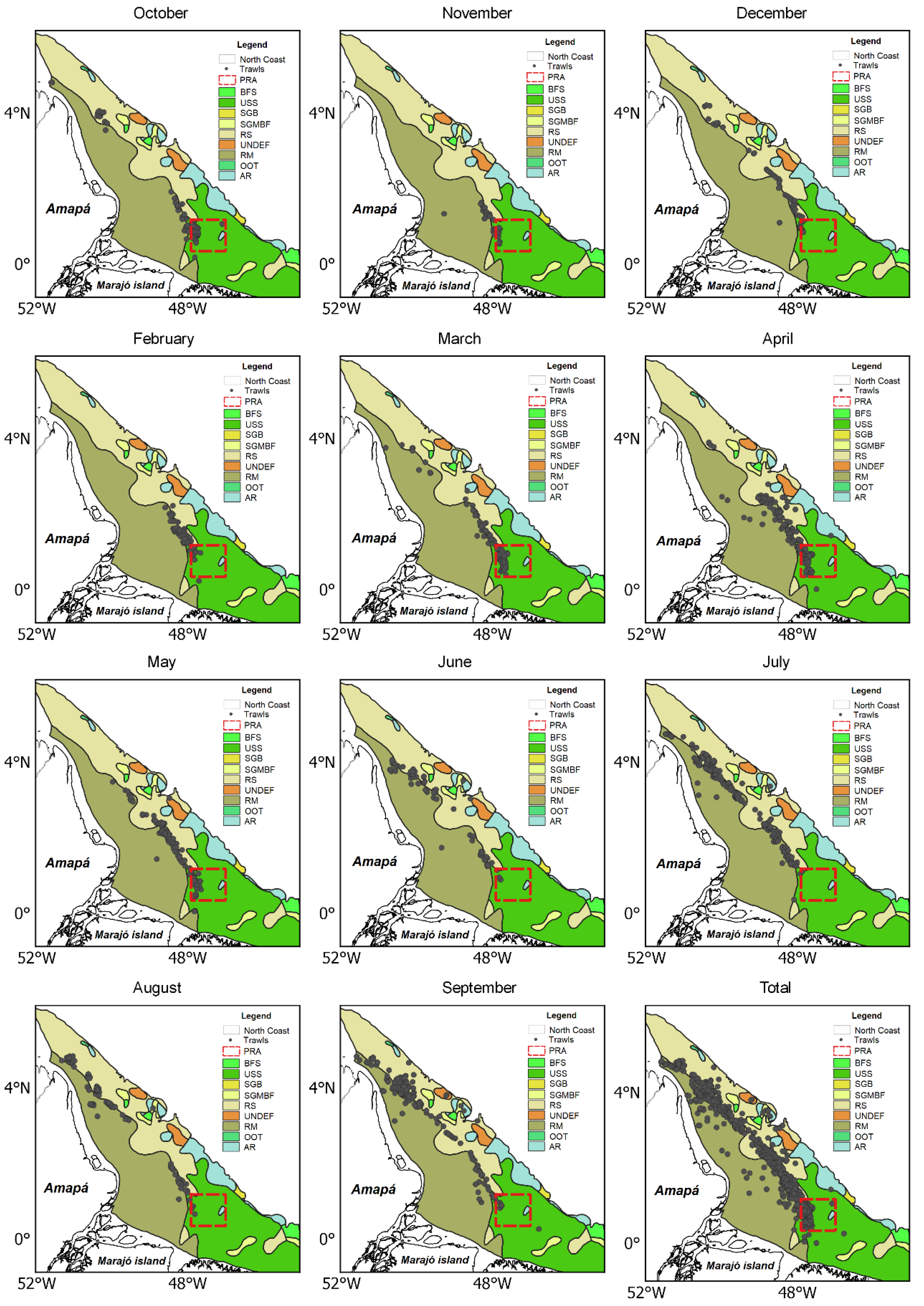
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Fleet Dynamic
3.3. Spatial and Temporal Shrimp Distribution Pattern
3.4. No-Take Area and Spatiotemporal Dynamics
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Fishing Fleet and Size Composition
4.2. Management Measures and No-Take Zones
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Farfante, I.; Kensley, B.F. Penaeids and Sergestoid Shrimps and Prawns of the World: Keys and Diagnoses for the Families and Genera. In Mémoires du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, 175; Muséum National d’Histoire naturelle: Paris, France, 1997; p. 233. [Google Scholar]
- Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Fisheries Department. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Sustainability in Action; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2020; p. 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, R. Global Study of Shrimp Fisheries; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2008; p. 331. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018—Meeting Thesustainable Development Goals; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2018; Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/I9540EN/ (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Silva-Júnior, C.A.B.; Lira, A.S.; Eduardo, L.N.; Viana, A.P.; Lucena-Frédou, F.; Frédou, T. Ichthyofauna bycatch of the artisanal fishery of penaeid shrimps in Pernambuco, northeastern, Brazil. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2019, 45, e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.E.G.; Camargo-Zorro, M.S.F.; Walfir, P.M.; Cintra, I.H.A.; Silva, K.C.A. Spatial distribution of southern brown shrimp (Farfantepenaeus subtilis) on the Amazon continental shelf: A fishery, marine geology and GIS integrated approach. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2015, 63, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noleto-Filho, E.M.; Pucciarelli, P.; Dumont, L.F.C. Spatial and temporal variation in juvenile size distribution of the pink shrimp (Penaeus paulensis) in the Patos Lagoon Estuary, Brazil. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Pesca e Aquicultura—MPA. Boletim Estatistico da Pesca e Aquicultura; Ministério da Pesca e Aquicultura: Brasilia, Brasil, 2011; p. 60.
- Tavares, C.; Gusmão, J. Description of a new Penaeidae (Decapoda: Dendrobranchiata) species, Farfantepenaeus isabelae sp. nov. Zootaxa 2016, 4171, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, N.; Alencar, C.; Mantelatto, F.; Freire, F. Filling biogeographic gaps about the shrimp Farfantepenaeus isabelae Tavares & Gusmão, 2016 (Decapoda: Penaeidae) in South America. Zootaxa 2020, 4718, 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Dragovich, A. Guianas-Brazil shrimp fishery and related U. S. research activity. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1981, 43, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Isaac, V.J.; Dias-Neto, J.; Damasceno, F.G. Camarão-Rosa da Costa Norte: Biologia, Dinâmica E Administração Pesqueira; Série de Estudos de Pesca, Coleção Meio Ambiente; Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis—IBAMA: Brasília, Brazil, 1992; p. 187.
- Isaac, V.J.; Braga, T. Rejeição de pescado nas pescarias da costa Norte do Brasil. Arq. Ciência Mar. 1999, 32, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, U.I.; Bentes, B.; Andrade, H.A.; Isaac, V.J. Length-based assessment of southern brown shrimp stock from trawl fisheries on the Amazon Continental Shelf. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e44410817394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, J.A.N.; Silva, K.C.A.; Ehrhardt, N.M.; Seijo, J.C.; Die, D. Brazil Northern pink shrimp fishery. FAO Fish. Rep. 2001, 651, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Aragão, J.A.N.; Cintra, I.H.A.; Silva, K.C.A. Situação da pesca de camarões na plataforma continental amazônica. Acta Fish. Aquat. Ressour. 2015, 3, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’incao, F. Taxonomia, Padrões Distribucionais E Ecológicos Dos Dendrobranchiata (Crustacea: Decapoda) Do Litoral Brasileiro. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dall, W.; Hill, B.J.; Rothisberg, P.C.; Staples, D.J. The biology of the Penaeidae. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1990, 27, 489. [Google Scholar]
- Macia, A. Juvenile penaeid shrimp density, spatial distribution and size composition in four adjacent habitats within a mangrove—Fringed bay on Inhaca Island, Mozambique. West. Indian Ocean. J. Marone Sci. 2004, 3, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rönnbäck, P.; Macia, A.; Almqvist, G.; Schultz, L.; Troell, M. Do penaeid shrimps have a preference for mangrove habitats? Distribution pattern analysis on Inhaca Island, Mozambique. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 55, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra, I.H.A.; Aragão, J.A.N.; Silva, K.C.A.; Petrere Júnior, M. Crescimento e mortalidade de Penaeus subtilis (Decapoda, Penaeidae) na Plataforma Continental Amazônica. Arquivo Ciências Mar. 2021, 54, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentes, B.; Isaac, V.J.; Espírito-Santo, R.V.; Frédou, T.; Almeida, M.C.; Mourão, K.R.M.; Frédou, F.L. Multidisciplinary approach to identification of fishery production systems on the northern coast of Brazil. Biota Neotropica 2012, 12, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis—IBAMA. Estatística da Pesca 2007 Brasil: Grandes Regiões E Unidades da Federação; IBAMA: Brasília, Brazil, 2007; p. 151.
- Araújo, J.G.; Mello Filho, A.S.; Peixoto, U.I.; Bentes, B.; Santos, M.A.S.; Dutka-Gianelli, J.; Isaac, V. Multidimensional Evaluation of Brown Shrimp Trawling Fisheries on the Amazon Continental Shelf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, e801758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, Portaria Interministerial MDIC/MMA nº 15, de 10 de Janeiro de 2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/aquicultura-e-pesca/legislacao/arrasto/portaria-mdic-mma-no-15-de-10-01-2018.pdf/view (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Brasil, Portaria Interministerial nº 75, de 20 de dezembro de 2017. 2017. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/aquicultura-e-pesca/legislacao/defesos/portaria-interministerial-mdic-mma-no-75_12_2017.pdf/view (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Brasil, Portaria SUDEPE nº N-11 de 13 de maio de 1987. 1980. Available online: https://www.icmbio.gov.br/cepsul/images/stories/legislacao/Portaria/1987/p_sudepe_11_n_1987_areaexclusaopescaarrasto_pa_ma_am_ap.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Cutrim, R.S.F.; Silva, K.C.A.; Cintra, I.H.A. Composição dos recursos pesqueiros capturados na área da “lixeira”, Pará, Brasil. Bol. Técnico Cient. CEPNOR 2001, 1, 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- MMA. Áreas Prioritárias Para a Conservação, Uso Sustentável E Repartição De Benefícios da Biodiversidade Brasileira: Atualização, 2nd ed.; Série Biodiversidade, 31; Portaria MMA n. 9; MMA/SBF: Brasília, Brazil, 2007; p. 328.
- Rufino, M.L. Projeto Áreas Marinhas E Costeiras Protegidas—GEFMar Identificação E Caracterização Das Áreas Relevantes Para a Pesca Artesanal E Das Principais Interações Com Espécies da Megafauna Marinha Sensíveis Biologicamennte Na Região Norte (AP, PA, MA e PI); Ministerio do Meio Ambiente—MMA: Brasilia, Brasil, 2018.
- Respondek, G.; Gröger, J.; Floeter, J.; Temming, A. Variability of fishing effort for the German brown shrimp (Crangon crangon) fishing fleet: Influencing factors, and seasonal and spatial patterns. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Temming, A.; Günther, C.; Rückert, C.; Hufnagl, M. Understanding the life cycle of North Sea brown shrimp Crangon crangon: A simulation model approach. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 584, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milisenda, G.; Garofalo, G.; Fiorentino, F.; Colloca, F.; Maynou, F.; Ligas, A.; Musumeci, C.; Bentes, L.; Gonçalves, J.M.S.; Erzini, K.; et al. Identifying Persistent Hot Spot Areas of Undersized Fish and Crustaceans in Southern European Waters: Implication for Fishery Management Under the Discard Ban Regulation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J. Scientific Basis for Fishery Policy and Management. In The Future of Ocean Governance and Capacity Development E-Book; Boudreau, P.R., Brooks, M.R., Butler, M.J.A., Charles, A., Coffen-Smout, S., Griffiths, D., McAllister, I., McConnell, M.L., Porter, I., Rolston, S.J., et al., Eds.; International Ocean Institute: Halifax, NS, Canada, 2018; pp. 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Isaac, V.J.; Ferrari, S.F. Assessment and management of the North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystem. Environ. Dev. 2017, 22, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, N.A.; Gherardi, D.F.M.; Aragão, L.E.O.C. The role of the Amazon River plume on the intensification of the hydrological cycle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 12221–12229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthem, R.B.; Schwassmann, H.O. The Amazon river influence over the seasonal displacement of the salty wedges in Tocantins estuary, Brazil, 1983–1985. Bol. Mus. Para. Emílio Goeldi 1994, 10, 119–130. Available online: http://repositorio.museu-goeldi.br/handle/mgoeldi/496 (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Geyer, W.R.; Beardsley, R.C.; Lentz, S.J.; Candela, J.; Limeburner, R.; Johns, W.E.; Castro, B.M.; Soares, I.D. Physical oceanography of the amazon shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1996, 16, 575–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filizola, N.; Silva, A.V.; Santos, A.M.C.; Oliveira, M.A. Cheias e secas na Amazônia: Breve abordagem de um contraste na maior bacia hidrográfica do mundo. TC Amaz. 2006, 9, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, J.; Seo, K.W.; Ryu, D. Estimation of amazon river discharge based on EOF analysis of grace gravity data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.M.; Guyot, J.L.; Filizola, N.; Sondag, F. Increase in suspended sediment discharge of the Amazon River assessed bymonitoring network and satellite data. Catena 2009, 79, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varona, H.L.; Veleda, D.; Silva, M.; Cintra, M.; Araujo, M. Amazon River plume influence on Western Tropical Atlantic dynamic variability, Dynam. Atmos. Ocean. 2019, 85, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Santos, M.L.S.; Araujo, M.C.; Bourlès, B. Observações hidrológicas e resultados de modelagem no espalhamento sazonal e espacial da pluma de água Amazônica. Acta Amaz. 2009, 39, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Araújo, M.; Medeiros, C.; Silva, M.; Bourlès, B. Seasonal changes in the mixed and barrier layers in the western equatorial Atlantic. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2005, 53, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ffield, A. North Brazil current rings viewed by TRMM Microwave Imager SST and the influence of the Amazon Plume, Deep Sea Research Part I. Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2005, 52, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cintra, I.H.A.; Aragão, J.A.N.; Silva, K.C.A. Maturação gonadal do camarão-rosa, Farfantepenaeus subtilis (Pérez-Farfante, 1967), na região norte do Brasil. Bol. Técnico Cient. CEPNOR 2004, 4, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Johannes, R.E.; Freeman, M.M.R.; Hamilton, R.J. Ignore fishers’ knowledge and miss the boat. Fish Fish. 2000, 1, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.S.P.; Oliveira, J.E.L.; De Nóbrega, M.F.; Lopes, P.F.M. The use of Local Ecological Knowledge as a complementary approach to understand the temporal and spatial patterns of fishery resources distribution. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine 2017, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgess, M.G.; Polasky, S.; Tilman, D. Predicting overfishing and extinction threats in multispecies fisheries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15943–15948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romney, A.K.; Weller, S.C.; Batchelder, W.H. Culture as consensus: A theory of culture and informant accuracy. Am. Anthropol. 1986, 88, 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hind, E.J. A review of the past, the present, and the future of fishers’ knowledge research: A challenge to established fisheries science. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 72, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, S.M. Reproduction, stock-assessment models and population parameters in exploited penaeid shrimp populations. In Second Australian National Prawn Seminar; Rothlisberg, P.C., Hill, B.J., Staples, D.J., Eds.; NPS2: Cleveland, Australia, 1985; pp. 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- García, S. Tropical penaeid prawns. In Fish Population Dynamics: The Implications for Management, 2nd ed.; Gulland, J.A., Ed.; American Fisheries Society: Sydney, Australia, 1988; pp. 219–249. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, E.F.; Calazans, N.; Nolé, L.; Viana, A.; Soares, R.; Peixoto, S.; Frédou, F.L. Population dynamics of the pinkshrimp Farfantepenaeus subtilis (Pérez-Farfante, 1967) in northeastern Brazil. J. Crustacean Biol. 2015, 35, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, R.R.C. Field experiments on growth and mortality of Penaeus vannamei in a Mexico coastal lagoon complex. Estuarine Coast. Mar. Sci. 1977, 5, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Reyna, C.E. Growth and Emigration of White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in the Mar Muerto Lagoon, Southern Mexico. Naga. ICLARM Q. 2001, 24, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, R.G.; Greenwood, J.G. Seasonal movement and size distribution of three commercially important Australian prawn species (Crustacea: Penaeidae) within an estuarine system. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1983, 34, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillanders, B.; Kingsford, M. Impact of Changes in Flow of Freshwater on Estuarine and Open Coastal Habitats and the Associated Organisms. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2002, 40, 233–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwyther, D. The importance of the Purari River Delta to the prawn trawl fishery of the Gulf of Papua. In The Purari—Tropical Environment of a High Rainfall River Basin; Petr, T., Ed.; Monographiae Biologicae; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdussamad, E.M. Emigration dynamics of three species of penaeid prawn from backwaters and tidal ponds of Cochin, India. Bengladesh J. Fish. Res. 2008, 12, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Souza-Júnior, A.N.; Magalhães, A.; Pereira, L.C.C.; Costa, R.M.D. Zooplankton dynamics in a tropical Amazon estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.L.; Hufford, G.; Limeburner, R.; Brown, W. North Brazil Current retroflection eddies. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 5081–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.R.; Garcia, S. The relationship between stock and recruitment in the shrimp stocks of Kuwait and Saudi Arabia. Océanogrphie Trop. 1982, 17, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Penn, J.W.; Caputi, N. Spawning stock recruitment relationships and environmental influenceson the tiger prawn (Penaeus esculentus) fishery in Exmouth Gulf, Western Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1986, 37, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A. Spawning Stock–Recruitment Relationships of White Shrimp in the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1991, 120, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.M. Stock-recruitment relationships and the precautionary approach to management of tropical shrimp fisheries. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1996, 47, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y. Is recruitment related to spawning stock in penaeid shrimp fisheries? ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minello, T.J.; Zimmerman, R.J.; Martinez, E.X. Mortality of young brown shrimp Penaeus aztecus in estuarine nurseries. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1989, 118, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, M.J.; Sissenwine, M.P.; Cohen, E.B. Recruitment variability and the dynamics of exploited marine populations. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1991, 6, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, R.W. Influence of environmental variation and spawning stock Bevels on recruitment of ocean shrimp (Pandalus jordani). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Die, D. Stock-recruitment relationships of the tiger prawns (Penaeus esculentus and Penaeus semisulcatus) in the Australian northern prawn fishery. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1996, 47, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Castañeda, R.; Defeo, O. Growth and mortality of transient shrimp populations (Farfantepenaeus spp.) in a coastal lagoon of Mexico: Role of the environment and density-dependence. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, N.; Diop, B.; Blanchard, F.; Lampert, L. On the influence of environmental factors on harvest: The French Guiana shrimp fishery paradox. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2016, 19, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peixoto, U.I.; Mesquita, E.M.C.; Cintra, I.A.H.; Klautau, A.G.M.; Gouveia, N.A.; Paes, E.T.; Isaac, V.J. 2020. Population dynamics and sustainability of the spiny lobster (Panulirus meripurpuratus Giraldes & Smyth, 2016) fishery on the Amazon continental shelf. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 72, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, R.; Sanderson, M.; Woodward, S. Effects of large-scale Amazon forest degradation on climate and air quality through fluxes of carbon dioxide, water, energy, mineral dust, and isoprene. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, V. Conditional Fishery Status as a Solution to Overcapitalization in the Gulf of Mexico Shrimp Fishery. Mar. Fish. Rev. 2004, 43, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chemonics. Subsector Assessment of the Nigerian Shrimp and Prawn Industry; Chemonics International Inc., Agricultural Development Assistance in Nigeria: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D.; Ingles, J. The relationship between shrimp yields and intertidal vegetation (mangrove) areas: A reassessment. In Ecosistemas de Manglar en América Tropical; Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Lara-Domínguez, A.L., Eds.; UNESCO IOC/FAO Workshop Report Suplement: Ciudade del Carmen, Mexico, 1999; Volume 44, p. 380. Available online: http://www1.inecol.edu.mx/cv/CV_pdf/libros/Ecosistemas_Manglar_2014.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Andriguetto-Filho, J.; Natividade, C.; Brandini, F.; Teixeira, R. Local hydrography and fishing drive life cycle strategies and population dynamics of the sea-bob shrimp Xiphopenaeus kroyeri in a coastal subtropical environment in Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2016, 771, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, N.; Pepin, P.; Han, G.; Ma, Z. Potential impact of climate change on northern shrimp habitats and connectivity on the Newfoundland and Labrador continental shelves. Fish Oceanogr. 2021, 30, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Mare, W.K. Marine ecosystem based management as a hierarchical control system. Marine Policy 2005, 29, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.W.D.; Cripps, S.J.; Nickson, A.; Porter, G. Defining and estimating global marine fisheries bycatch. Mar. Policy 2009, 33, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Source | df | SS | MS | F. Model | R2 | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F.G. | 5 | 765.16 | 153.031 | 228.387 | 0.30177 | *** |
| Months | 10 | 391.99 | 39.199 | 58.501 | 0.15460 | *** |
| Depths | 4 | 17.64 | 4.411 | 6.583 | 0.00696 | *** |
| Residuals | 1124 | 753.14 | 0.670 | 0.29214 | ||
| Total | 1280 | 2535.58 | 1.00000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peixoto, U.I.; Mello-Filho, A.S.; Bentes, B.; Isaac, V.J. Trawl Fishing Fleet Operations Used to Illustrate the Life Cycle of the Southern Brown Shrimp: Insights to Management and Sustainable Fisheries. Fishes 2022, 7, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030141
Peixoto UI, Mello-Filho AS, Bentes B, Isaac VJ. Trawl Fishing Fleet Operations Used to Illustrate the Life Cycle of the Southern Brown Shrimp: Insights to Management and Sustainable Fisheries. Fishes. 2022; 7(3):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030141
Chicago/Turabian StylePeixoto, Ualerson I., Adauto S. Mello-Filho, Bianca Bentes, and Victoria J. Isaac. 2022. "Trawl Fishing Fleet Operations Used to Illustrate the Life Cycle of the Southern Brown Shrimp: Insights to Management and Sustainable Fisheries" Fishes 7, no. 3: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030141
APA StylePeixoto, U. I., Mello-Filho, A. S., Bentes, B., & Isaac, V. J. (2022). Trawl Fishing Fleet Operations Used to Illustrate the Life Cycle of the Southern Brown Shrimp: Insights to Management and Sustainable Fisheries. Fishes, 7(3), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030141






