Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen Lead to Behavior and Respiration Changes in Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) during Transport
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Preparation
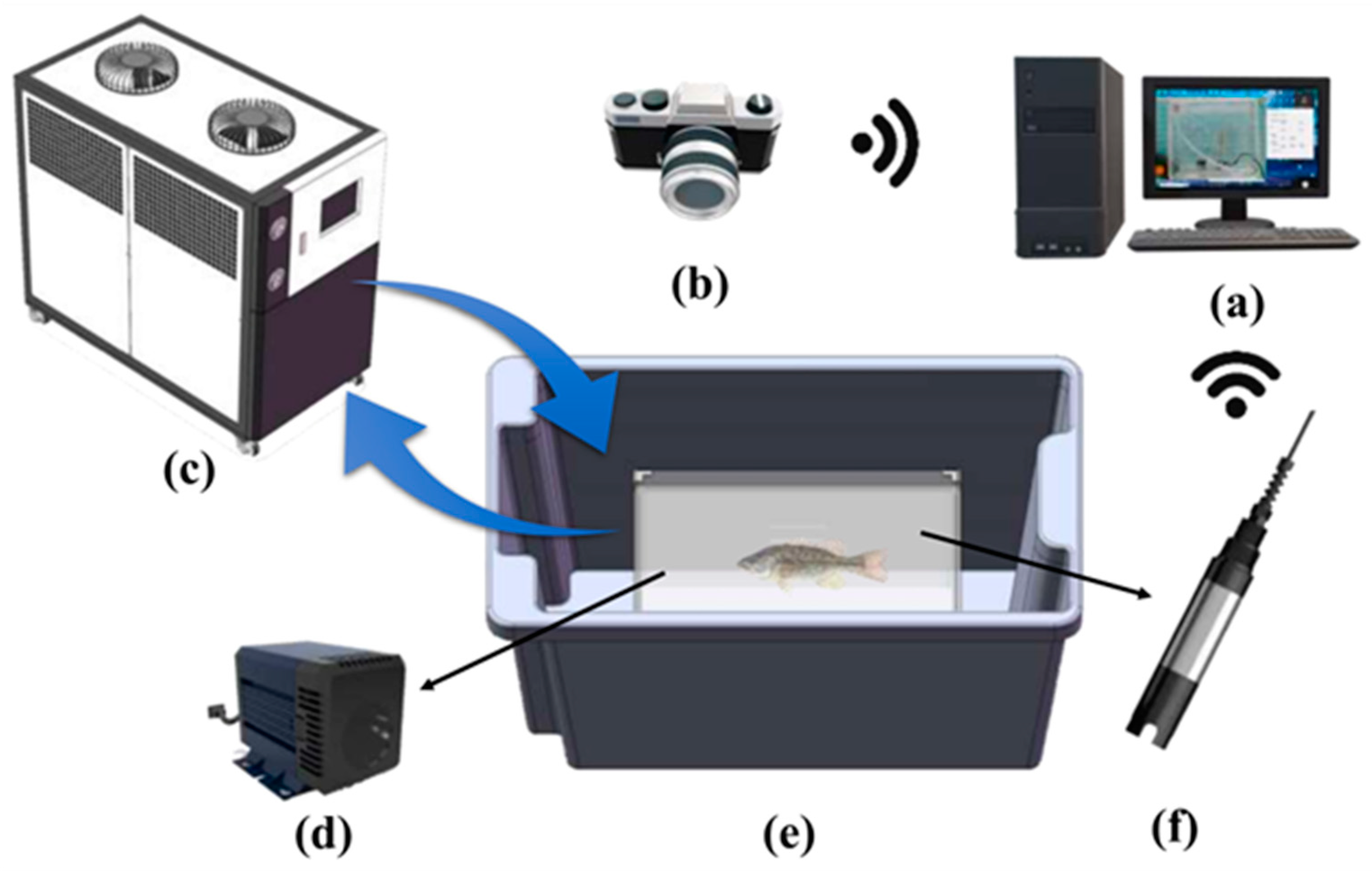
2.2. Experiment Equipment
2.3. Experiment Design
2.4. Determination of Tail-Beat Frequency
2.5. Relate Index
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Cooling on Juvenile Largemouth Bass Behavior and Tail-Beat Frequency
3.2. Effects of Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen on Juvenile Largemouth Bass
3.2.1. Effects of Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen on Oxygen Consumption Rate
3.2.2. Effect of Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen on Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrivastava, J.; Sinha, A.K.; Cannaerts, S.; Blust, R.; De Boeck, G. Temporal assessment of metabolic rate, ammonia dynamics and ion-status in common carp during fasting: A promising approach for optimizing fasting episode prior to fish transportation. Aquaculture 2017, 481, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikson, U.; Rosten, C.; Klebert, P.; Aspaas, S.; Rosten, T. Live transport of Atlantic salmon in open and closed systems: Water quality, stress and recovery. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3913–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderzwalmen, M.; McNeill, J.; Delieuvin, D.; Senes, S.; Sanchez-Lacalle, D.; Mullen, C.; McLellan, I.; Carey, P.; Snellgrove, D.; Foggo, A. Monitoring water quality changes and ornamental fish behaviour during commercial transport. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Jiang, T.; Li, Y.Q.; Song, F.B.; Wen, X.; Luo, J. Golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) adapts to acute hypoxic stress by altering the preferred mode of energy metabolism. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, F.D.; Freire, C.A. An overview of stress physiology of fish transport: Changes in water quality as a function of transport duration. Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 1055–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.W.S.; Oliveira, A.T.; Carvalho, T.B. Water temperature modulates social behavior of ornamental cichlid (Pterophyllum scalare) in an artificial system. J. Appl. Aquac. 2023, 35, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yan, L.; Thi Tuyet Nga, M.; Zhang, X. Survival prediction system for waterless live Chinese Sturgeon transportation based on temperature related glucose changes. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, M.; Salis, P.; Laudet, V.; Lecchini, D. Complete and rapid reversal of the body color pattern in juveniles of the convict surgeonfish Acanthurus triostegus at Moorea Island (French Polynesia). Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, G.; Du, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z. Recent advances in intelligent recognition methods for fish stress behavior. Aquac. Eng. 2022, 96, 102222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Xiong, G.; Xu, P.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Liao, T. Effect of cold-anesthetization rate on blood biochemical parameters and muscle composition during live channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus waterless preservation. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.R.; Brandt, S.B.; Houde, E.D.; Pierson, J.J. Interactive effects of hypoxia and temperature on coastal pelagic zooplankton and fish. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Abraham, J.; Hausfather, Z.; Trenberth, K.E. How fast are the oceans warming? Science 2019, 363, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doney, S.C. The growing human footprint on coastal and open-ocean biogeochemistry. Science 2010, 328, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cui, C.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; He, K.; Adam, A.A.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S. Combined exposure to hypoxia and ammonia aggravated biological effects on glucose metabolism, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 224, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W. The hypoxia signaling pathway and hypoxic adaptation in fishes. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dong, S.; Xu, Q. Respiratory response of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus to dissolved oxygen changes at three acclimation temperatures. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.K.; King, H.; Carter, C.G. Hypoxia tolerance and oxygen regulation in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar from a Tasmanian population. Aquaculture 2011, 318, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.J.; Mckenzie, D.J. Behavioral responses and ecological consequences. In Fish Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 27, pp. 25–77. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, S.; Jonz, M.; Gilmour, K. Oxygen sensing and the hypoxic ventilatory response. In Fish Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 27, pp. 193–253. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.-J.; Fu, S.-J.; Cao, Z.-D.; Wang, Y.-X. Effect of temperature on critical oxygen tension (Pcrit) and gill morphology in six cyprinids in the Yangtze River, China. Aquaculture 2019, 508, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Lutz-Carrillo, D.J.; Quan, Y.; Liang, S. Taxonomic status and genetic diversity of cultured largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides in China. Aquaculture 2008, 278, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisheries, B. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Yu, H.; Liang, X.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, M. Dietary butylated hydroxytoluene improves lipid metabolism, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic response of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 72, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.; Nadler, L.E.; Bayley, J.; Svendsen, M.; Johansen, J.; Domenici, P.; Steffensen, J. Effect of closed v. intermittent-flow respirometry on hypoxia tolerance in the shiner perch Cymatogaster aggregata. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, E.S.; Gamperl, A.K. Cardiorespiratory physiology and swimming capacity of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) at cold temperatures. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb245990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candebat, C.L.; Booth, M.; Williamson, J.E.; Pirozzi, I. The critical oxygen threshold of Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, T.S. Methods for reducing stressors and maintaining water quality associated with live fish transport in tanks: A review of the basics. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, T.; Faber, D.S. Central cellular mechanisms underlying temperature-dependent changes in the goldfish startle-escape behavior. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 5617–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, T.M.; Brookings, T.; Preuss, T.; Faber, D.S. Effects of temperature acclimation on a central neural circuit and its behavioral output. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 2997–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, A.M.; Cozzi, R.R.; Marshall, W.S. Cold acclimation allows regulation of chloride secretion in a eurythermic teleost fish Fundulus heteroclitus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 180, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, C.K.; Bright, L.A.; Marx, J.O.; Andersen, R.P.; Mullins, M.C.; Carty, A.J. Effectiveness of rapid cooling as a method of euthanasia for young zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2018, 57, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, R. Application of machine learning in intelligent fish aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Fang, X.; Song, L.; Li, D.; Chen, Y. Computer vision models in intelligent aquaculture with emphasis on fish detection and behavior analysis: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 2785–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Huang, J.; Wei, Y. A survey of fish behaviour quantification indexes and methods in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2169–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, T.; Mwaffo, V.; Butail, S.; Porfiri, M. Effect of acute ethanol administration on zebrafish tail-beat motion. Alcohol 2015, 49, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Feng, M.; Cheng, Z.; Zhao, M.; Mao, J.; Mirowski, L. Water quality monitoring using abnormal tail-beat frequency of crucian carp. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 111, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, A.; Latombe, G.; Chown, S.L. Rate dynamics of ectotherm responses to thermal stress. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20190174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Noor, N.M.; Kai, K.S.; Juan, Q.Z.; Iskandar, N.S.M.; De, M. Effects of temperature on the growth, gastric emptying time, and oxygen consumption rate of mahseer (Tor tambroides) under laboratory conditions. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 12, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.; Tomasso, J.; Simco, B.; Davis, K. Characterization and alleviation of stress associated with hauling largemouth bass. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1984, 113, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Study on Keep-Alive Transportation of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Artigaud, S.; Lacroix, C.; Pichereau, V.; Flye-Sainte-Marie, J. Respiratory response to combined heat and hypoxia in the marine bivalves Pecten maximus and Mytilus spp. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2014, 175, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlecar, X.; Jena, K.; Chainy, G. Biochemical markers of oxidative stress in Perna viridis exposed to mercury and temperature. Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2007, 167, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-L.; Zhao, L.-L.; Liao, L.; Tang, X.-H.; Cui, C.; Liu, Q.; He, K.; Ma, J.-D.; Jin, L.; Yan, T. Interactive effect of thermal and hypoxia on largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) gill and liver: Aggravation of oxidative stress, inhibition of immunity and promotion of cell apoptosis. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 98, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggren, W.W.; Mendez-Sanchez, J.F.; Martinez Bautista, G.; Peña, E.; Martinez Garcia, R.; Alvarez Gonzalez, C.A. Developmental changes in oxygen consumption and hypoxia tolerance in the heat and hypoxia-adapted tabasco line of the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus, with a survey of the metabolic literature for the genus Oreochromis. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, M.; Best, C.; Perry, S.F. Loss of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α affects hypoxia tolerance in larval and adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, D.; Lund, I.; Pedersen, P.B. Essential fatty acids influence metabolic rate and tolerance of hypoxia in Dover sole (Solea solea) larvae and juveniles. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Temperature °C | Oxygen Level mg·L−1 | Behavior Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 2.02 to 1.49 | Normal |
| 1.49 to 0.62 | Increased swimming, floating head, gill movement amplitude and frequency | |
| 15 | 1.65 to 0.90 | Normal |
| 0.90 to 0.54 | Increased swimming, floating head, gill movement amplitude and frequency | |
| 10 | 1.22 to 0.99 | Increased swimming, floating head |
| 0.99 to 0.61 | Standing still in the water | |
| 0.61 to 0.48 | Increased swimming, floating head, gill movement amplitude and frequency | |
| 5 | 1.41 to 0.72 | Normal |
| 0.72 to 0.62 | Floating head and gill movement increased in amplitude and frequency |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gui, F.; Sun, H.; Qu, X.; Niu, S.; Zhang, G.; Feng, D. Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen Lead to Behavior and Respiration Changes in Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) during Transport. Fishes 2023, 8, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120565
Gui F, Sun H, Qu X, Niu S, Zhang G, Feng D. Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen Lead to Behavior and Respiration Changes in Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) during Transport. Fishes. 2023; 8(12):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120565
Chicago/Turabian StyleGui, Fukun, Haofeng Sun, Xiaoyu Qu, Shuai Niu, Guangyang Zhang, and Dejun Feng. 2023. "Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen Lead to Behavior and Respiration Changes in Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) during Transport" Fishes 8, no. 12: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120565
APA StyleGui, F., Sun, H., Qu, X., Niu, S., Zhang, G., & Feng, D. (2023). Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen Lead to Behavior and Respiration Changes in Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) during Transport. Fishes, 8(12), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120565







