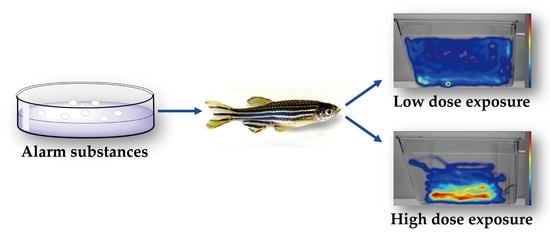
Non-Dose-Dependent Relationship between Antipredator Behavior and Conspecific Alarm Substance in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
2.2. Novel Tank Diving Test Procedure
2.3. Alarm Substance Extraction and Administration
2.4. Quantification of Behavioral Responses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chivers, D.P.; Smith, R.J.F. Chemical alarm signalling in aquatic predator-prey systems: A review and prospectus. Ecoscience 1998, 5, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.C.O.; Wisenden, B.D.; Chivers, D.P. Chemical ecology of predator-prey interactions in aquatic ecosystems: A review and prospectus. Can. J. Zool. 2010, 88, 698–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, A.L.; Bairos-Novak, K.R.; Goldman, J.A.; Brown, G.E. Chemical disturbance cues in aquatic systems: A review and prospectus. Ecol. Monogr. 2022, 92, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathuru, A.S.; Kibat, C.; Cheong, W.F.; Shui, G.; Wenk, M.R.; Friedrich, R.W.; Jesuthasan, S. Chondroitin fragments are odorants that trigger fear behavior in fish. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulin, R.X.; Lavoie, S.; Siegel, K.; Gaul, D.A.; Weissburg, M.J.; Kubanek, J. Chemical encoding of risk perception and predator detection among estuarine invertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.F. Alarm signals in fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fisher. 1992, 2, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.E. Learning about danger: Chemical alarm cues and local risk assessment in prey fishes. Fish Fish. 2003, 4, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Bencan, Z.; Cerutti, D.T. Anxiolytic effects of nicotine in zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 90, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shuraiqi, A.; Al-Habsi, A.; Barry, M.J. Time-, dose- and transgenerational effects of fluoxetine on the behavioural responses of zebrafish to a conspecific alarm substance. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, B. Quantitative and developmental analyses of the alarm reaction in the zebra danio, brachydanio-rerio. Copeia 1982, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speedie, N.; Gerlai, R. Alarm substance induced behavioral responses in zebrafish (danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 188, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadros, V.A.; Silveira, A.; Giuliani, G.S.; Didonet, F.; Silveira, A.S.; Nunes, M.E.; Silva, T.O.; Loro, V.L.; Rosemberg, D.B. Strain- and context-dependent behavioural responses of acute alarm substance exposure in zebrafish. Behav. Process. 2016, 122, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximino, C.; Meinerz, D.L.; Fontana, B.D.; Mezzomo, N.J.; Stefanello, F.V.; Prestes, A.D.S.; Batist, C.B.; Rubin, M.A.; Barbosa, N.V.; Rocha, J.B.T.; et al. Extending the analysis of zebrafish behavioral endophenotypes for modeling psychiatric disorders: Fear conditioning to conspecific alarm response. Behav. Process. 2018, 149, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenki, K.C.; De Souza, L.S.; Gois, A.M.; Lima, B.D.S.; De Souza Araujo, A.A.; Vieira, J.S.; Camargo, E.A.; Kalinine, E.; De Oliveira, D.L.; Bandero Walker, C.I. Coriandrum sativum extract prevents alarm substance-induced fear- and anxiety-like responses in adult zebrafish. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, S.N.; Hausen, J.; Smith, K.; Ottermanns, R.; Schaeffer, A.; Schiwy, S.; Hollert, H. Do you smell the danger? Effects of three commonly used pesticides on the olfactory-mediated antipredator response of zebrafish (danio rerio). Chemosphere 2020, 241, 124963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.A.; Konemann, S.; Krumpelmann, L.; Zupanic, A.; Vom Berg, C. Approaches to test the neurotoxicity of environmental contaminants in the zebrafish model: From behavior to molecular mechanisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, B.D.; Alnassar, N.; Parker, M.O. The impact of water changes on stress and subject variation in a zebrafish (danio rerio) anxiety-related task. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2021, 363, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigis, A.C.; Ottermanns, R.; Schiwy, A.; Hollert, H.; Legradi, J. Getting more out of the zebrafish light dark transition test. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachat, J.; Stewart, A.; Grossman, L.; Gaikwad, S.; Kadri, F.; Chung, K.M.; Wu, N.; Wong, K.; Roy, S.; Suciu, C.; et al. Measuring behavioral and endocrine responses to novelty stress in adult zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayman, C.L.; Connaughton, V.P. Neurochemical and behavioral consequences of ethanol and/or caffeine exposure: Effects in zebrafish and rodents. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Hart, P.C.; Elegante, M.F.; Beeson, E.C.; Laffoon, A.L.; Haymore, W.A.M.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Video-aided analysis of zebrafish locomotion and anxiety-related behavioral responses. In Zebrafish Neurobehavioral Protocols; Kalueff, A.V., Cachat, J.M., Eds.; Humana Press: New Jersey, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 51, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Blaser, R.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral phenotyping in zebrafish: Comparison of three behavioral quantification methods. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R.; Lahav, M.; Guo, S.; Rosenthal, A. Drinks like a fish: Zebra fish (danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Wong, K.; Cachat, J.; Gaikwad, S.; Kyzar, E.; Wu, N.; Hart, P.; Piet, V.; Utterback, E.; Elegante, M.; et al. Zebrafish models to study drug abuse-related phenotypes. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 22, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackerman, J.; Donegan, J.J.; Cunningham, C.S.; Nguyen, N.N.; Lawless, K.; Long, A.; Benno, R.H.; Gould, G.G. Zebrafish behavior in novel environments: Effects of acute exposure to anxiolytic compounds and choice of danio rerio line. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2010, 23, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.; Elegante, M.; Bartels, B.; Elkhayat, S.; Tien, D.; Roy, S.; Goodspeed, J.; Suciu, C.; Tan, J.L.; Grimes, C.; et al. Analyzing habituation responses to novelty in zebrafish (danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audira, G.; Lai, Y.H.; Huang, J.C.; Chen, K.H.C.; Hsiao, C.D. Phenomics approach to investigate behavioral toxicity of environmental or occupational toxicants in adult zebrafish (danio rerio). Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Gebhardt, M.; Stewart, A.M.; Cachat, J.M.; Brimmer, M.; Chawla, J.S.; Craddock, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Roth, A.; Landsman, S.; et al. Towards a comprehensive catalog of zebrafish behavior 1.0 and beyond. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saverino, C.; Gerlai, R. The social zebrafish: Behavioral responses to conspecific, heterospecific, and computer animated fish. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 191, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencan, Z.; Sledge, D.; Levin, E.D. Buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam effects in a zebrafish model of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; Duperreault, E.; Newton, D.; Krook, J.; Ingraham, E.; Gallup, J.; Franczak, B.C.; Hamilton, T.J. Opposing effects of acute and repeated nicotine exposure on boldness in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijevic, O.; Jaka, O.; Alzualde, A.; Maradze, D.; Xia, W.H.; Frentzel, S.; Gifford, A.N.; Peitsch, M.C.; Hoeng, J.; Koshibu, K. Differentiating the neuropharmacological properties of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-activating alkaloids. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 668065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Verdugo, C.; Sun, G.J.; Fawcett, C.H.; Zhu, P.; Fishman, M.C. Mating suppresses alarm response in zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.E.; Adrian, J.C.; Smyth, E.; Leet, H.; Brennan, S. Ostariophysan alarm pheromones: Laboratory and field tests of the functional significance of nitrogen oxides. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durajczyk, M.M.; Stabell, O.B. Coping with continual danger: Assessing alertness to visual disturbances in crucian carp following long-term exposure to chemical alarm signals. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 126, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.E. Mianserin affects alarm reaction to conspecific chemical alarm cues in nile tilapia. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, D.L.; Hoefnagels, C.C.M.; De Kloet, R.E.; Richardson, M.K. Translating rodent behavioral repertoire to zebrafish (danio rerio): Relevance for stress research. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, B.J.; Smith, R.J.F. Behavioral-response of solitary fathead minnows, pimephales-promelas, to alarm substance. J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisenden, B.D. Active space of chemical alarm cue in natural fish populations. Behaviour 2008, 145, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Lin, A.; Li, X.; Li, K. Non-Dose-Dependent Relationship between Antipredator Behavior and Conspecific Alarm Substance in Zebrafish. Fishes 2023, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020076
Li Y, Yan Z, Lin A, Li X, Li K. Non-Dose-Dependent Relationship between Antipredator Behavior and Conspecific Alarm Substance in Zebrafish. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020076
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yaxi, Zhi Yan, Ainuo Lin, Xiaodong Li, and Ke Li. 2023. "Non-Dose-Dependent Relationship between Antipredator Behavior and Conspecific Alarm Substance in Zebrafish" Fishes 8, no. 2: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020076
APA StyleLi, Y., Yan, Z., Lin, A., Li, X., & Li, K. (2023). Non-Dose-Dependent Relationship between Antipredator Behavior and Conspecific Alarm Substance in Zebrafish. Fishes, 8(2), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020076