Adverse Impacts of Toxic Metal Pollutants on Sex Steroid Hormones of Siganus rivulatus (Teleostei: Siganidae) from the Red Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
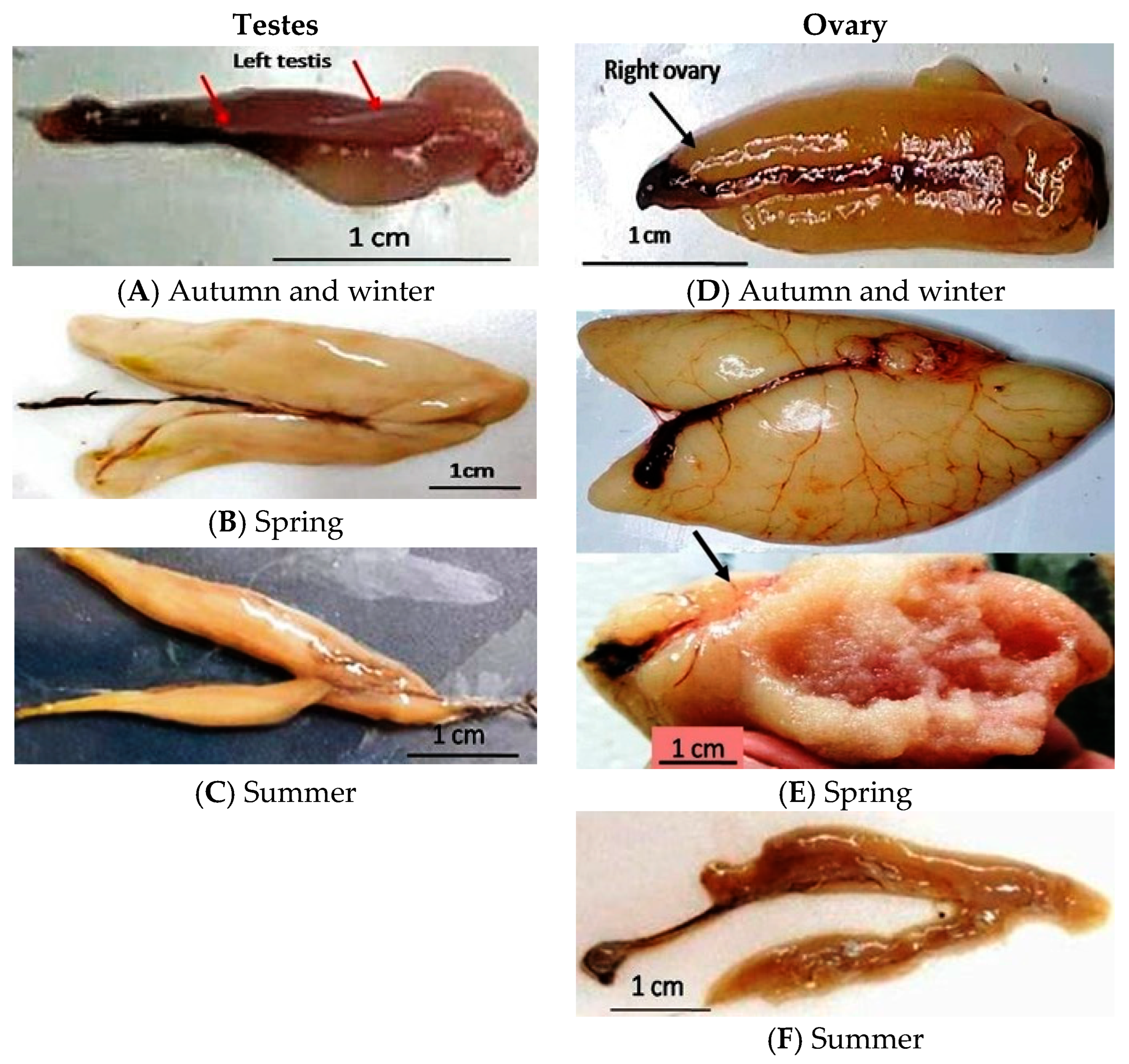
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Sample Analyses
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Temperature in the Two Bays
3.2. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Two Bays
3.3. Serum Levels of Sex Steroid Hormones in Both Sexes of S. rivulatus in the Two Bays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wakawa, R.J.; Uzairu, A.; Kagbu, J.A.; Balarabe, M.L. Impact assessment of effluent discharge on physicochemical parameters and some heavy metal concentrations in surface water of river Challawa Kano. Afr. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 2, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Merian, E.; Anke, M.; Ihnat, M.; Stoeppler, M. Elements and Their Compounds in the Environment: Occurrence, Analysis and Biological Relevance, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 1–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, F.; Piccione, G.; Tribulato, K.; Ferrantelli, V.; Giangrosso, G.; Arfuso, F.; Faggio, C. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped mullet in two Italian lakes. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2014, 26, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, R.C. Metal Toxicity–An Introduction. In Metal Chelation in Medicine, 1st ed.; Robert, R.C., Roberta, J.W., Robert, C., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. An overview of the adverse effects of heavy metal contamination on fish health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 89, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahity, T.; Islam, M.R.U.; Bhuiyan, N.Z.; Choudhury, T.R.; Yu, J.; Noman, M.A.; Hosen, M.M.; Quraishi, S.B.; Paray, B.A.; Arai, T.; et al. Heavy metals accumulation in tissues of wild and farmed barramundi from the northern Bay of Bengal coast, and its estimated human health risks. Toxics 2022, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottmann, R.W.; Shireman, J.V.; Chapman, F.A. Hormonal control of reproduction in fish for induced spawning. SRAC Publ. 1991, 424, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rainis, S.; Ballestrazzi, R. The control of reproduction in finfish species through GnRH treatments, Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 4, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Nagahama, Y. Endocrine regulation of gametogenesis in fish. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1994, 38, 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, H.M.; Ky, P.X.; Lam, H.S.; Thu, P.M. Steroid hormones in reproduction and roles of gnrh-a in gonadal maturation of marine fish: A Review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2019, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahama, Y.; Yoshikuni, M.; Yamashita, M.; Tokumoto, T.; Katsu, Y. Regulation of oocyte growth and maturation in fish. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Pedersen, R.A., Schatten, G.P., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 103–145. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Taherianfard, M. The effects of heavy metals exposure on reproductive systems of cyprinid fish from Kor River. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2011, 10, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hedayati, A.; Zare, P.; Abarghouei, S. Effect of environmental mercury on some hormonal parameters of the main mariculture fish of Persian Gulf. Glob. Vet. 2012, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, N.B. Effect of heavy metal (loid)s on the level of gonadal hormone during the sexual maturity and breeding period of catfish, Clarias batrachus (L.). JETIR 2019, 6, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, F. Fish hematology analysis as an important tool of aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.K.D.K.; Rranne, P.A.M.; Rodwell, V.W. Harper’s Biochemistry Publisher, 22nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: Norwalk, CT, USA; Los Altos, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 1–720. [Google Scholar]
- Abalaka, S.E. Evaluation of the haematology and biochemistry of Clarias gariepinus as biomakers of environmental pollution in Tiga dam Nigeria. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashem, M.T. Biological studies on Siganus rivulatus (Forsk.) in the Red Sea. J. Mar. Sci. 1983, 3, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- El-Drawany, M. On the biology of Siganus rivulatus inhabits Bitter Lakes in Egypt. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 342. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhak, E.M.; Madkour, F.F.; El Ganainy, A.A.; Abu El-Regal, M.A.; Ahmed, M.I. Reproductive biology of Siganus rivulatus (Forsskal, 1775) in the Red Sea, Suez Canal and the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. EJABF 2020, 24, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency (EEAA). Marine Pollution in the Gulf of Aqaba and Gulf of Suez and Its Effects on South Sinai. A Comprehensive Review. 2003. Available online: http://st-katherine.net/en/downloads/Marine%20Pollution.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Aly Salem, D.M.S.; Khaled, A.; El Nemr, A.; El-Sikaily, A. Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nour, H.E.; Helal, S.A.; Abdel Wahab, M. Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in beach sediments of Red Sea and Gulf of Aqaba, Egypt. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Menzel, C.; Berner, Z.; Eckhardt, J.D.; Stüben, D.; Alt, F.; Messerschmidt, J.; Taraschewski, H.; Sures, B. Trace analysis of platinum in biological samples: A comparison between high resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (HR-ICP-MS) following microwave digestion and adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry (ACSV) after high pressure ashing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 439 (Suppl. 2), 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, E.M. Seasonal developmental changes in the ovaries of Siganus rivulatus from The Red Sea. Bull. Inst. Ocean. Fish. 1985, 11, 131–147. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, E.M. Reproductive cycle of male Siganus rivulatus Forsk. With indication to gonadosomatic and hepatosomatic indices. Bull. Inst. Ocean. Fish. (ARE) 1985, 11, 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- Nachev, M. Bioindication Capacity of Fish Parasites for the Assessment of Water Quality in the Danube River. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and Multiple F-test. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization WHO. WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO Publications: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 307–340. ISBN 978-92-4-154815-1.
- Dural, M.; LugalGöksu, M.Z.; Özak, A.A.; Derici, B. Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals in different tissues of Dicentrarchus Labrax L., 1758, Sparus Aurata L., 1758 and Mugil Cephalus L., 1758 from the ÇamlIk lagoon of the eastern cost of Mediterranean (Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 118, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenšova, R.; Čelehovska, O.; Doubravova, J.; Svobodova, Z. Concentration of metals in tissues of fish from the Vestonice Reservoir. Acta Vet. Brno 2010, 79, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelle, H.I.; Ngbede, E.O.; Oguezi, V.U.; Ibekwe, F.C. Determination of heavy metals in fish (Clarias gariepinus) organs from Asaba Major Markets, Delta State, Nigeria. Am. Chem. Sci. J. 2015, 5, 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Carpene, E.; Vašák, M. Hepatic metallothioneins from goldfish (Carassius auratus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1989, 92B, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yousuf, M.H.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Al-Ghais, S.M. Trace elements in liver, skin and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 256, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousafzai, A.M.; Khan, A.R.; Shakoori, A.R. Trace metal accumulation in the liver of an endangered South Asian fresh water fish dwelling in sub-lethal pollution. Pak. J. Zool. 2009, 41, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, Y.; Kagi, J.H.R. Metallothionein. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1978, 3, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.J.; Soh, C.L. Effect of photoperiod on gonadal maturation in the rabbitfish, Siganus canaliculatus Park 1797. Aquaculture 1975, 5, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, D.; May, R.C.; Lichatowich, T. An experiment in rearing larval Siganus vermiculatus (Valenciennes) and some observations on its spawning cycle. Aquaculture 1976, 7, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariche, M.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; Quignard, J.-P. Reproductive cycles and spawning periods of two Lessepsiansiganid fishes on the Lebanese coast. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 62, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Nakamura, S.; Park, Y.J.; Takano, K. Lunar cycles and reproductive activity in reef fishes with particular attention to rabbitfishes. Fish Fish. 2004, 5, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, C.J. Notes on the breeding and movements of the rabbitfishes, Siganus rivulatus (ForsskDl) and S. luridus Rüppell, in the coastal waters of the Lebanon. Ann. Mus. Civ. Stor. 1972, 9, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Popper, D.; Gundermann, N. Some ecological and behavioural aspects of siganid populations in the Red Sea and Mediterranean coasts of Israel in relation to their suitability for aquaculture. Aquaculture 1975, 6, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, B. Androgens in teleost fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1994, 109C, 219–245. [Google Scholar]
- Nagahama, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Chang, X.T.; Nagahama, Y. Gonadal sex differentiation in teleost fish. J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 281, 362–373. [Google Scholar]
- Harbott, L.K.; Burmeister, S.S.; White, R.B.; Vagell, M.; Fernald, R.D. Androgen receptors in a cichlid fish, Astatotilapia burtoni: Structure, localization, and expression levels. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 504, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Yue, S.; Solarz, J.; Lee, J.; Li, L. Improving the sexual activity and reproduction of female zebrafish with high testosterone levels. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, Y.P.; Idler, D.R.; Truscott, B.; Walsh, J.M. Progestogens androgens and their glucuronides in the terminal stages of oocyte maturation in landlocked Atlantic salmon. J. Steroid Biochem. 1985, 23, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.M.; Idler, D.R. Hormonal control of vitellogenesis in hypophysectomized winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus Walbaum). J. Endocrinol. 1976, 28, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.; Haley, S.R. Steroid profiles of the female tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, and correlation with oocyte growth and mouthbrooding behavior. J. Endocrinol. 1988, 69, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, D.A. Seasonal steroid hormone profiles in plasma and gonads of the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Water SA 1998, 24, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Taghizadeh, V.; Imanpoor, M.R.; Mehdinejad, N. Study the seasonal steroid hormones of common carp in Caspian Sea, Iran. Springerplus 2013, 2, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, T.; Miura, C.; Ohta, T.; Nader, M.R.; Todo, T.; Yamauchi, K. Estradiol-17 β stimulates the renewal of spermatogonial stem cells in males. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Miura, C. Japanese eel: A model for analysis of spermatogenesis. Zool. Sci. 2001, 18, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis and its endocrine regulation. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 26, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Gutzeit, H.O. Effect of 17-alpha-ethynylestradiol on germ cell proliferation in organ and primary culture of medaka (Oryziaslatipes) testis. Dev. Growth Differ. 2003, 45, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, R.W.; de França, L.R.; Lareyre, J.-J.; Le Gac, F.; ChiariniGarcia, H.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kime, D.E. A strategy for assessing the effects of xenobiotics on fish reproduction. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilinger, J.; Steger-hartmann, T.; Maser, E.; Goller, S.; Vonk, R.; Lange, R. Effects of synthetic gestagens on fish reproduction. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.; Bird, D.J. Modulation of the fish immune system by hormones. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2000, 77, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, T.M.; Moser, M.T.; Le, P.T.; Flanigan, R.C.; Kwon, E.D. Alterations in peripheral B cells and B cell progenitors following androgen ablation in mice. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bugel, S.M.; White, L.A.; Cooper, K.R. Decreased vitellogenin inducibility and 17β-estradiol levels correlated with reduced egg production in killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) from Newark Bay, NJ. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, C.; Xiong, K.; Wang, X. Effects of progesterone on the reproductive physiology in zebrafish. bioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciuszek, M.; Pijanowski, L.; Pekala-Safinska, A.; Agnieszka, P.-S.; LidyVerburg-van Kemenade, B.M.; Magdalena, C. 17β-Estradiol affects the innate immune response in common carp. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 1775–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.A.H.; Feist, G.W.; Fitzpatrick, M.S.; Foster, E.P.; Schreck, C.B.; Plumlee, M.; Wong, C.; Gundersen, D.T. Mercury Concentrations in Gonad, Liver and Muscle of White Sturgeon Acipenser transmontanus in the Lower Columbia River. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kader, H.H.; Mourad, M.H. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and physiological/histological changes in gonads of catfish (Clarias gariepinus) inhabiting Lake Maryout, Alexandria, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waisberg, M.; Joseph, P.; Hale, B.; Beyersmann, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 2003, 192, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, C.A. Endocrine-Disrupting chemicals: From basic research to clinical practice. In Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, 1st ed.; Gore, A.C., Ed.; Humana Press, Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Arcand-Hoy, L.D.; Benson, W.H. Fish reproduction: An ecologically relevant indicator of endocrine disruption. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1988, 17, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Season | Month | Mean Water Temperature (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uninhabited Bay (Unpolluted) | Sharm El-Maya Bay (Polluted) | ||
| Autumn | September 2020 | 30.8 | 31.1 |
| October | 30.7 | 30.9 | |
| November | 28.0 | 28.3 | |
| Winter | December | 24.4 | 24.9 |
| January 2021 | 23.3 | 23.6 | |
| February | 25.1 | 25.4 | |
| Spring | March | 25.7 | 25.7 |
| April | 26.5 | 27.1 | |
| May | 28.1 | 28.3 | |
| Summer | June | 29.2 | 29.4 |
| July | 30.5 | 31.0 | |
| August | 31.4 | 31.9 | |
| Standard Reference Material | Metal | Certified Value | Recovered Value | Accuracy (%) | Detection Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRM–NIST 1640-Trace Elements in Natural Water | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | ||
| Cd | 3.961 ± 0.072 | 3.883 ± 0.013 | 98.03 | 0.004 | |
| Pb | 12.005 ± 0.040 | 11.584 ± 0.015 | 96.50 | 0.005 | |
| Dogfish liver DOLT-5 | (mg/kg) | (mg/kg) | (mg/kg) | ||
| Cd | 14.5 ± 0.400 | 14.282 ± 0.014 | 98.50 | 0.005 | |
| Pb | 0.162 ± 0.032 | 0.157 ± 0.003 | 97.06 | 0.003 |
| Season | Uninhabited Bay (Unpolluted) | Sharm El-Maya Bay (Polluted) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Metal Concentration For Water (mg·L−1), for Tissue (mg kg –1 wet wt.) | Mean Metal Concentration For Water (mg·L−1), for Tissue (mg kg –1 wet wt.) | |||||
| Cd | Pb | Cd | Pb | |||
| Water | Autumn | Undetected | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 3.43 ± 0.17 | |
| Winter | Undetected | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 3.23 ± 0.26 | ||
| Spring | Undetected | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.08 | 3.35 ± 0.16 | ||
| Summer | Undetected | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 3.51 ± 0.24 | ||
| Male S. rivulatus | Intestine | Autumn | Undetected | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 2.53 ± 0.18 |
| Winter | Undetected | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 2.51 ± 0.11 | ||
| Spring | Undetected | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 2.05 ± 0.13 | ||
| Summer | Undetected | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 2.55 ± 0.17 | ||
| Liver | Autumn | Undetected | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.05 | 6.30 ± 0.28 | |
| Winter | Undetected | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 6.11 ± 0.41 | ||
| Spring | Undetected | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 4.20 ± 0.19 | ||
| Summer | Undetected | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.45 ± 0.07 | 6.40 ± 0.32 | ||
| Tests | Autumn | Undetected | Undetected | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 1.27 ± 0.18 | |
| Winter | Undetected | Undetected | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 1.24 ± 0.12 | ||
| Spring | Undetected | Undetected | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 2.28 ± 0.10 | ||
| Summer | Undetected | Undetected | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 1.26 ± 0.16 | ||
| Female S. rivulatus | Intestine | Autumn | Undetected | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 2.46 ± 0.17 |
| Winter | Undetected | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 2.43 ± 0.14 | ||
| Spring | Undetected | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 1.97 ± 0.11 | ||
| Summer | Undetected | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 2.45 ± 0.19 | ||
| Liver | Autumn | Undetected | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 5.11 ± 0.14 | |
| Winter | Undetected | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 5.10 ± 0.23 | ||
| Spring | Undetected | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 3.60 ± 0.34 | ||
| Summer | Undetected | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.08 | 5.12 ± 0.19 | ||
| Ovary | Autumn | Undetected | Undetected | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 1.15 ± 0.13 | |
| Winter | Undetected | Undetected | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 1.14 ± 0.11 | ||
| Spring | Undetected | Undetected | 0.22 ± 0.07 | 1.98 ± 0.21 | ||
| Summer | Undetected | Undetected | 0.13 ± 0.07 | 1.13 ± 0.10 | ||
| Metal Concentration | Male S. rivulatus | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd Liver | Pb Liver | Cd Testes/Ovaries | Pb Testes/Ovaries | Serum Levels of Sex Steroid Hormones | ||||||||||
| T | E2 | P4 | ||||||||||||
| rs | p | rs | p | rs | p | rs | p | rs | p | rs | p | rs | p | |
| Cd intestine | 0.574 | 0.005 | 0.189 | 0.292 | 0.598 | 0.005 | 0.159 | 0.294 | −0.598 | 0.004 | −0.618 | 0.004 | −0.641 | 0.004 |
| Pb intestine | 0.352 | 0.412 | 0.598 | 0.003 | 0.439 | 0.172 | 0.628 | 0.004 | −0.525 | 0.005 | −0.612 | 0.005 | −0.572 | 0.005 |
| Cd liver | 0.289 | 0.384 | −0.811 | 0.001 | 0.426 | 0.370 | −0.602 | 0.003 | −0.601 | 0.002 | −0.563 | 0.003 | ||
| Pb liver | 0.279 | 0.219 | −0.907 | 0.001 | −0.549 | 0.003 | −0.627 | 0.003 | −0.529 | 0.005 | ||||
| Cd testes | 0.269 | 0.311 | −0.947 | 0.001 | −0.919 | 0.001 | −0.837 | 0.001 | ||||||
| Pb testes | −0.838 | 0.003 | −0.823 | 0.003 | −0.893 | 0.002 | ||||||||
| Female S. rivulatus | ||||||||||||||
| Cd intestine | 0.509 | 0.005 | 0.208 | 0.437 | 0.651 | 0.004 | 0.199 | 0.393 | −0.550 | 0.005 | −0.501 | 0.005 | −0.584 | 0.004 |
| Pb intestine | 0.297 | 0.317 | 0.539 | 0.004 | 0.379 | 0.259 | 0.513 | 0.004 | −0.513 | 0.005 | −0.554 | 0.004 | −0.591 | 0.005 |
| Cd liver | 0.492 | 0.251 | −0.879 | 0.001 | 0.339 | 0.283 | −0.569 | 0.004 | −0.589 | 0.005 | −0.547 | 0.004 | ||
| Pb liver | 0.320 | 0.426 | −0.932 | 0.001 | −0.642 | 0.003 | −0.568 | 0.004 | −0.609 | 0.004 | ||||
| Cd testes | 0.467 | 0.407 | −0.867 | 0.001 | −0.945 | 0.001 | −0.858 | 0.001 | ||||||
| Pb testes | −0.901 | 0.002 | −0.848 | 0.002 | −0.809 | 0.001 | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Hasawi, Z.M. Adverse Impacts of Toxic Metal Pollutants on Sex Steroid Hormones of Siganus rivulatus (Teleostei: Siganidae) from the Red Sea. Fishes 2022, 7, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060367
Al-Hasawi ZM. Adverse Impacts of Toxic Metal Pollutants on Sex Steroid Hormones of Siganus rivulatus (Teleostei: Siganidae) from the Red Sea. Fishes. 2022; 7(6):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060367
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Hasawi, Zaki M. 2022. "Adverse Impacts of Toxic Metal Pollutants on Sex Steroid Hormones of Siganus rivulatus (Teleostei: Siganidae) from the Red Sea" Fishes 7, no. 6: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060367
APA StyleAl-Hasawi, Z. M. (2022). Adverse Impacts of Toxic Metal Pollutants on Sex Steroid Hormones of Siganus rivulatus (Teleostei: Siganidae) from the Red Sea. Fishes, 7(6), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060367






