Differential Study of Microbiota in the Gill and Intestine of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from the Algae-Dominated and Hydrophyte-Dominated Areas of Taihu Lake, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Measurements of Physicochemical Parameters
2.4. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification, and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characterization of Fish and Physicochemical Parameters of Water
3.2. High-Throughput Sequencing Data and Microbial Composition in Fish and Water
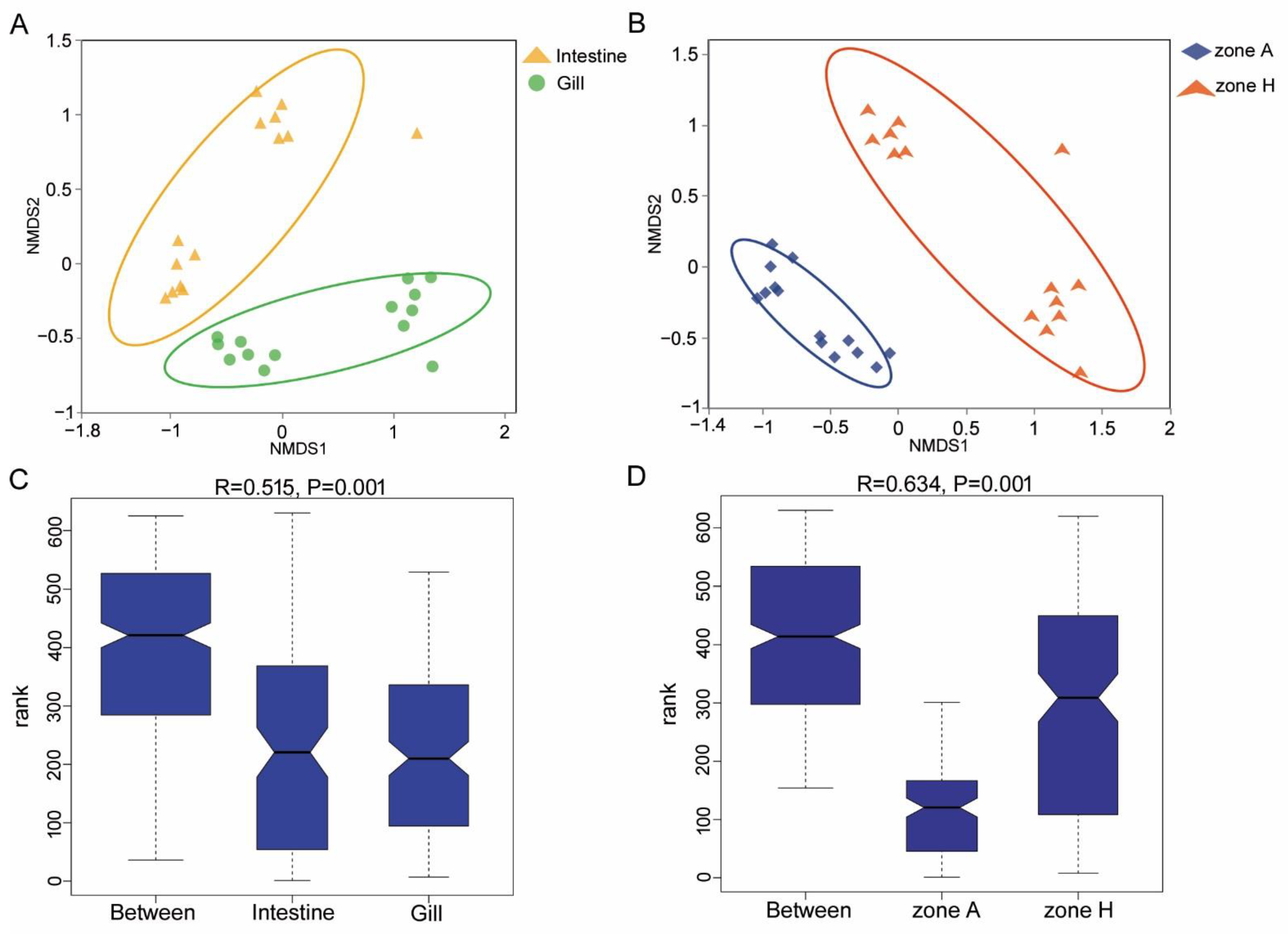
3.3. Diversity Analysis
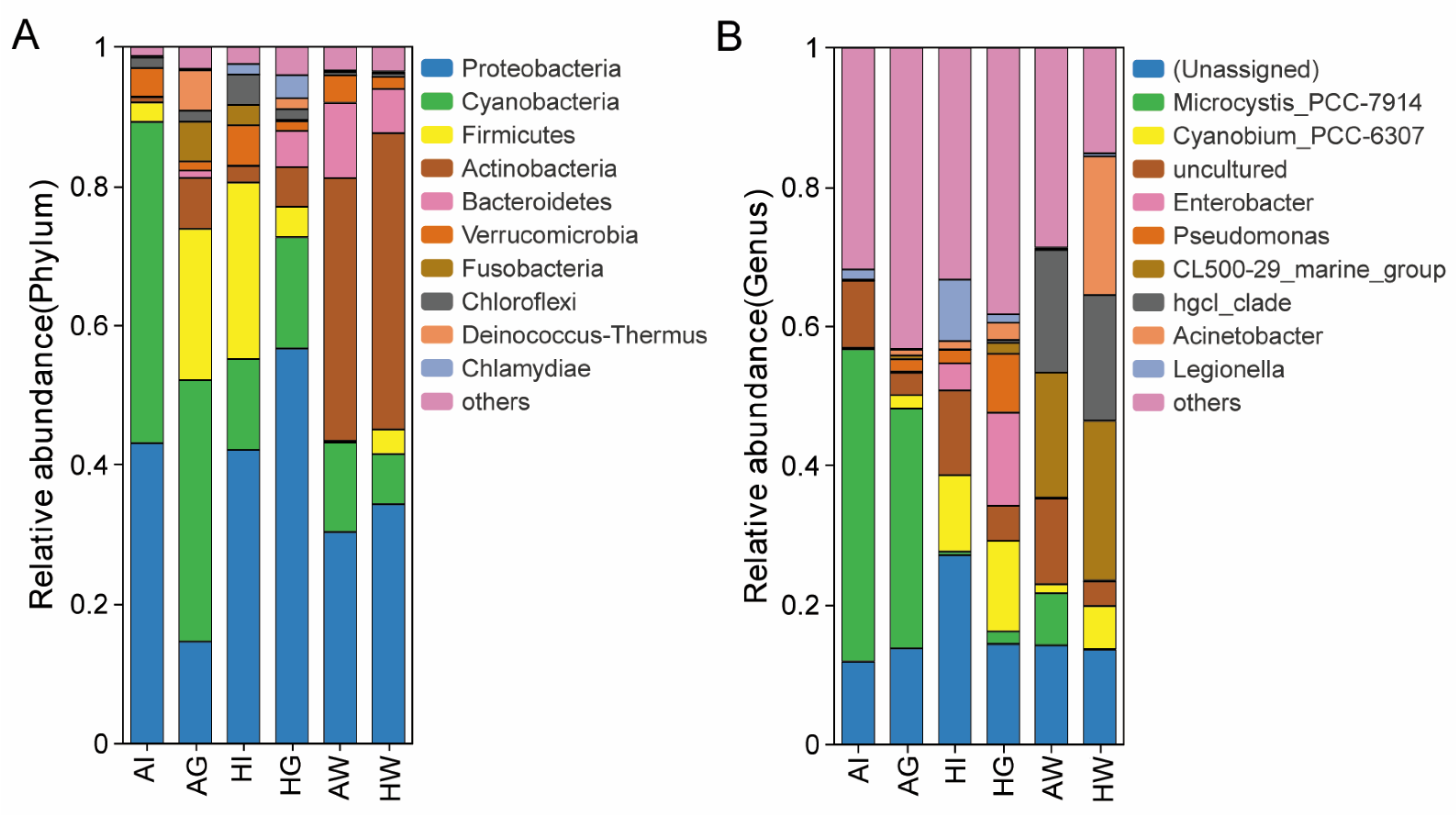
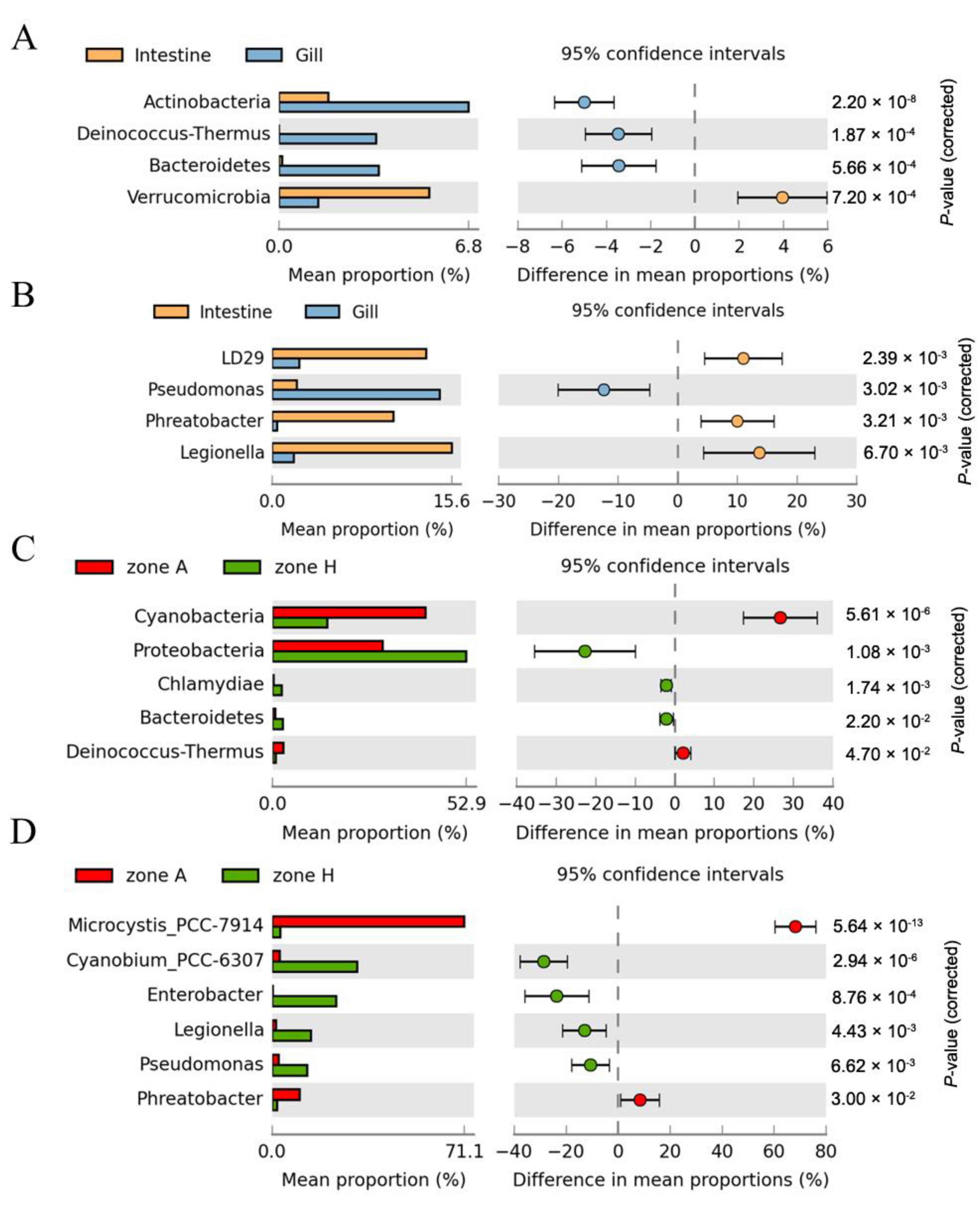
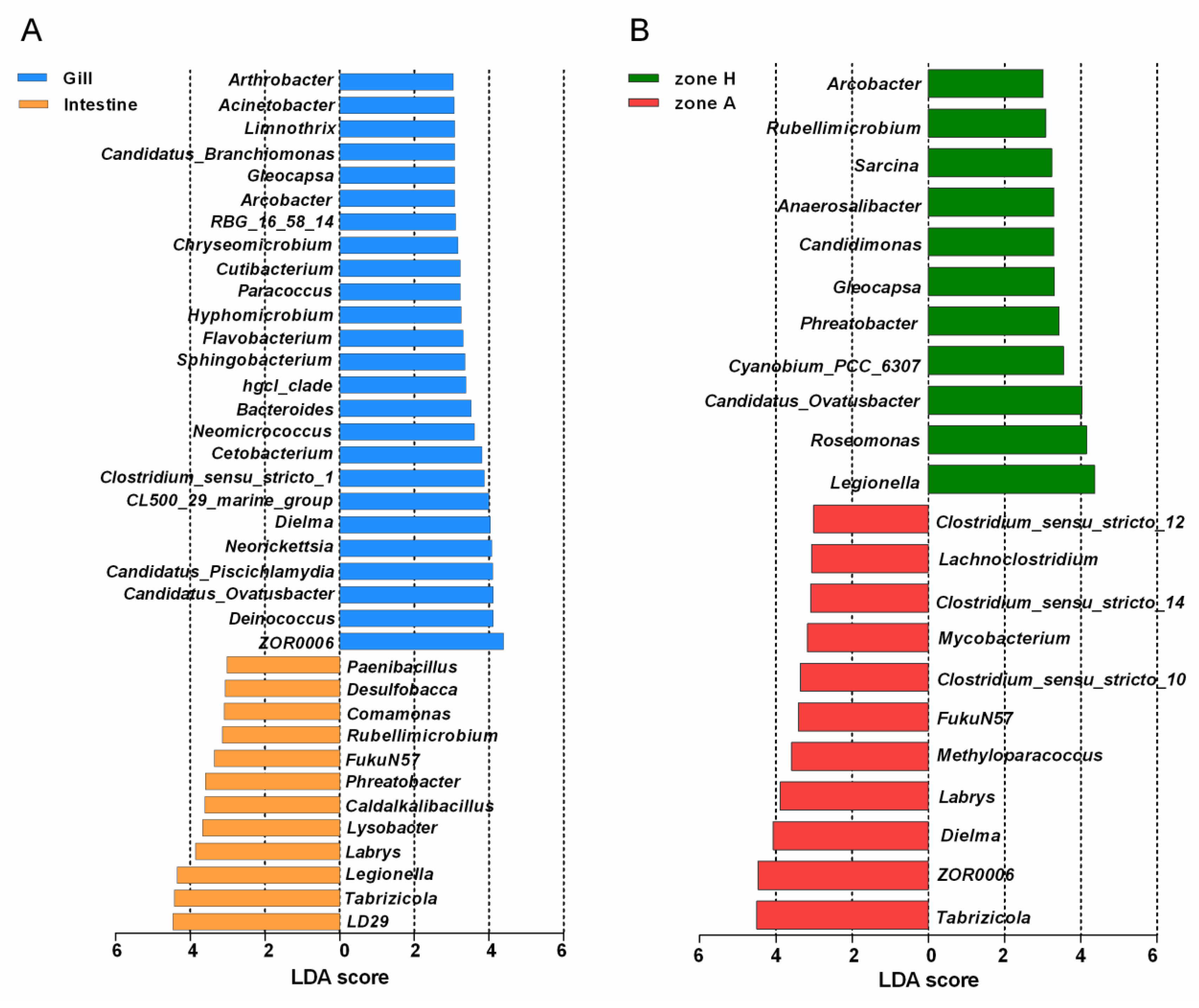
3.4. Composition Analysis
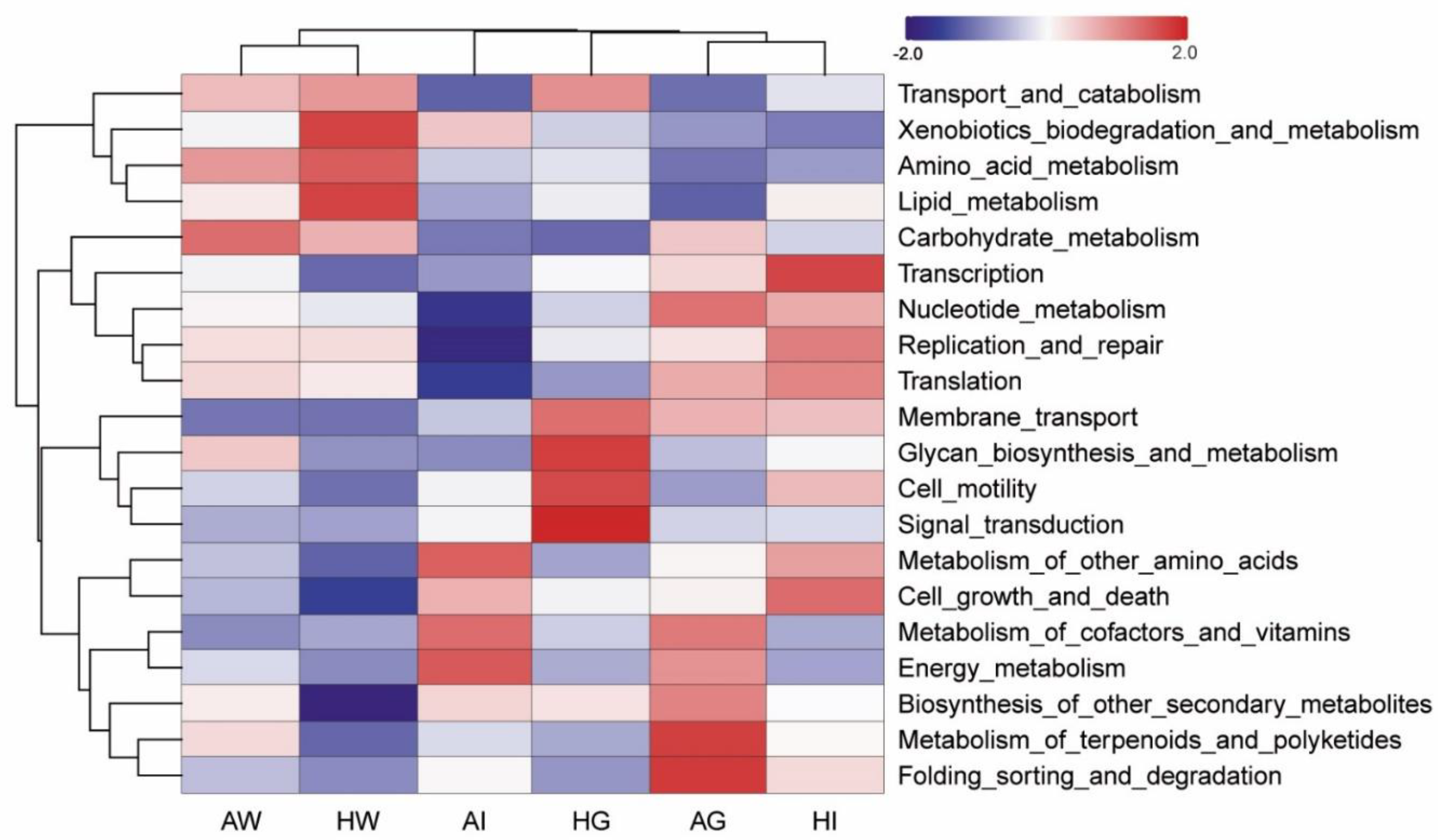
3.5. Function Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Kessel, M.A.; Dutilh, B.E.; Neveling, K.; Kwint, M.P.; Veltman, J.A.; Flik, G.; Jetten, M.S.; Klaren, P.H.; Op den Camp, H.J. Pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons to study the microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). AMB Express 2011, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, G.; Ray, A.K. Bacterial symbiosis in the fish gut and its role in health and metabolism. Symbiosis 2017, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.M.; Mohammed, H.H.; Arias, C.R. Characterization of the gut microbiota of three commercially valuable warmwater fish species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.; Nguyen, P.; Nguyen, D.; Dierckens, K.; Boon, N.; Lacoere, T.; Kerckhof, F.M.; De Vrieze, J.; Vadstein, O.; Bossier, P. Gut Microbiota of Migrating Wild Rabbit Fish (Siganus guttatus) Larvae Have Low Spatial and Temporal Variability. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 79, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.S.; Zhu, W.G.; Yu, Y.H.; He, Z.L.; Wu, B.; Wang, C.; Shu, L.F.; Li, X.H.; Yin, H.Q.; Wang, J.J.; et al. Host development overwhelms environmental dispersal in governing the ecological succession of zebrafish gut microbiota. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, F.-É.; Holland, A.; Bouslama, S.; Audet-Gilbert, É.; Lavoie, C.; Val, A.L.; Derome, N. Fish Skin and Gut Microbiomes Show Contrasting Signatures of Host Species and Habitat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00789-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, G.; Angert, E.R.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zou, H. Composition, diversity, and origin of the bacterial community in grass carp intestine. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, J.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Nakazawa, T.; Sakai, Y.; Papa, R.D.; Hsieh, C.H.; Okuda, N. Long-term changes in the diet of Gymnogobius isaza from Lake Biwa, Japan: Effects of body size and environmental prey availability. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, M.; Ying, C.; Yin, D.; Dai, P.; Yang, Y.; Ye, K.; Liu, K. The intestinal microbiota of lake anchovy varies according to sex, body size, and local habitat in Taihu Lake, China. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e00955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F. Intestinal microbiota composition in fishes is influenced by host ecology and environment. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3100–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Z. Insights into the intestinal microbiota of several aquatic organisms and association with the surrounding environment. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost microbiomes: The state of the art in their characterization, manipulation and importance in aquaculture and fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, D.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Pereira, A.; Severino, R.; Xavier, R. Effects of aging on the skin and gill microbiota of farmed seabass and seabream. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, T.; Catalano, S.R.; Wos-Oxley, M.L.; Stephens, F.; Landos, M.; Bansemer, M.S.; Stone, D.A.J.; Qin, J.G.; Oxley, A.P.A. The Inner Workings of the Outer Surface: Skin and Gill Microbiota as Indicators of Changing Gut Health in Yellowtail Kingfish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.B.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Lin, Y.Y.; Hao, J.W.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, A.H. Taxonomic and Functional Characteristics of the Gill and Gastrointestinal Microbiota and Its Correlation with Intestinal Metabolites in NEW GIFT Strain of Farmed Adult Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guivier, E.; Pech, N.; Chappaz, R.; Gilles, A. Microbiota associated with the skin, gills, and gut of the fish Parachondrostoma toxostoma from the Rhone basin. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, T.; He, A.; Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhou, L. Comparative analysis of microbial communities associated with the gill, gut, and habitat of two filter-feeding fish. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Cai, C.; He, J.; Song, X.; Xu, G.; Zhou, J. A comparative study of the algae control effect of bighead carp in three lakes of Yangcheng Lake. J. Water Ecol. 2020, 41, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Xu, D.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Shan, J. Effects of bighead carp release on phytoplankton in the Sanguocheng waters of Taihu Lake. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2018, 33, 666–673. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ni, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Yan, Q. Comparative study on gastrointestinal microbiota of eight fish species with different feeding habits. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Sun, J.; Pang, Y. Effects of different habitats on the bacterial community composition in the water and sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44983–44994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C. Eutrophication and Aquatic Community Structure in Taihu Lake. Master’s Thesis, Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Fang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Yuan, Z. Analysis of the current pollution situation of water bodies around Taihu Lake. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 29, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.L.; Zwart, G.; Wu, J.; Kamst-van Agterveld, M.P.; Liu, S.; Hahn, M.W. Submersed macrophytes play a key role in structuring bacterioplankton community composition in the large, shallow, subtropical Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jia, G.; Wu, H. Chlorophyll-a concentration variation characteristics of the alage-dominated and macrophyte-dominant ares in Taihu and its driving factors, 2007–2019. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.L.; Wen, S.L.; Li, X.; Gong, W.Q.; Liu, D.H.; Zhong, J.C. Characteristics of N2O release and influencing factors in grass-type and algea-type zones of taihu lake during summer. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, W.; Hyde, E.R.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Parada, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Caporaso, J.G.; Fuhrman, J.A.; et al. Improved Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene (V4 and V4-5) and Fungal Internal Transcribed Spacer Marker Gene Primers for Microbial Community Surveys. mSystems 2015, 1, e00009-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, M.T.; Lawrence, A.D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Nature 2005, 438, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.G.; Yong, C.; Li, J.L.; Chen, L.Q. The food web structure and ecosystem properties of a filter-feeding carps dominated deep reservoir ecosystem. Ecol. Model. 2007, 203, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnecki, A.M.; Brennan, N.P.; Schloesser, R.W.; Rhody, N.R. Shifts in the Skin-Associated Microbiota of Hatchery-Reared Common Snook Centropomus undecimalis during Acclimation to the Wild. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttaswamygowda, G.H.; Olakkaran, S.; Antony, A.; Kizhakke Purayil, A. Chapter 22—Present Status and Future Perspectives of Marine Actinobacterial Metabolites. In Recent Developments in Applied Microbiology and Biochemistry; Buddolla, V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 307–319. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Ussery, D.W.; Nielsen, J.; Nookaew, I. A closer look at bacteroides: Phylogenetic relationship and genomic implications of a life in the human gut. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardman, Z.; Arnosti, C.; Durbin, A.; Ziervogel, K.; Cox, C.; Steen, A.D.; Teske, A. Verrucomicrobia are candidates for polysaccharide-degrading bacterioplankton in an arctic fjord of Svalbard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, M.; Mulet, M.; Altun, S.; Saticioglu, I.B.; Gomila, M.; Lalucat, J.; García-Valdés, E. Pseudomonas anatoliensis sp. nov and Pseudomonas iridis sp. nov. isolated from fish. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, S.; Modry, D.; Pafčo, B.; Zurek, L. Bacterial Community of the Digestive Tract of the European Medicinal Leech (Hirudo verbana) from the Danube River. Invertebr. Microbiol. 2019, 77, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Q.Z.; Zhen, Y.T.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Lan, T.C.; Huang, L.D.; Shen, P.H. Effects of dietary Metschnikowia sp. GXUS03 on growth, immunity, gut microbiota and Streptococcus agalactiae resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duperron, S.; Halary, S.; Habiballah, M.; Gallet, A.; Huet, H.; Duval, C.; Bernard, C.; Marie, B. Response of Fish Gut Microbiota to Toxin-Containing Cyanobacterial Extracts: A Microcosm Study on the Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Gao, R.; Yan, X.; Huang, L.; Qin, H. Probiotics improve gut microbiota dysbiosis in obese mice fed a high-fat or high-sucrose diet. Nutrition 2019, 60, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabadé, D.S.; Wolkers-Rooijackers, J.C.; Azokpota, P.; Hounhouigan, D.J.; Zwietering, M.H.; Nout, M.J.; den Besten, H.M. Bacterial concentration and diversity in fresh tropical shrimps (Penaeus notialis) and the surrounding brackish waters and sediment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassenruck, C.; Reinwald, H.; Kunzmann, A.; Tiedemann, I.; Gardes, A. Effects of Thermal Stress on the Gut Microbiome of Juvenile Milkfish (Chanos chanos). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, F.; Cheaib, B.; Llewellyn, M.; Gabriel Correia, T.; Barros Fagundes, D.; Luis Val, A.; Derome, N. pH drop impacts differentially skin and gut microbiota of the Amazonian fish tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, D. Impairment of the intestine barrier function in Litopenaeus vannamei exposed to ammonia and nitrite stress. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 78, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yan, Z.; Sun, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Sun, B. Toxic effects of ammonia on the intestine of the Asian clam (Corbicula fluminea). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Z.; Xue, M.Y.; Yang, S.B.; Zha, J.W.; Wang, G.X.; Ling, F. Ammonia exposure alters the expression of immune-related and antioxidant enzymes-related genes and the gut microbial community of crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.X.; Dong, H.B.; Wang, W.H.; Cao, M.; Duan, Y.F.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.S.; Zhang, J.S. Effects of periodic hypoxia stress on intestinal microflora structure of Lateolabrax maculatus. South China Fish. Sci. 2019, 15, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Xue, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, L. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Microcystin Variants and Relationships with Environmental Parameters in Lake Taihu, China. Toxins 2015, 7, 3224–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Kholodkevich, S.; Sharov, A.; Feng, Y.J.; Ren, N.Q.; Sun, K. Microcystin-LR-induced changes of hepatopancreatic transcriptome, intestinal microbiota, and histopathology of freshwater crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, M.I.; Taylor-Brown, A.; Schlacher, T.A.; Nowak, B.; Polkinghorne, A. Epitheliocystis in fish: An emerging aquaculture disease with a global impact. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Hao, F.; Chen, F.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Tao, Y. Reduction of gut microbial diversity and short chain fatty acids in BALB/c mice exposure to microcystin-LR. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, B.; Liang, J.C.; Ma, Y.Q.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y. Bacterial community and eutrophic index analysis of the East Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.Q.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Wei, Q.G.; Ma, S.C.; Sun, G.L.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, L.D.; Dou, H.S.; Zhang, H.Z. Factors affecting seasonal variation of microbial community structure in Hulun Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Liang, J.C.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Ji, B.; Luo, S.Y. Bacterial Community Analysis of Two Neighboring Freshwater Lakes Originating from One Lake. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Zhang, T.; Ren, L.; Fang, D.-A.; Xu, D.-P. Differential Study of Microbiota in the Gill and Intestine of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from the Algae-Dominated and Hydrophyte-Dominated Areas of Taihu Lake, China. Fishes 2022, 7, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060304
Zhou D, Zhang T, Ren L, Fang D-A, Xu D-P. Differential Study of Microbiota in the Gill and Intestine of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from the Algae-Dominated and Hydrophyte-Dominated Areas of Taihu Lake, China. Fishes. 2022; 7(6):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060304
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dan, Ting Zhang, Long Ren, Di-An Fang, and Dong-Po Xu. 2022. "Differential Study of Microbiota in the Gill and Intestine of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from the Algae-Dominated and Hydrophyte-Dominated Areas of Taihu Lake, China" Fishes 7, no. 6: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060304
APA StyleZhou, D., Zhang, T., Ren, L., Fang, D.-A., & Xu, D.-P. (2022). Differential Study of Microbiota in the Gill and Intestine of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from the Algae-Dominated and Hydrophyte-Dominated Areas of Taihu Lake, China. Fishes, 7(6), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060304





