Rodlet Cells Provide First Line of Defense against Swimbladder Nematode and Intestinal Coccidian in Anguilla anguilla
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
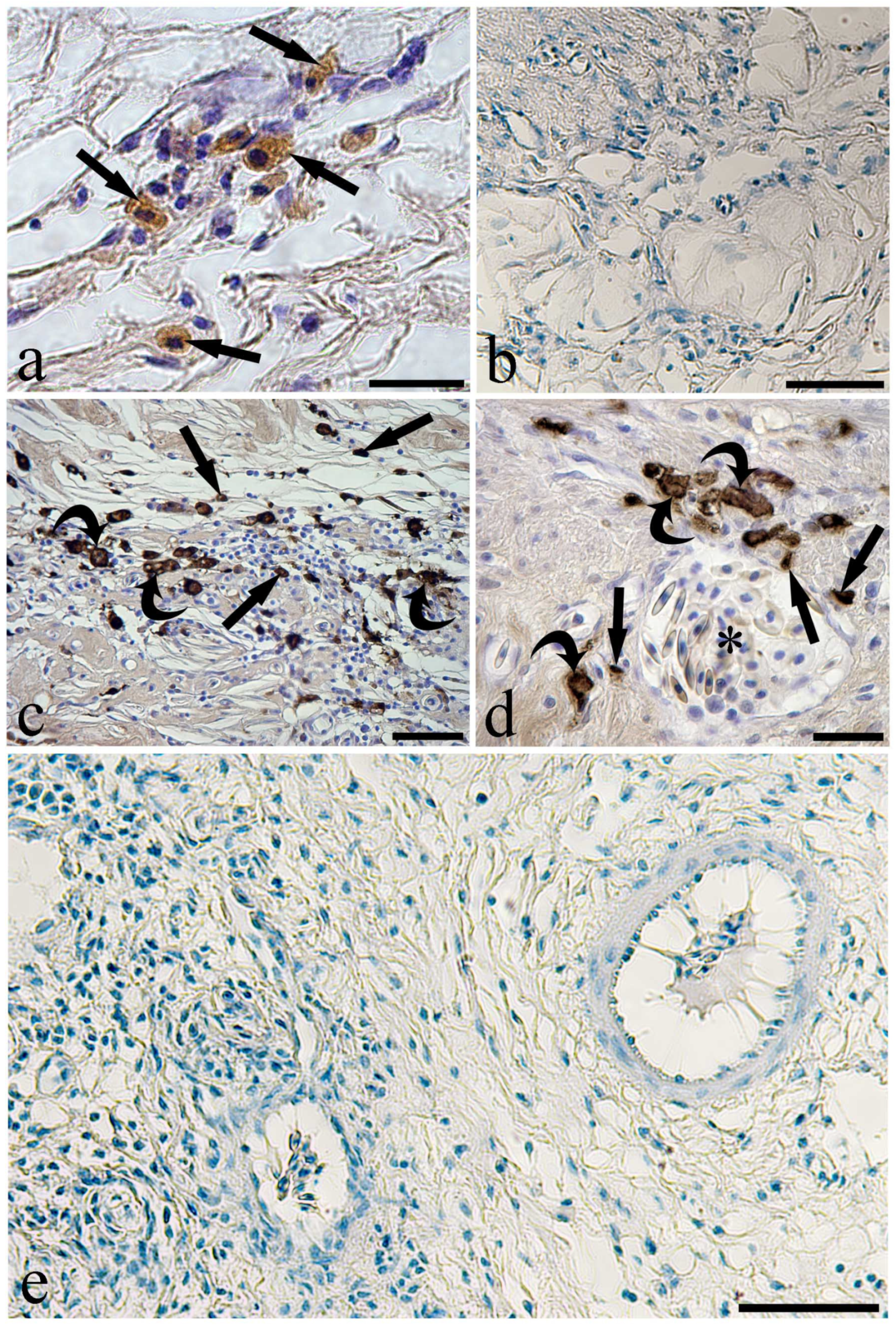
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelster, B. Swimbladder function and the spawning migration of the European eel Anguilla anguilla. Front. Physiol. 2015, 5, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, F.; Wielgoss, S.; Nagasawa, K.; Moravec, F. On the origin of Anguillicoloides crassus, the invasive nematode of anguillid eels. Aquat. Invasions 2012, 7, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Maestri, C.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Maynard, B.J.; Bosi, G. The impact of Anguillicoloides crassus (Nematoda) on European eel swimbladder: Histopathology and relationship between neuroendocrine and immune cells. Parasitology 2021, 148, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopf, K. The swimbladder nematode Anguillicola crassus in the European eel Anguilla anguilla and the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica: Differences in susceptibility and immunity between a recently colonized host and the original host. J. Helminthol. 2006, 80, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B.; Knopf, K.; Kloas, W. Induction of stress by the swimbladder nematode Anguillicola crassus in European eels, Anguilla anguilla, after repeated experimental infection. Parasitology 2001, 123, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, D.M.P.; Casselman, J.M.; Crook, V.; DeLucia, M.B.; Ahn, H.; Kaifu, K.; Kurwie, T.; Sasal, P.; Silfvergrip, A.M.C.; Smith, K.G.; et al. Synergistic patterns of threat and the challenges facing global anguillid eel conservation. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 4, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, R.M. Regulation of immunity and allergy by helminth parasites. Allergy 2020, 75, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.A.; Friberg, I.M.; Little, S.; Bradley, J.E. Review series on helminths, immune modulation and the hygiene hypothesis: Immunity against helminths and immunological phenomena in modern human populations: Coevolutionary legacies? Immunology 2009, 126, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Giari, L.; Bosi, G. Survival of metazoan parasites in fish: Putting into context the protective immune responses of teleost fish. Adv. Parasitol. 2021, 112, 77–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Pellitero, P. Mucosal Intestinal Immunity and Response to Parasite Infections in Ectothermic Vertebrates; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011; 108p. [Google Scholar]
- Conforto, E.; Vilchez-Gomez, L.; Parrinello, D.; Parisi, M.G.; Esteban, M.A.; Cammarata, M.; Guardiola, F.A. Role of mucosal immune response and histopathological study in European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) intraperitoneal challenged by Vibrio anguillarum or Tenacibaculum soleae. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 114, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzinger, A.; Evans, T. Gata4 regulates the formation of multiple organs. Development 2005, 132, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würtz, J.; Taraschewski, H. Histopathological changes in the swimbladder wall of the European eel Anguilla anguilla due to infections with Anguillicola crassus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 39, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyková, I.; Lom, J. Histopathology of Protistan and Myxozoan Infections in Fishes, an Atlas; Academia Press: Prague, Czech Republic, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kristmundsson, A.; Hansen, H.; Alarcon, M.; Freeman, M.A. An eimerid apicomplexan causing pathology in wild and farmed lumpfish, Cyclopterus lumpus. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 2018, 38, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Matsche, M.A.; Blazer, V.S.; Mazik, P.M. Seasonal development of the coccidian parasite Goussia bayae and hepatobiliary histopathology in white perch Morone americana from Chesapeake Bay. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2019, 134, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, K.; Baska, F. Light and electron microscopic studies on Epieimeria anguillae (Léger & Hollande, 1922), a coccidium parasitizing the European eel, Anguilla anguilla L. J. Fish Dis. 1986, 9, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benajiba, M.H.; Marques, A.; Lom, J.; Bouix, G. Ultrastructure and sporogony of Eimeria (syn. Epieimeria) anguillae (Apicomplexa) in the eel (Anguilla anguilla). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1994, 41, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hine, P.M. Eimeria anguillae Léger & Hollande, 1922 parasitic in New Zealand eels. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1975, 9, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhner, S.; Schemann, M. Mast cell-nerve axis with a focus on the human gut. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulero, I.; Sepulcre, M.P.; Meseguer, J.; García-Ayala, A.; Mulero, V. Histamine is stored in mast cells of most evolutionarily advanced fish and regulates the fish inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19434–19439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Castaldelli, G.; Tomaini, R.; Manera, M.; DePasquale, J.A.; Bosi, G. Challenge for macrophages and mast cells of Chelon ramada to counter an intestinal microparasite, Myxobolus mugchelo (Myxozoa). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2020, 138, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Giari, L.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Manera, M.; Bosi, G. Pike intestinal reaction to Acanthocephalus lucii (Acanthocephala): Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural surveys. Parasite Vector 2018, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; DePasquale, J.A.; Castaldelli, G.; Giari, L.; Bosi, G. A fish model for the study of the relationship between neuroendocrine and immune cells in the intestinal epithelium: Silurus glanis infected with a tapeworm. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccotti, C.; Giaroni, C.; Bistoletti, M.; Viola, M.; Crema, F.; Terova, G. Neurochemical characterization of myenteric neurons in the juvenile gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) intestine. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.F.; Simões, M.J.; Gutierre, R.C.; Egami, M.I.; Santos, A.A.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Sasso, G.R.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Special dyeing, histochemistry, immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure: A study of mast cells/eosinophilic granules cells (MCs/EGC) from Centropomus parallelus intestine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenaga, H.; Nagamine, R.; Sakai, M.; Kono, T. Expression profile of cytokine genes in Fugu monocytes stimulated with TLR agonists. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahla, R.S.; Reddy, M.C.; Prasad, D.V.R.; Kumar, H. Sweeten PAMPs: Role of sugar complexed PAMPs in innate immunity and vaccine biology. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, G.; DePasquale, J.A.; Manera, M.; Castaldelli, G.; Giari, L.; Sayyaf Dezfuli, B. Histochemical and immunohistochemical characterization of rodlet cells in the intestine of two teleosts, Anguilla anguilla and Cyprinus carpio. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePasquale, J.A. Tropomyosin and alpha-actinin in teleost rodlet cells. Acta Zool. 2020, 102, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.D.; Murray, C.I.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, X.; DuMond, J.F.; Shen, X.; Stanley, B.A.; Foster, D.B.; Wink, D.A.; King, S.B.; et al. Nitroxyl-mediated disulfide bond formation between cardiac myofilament cysteines enhances contractile function. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, W.; Morgan, K.G. Structure and dynamics of the actin-based smooth muscle contractile and cytoskeletal apparatus. J. Muscle Res. Cell. Motil. 2012, 33, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Manera, M.; Bosi, G.; Merella, P.; DePasquale, J.A.; Giari, L. Intestinal granular cells of a cartilaginous fish, thornback ray Raja clavata: Morphological characterization and expression of different molecules. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Sears, J.D.; Ylaya, K.; Perry, C.; Choi, C.H.; Hong, S.-M.; Cho, H.; Brown, K.M.; Hewitt, S.M. A melanin-bleaching methodology for molecular and histopathological analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesch, F.W. The Eel, 5th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Secombes, C.J.; Ellis, A.E. The immunology of teleosts. In Fish Pathology; Roberts, R.J., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Chicester, UK, 2012; Volume 4, pp. 144–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Pironi, F.; Maynard, B.J.; Simoni, E.; Bosi, G. Rodlet cells, fish immune cells and a sentinel of parasitic harm in teleost organs. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 121, 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Bo, T.; Lorenzoni, M.; Shinn, A.P.; Giari, L. Fine structure and cellular responses at the host-parasite interface in a range of fish-helminth systems. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 208, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, A.M.; Hall, B.E.; Barreda, D.R. Macrophage activation differentially modulates particle binding, phagocytosis and downstream antimicrobial mechanisms. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1144–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Sharkey, K.A.; McKay, D.M. Modulation of the immune response by helminths: A role for serotonin? Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da’as, S.; Teh, E.M.; Dobson, J.T.; Nasrallah, G.K.; McBride, E.R.; Wang, H.; Neuberg, D.S.; Marshall, J.S.; Lin, T.-J.; Berman, J.N. Zebrafish mast cells possess an FcεRI-like receptor and participate in innate and adaptive immune responses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, H.P.; Adachi, R.; Stevens, R.L. Mast cell-restricted tryptases: Structure and function in inflammation and pathogen defense. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20785–20789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreakis, N.; D’Aniello, S.; Albalat, R.; Patti, F.P.; Garcia-Fernandez, J.; Procaccini, G.; Sordino, P.; Palumbo, A. Evolution of the nitric oxide synthase family in metazoans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losada, A.P.; Bermúdez, R.; Faílde, L.D.; Quiroga, M.I. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of iNOS expression in turbot (Psetta maxima) infected with Enteromyxum scophthalmi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giari, L.; Konecny, R.; Jaeger, P.; Manera, M. Immunohistochemistry, ultrastructure and pathology of gills of Abramis brama from Lake Mondsee, Austria, infected with Ergasilus sieboldi (Copepoda). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 53, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.; Zou, J.; Holland, J.W.; Martin, S.A.; Collet, B.; Kanellos, T.; Secombes, C.J. Identification and characterisation of TLR18-21 genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, N.W.; Morath, S.; Alexander, C.; Hamann, L.; Hartung, T.; Zähringer, U.; Göbel, U.B.; Weber, J.R.; Schumann, R.R. Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus activates immune cells via Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2, lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP), and CD14, whereas TLR-4 and MD-2 are not involved. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 15587–15594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.M.; Hermsen, T.; Taverne-Thiele, A.J.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Evolution of recognition of ligands from Gram-positive bacteria: Similarities and differences in the TLR2-mediated response between mammalian vertebrates and teleost fish. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2355–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-García, M.M.; Rojas-Bernabé, A.; Gómez-García, A.P.; Escalona-Montaño, A.R. TLR-mediated host immune response to parasitic infectious diseases. In Toll-Like Receptors; Rezaei, N., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, M.; Kiessling, S.; Mestermann, S.; Webb, G.; Spöttl, T.; Andus, T.; Schölmerich, J.; Herfarth, H.; Ray, K.; Falk, W.; et al. Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are upregulated during intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Li, Y.W.; Pan, H.J.; Shi, C.B.; Luo, X.C.; Li, A.X.; Wu, S.-Q. Expression profiles of toll-like receptors in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) after infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Kweon, M.-N.; Iwatani, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Terhara, K.; Sesakawa, C.; Suzuki, T.; Nochi, T.; Yokota, Y.; Rennert, P.D.; et al. Intestinal villous Mcells: An antigen entry site in the mucosal epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6110–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglem, B.; Jirillo, E.; Bjerkås, I.; Kiyono, H.; Nochi, T.; Yuki, Y.; Raida, M.; Fischer, U.; Koppang, E.O. Antigen-sampling cells in the salmonid intestinal epithelium. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovy, J.; Friend, S.E.; Lewis, N.L. Seasonal intestinal coccidiosis in wild bluegill Lepomis macrochirus is associated with a spring bacterial epizootic. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasnik, D.J.; Smith, S.A.; Lindsay, D.S. Intestinal Coccidiosis in Bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, K.; Hanek, G. Seven new Eimeria spp. (Protozoa, Coccidia) from freshwater fishes of Canada. J. Protozool. 1974, 21, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, K.; Szekely, C.S.; Baska, F. Mass mortality of eel in Lake Balaton due to Anguillicola crassus infection. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1991, 11, 211–212. [Google Scholar]
- Silphaduang, U.; Colorni, A.; Noga, E.J. Evidence for widespread distribution of piscidin antimicrobial peptides in teleost fish. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2006, 72, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazon, A.F.; Huising, M.O.; Taverne-Thiele, A.J.; Bastiaans, J.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M.L. The first appearance of Rodlet cells in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) ontogeny and their possible roles during stress and parasite infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manera, M.; Dezfuli, B.S. Rodlet cells in teleosts: A new insight into their nature and functions. J. Fish. Biol. 2004, 65, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuchel, L.W.; Thompson, M.A.; Cassivi, S.D.; Pabelick, C.M.; Prakash, Y.S. Neurotrophins induce nitric oxide generation in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 91, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocchetti, C.G.; Wang, W.; Froehlich, J.P.; Huke, S.; Aon, M.A.; Wilson, G.M.; Di Benedetto, G.; O’Rourke, B.; Gao, W.D.; Wink, D.A.; et al. Nitroxyl improves cellular heart function by directly enhancing cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ cycling. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Antibody Anti- | Host | Dilution | Source | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD4 | Rabbit | 1:50 | Biorbyt Ltd., Cambridge, UK | orb4830 |
| Histamine | Rabbit | 1:100 | Novus Biologicals, Centennial, CO, USA | NBP2-45266 |
| IgM | Mouse | 1:50 | Biorbyt Ltd., Cambridge, UK | orb510864 |
| Interleukin-6 | Mouse | 1:25 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA | sc-28343 |
| Lysozyme | Mouse | 1:50 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA | sc-518012 |
| NOS 2 | Rabbit | 1:10 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA | sc-651 |
| Universal-NOS | Rabbit | 1:25 | NeoMarkers Inc., Fremont, CA, USA | RB-9261-P |
| Serotonin | Rabbit | 1:100 | Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA | S5545 |
| Serotonin | Rabbit | 1:100 | Novus Biologicals, Centennial, CO, USA | NB100-65218 |
| TLR-2 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Biorbyt Ltd., Cambridge, UK | orb573647 |
| TNF-α | Rabbit | 1:50 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK | ab6671 |
| Tryptase ξ | Mouse | 1:50 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA | sc-377427 |
| Anti-Biotinylated Secondary Antibodies | ||||
| Anti-rabbit IgG | Goat | 1:200 | Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA, USA | BA-1000 |
| Anti-mouse IgG | Goat | 1:200 | Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA, USA | BA-9200 |
| Blocking Molecules | Source | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Histamine | Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA | 59964 |
| Neuronal-Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS 1) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA | Sc-5302 |
| inducible-Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS 2) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA | sc-7271 P |
| Serotonin | Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA | 14927 |
| Toll-Like Receptor-2 (TLR-2) | Novus Biologicals, Centennial, CO, USA | NB100-56720PEP |
| Tryptase | Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA | T7063 |
| Acronym | Lectin | Species Source: Latin Name (Common Name) | Major Carbohydrate Specificity | Vector Laboratories Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UEA I | Ulex europaeus agglutinin I | Ulex europaeus (gorse seed) | Fucose | B-1065 |
| WGA | Wheat germ agglutinin | Triticum vulgare (wheat germ) | N-acetylglucosamine, sialic acid | B-1025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Castaldelli, G.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Ovcharenko, M.; Bosi, G. Rodlet Cells Provide First Line of Defense against Swimbladder Nematode and Intestinal Coccidian in Anguilla anguilla. Fishes 2023, 8, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020066
Sayyaf Dezfuli B, Castaldelli G, Lorenzoni M, Carosi A, Ovcharenko M, Bosi G. Rodlet Cells Provide First Line of Defense against Swimbladder Nematode and Intestinal Coccidian in Anguilla anguilla. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayyaf Dezfuli, Bahram, Giuseppe Castaldelli, Massimo Lorenzoni, Antonella Carosi, Mykola Ovcharenko, and Giampaolo Bosi. 2023. "Rodlet Cells Provide First Line of Defense against Swimbladder Nematode and Intestinal Coccidian in Anguilla anguilla" Fishes 8, no. 2: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020066
APA StyleSayyaf Dezfuli, B., Castaldelli, G., Lorenzoni, M., Carosi, A., Ovcharenko, M., & Bosi, G. (2023). Rodlet Cells Provide First Line of Defense against Swimbladder Nematode and Intestinal Coccidian in Anguilla anguilla. Fishes, 8(2), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020066










