17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
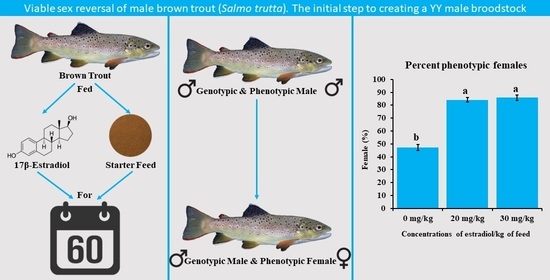
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piferrer, F. Endocrine sex control strategies for the feminization of teleost fish. Aquaculture 2001, 197, 229–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, T.J.; Sheela, S.G. Hormonal induction of sex reversal in fish. Aquaculture 1995, 138, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.B.; Teem, J.L. A model describing the effect of sex-reversed YY fish in an established wild population: The use of the Trojan Y chromosome to cause extinction of an introduced exotic species. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 241, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teem, J.L.; Gutierrez, J.B. A Theoretical Strategy for Eradication of Asian Carps using a Trojan Y Chromosome to Shift the Sex Ratio of the Population. In Proceedings of the Invasive Asian Carps in North America: A Forum to Understand the Biology and Manage the Problem, Peoria, IL, USA, 22–23 August 2006; Chapman, D.C., Hoff, M.H., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Schill, D.J.; Meyer, K.A.; Hansen, M.J. Simulated effects of YY-male stocking and manual suppression for eradicating nonnative brook trout populations. N. Am. J. Fish Manag. 2017, 37, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, S.; Wedekind, C. Control of introduced species using trojan sex chromosomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schill, D.J.; Heindel, J.A.; Campbell, M.R.; Meyer, K.A.; Mamer, E.R.J.M. Production of a YY male brook trout broodstock for potential eradication of undesired brook trout populations. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2016, 78, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teem, J.; Alphey, L.; Descamps, S.; Edgington, M.; Edwards, O.; Gemmell, N.; Harvey-Samuel, T.; Melnick, R.; Oh, K.; Piaggio, A.; et al. Genetic biocontrol for invasive species. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, T.J.; Kirankumar, S. Recent advances in hormonal injection of sex-reversal in fish. J. Appl. Aquac. 2003, 13, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.; Macintosh, D.J.; Wright, R.S. Elimination of orally administered 17α-methyltestosterone by Oreochromis mossambicus (tilapia) and Salmo gairdneri (rainbow trout) juveniles. Aquaculture 1983, 3, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. Effects of estradiol-17β on gonadal sex differentiation in two species of salmonids, the masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou and the chum salmon, O. keta. Aquaculture 1984, 48, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.A.; Solar, I.I.; Baker, I.J.; Donaldson, E.M. Feminization of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) by immersion of alevins in a solution of estradiol-11β. Aquaculture 1986, 53, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Donaldson, E.M. The comparative effectiveness of the natural and a synthetic estrogen for the direct feminization of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Aquaculture 1992, 106, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.; Simpson, T.H.; Youngson, A.F. Sex reversal in salmonid culture. Aquaculture 1978, 13, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.; Simpson, T.H.; Walker, A.F. Sex reversal in salmonid culture. Part III. The production and performance of all female populations of brook trout. Aquaculture 1979, 18, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, E.M.; Hunter, G.A. Sex control in fish with particular reference to salmonids. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.A.; Donaldson, E.M.; Stoss, J.; Baker, I. Production of monosex female groups of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) by the fertilization of normal ova with sperm from sex-reversed females. Aquaculture 1983, 33, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, G.; Yeoh, C.G.; Fitzpatrick, M.S.; Schreck, C.B. The production of functional sex reversed rainbow trout with 17α-methyltestosteron and 11β-hydroxyanderostenedione. Aquaculture 1995, 131, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, G.; Schreck, C.B.; Gharrett, A.J. Controlling the Sex of Salmonids. Oregon Sea Grant, Ploidy/Sex Manipulation Work Group, 1996, ORESU-H-96-001:26. Available online: https://seagrant.oregonstate.edu/sites/seagrant.oregonstate.edu/files/sgpubs/onlinepubs/h96001.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Ashby, K.R. The effect of steroid hormones on the brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) during the period of gonadal differentiation. Development 1957, 5, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database; Invasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2004; Volume 12, Available online: https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2000-126.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Simberloff, D. Invasive species. In Conservation Biology for All; Sodhi, N.S., Ehrlich, P.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypel, A.L. Do invasive freshwater fish species grow better when they are invasive? Okios 2014, 123, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, W.C.; Budy, P.; Thiede, G.P. Demographic changes following mechanical removal of exotic brown trout in an intermountain West (USA), high-elevation stream. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2015, 24, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.A.; Meyer, K.A.; Schill, D.J.; Campbell, M.R.; Vu, N.V. Survival and reproductive success of hatchery YY male brook trout stocked in Idaho streams. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2018, 147, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buterbaugh, G.L.; Willoughby, H. A feeding guide to brook, brown, and rainbow trout. Progr. Fish.-Cult. 1967, 29, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warton, D.I.; Hui, F.K.C. Arcsine is asinine: The analysis of proportions in ecology. Ecology 2011, 92, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudie, C.A.; Redner, B.D.; Simco, B.A.; Davis, K.B. Feminization of channel catfish by oral administration of steroid sex hormones. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1983, 112, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.; Pandian, T.J. Hormonal induction of sex reversal and progeny testing in the zebra cichlid Cichlasoma nigrofasciatum. J. Exp. Zool. 1996, 275, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strüssmann, C.A.; Takashima, F.; Toda, K. Sex differentiation and hormonal feminization in pejerrey Odonthesthes bonariensis. Aquaculture 1996, 139, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Gao, Z.; Beres, B.; Ottobre, J.; Wallat, G.; Tiu, L.; Rapp, D.; O’Bryant, P.; Yao, H. Effects of estradiol-17β on survival, growth performance, sex reversal and gonadal structure of bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malison, I.A.; Kayes, T.B.; Wentworth, B.C.; Amundson, C.H. Growth and feeding responses of male versus female yellow perch (Perca flavescens) treated with estradiol-17β. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Nimura, Y. Growth promotion in Japanese eel by the oral administration of an estrogen (diethylstilbestrol). Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1991, 57, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, M.E.; Wintersteen, K.; Krebs, E.; Nero, P.; Tycz, J.; Reichert, S.; Zimmerman, S. 2010 McNenny State Fish Hatchery Annual Production Report. Annual Report No. 11-03; South Dakota Department of Game, Fish and Parks: Pierre, SD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kissil, G.W.; Lupatsch, I.; Higgs, D.A.; Hardy, R.W. Dietary substitution of soy and rapeseed protein concentrations for fish meal, and their effects on growth and nutrient utilization in gilthead seabream Sparus aurata L. Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.; Sindelar, S.C.; Voorhees, J.M.; Brown, M.L.; Barnes, M.E. Performance and immunological responses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed bioprocessed plant-based proteins. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regost, C.; Arzel, J.; Cardinal, M.; Laroche, M.; Kaushik, S.J. Fat deposition and flesh quality in seawater reared, triploid brown trout (Salmo trutta) as affected by dietary fat levels and starvation. Aquaculture 2001, 193, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.E.; Miller, J.; Durben, D.J. Partial overhead tank cover use during feral brown trout rearing. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2005, 67, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, J.M.; Barnes, M.E.; Chipps, S.R.; Brown, M.L. Rearing performance of juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta) subjected to exercise and dietary bioprocessed soybean meal. Open. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 8, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, J.M.; Barnes, M.E.; Chipps, S.R.; Brown, M.L. Direct substitution of fishmeal with bioprocessed soybean meal in brown trout diets. J. Fish. Aquac. Dev. 2018, JFAD-143, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, R.L.; Kincaid, H.L. Pathological effects of orally administered estradiol to rainbow trout. Aquaculture 1988, 72, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sower, S.A.; Dickhoff, W.W.; Flagg, T.A.; Mighell, J.L.; Mahnken, C.V.W. Effects of estradiol and diethylstilbesterol on sex reversal and mortality in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 1984, 43, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schill, D.J.; Coykendall, D.K.; Campbell, M.R.; Mamer, E.R.J.M. Development of YY male technology for eradicating invasive fish populations in Arizona streams—genetic sex marker development and field testing. IIAPM Funding Window Criterion: Development of YY male technology for salmonid species. Herit. Grant Proj. 2020, I18007, 39. [Google Scholar]

| Rearing Day | Estradiol (mg/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 30 | p-Value | ||
| 60 | Gain (kg) | 0.59 ± 0.02 z | 0.44 ± 0.02 y | 0.42 ±0.02 y | <0.001 |
| Gain (%) | 1465 ± 42 z | 1103 ± 54 y | 1053 ± 55 y | <0.001 | |
| FCR | 1.43 ± 0.04 z | 1.91 ± 0.09 y | 2.01 ± 0.10 y | <0.001 | |
| Mortality (%) | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.7 | 0.08 | |
| 105 | Gain (kg) | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.04 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.25 |
| Gain (%) | 84 ± 5 | 101 ± 9 | 97 ± 7 | 0.27 | |
| FCR | 2.65 ± 0.11 | 2.94 ± 0.31 | 3.15 ± 0.17 | 0.31 | |
| Rearing Day | Estradiol (mg/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 30 | p-Value | ||
| 60 | Length (mm) | 52.28 ± 0.20 z | 46.12 ± 0.31 y | 43.53 ± 0.62 x | <0.001 |
| Weight (g) | 1.46 ± 0.01 z | 1.07 ± 0.02 y | 0.96 ± 0.05 y | <0.001 | |
| 105 | Length (mm) | 65.86 ± 1.22 | 61.99 ± 2.36 | 60.98 ± 0.79 | 0.13 |
| Weight (g) | 2.86 ± 0.12 | 2.29 ± 0.25 | 2.42 ± 0.12 | 0.10 | |
| 170 | Length (mm) | 95 ± 1 z | 92 ± 0 y | 89 ± 1 x | <0.001 |
| Weight (g) | 9.7 ± 0.2 z | 9.1 ± 0.1 y | 8.2 ± 0.2 x | <0.001 | |
| 456 | Length (mm) | 188 ± 1 y | 201 ± 8 z | 191 ± 1 zy | 0.03 |
| Weight (g) | 69.8 ± 1.3 y | 79.7 ± 3.5 z | 72.2 ± 1.3 zy | 0.03 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voorhees, J.M.; Mamer, E.R.J.M.; Schill, D.J.; Adams, M.; Martinez, C.; Barnes, M.E. 17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout. Fishes 2023, 8, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103
Voorhees JM, Mamer ERJM, Schill DJ, Adams M, Martinez C, Barnes ME. 17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoorhees, Jill M., Elizabeth R. J. M. Mamer, Daniel J. Schill, Mitchel Adams, Carlos Martinez, and Michael E. Barnes. 2023. "17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout" Fishes 8, no. 2: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103
APA StyleVoorhees, J. M., Mamer, E. R. J. M., Schill, D. J., Adams, M., Martinez, C., & Barnes, M. E. (2023). 17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout. Fishes, 8(2), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103