The Role of Spatial Exploration and Territoriality in Establishing Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Hierarchies, and Their Effects upon Underlying Stress Physiology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
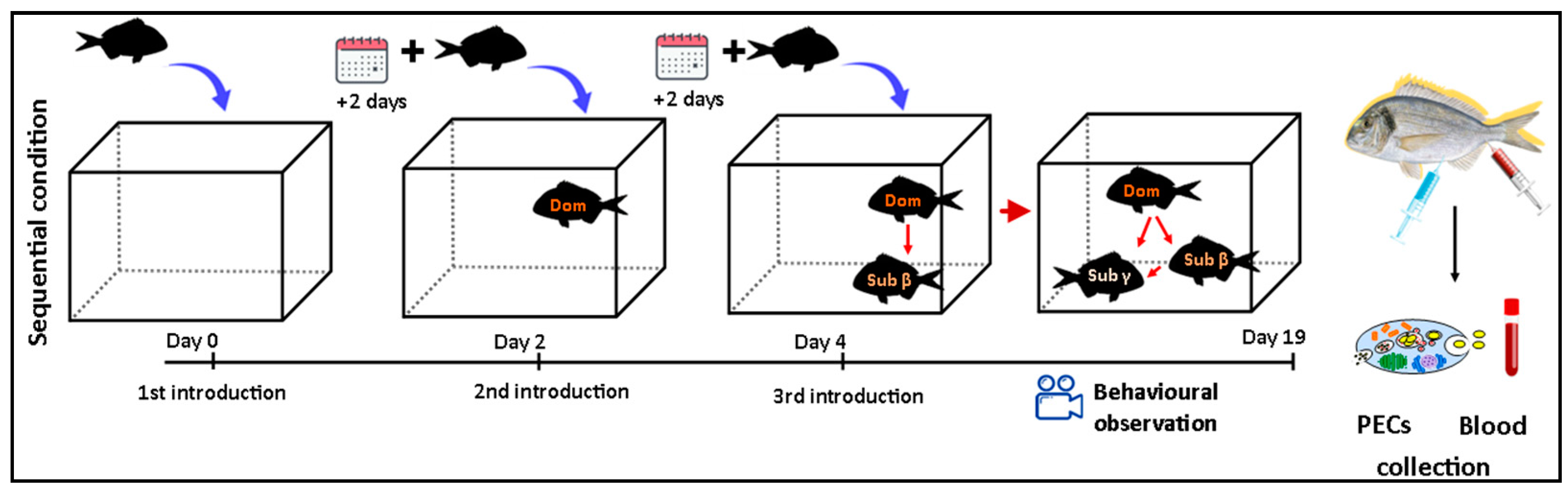
2.2. Sequential Model
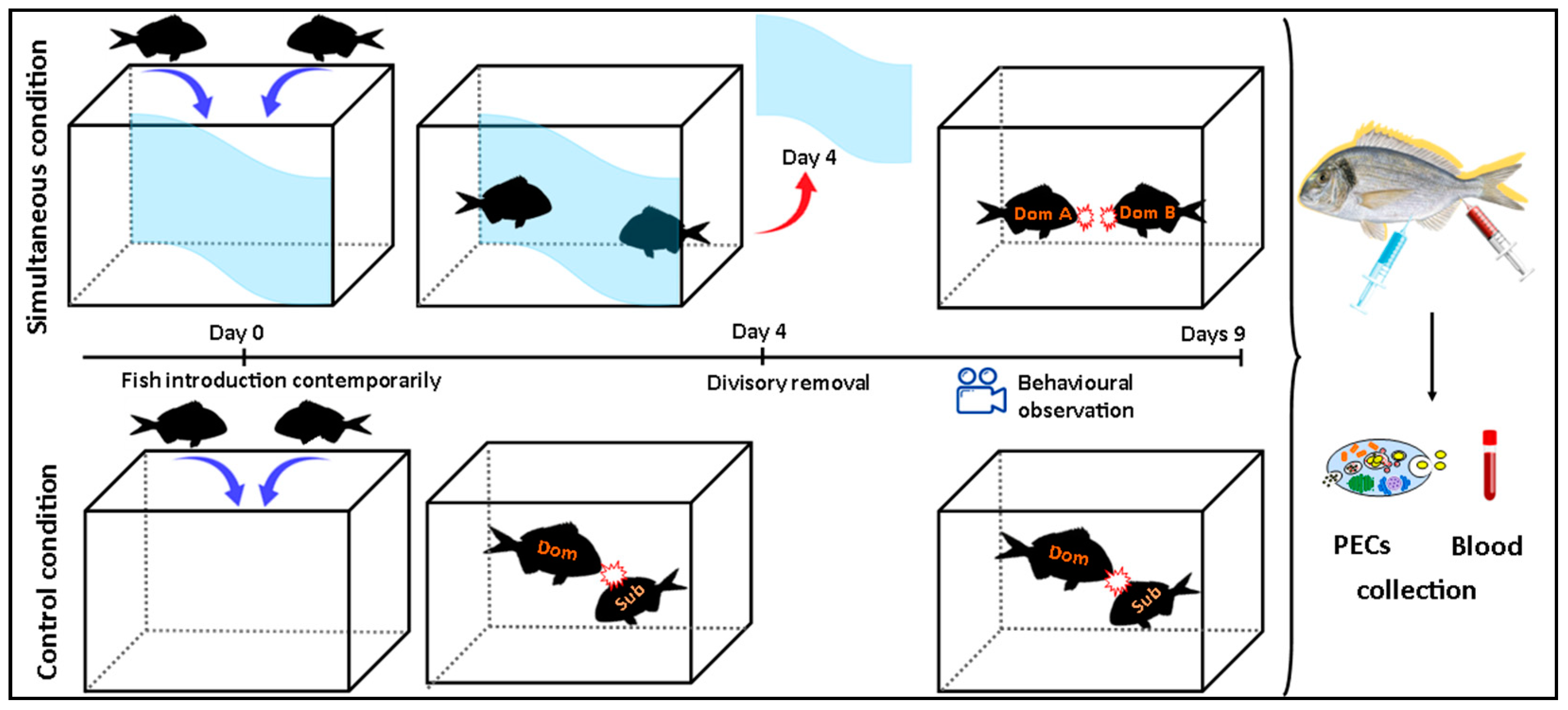
2.3. Simultaneous Model
2.4. Behavioral Observations
2.5. Blood Sampling
2.6. Cell Suspensions and PEC
2.7. Hematological Parameter Quantification
2.8. Phagocytosis Assay
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
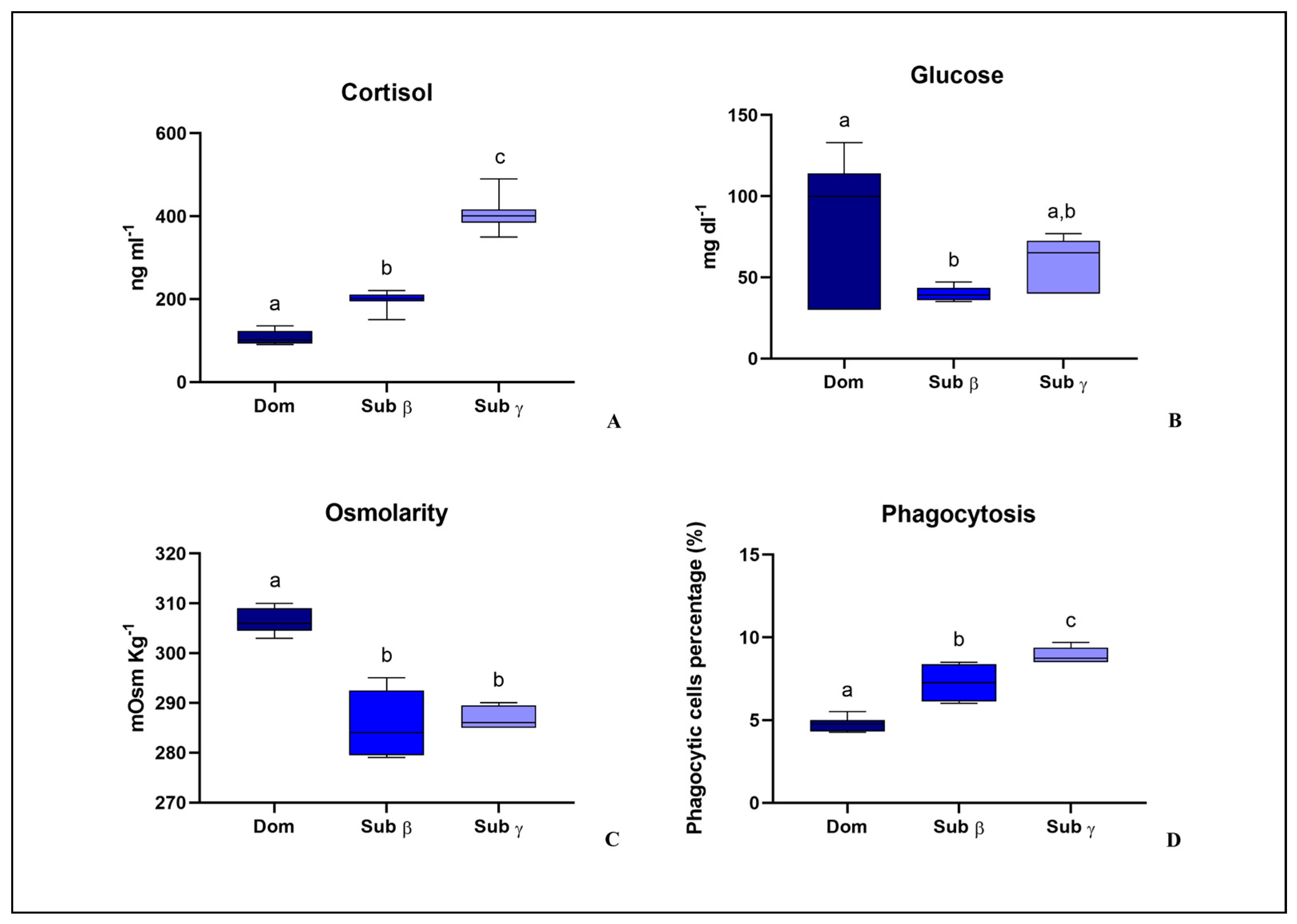
3.1. Sequential Model: Behavioral Observation, Establishment of a Social Hierarchy, Blood Stress Parameter and Phagocytosis Activity Evaluation
3.2. Simultaneous Model: Behavioral Observation, Establishment of a Social Hierarchy, Blood Stress Parameter and Phagocytosis Activity Evaluation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashley, P.J. Fish welfare: Current issues in aquaculture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Føre, M.; Frank, K.; Norton, T.; Svendsen, E.; Alfredsen, J.A.; Dempster, T.; Eguiraun, H.; Watson, W.; Stahl, A.; Sunde, L.M.; et al. Precision fish farming: A new framework to improve production in aquaculture. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 173, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, F.S. Stress and the welfare of cultured fish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2004, 86, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, V.A.; Huntingford, F.A. Fish and welfare: Do fish have the capacity for pain perception and suffering? Anim. Welf. 2004, 13, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, L.U.; Wolfenden, D.C.C.; Thomson, J.S. Stress Management and Welfare; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 35, ISBN 9780128027288. [Google Scholar]
- Huntingford, F.A.; Adams, C.; Braithwaite, V.A.; Kadri, S.; Pottinger, T.G.; Sandøe, P.; Turnbull, J.F. Current issues in fish welfare. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 68, 332–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, M.; Vazzana, M.; Accardi, D.; Parrinello, N. Seabream (Sparus aurata) long-term dominant-subordinate interplay affects phagocytosis by peritoneal cavity cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, M.; Dioguardi, M.; Vazzana, M.; Vazzana, I.; Accardi, D.; Carbonara, P.; Alfonso, S.; Cammarata, M. Effects of social hierarchy establishment on stress response and cell phagocytosis in gilt-head sea bream (Sparus aurata). Fishes 2022, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez-Cepa, I.; Ruiz-Jarabo, I. Physiology: An important tool to assess the welfare of aquatic animals. Biology 2021, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazzana, M.; Cammarata, M.; Cooper, E.; Parrinello, N. Confinement stress in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) depresses peritoneal leukocyte cytotoxicity. Aquaculture 2002, 210, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, A.; Vazzana, M.; Cammarata, M.; Parrinello, N. Peritoneal cavity phagocytes from the teleost sea bass express a glucocorticoid receptor (cloned and sequenced) involved in genomic modulation of the in vitro chemiluminescence response to zymosan. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 150, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommsen, T.P.; Vijayan, M.M.; Moon, T.W. Cortisol in teleosts: Dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1999, 9, 211–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, C.B.; Tort, L. The Concept of Stress in Fish, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 35, ISBN 9780128027288. [Google Scholar]
- Tracey, S.R.; Hartmann, K.; Leef, M.; McAllister, J. Capture-induced physiological stress and postrelease mortality for southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) from a recreational fishery. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, S.; Gesto, M.; Sadoul, B. Temperature increase and its effects on fish stress physiology in the context of global warming. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVries, A.C.; Craft, T.K.S.; Glasper, E.R.; Neigh, G.N.; Alexander, J.K. 2006 Curt P. Richter award winner. Social influences on stress responses and health. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paull, G.C.; Filby, A.L.; Giddins, H.G.; Coe, T.S.; Hamilton, P.B.; Tyler, C.R. Dominance hierarchies in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and their relationship with reproductive success. Zebrafish 2010, 7, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.F.; Hirschenhauser, K.; Carneiro, L.A.; Canario, A.V.M. Social modulation of androgen levels in male teleost fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 132, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.I.M.; Galhardo, L.; Noble, C.; Damsgård, B.; Spedicato, M.T.; Zupa, W.; Beauchaud, M.; Kulczykowska, E.; Massabuau, J.C.; Carter, T.; et al. Behavioural indicators of welfare in farmed fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloman, K. Physiological effects of dominance hierarchies: Laboratory artefacts or natural phenomena? J. Fish Biol. 2002, 61, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoul, B.; Vijayan, M.M. Stress and Growth; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 35, ISBN 9780128027288. [Google Scholar]
- Höglund, E.; Kolm, N.; Winberg, S. Stress-induced changes in brain serotonergic activity, plasma cortisol and aggressive behavior in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) is counteracted by L-dopa. Physiol. Behav. 2001, 74, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfman, G.; Collette, B.B.; Facey, D.E.; Bowen, B.W. The Diversity of Fishes: Biology, Evolution, and Ecology, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 736. ISBN 978-1-405-12494-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hellinger, J.; Jägers, P.; Spoida, K.; Weiss, L.C.; Mark, M.D.; Herlitze, S. Analysis of the Territorial Aggressive Behavior of the bioluminescent flashlight fish photoblepharon steinitzi in the Red Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winberg, S.; Sneddon, L. Impact of intraspecific variation in teleost fishes: Aggression, dominance status and stress physiology. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb169250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldan, O.; Popper, D.; Karplus, I. Food competition in small groups of juvenile gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Isr. J. Aquac.-Bamidgeh 2003, 55, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Nazzaro-Alvarez, J.; Jardí-Pons, A.; Reig, L.; Carella, F.; Carrassón, M.; Roque, A. Linking stocking densities and feeding strategies with social and individual stress responses on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Physiol. Behav. 2020, 213, 112723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, M.F.; Herrera, M.; Costas, B.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Martins, C.I.M. Linking cortisol responsiveness and aggressive behaviour in gilthead seabream Sparus aurata: Indication of divergent coping styles. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 143, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimodt, C.; Dore, I. Multilingual Illustrated Guide to the World’s Commercial Coldwater Fish; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-852-38213-4. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020; ISBN 9789251072257. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, G.; Moore, A.R.; Fildes, J. Toxicity of Aeromonas salmonicida cells to atlantic salmon Salmo salar peritoneal macrophages. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1992, 16, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, I.D.; Gair, D.J.; Houlihan, D.F. Feeding rank and dominance in Tilapia rendalli under defensible and indefensible patterns of food distribution. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 55, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverli, Ø.; Kotzian, S.; Winberg, S. Effects of cortisol on aggression and locomotor activity in rainbow trout. Horm. Behav. 2002, 42, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerends, G.P.; Baerends-van Roon, J.M. An introduction to the study of the ethology of the cichlid fishes. Behaviour 1950, III–VII (Suppl. 1), 1–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.F.; Almada, V.C.; Canario, A.V.M. Social modulation of sex steroid concentrations in the urine of male cichlid fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Horm. Behav. 1996, 30, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hed, J. Methods for distinguishing ingested from adhering particles. Methods Enzymol. 1986, 132, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Fatsini, E.; Rey, S.; Ibarra-Zatarain, Z.; Mackenzie, S.; Duncan, N.J. Dominance behaviour in a non-aggressive flatfish, Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) and brain mRNA abundance of selected transcripts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overli, O.; Harris, C.A.; Winberg, S. Short-term effects of fights for social dominance and the establishment of dominant-subordinate relationships on brain monoamines and cortisol in rainbow trout. Brain Behav. Evol. 1999, 54, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverli, Ø.; Korzan, W.J.; Ho, E.; Winberg, S.; Bollig, H.; Watt, M.; Forster, G.L.; Barton, B.A.; Øverli, E.; Renner, K.J.; et al. Stress coping style predicts aggression and social dominance in rainbow trout. Horm. Behav. 2004, 45, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverli, Ø. Preface: Plasticity and diversity in behavior and brain function--important raw material for natural selection? Brain Behav. Evol. 2007, 70, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzan, W.J.; Øverli, Ø.; Summers, C.H. Future social rank: Forecasting status in the green anole (Anolis carolinensis). Acta Ethologica 2006, 9, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, P.C.; Volpato, G.L. Chemical communication, aggression, and conspecific recognition in the fish Nile tilapia. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 62, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Gomez, M.L.; Huntingford, F.A. Boldness and aggressiveness in early and late hatched three-spined sticklebacks Gasterosteus aculeatus. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.Å.; Höglund, E. Linking personality to larval energy reserves in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beacham, J.L. The relative importance of body size and aggressive experience as determinants of dominance in pumpkinseed sunfish, Lepomis gibbosus. Anim. Behav. 1988, 36, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.; Delventhal, H.; Klinger, H. Physiological and morphological effects of social stress on the eel, Anguilla anguilla L. In Fish Diseases; Proceedings in Life Sciences; Ahne, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980; pp. 225–227. [Google Scholar]
- Halperin, J.R.P.; Dunham, D.W. Social overstimulation reduces subsequent aggression in Betta splendens. Aggress. Behav. 1994, 20, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, N.; Sorensen, P. Function and Evolution of Fish Hormonal Pheromones; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Raab, T.; Linhart, L.; Wurm, A.; Benda, J. Dominance in habitat preference and diurnal explorative behavior of the weakly electric fish Apteronotus leptorhynchus. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, J.H. On the definitions and functions of dominance and territoriality. Biol. Rev. 1983, 58, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, I.R.; Hardin, E.E.; Baldwin, C.M.; Schwartz, G.E. Increased limbic system symptomatology and sensitizability of young adults with chemical and noise sensitivities. Environ. Res. 1995, 70, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.N.; Blight, C.M. Algorithmic behaviour and spatial memory are used by two intertidal fish species to solve the radial maze. Anim. Behav. 1999, 58, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottinger, T.G.; Carrick, T.R. Stress responsiveness affects dominant-subordinate relationships in rainbow trout. Horm. Behav. 2001, 40, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonara, P.; Dioguardi, M.; Cammarata, M.; Zupa, W.; Vazzana, M.; Spedicato, M.T.; Lembo, G. Basic knowledge of social hierarchies and physiological profile of reared sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.C.; Sakai, R.R.; McEwen, B.; Weiss, S.M.; Blanchard, R.J. Subordination stress: Behavioral, brain, and neuroendocrine correlates. Behav. Brain Res. 1993, 58, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonara, P.; Alfonso, S.; Zupa, W.; Manfrin, A.; Fiocchi, E.; Pretto, T.; Spedicato, M.T.; Lembo, G. Behavioral and physiological responses to stocking density in sea bream (Sparus aurata): Do coping styles matter? Physiol. Behav. 2019, 212, 112698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.C.; Canário, A.V.M.; Hubbard, P.C.; Gonçalves, D.M.F. Physiology, endocrinology and chemical communication in aggressive behaviour of fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, D.; Lalumera, G.; Izquierdo, M.S.; Caballero, M.J.; Saroglia, M.; Tort, L. Establishment of dominance relationships in gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata juveniles during feeding: Effects on feeding behaviour, feed utilization and fish health. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 790–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.; Lazard, J. Subordination stress in Nile tilapia and its effect on plasma lysozyme activity. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 55, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, C.B.; Contreras-Sanchez, W.; Fitzpatrick, M.S. Effects of stress on fish reproduction, gamete quality, and progeny. Aquaculture 2001, 197, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesto, M.; Zupa, W.; Alfonso, S.; Spedicato, M.T.; Lembo, G.; Carbonara, P. Using acoustic telemetry to assess behavioral responses to acute hypoxia and ammonia exposure in farmed rainbow trout of different competitive ability. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2020, 230, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, M.F.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Millot, S.; Rey, S.; Bégout, M.L.; Damsgård, B.; Kristiansen, T.; Höglund, E.; Øverli, Ø.; Martins, C.I.M. Coping styles in farmed fish: Consequences for aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, S.; Zupa, W.; Manfrin, A.; Fiocchi, E.; Spedicato, M.T.; Lembo, G.; Carbonara, P. Stress coping styles: Is the basal level of stress physiological indicators linked to behaviour of sea bream? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2020, 231, 105085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pérez, J.; Naderi, F.; Chivite, M.; Soengas, J.L.; Míguez, J.M.; López-Patiño, M.A. Influence of stress on liver circadian physiology. A study in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, as fish model. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Simó-Mirabet, P.; de las Heras, V.; Calduch-Giner, J.À.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Tissue-specific orchestration of gilthead sea bream resilience to hypoxia and high stocking density. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberry, R.C. Environmental enrichment: Increasing the biological relevance of captive environments. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1995, 44, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Diaz-Gil, C.; Saraiva, J.L.; Moranta, D.; Castanheira, M.F.; Nuñez-Velázquez, S.; Ledesma-Corvi, S.; Mora-Ruiz, M.R.; Grau, A. Effects of structural environmental enrichment on welfare of juvenile seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquac. Rep. 2019, 15, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzina, A.; Karakatsouli, N. The presence of substrate as a means of environmental enrichment in intensively reared gilthead seabream Sparus aurata: Growth and behavioral effects. Aquaculture 2012, 370–371, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Caballero-Froilán, J.C.; Jiménez-García, M.; Capó, X.; Tejada, S.; Saraiva, J.L.; Sureda, A.; Moranta, D. Enriched environments enhance cognition, exploratory behaviour and brain physiological functions of Sparus aurata. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sequential Model | Aggressive Acts (A+) Mean % ± SD | Preferential Food Accession (FO) Mean % ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Dom > Sub (β) | 95 ± 5% | 100 ± 0% |
| Sub (β) > Dom | 5 ± 5% | 0% |
| Dom > Sub (γ) | 85 ± 5% | 100 ± 0% |
| Sub (γ) > Dom | 15 ± 5% | 0% |
| Sub (β) > Sub (γ) | 90 ± 5% | 95 ± 3% |
| Sub (γ) > Sub (β) | 10 ± 5% | 5 ± 3% |
| Simultaneous Model | Aggressive Acts (A+) Mean% ± SD | Preferential Food Accession (FO) Mean% ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Dom A > Dom B | 49 ± 5% | 51 ± 3% |
| Dom B > Dom A | 53 ± 5% | 48 ± 3% |
| Dom control > Sub control | 94 ± 3% | 96 ± 4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dara, M.; Dioguardi, M.; Vazzana, M.; Vazzana, I.; Carbonara, P.; Alfonso, S.; Cammarata, M. The Role of Spatial Exploration and Territoriality in Establishing Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Hierarchies, and Their Effects upon Underlying Stress Physiology. Fishes 2023, 8, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030132
Dara M, Dioguardi M, Vazzana M, Vazzana I, Carbonara P, Alfonso S, Cammarata M. The Role of Spatial Exploration and Territoriality in Establishing Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Hierarchies, and Their Effects upon Underlying Stress Physiology. Fishes. 2023; 8(3):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030132
Chicago/Turabian StyleDara, Mariano, Maria Dioguardi, Mirella Vazzana, Irene Vazzana, Pierluigi Carbonara, Sébastien Alfonso, and Matteo Cammarata. 2023. "The Role of Spatial Exploration and Territoriality in Establishing Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Hierarchies, and Their Effects upon Underlying Stress Physiology" Fishes 8, no. 3: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030132
APA StyleDara, M., Dioguardi, M., Vazzana, M., Vazzana, I., Carbonara, P., Alfonso, S., & Cammarata, M. (2023). The Role of Spatial Exploration and Territoriality in Establishing Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Hierarchies, and Their Effects upon Underlying Stress Physiology. Fishes, 8(3), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030132







