A Novel Method for Sensitive Detection of Vibrio alginolyticus Based on Aptamer and Hybridization Chain Reaction in Aquaculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Bacterial Culture
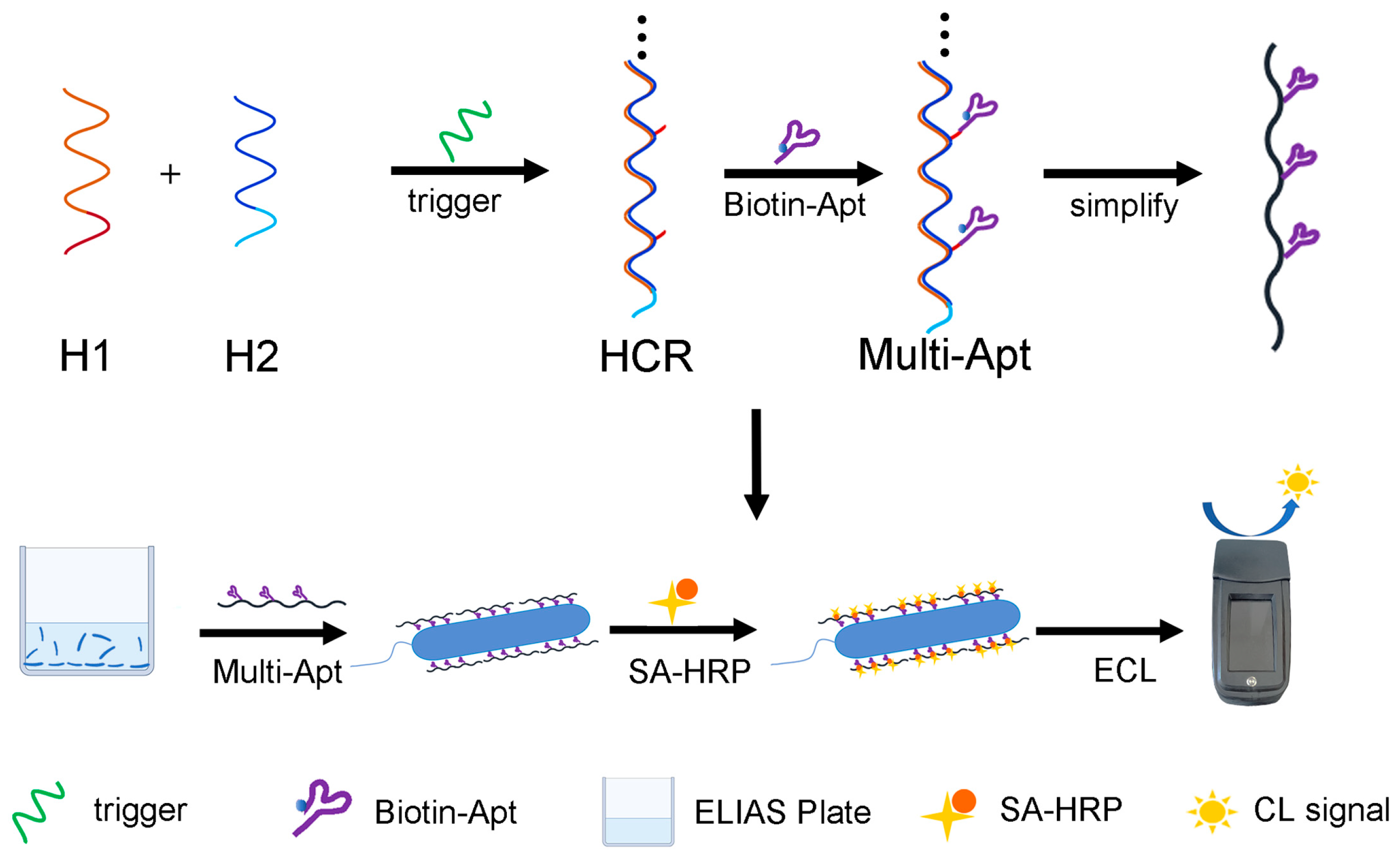
2.3. Preparation of HCR-Based Multi-Apt Structure
2.4. ELISA Assays
2.5. Binding Affinity between the Aptamer and V. alginolyticus
2.6. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.7. Detection of the Spiked Sample
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Principle of the HCR-Based Multi-Apt
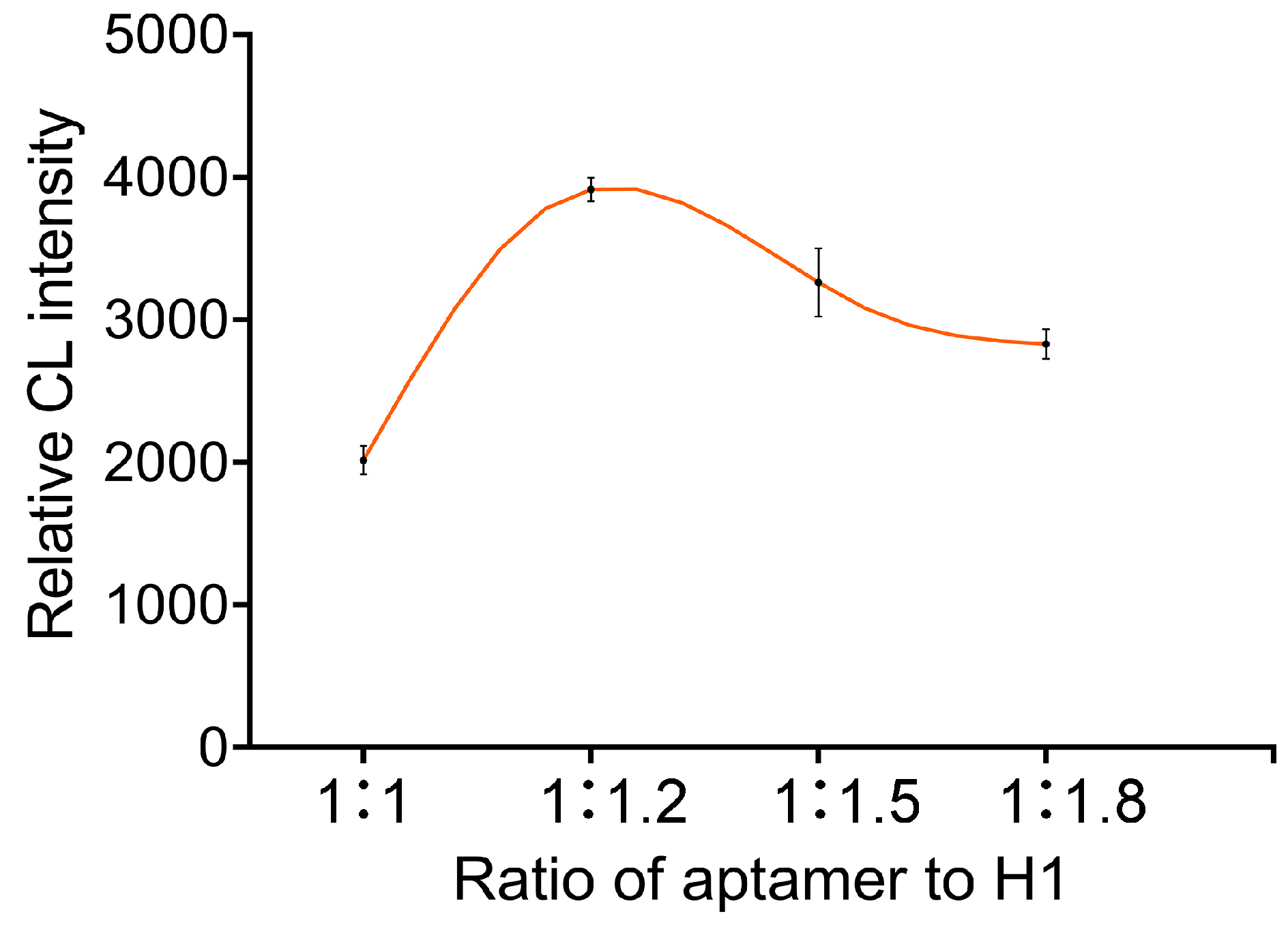
3.2. Optimization of the Aptamer-to-H1 Ratio
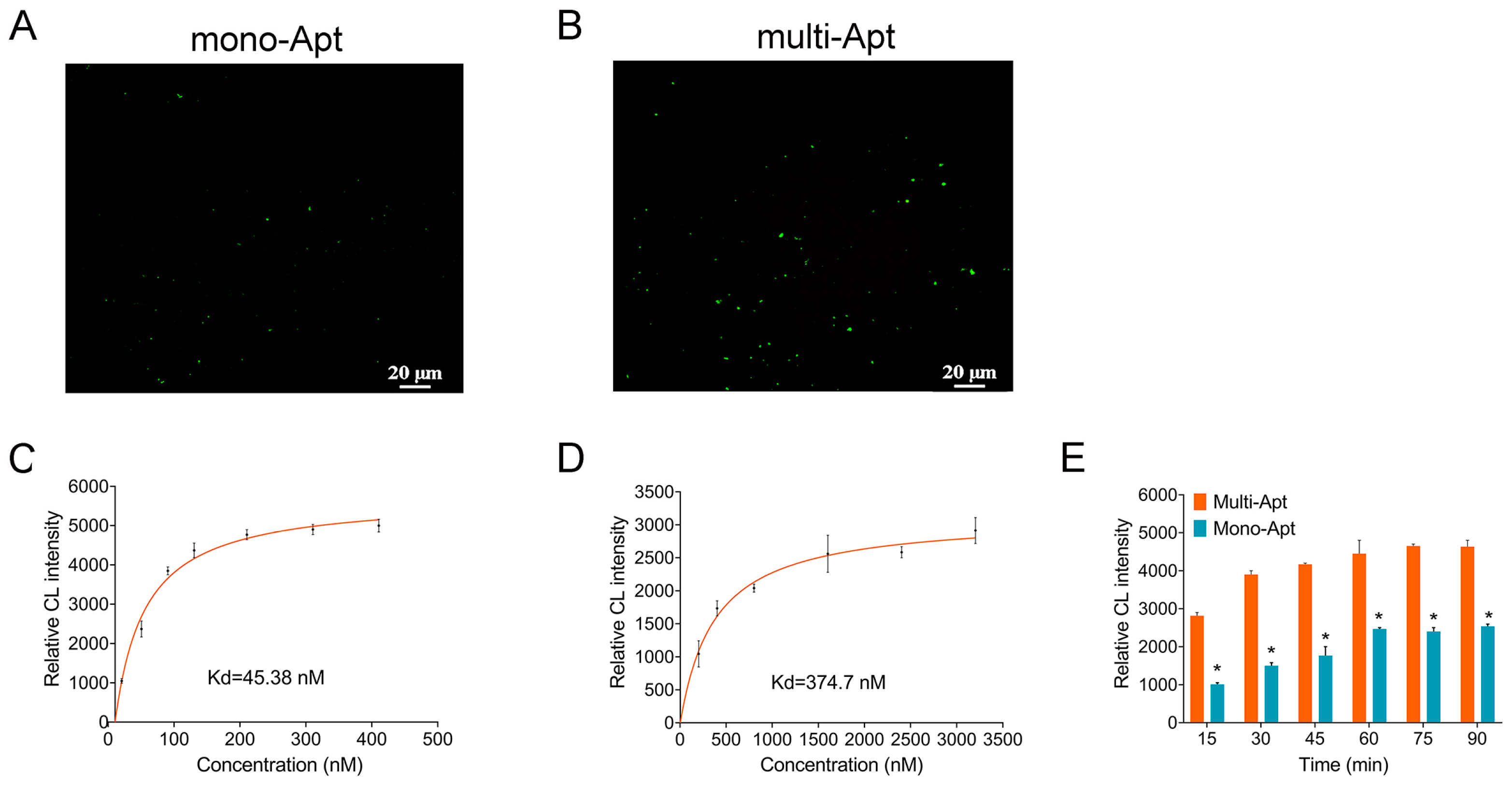
3.3. The Affinity of V. alginolyticus and Multi-Apt
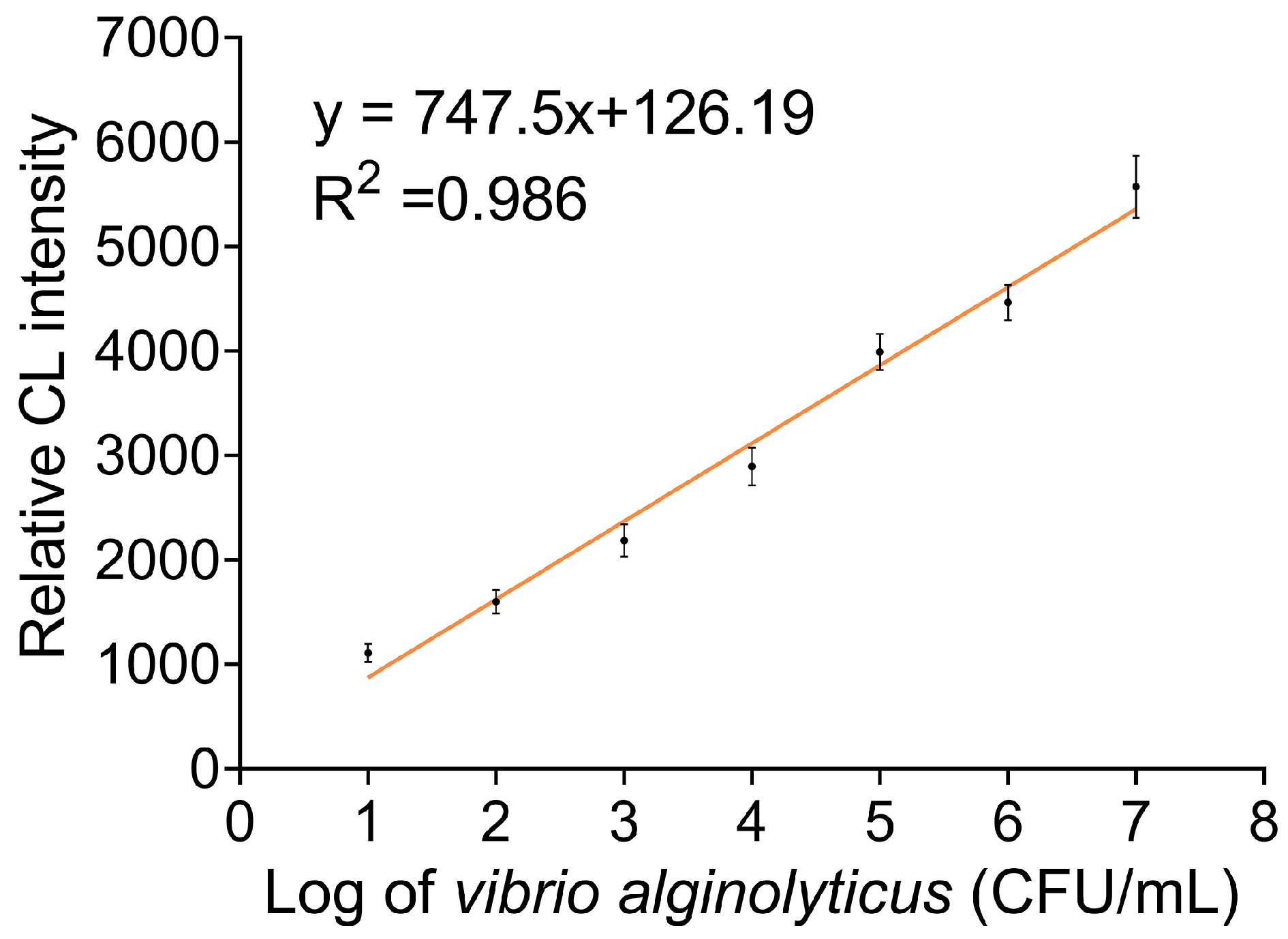
3.4. Sensitivity Investigation of Multi-Apt Amplifier
3.5. Specificity Investigation of the Multi-Apt
3.6. Application of the Developed Method in Spiked Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loo, K.Y.; Law, J.W.F.; Tan, L.T.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Letchumanan, V.; Lee, L.H. Diagnostic techniques for rapid detection of Vibrio species. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanayake, T.; Salleh, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Zamri-Saad, M. Pathology and pathogenesis of Vibrio infection in fish: A review. Aquacult. Rep. 2023, 28, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs Slifka, K.M.; Newton, A.E.; Mahon, B.E. Vibrio alginolyticus infections in the USA, 1988–2012. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ding, Q.; Yang, Q.; Fan, H.; Yu, G.; Liu, F.; Bello, B.K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Dong, J.; et al. Vibrio alginolyticus triggers inflammatory response in mouse peritoneal macrophages via activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Front. Cell. Infect. Mi. 2021, 11, 769777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.C.; Lu, J.F.; Luo, S.; Wang, L.C.; Lu, X.J.; Chen, J. Characterization of large yellow croaker (larimichthys crocea) osteoprotegerin and its role in the innate immune response against to Vibrio alginolyticus. Comp. Biochem. Phys. Part B 2022, 258, 110680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, M.; Su, H.; Xiao, H.; Wu, S.; Qin, X.; Li, S.; Mi, H.; Lu, Z.; Shi, D.; et al. Selection and characterization of ssDNA aptamers specifically recognizing pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.; John, A.; Musa, N.; Abdulrazzak, L.A.; Alfatama, M.; Fadhlina, A. Vibrio spp. and their vibriocin as a vibriosis control measure in aquaculture. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2022, 194, 4477–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudet, J.; d’Orbcastel, E.R.; Bouvier, T.; Godreuil, S.; Dyall, S.; Bouvy, S.; Rieuvilleneuve, F.; Restrepo-Ortiz, C.X.; Bettarel, Y.; Auguet, J.C. Identifying macroplastic pathobiomes and antibiotic resistance in a subtropical fish farm. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.P.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, J.M.; Hasan, M.T.; Kim, C.H.; Kong, I.S. Detection of Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio alginolyticus by singleplex and duplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays targeted to GROEL and FKLB genes. Int. microbiol. 2019, 22, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.F.; Wang, M.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Yin, H.Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, M.Q.; Liu, A.Y.; Hu, C.J. Direct detection of Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Vibrio alginolyticus from clinical and environmental samples by a multiplex touchdown polymerase chain reaction assay. Surg. Infect. 2018, 19, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hu, J.; Wei, T.; Ding, W.; Miao, Q.; Ning, Z.; Fan, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.; Lyu, M.; et al. Fast and sensitive graphene oxide-dnazyme-based biosensor for Vibrio alginolyticus detection. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.; Faucher, S.P. Aptamers and aptamer-coupled biosensors to detect water-borne pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.M.; Hao, J.M.; Xu, J.; Yan, Q.P.; Gao, H.; Zheng, J. Selection and identification of common aptamers against both Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S. Use of dot immunoassay for rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria Vibrio alginolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila from shrimps and fishes. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 27, 222–226. [Google Scholar]
- Hayrapetyan, H.; Tran, T.; Tellez-Corrales, E.; Madiraju, C. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay: Types and Applications. Methods. Mol. Biol. 2023, 2612, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.Q.; Xu, Z.G.; Liu, Z.M. Molecularly Imprinting-Aptamer Techniques and Their Applications in Molecular Recognition. Biosensors 2022, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ni, S.; Wang, Y. An aptamer-functionalized magnetic relaxation switch sensor for the rapid detection of Vibrio alginolyticus in water. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2021, 52, 1561–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, M.; Xiao, H.; Wu, S.; Qin, X.; Ke, K.; Li, S.; Mi, H.; Shi, D.; Li, P. Development of novel aptamer-based enzyme-linked apta-sorbent assay (elasa) for rapid detection of mariculture pathogen Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.T.; Zheng, J.; Bo, J.; Jiang, X.L.; Liu, H.M.; Hang, j.y. Detection of Vibrio anguillarum by differential fluorescence method using aptamer. Oceanologia Limnologia Sinica 2023, 54, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.L.; Gu, L.; Liu, S.; Ren, W.; Lyu, M.S.; Wang, S.J. Identification of a highly specific DNA aptamer for Vibrio vulnificus using systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment coupled with asymmetric PCR. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.J.; Chu, X. Structure-switching aptamer triggering hybridization chain reaction on the cell surface for activatable theranostics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6470–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirks, R.M.; Pierce, N.A. Triggered amplification by hybridization chain reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004, 101, 15275–15278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.P.; Zhao, R.N.; Wang, L.J.; Ma, R.N.; Zhang, W.; Shang, L.; Wang, H.S. Aptamer based electrochemical assay for protein kinase activity by coupling hybridization chain reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeldell, S.B.; Seitz, O. Nucleic acid constructs for the interrogation of multivalent protein interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6848–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, T.; Xu, L.P.; Zhang, X. Portable detection of Staphylococcus aureus using personal glucose meter based on hybridization chain reaction strategy. Talanta 2021, 226, 122132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.N.; Ma, N.; Shi, H.X.; Cheong, L.Z.; Yang, W.G.; Qiao, Z.H. A hcr based multivalent aptamer amplifier for ultrasensitive detection of Salmonella. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2023, 375, 132860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, L.C.; Shuai, Z.H.; Yang, G.J.; Lu, J.F.; Chen, J. A short peptidoglycan recognition protein protects boleophthalmus pectinirostris against bacterial infection via inhibiting bacterial activity. Fish. Shellfish. Immun. 2022, 127, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zuo, P.; Ye, B.C. An aptamer biosensor based dual signal amplification system for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 615, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Sun, C.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y. A novel fret biosensor based on four-way branch migration hcr for Vibrio parahaemolyticus detection. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2019, 296, 126577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ding, J.; Yu, H.; Yin, T.; Qin, W. Potentiometric aptasensing of Vibrio alginolyticus based on DNA nanostructure-modified magnetic beads. Sensors 2016, 16, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, C.; Qin, P.; Yao, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W. Trigging isothermal circular amplification-based tuning of rigorous fluorescence quenching into complete restoration on a multivalent aptamer probe enables ultrasensitive detection of Salmonella. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadsri, V.; Trakulsujaritchok, T.; Tangwattanachuleeporn, M.; Hoven, V.P.; Na Nongkhai, P. Simple Colorimetric Assay for Vibrio parahaemolyticus Detection Using Aptamer-Functionalized Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 21437–21442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Oligonucleotide | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Aptamer DNA | GAGAGAGAATATAAGGGAAAAAAAATCAGTCGCTTCGCCGTCTCCTTCGGGGGCGCGGTGAGGGGCTGCACAAGAGGGAGGCACAAGAGGGAGACCCCAGAGGG |
| H 1 DNA | TTTCCCTTATATTCTCTCTCTCTCCTGCGGGAATGTCTAGGTGATTGAGTGGTGTGTTATCCCACTCAATCACCTAGACCATTCCGCAACAACATAC |
| H 2 DNA | GATAACACACCACTCAATCACCTAGACATTCCCGCAGTATGTTGTTGCGGAATGGTCTAGGTGATTGAGTGG |
| Trigger DNA | GTATGTTGTTGCGGAATGGTCTAGGTGATTGAGTGG |
| Sample | Spiked (CFU/mL) | Average Relative Chemiluminescent Intensity | Relative Standard Deviation (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1-1 | 1 × 103 | 2365 | 4.17 | 98.9% |
| S1-2 | 1 × 104 | 3097 | 3.96 | 94.3% |
| S1-3 | 1 × 105 | 3891 | 4.32 | 108.8% |
| S2-1 | 1 × 103 | 2379 | 4.39 | 103.2% |
| S2-2 | 1 × 104 | 3107 | 2.17 | 97% |
| S2-3 | 1 × 105 | 3842 | 6.73 | 93.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Luo, S.; Qiao, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, J.; Lu, J.; Chen, J. A Novel Method for Sensitive Detection of Vibrio alginolyticus Based on Aptamer and Hybridization Chain Reaction in Aquaculture. Fishes 2023, 8, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100477
Zhao Y, Luo S, Qiao Z, Zhou Q, Fan J, Lu J, Chen J. A Novel Method for Sensitive Detection of Vibrio alginolyticus Based on Aptamer and Hybridization Chain Reaction in Aquaculture. Fishes. 2023; 8(10):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100477
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yifan, Sheng Luo, Zhaohui Qiao, Qianjin Zhou, Jianzhong Fan, Jianfei Lu, and Jiong Chen. 2023. "A Novel Method for Sensitive Detection of Vibrio alginolyticus Based on Aptamer and Hybridization Chain Reaction in Aquaculture" Fishes 8, no. 10: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100477
APA StyleZhao, Y., Luo, S., Qiao, Z., Zhou, Q., Fan, J., Lu, J., & Chen, J. (2023). A Novel Method for Sensitive Detection of Vibrio alginolyticus Based on Aptamer and Hybridization Chain Reaction in Aquaculture. Fishes, 8(10), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100477







