Shellfish as Biosensors in Online Monitoring of Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review of Russian Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Solutions
2.1. Valvometry
2.2. Photoplethysmography
3. Biological Aspects of Test Organisms
3.1. Blue Mussels
3.2. Black Sea Mussels
3.3. Iceland Scallops
3.4. Freshwater Mussels Anodonta
3.5. Painter’s Mussels
3.6. Crayfish
3.7. Red King Crabs
4. Mollusks as Biomonitors
4.1. Blue Mussels
4.2. Black Sea Mussels
4.3. Iceland Scallops
4.4. Freshwater Mussels Anodonta
4.5. Painter’s Mussels
5. Crustaceans as Biomonitors
5.1. Crayfish
5.2. Red King Crabs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oertel, N.; Salánki, J. Biomonitoring and bioindicators in aquatic ecosystems. In Modern Trends in Applied Aquatic Ecology; Ambasht, R.S., Ambasht, N.K., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 219–246. [Google Scholar]
- Feio, M.J.; Hughes, R.M.; Callisto, M.; Nichols, S.J.; Odume, O.N.; Quintella, B.R.; Kuemmerlen, M.; Aguiar, F.C.; Almeida, S.F.P.; Alonso-EguíaLis, P.; et al. The biological assessment and rehabilitation of the World’s rivers: An overview. Water 2021, 13, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Zamparas, M.G.; Kapsalis, V.C. Investigating the human impacts and the environmental consequences of microplastics disposal into water resources. Sustainability 2022, 14, 828. [Google Scholar]
- Zolkefli, N.; Sharuddin, S.S.; Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Maeda, T.; Ramli, N.A. Review of current and emerging approaches for water pollution monitoring. Water 2020, 12, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, H.; Zheng, F.; Huang, C.; Hu, L. Spatial distribution characteristics and risk assessment of nutrient elements and heavy metals in the Ganjiang River basin. Water 2021, 13, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lin, L.; Li, W.; Fang, D.; Lv, Z.; Li, M.; Ma, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; He, L. Long-term study of monitoring history and change trends in surface water quality in China. Water 2022, 14, 2134. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, H.; Fonseca, V.; Sousa, T.; Costa Leal, M. Synergistic effects of climate change and marine pollution: An overlooked interaction in coastal and estuarine areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2737. [Google Scholar]
- Miloloža, M.; Kučić Grgić, D.; Bolanča, T.; Ukić, Š.; Cvetnić, M.; Ocelić Bulatović, V.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kušić, H. Ecotoxicological assessment of microplastics in freshwater sources—A review. Water 2021, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depledge, M.H.; Galloway, T.S. Healthy animals, healthy ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.; Werner, I. Effect-Based tools for monitoring and predicting the ecotoxicological effects of chemicals in the aquatic environment. Sensors 2012, 12, 12741–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklina, I.; Kouba, A.; Kozák, P. Real-time monitoring of water quality using fish and crayfish as bio-indicators: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 5043–5053. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.; Gopal, K. Biomonitoring of Water and Waste Water; Springer: New Dehli, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Savoca, D.; Pace, A. Bioaccumulation, biodistribution, toxicology and biomonitoring of organofluorine compounds in aquatic organisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depledge, M.H.; Aagard, A.; Györkös, P. Assessment of trace metal toxicity using molecular, physiological and behavioural biomarkers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, M.-J.; Park, Y.-S. Biological early warning system based on the responses of aquatic organisms to disturbances: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravera, O. Monitoring of the aquatic environment by species accumulator of pollutants: A review. J. Limnol. 2001, 60 (Suppl. 1), 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E. Pollution Biomarkers in the Framework of Marine Biodiversity Conservation: State of Art and Perspectives. Water 2021, 13, 1847. [Google Scholar]
- Borcier, E.; Charrier, G.; Couteau, J.; Maillet, G.; Le Grand, F.; Bideau, A.; Waeles, M.; Le Floch, S.; Amara, R.; Pichereau, V.; et al. An integrated biomarker approach using flounder to improve chemical risk assessments in the heavily polluted seine estuary. J. Xenobiot. 2020, 10, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, C.; Kashiwada, S. Ecological risks due to immunotoxicological effects on aquatic organisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8305. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt, A.; Ingram, M.K.; Kang, J. In situ on-line toxicity biomonitoring in water: Recent developments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giacinto, F.; Berti, M.; Carbone, L.; Caprioli, R.; Colaiuda, V.; Lombardi, A.; Tomassetti, B.; Tuccella, P.; De Iuliis, G.; Pietroleonardo, A.; et al. Biological early warning systems: The experience in the Gran Sasso-Sirente aquifer. Water 2021, 13, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Y.; Glenn, E.; Thoen, H.; Escher, B.I. In vitro bioassay for reactive toxicity towards proteins implemented for water quality monitoring. J. Environ. Monitor. 2012, 14, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, P.; Srinivasan, G.; Janardhanam, M.; Sivakumar, R.; Niranjani Marcus, P.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Singaram, G.; Harikrishnan, T. A Rapid bioassay test for assessing environmental contamination using the marine sedentary polychaete Hydroides elegans. Water 2022, 14, 1713. [Google Scholar]
- Haron, F.K.; Shah, M.D.; Yong, Y.S.; Tan, J.K.; Lal, M.T.M.; Venmathi Maran, B.A. Antiparasitic Potential of methanol extract of brown alga Sargassum polycystum (Phaeophyceae) and its LC-MS/MS metabolite profiling. Diversity 2022, 14, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.F.L.; Duarte, B.; Fonseca, V.F.; Novais, S.C. Effects on biomarkers in stress ecology studies. Well, So What? What Now? Biology 2022, 11, 1777. [Google Scholar]
- Ates, M.; Arslan, Z.; Demir, V.; Daniels, J.; Farah, I.O. Accumulation and toxicity of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles through waterborne and dietary exposure of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leese, J.M.; McMahon, J.; Colosi, J.C. Effects of wastewater treatment plant effluent in a receiving stream on reproductive behavior of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Fishes 2021, 6, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbane, M.G.; Kabir, M.A.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Mustafa, M.G. Toxic effects of arsenic in commercially important fish Rohu Carp, Labeo rohita of Bangladesh. Fishes 2022, 7, 217. [Google Scholar]
- De Araújo, E.R.L.; Torres, M.F.; Da Costa, B.M.P.A.; Hamoy, M.; Sampaio, L.A.; Barbas, L.A.L. Electroencephalographic response in juvenile tambaqui, Colossoma macropomum, exposed to short-term anaesthetic baths with geraniol and citronellol. Biology 2023, 12, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Pang, B.H.; Cheng, W.H.; Kumar, K.; Avtar, R.; Okamura, H.; Horie, Y.; Sharifinia, M.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Ong, M.C.; et al. Heavy metal exposures on freshwater snail Pomacea insularum: Understanding its biomonitoring potentials. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, K.J.M.; Foekema, E.M. The “Musselmonitor®” as biological early warning system. In Biomonitors and Biomarkers as Indicators of Environmental Change 2: A Handbook; Butterworth, F.M., Gunatilaka, A., Gonsebatt, M.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 59–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, K.G.M.; Jenner, H.A.; de Zwart, D. The valve movement response of mussels: A tool in biological monitoring. Hydrobiologia 1989, 188, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluyts, H.; van Hoof, F.; Cornet, A.; Paulussen, J. A dynamic new alarm system for use in biological early warning systems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1995, 15, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Scully, P. Optical techniques for water quality monitoring. In Monitoring of Water Quality; Colin, F., Quevauviller, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta-Artero, I.; Witbaard, R.; Carroll, M.L.; van der Meer, J. Environmental factors regulating gaping activity of the bivalve Arctica islandica in northern Norway. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeau, E.J.; Smith, A.K.; Stone, J.; Sarina, J. Freshwater Mussels of the Pacific Northwest; The Xerces Society: Portland, OR, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.H. Experimental tests of bivalve shell shape reveal potential tradeoffs between mechanical and behavioral defenses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikac, B.; Tarullo, A.; Colangelo, M.A.; Abbiati, M.; Costantini, F. Shell infestation of the farmed Pacific oyster Magallana gigas by the endolith bivalve Rocellaria dubia. Diversity 2021, 13, 526. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Biological aspects, fisheries, and aquaculture of yesso scallops in Russian waters of the Sea of Japan. Diversity 2022, 14, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Sow, M.; Durrieu, G.; Briollais, L.; Ciret, P.; Massabuau, J.-C. Water quality assessment by means of HFNI valvometry and high-frequency data modeling. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 182, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Nadau, A.; Durrieu, G.; Ciret, P.; Parisot, J.-P.; Massabuau, J.-C. Field chronobiology of a molluscan bivalve: How the moon and sun cycles interact to drive oyster activity rhythms. Chronobiol. Int. 2011, 28, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcherding, J. Ten years of practical experience with the Dreissena-Monitor, a biological early warning system for continuous water quality monitoring. Hydrobiologia 2006, 556, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnyubkin, V.F. An early warning system for aquatic environment state monitoring based on an analysis of mussel valve movement. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2009, 35, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Guarini, J.-M.; Hinz, S.; Coston-Guarini, J. Designing the next generation of condition tracking and early warning systems for shellfish aquaculture. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, R.W. Report on mussels purification. In Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries: Investigations; Her Majesty’s Stationary Office: London, UK, 1928; Series II; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Behavioral Reactions of Mussels under Fluctuations of Environmental Factors of the Eastern Murmansk Coast. Ph.D. Thesis, Murmansk Marine Biological Institute, Murmansk, Russia, 2004. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Method of Operational Bioindication. Patent RF. RU 2,395,082, C1. G01N 33/18. (2006.01), 20 July 2010. Bull. 20. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. System for Rapid Biological Monitoring and Indication. Patent RF. 2,437,093, Int. Cl. G01N 33/18 (2006.01), 20 December 2011. Bull. 35. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Autonomous System of Operational Biological Monitoring and Indications (Variants). Patent RF. RU 101,838, U1. G01N 33/18 (2006.01), 27 January 2011. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V.; Burdygin, A.I.; Nesterov, V.P.; Mitrofanov, V.F. Equipment System for Continuous Detection and Measurement of Motor Activity of Bivalve Mollusks. Patent RF. RU 2,452,949, C1. G01N 33/18. (2006.01), 10 June 2012. Bull. 16. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V.; Komarova, E.P. Environmental control: From inertia of the standard biomonitoring to speed of the online one. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 625, 12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, E.P.; Gudimov, A.V.; Burdygin, A.I. Sensors selection in the system online biomonioring of aquatic media. Vestn. Lugansk Vladimir Dahl Nat. Univ. 2019, 7, 202–205. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Komarova, E.P.; Gudimov, A.V.; Burdygin, A.I.; Yurasov, Y.I. Sensors for online biomonitoring of the water quality. In The Future of the Arctic Begins Here: Materials of the All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference with International Participation; Dyachenko, N.G., Ed.; Apatity Branch of MAGU: Apatity, Russia, 25–26 April 2019; pp. 173–179. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Elementary behavioral acts of valve movements in mussels (Mytilus edulis L.). Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2003, 391, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Massabuau, J.C.; Gudimov, A.; Blanc, P. Environmental monitoring of Arctic waters with unmanned bivalve biosensor technology: One year of background data acquisition in the Barents Sea. In Proceedings of the SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference, Moscow, Russia, 26–28 October 2015. SPE-176681-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, K.J.M. Continuous monitoring of waters by biological early warning systems. In Rapid Chemical and Biological Techniques for Water Monitoring; Gonzalez, C., Greenwood, R., Quevauviller, P.P., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 197–219. [Google Scholar]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Stolbov, A.A.; Mishurov, V.Z.; Shejanov, V.A. Locomotor activity of valves as an instrument for biological monitoring of water environment. Mar. Ecol. 2006, 71, 64–67. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Gaiskii, P.V.; Kuz’min, K.A. Automatic biomonitoring of aqueous media based on the response of bivalves. Mar. Hydrophys. J. 2010, 3, 75–83. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gaisky, P.V.; Trusevich, V.V.; Zaburdaev, V.I. Automatic bioelectronic complex designed for early detection of toxic pollution of fresh and marine waters. Mar. Hydrophys. J. 2014, 3, 44–53. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gajskij, P.V. Device for Measuring Motor Activity of Clam Shells. Patent RF. RU 2,625,673, A01K 61/00 (2006.01), G01N 33/18 (2006.01), 18 July 2017. Bull. 20. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Gaisky, V.A.; Gaisky, P.V. Bioelectronic automatic aquaculture monitoring station. Tr. VNIRO 2021, 184, 159–168. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Gaysky, P.V.; Mishurov, V.Z.; Kuzmin, K.A. Automated monitoring of the aquatic environment based on behavioral reactions of the Black Sea mussels. Assessment of sensitivity to some toxicants. In Environmental Control Systems—2016, Proceedings of the International Scientific and Technical Conference, Sevastopol, Russia, 27–27 October 2016; Polonsky, A.B., Voskresenskaya, E.N., Gaisky, V.A., Grekov, N.A., Krasnodubets, L.A., Gaisky, P.V., Eds.; Federal State Budgetary Scientific Institution “Institute of Natural and Technical Systems”: Sevastopol, Russia, 2016; p. 57. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Depledge, M.H. Photoplethysmograph—A non-invasive technique for monitoring heart beat and ventilation rate in decapod crustaceans. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1984, 77, 369–371. [Google Scholar]
- Aagaard, A.; Andersen, B.B.; Depledge, M.H. Simultaneous monitoring of physiological and behavioural activity in marine organisms using non-invasive, computer-aided techniques. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 73, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, A.; Styrishave, B.; Warman, C.G.; Depledge, M.H. The use of cardiac monitoring in the assessment of mercury toxicity in the subtropical pebble crab (Gaetice deoressus). Sci. Mar. 2000, 64, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederich, M.; Pörtner, H.O. Oxygen limitation of thermal tolerance defined by cardiac and ventilatory performance in spider crab, Maja squinado. Am. J. Physiol. Regulat. Integr. Compar. Physiol. 2000, 279, R1531–R1538. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, E.; Sazi, T.; Togawa, M.; Nagata, O.; Murakami, M.; Kojima, S.; Seo, Y. A portable infrared photoplethysmograph: Heartbeat of Mytilus galloprovincialis analyzed by MRI and application to Bathymodiolus septemdierum. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kushinsky, D.; Morozova, E.O.; Marder, E. In vivo effects of temperature on the heart andpyloric rhythms in the crab Cancer borealis. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb199190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zarykhta, V.V.; Zhang, Z.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Lv, M.; Feng, Y. Comprehensive assessments of ecological states of Songhua River using chemical analysis and bivalves as bioindicators. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33341–33350. [Google Scholar]
- Maus, B.; Gutsfeld, S.; Bock, C.; Pörtner, H.-O. Non-invasive MRI studies of ventilatory and cardiovascular performance in edible crabs Cancer pagurus during warming under elevated CO2 levels. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 596529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, B.; Gutsfeld, S.; Pörtner, H.O.; Bock, C. Non-invasive quantification of cardiac stroke volume in the edible crab Cancer Pagurus. Front. Zool. 2019, 16, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Martinović, R.; Joksimović, D.; García-March, J.R.; Vicente, N.; Gačić, Z. Evaluation of physiological state of pen shell Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758) by a non-invasive heart rate recording under short-term hyposalinity test. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1549. [Google Scholar]
- Fedotov, V.P.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Strochilo, A.G. Study of contractile activity of the crayfish heart with the aid of a new non-invasive technique. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 36, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Donchenko, V.K.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kornienko, E.L.; Kurakin, A.S.; Fedotov, V.P. A Sensor of Physiological Activity of Invertebrate with Hard Skeleton and a System Based on the Sensor for Biological Monitoring of Environment. Patent RF (Useful Model) RU 52,190, U1. Int. Cl. G01N 33/18 (2006.01), 10 March 2006. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Fedotov, V.P.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kurakin, A.S.; Kornienko, E.L. Fiber-optical remote biosensor systems for permanent biological monitoring of the surface waters quality and bottom sediments in the real time. ICES CM CM 2007, 1, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kurakin, A.S.; Kornienko, E.L.; Fedotov, V.P. Real time biomonitoring of surface water toxicity level at water supply stations. J. Environ. Bioindic. 2008, 3, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kurakin, A.S.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Ivanov, A.V. Software and algorithmic aspects of the real-time bioelectronic systems for heart rhythm analysis in exoskeleton invertebrates applied to the surface water quality assessment. Environ. Control Syst. 2017, 10, 38–47. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Trusevich, V.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V. New physiological biomarkers for express indication of aquatic ecosystems state on the base of adaptive capacities assessment of bivalves using standard test-stimuli. In Ecosystem Protection in a Sustainable World: A Challenge for Science and Regulation, Proceedings of the SETAC Europe 21th Annual Meeting, Milan, Italy, 15–19 May 2011; pp. 168–169. Available online: https://www.setac.org/store/ (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Kurakin, A.S.; Lips, U.; Kolesova, N.; Lehtonen, K.K. Applicability of a bioelectronic cardiac monitoring system for the determination of biological effects of pollution in bioindicator species in the Gulf of Finland. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 171, 8151–8158. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kurakin, A.S. Experience on ecological status assessment based on adaptive potential diagnostics in selected invertebrates of the Baltic Sea sub–regions. Fundamental. Prikladn. Gidrofiz. 2018, 11, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sladkova, S.V.; Lyubimtsev, V.A.; Kholodkevich, S.V. A study of the impact of biologically treated wastewater discharged into the Neva Bay on the functional state of crustaceans. In Anthropogenic Impact on Aquatic Organisms and Ecosystems, Proceedings of VII All-Russian Conference on Aquatic Ecotoxicology Dedicated to the Memory of Doctor of Biological Sciences, Professor B.A. Flerov. Modern Methods of Research and Assessment of Water Quality, the State of Aquaticorganisms and Ecosystems under Anthropogenic Stress: Materials of the School-Seminar for Young Scientists, Graduate Students and Students, Borok, Russia, 16–19 September 2020; Filigran: Yaroslavl, Russia, 2020; pp. 180–182. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ipatov, A.A.; Bakhmet, I.N.; Yekimov, D.A.; Kuldin, N.A. Automatic early warning device for environmental risks at waterbodies and its trials. Proc. Karelian Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2015, 12, 80–86. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmet, I.; Aristov, D.; Marchenko, J.; Nikolaev, K. Handling the heat: Changes in the heart rate of two congeneric blue mussel species and their hybrids in response to water temperature. J. Sea Res. 2022, 185, 102218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, V.H. Which group is best? Attributes of different biological assemblages used in freshwater biomonitoring programs. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 138, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, A.S.; Salierno, J.D.; Brewer, S.K. Fish models in behavioral toxicology: Automated techniques, updates and perspectives. In Methods in Aquatic Toxicology; Ostrander, G.K., Ed.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 559–590. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Discharge of drill cuttings in the Arctic seas and responses of bottom fauna: Bivalve Mytilus edulis L. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 937, 22041. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V.; Malavenda, S.S. Responses of bottom invertebrates to pollution in the Arctic: Bioassays with blue mussel Mylilus edulis L. BIO Web Conf. EDP Sci. 2022, 52, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.N. Estimation of oil product’s effects on the mussel cardiac rhythm. Probl. Ecol. Monit. Ecosyst. Model. 2009, 22, 267–277. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmet, I.N. Bioindication role of filterers: Response of mussels Mytilus edulis L. to heavy metals. Probl. Ecol. Monit. Ecosyst. Model. 2010, 23, 268–275. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmet, I.; Fokina, N.; Ruokolainen, T. Changes of heart rate and lipid composition in Mytilus edulis and Modiolus modiolus caused by crude oil pollution and low salinity effects. J. Xenobiot. 2021, 11, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Gaysky, P.V.; Kuzmin, K.A.; Mishurov, V.Z. Biomarkers of behavioural reactions of black sea mussel for the automated biomonitoring of ecological state of water environment. Environ. Control Syst. 2015, 1, 13–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Vyshkvarkova, E.V.; Zhuravsky, V.Y. Shellfish reactions to pollution of the aquatic environment by extracts of drilling sludge and diesel fuel. In Environmental Control Systems—2020, Proceedings of the International Scientific and Technical Conference, Sevastopol, Russia, 9–12 November 2020; Bardin, M.Y., Voskresenskaya, E.N., Vyshkvarkova, E.V., Gaisky, V.A., Gaisky, P.V., Grekov, N.A., Grekov, A.N., Eds.; IP Kulikov: Sevastopol, Russia, 2020; p. 83. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kurakin, A.S.; Soldatov, A.A.; Gostukhina, O.L.; Golovina, I.V.; Andreenko, T.I.; Kirin, M.P. New methodological approach to express assessment of ecological state for the coastal sea waters. Izv. TINRO 2018, 194, 215–238. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Bioassay of diesel oil for the online bio-indicating. In Pollution of Marine Environment: Ecological Monitoring, Bioassay, Standardization, Proceedings of the Russian Scientific Conference with International Participation Devoted to 125th Anniversary of prof. V.A. Vodyanitsky, Sevastopol, Russia, 28 May 2018–1 June 2018; Rudneva, I.I., Ed.; Colorit: Sevastopol, Russia, 2018; pp. 78–82. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.; Sharov, A.; Nikolić, M.; Joksimović, A. Bioindication of aquatic ecosystems on the base of the assessment of functional state of freshwater bivalve mollusks biomarkers. In Proceedings of the 4th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing, MECO, IEEE, Budva, Montenegro, 14–18 June 2015; MECO: Budva, Montenegro, 2015; pp. 345–348. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7181939 (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Kuznetsova, T.V. Perspectives and problems of application of bioelectronic systems for monitoring of environmental safety state in the Gulf of Finland aquatoria. Reg. Ecol. 2015, 2, 16–26. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Chuiko, G.M.; Sharov, A.N.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Pesnya, D.S. Indicators of cardiac activity and oxidative stress in the mollusk Anodonta cygnea under short-term salt test load as biomarkers for assessing the state of the organism and the quality of the environment. Inland Water Biol. 2021, 14, 739–746. [Google Scholar]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Kuzmin, K.A.; Mishurov, V.J. Biomonitoring of the surface water quality with use of fresh-water bivalvia moluscs. Environ. Control Syst. 2017, 7, 83–93. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Mishurov, V.Z.; Kuzmin, K.A. Assessment of the sensitivity of pearl oysters (Unio pictorum) used in automated control systems biomonitoring of the aquatic environment, to oil pollution. In Environmental Control Systems—2021, Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practic Conference, Sevastopol, Russia, 9–12 November 2021; Bardin, M.Y., Voskresenskaya, E.N., Gaisky, V.A., Grekov, N.A., Grekov, A.N., Kebkal, K.G., Krasnodubets, L.A., Eds.; IP Kulikov: Sevastopol, Russia, 2021; p. 41. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berezina, N.A.; Sharov, A.N.; Chernova, E.N.; Malysheva, O.A. Effects of diclofenac on the reproductive health, respiratory rate, cardiac activity, and heat tolerance of aquatic animals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovatcheva, N.P.; Kholodkevitch, S.V.; Vasilyev, R.M.; Ivanov, A.V.; Zagorsky, I.A.; Kornienko, E.L. Real time assessment of red king crabs functional status by measuring of its cardioactivity. Probl. Fish. 2008, 9, 513–517. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kovacheva, N.P.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Vasilyev, R.M.; Zagorsky, I.A.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kornienko, E.L. Red king crab functional state assessment by non-invasive real-time control of their cardiac activity in aquaculture. Izv. TINRO 2009, 157, 197–205. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gosling, E. Bivalve Molluscs Biology, Ecology and Culture; Fishing News Books: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, A.L.; Carver, C.E. Comparative growth and survival patterns of Mytilus trossulus and Mytilus edulis in Atlantic Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar]
- Seed, R.; Suchanek, T.H. Population and community ecology of Mytilus. In The Mussel Mytilus: Ecology, Physiology, Genetics and Culture; Gosling, E.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 87–169. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Research of mussels in the Barents Sea: From theory to practice. In Formation of the Foundations of a Modern Strategy of Environmental Management in the Euro-Arctic Region; Vinogradov, A.N., Ed.; Kola Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Apatity, Russia, 2005; pp. 304–315. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Matveeva, T.A. The biology of Mytilus edulis L. in the Eastern Murman. Tr. Murm. Mar. Biol. Stn. USSR 1948, 1, 215–241. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.J. Fecundity and reproductive effort in the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis), the sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis), and the snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) from populations in Nova Scotia and Newfoundland. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 1979, 36, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudimov, A.V. Blue mussels Mytilus edulis L. In Harvesting and Perspective for Uses Algae and Invertebrates of the Barents and White Seas; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 1998; pp. 529–580. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lande, E. Growth, spawning and mortality of the mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) in Prestvaagen, Trondheimsfjorden. Det Kgl. Nor. Vidensk. Selsk. Mus. Misc. 1973, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, V.V.; Matveeva, T.A. Materials on the biological characteristics of marine invertebrates in the Eastern Murman. Tr. Murm. Mar. Biol. Stn. USSR 1948, 1, 242–260. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen, S.S.; Thyrring, J.; Hemmer-Hansen, J.; Berge, J.; Sukhotin, A.; Leopold, P.; Bekaert, M.; Sejr, M.K.; Nielsen, E.E. Genetic diversity and connectivity within Mytilus spp. in the subarctic and Arctic. Evol. Appl. 2017, 10, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonham, M.J. Mini-review: Distribution of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) and hybrids in the Northeast Pacific. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, W.S.; Cherry, M.I. Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. in Southern Africa. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 90, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutaenko, K.A.; Kolpakov, E.V. The extension of the distributional range of an invasive mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) in the Sea of Japan. Bull. Russ. Far East Malacol. Soc. 2016, 20, 57–76. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gosling, E.M. The systematic status of Mytilus galloprovincialis in Western Europe: A review. Malacologia 1984, 55, 551–568. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Kholodov, V.I.; Senicheva, M.I.; Pirkova, A.V.; Bulatov, K.V. Biology of Cultivated Mussels; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Russia, 1989. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zaika, V.E.; Valovaya, N.A.; Povchun, A.C.; Revkov, N.K. Mytilids of the Black Sea; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Russia, 1989. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chertok, A.I.; Belous, K.A.; Sytnik, N.A. Current state of natural mussel populations in the Black Sea. In Education, Science and youth—2018, Proceedings of the Scientific and Practical Conferences of the KSMTU, Kerch, Russia, 2–13 April 2018; Masyutkin, E.P., Ed.; Kerch State Marine Technological University: Kerch, Russia, 2018; pp. 67–77. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chelyadina, N.S.; Popov, M.A. Mortality of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamark, 1819) depending on sex. Tomsk State Univ. J. Biol. 2021, 55, 166–176. [Google Scholar]
- Pirkova, A.V. Reproduction, embryogenesis, larval development and growth of Mytilus galloprovincialis. In Mariculture of Mussel on the Black Sea; Ivanov, V.N., Ed.; EKOSI-Gidrofizika: Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2007; pp. 138–167. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sytnik, N.A.; Zolotnitsky, A.P. State of natural populations and dynamics of the number of mussel larvae in the Kerch Strait and the Black Sea Pre-strait. Vestn. Kerch State Mar. Technol. Univ. 2020, 1, 53–68. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gorbunova, T.L.; Basharova, M.P.; Matova, N.I. Morphometric characteristics of Black Sea mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. as biomarkers of the anthropogenic impact on the Black Sea coastal biocenoses in tourist destinations. Amur. Zool. J. 2022, 14, 516–530. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pospelova, N.V.; Bulycheva, D.S.; Ryabushko, L.I. Microalgae in the nutrition spectrum of cultivated mussels (Crimea, Black Sea). In Proceedings of the V International Scientific and Practical Conference “Marine Research and Education (MARESEDU-2016)”, Moscow, Russia, 18–21 October 2016; Feoria: Moscow, Russia, 2016; pp. 434–438. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Priymak, A.S.; Pospelova, N.V. On the feeding of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819. In Study of Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecosystems: History and Contemporary State, Proceedings of the 2nd International Academic Conference, Sevastopol, Russia, 5–9 September 2022; IBSS: Sevastopol, Russia, 2022; pp. 134–135. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, E.G. The fishery for Iceland scallop (Chlamys islandica) in the Northeast Atlantic. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2006, 51, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duncan, P.F.; Brand, A.R.; Strand, Ø.; Foucher, E. The European scallop fisheries for Pecten maximus, Aequipecten opercularis, Chlamys islandica, and Mimachlamys varia. In Scallops Biology, Ecology, Aquaculture, and Fisheries, 3rd ed.; Shumway, S.E., Parsons, G.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 781–858. [Google Scholar]
- Denisenko, S.G. Ecology and Resources of the Iceland Scallop in the Barents Sea; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 1989. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Denisenko, S.G. Temperature conditions and spawning periods of the Iceland scallop in the Eastern Murmansk coast. In Studies of the Biology, Morphology and Physiology of Hydrobionts; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; MMBI Press: Apatity, Russia, 1983; pp. 90–94. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zolotarev, P.N. Biology and Fishery of the Icelandic Scallop Chlamys Islandica in the Barents and White Seas; PINRO Press: Murmansk, Russia, 2016. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gruffydd, L.D. Swimming in Chlamys islandica in relation to current speed and an investigation of hydrodynamic lift in this and other scallops. Norw. J. Zool. 1976, 24, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zolotarev, P.N. Shell morphometry of the Icelandic scallop (Chlamys islandica, Pectinidae, Bivalvia) from the Barents and White Seas. Zool. Zh. 2010, 89, 1200–1204. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bogolubov, A.S. Computer Digital Atlas-Guide of Freshwater Invertebrates of Russia. 2018. Available online: http://ecosystema.ru/04materials/guides/10water.htm (accessed on 12 September 2022). (In Russian).
- Aldridge, D.C.; McIvor, A.L. Gill evacuation and release of glochidia by Unio pictorum and Unio tumidus (Bivalvia: Unionidae) under thermal and hypoxic stress. J. Mollusc. Stud. 2003, 69, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn, C.C.; Nichols, S.J.; Spooner, D.E. Community and foodweb ecology of freshwater mussels. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, D.L.; Cummings, K.S. Review of the systematics and global diversity of freshwater mussel species (Bivalvia: Unionoida). J. Mollusc. Stud. 2007, 73, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomilova, A.A. Morphological Variability and Phylogeography of the Duck Mussel Anodonta Anatina in Russia and Adjacent Territories. Ph.D. Thesis, FIC KIA RAS, Arkhangelsk, Russia, 2021. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Schultes, F.W. Species Summary for Anodonta anatine. 2013. Available online: http://www.animalbase.uni-goettingen.de/zooweb/servlet/AnimalBase/home/species?id=2118 (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Hinzmann, M.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Teixeira, A.; Varandas, S.; Sousa, R.; Lopes, A.; Froufe, E.; Machado, J. Sexual strategy and reproductive cycle of Anodonta anatina (L., 1758): Notes on hermaphroditism. J. Exp. Zool. A 2013, 309, 378–390. [Google Scholar]
- Strayer, D.L. Freshwater Mussel Ecology. A Multifactor Approach to Distribution and Abundance; Freshwater Ecological Series; University of California Press: Berkely, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, P.; Carvalho, F.; Vasconcelos, V.; Machado, J. Studies on growth in the early adult of the freshwater mussel, Anodonta cygnea. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2004, 45, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, D.C. The morphology, growth and reproduction of Unionidae (Bivalvia) in a fenland waterway. J. Mollusc. Stud. 1999, 65, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rizhinashvili, A.L. Determination of the Maximum lifespan of bivalves as exemplified by Unio-like mussels (Bivalvia, Unionidae). Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2009, 424, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryger, J.; Riisgård, H.U. Filtration rate capacities in 6 species of European freshwater bivalves. Oecologia 1988, 77, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdich, D.M.; Pöckl, M. Invasive crustaceans in European inland waters. In Biological Invaders in Inland Waters: Profiles, Distribution and Threats; Invading Nature—Springer Series in Invasion Ecology; Gherardi, F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 29–75. [Google Scholar]
- Berezina, N.A.; Terentiev, P.M.; Sharov, A.N.; Maximov, A.A. New records and disappearance from old sites of narrow-clawed crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus in northwestern Russia. BioInvas. Rec. 2021, 10, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurdal, J.; Taugbøl, T. Astacus. In Biology of Freshwater Crayfish; Holdich, D.M., Ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 467–510. [Google Scholar]
- Füreder, L. Crayfish in Europe. Biogeography, ecology and conservation. In Freshwater Crayfish: A Global Overview; Faulkes, Z., Kawai, T., Scholtz, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 594–697. [Google Scholar]
- Souty-Grosset, C.; Holdich, D.M.; Noël, P.Y.; Reynolds, J.D.; Haffner, P. Atlas of Crayfish in Europe; Museum National D’Histoire Naturelle: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov, B.M. About crayfish of Karelia. Proc. Karelian Branch GosNIORKH 1966, 4, 188–209. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmin, S.A.; Gudimova, E.N. Introduction of the Kamchatka (Red King) Crab in the Barents Sea: Peculiarities of Biology, Perspectives of Fishery; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 2002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acid composition of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) leg meat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103826. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acids in the circulatory system of an invasive king crab from the Barents Sea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104528. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) fisheries in Russian waters: Historical review and present status. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2018, 28, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. New echinoderm-crab epibiotic associations from the coastal Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Distribution of amphipods Ischyrocerus on the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus: Possible interactions with the host in the Barents Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Some aspects of the biology of the amphipods Ischyrocerus anguipes associated with the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Commercial fish and shellfish in the Barents Sea: Have introduced crab species affected the population trajectories of commercial fish? Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epibiotic communities of common crab species in the coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and infestation patterns. Diversity 2022, 14, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Renewal of the recreational red king crab fishery in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Potential benefits and costs. Mar. Policy 2022, 136, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Inter-annual dynamics of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) stock indices in relation to environmental factors. Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Effects of environmental factors on the abundance, biomass, and individual weight of juvenile red king crabs in the Barents Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 726. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epibionts of an introduced king crab in the Barents Sea: A second five-year study. Diversity 2023, 15, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Population dynamics of the invasive lithodid crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, in a typical bay of the Barents Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyushkin, V.B. Peculiarities of reproduction of the red king crab in fjord waters of the western Murman. In The Red King Crab in the Barents Sea; Berenboim, B.I., Ed.; PINRO Press: Murmansk, Russia, 2003; pp. 88–100. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size at maturity of female red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, from the costal zone of Kola Peninsula (southern Barents Sea). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2015, 56, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Tipisova, E.V.; Elfimova, A.E.; Alikina, V.A.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Sex hormones in hemolymph of red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Tipisova, E.V.; Alikina, V.A.; Elfimova, A.E.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Thyroid hormones in hemolymph of red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Animals 2022, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakanev, S.V. Fecundity and some other reproductive parameters of red king crab in the Barents Sea. In The Red King Crab in the Barents Sea; Berenboim, B.I., Ed.; PINRO Press: Murmansk, Russia, 2003; pp. 78–88. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bakanev, S.V. Larvae of red king crab in the coastal areas and large bays of Murman. In The Red King Crab in the Barents Sea; Berenboim, B.I., Ed.; PINRO Press: Murmansk, Russia, 2003; pp. 122–133. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Ecology and distribution of red king crab larvae in the Barents Sea: A review. Water 2022, 14, 2328. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acid profiles in the gonads of red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) from the Barents Sea. Animals 2023, 13, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Hemolymph molting hormone concentrations in red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Pinchukov, M.A.; Berenboim, B.I. Molting and growth of red king crab in the Barents Sea. In The Red King Crab in the Barents Sea; Berenboim, B.I., Ed.; PINRO Press: Murmansk, Russia, 2003; pp. 100–106. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size-at-age of juvenile red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the coastal Barents Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2014, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, L.V.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Prey selectivity in juvenile red king crabs from the coastal Barents Sea. Diversity 2022, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V.; Zuyev, Y.A.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Shallow-water benthic communities on soft bottoms of a sub-arctic fjord (southern Barents Sea, Russia) along a gradient of ecological factors. Diversity 2023, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evseeva, O.Y.; Ishkulova, T.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Environmental drivers of an intertidal bryozoan community in the Barents Sea: A case study. Animals 2022, 12, 552. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Behavior of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) under the fluctuating environmental conditions. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2006, 409, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudimov, A.V. Continuous biomonitoring of behavioral responses of mussels: The first experience in the Kola Bay (Barents Sea). Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2011, 439, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.N.; Zdorovenov, P.E. Variability in cardiac activity of the bivalves Mytilus edulis and Modiolus modiolus. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2010, 36, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudimov, A.V. Cardiac activity and behavior of blue mussels from the Barents Sea under controlled conditions. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2009, 427, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bakhmet, I.N. Cardiac activity and oxygen consumption of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) from the White Sea in relation to body mass, ambient temperature and food availability. Polar Biol. 2017, 40, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmet, I.N.; Sazhin, A.; Maximovich, N.; Ekimov, D. In situ long-term monitoring of cardiac activity of two bivalve species from the White Sea, the blue mussel Mytilus edulis and horse mussel Modiolus Modiolus. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2019, 99, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, H.; Massabuau, J.-C.; Cochrane, S.; Ciret, P.; Tran, D.; Sow, M.; Camus, L. High frequency non-invasive (HFNI) bio-sensors as a potential tool for marine monitoring and assessments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmet, I.N.; Berger, V.J.; Halaman, V.V. Heart rate in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis (Bivalvia) under salinity change. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2005, 31, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.N. Characteristic property of blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. adaptation to pollutants. Proc. Petrozavodsk. State Univ. 2013, 8, 17–19. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sharov, A.N.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Heart activity in the littoral and sublittoral White Sea blue mussels Mytilus edulis. In Marine Biological Research: Achievements and Perspectives, Proceedings of All-Russian Scientific-Practical Conference with International Participation Dedicated to the 145th Anniversary of Sevastopol Biological Station, Sevastopol, Russia, 19–24 September 2016; Gaevskaya, A.V., Ed.; EKOSI-Gidrofizika: Sevastopol, Russia, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 346–349. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chuiko, G.M.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kurakin, A.S. The reaction of the cellular system of antioxidant protection, cardioactivity and motor activity of the White Sea mussel (Mytilus edulis Linnaeus, 1758) to a short-term decrease in water salinity. In Study of Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecosystems: History and Contemporary State, Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Dedicated to the 150th Anniversary of the Sevastopol Biological Station—A. O. Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas and to the 45th Anniversary of Research Vessel “Professor Vodyanitsky”, Sevastopol, Russia, 13–18 September 2021; Egorov, V.N., Gorbunov, R.V., Eds.; IBSS RAS: Sevastopol, Russia, 2021; pp. 448–449. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, P.V.; Winter, M.A.; Pegg, R.K. Effects of whole drilling mud and selected components on the shell movements of the bay scallop, Argopecten irradians. Gulf Mex. Sci. 1981, 5, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.N.; Fokina, N.N.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Ruokolainen, T.R.; Nemova, N.N. Blue mussels Mytilus edulis L. in the White Sea as bioindicators under diluted oil impact. Proc. Karelian Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2012, 2, 38–46. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmet, I.N.; Kantserova, N.P.; Lysenko, L.A.; Nemova, N.N. Effect of copper and cadmium ions on heart function and calpain activity in blue mussel Mytilus edulis. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2012, 47, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, T.M.; Williamson, R.; Depledge, M.H. Simultaneous, long-term monitoring of valve and cardiac activity in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis exposed to copper. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 837–846. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmet, I.N.; Ekimov, D.A. Effect of nikel ions on cardiac activity in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis Linnaeus, 1758. Proc. Karelian Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2020, 11, 64–69. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Ecological biomonitoring of aquatic ecosystems: On the way to the newest technologies. In Marine Ecosystems and Communities in the Conditions of Current Climatic Changes; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; Renome: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2014; pp. 326–344. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Methods of online biosensor monitoring and online bioindication: Responses to toxicants on mussel behavior and cardiac activity. In Proceedings of the VII International Conference “Marine Research and Education”, Moscow, Russia, 19–22 November 2018; OOO PolyPRESS: Tver, Russia, 2019; pp. 385–392. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Kuz’min, K.A.; Mishurov, V.Z.; Zhuravsky, V.Y.; Vyshkvarkova, E.V. Features of behavioral responses of the Mediterranean mussel in its natural habitat of the Black Sea. Inland Water Biol. 2021, 14, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravsky, V.Y.; Voskresenskaya, E.N.; Trusevich, V.V.; Lubkov, A.S. Data analysis for automation of aquatic biomonitoring in the Black Sea region. Environ. Control Syst. 2019, 4, 66–71. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gnyubkin, V.F. The circadian rhythms of valve movements in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2010, 36, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Vyshkvarkova, E.V.; Trusevich, V.V.; Kuzmin, K.A.; Mishurov, V.Z.; Zhuravsky, V.Y. Features of behavioral reactions of the Black Sea mussel. In Comprehensive Research of the World Ocean, Proceedings of the V All-Russian Scientific Conference of Young Scientists, Kaliningrad, Russia, 18–22 May 2020; Mevedev, I.P., Ed.; Atlantic Branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution of Science “P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanology of the Russian Academy of Sciences”: Kaliningrad, Russia, 2020; pp. 241–242. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Comeau, L.A.; Babarro, J.M.; Longa, A.; Padin, X.A. Valve-gaping behavior of raft-cultivated mussels in the Ría de Arousa, Spain. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 9, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kurakin, A.S.; Kornienko, E.L.; Khalatov, A.N.; Pan’Kov, S.L. Ultradian rhythms in cardiac activity of Bivalvia. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2009, 426, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazankova, I.I.; Gaisky, P.V.; Kazantsev, S.V. Individual variability of biorhythmic elements of Mytilus galloprovincialis mussels under experimental conditions. In Terrestrial and Marine Ecosystems of the Black Sea Region and Their Protection, Proceedings of the Scientific and Practical School-Conference, Novorossiysk, Russia, 23–27 April 2018; Bykhalova, O.N., Korobushkin, D.I., Marin, I.N., Maslova, V.N., Skuratovskaya, E.N., Eds.; Institute of Natural and Technical Systems: Sevastopol, Russia, 2018; pp. 53–54. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kazankova, I.I.; Gaisky, P.V.; Kazantsev, S.V. Variability of the level of opening of the flaps of adult mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis lam. in laboratory conditions. In Environmental Control Systems—2018, Proceedings of the International Scientific and Technical Conference, Sevastopol, Russia, 5–9 November 2018; Bardin, M.Y., Voskresenskaya, E.N., Vyshkvarkova, E.V., Gaisky, V.A., Gaisky, P.V., Grekov, N.A., Grekov, A.N., Eds.; Kolorit: Sevastopol, Russia, 2018; p. 114. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Marine mussels of the Karadag (Black Sea): Population decay, ecology, and physiological adaptations. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2008, 422, 330–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ait Fdil, M.; Mouabad, A.; Outzourhit, A.; Benhra, A.; Maarouf, A.; Pihan, J.C. Valve movement response of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis to metals (Cu, Hg, Cd and Zn) and phosphate industry effluents from Moroccan Atlantic coast. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyshkvarkova, E.V.; Trusevich, V.V.; Grekov, A.N.; Kuzmin, K.A.; Mishurov, V.Z.; Zhuravsky, V.Y. Biomarkers of behavioral reactions of mollusks in automated biomonitoring systems in conditions of pollution of the aquatic environment with petroleum hydrocarbons and drilling sludge. In Comprehensive Research of the World Ocean, Proceedings of the VI All-Russian Scientific Conference of Young Scientists, Moscow, Russia, 18–24 April 2021; Alekseev, D.A., Ed.; IO RAN: Moscow, Russia, 2021; pp. 242–243. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Martinovic, R.; Gacic, Z.; Kljajic, Z. The influence of oil, dispersed oil and the oil dispersant sd-25, on the heart rate of the Mediterranean Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis L.). In Sustainable Development of Sea-Corridors and Coastal Waters; Stylios, C., Floqi, T., Marinski, J., Damiani, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Guterres, B.D.V.; Guerreiro, A.D.S.; Botelho, S.S.D.C.; Sandrini, J.Z. Perna perna mussels network as pollution biosensors of oil spills and derivatives. IFAC Pap. 2020, 53, 16727–16732. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silveira Guerreiro, A.; de Vargas Guterres, B.; Costa, P.G.; Bianchini, A.; da Costa Botelho, S.S.; Sandrini, J.Z. Combined physiological and behavioral approaches as tools to evaluate environmental risk assessment of the water accommodated-fraction of diesel oil. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 249, 106230. [Google Scholar]
- Miserazzi, A.; Sow, M.; Gelber, C.; Charifi, M.; Ciret, P.; Dalens, J.M.; Weber, C.; Le Floch, S.; Lacroix, C.; Blanc, P.; et al. Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea exhibits distinguishable behavioural responses to crude oil under semi-natural multiple stress conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 219, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axiak, V.; George, J.J. Behavioral responses of a marine bivalve (Venus verrucosa) to pollution by petroleum hydrocarbons. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1987, 35, 395–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ait Ayad, M.; Ait Fdil, M.; Mouabad, A. Effects of Cypermethrin (pyrethroid insecticide) on the valve activity behavior, byssal thread formation, and survival in air of the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sigacheva, T.B.; Chesnokova, I.I.; Gostyukhina, O.L.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Andreenko, T.I.; Kovrigina, N.P.; Gavruseva, T.V.; Kirin, M.P.; Kurakin, A.S. Assessment of recreational potential of Sevastopol bays using bioindication methods. South Russ. Ecol. Dev. 2021, 16, 151–167. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nikolic, M.; Kuznetsova, T.; Kholodkevich, S.; Gvozdenovic, S.; Mandic, M.; Joksimovic, D.; Teodorovic, I. Cardiac activity in the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) as a biomarker for assessing sea water quality in Boka Kotorska Bay, South Adriatic Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 680–687. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. The first records of behavioral responses of the bivalves, Icelandic scallop Chlamys islandica and horse mussel Modiolus modiolus. Vestn. KamchatGTU 2012, 20, 50–55. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Evseeva, O.Y.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Shallow-water bryozoan communities in a glacier fjord of West Svalbard, Norway: Species composition and effects of environmental factors. Biology 2023, 12, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. The behavior of Svalbard bivalves in controlled conditions. Vestn. KamchatGTU 2012, 22, 77–82. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gudimov, A.V. Behavioral research of the bivalve Chlamys islandica in the Grønfjord (West Spitsbergen). In Complex Investigations of Spitsbergen and Offshore Nature, Proceedings of the XIV Scientific Conference with International Participation, Murmansk, Russia, 30 October 2018–2 November 2018; Makarevich, P.R., Ed.; FRC Kola Science Centre RAS: Apatity, Russia, 2018; pp. 27–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sharov, A.; Kholodkevich, S. Some features of using heart rate monitoring of freshwater bivalve molluscs with a fiber-optical method for ecotoxicological research. Principy Èkologii 2015, 4, 21–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, I.S.; Sharov, A.N.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Cardioactivity features of bivalve mollusks of the Gulf of Finland. Reg. Ecol. 2017, 2, 35–39. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Chuiko, G.M.; Gapeeva, M.V.; Lozhkina, R.A. Quality assessment of freshwater ecosystems by the functional state of bivalved mollusks. Water Res. 2019, 46, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Motruk, M.K.; Lyubimtsev, V.A.; Susloparova, O.N. Comparative bioelectronic diagnostics of the ecological state of contaminated water areas (on the example of some ducts of the Volga River Delta). Pharm. Formulas 2021, 3, 84–91. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Lyubimtsev, V.A.; Susloparova, O.N. Assessment of the ecosystem health of coastal waters of the eastern Gulf of Finland (case study of recreational waters quality of the Kurortny district of St. Petersburg) based on the study of the functional state of the mollusks living in them. In Proceedings of the XXI International Environmental Forum «Baltic Sea Day», St. Petersburg, Russia, 23–24 March 2021; OOO Svoe Izdatelstvo: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2021; pp. 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Verbitsky, V.B.; Sharov, A.N.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Determination of the bivalve Unio pictorum critical temperature maximum by cardioactivity. Trans. IBIW 2020, 89, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Manvelova, A.B.; Frumin, G.T. Some problems and approaches for their solution in searching reference sites and reference values in assessing the ecological state of aquatoria in the Eastern Gulf of Finland. Reg. Ecol. 2019, 3, 102–114. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Manvelova, A.B. Searching for reference sites and reference functional indicators for a comparative assessment of the ecological state of water areas on the basis of heart rate of bivalve mollusks of the family Unionidae (Mollusca, Bivalvia) and crustaceans (Crustacea, Decapoda). In Anthropogenic Impact on Aquatic Organisms and Ecosystems, Proceedings of the VII All-Russian Conference on Aquatic Ecotoxicology Dedicated to the Memory of Doctor of Biological Sciences, Professor, B.A. Flerov. Modern Methods of Research and Assessment of Water Quality, the State of Aquaticorganisms and Ecosystems under Anthropogenic Stress: Materials of the School-Seminar for Young Scientists, Graduate Students and Students, Borok, Russia, 16–19 September 2020; Filigran: Yaroslavl, Russia, 2020; pp. 112–115. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Trusevich, V.V.; Mishurov, V.J.; Kuzmin, K.A. System of the continuous quality control of water and the warning of threats of ecological danger automated in real time on water intakes of city water supply. In Environmental, Industrial and Energy Security—2018, Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference, Sevastopol, Russia, 24–27 September 2018; Lukina, L.I., Ed.; Sevastopol State University: Sevastopol, Russia, 2018; pp. 1177–1181. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Jou, L.J.; Chen, B.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Liao, C.M. Sensory determinants of valve rhythm dynamics provide in situ biodetection of copper in aquatic environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5374–5389. [Google Scholar]
- Gaisky, P.V.; Stepanova, O.A. Behavioral responses of freshwater bivalve mussel Unio pictorum to a number of common abiotic chemical contaminants. Monitor. Syst. Environ. 2020, 2, 87–96. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berezina, N.A.; Verbitsky, V.B.; Sharov, A.N.; Chernova, E.N.; Meteleva, N.Y.; Malysheva, O.A. Biomarkers in bivalve mollusks and amphipods for assessment of effects linked to cyanobacteria and elodea: Mesocosm study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.; Haberkorn, H.; Soudant, P.; Ciret, P.; Massabuau, J.C. Behavioral responses of Crassostrea gigas exposed to the harmful algae Alexandrium minutum. Aquaculture 2010, 298, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kirin, M.P.; Smirnov, I.S.; Rudakova, O.A.; Lyubimtsev, V.A.; Manvelova, A.B.; Susloparova, O.N.; Perelygin, V.V.; Sakharova, O.A. Bioindication of the ecological state (health) of coastal waters based on the use of automated bioelectronic systems. Pharm. Formulas 2020, 2, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Rudakova, O.A.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Manvelova, A.B.; Susloparova, O.N. Ranking of the ecosystem state of water areas on the basis of operational testing of the functional state of bivalve mollusks inhabiting them (on the example of recreational water areas of the Kurortny District of St. Petersburg). In Anthropogenic Impact on Aquatic Organisms and Ecosystems, Proceedings of the VII All-Russian Conference on Aquatic Ecotoxicology Dedicated to the Memory of Doctor of Biological Sciences, Professor B.A. Flerov. Modern Methods of Research and Assessment of Water Quality, the State of Aquaticorganisms and Ecosystems under Anthropogenic Stress: Materials of the School-Seminar for Young Scientists, Graduate Students and Students, Borok, Russia, 16–19 September 2020; Filigran: Yaroslavl, Russia, 2020; pp. 216–219. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, T.V.; Sladkova, G.V.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Evaluation of functional state of crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus in normal and toxic environment by characteristics of their cardiac activity and hemolymph biochemical parameters. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 46, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sladkova, S.; Kholodkevich, S.; Safronova, D.; Borisov, R. Cardiac activity of crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens 1868) in different physiological states. Principy Èkologii 2017, 6, 40–53. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sladkova, S.V.; Lyubimtsev, V.A.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Study of cardioactivity of Astacus leptodactylus Crayfish and Cherax quadricarinatus in a wide temperature range. In Actual Problems of Studying Crustaceans, Proceedings of the Scientific and Practical Conference, Borok, Russia, 23–25 May 2022; Institute of Natural and Technical Systems: Sevastopol, Russia, 2022; p. 59. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kozák, P.; Policar, T.; Fedotov, V.P.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Buric, M.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Effect of chloride content in water on heart rate in narrow-clawed crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2009, 394–395, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, T.V. Change of salinity of medium as a function loading in estimating functional state of the crayfish Astacus leptodactylus. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 49, 498–502. [Google Scholar]
- Kozák, P.; Policar, T.; Fedotov, V.P.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Buric, M.; Kouba, A.; Kuklina, I.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Stress reaction in crayfish: Chlorides help to withstand stress in high nitrite concentration conditions—Preliminary study. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2011, 401, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Udalova, G.P.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Fedotov, V.P.; Kornienko, E.L. Changes in heart rate and circadian cardiac rhythm as physiological biomarkers for estimation of functional state of crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus Esch. upon acidification of the environment. Inland Water Biol. 2012, 5, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sladkova, S.V.; Lyubimtsev, V.A.; Kholodkevich, S.V. On the use of river crayfish as bioindicators in bioelectronic water quality monitoring systems at wastewater discharge sites in the Gulf of Finland. In Biodiagnostics of the State of Natural and Natural-Technogenic Systems, Proceedings of the XIV All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference with International Participation, Kirov, Russia, 5–8 December 2016; Degteva, S.V., Litvinets, S.G., Ashikhmina, T.Y., Domracheva, L.I., Kondakova, L.V., Shirokikh, I.G., Dabakh, E.V., Eds.; LLC Raduga-PRESS: Kirov, Russia, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 245–249. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lyubimtsev, V.A.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Druzhinin, I.I. Measuring systems designed for working with living organisms as biosensors. Features of their metrological maintenance. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1379, 12077. [Google Scholar]
- Fedotov, V.P.; Zhuravlev, V.L.; Khalatov, A.N.; Kholodkevich, S.V. Comparative analysis of heart activity of the crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus by methods of plethysmography and electrocardiography. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 45, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaw, I.J. Does feeding limit cardiovascular modulation in the Dungeness crab Cancer magister during hypoxia? J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Worden, M.K.; Clark, C.M.; Conaway, M.; Qadri, S.A. Temperature dependence of cardiac performance in the lobster Homarus americanus. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Giomi, F.; Pörtner, H.-O. A role for haemolymph oxygen capacity in heat tolerance of eurythermal crabs. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 110. [Google Scholar]

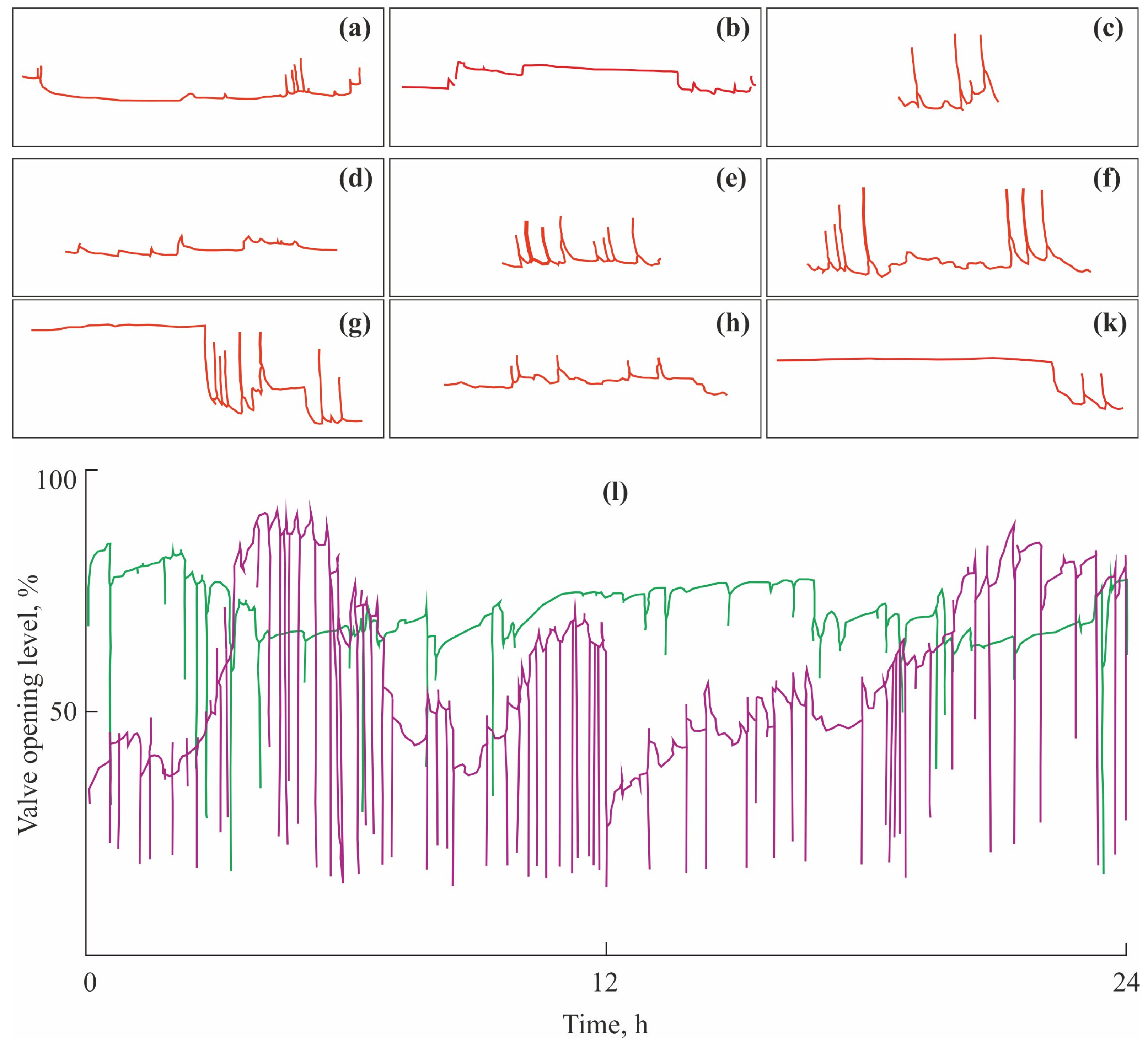

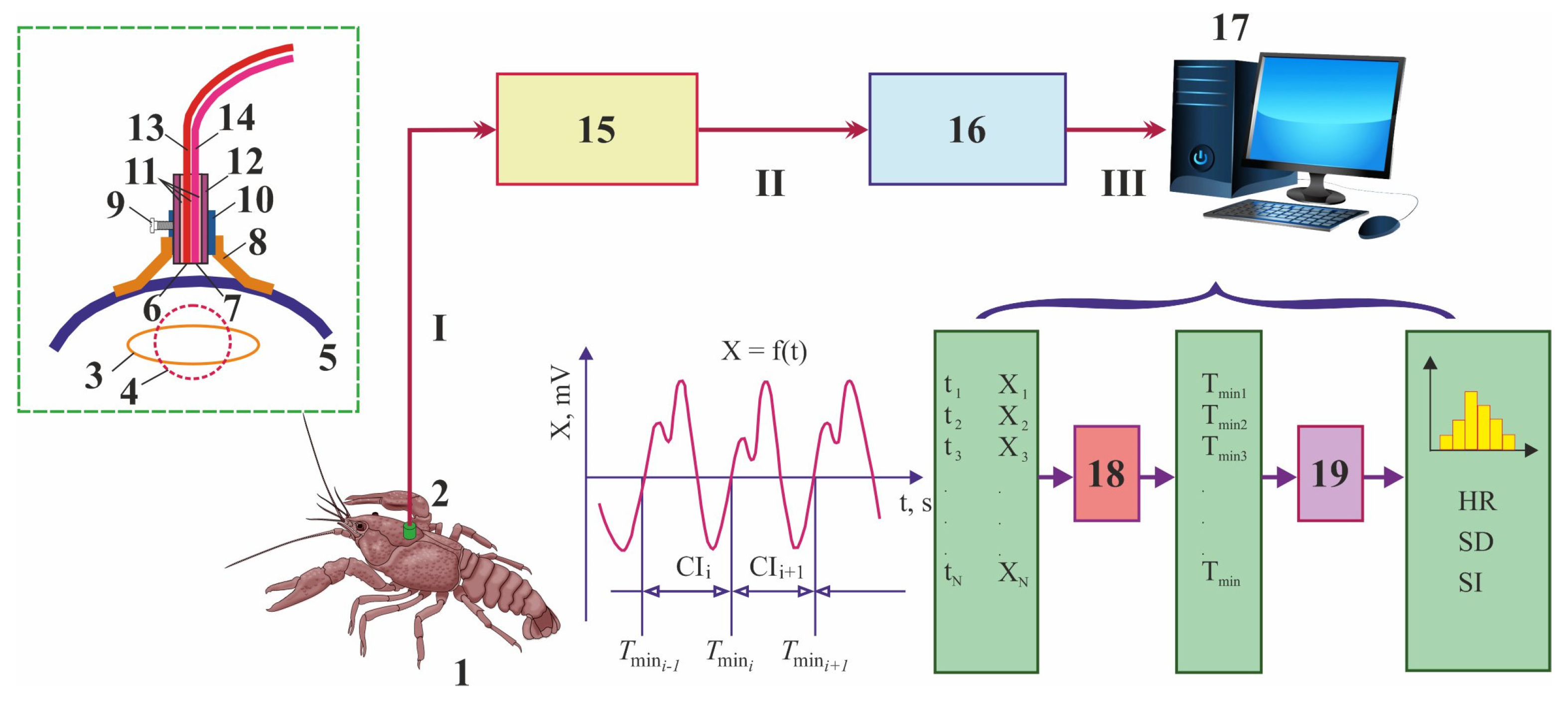
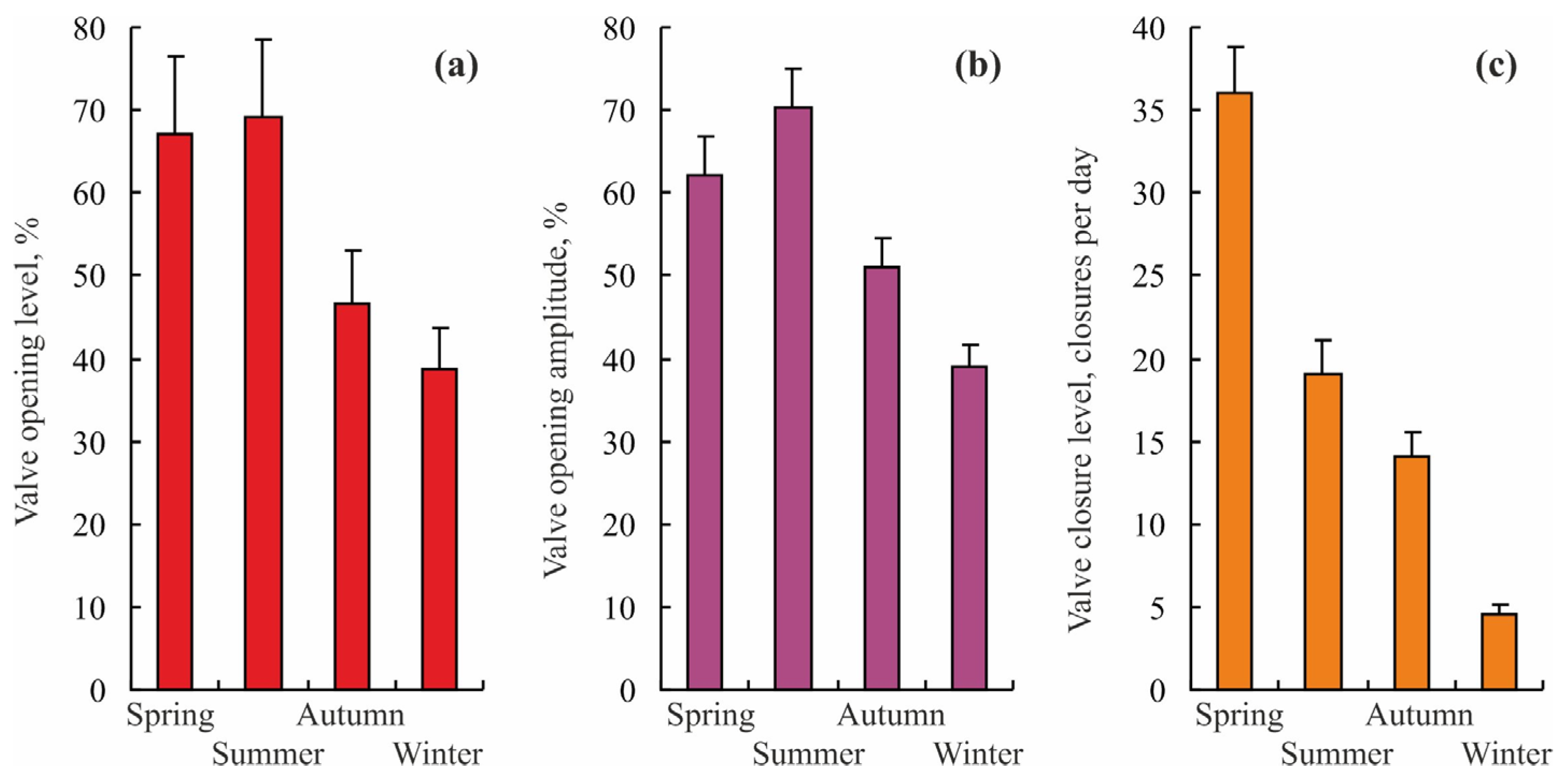
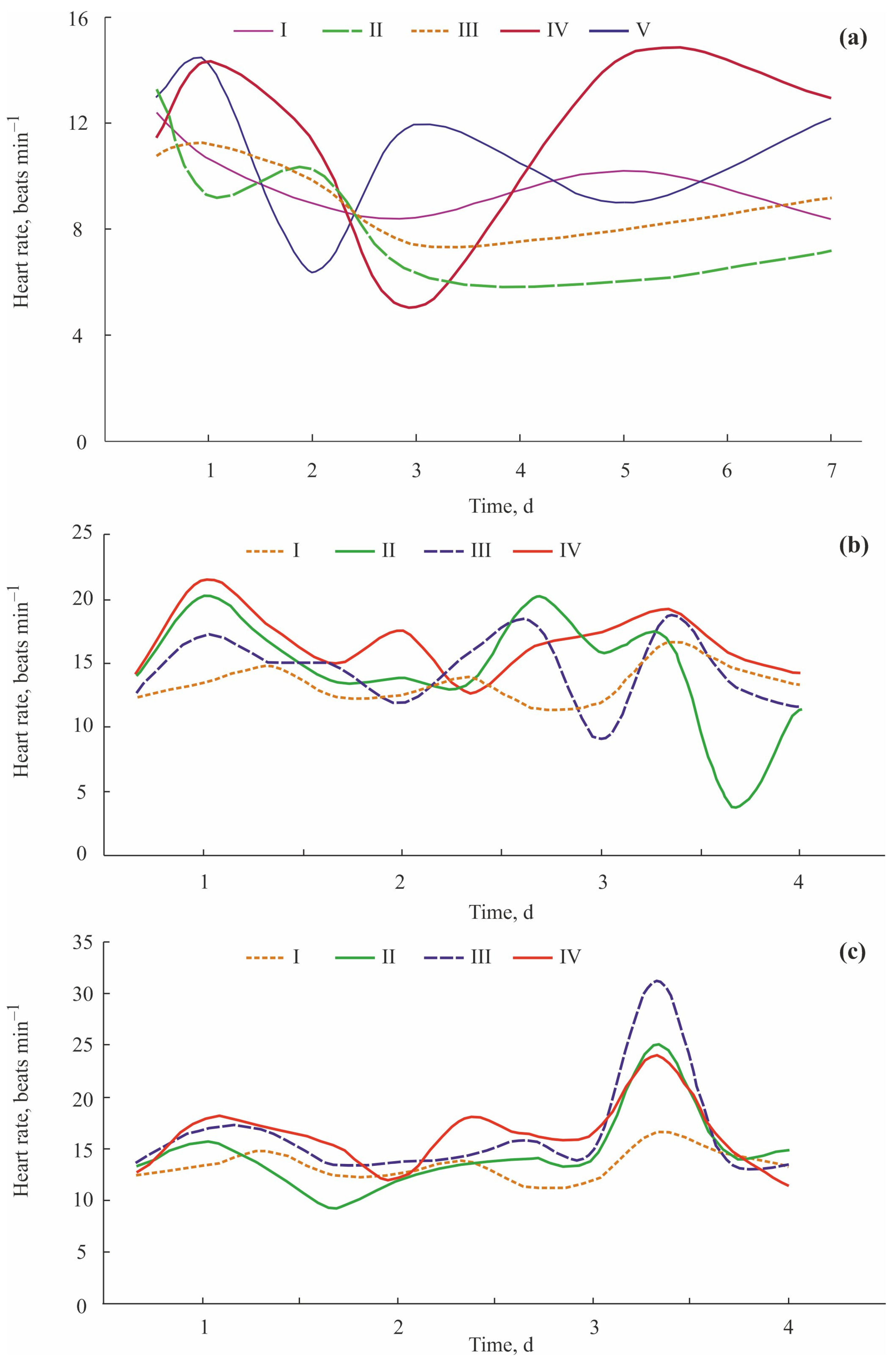

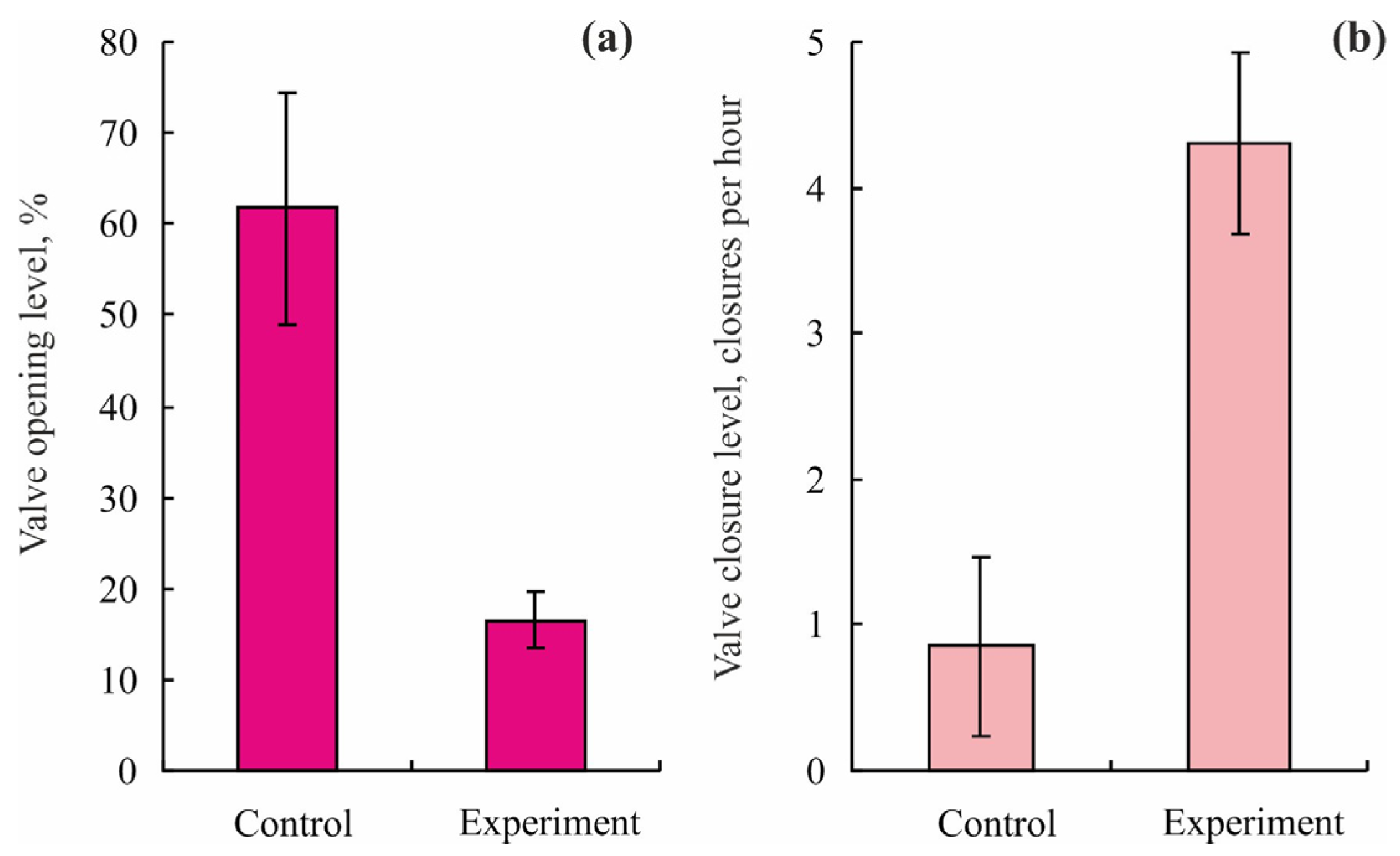

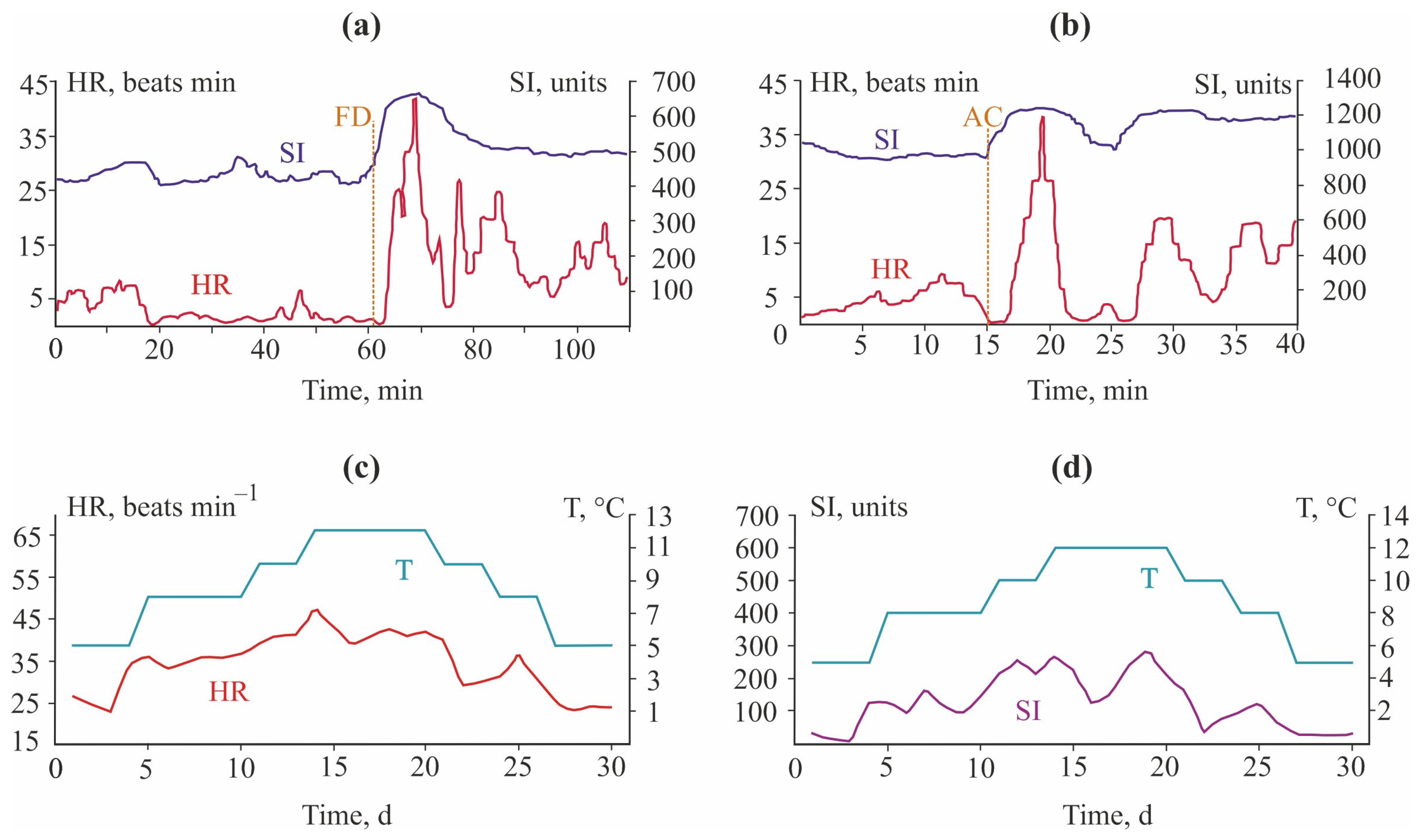
| Toxicant | Concentration, mg L−1 | Flowing Water | Non-Flowing Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| NH4OH | 0.1 | No | Slight ↑ in valve closing frequency in single mollusks. |
| 1 | Practically no | Slight ↑ in valve closing frequency in all mollusks. | |
| 10 | ↑ in VCF to 15–20 cph, 2–fold ↓ in valve opening amplitude. | ↑ in VCF to 15–20 cph, 2–fold ↓ in valve opening amplitude. | |
| CuSO4 * 5H2O | 0.002 | Practically no | Synchronous fast (5–8 min) valve closure. Trec = 2–3 h. Post–stress reactions for 3–4 h. |
| 0.0625 | Synchronous ↑ in VCF to 1–2 cpm, VOA remains unaffected. Trec = 0 min. | Synchronous ↑ in VCF, slow ↓ in VOA. Valves are closed in all mollusks. Trec = 1.5–2 h. | |
| 0.125 | Synchronous ↑ in VCF for 30 min ↓ in VOA for 3–40 min. | Synchronous slow ↓ in VOA. Valves are closed in all mollusks after 1 h. | |
| 0.25 | Synchronous ↓ in VOA and ↑ in VCF during 30 min. Further ↓ in VCF. Trec = 1.5–2 h. | Synchronous ↓ in VOA during 30 min. Valves are closed in most mollusks. Trec = 2–3 h. Post–stress reactions for 4–5 h | |
| 0.5 | Synchronous ↓ in VOA and ↑ in VCF during 30 min. Trec = 2.5–3 h. | Synchronous ↓ in VOA during 20 min. Valves are closed for the whole exposure period. Trec = 4–5 h. | |
| 1 | Synchronous closure of shell valves during 5–7 min, increased gaping activity for 1 h. Trec = 2 h. | Synchronous closure of shell valves during 5 min. Valves are closed for the whole exposure period. Trec = 4 h. | |
| 2 | Synchronous closure of shell valves during 5–7 min, asynchronous gaping activity for 2–3 min. Trec = 3 h. Post–stress reactions for 5–7 h. | Synchronous closure of shell valves during 3–4 min, asynchronous gaping activity for 2–3 min. Trec = 4–5 h. Post–stress reactions for 7–9 h | |
| Pb(CH3COO)2 | 0.005 | No | No |
| 0.01 | No | Practically no | |
| 0.025 | No | Slight ↑ in VCF in 30% of mollusks. | |
| 0.5 | Slight ↑ in VCF in 3–4 mollusks. | Slight ↑ in VCF in 50% of mollusks. | |
| 3CdSO4 * 8H2O | 0.025 | No | Slight ↑ in VCF. |
| 0.5 | Synchronous ↑ in VCF with fast ↓ in VOA. Immediate recovery. | Synchronous ↑ in VCF with fast ↓ in VOA. After 30 min, 75% of mollusks are closed and remained closed for 3–5 h. | |
| 1 | Synchronous ↑ VCF with fast ↓ in VOA. Fast recovery. | Synchronous ↑ in VCF with fast ↓ in VOA in all mollusks. Trec = 2 h. | |
| Sodium lauryl sulfate | 0.5 | No | Practically no |
| 5 | Expressed synchronous ↑ in VCF with 50% ↓ VOA. 50% of mollusks remained closed after exposure. Trec = 2–3 h. | Expressed synchronous ↑ in VCF with 100% ↓ in VOA after 25–35 min. Trec = 3–3.5 h. |
| Conditions | Heart Rate, Beats min−1 | Stress Index, Units |
|---|---|---|
| At rest, 5 °C | 18–25 | 1–50 |
| ↑ in temperature to 8 °C | 25–35 | 50–220 |
| ↑ in temperature to 12 °C | 35–45 | 150–600 |
| 1st week after 12 h transportation | 45–60 | – |
| 2nd week after 12 h transportation | 30–45 | – |
| 3rd week after 12 h transportation | 25–45 | – |
| 4th week after 12 h transportation | 18–25 | – |
| Cleaning of the rearing aquarium | 40 | Up to 1200 |
| Feeding | 40 | 650 |
| Before 24 h air exposure | 27–30 | 10–500 |
| Immediately after 24 h air exposure | 17 | 1 |
| 30 min after 24 h air exposure | 40 | Up to 3500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Shellfish as Biosensors in Online Monitoring of Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review of Russian Studies. Fishes 2023, 8, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020102
Dvoretsky AG, Dvoretsky VG. Shellfish as Biosensors in Online Monitoring of Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review of Russian Studies. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020102
Chicago/Turabian StyleDvoretsky, Alexander G., and Vladimir G. Dvoretsky. 2023. "Shellfish as Biosensors in Online Monitoring of Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review of Russian Studies" Fishes 8, no. 2: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020102
APA StyleDvoretsky, A. G., & Dvoretsky, V. G. (2023). Shellfish as Biosensors in Online Monitoring of Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review of Russian Studies. Fishes, 8(2), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020102









