Success of Aquaculture Industry with New Insights of Using Insects as Feed: A Review
Abstract
1. Background
1.1. Emergent Non-Conventional Feed Ingredients
1.2. Ecological Advantages of Using Insects in Fishmeal Diet
1.3. Waste to Wealth Concept
2. Nutritional Value of Insects
2.1. Proteins
2.2. Carbohydrates
2.3. Lipids
2.4. Vitamins
2.5. Minerals
2.6. Functional Properties of Insect Meals
3. Factors Influencing the Nutritional Value of Insects
3.1. Insect’s Species
3.2. The Developmental Stage of Insects
3.3. Diet
3.4. Processing of Insects
3.4.1. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
3.4.2. Drying and Thermal Processing
3.4.3. Fermentation and Antibiotic Resistance
4. Potential Insects Used as Fishmeal
4.1. Black Soldier Fly
4.2. Common Housefly
4.3. Mealworm
4.4. Cricket
4.5. Locust
4.6. Silkworm
5. Insects as Feed for Crustaceans
5.1. Shrimp
5.2. Prawns
6. Physiological Responses of Fish Using Insects as Fishmeal
7. Challenges of Using Insects as Feed in Aquaculture
8. Possible Solutions to Challenges in Introducing the Insects in Aquafeed
9. Future Perspective
10. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture, Sustainability in Action; 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; ISBN 9789251326923. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A. Aquaculture Role in Global Food Security with Nutritional Value: A Review. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2019, 3, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azra, M.N.; Okomoda, V.T.; Tabatabaei, M.; Hassan, M.; Ikhwanuddin, M. The Contributions of Shellfish Aquaculture to Global Food Security: Assessing Its Characteristics from a Future Food Perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Leung, P.S. A Note on Linkage between Gross Value Added and Final Use at the Industry Level. Econ. Syst. Res. 2020, 32, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broitman, B.R.; Halpern, B.S.; Gelcich, S.; Lardies, M.A.; Vargas, C.A.; Vásquez-Lavín, F.; Widdicombe, S.; Birchenough, S.N.R. Dynamic Interactions among Boundaries and the Expansion of Sustainable Aquaculture. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J. Trends in Global Aquaculture and Aquafeed Production: 2000–2017. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.R.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Tavares, F. Gut Microbiota Dynamics in Carnivorous European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Fed Plant-Based Diets. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, G.S.; McCracken, V.J.; Wojno, M.; Rimoldi, S.; Terova, G.; Kwasek, K. Can Intestinal Absorption of Dietary Protein Be Improved through Early Exposure to Plantbased Diet? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magbanua, T.O.; Ragaza, J.A. Selected Dietary Plant-Based Proteins for Growth and Health Response of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus. Aquac. Fish. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawles, S.D.; Green, B.W.; McEntire, M.E.; Gaylord, T.G.; Barrows, F.T. Reducing Dietary Protein in Pond Production of Hybrid Striped Bass (Morone chrysops × M. saxatilis): Effects on Fish Performance and Water Quality Dynamics. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudioso, G.; Marzorati, G.; Faccenda, F.; Weil, T.; Lunelli, F.; Cardinaletti, G.; Marino, G.; Olivotto, I.; Parisi, G.; Tibaldi, E.; et al. Processed Animal Proteins from Insect and Poultry By-products in a Fish Meal-free Diet for Rainbow Trout: Impact on Intestinal Microbiota and Inflammatory Markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, B.; Zarantoniello, M.; Cardinaletti, G.; Cerri, R.; Giorgini, E.; Belloni, A.; Contò, M.; Tibaldi, E.; Olivotto, I. Hermetia illucens and Poultry By-Product Meals as Alternatives to Plant Protein Sources in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Diet: A Multidisciplinary Study on Fish Gut Status. Animals 2021, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, B.; Zarantoniello, M.; Gioacchini, G.; Cardinaletti, G.; Belloni, A.; Giorgini, E.; Faccenda, F.; Cerri, R.; Tibaldi, E.; Olivotto, I. Physiological Response of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to Graded Levels of Hermetia illucens or Poultry by-Product Meals as Single or Combined Substitute Ingredients to Dietary Plant Proteins. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Gai, F.; Maricchiolo, G.; Genovese, L.; Ragonese, S.; Bottari, T.; Caruso, G. Feeds for the Aquaculture Sector Current Situation and Alternative Sources. In Feeds for the Aquaculture Sector; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–103. ISBN 9783319779409. [Google Scholar]
- López-Pedrouso, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cantalapiedra, J.; Zapata, C.; Franco, J.M.; Franco, D. Aquaculture and By-Products: Challenges and Opportunities in the Use of Alternative Protein Sources and Bioactive Compounds. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 92, 127–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, G.; Tulli, F.; Fortina, R.; Marino, R.; Bani, P.; Dalle Zotte, A.; De Angeli, A.; Piccolo, G.; Pinotti, L.; Schiavone, A.; et al. Protein Hunger of the Feed Sector: The Alternatives Offered by the Plant World. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 19, 1205–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameixa, O.M.C.C.; Duarte, P.M.; Rodrigues, D.P. Insects, Food Security, and Sustainable Aquaculture. In Zero Hunger; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, K.; Cobcroft, J.M.; Cole, A.; Condon, K.; Jerry, D.R.; Mangott, A.; Praeger, C.; Vucko, M.J.; Zeng, C.; Zenger, K.; et al. The Future of Aquatic Protein: Implications for Protein Sources in Aquaculture Diets. One Earth 2019, 1, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, E.S.M.; Al-Quffail, A.S.; Al-Asgah, N.A.; Abdel-Warith, A.W.A.; Al-Hafedh, Y.S. Effect of Dietary Fish Meal Replacement by Red Algae, Gracilaria Arcuata, on Growth Performance and Body Composition of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, A.T.O.; Ishikawa, M.; Koshio, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Moss, A.S.; Serge, D. Nutritional Evaluation of Nannochloropsis Powder and Lipid as Alternative to Fish Oil for Kuruma Shrimp, Marsupenaeus Japonicus. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitei, M.M.; Singh, S.K.; Mangang, Y.A.; Meena, D.K.; Debbarma, R.; Biswas, P.; Waikhom, G.; Patel, A.B.; Ngasotter, S.; Newmei, T.; et al. Effective Valorization of Precision Output of Algaquaculture towards Eco-Sustainability and Bioeconomy Concomitant with Biotechnological Advances: An Innovative Concept. Clean. Waste Syst. 2022, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.; Meena, D.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Das, B.K.; Sen, R. Effective Valorization of Microalgal Biomass for the Production of Nutritional Fish-Feed Supplements. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Das, S.K. Comparative Efficacy of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) and Non-Neem Supplemented Biofloc Media in Controlling the Harmful Luminescent Bacteria in Natural Pond Culture of Litopenaeus Vannaemei. Aquaculture 2018, 492, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosain, M.E.; Amin, S.M.N.; Arshad, A.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Karim, M. Effects of Carbon Sources on the Culture of Giant River Prawn in Biofloc System during Nursery Phase. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbarma, R.; Meena, D.K.; Biswas, P.; Meitei, M.M.; Singh, S.K. Portioning of Microbial Waste into Fish Nutrition via Frugal Biofloc Production: A Sustainable Paradigm for Greening of Environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.W.; Patro, B.; Pujol-Baxley, C.; Marx, C.J.; Feinberg, L. Partial Replacement of Soybean Meal with Methylobacterium Extorquens Single-Cell Protein in Feeds for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.W.; Karpol, A.; Friedman, S.; Maru, B.T.; Tracy, B.P. Recent Advances in Single Cell Protein Use as a Feed Ingredient in Aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irm, M.; Taj, S.; Jin, M.; Luo, J.; Andriamialinirina, H.J.T.; Zhou, Q. Effects of Replacement of Fish Meal by Poultry By-Product Meal on Growth Performance and Gene Expression Involved in Protein Metabolism for Juvenile Black Sea Bream (Acanthoparus schlegelii). Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Pulido Rodriguez, L.F.; Randazzo, B.; Cardinaletti, G.; Giorgini, E.; Belloni, A.; Secci, G.; Faccenda, F.; Pulcini, D.; Parisi, G.; et al. Conventional Feed Additives or Red Claw Crayfish Meal and Dried Microbial Biomass as Feed Supplement in Fish Meal-Free Diets for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Possible Ameliorative Effects on Growth and Gut Health Status. Aquaculture 2022, 554, 738137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Rodriguez, L.F.; Cardinaletti, G.; Secci, G.; Randazzo, B.; Bruni, L.; Cerri, R.; Olivotto, I.; Tibaldi, E.; Parisi, G. Appetite Regulation, Growth Performances and Fish Quality Are Modulated by Alternative Dietary Protein Ingredients in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Culture. Animals 2021, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Hasan, M.R.; Metian, M. Demand and Supply of Feed Ingredients for Farmed Fish and Crustaceans: Trends and Prospects. FAO Fish. Aquac. Tech. Pap. 2011, 564, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Ayensu, J.; Annan, R.A.; Edusei, A.; Lutterodt, H. Beyond Nutrients, Health Effects of Entomophagy: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 49, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, R.J.S.; Ohara, A.; dos SantosAguilara, J.G.; Domingues, M.A.F. Nutritional, Functional and Biological Properties of Insect Proteins: Processes for Obtaining, Consumption and Future Challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giron, R.C.; Hidalgo, G.G.; Garcia, J.P.B.; Pino-Hernández, E.; Villa, P. Exploring the Food and Nutritional Potential of Three Edibles Amazonian Arthropods. Rev. Etnobiol. 2017, 15, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Suleria, H.A.R.; Rauf, A. Edible Insects as Innovative Foods: Nutritional and Functional Assessments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Prokešová, M.; Gebauer, T.; Van Doan, H.; Stejskal, V. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Production Performance of Aquaculture Species Fed Dietary Insect Meals. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1637–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K. A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Replacing Fish Meals with Insect Meals on Growth Performance of Fish. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liland, N.S.; Araujo, P.; Xu, X.X.; Lock, E.J.; Radhakrishnan, G.; Prabhu, A.J.P.; Belghit, I. A Meta-Analysis on the Nutritional Value of Insects in Aquafeeds. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the Use of Insects in the Diet of Farmed Fish: Past and Future. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaneto, D.; Tommaseo-Ponzetta, M.; Galli, C.; Risé, P.; Glew, R.H.; Paoletti, M.G. Differences in Fatty Acid Composition between Aquatic and Terrestrial Insects Used as Food in Human Nutrition. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2011, 50, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Laurent, S.; Veenenbos, M.E.; van Loon, J.J.A. Dietary Enrichment of Edible Insects with Omega 3 Fatty Acids. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Global Overview on the Use of Fish Meal and Fish Oil in Industrially Compounded Aquafeeds: Trends and Future Prospects. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, R.; Grooten, M.; Petersen, T. Living Planet Report 2020: Bending the Curve of Biodiversity Loss; World Wildlife Fund: Gland, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 294052999X. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga-Corral, M.; Ronza, P.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Pereira, A.G.; Losada, A.P.; Prieto, M.A.; Quiroga, M.I.; Simal-Gandara, J. Aquaculture as a Circular Bio-Economy Model with Galicia as a Study Case: How to Transform Waste into Revalorized by-Products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Global Diets Link Environmental Sustainability and Human Health. Nature 2014, 515, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Féon, S.; Thévenot, A.; Maillard, F.; Macombe, C.; Forteau, L.; Aubin, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Fish Fed with Insect Meal: Case Study of Mealworm Inclusion in Trout Feed, in France. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smárason, B.Ö.; Ögmundarson, Ó.; Árnason, J.; Björnsdóttir, R.; Davíðsdóttir, B. Life Cycle Assessment of Icelandic Arctic Char Fed Three Different Feed Types. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 17, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayant, M.; Hassan, M.A.; Srivastava, P.P.; Meena, D.K.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Wagde, M.S. Brewer’s Spent Grains (BSGs) as Feedstuff for Striped Catfish, Pangasianodon Hypophthalmus Fingerlings: An Approach to Transform Waste into Wealth. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayant, M.; Sahu, N.P.; Deo, A.D.; Gupta, S.; Rajendran, K.V.; Garg, C.K.; Meena, D.K.; Wagde, M.S. Effective Valorization of Bio-Processed Castor Kernel Meal Based Fish Feed Supplements Concomitant with Oil Extraction Processing Industry: A Prolific Way towards Greening of Landscaping/Environment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K. Prevention of Fish Oil Oxidation. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, N.; Félix, R.; Meggiolaro, D.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Sousa, E.; Silva, G.; Hartmann, C.; Hidalgo, J.; Köbler, H.; Mosconi, E.; et al. The Doping Mechanism of Halide Perovskite Unveiled by Alkaline Earth Metals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.P.; Calado, R.; Pinho, M.; Rosário Domingues, M.; Antonio Vázquez, J.; Ameixa, O.M.C.C. Bioconversion and Performance of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) in the Recovery of Nutrients from Expired Fish Feeds. Waste Manag. 2022, 141, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-Art on Use of Insects as Animal Feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Palanisamy, M.; Mathys, A.; Heinz, V. Sustainability of Insect Use for Feed and Food: Life Cycle Assessment Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohri, C.R.; Diener, S.; Zabaleta, I.; Mertenat, A.; Zurbrügg, C. Treatment Technologies for Urban Solid Biowaste to Create Value Products: A Review with Focus on Low- and Middle-Income Settings. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 81–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Conversion of Organic Material by Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Establishing Optimal Feeding Rates. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Edible Insects. Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 171, ISBN 9789251075951. [Google Scholar]
- Bruni, L.; Pastorelli, R.; Viti, C.; Gasco, L.; Parisi, G. Characterisation of the Intestinal Microbial Communities of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fed with Hermetia illucens (Black Soldier Fly) Partially Defatted Larva Meal as Partial Dietary Protein Source. Aquaculture 2018, 487, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food Wastage Footprint; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; 62p. [Google Scholar]
- Durst, P.B.; Shono, K. Edible Forest Insects: Exploring New Horizons and Traditional Practices. In Forest Insects as Food Humans Bite Back, Proceedings of the a Workshop on Asia-Pacific Resources and Their Potential for Development, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 19–21 February 2008; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific: Rome, Italy, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lecocq, T. Insects: The Disregarded Domestication Histories. In Animal Domestication; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- EL-Haroun, E.R.; Azevedo, P.A.; Bureau, D.P. High Dietary Incorporation Levels of Rendered Animal Protein Ingredients on Performance of Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1972). Aquaculture 2009, 290, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.H.; Ko, J.H.; Ahn, C.W.; Lee, H.H.; Shin, J.K.; Chang, S.J.; Park, C.S.; Kang, J.H. In Vivo and in Vitro Application of Black Soybean Peptides in the Amelioration of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Improvement of Insulin Resistance. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Peres, H. Replacing Fishmeal and Fish Oil in Industrial Aquafeeds for Carnivorous Fish. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 203–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, F.T.; Gaylord, T.G.; Stone, D.A.J.; Smith, C.E. Effect of Protein Source and Nutrient Density on Growth Efficiency, Histology and Plasma Amino Acid Concentration of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin, D.M.; Barrows, F.T.; Brown, P.; Dabrowski, K.; Gaylord, T.G.; Hardy, R.W.; Herman, E.; Hu, G.; Krogdahl, Å.; Nelson, R.; et al. Expanding the Utilization of Sustainable Plant Products in Aquafeeds: A Review. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogdahl, Å.; Penn, M.; Thorsen, J.; Refstie, S.; Bakke, A.M. Important Antinutrients in Plant Feedstuffs for Aquaculture: An Update on Recent Findings Regarding Responses in Salmonids. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rahimnejad, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, K.; Song, K.; Zhang, C. Substituting Fish Meal with Housefly (Musca domestica) Maggot Meal in Diets for Bullfrog Rana (Lithobates) Catesbeiana: Effects on Growth, Digestive Enzymes Activity, Antioxidant Capacity and Gut Health. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousoulaki, K.; Albrektsen, S.; Langmyhr, E.; Olsen, H.J.; Campbell, P.; Aksnes, A. The Water Soluble Fraction in Fish Meal (Stickwater) Stimulates Growth in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) given High Plant Protein Diets. Aquaculture 2009, 289, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, W.; Rønnestad, I.; Dinis, M.T.; Aragão, C. Taurine and Fish Development: Insights for the Aquaculture Industry. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 776, pp. 329–334. ISBN 9781461460923. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Ai, Q.; Mao, P.; Tian, Q.; Zhong, L.; Xiao, T.; Chu, W. Effect of Dietary Taurine Supplementation on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activities and Antioxidant Status of Juvenile Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Fed with Low Fish Meal Diet. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Domínguez, D.; Jiménez, J.I.; Saleh, R.; Hernández-Cruz, C.M.; Zamorano, M.J.; Hamre, K. Interaction between Taurine, Vitamin E and Vitamin C in Microdiets for Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Larvae. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Murata, H.; Goto, T.; Endo, M.; Yamashita, H.; Ukawa, M. Taurine Is an Essential Nutrient for Yellowtail Seriola Quinqueradiata Fed Non-Fish Meal Diets Based on Soy Protein Concentrate. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, F.; Stuart, K.; Drawbridge, M. Effects of Taurine Supplementation in Live Feeds on Larval Rearing Performance of California Yellowtail Seriola Lalandi and White Seabass Atractoscion Nobilis. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Z. Common Edible Insects and Their Utilization in China: Invited Review. Entomol. Res. 2009, 39, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Davis, D.A.; Saoud, I.P. Evaluation of Alternative Protein Sources to Replace Fish Meal in Practical Diets for Juvenile Tilapia, Oreochromis Spp. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2009, 40, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Elorduy, J. Energy Supplied by Edible Insects from Mexico and Their Nutritional and Ecological Importance. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2008, 47, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Totakul, P.; Matra, M.; Cherdthong, A.; Hanboonsong, Y.; Wanapat, M. Nutritional Composition of Various Insects and Potential Uses as Alternative Protein Sources in Animal Diets. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.R.H.; Steenbekkers, L.P.A. All Insects Are Equal, but Some Insects Are More Equal than Others. Br. Food J. 2018, 120, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, M.D. Complete Nutrient Composition of Commercially Raised Invertebrates Used as Food for Insectivores. Zoo Biol. 2002, 21, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockley, M.; Dossey, A.T. Insects for Human Consumption. In Mass Production of Beneficial Organisms; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 617–652. ISBN 9780123914538. [Google Scholar]
- Finke, M.D. Complete Nutrient Content of Four Species of Commercially Available Feeder Insects Fed Enhanced Diets during Growth. Zoo Biol. 2015, 34, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, M.D.; Oonincx, D. Insects as Food for Insectivores. In Mass Production of Beneficial Organisms: Invertebrates and Entomopathogens; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 583–616. ISBN 9780123914538. [Google Scholar]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; de Boer, I.J.M. Environmental Impact of the Production of Mealworms as a Protein Source for Humans—A Life Cycle Assessment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Van Der Poel, A.F.B. Effects of Diet on the Chemical Composition of Migratory Locusts (Locusta migratoria). Zoo Biol. 2011, 30, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawski, M.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Kierończyk, B.; Józefiak, D. Black Soldier Fly Full-Fat Larvae Meal as an Alternative to Fish Meal and Fish Oil in Siberian Sturgeon Nutrition: The Effects on Physical Properties of the Feed, Animal Growth Performance, and Feed Acceptance and Utilization. Animals 2020, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.S.O. Recent Advances in Sturgeon Nutrition. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; van Broekhoven, S.; van Huis, A.; van Loon, J.J.A. Correction: Feed Conversion, Survival and Development, and Composition of Four Insect Species on Diets Composed of Food Byproducts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, S.; Tännler, A.; Nyström, L. Nitrogen-to-Protein Conversion Factors for Edible Insects on the Swiss Market: T. molitor, A. domesticus, and L. migratoria. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukkens, S.G.F. Insects in the Human Diet: Nutritional Aspects. In Ecological Implications of Minilivestock; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 559–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Potential and Challenges of Insects as an Innovative Source for Food and Feed Production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, F.G.; de Haro, C.; Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Venegas, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Pérez-Bañón, C. The Potential of Various Insect Species for Use as Food for Fish. Aquaculture 2014, 422–423, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blásquez, J.R.-E.; Moreno, J.M.P.; Camacho, V.H.M. Could Grasshoppers Be a Nutritive Meal? Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Elorduy, J.; Costa Neto, E.M.; Cuevas Correa, M.S.; García-Figueroa, J.; Zentina, D.H. Conocimiento de La Entomofauna Útil En El Poblado La Purísima Palmar de Bravo, Estado de Puebla, México. Biotemas 2007, 20, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Okey Aniebo, A.; Erondu, E.S.; Owen, O.J. Replacement of Fish Meal with Maggot Meal in African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Diets. Rev. UDO Agrícola 2009, 9, 666–671. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Bi, J.; Yang, Z. Nutritional Composition and Protein Quality of the Edible Beetle Holotrichia Parallela. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravzanaadii, N.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, W.-H.; Hong, S.-J.; Kim, N.-J. Nutritional Value of Mealworm, Tenebrio molitor as Food Source. Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2012, 25, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadykova, E.O.; Shumakova, A.A.; Shestakova, S.I.; Tyshko, N.V. Nutritional and Biological Value of Hermetia illucens Larvae Biomass. Vopr. Pitan. 2021, 90, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dossey, A.T.; Tatum, J.T.; McGill, W.L. Modern Insect-Based Food Industry: Current Status, Insect Processing Technology, and Recommendations Moving Forward. In Insects as Sustainable Food Ingredients; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 113–152. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E. Determination of Nutritive Value of the Edible Migratory Locust Locusta migratoria, Linnaeus, 1758 (Orthoptera: Acrididae) Impact of Environmental Changes on Fish Availability and Fishery Landings in Khartoum State View Project Impact of Environmental Cha. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2015, 4, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-K.; Weaver, C.M.; Choi, M.-K. Proximate Composition and Mineral Content of Five Edible Insects Consumed in Korea. CyTA J. Food 2016, 15, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjo, A.D.; Lawal, O.A.; Songonuga, E.A. The Nutritional Value of Fourteen Species of Edible Insects in Southwestern Nigeria. African J. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siulapwa, N.; Mwambungu, A.; Lungu, E.; Sichilima, W. Nutritional Value of Four Common Edible Insects in Zambia. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 2319–7064. [Google Scholar]
- Adeolu, A. Proximate and Anti-Nutritional Composition of Two Common Edible Insects: Yam Beetle (Heteroligus meles) and Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus phoenicis). Elixir Food Sci. 2012, 49, 9782–9786. [Google Scholar]
- Kinyuru, J.N.; Mogendi, J.B.; Riwa, C.A.; Ndung’u, N.W. Edible Insects-A Novel Source of Essential Nutrients for Human Diet: Learning from Traditional Knowledge. Anim. Front. 2015, 5, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Pinckaers, P.J.M.; van Loon, J.J.A.; van Loon, L.J.C. Consideration of Insects as a Source of Dietary Protein for Human Consumption. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackewitz, L. von The House Cricket Acheta Domesticus, a Potential Source of Protein for Human Consumption. Mol. Sci. 2018, 17, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O. Insect-Based Protein Sources and Their Potential for Human Consumption: Nutritional Composition and Processing. Anim. Front. 2015, 5, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, D.; Ray, M.; Sinha, S. Comparison of Amino Acid Profiles and Vitamin Contents of Male and Female Prepupae and Pupae of Eri Silkworm, Samia Ricini. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 113, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouřimská, L.; Adámková, A. Nutritional and Sensory Quality of Edible Insects. NFS J. 2016, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlcek, J.; Rop, O.; Borkovcova, M.; Bednarova, M. A Comprehensive Look at the Possibilities of Edible Insects as Food in Europe—A Review. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 64, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksakantong, P.; Meeso, N.; Kubola, J.; Siriamornpun, S. Fatty Acids and Proximate Composition of Eight Thai Edible Terricolous Insects. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Younes, I.; Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O.; Hajji, R.; Rinaudo, M.; Nasri, M.; Jellouli, K. Structural Differences between Chitin and Chitosan Extracted from Three Different Marine Sources. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoushab, F.; Yamabhai, M. Chitin Research Revisited. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1988–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Elorduy, J.; González, E.A.; Hernández, A.R.; Pino, J.M. Use of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) to Recycle Organic Wastes and as Feed for Broiler Chickens. J. Econ. Entomol. 2002, 95, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpo, K.E.; Onigbinde, A.O. Nutritional Potentials of the Larva of Rhynchophorus phoenicis (F). Pak. J. Nutr. 2005, 4, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzollini, D.; Derossi, A.; Fogliano, V.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Severini, C. Effects of Formulation and Process Conditions on Microstructure, Texture and Digestibility of Extruded Insect-Riched Snacks. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Vázquez-Gutiérrez, J.L.; Johansson, D.P.; Landberg, R.; Langton, M. Yellow Mealworm Protein for Food Purposes—Extraction and Functional Properties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Nutritional Composition and Safety Aspects of Edible Insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Lee, S.M.; Jung, C.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B. Nutritional Composition of Five Commercial Edible Insects in South Korea. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzompa-Sosa, D.A.; Yi, L.; van Valenberg, H.J.F.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Lakemond, C.M.M. Insect Lipid Profile: Aqueous versus Organic Solvent-Based Extraction Methods. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpo, K.E.; Onigbinde, A.O.; Asia, I.O. Pharmaceutical Potentials of the Oils of Some Popular Insects Consumed in Southern Nigeria. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 3, 051–057. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey, K.J.; Lopez-Viso, C.; Brameld, J.M.; Parr, T.; Salter, A.M. Insects: A Potential Source of Protein and Other Nutrients for Feed and Food. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 9, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschioni, S.; Loreto, N.; Foligni, R.; Mannozzi, C.; Raffaelli, N.; Zamporlini, F.; Pasquini, M.; Roncolini, A.; Cardinali, F.; Osimani, A. Addition of Olive Pomace to Feeding Substrate Affects Growth Performance and Nutritional Value of Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) Larvae. Foods 2020, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, D.; Swift, J.A.; Field, L.M. Opportunities and Hurdles of Edible Insects for Food and Feed. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, L.; Varriale, L.; Dipineto, L.; Pace, A.; Menna, L.F.; Fioretti, A. Insect Derived Lauric Acid as Promising Alternative Strategy to Antibiotics in the Antimicrobial Resistance Scenario. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 620798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.Y.; Lin, K.W.; Wang, Y.M.; Yen, C.Y. Revealing Interactive Toxicity of Aromatic Amines to Azo Dye Decolorizer Aeromonas Hydrophila. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oonincx, D.G.; Dierenfeld, E.S. An Investigation into the Chemical Composition of Alternative Invertebrate Prey. Zoo Biol. 2012, 31, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponton, F.; Wilson, K.; Cotter, S.C.; Raubenheimer, D.; Simpson, S.J. Nutritional Immunology: A Multi-Dimensional Approach. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponton, F.; Wilson, K.; Holmes, A.J.; Cotter, S.C.; Raubenheimer, D.; Simpson, S.J. Integrating Nutrition and Immunology: A New Frontier. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 9251075964. [Google Scholar]
- Zielińska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karaś, M.; Rybczyńska, K.; Jakubczyk, A. Selected Species of Edible Insects as a Source of Nutrient Composition. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; van Itterbeeck, J.; Heetkamp, M.J.W.; van den Brand, H.; van Loon, J.J.A.; van Huis, A. An Exploration on Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Production by Insect Species Suitable for Animal or Human Consumption. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.H.; Kwon, K.H.; Park, K.H.; Jeong, H.C.; Kwon, O.; Tindwa, H.; Han, Y.S. Evaluation of Nutritional Status of an Edible Grasshopper, Oxya Chinensis Formosana. Entomol. Res. 2012, 42, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latunde-Dada, G.O.; Yang, W.; Vera Aviles, M. In Vitro Iron Availability from Insects and Sirloin Beef. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8420–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosečková, P.; Zvěřina, O.; Pěchová, M.; Krulíková, M.; Duborská, E.; Borkovcová, M. Mineral Profile of Cricket Powders, Some Edible Insect Species and Their Implication for Gastronomy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A. Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in Assuring Food Security. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravel, A.; Doyen, A. The Use of Edible Insect Proteins in Food: Challenges and Issues Related to Their Functional Properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaseñor, V.M.; Enriquez-Vara, J.N.; Urías-Silva, J.E.; Mojica, L. Edible Insects: Techno-Functional Properties Food and Feed Applications and Biological Potential. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-K.; Cha, J.Y.; Yong, H.I.; Jang, H.W.; Jung, S.; Choi, Y.-S. Application of Edible Insects as Novel Protein Sources and Strategies for Improving Their Processing. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 372–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-K.; Yong, H.I.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kim, H.-W.; Choi, Y.-S. Edible Insects as a Protein Source: A Review of Public Perception, Processing Technology, and Research Trends. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2019, 39, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-K.; Yong, H.I.; Chun, H.H.; Lee, M.-A.; Kim, Y.-B.; Choi, Y.-S. Changes of Amino Acid Composition and Protein Technical Functionality of Edible Insects by Extracting Steps. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintah, B.K.; He, R.; Agyekum, A.A.; Dabbour, M.; Golly, M.K.; Ma, H. Edible Insect Protein for Food Applications: Extraction, Composition, and Functional Properties. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, B.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Horn, C.; Rieder, O.; Jäger, H. Improvement of Techno-Functional Properties of Edible Insect Protein from Migratory Locust by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, B.; Tanzmeister, H.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Baumgartner, S.; Lauter, K.; Jäger, H. Recovery of Soluble Proteins from Migratory Locust (Locusta migratoria) and Characterisation of Their Compositional and Techno-Functional Properties. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion-Poulin, A.; Laroche, M.; Doyen, A.; Turgeon, S.L. Functionality of Cricket and Mealworm Hydrolysates Generated after Pretreatment of Meals with High Hydrostatic Pressures. Molecules 2020, 25, 5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Cheng, K.; Ma, X.; Wu, G. Use of Alternative Protein Sources for Fishmeal Replacement in the Diet of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Part II: Effects of Supplementation with Methionine or Taurine on Growth, Feed Utilization, and Health. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokeshkumar, V.; Daniel, B.A.; Jayanthi, J.; Ragunathan, M.G. Nutritive Evaluations of Laboratory-Reared Edible Field Cricket Coiblemmus compactus Chopard, 1928 (Orthoptera: Gryllidae), for Utilising Them as an Alternate Protein Source. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2022, 83, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurečka, M.; Kulma, M.; Petříčková, D.; Plachý, V.; Kouřimská, L. Larvae and Pupae of Alphitobius Diaperinus as Promising Protein Alternatives. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunji, J.O.; Kloas, W.; Wirth, M.; Neumann, N.; Pietsch, C. Effect of Housefly Maggot Meal (Magmeal) Diets on the Performance, Concentration of Plasma Glucose, Cortisol and Blood Characteristics of Oreochromis Niloticus Fingerlings. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunji, J.O.; Nimptsch, J.; Wiegand, C.; Schulz, C. Evaluation of the Influence of Housefly Maggot Meal (Magmeal) Diets on Catalase, Glutathione S-Transferase and Glycogen Concentration in the Liver of Oreochromis niloticus Fingerling. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, M.D. Estimate of Chitin in Raw Whole Insects. Zoo Biol. 2007, 26, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranghers, T.; Michiels, J.; Vrancx, J.; Ovyn, A.; Eeckhout, M.; De Clercq, P.; De Smet, S. Gut Antimicrobial Effects and Nutritional Value of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Prepupae for Weaned Piglets. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 235, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Makkar, H.P.S. Insects in Fish Diets. Anim. Front. 2015, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Eisner-Schadler, V.; Van Huis, A.; Boekel, M.A.J.S.V. Extraction and Characterisation of Protein Fractions from Five Insect Species. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmawati, R.; Buchori, D.; Hidayat, P.; Hem, S.; Fahmi, M.R. Perkembangan Dan Kandungan Nutrisi Larva Hermetia illucens (Linnaeus) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Pada Bungkil Kelapa Sawit. J. Entomol. Indones. 2015, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sohn, H.-Y.; Pyo, S.-J.; Jensen, A.B.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Jung, C. Nutritional Composition of Apis Mellifera Drones from Korea and Denmark as a Potential Sustainable Alternative Food Source: Comparison Between Developmental Stages. Foods 2020, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ademolu, K.O.; Idowu, A.B.; Olatunde, G.O. Nutritional Value Assessment of Variegated Grasshopper, Zonocerus variegatus (L.) (Acridoidea: Pygomorphidae), during Post-Embryonic Development. Afr. Entomol. 2010, 18, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulma, M.; Plachý, V.; Kouřimská, L.; Vrabec, V.; Bubová, T.; Adámková, A.; Hučko, B. Nutritional Value of Three Blattodea Species Used as Feed for Animals. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2016, 25, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, V.; Persijn, D.; Rittenschober, D.; Charrondiere, U.R. Review of Food Composition Data for Edible Insects. Food Chem. 2016, 193, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, M.D. Nutrient Content of Insects. In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1563–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Jung, C.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B. Nutritional Value and Chemical Composition of Larvae, Pupae, and Adults of Worker Honey Bee, Apis Mellifera Ligustica as a Sustainable Food Source. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, F.G.; Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Segura, M.; Morote, E.; Torres, A.; Ramos, R.; Guil, J.L. Insects as Food: Enrichment of Larvae of Hermetia illucens with Omega 3 Fatty Acids by Means of Dietary Modifications. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 62, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Insects to Feed the World. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Zimbelli, A.; Randazzo, B.; Compagni, M.D.; Truzzi, C.; Antonucci, M.; Riolo, P.; Loreto, N.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; et al. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Roasted Coffee by-Product and Schizochytrium Sp. as a Sustainable Terrestrial Ingredient for Aquafeeds Production. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemello, G.; Zarantoniello, M.; Randazzo, B.; Gioacchini, G.; Truzzi, C.; Cardinaletti, G.; Riolo, P.; Olivotto, I. Effects of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Enriched with Schizochytrium Sp. on Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Reproductive Performances. Aquaculture 2022, 550, 737853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, J.D.; Park, C.; Park, J.H.; Chung, T.H. Replacing Fish Meal by Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) on the Growth Performance and Immunologic Responses of White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2018, 40, e35015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, G.L.; Sheppard, D.C.; Watson, D.W.; Burtle, G.J.; Dove, C.R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Thelen, E.E. The Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens, as a Manure Management/Resource Recovery Tool. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the state of the science of Animal Manure and Waste Management, San Antonio, TX, USA, 16 September 2005; Volume 57, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kinyuru, J.N.; Kenji, G.M.; Njoroge, S.M.; Ayieko, M. Effect of Processing Methods on the in Vitro Protein Digestibility and Vitamin Content of Edible Winged Termite (Macrotermes subhylanus) and Grasshopper (Ruspolia differens). Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madibela, O.R.; Seitiso, T.K.; Thema, T.F.; Letso, M. Effect of Traditional Processing Methods on Chemical Composition and in Vitro True Dry Matter Digestibility of the Mophane Worm (Imbrasia belina). J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshulam-Pascoviche, D.; David-Birman, T.; Refael, G.; Lesmes, U. Big Opportunities for Tiny Bugs: Processing Effects on the Techno-Functionality and Digestibility of Edible Insects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 122, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, N.T.; Klein, G. Microbiology of Cooked and Dried Edible Mediterranean Field Crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus) and Superworms (Zophobas atratus) Submitted to Four Different Heating Treatments. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2017, 23, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantanga, K.K.M.; Amakali, T. Diversification of Mopane Caterpillars (Gonimbrasia belina) Edible Forms for Improved Livelihoods and Food Security. J. Arid Environ. 2020, 177, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bußler, S.; Rumpold, B.A.; Jander, E.; Rawel, H.M.; Schlüter, O.K. Recovery and Techno-Functionality of Flours and Proteins from Two Edible Insect Species: Meal Worm (Tenebrio molitor) and Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Bußler, S.; Psarianos, M.; Rossi, G.; Schlüter, O.K. Edible Insect Processing Pathways and Implementation of Emerging Technologies. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 877–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishyna, M.; Chen, J.; Benjamin, O. Sensory Attributes of Edible Insects and Insect-Based Foods–Future Outlooks for Enhancing Consumer Appeal. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Unlocking the Biological Potential of Proteins from Edible Insects through Enzymatic Hydrolysis: A Review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 43, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yan, R.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Raffinose Fatty Acid Monoesters under Ultrasonic Irradiation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Karaś, M.; Baraniak, B. Comparison of Functional Properties of Edible Insects and Protein Preparations Thereof. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamidi, R.O.; Jiang, L.; Pathare, P.B.; Wang, Y.D.; Roskilly, A.P. Recent Advances in Sustainable Drying of Agricultural Produce: A Review. Appl. Energy 2019, 233–234, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.A.; Yahya, F.; Mustapha, W.A.W. Effect of Different Drying Methods on the Morphological Structure, Colour Profile and Citral Concentration of Lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) Powder. Asian J. Agric. Biol 2019, 7, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tantiyani, N.; Othman, A.; Elmi, M.; Mohd, F. Drying of Instant Coffee in a Spray Dryer. J. Kejuruter. 2019, 31, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, M.; Yoon, Y.-I.; Kim, M.A.; Hwang, J.-S.; Goo, T.-W.; Yun, E.-Y. Physical and Sensory Evaluation of Tenebrio molitor Larvae Cooked by Various Cooking Methods. Korean J. Food Cook. Sci. 2015, 31, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahwal, E.N.; Fang, C.P.; Ibrahim, N.N.A.; Razali, N.S.M.; Rahman, H.A. Effect of Different Drying Methods and Solvents on Phenolic Content, Antioxidant and Anti-Hyperglycemic Activities of Melastoma Malabathricum Leaves Extract. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2018, 47, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Norafida, A.; Aminah, A. Effect of Blanching Treatments on Antioxidant Activity of Frozen Green Capsicum (Capsicum annuum L. var bell pepper). Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boekel, M.; Fogliano, V.; Pellegrini, N.; Stanton, C.; Scholz, G.; Lalljie, S.; Somoza, V.; Knorr, D.; Jasti, P.R.; Eisenbrand, G. A Review on the Beneficial Aspects of Food Processing. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1215–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelaert, C.; Francis, F.; Alabi, T.; Caparros Megido, R.; Crahay, B.; Bindelle, J.; Beckers, Y. Protein Value of Two Insects, Subjected to Various Heat Treatments, Using Growing Rats and the Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score. J. Insects Food Feed 2018, 4, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewuyemi, Y.O.; Kesa, H.; Chinma, C.E.; Adebo, O.A. Fermented Edible Insects for Promoting Food Security in Africa. Insects 2020, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-López, C.; Santiago-López, L.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Liceaga, A.M.; García, H.S.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. An Insight to Fermented Edible Insects: A Global Perspective and Prospective. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Garofalo, C.; Clementi, F.; Ruschioni, S.; Riolo, P.; Isidoro, N.; Loreto, N.; Galarini, R.; et al. Distribution of Transferable Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Laboratory-Reared Edible Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor L.). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, L.; Ghosh, A. Los Insectos Representan Un Vínculo Entre Las Granjas de Animales de Consumo y El Entorno Urbano Para Los Rasgos de Resistencia a Los Antibióticos. Müller V., Ed. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3562–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeweyer, D.; Milanović, V.; Garofalo, C.; Osimani, A.; Clementi, F.; Van Campenhout, L.; Aquilanti, L. Real-Time PCR Detection and Quantification of Selected Transferable Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Fresh Edible Insects from Belgium and the Netherlands. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanović, V.; Osimani, A.; Pasquini, M.; Aquilanti, L.; Garofalo, C.; Taccari, M.; Cardinali, F.; Riolo, P.; Clementi, F. Getting Insight into the Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Specimens of Marketed Edible Insects. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 227, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimani, A.; Cardinali, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Garofalo, C.; Roncolini, A.; Milanović, V.; Pasquini, M.; Tavoletti, S.; Clementi, F. Occurrence of Transferable Antibiotic Resistances in Commercialized Ready-to-Eat Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor L.). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 263, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osimani, A.; Garofalo, C.; Aquilanti, L.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Taccari, M.; Pasquini, M.; Tavoletti, S.; Clementi, F. Transferable Antibiotic Resistances in Marketed Edible Grasshoppers (Locusta migratoria migratorioides). J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchini, G.M.; Trushenski, J.T.; Glencross, B.D. Thoughts for the Future of Aquaculture Nutrition: Realigning Perspectives to Reflect Contemporary Issues Related to Judicious Use of Marine Resources in Aquafeeds. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2019, 81, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, J.P.; Love, D.C.; MacDonald, G.K.; West, P.C.; Engstrom, P.M.; Nachman, K.E.; Lawrence, R.S. Environmental Health Impacts of Feeding Crops to Farmed Fish. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokou, F.; Fountoulaki, E. Aquaculture Waste Production Associated with Antinutrient Presence in Common Fish Feed Plant Ingredients. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Li, H.L.; Pang, H.; Zhu, C.D.; Zhang, Y.Z. Investigating the Parasitoid Community Associated with the Invasive Mealybug Phenacoccus Solenopsis in Southern China. Insects 2021, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Barroso, F.G.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Insect Meal as Renewable Source of Food for Animal Feeding: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendra, K.C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; van Huis, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Heckmann, L.H.L.; Khanal, S.K. Rethinking Organic Wastes Bioconversion: Evaluating the Potential of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens (L.)) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) (BSF). Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Singh, P.; Nataraj, B.H.; Kokkiligadda, A.; Naithani, H.; Azmal Ali, S.; Behare, P.V.; Nagpal, R. Fostering Next-Generation Probiotics in Human Gut by Targeted Dietary Modulation: An Emerging Perspective. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Tabashsum, Z.; Anderson, M.; Truong, A.; Houser, A.K.; Padilla, J.; Akmel, A.; Bhatti, J.; Rahaman, S.O.; Biswas, D. Effectiveness of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Prebiotic-like Components in Common Functional Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1908–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumari, K. An Inclusive Approach for Organic Waste Treatment and Valorisation Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, V.C.; Rawles, S.D.; Thompson, K.R.; Velasquez, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hager, J.; Webster, C.D. Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal as Partial or Total Replacement of Marine Fish Meal in Practical Diets for Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2017, 473, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, A.; Raggi, T.; Barkhouse, J.; Lewis, E.; Weltzien, E. The Oil Fraction and Partially Defatted Meal of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Affect Differently Growth Performance, Feed Efficiency, Nutrient Deposition, Blood Glucose and Lipid Digestibility of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2018, 492, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, E.R.; Arsiwalla, T.; Waagbø, R. Insect Larvae Meal as an Alternative Source of Nutrients in the Diet of a Tlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Postsmolt. Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renna, M.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F.; Dabbou, S.; Lussiana, C.; Malfatto, V.; Prearo, M.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasato, I.; Biasibetti, E.; et al. Evaluation of the Suitability of a Partially Defatted Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Larvae Meal as Ingredient for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) Diets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moula, N.; Scippo, M.L.; Douny, C.; Degand, G.; Dawans, E.; Cabaraux, J.F.; Hornick, J.L.; Medigo, R.C.; Leroy, P.; Francis, F.; et al. Performances of Local Poultry Breed Fed Black Soldier Fly Larvae Reared on Horse Manure. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Van Loon, J.J.A.; De Boer, I.J.M.; Aarnink, A.J.A.; Van Zanten, H.H.E. Black Soldier Fly Reared on Pig Manure: Bioconversion Efficiencies, Nutrients in the Residual Material, Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Emissions. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguz, M.; Gasco, L.; Tomberlin, J.K. Impact of PH and Feeding System on Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens, L.; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larval Development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202591. [Google Scholar]
- Liland, N.S.; Biancarosa, I.; Araujo, P.; Biemans, D.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbø, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.J. Modulation of Nutrient Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae by Feeding Seaweed-Enriched Media. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danieli, P.P.; Lussiana, C.; Gasco, L.; Amici, A.; Ronchi, B. The Effects of Diet Formulation on the Yield, Proximate Composition, and Fatty Acid Profile of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Prepupae Intended for Animal Feed. Animals 2019, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aini, N.; Nugroho, R.A.; Hariani, N. Growth and Survival Evaluation of Oreochromis Sp Fed Hermetia Illucens Larva and Manihot Esculenta Leaves Meal. Biosaintifika J. Biol. Biol. Educ. 2018, 10, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippayadara, N.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Krutmuang, P.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Van Doan, H.; Paolucci, M. Replacement of Fish Meal by Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal: Effects on Growth, Haematology, and Skin Mucus Immunity of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus. Animals 2021, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, N. Effects of Substitution of Fish Meal with Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal, in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Diets. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2017, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Khalil, R.H.; Metwally, A.A.; Shakweer, M.S.; Khallaf, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. Effects of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Larvae Meal on Growth Performance, Organs-Somatic Indices, Body Composition, and Hemato-Biochemical Variables of European Sea Bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.X.; Yao, Y.L.; Wang, S.J.; Du, R.G.; Wang, W.P.; Chen, X.Y.; Hong, C.L.; Qi, B.; Xue, Z.Y.; Yang, H.Q. Housefly Maggot-Treated Composting as Sustainable Option for Pig Manure Management. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.; Ortuño, J.; Stratakos, A.C.; Linton, M.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Elliot, T.; Koidis, A.; Theodoridou, K. Impact of Thermal and High-Pressure Treatments on the Microbiological Quality and in Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Animals 2020, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreki, J.C.; Tiroesele, B.; Chiripasi, S.C. Prospects of Utilizing Insects as Alternative Sources of Protein in Poultry Diets in Botswana: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. Adv. 2012, 2, 649–658. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Jin, J.N.; Zhu, F.; Roffeis, M.; Zhang, X.Z. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Replacing Fishmeal with Housefly (Musca domestica) Maggot Meal in the Diet of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Growth Performance, Flesh Quality, Innate Immunity and Water Environment. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunji, J.; Schulz, C.; Kloas, W. Growth Performance, Nutrient Utilization of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus Fed Housefly Maggot Meal (Magmeal) Diets. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 8, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sing, K.W.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Wilson, J.J.; Sofian-Azirun, M. Evaluation of Blowfly (Chrysomya megacephala) Maggot Meal as an Effective, Sustainable Replacement for Fishmeal in the Diet of Farmed Juvenile Red Tilapia (Oreochromis Sp.). Pak. Vet. J. 2014, 34, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Mui, J.J. Evaluation of Dietary Inclusion of Housefly Maggot (Musca domestica) Meal on Growth, Fillet Composition and Physiological Responses for Barramundi, Lates Calcarifer. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2478–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Qin, L.; Zhao, D.; Xiong, F.; Wang, G.; Zou, H.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Song, K.; Wu, S. Growth Performance, Immunity and Intestinal Microbiota of Swamp Eel (Monopterus albus) Fed a Diet Supplemented with House Fly Larvae (Musca domestica). Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbou, S.; Gasco, L.; Lussiana, C.; Brugiapaglia, A.; Biasato, I.; Renna, M.; Cavallarin, L.; Gai, F.; Schiavone, A. Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) Larvae Inclusion in Diets for Free-Range Chickens: Effects on Meat Quality and Fatty Acid Profile. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2020, 35, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, G.; Iaconisi, V.; Marono, S.; Gasco, L.; Loponte, R.; Nizza, S.; Bovera, F.; Parisi, G. Effect of Tenebrio molitor Larvae Meal on Growth Performance, in Vivo Nutrients Digestibility, Somatic and Marketable Indexes of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 226, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales-Mérida, S.; Gobbi, P.; Józefiak, D.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Dudek, K.; Rawski, M.; Kierończyk, B.; Józefiak, A. Insect Meals in Fish Nutrition. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 1080–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belforti, M.; Gai, F.; Lussiana, C.; Renna, M.; Malfatto, V.; Rotolo, L.; De Marco, M.; Dabbou, S.; Schiavone, A.; Zoccarato, I.; et al. Tenebrio molitor Meal in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Diets: Effects on Animal Performance, Nutrient Digestibility and Chemical Composition of Fillets. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Henry, M.; Piccolo, G.; Marono, S.; Gai, F.; Renna, M.; Lussiana, C.; Antonopoulou, E.; Mola, P.; Chatzifotis, S. Tenebrio molitor Meal in Diets for European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Juveniles: Growth Performance, Whole Body Composition and in Vivo Apparent Digestibility. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 220, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.M.; Khosravi, S.; Yoon, K.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, B.J.; Hur, S.W.; Lee, S.M. Mealworm, Tenebrio molitor, as a Feed Ingredient for Juvenile Olive Flounder, Paralichthys Olivaceus. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panini, R.L.; Freitas, L.E.L.; Guimarães, A.M.; Rios, C.; da Silva, M.F.O.; Vieira, F.N.; Fracalossi, D.M.; Samuels, R.I.; Prudêncio, E.S.; Silva, C.P.; et al. Potential Use of Mealworms as an Alternative Protein Source for Pacific White Shrimp: Digestibility and Performance. Aquaculture 2017, 473, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncarati, A.; Gasco, L.; Parisi, G.; Terova, G. Growth Performance of Common Catfish (Ameiurus melas Raf.) Fingerlings Fed Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) Diet. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, V.J.; Finer, E.; Bergmans, R.S.; Febvre, H.P.; Longhurst, C.; Manter, D.K.; Patz, J.A.; Weir, T.L. Impact of Edible Cricket Consumption on Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults, a Double-Blind, Randomized Crossover Trial. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.M.; Khosravi, S.; Mauliasari, I.R.; Lee, B.J.; You, S.G.; Lee, S.M. Nutritional Evaluation of Cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus, Meal as Fish Meal Substitute for Olive Flounder, Paralichthys Olivaceus, Juveniles. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 52, 859–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phesatcha, B.; Phesatcha, K.; Viennaxay, B.; Matra, M.; Totakul, P.; Wanapat, M. Cricket Meal (Gryllus bimaculatus) as a Protein Supplement on In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics and Methane Mitigation. Insects 2022, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Bai, Y.Y.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, C.X. Nutritional Value of the Field Cricket (Gryllus Testaceus Walker). Insect Sci. 2004, 11, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufek, N.M.; Aspani, F.; Muin, H.; Raji, A.A.; Razak, S.A.; Alias, Z. The Effect of Dietary Cricket Meal (Gryllus bimaculatus) on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Enzyme Activities, and Haematological Response of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taufek, N.M.; Muin, H.; Raji, A.A.; Md Yusof, H.; Alias, Z.; Razak, S.A. Potential of Field Crickets Meal (Gryllus bimaculatus) in the Diet of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufek, N.M.; Razak, S.A.; Alias, Z. Potential Value of Black Crickets M Eal as Protein Replacement for Fish M Eal in African Catfish, (Clarias gariepinus) Fingerlings Nutrition. In Proceedings of the Advancement in Marine and Freshwater Sciences, Terengganu, Malaysia, 8–10 October 2013; pp. 520–525. [Google Scholar]
- Permatahati, D.; Mutia, R.; Astuti, D.A. Effect of Cricket Meal (Gryllus bimaculatus) on Production and Physical Quality of Japanese Quail Egg. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 42, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilami, S.K.; Turek, J.; Červený, D.; Lepič, P.; Kozák, P.; Burkina, V.; Sakalli, S.; Tomčala, A.; Sampels, S.; Mráz, J. Insect Meal as a Partial Replacement for Fish Meal in a Formulated Diet for Perch Perca Fluviatilis. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 20, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, M.Y.; Amatul-Samahah, M.A.; Jaapar, M.Z.; Mohamad, S.N. The Effects of Field Cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus) Meal Substitution on Growth Performance and Feed Utilization of Hybrid Red Tilapia (Oreochromis Spp.). Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100070. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, A.; Frederich, M.; Uyttenbroeck, R.; Malik, P.; Filocco, S.; Richel, A.; Heuskin, S.; Alabi, T.; Megido, R.C.; Franck, T.; et al. Nutritional Composition and Rearing Potential of the Meadow Grasshopper (Chorthippus Parallelus Zetterstedt). J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuzé, V.; Tran, G. Locust Meal, Locusts, Grasshoppers and Crickets; Feedipedia, a Programme by INRA, CIRAD, AFZ and FAO; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alegbeleye, W.O.; Obasa, S.O.; Olude, O.O.; Otubu, K.; Jimoh, W. Preliminary Evaluation of the Nutritive Value of the Variegated Grasshopper (Zonocerus variegatus L.) for African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell. 1822) Fingerlings. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emehinaiye, P.A. Growth Performance of Oreochromis Niloticus Fingerlings Fed with Varying Levels of Migratory Locust (Locusta migratoria) Meal. Bachelor’s Thesis, Federal University of Agriculture Abeokuta, Abeokuta, Nigeria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, O.I. Effects of Grasshopper Meal in the Diet of Clarias Gariepinus Fingerlings. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yu, H.S.; Shen, Y.H.; Banno, Y.; Xiang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z. Phylogeny and Evolutionary History of the Silkworm. Sci. China Life Sci. 2012, 55, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomotake, H.; Katagiri, M.; Yamato, M. Silkworm Pupae (Bombyx mori) Are New Sources of High Quality Protein and Lipid. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2010, 56, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanov, A.R.; Milusheva, R.; Rashidova, S.; Kamilov, B. Effect of Replacement of Fish Meal with Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Pupa Protein on the Growth of Clarias Gariepinus Fingerling. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 2, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Choi, I.C.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, S.H.; Yoo, J.Y. Response of Dietary Substitution of Fishmeal with Various Protein Sources on Growth, Body Composition and Blood Chemistry of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus, Temminck & Schlegel, 1846). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jintasataporn, O.; Chumkam, S.; Jintasataporn, O. Substitution of Silkworm Pupae (Bombyx mori) for Fish Meal in Broodstock Diets for Snakeskin Gourami (Trichogaster pectoralis). J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Dheke, S.; Gubhaju, S.R. Growth Response of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) on Substitution of Shrimp Meal by Different Protein Sources. Nepal. J. Zool. Online 2013, 1, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney, S. Effect of Partial Substitution of Expensive Ingredient Ie Fishmeal on the Growth of Tor putitora Fed Practical Diets. J. Int. Acad. Res. Multidiscipl. 2014, 2, 482–489. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Studies on Blood Chemistry Indices and Histopathology of Pseudosciaena Crocea Artificially Challenged with Vibrio Harveyi. J. Fish. China 2010, 34, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo, W.R.; Hayashi, C.; Meurer, F. Digestibilidade Aparente Da Energia e Nutrientes de Alimentos Convencionais e Alternativos Para a Tilápia Do Nilo (Oreochromis niloticus, L.). Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2002, 31, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhang, J.L.; Huang, J.Q.; Cheng, X.F.; Liu, C. Effect of Replacement of Dietary Fish Meal with Silkworm Pupae Meal on Growth Performance, Body Composition, Intestinal Protease Activity and Health Status in Juvenile Jian Carp (Cyprinus carpio var. jian). Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.H.L.; Snellgrove, D.L.; Davies, S.J. A Comparison between Marine and Terrestrial Invertebrate Meals for Mirror Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) Diets: Impact on Growth, Haematology and Health. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 5004–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.K.; Aanand, S.; Sampathkumar, J.S.; Padmavathy, P. Effect of Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Pupae on the Growth and Maturation of Rainbow Shark Epalzeorhynchos Frenatum (Fowler, 1934) under Captive Rearing. Indian J. Fish. 2020, 67, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.J.; Francis, D.S.; Blyth, D.; Moyano, F.J.; Smullen, R.P.; Turchini, G.M.; Booth, M.A. A Comparison of In-Vivo and in-Vitro Methods for Assessing the Digestibility of Poultry by-Product Meals Using Barramundi (Lates calcarifer); Impacts of Cooking Temperature and Raw Material Freshness. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtlander, T.; Stamer, A.; Buser, A.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Leiber, F.; Sandrock, C. Hermetia illucens Meal as Fish Meal Replacement for Rainbow Trout on Farm. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, C.; Rios, A.; Lefebvre, T.; Do, H.; Henry, M.; Jintasataporn, O. Replacing Fish Meal with Defatted Insect Meal (Yellow Mealworm Tenebrio molitor) Improves the Growth and Immunity of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Animals 2019, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, J.M.; Attademo, A.M.; Mammana, S.B.; Altamirano, J.C.; Lajmanovich, R.C. Impact of Dietary Lipid Level on Esterase Enzyme Activities in the Non-Target Freshwater Shrimp Macrobrachium Borellii Exposed to Chlorpyrifos. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19497–19504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoraki, M.; Mollá Ferrándiz, P.; Vardali, S.C.; Kontodimas, D.C.; Kotzamanis, Y.P.; Gasco, L.; Chatzifotis, S.; Antonopoulou, E. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Fish Meal Substitution with Three Different Insect Meals on Growth, Body Composition and Metabolism of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, S.; Bakhtiyar, Y.; Lakhnotra, R. Replacement of Fishmeal with Locally Available Ingredients in Diet Composition of Macrobrachium dayanum. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Mccallum, M.L.; Weston, S.D.; Tilahun, Y. Performance of Early Juvenile Giant River Prawns (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) Fed Fish, Soybean, Shrimp and Four Insect Based Diets While Under Low Temperature Stress. Proc. Okla. Acad. Sci. 2020, 100, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, A.; Poku, G. Nutritive Value of Termite as Fish Meal Supplement in the Diet of Freshwater Prawns (Macrobrachium rosenbergii de Man) Juveniles. Extrem. Life Biospeology Astrobiol. 2014, 6, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Long, S.; You, Y.; Dong, X.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Xie, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. Effect of Dietary Oxidized Fish Oil on Growth Performance, Physiological Homeostasis and Intestinal Microbiome in Hybrid Grouper (♀ Epi-Nephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂ Epinephelus lanceolatus). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, B.; Zarantoniello, M.; Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Truzzi, C.; Notarstefano, V.; Cardinaletti, G.; Huyen, K.T.; Carnevali, O.; Olivotto, I. Can Insect-Based Diets Affect Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Reproduction? A Multidisciplinary Study. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terova, G.; Rimoldi, S.; Ascione, C.; Gini, E.; Ceccotti, C.; Gasco, L. Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Gut Microbiota Is Modulated by Insect Meal from Hermetia illucens Prepupae in the Diet. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, L.; Randazzo, B.; Cardinaletti, G.; Zarantoniello, M.; Mina, F.; Secci, G.; Tulli, F.; Olivotto, I.; Parisi, G. Dietary Inclusion of Full-Fat Hermetia illucens Prepupae Meal in Practical Diets for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Lipid Metabolism and Fillet Quality Investigations. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinaletti, G.; Randazzo, B.; Messina, M.; Zarantoniello, M.; Giorgini, E.; Zimbelli, A.; Bruni, L.; Parisi, G.; Olivotto, I.; Tulli, F. Effects of Graded Dietary Inclusion Level of Full-Fat Hermetia illucens Prepupae Meal in Practical Diets for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Animals 2019, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Müller, A.; Heckel, D.G.; Gutzeit, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Nutritional Immunology: Diversification and Diet-Dependent Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Roncolini, A.; Riolo, P.; Ruschioni, S.; Isidoro, N.; Loreto, N.; Franciosi, E.; Tuohy, K.; Olivotto, I.; et al. Hermetia illucens in Diets for Zebrafish (Danio Rerio): A Study of Bacterial Diversity by Using PCR-DGGE and Metagenomic Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Randazzo, B.; Secci, G.; Notarstefano, V.; Giorgini, E.; Lock, E.J.; Parisi, G.; Olivotto, I. Application of Laboratory Methods for Understanding Fish Responses to Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Based Diets. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 8, 1173–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; Salem, M.E.S. Effects of Dietary Chitosan Supplementation on Farmed Fish: A Review. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, C.; Ahilan, B.; Felix, N.; Uma, A.; Prabu, E. Effects of Dietary Protein Substitution of Fishmeal with Black Soldier Fly Larval Meal on Growth and Physiological Responses of Juvenile Striped Catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 2204–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeckel, S.; Harjes, A.G.E.; Roth, I.; Katz, H.; Wuertz, S.; Susenbeth, A.; Schulz, C. When a Turbot Catches a Fly: Evaluation of a Pre-Pupae Meal of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Fish Meal Substitute—Growth Performance and Chitin Degradation in Juvenile Turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture 2012, 364–365, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiani, A.; Marseglia, A.; Leni, G.; Baldassarre, S.; Maistrello, L.; Dossena, A.; Sforza, S. Composition of Black Soldier Fly Prepupae and Systematic Approaches for Extraction and Fractionation of Proteins, Lipids and Chitin. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; He, S.; Huo, F.; Qin, C.; Yao, B.; Ringø, E. High-Yield Production of a Chitinase from Aeromonas Veronii B565 as a Potential Feed Supplement for Warm-Water Aquaculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, N.; Vidakovic, A.; Langeland, M.; Kiessling, A.; Sampels, S.; Lalander, C. Fatty Acid Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens)—Possibilities and Limitations for Modification through Diet. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arru, B.; Furesi, R.; Gasco, L.; Madau, F.A.; Pulina, P. The Introduction of Insect Meal into Fish Diet: The First Economic Analysis on European Sea Bass Farming. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer Llagostera, P.; Kallas, Z.; Reig, L.; Amores de Gea, D. The Use of Insect Meal as a Sustainable Feeding Alternative in Aquaculture: Current Situation, Spanish Consumers’ Perceptions and Willingness to Pay. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.K.; Bose, M.; Harish, D. Haematological Changes in the Blood of Clarias Batrachus Exposed to Mercuric Chloride. J. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Monit. 2002, 12, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Truzzi, C.; Girolametti, F.; Giovannini, L.; Olivotto, I.; Zarantoniello, M.; Scarponi, G.; Annibaldi, A.; Illuminati, S. New Eco-Sustainable Feed in Aquaculture: Influence of Insect-Based Diets on the Content of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Experimental Model Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Molecules 2022, 27, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, D.; Hogstrand, C.; Bury, N.R. Physiological Response to a Metal-Contaminated Invertebrate Diet in Zebrafish: Importance of Metal Speciation and Regulation of Metal Transport Pathways. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Camenzuli, L.; Belluco, S.; Meijer, N.; Ricci, A. Food Safety Issues Related to Uses of Insects for Feeds and Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, H.S.; Yusuf, A.A. Legislation and Legal Frame Work for Sustainable Edible Insects Use in Nigeria. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 2201–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbos, C.I.; Mente, E.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Vlontzos, G.; Athanassiou, C.G. Insect-Based Feed Ingredients for Aquaculture: A Case Study for Their Acceptance in Greece. Insects 2021, 12, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, L.; Mancuso, T.; Peri, M.; Gasco, L.; Trentinaglia, M.T. Consumer Attitude and Acceptance toward Fish Fed with Insects: A Focus on the New Generations. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Schmitt, E.; Mathys, A. Sustainable Use of Hermetia illucens Insect Biomass for Feed and Food: Attributional and Consequential Life Cycle Assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffeis, M.; Fitches, E.C.; Wakefield, M.E.; Almeida, J.; Alves Valada, T.R.; Devic, E.; Koné, N.G.; Kenis, M.; Nacambo, S.; Koko, G.K.D.; et al. Ex-Ante Life Cycle Impact Assessment of Insect Based Feed Production in West Africa. Agric. Syst. 2020, 178, 102710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolo, S.; Parisi, G.; Biondi, N.; Lunelli, F.; Tibaldi, E.; Pastres, R. Fishmeal Partial Substitution within Aquafeed Formulations: Life Cycle Assessment of Four Alternative Protein Sources. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 1455–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, A.; Rivera, J.L.; Wilfart, A.; Maillard, F.; Hassouna, M.; Senga-Kiesse, T.; Le Féon, S.; Aubin, J. Mealworm Meal for Animal Feed: Environmental Assessment and Sensitivity Analysis to Guide Future Prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Xiong, H.; Wang, W.; Duan, X.; Yang, T.; Wu, C.; Yang, F.; Xiong, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Energy Consumption Analysis of Lipid Extraction from Black Soldier Fly Biomass. Energy 2019, 185, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józefiak, A.; Nogales-Mérida, S.; Mikołajczak, Z.; Rawski, M.; Kierończyk, B.; Mazurkiewicz, J. The Utilization of Full-Fat Insect Meal in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Nutrition: The Effects on Growth Performance, Intestinal Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Tract Histomorphology. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2019, 19, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrikov, D.; Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Barroso, F.G.; Tomás-Almenar, C.; Melenchón, F.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Morales, A.E.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, M.; Montes-Lopez, J. Comparative Study of Growth Performance and Amino Acid Catabolism in Oncorhynchus mykiss, Tinca tinca and Sparus aurata and the Catabolic Changes in Response to Insect Meal Inclusion in the Diet. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basto, A.; Matos, E.; Valente, L.M.P. Nutritional Value of Different Insect Larvae Meals as Protein Sources for European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Juveniles. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sealey, W.M.; Gaylord, T.G.; Barrows, F.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; McGuire, M.A.; Ross, C.; St-Hilaire, S. Sensory Analysis of Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, Fed Enriched Black Soldier Fly Prepupae, Hermetia illucens. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weththasinghe, P.; Hansen, J.; Nøkland, D.; Lagos, L.; Rawski, M.; Øverland, M. Full-Fat Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Meal and Paste in Extruded Diets for Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar): Effect on Physical Pellet Quality, Nutrient Digestibility, Nutrient Utilization and Growth Performances. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irungu, F.G.; Mutungi, C.M.; Faraj, A.K.; Affognon, H.; Kibet, N.; Tanga, C.; Ekesi, S.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Fiaboe, K.K.M. Physico-Chemical Properties of Extruded Aquafeed Pellets Containing Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Adult Cricket (Acheta domesticus) Meals. J. Insects Food Feed 2018, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPIFF. The European Insect Sector Today: Challenges, Opportunities and Regulatory Landscape; IPIFF Vision Paper on the Future of the Insect Sector towards 2030; IPIFF: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, M.E.; González-Montaña, J.R.; Lomillos, J.M. Consumers’ Concerns and Perceptions of Farm Animal Welfare. Animals 2020, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, H.; Blokhuis, H.; Jensen, P.; Keeling, L. Towards Farm Animal Welfare and Sustainability. Animals 2018, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weary, D.M.; Robbins, J.A. Understanding the Multiple Conceptions of Animal Welfare. Anim. Welf. 2019, 28, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K.G.; Sonntag, W.I.; Glanz-Chanos, V.; Forum, S. Consumer Interest in Environmental Impact, Safety, Health and Animal Welfare Aspects of Modern Pig Production: Results of a Cross-National Choice Experiment. Meat Sci. 2018, 137, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, D.J.; Beausoleil, N.J.; Littlewood, K.E.; McLean, A.N.; McGreevy, P.D.; Jones, B.; Wilkins, C. The 2020 Five Domains Model: Including Human–Animal Interactions in Assessments of Animal Welfare. Animals 2020, 10, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-de la Lama, G.C.; Estévez-Moreno, L.X.; Villarroel, M.; Rayas-Amor, A.A.; María, G.A.; Sepúlveda, W.S. Consumer Attitudes Toward Animal Welfare-Friendly Products and Willingness to Pay: Exploration of Mexican Market Segments. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2019, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
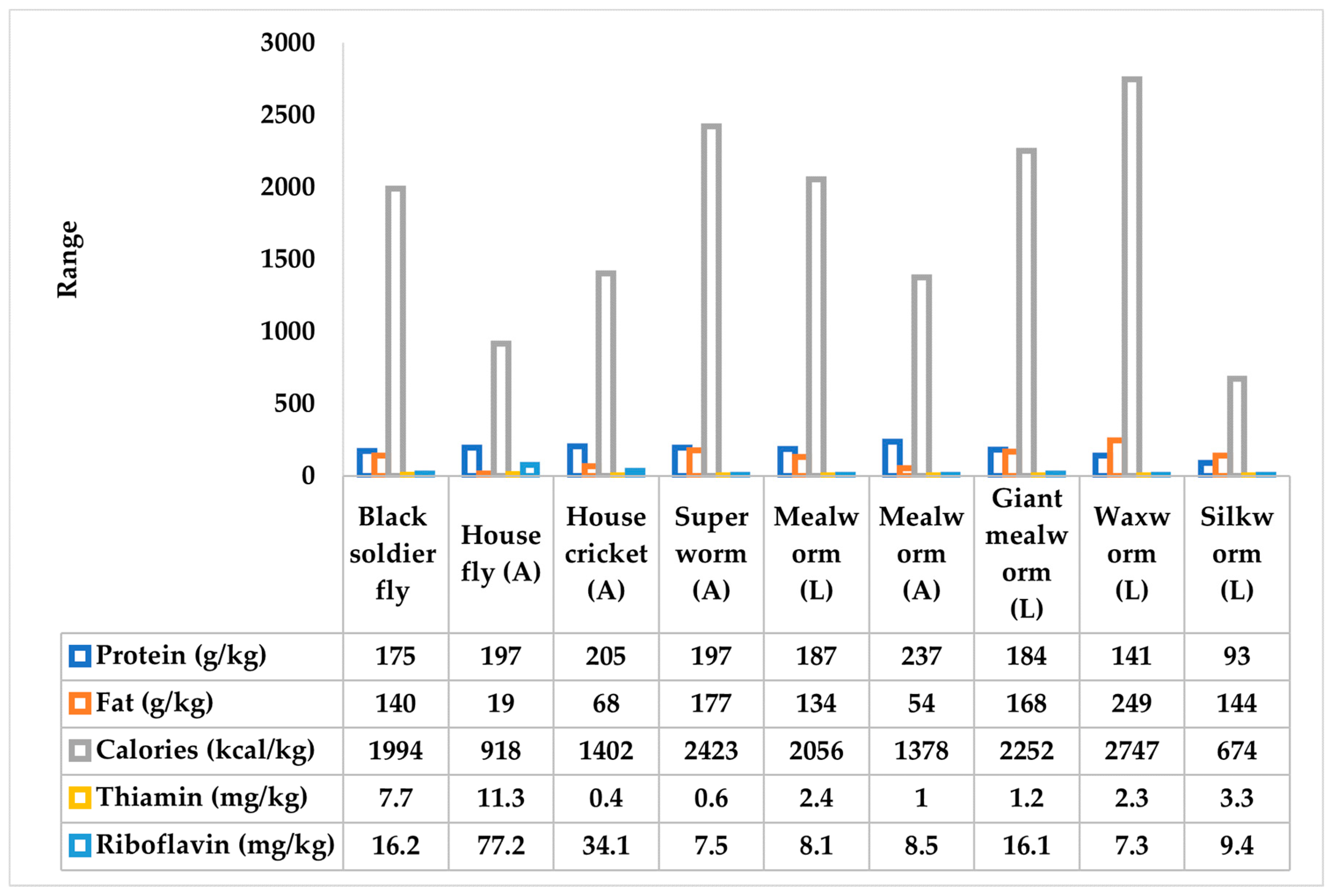
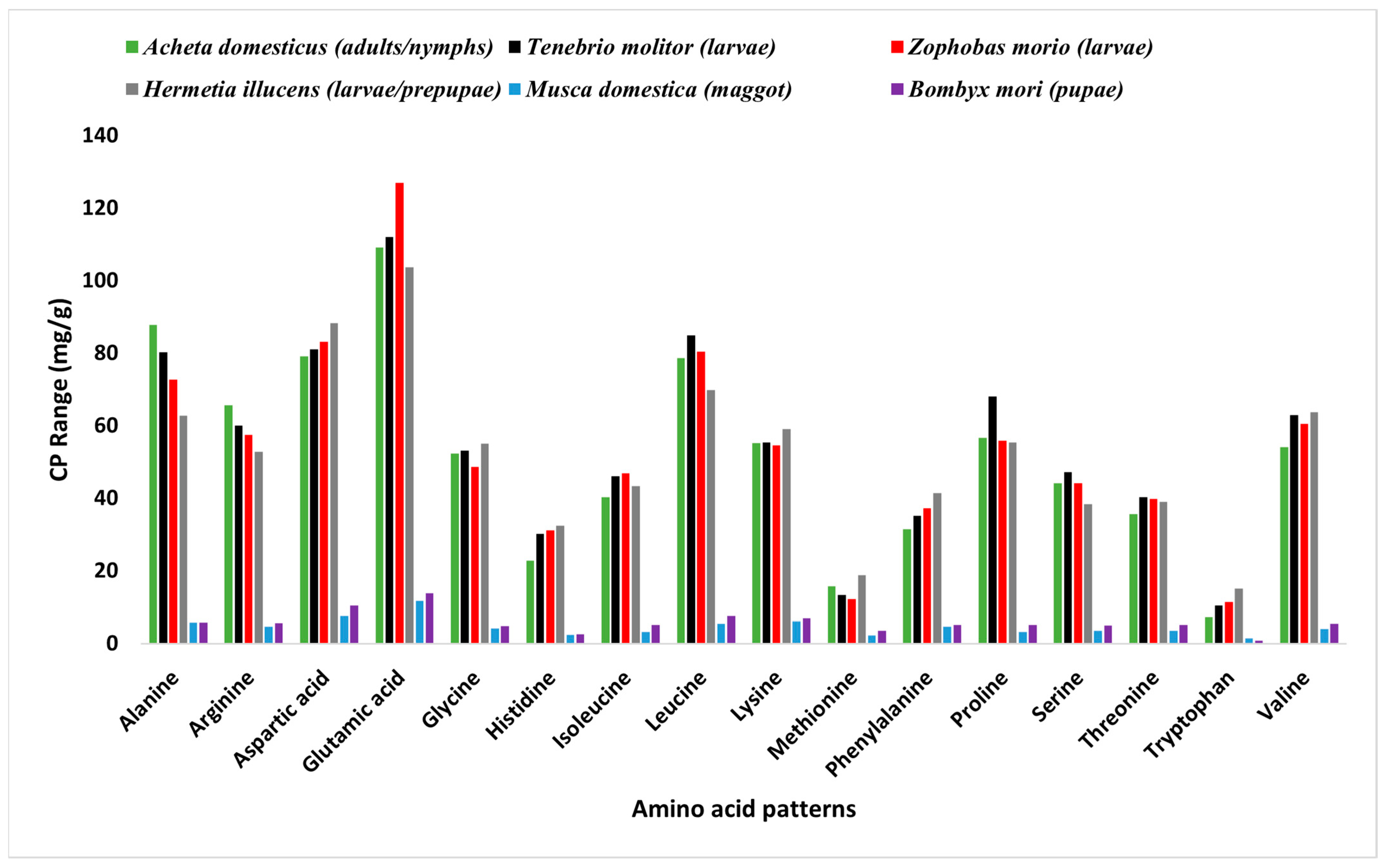

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hameed, A.; Majeed, W.; Naveed, M.; Ramzan, U.; Bordiga, M.; Hameed, M.; Ur Rehman, S.; Rana, N. Success of Aquaculture Industry with New Insights of Using Insects as Feed: A Review. Fishes 2022, 7, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060395
Hameed A, Majeed W, Naveed M, Ramzan U, Bordiga M, Hameed M, Ur Rehman S, Rana N. Success of Aquaculture Industry with New Insights of Using Insects as Feed: A Review. Fishes. 2022; 7(6):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060395
Chicago/Turabian StyleHameed, Amna, Waqar Majeed, Muhammad Naveed, Uzma Ramzan, Matteo Bordiga, Maryam Hameed, Saud Ur Rehman, and Naureen Rana. 2022. "Success of Aquaculture Industry with New Insights of Using Insects as Feed: A Review" Fishes 7, no. 6: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060395
APA StyleHameed, A., Majeed, W., Naveed, M., Ramzan, U., Bordiga, M., Hameed, M., Ur Rehman, S., & Rana, N. (2022). Success of Aquaculture Industry with New Insights of Using Insects as Feed: A Review. Fishes, 7(6), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060395







