Recent Advances in Tilapia Production for Sustainable Developments in Indian Aquaculture and Its Economic Benefits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Tilapia Aquaculture in India
2.1. India’s Contributions to Tilapia Production
2.2. Guidelines for Tilapia Culture in India
3. Farming Strategies of Tilapia Culture: The State of The Art
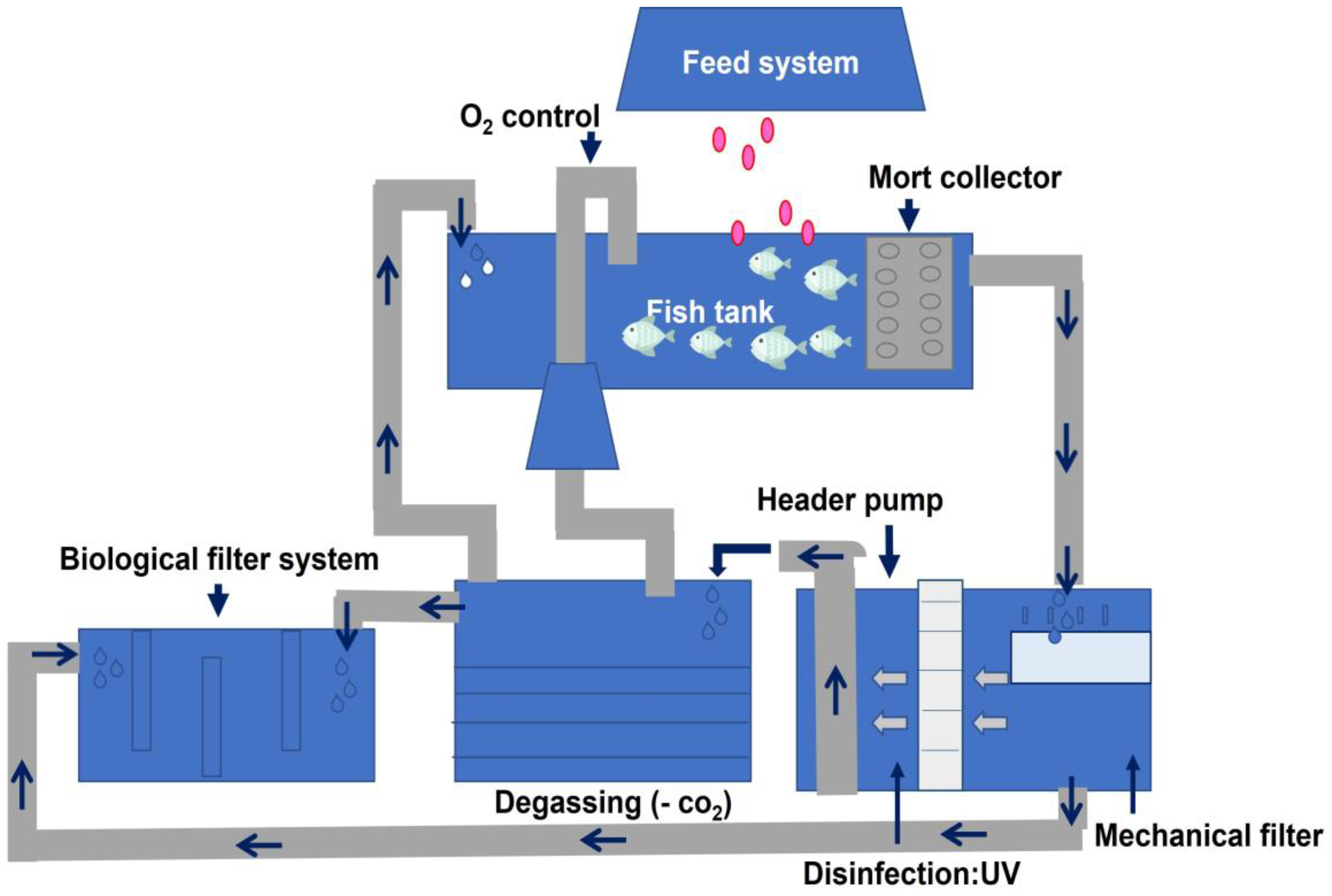
3.1. Recirculatory Aquaculture System (RAS)
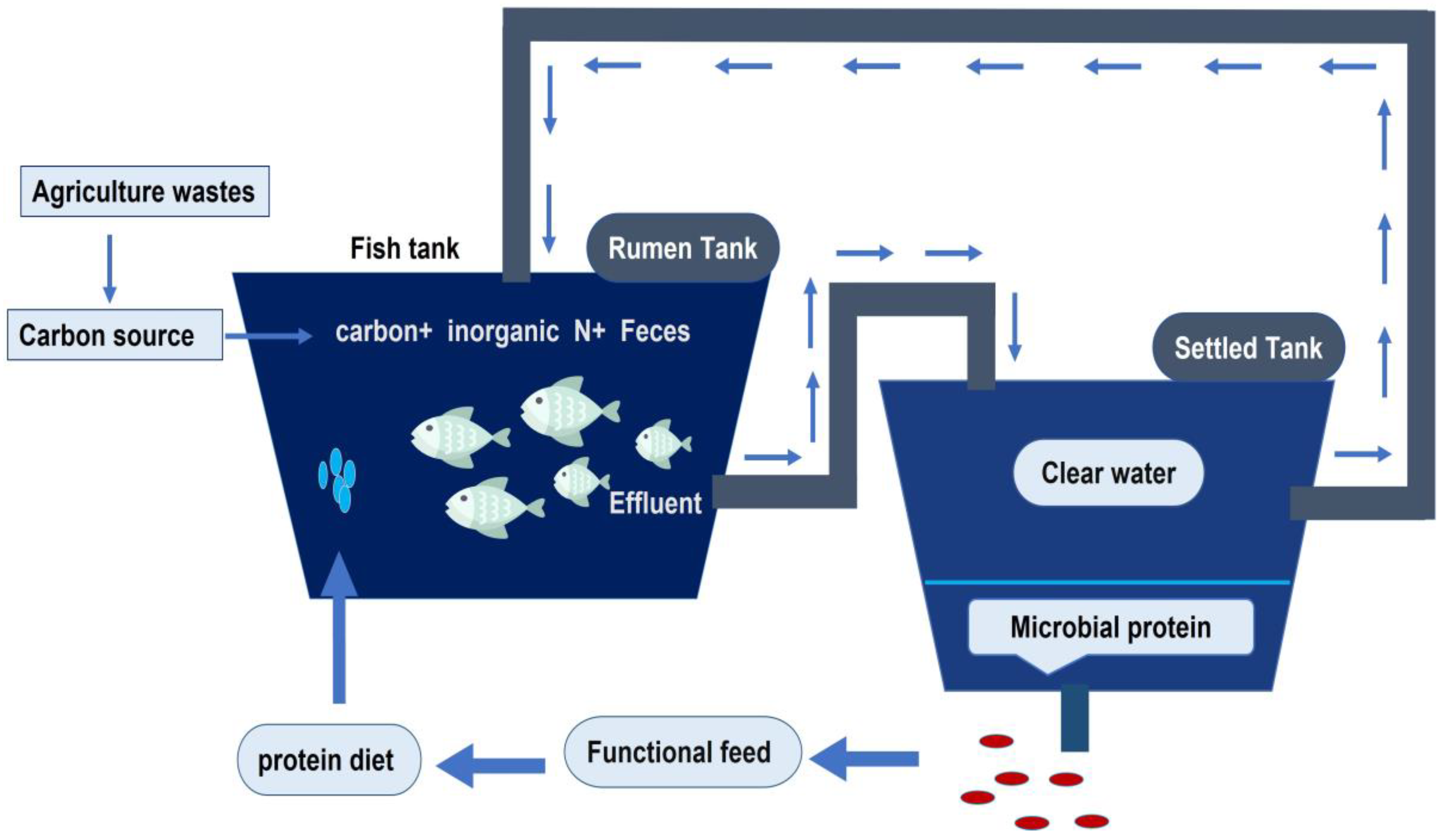
3.2. Biofloc Technology (BFT)
3.3. Cage Farming
3.4. Polyculture Tilapia Farming
3.5. The Integrated Farming of Tilapia
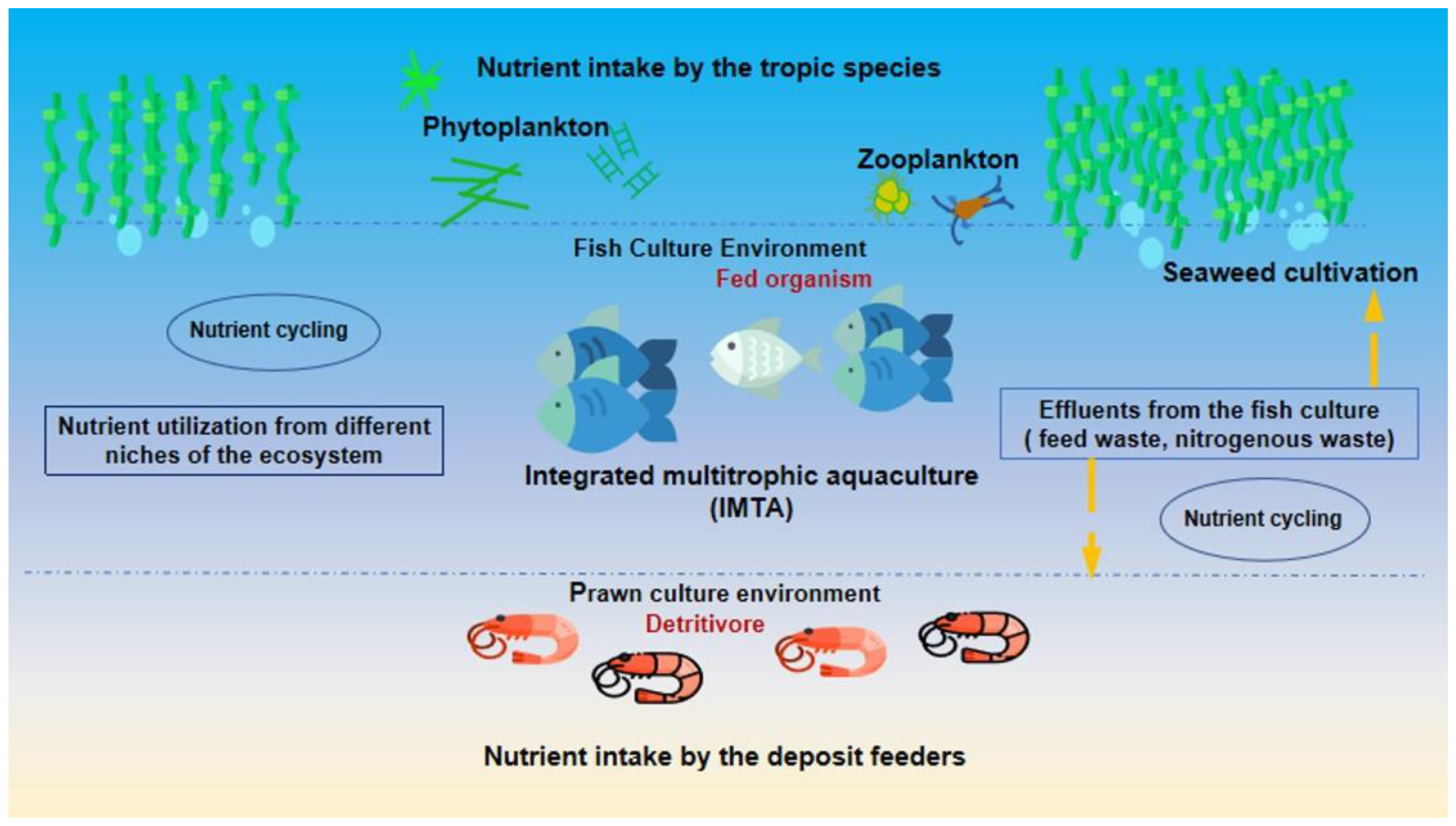
3.6. Integrated Multi Tropic Aquaculture (IMTA)
4. Strategies for Species Selection in Tilapia Farming
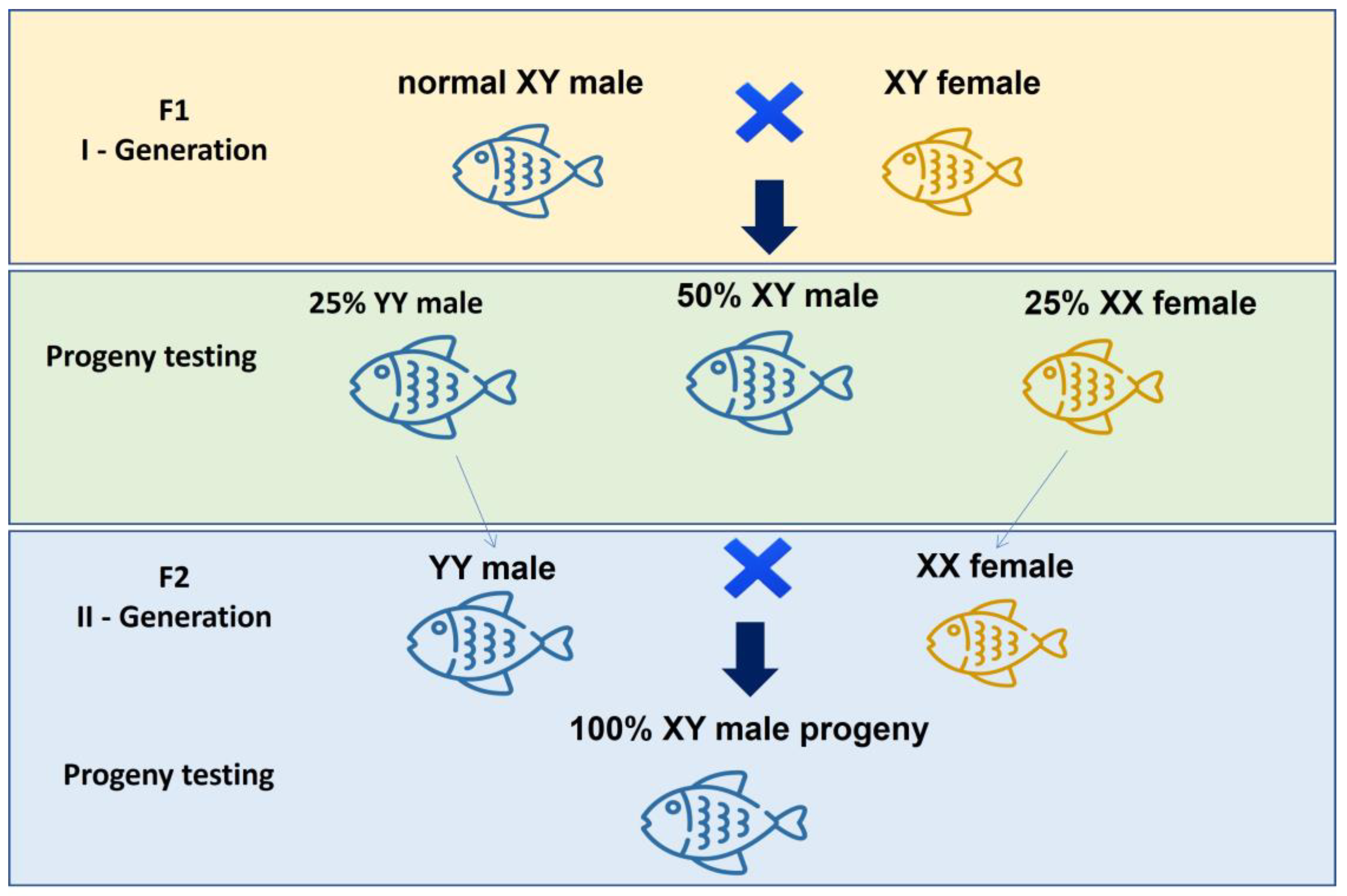
4.1. Farming of Monosex Tilapia
4.2. Farming of GIFT Tilapia
4.3. Farming of Hybrid Tilapia
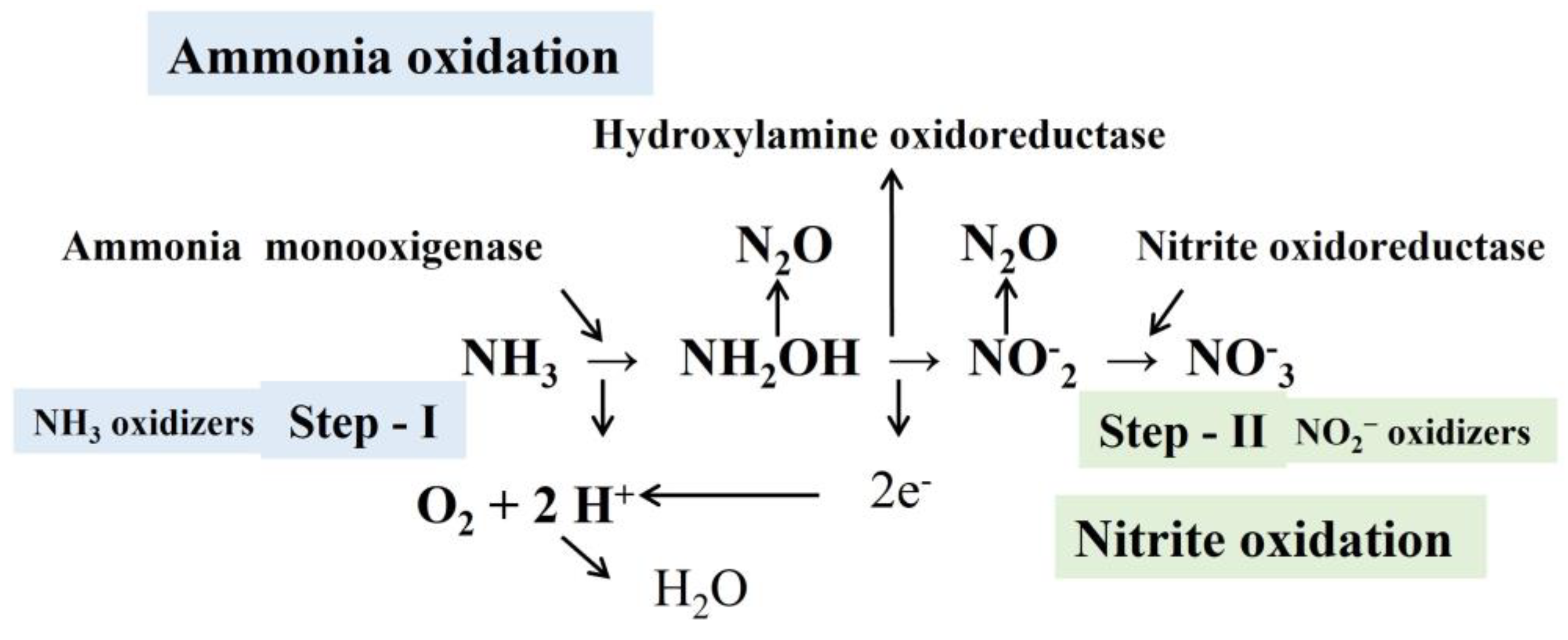
5. Management of Feed and Nutrients
| S. No | Feed Supplement | Performance | Fish Species | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tridax procumbens | Improves growth, production of antioxidants, immunity, and resistance to monogenean parasitic infection | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [123] |
| 2. | Caraway seed | Improves growth performance | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [124] |
| 3. | Silybum marianum | Promotes growth and enhances serum biochemical indices, antioxidant status, and gene expression | Oreochromis niloticus Nile tilapia | [125] |
| 4. | Trigonella foenum-graecum | Improves oxidative status and immune gene expression and histopathology | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [126] |
| 5. | Salvadora persica | Improves hematoimmunological parameters and enhances antioxidant responses against A. hydrophila infection | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [127] |
| 6. | Yucca schidigera | Improves growth performance, hepato-renal function, and antioxidative status and effects histopathological alterations against hypoxia | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [128] |
| 7. | Menthol essential oil | Improves growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, immune-related genes, resistance against acute ammonia exposure | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [129] |
| 8. | Dietary coenzyme Q10 and Vitamin C | Enhances growth, digestive enzyme activity, immune-related genes, and resistance against acute ammonia exposure | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [130] |
| 9. | Soybean meal diet combined with bokashi leachate | Improves feed intake and growth performance | (Oreochromis mossambicus × Oreochromis niloticus) Red tilapia | [131] |
| 10. | Enzymatic feather meal | Enhances growth, nutrient retention, and digestibility | (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus) | [132] |
| 11. | Organic acid salt blend and protease complex combination | Improves growth and nutrient digestibility | Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus | [133] |
| 12. | Methylated soy protein isolates | Acts as good immune-modulating substance and improved gut health | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [134] |
| 13. | Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC) | Improves gut health, total weight gain, survival rate, and immune status of fish against Aeromonas hydrophila | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [135] |
| 14. | Bacillus subtills and Lactobacillus plantarun | Increases amylase (enzymatic) activity, modulates intestinal microbiota profile | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [136] |
| 15. | Bacillus pumilus and exogenous protease | Enhances growth, immunity, serum parameters, gene expression and gut bacteria | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [137] |
| 16. | Enterococcus faecium | Improves growth, hematological and biochemical parameters, and non-specific immune response | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [138] |
| 17. | Aspergillus oryzae | Improves oxidative status and immune response against hypoxia | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [139] |
| 18. | Clostridium butyricum | Improves growth, feed utilization, and gut health | Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus | [140] |
| 19. | Chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles | Improves health and phagocytic activity | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [141] |
| 20. | Zinc oxide nanoparticles | Improves health | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [142] |
| 21. | Dietary sodium butyrate nanoparticles | Enhances growth | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [143] |
| 22. | Synergized selenium and zinc oxide nanoparticles | Improves growth, hemato-biochemical profile, and immune status and reduces oxidative stress | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [144] |
| 23. | Cinnamon nanoparticles | Enhances antioxidant and digestive enzyme activity, growth, and health | (Oreochromis niloticus) Nile tilapia | [145] |
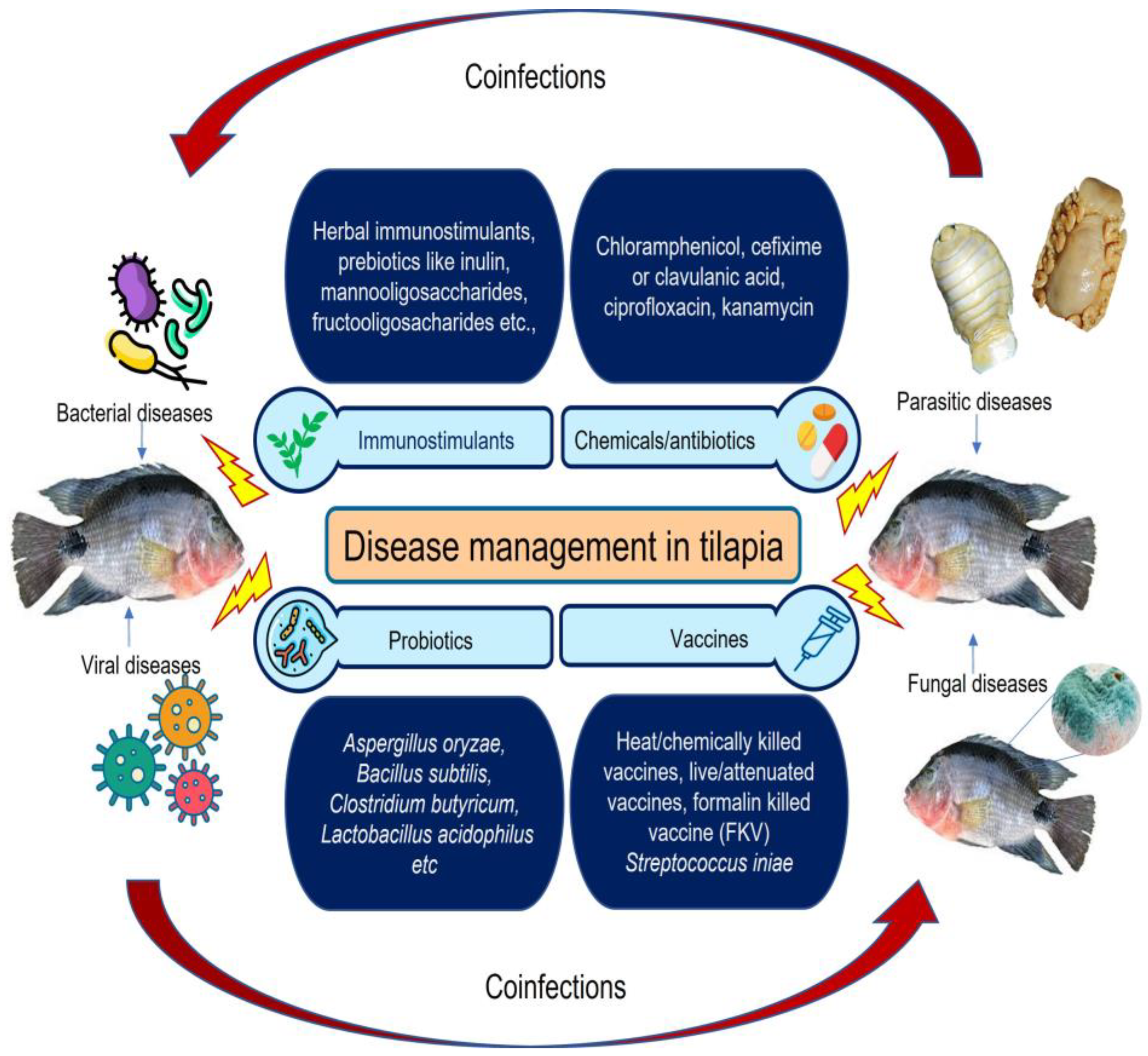
6. Strategies for Diseases Management of Tilapia
6.1. Vaccines
| S. No. | Pathogens | Type | Mode of Administration | Efficacy | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Streptococcus iniae improves the simulation of GALT (Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue) and specific antibodies | Attenuated | Intraperitoneal | 79–100% | Leads to higher antibody production conferred by cell-mediated immunity | [166] |
| Bath | 86% | Leads to higher antibody production | ||||
| Formalin-Inactivated | Intraperitoneal | 79–100% | Provides good immunogenicity | |||
| DNA Vaccine Modified PCI-neo plasmid or PBS (Streptococcal α-enolase gene in pCI-neo plasmid) | Intramuscular | 72.5% | Leads to increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines and S. iniae-specific neutralizing antibodies | [167] | ||
| 2. | Streptococcus agalactiae | DNA Vaccine (Recombinant bacteria with surface immunogenic protein) | Oral | 75% | Immunogenic | [168] |
| Attenuated with erythromycin. | Intraperitoneal | 82–100% | Leads to higher antibody production | [169] | ||
| 3. | Aeromonas hydrophila | Heat-Inactivated Formalin Inactivated | Intramuscular | 90%, 86.6% | Immunogenic and facilitates highest antibody production | [170] |
| 4. | Flavobacterium columnare | Attenuated (Rifampicin-resistant low-virulence strains) subunit vaccine | Bath | 80% | Provides good immunogenicity and cross-protection to multiple genomovar co-infections | [171] |
| 5. | Vibrio anguillarum | DNA Vaccine (Recombinant flagellin A protein) | Intraperitoneal | Higher survival rate | Facilitates greater agglutination and bactericidal activity | [172] |
| 6. | Edwardsiella tarda | Whole-cell formalin-inactivated + recombinant GAPDH proteins that were emulsified with Montanide adjuvant | Intraperitoneal | 71.4% | Promotes greater antibody response | [172] |
6.2. Antibiotics
6.3. Immunostimulants
6.4. Probiotics
7. Projects Developed for The Production of Tilapia in India
8. Blue Economy—Future Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2018: Building Climate Resilience for Food Security and Nutrition; Food & Agriculture Org.: Rome, Italy, 2018.
- Tacon, A.G.J. Trends in global aquaculture and aquafeed production: 2000–2017. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.-K.; Chong, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Romano, N. Effects of dietary fish and vegetable oils on the growth, tissue fatty acid composition, oxidative stability and vitamin E content of red hybrid tilapia and efficacy of using fish oil finishing diets. Aquaculture 2013, 372–375, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarto, A.; Grimm, J.; McColl, K.A.; Ariel, E.; Nair, K.K.; Corbeil, S.; Hardaker, T.; Tizard, M.; Strive, T.; Holmes, B. Bioprospecting for biological control agents for invasive tilapia in Australia. Biol. Control 2022, 174, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, E.; Rajagopalsamy, C.; Ahilan, B.; Jeevagan, I.; Renuhadevi, M. Tilapia—An excellent candidate species for world aquaculture: A review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2019, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.V.; Lin, C. Effect of stocking density on water quality and production of red tilapia in a recirculated water system. Aquac. Eng. 1992, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, H.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. Transcriptome changes for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in response to alkalinity stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D: Genom. Proteom. 2020, 33, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popma, T.J.; Lovshin, L.L. Worldwide Prospects for Commercial Production of Tilapia; International Center for Aquaculture and Aquatic Environments: Auburn, AL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. 2013. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/458631468152376668/pdf/831770WP0P11260ES003000Fish0to02030.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Popma, T.; Masser, M. Tilapia Life History and Biology. 1999. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12364/145 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Kamal, A.H.M.M.; Mair, G.C. Salinity tolerance in superior genotypes of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, Oreochromis mossambicus and their hybrids. Aquaculture 2005, 247, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaga, M.; Fitzsimmons, K. Growth of the tilapia industry in India. World Aquac. 2017, 48, 49–52. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kevin-Fitzsimmons-4/publication/319681169_Growth_of_the_tilapia_industry_in_India/links/59b9501d458515bb9c486c4f/Growth-of-the-tilapia-industry-in-India.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Shenoy, L.; Rajpathak, S. Sustainable Blue Revolution in India: Way Forward; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakra, W.S.; Gopalakrishnan, A. Blue revolution in India: Status and future perspectives. Indian J. Fish. 2021, 68, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S.; Rakesh, D.; Dhiman, M.; Choudhary, P.; Debbarma, J.; Sahoo, S.N.; Mishra, C.K.I. Present status of fish disease management in freshwater aquaculture in India: State-of-the-art-review. J. Aquac. Fish. 2017, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngasotter, S.; Panda, S.P.; Mohanty, U.; Akter, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Waikhom, D.; Devi, L.S. Current scenario of fisheries and aquaculture in India with special reference to Odisha: A review on its status, issues and prospects for sustainable development. Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2020, 11, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Towards an integrated ‘Blue Economy’framework in the Bay of Bengal. ORF Issue Brief 2020, 411. Available online: https://orfonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/ORF_IssueBrief_411_BIMSTEC-BlueEconomy.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugunan, V.V.; Katiha, P.K. Impact of stocking on yield in small reservoirs in Andhra Pradesh, India. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2004, 11, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Fisheries Development Board (2015) Guidelines for Seaweed Cultivation. Available online: http://nfdb.gov.in/PDF/Draft%20National%20Policy%20on%20Mariculture%20NFDB%20-%20CMFRI%2028%20Sept.2018.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Johnson, C.; Sarkar, U.K.; Koushlesh, S.K.; Das, A.K.; Das, B.K.; Naskar, B.K. Population structure of Nile tilapia and its impact on fisheries of a tropical impacted reservoir, Central India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29091–29099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Sarkar, U.K.; Koushlesh, S.K.; Das, A.K.; Das, B.K.; Naskar, B.K. Fish assemblage, ecosystem status and potential impact of Nile Tilapia in Halali Reservoir of Central India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 7753–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panikkar, N.K. Possibilities of further expansion of fish and prawn cultural practices in India. Curr. Sci. 1952, 21, 29–33. Available online: http://eprints.cmfri.org.in/id/eprint/6916 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Singh, A.K.; Lakra, W.S. Risk and benefit assessment of alien fish species of the aquaculture and aquarium trade into India. Rev. Aquac. 2011, 3, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/sofa/2022/en/ (accessed on 20 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- MoFAHD; Ministry of Fisheries; Animal Husbandry and Dairying. Basic Framework of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)—A Scheme to Bring about Blue Revolution through Sustainable and Responsible Development of Fisheries Sector in India. 2020. Available online: http://dof.gov.in/sites/default/filess/Annexure%20Framework%20to%20statesUT%20%282%29.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- FAO. Tracking Progress on Food and Agriculture-Related SDG Indicators 2022. Rome—A Report on the Indicators under FAO Custodianship. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/sustainable-development-goals/indicators/en/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Cullhaj, M.; Gutierrez, A. Establishment of a Satellite Nucleus of the GIFT Strain at Rajiv Gandhi Center for Aquaculture (RGCA), India: Phase II. Project Brief April 2019–March 2020. 2020. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12348/4134 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Thomas, M.; Pasquet, A.; Aubin, J.; Nahon, S.; Lecocq, T. When more is more: Taking advantage of species diversity to move towards sustainable aquaculture. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saseendran, S.; Dube, K.; Chandrakant, M.; Rani, A.B. Enhanced growth response and stress mitigation of genetically improved farmed Tilapia in a biofloc integrated aquaponic system with bell pepper. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.M.; Lima, J.P.; David, L.H.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Goddek, S.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Keesman, K.J.; Portella, M.C. FLOCponics: The integration of biofloc technology with plant production. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 647–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisano, H.; Barbosa, P.T.L.; Hayd, L.A.; Mattioli, C.C. Evaluation of Nile tilapia in monoculture and polyculture with giant freshwater prawn in biofloc technology system and in recirculation aquaculture system. Int. Aquat. Res. 2019, 11, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparinde, L.O. Fish farmers’ welfare and climate change adaptation strategies in southwest, Nigeria: Application of multinomial endogenous switching regression model. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2021, 25, 450–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, M.; Thirumurthy, S.; Samynathan, M.; Kumararaja, P.; Muralidhar, M.; Vijayan, K. Multi-criteria based geospatial assessment to utilize brackishwater resources to enhance fish production. Aquaculture 2021, 537, 736528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitu, A.; Liu, G.; Muhammad, A.I.; Zhang, Y.; Tadda, M.A.; Qi, W.; Liu, D.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, S. Recent advances in application of moving bed bioreactors for wastewater treatment from recirculating aquaculture systems: A review. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 7, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losordo, T.M.; Westerman, P.W. An analysis of biological, economic, and engineering factors affecting the cost of fish production in recirculating aquaculture systems. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1994, 25, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdegem, M.C.J. Nutrient discharge from aquaculture operations in function of system design and production environment. Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Dai, Z.; Senbati, Y.; Li, L.; Song, K.; He, X. Aerobic denitrification microbial community and function in zero-discharge recirculating aquaculture system using a single biofloc-based suspended growth reactor: Influence of the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhao, J.; Han, Z.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Ruan, Y. Behavioral characteristics and statistics-based imaging techniques in the assessment and optimization of tilapia feeding in a recirculating aquaculture system. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnel, N.; Barak, Y.; Ezer, T.; Dafni, Z.; van Rijn, J. Design and performance of a zero-discharge tilapia recirculating system. Aquac. Eng. 2002, 26, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil, B.L. Performance and operation of a rotating biological contactor in a tilapia recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Eding, E.; Verdegem, M.; Heinsbroek, L.; Schneider, O.; Blancheton, J.; D’Orbcastel, E.R.; Verreth, J. New developments in recirculating aquaculture systems in Europe: A perspective on environmental sustainability. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angkha, B.; Verma, A.K.; Kumar, S.H.; Prakash, C.; Thomas, R.M. Mobilization of mica by Bacillus sp. and its effect on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cum holy basil (Ocimum tenuiflorum)–based aquaponic system. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, U.; Peng, D.; Mu, Y.; Sun, Y. A solution for sustainable utilization of aquaculture waste: A comprehensive review of biofloc technology and aquamimicry. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Sharifinia, M. Biofloc technology as a promising tool to improve aquaculture production. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1836–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, H.X.; Caipang, C.M.A. Biofloc technology (BFT) and its application towards improved production in freshwater tilapia culture. Aquacult. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2015, 8, 362–366. [Google Scholar]
- Green, B.W.; Rawles, S.D.; Schrader, K.K.; Gaylord, T.G.; McEntire, M.E. Effects of dietary protein content on hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis aureus × O. niloticus) performance, common microbial off-flavor compounds, and water quality dynamics in an outdoor biofloc technology production system. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1999, 176, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Romano, N. A review of the nutrition and feeding management of farmed tilapia throughout the culture cycle. Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, 220–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.M.; Molinari, D.; de Mello, G.L.; Fitzsimmons, K.M.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Effluent from a biofloc technology (BFT) tilapia culture on the aquaponics production of different lettuce varieties. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekasari, J.; Rivandi, D.R.; Firdausi, A.P.; Surawidjaja, E.H.; Zairin, M., Jr.; Bossier, P.; De Schryver, P. Biofloc technology positively affects Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) larvae performance. Aquaculture 2015, 441, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Gao, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Sun, D.; Li, L.; Tan, H. Growth, digestive activity, welfare, and partial cost-effectiveness of genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system and an indoor biofloc system. Aquaculture 2014, 422–423, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, C.; Wu, F. Effect of biofloc technology on growth, digestive enzyme activity, hematology, and immune response of genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2015, 448, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Little, D.C. The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: Water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2008, 283, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaga, M.; Felix, S.; Charulatha, M.; Gopalakannan, A.; Panigrahi, A. Effect of in-situ and ex-situ biofloc on immune response of Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 92, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.F.M. Tilapia Culture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Alizadeh, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Aliabad, H.S. The Effect of Adding Molasses in Different Times on Performance of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Raised in a Low-Salinity Biofloc System. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2021, 21, 1435–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, L.R.M.; Owatari, M.S.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Silva, B.C.; Vieira, F.D.N. Nile tilapia nursery in a biofloc system: Evaluation of different stocking densities. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2020, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coche, A.G. Cage culture of tilapia [mostly in tropical freshwaters]. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Biology and Culture of Tilapias, Bellagio, Italy, 2–5 September 1980; Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=XB8210677 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Bridson, P.B.; Stoner, J.M.; Fransen, M.H.; Ireland, J. The aquaculture sustainability continuum—Defining an environmental performance framework. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2020, 8, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, P. Present status of freshwater aquaculture in India—A review. Indian J. Fish. 2018, 65, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.B.; Mazumdar, D.; Banerjee, S. Determination of ideal stocking density for cage culture of monosex Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in India. Proc. Zool. Soc. 2010, 63, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Wahab, M.A.; Van Dam, A.A.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Milstein, A.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Optimization of fertilization rate for maximizing periphyton production on artificial substrates and the implications for periphyton-based aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delphino, M.; Joshi, R.; Alvarez, A.T. Economic appraisal of using genetics to control Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile tilapia under cage and pond farming system in Malaysia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguti, J.M.; Nairuti, R.; Iteba, J.O.; Obiero, K.O.; Kyule, D.; Opiyo, M.A.; Abwao, J.; Kirimi, J.G.; Outa, N.; Muthoka, M.; et al. Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus, 1758) culture in Kenya: Emerging production technologies and socio-economic impacts on local livelihoods. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2022, 2, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.; Zimmermann, S. Grow-out systems—Water quality and soil management. In Freshwater Prawn Culture: The Farming of Macrobrachium Rosenbergii; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lu, M. Tilapia polyculture: A global review. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, S. Horizontally integrated aquaculture development: Exploring consensus on constraints and opportunities with a stakeholder Delphi. Aquac. Int. 2008, 16, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, D.; Dong, S.; Yan, X.; Qi, Z.; Liu, G.; Lu, J. An experimental study on closed-polyculture of penaeid shrimp with tilapia and constricted tagelus. Aquaculture 2001, 202, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, A. Fish-management relationships in Israeli commercial fish farming. Aquac. Int. 1995, 3, 292–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, H.L.A.; New, M.B.; Boock, M.V.; Barros, H.P.; Mallasen, M.; Valenti, W.C. Integrated Freshwater Prawn Farming: State-of-the-art and future potential. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 264–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisano, H.; Barbosa, P.T.L.; Hayd, L.D.A.; Mattioli, C.C. Comparative study of growth, feed efficiency, and hematological profile of Nile tilapia fingerlings in biofloc technology and recirculating aquaculture system. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.K.; Bhandari, M.P.; Diana, J.S.; Jaiswal, R.; Mishra, R.N.; Pandit, N.P. Positive impacts of Nile tilapia and predatory sahar on carp polyculture production and profits. Aquac. Fish. 2018, 3, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsoglou, S.; Miliou, H.; Karakatsouli, N.; Tzitzinakis, M.; Chadio, S. Growth and physiological changes in scaled carp and blue tilapia under behavioral stress in mono- and polyculture rearing using a recirculated water system. Aquac. Int. 2001, 9, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knud-Hansen, C.F.; Batterson, T.R.; McNabb, C.D.; Harahat, I.S.; Sumantadinata, K.; Eidman, H. Nitrogen input, primary productivity and fish yield in fertilized freshwater ponds in Indonesia. Aquaculture 1991, 94, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang’Ombe, J.; Brown, J.A.; Halfyard, L.C. Effect of using different types of organic animal manure on plankton abundance, and on growth and survival of Tilapia rendalli (Boulenger) in ponds. Aquac. Res. 2006, 37, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, A.P.B.; Azevedo, C.M.D.S.B.; Pontes, F.S.T.; Henry-Silva, G.G. Polyculture of Nile tilapia and shrimp at different stocking densities. Rev. Bras. de Zootec. 2012, 41, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliyasu, A.; Mohamed, Z.A.; Terano, R. Comparative analysis of technical efficiency for different production culture systems and species of freshwater aquaculture in Peninsular Malaysia. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 3, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.; Andersen, J.S.; Kaewmak, T.; Somsiri, T.; Dalsgaard, A. Impact of integrated fish farming on antimicrobial resistance in a pond environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 6036–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollas, C.E.; Rodrigues, H.C.; Oyadomari, V.M.A.; Bolsan, A.C.; Venturin, B.; Bonassa, G.; Tápparo, D.C.; Abilhôa, H.C.Z.; da Silva, J.F.F.; Michelon, W.; et al. The potential of animal manure management pathways toward a circular economy: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 73599–73621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa-Murillo, L.M.; Villegas, L.M.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, A.R.; Duque-Acevedo, M.; Cortés-García, F.J. Management of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste in the context of a sustainable and circular model: Analysis of trends in Latin America and the Caribbean. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Tan, P.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Advances in organophosphorus pesticides pollution: Current status and challenges in ecotoxicological, sustainable agriculture, and degradation strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.; Raja, R.A.; De, D.; Sundaray, J.K.; Ghoshal, T.K.; Anand, S.; Kumar, S.; Panigrahi, A.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.R.; Ponniah, A.G. Evaluation of productions and economic returns from two brackish water polyculture systems in tide-fed ponds. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravartty, D.; Mondal, A.; Raychowdhury, P.; Bhattacharya, S.B.; Mitra, A. Role of aquaponics in the sustenance of coastal India-Aquaponics is a solution for modern agriculture in ecologically sensitive Indian mangrove Sundarbans: A review. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 5, 441–448. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Abhijit-Mitra4/publication/344799587_Livelihood_through_Aquaponics/links/5f90c3ba299bf1b53e3a1ed2/Livelihood-through-Aquaponics.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- David, F.S.; Proença, D.C.; Valenti, W.C. Phosphorus budget in integrated multitrophic aquaculture systems with Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, and Amazon River Prawn, Macrobrachium amazonicum. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2017, 48, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.B.; Choudhury, A. Mangroves of the Sundarbans. Volume 1: India; International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN): Gland, Switzerland, 1994; ISBN 978-2-8317-0209-4. [Google Scholar]
- Nurfadillah, N.; Hasri, I.; Purnama, M.R.; Damora, A.; Mellisa, S. The application of integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) using floating net cages on Tilapia fish with native fish (Peres, Lemeduk, and Depik). Depik 2021, 10, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.G.; Garcia, B.F.; Verdegem, M.; Santos, M.R.; Amorim, R.V.; Valenti, W.C. Integrated culture of Nile tilapia and Amazon river prawn in stagnant ponds, using nutrient-rich water and substrates. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.S.; Proença, D.C.; Flickinger, D.L.; Bueno, G.W.; Valenti, W.C. Carbon budget in integrated aquaculture systems with Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Amazon river prawn (Macrobrachium amazonicum). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 5155–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Sau, S.K.; Khatua, S.; Bera, M.; Paul, B.N. A Review on the production and culture techniques of Monosex tilapia. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, G.C.; Abucay, J.S.; Beardmore, J.A.; Skibinski, D.O. Growth performance trials of genetically male tilapia (GMT) derived from YY-males in Oreochromis niloticus L.: On station comparisons with mixed sex and sex reversed male populations. Aquaculture 1995, 137, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardmore, J.; Mair, G.; Lewis, R. Monosex male production in finfish as exemplified by tilapia: Applications, problems, and prospects. In Reproductive Biotechnology in Finfish Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edea, G.O.; Hinvi, L.C.; Abou, Y.; Gbangboche, A.B. Growth and Body Development of Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) Fattened in Floating Cages Based on Commercial Feed in Benin. J. Biol. Life Sci. 2020, 11, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, A.M.; Banh, Q.Q.; Domingos, J.A.; Jerry, D.R. Sex control in fish: Approaches, challenges and opportunities for aquaculture. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 329–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenhai, L.; Cusack, C.; Baker, M.; Tao, W.; Mingbao, C.; Paige, K.; Xiaofan, Z.; Levin, L.; Escobar, E.; Amon, D.; et al. Successful blue economy examples with an emphasis on international perspectives. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraju, Y. Monosex population in aquaculture. In Frontiers in Aquaculture Biotechnology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.E.-D.H.; Moneeb, R.H. Hematological and biochemical characters of monosex tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Linnaeus, 1758) cultivated using methyltestosterone. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2015, 72, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaho, I.; Masembe, C.; Akoll, P.; Jones, C.L.W. The use of plant extracts to control tilapia reproduction: Current status and future perspectives. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 53, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, I.; Mukherjee, D.; Chakraborty, S.B. The effects of four plant extracts on growth, sex reversal, immunological and haemato-biochemical parameters in Nile tilapia, Oreochmomis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dey, M.M.; Barik, N.K. Farm-Economics of Genetically Improved Carp Strains in Major Asian Countries and Carp Seed Price Policy Model. 2008. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12348/1541 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Nguyen, N.H. Genetic improvement for important farmed aquaculture species with a reference to carp, tilapia and prawns in Asia: Achievements, lessons and challenges. Fish 2016, 17, 483–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoa, N.P.; Ninh, N.H.; Knibb, W.; Nguyen, N.H. Does selection in a challenging environment produce Nile tilapia genotypes that can thrive in a range of production systems? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Shikuku, K.M.; Rossignoli, C.M.; Barman, B.K.; Cheong, K.C.; Ali, M.S.; Benzie, J.A. Growth, yield and profitability of genetically improved farmed tilapia (GIFT) and non-GIFT strains in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.H.; Bai, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Jing, W.; Wan, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; et al. Signatures of selection in tilapia revealed by whole genome resequencing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep14168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, R.; Chong, A.S.C.; Fatan, N.A.; Layman, N.; Ali, A. Production of hybrid red tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus× O. niloticus, at varying stocking densities in portable canvas tanks. J. Appl. Aquac. 2002, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Setyawan, P.; Bastiaansen, J.W.; Liu, L.; Imron, I.; Groenen, M.A.; Komen, H.; Megens, H.-J. Genomic analysis of a Nile tilapia strain selected for salinity tolerance shows signatures of selection and hybridization with blue tilapia (Oreochromis aureus). Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, J.M.; Joshi, R.; Yoshida, G.M. Genomics to accelerate genetic improvement in tilapia. Anim. Genet. 2020, 51, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, C.; Li, J.; Lin, X.; Chen, X.; Yi, Y.; You, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Shi, Q. Whole genome sequencing of the blue tilapia (Oreochromis aureus) provides a valuable genetic resource for biomedical research on tilapias. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avallone, A.; Bartie, K.L.; Selly, S.-L.C.; Taslima, K.; Mendoza, A.C.; Bekaert, M. Local ancestry inference provides insight into Tilapia breeding programmes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansah, Y.B.; Frimpong, E.A.; Hallerman, E.M. Genetically-improved tilapia strains in Africa: Potential benefits and negative impacts. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3697–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, M.; Chauka, L.J.; de Koning, D.J.; Palaiokostas, C.; Mtolera, M.S.P. Growth performance of five different strains of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) introduced to Tanzania reared in fresh and brackish waters. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.A.; de Alvarenga, R.; da Costa, F.F.B.; Turra, E.M.; Alves, G.F.D.O.; Manduca, L.G.; de Sales, S.C.M.; Leite, N.R.; Bezerra, V.M.; Moraes, S.G.D.S.; et al. Feeding management strategies to optimize the use of suspended feed for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultivated in bioflocs. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, S.P.; Dumas, A. Nutritional requirements of cultured fish: Formulating nutritionally adequate feeds. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Woodhead publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 65–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaza, M.S.; Dhraief, M.N. Modeling the effects of water temperature on growth rates, gastric evacuation and the return of appetite in juvenile nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 12, p191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, S.S.; Satoh, S. 15.1 Overview of the problem. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Woodhead publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2020; p. 427. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H.U.; Ali, Q.M.; Khan, W.; Masood, Z.; Abdel-Aziz, M.A.; Shah, M.I.A.; Gabol, K.; Wattoo, J.; Chatta, A.M.; Kamal, M.; et al. Effect of feeding frequency as a rearing system on biological performance, survival, body chemical composition and economic efficiency of Asian seabass Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790) reared under controlled environmental conditions. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7360–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Glencross, B.D.; Huyben, D.C.; Juarez, L.M.; Lockwood, G.S.; McNevin, A.A.; Tacon, A.G.J.; Teletchea, F.; Tomasso, J.R., Jr.; et al. Achieving sustainable aquaculture: Historical and current perspectives and future needs and challenges. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 578–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, J.P.; Love, D.C.; MacDonald, G.K.; West, P.C.; Engstrom, P.M.; Nachman, K.E.; Lawrence, R.S. Environmental health impacts of feeding crops to farmed fish. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, D.; Minguez, M.I. Evolution not revolution of farming systems will best feed and green the world. Glob. Food Secur. 2012, 1, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbos, C.; Mente, E.; Karapanagiotidis, I.; Vlontzos, G.; Athanassiou, C. Insect-based feed ingredients for aquaculture: A case study for their acceptance in Greece. Insects 2021, 12, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gule, T.T.; Geremew, A. Dietary strategies for better utilization of aquafeeds in Tilapia farming. Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 9463307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeshina, I.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Tijjani, Z.A.; Tiamiyu, L.O.; Jahanbakhshi, A. Dietary Tridax procumbens leaves extract stimulated growth, antioxidants, immunity, and resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, to monogenean parasitic infection. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.H.; Abdel-Tawwab, M. The use of caraway seed meal as a feed additive in fish diets: Growth performance, feed utilization, and whole-body composition of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2011, 314, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Mohammady, E.Y.; Soaudy, M.R.; El-Garhy, H.A.; Moustafa, M.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; El-Haroun, E.R. Effect of Silybum marianum seeds as a feed additive on growth performance, serum biochemical indices, antioxidant status, and gene expression of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2019, 509, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E.M.; Dawood, M.A.; Assar, D.H.; Omar, A.A.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Farrag, F.A.; Shukry, M.; Zayed, M.M. Modulatory effects of fenugreek seeds powder on the histopathology, oxidative status, and immune related gene expression in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Latif, A.M.A.; El-Gawad, E.A.A.; Soror, E.I.; Shourbela, R.M.; Zahran, E. Dietary supplementation with miswak (Salvadora persica) improves the health status of Nile tilapia and protects against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, Z.I.; Rizk, M.; Al-Hawary, I.I.; Salah, A.S.; Mohammed, R.A.; Assar, D.H.; Almeer, R.; Dawood, M.A.O. Yucca schidigera extract mediated the growth performance, hepato-renal function, antioxidative status and histopathological alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to hypoxia stress. Aquac. Res. 2020, 52, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magouz, F.I.; Mahmoud, S.A.; El-Morsy, R.A.; Paray, B.A.; Soliman, A.A.; Zaineldin, A.I.; Dawood, M.A. Dietary menthol essential oil enhanced the growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, immune-related genes, and resistance against acute ammonia exposure in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Basuini, M.F.; Shahin, S.A.; Teiba, I.I.; Zaki, M.A.; El-Hais, A.M.; Sewilam, H.; Almeer, R.; Abdelkhalek, N.; Dawood, M.A. The influence of dietary coenzyme Q10 and vitamin C on the growth rate, immunity, oxidative-related genes, and the resistance against Streptococcus agalactiae of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.-S.; Tan, K.S.; Fu, M.-Y.; Au, H.-L.; Ebi, I.; Lal, M.T.M.; Kawamura, G.; Shapawi, R.; Lam, S.S. Valorization of Bokashi leachate as feed additive in tilapia farming. Environ. Res. 2020, 198, 110472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poolsawat, L.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y.-F.; Li, X.-Q.; Liang, G.-Y.; Leng, X.-J. Effect of replacing fish meal with enzymatic feather meal on growth and feed utilization of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus). Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 274, 114895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, D.; Li, X.; Chowdhury, M.A.K.; Yang, H.; Liang, G.; Leng, X. Organic acid salts, protease and their combination in fish meal-free diets improved growth, nutrient retention and digestibility of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus). Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.A.; Ahmed, S.A.; Ibrahim, R.E.; Al-Gabri, N.A.; Osman, A.; Sitohy, M. Impact of partial substitution of fish meal by methylated soy protein isolates on the nutritional, immunological, and health aspects of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.A.; Osman, A.; Al-Gabri, N.A.; Elsayed, S.A.M.; El-Rahman, G.I.A.; Elabbasy, M.T.; Ahmed, S.A.A.; Ibrahim, R.E. The effect of dietary replacement of fish meal with whey protein concentrate on the growth performance, fish health, and immune status of nile tilapia fingerlings, Oreochromis niloticus. Animals 2019, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, M.C.; Guimarães, A.I.C.D.S.; Natori, M.M.; Alarcon, M.F.F.; Dias, D.D.C.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.; Moriñigo, M.; Moyano, F.J.; Tachibana, L. Oral administration of Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum modulates the gut microbiota and increases the amylase activity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Mohammady, E.Y.; Soaudy, M.R.; Elashry, M.A.; Moustafa, M.M.; Wassel, M.A.; El-Garhy, H.A.; El-Haroun, E.R.; Elsaied, H.E. Synergistic effects of Bacillus pumilus and exogenous protease on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth, gut microbes, immune response and gene expression fed plant protein diet. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 275, 114892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, L.; Telli, G.S.; Dias, D.D.C.; Gonçalves, G.S.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Cavalcante, R.B.; Natori, M.M.; Ben Hamed, S.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Effect of feeding strategy of probiotic Enterococcus faecium on growth performance, hematologic, biochemical parameters and non-specific immune response of Nile tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Eweedah, N.M.; Moustafa, E.M.; Farahat, E.M. Probiotic effects of Aspergillus oryzae on the oxidative status, heat shock protein, and immune related gene expression of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under hypoxia challenge. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poolsawat, L.; Li, X.; He, M.; Ji, D.; Leng, X. Clostridium butyricumas probiotic for promoting growth performance, feed utilization, gut health and microbiota community of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus). Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.; Salaah, S.; El-Shabaka, H.; El-Rahman, F.A.; Khalil, M.; Suloma, A. Efficacy of dietary chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles supplementation on health status of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, A.; Elumalai, P. Study on the impacts of chemical and green synthesized (Leucas aspera and oxy-cyclodextrin complex) dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20344–20361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Shukry, M.; Farrag, F.A.; El-Shafai, N.M.; Dawood, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Dietary sodium butyrate nanoparticles enhanced growth, digestive enzyme activities, intestinal histomorphometry, and transcription of growth-related genes in Nile tilapia juveniles. Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, S.; Diab, A.M.; Khalafalla, M.M.; Mohamed, R.A. Synergistic Effects of Selenium and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Growth Performance, Hemato-biochemical Profile, Immune and Oxidative Stress Responses, and Intestinal Morphometry of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biol. Trace Element Res. 2021, 200, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Samir, F.; El-Naby, A.S.A.; Monier, M.N. Antioxidative and immunostimulatory effect of dietary cinnamon nanoparticles on the performance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) and its susceptibility to hypoxia stress and Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 74, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sribounoy, U.; Pirarat, N.; Solval, K.M.; Sathivel, S.; Chotiko, A. Development of pelleted feed containing probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Jerusalem artichoke for Nile Tilapia and its biocompatibility studies. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgnaulin, T.; Durigon, E.G.; Pinho, S.M.; Jerônimo, G.T.; Lopes, D.L.D.A.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Nutrition of Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (GIFT) in biofloc technology system: Optimization of digestible protein and digestible energy levels during nursery phase. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 734998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, C.P.; Adjei-Boateng, D.; Amponsah, A.K.; Andrews, P.; Obirikorang, K.A. The effect of plant protein-based diets on apparent nutrient digestibility, growth response, egesta quantity, postprandial ammonia excretion rate and serum quality of Nile tilapia. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyadjeu, P.; Djopnang, J.D.; Ndjuissi, N.A.T.; Ayamba, A.E.; Alim, H.; Tabi-Tomedi, M.E. Replacing fishmeal with pretreated Lima bean improves growth, feed utilization, whole-body composition and nutrient retention in Nile-tilapia fingerlings. J. Appl. Aquac. 2021, 34, 922–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.M.; Renukdas, N.N. Disease management of aquatic animals. In Aquaculture Health Management; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitmanat, C.; Lebel, P.; Whangchai, N.; Promya, J.; Lebel, L. Tilapia diseases and management in river-based cage aquaculture in northern Thailand. J. Appl. Aquac. 2016, 28, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic use in agriculture and its consequential resistance in environmental sources: Potential public health implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polianciuc, S.I.; Gurzău, A.E.; Kiss, B.; Ștefan, M.G.; Loghin, F. Antibiotics in the environment: Causes and consequences. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 93, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, B.; Pradhan, P.; Swaminathan, T.; Sood, N.; Paria, P.; Das, A.; Verma, D.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, M.; Dev, A.; et al. Emergence of tilapia lake virus associated with mortalities of farmed Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus 1758) in India. Aquaculture 2018, 484, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, C.-M. Aeromonas hydrophila as an environmental indicator to detect TiLV-infected tilapia under coinfection threat. J. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 11, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Trujillo, A.; Velázquez-Abunader, I.; Papiol, V.; del Rio-Rodríguez, R.E.; Vidal-Martínez, V.M. Negative effect of ectoparasite burdens on the condition factor from farmed tilapia Oreochromis niloticus in the Yucatan, Mexico. Veter-Parasitol. 2021, 292, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, K.D.; Harvell, C.D.; Conrad, J.M.; Friedman, C.S.; Kent, M.L.; Kuris, A.M.; Powell, E.N.; Rondeau, D.; Saksida, S.M. Infectious diseases affect marine fisheries and aquaculture economics. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayansamruaj, P.; Pirarat, N.; Hirono, I.; Rodkhum, C. Increasing of temperature induces pathogenicity of Streptococcus agalactiae and the up-regulation of inflammatory related genes in infected Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Veter-Microbiol. 2014, 172, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.; Syafiq, M.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Fahmi, S.; Shahidan, H.; Hanan, Y.; Amal, M.; Saad, M.Z. The effect of feed-based vaccination on tilapia farm endemic for streptococcosis. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 60, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.L.; Feist, S.W.; Harper, C.; Hoogstraten-Miller, S.; Mac Law, J.; Sánchez-Morgado, J.M.; Tanguay, R.L.; Sanders, G.E.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Whipps, C.M. Recommendations for control of pathogens and infectious diseases in fish research facilities. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiyo, M.; Mziri, V.; Musa, S.; Kyule, D.; Hinzano, S.; Wainaina, M.; Ombwa, V. Fish Disease Management and Biosecurity Systems. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mary-Opiyo/publication/351050775_Fish_Disease_Management_and_Biosecurity_Systems/links/60815e688ea909241e17589b/Fish-Disease-Management-and-Biosecurity-Systems.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Aljahdali, M.; Molla, M.; Filfilan, W. Whole Genome Sequence of the Newly Prescribed Subspecies Oreochromis spilurus saudii: A Valuable Genetic Resource for Aquaculture in Saudi Arabia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embregts, C.W.; Forlenza, M. Oral vaccination of fish: Lessons from humans and veterinary species. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, D.C.B. The oral immunization of trout against Bacterium salmonicida. J. Immunol. 1942, 44, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bruce, T.J.; Jones, E.M.; Cain, K.D. A review of fish vaccine development strategies: Conventional methods and modern biotechnological approaches. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Development and efficacy of a novobiocin-resistant Streptococcus iniae as a novel vaccine in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Vaccine 2011, 29, 5986–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayansamruaj, P.; Dong, H.T.; Pirarat, N.; Nilubol, D.; Rodkhum, C. Efficacy of α-enolase-based DNA vaccine against pathogenic Streptococcus iniae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2017, 468, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HHuang, L.Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Xiao, D.; Chen, D.F.; Geng, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, E.L.; Huang, J.L.; Xiao, G.Y. Safety and immunogenicity of an oral DNA vaccine encoding Sip of Streptococcus agalactiae from Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus delivered by live attenuated Salmonella typhimurium. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 38, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lu, D.; Xu, J.; Luo, H.; Li, A. Development of attenuated erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus agalactiae vaccine for tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) culture. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bactol, I.D.C.; Padilla, L.V.; Hilario, A.L. Immune response of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) after vaccination with autoclave killed, heat-killed, and formalin-killed whole cell Aeromonas hydrophila vaccines as possible serotype-independent vaccines. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.C.; Kang, Y.J. Effects of a subunit vaccine (FlaA) and immunostimulant (CpG-ODN 1668) against Vibrio anguillarum in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2016, 454, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.T.; Tsai, M.-A.; Yang, C.-D.; Wang, P.-C.; Kuo, T.-Y.; Chen, H.-C.G.; Chen, S.-C. Vaccine efficacy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) from Edwardsiella ictaluri against E. tarda in tilapia. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; Albutti, A.S.; Rahmani, A.H.; Atti, N.M.A. The response of new-season Nile tilapia to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 4508. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc4443210/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Chen, M.; Li, L.-P.; Wang, R.; Liang, W.-W.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, A.-Y.; Huang, W.-Y.; Gan, X. PCR detection and PFGE genotype analyses of streptococcal clinical isolates from tilapia in China. Veter- Microbiol. 2012, 159, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldar, A.; Bejerano, Y.; Livoff, A.; Horovitcz, A.; Bercovier, H. Experimental streptococcal meningo-encephalitis in cultured fish. Vet. Microbiol. 1995, 43, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klesius, P.H.; Shoemaker, C.; Evans, J.J. Efficacy of single and combined Streptococcus iniae isolate vaccine administered by intraperitoneal and intramuscular routes in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2000, 188, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K.M.; Pires, D.S.; Franco, O.L.; Saad, A.; Hamed, M.; Naim, H.; Ali, A.H.; Elbehiry, A. Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) as an aquatic vector for Pseudomonas species of medical importance: Antibiotic Resistance Association with Biofilm Formation, Quorum Sensing and Virulence. Aquaculture 2020, 532, 736068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangpan, L.; Kitao, T.; Yoshida, T. Protective efficacy ofAeromonas hydrophila vaccines in Nile tilapia. Veter- Immunol. Immunopathol. 1986, 12, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, C.A.; LaFrentz, B.R.; Klesius, P.H. Bivalent vaccination of sex reversed hybrid tilapia against Streptococcus iniae and Vibrio vulnificus. Aquaculture 2012, 354–355, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhou, Z. Effects of partially replacing dietary soybean meal or cottonseed meal with completely hydrolyzed feather meal (defatted rice bran as the carrier) on production, cytokines, adhesive gut bacteria, and disease resistance in hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus (female) × Oreochromis aureus (male)). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 41, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.; Yusoff, M.; Samad, M.; Razak, I.A.; Yasin, I.; Thompson, K.; Hasni, K. Efficacy of Feed-Based Formalin-Killed Vaccine of Streptococcus iniae Stimulates the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues and Immune Response of Red Hybrid Tilapia. Vaccines 2021, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tantawy, M.M.; Ayoub, H.F. Efficiency of oral Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine and Tumeric powder mixture on immune response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Aquat. Biol. Fish 2016, 6, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.M.; Samir, A.; Wasfy, M.; Elsayed, M. Efficacy of Injectable and Immersion Polyvalent Vaccine against Streptococcal Infections in Broodstock and Offspring of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 88, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, K.; Shinn, A.P.; Metselaar, M.; Ramirez-Paredes, J.G.; Monaghan, S.J.; Thompson, K.D.; Hoare, R.; Adams, A. Efficacy of an inactivated whole-cell injection vaccine for nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus(L), against multiple isolates of Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis from diverse geographical regions. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 89, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, N.; Pradhan, P.K.; Ravindra; Verma, D.K.; Yadav, M.K.; Mishra, R.K.; Kumar, U.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Sood, N.K. Large-scale mortality in cultured tilapia Oreochromis niloticus due to infection with Shewanella putrefaciens in India. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.S.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Raja, S.A.; Ramraj, D.; Lal, K. Aeromonas veronii caused bilateral exophthalmia and mass mortality in cultured Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus(L.) in India. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Focardi, S. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquaculture and climate change: A challenge for health in the Mediterranean area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallali, E.; Kokou, F.; Chourasia, T.K.; Nitzan, T.; Con, P.; Harpaz, S.; Mizrahi, I.; Cnaani, A. Dietary salt levels affect digestibility, intestinal gene expression, and the microbiome, in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.; Fiol, F.D.S.D.; Balcão, V. Prospects for the use of new technologies to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, C.J.; Turnbull, J.F.; MacKenzie, S.; Crumlish, M. Investigating the Effect of an Oxytetracycline Treatment on the Gut Microbiome and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Dynamics in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroma, L.S.; Soares, M.P.; Cardoso, I.L.; Ishikawa, M.M.; Jonsson, C.M.; Queiroz, S.C.N. Evaluation of health and environmental risks for juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to florfenicol. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiogiri, N.S.; Ikefuti, C.V.; Carraschi, S.P.; da Cruz, C.; Fernandes, M.N. Effects of azithromycin on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Health status evaluation using biochemical, physiological and morphological biomarkers. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3669–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Chen, X.; Shan, X.; Qiu, L.; Fan, L.; Meng, S.; Song, C. Antibiotic accumulation, growth performance, intestinal diversification, and function of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) feed by diets supplemented with different doses of sulfamethoxazole. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65255–65264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisyhah, M.A.S.; Amal, M.N.A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Shaqinah, N.N. Streptococcus agalactiae isolates from cultured fishes in Malaysia manifesting low resistance pattern towards selected antibiotics. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Módenes, A.N.; Bazarin, G.; Borba, C.E.; Locatelli, P.P.P.; Borsato, F.P.; Pagno, V.; Pedrini, R.; Trigueros, D.E.G.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Scheufele, F.B. Tetracycline adsorption by tilapia fish bone-based biochar: Mass transfer assessment and fixed-bed data prediction by hybrid statistical-phenomenological modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, M.S.; Thangam, R.; Sakthidhasan, P.; Arun, S.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Thirumurugan, R. Combined effect of a natural flavonoid rutin from Citrus sinensis and conventional antibiotic gentamicin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Food Control 2018, 90, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, M.S.; Thangam, R.; Vijayakumar, T.S.; Sasirekha, R.; Vimala, R.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Arun, S.; Babu, M.D.; Thirumurugan, R. Antibacterial synergy between rutin and florfenicol enhances therapeutic spectrum against drug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Esteban, M.; Cuesta, A.; Sun, Y.-Z. Prebiotics and fish immune response: A review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2015, 23, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Song, S. Application of dietary supplements (synbiotics and probiotics in combination with plant products and β-glucans) in aquaculture. Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangaby, M. Intraspecific Variation in Life History Traits of the Panamanian Electric Fish Brachyhypopomus Occidentalis. Ph.D. Thesis, Laurentian University of Sudbury, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2021. Available online: https://zone.biblio.laurentian.ca/handle/10219/3899 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Bricknell, I.; Dalmo, R.A. The use of immunostimulants in fish larval aquaculture. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2005, 19, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, D.K.; Das, P.; Kumar, S.; Mandal, S.C.; Prusty, A.; Singh, S.K.; Akhtar, M.S.; Behera, B.K.; Kumar, K.; Pal, A.K.; et al. Beta-glucan: An ideal immunostimulant in aquaculture (a review). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 431–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nya, E.J.; Austin, B. Use of garlic, Allium sativum, to control Aeromonas hydrophila infection in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, H.K.; Al-Sagheer, A.A.; Reda, F.M.; Mahgoub, S.A.; Ayyat, M.S. Dietary curcumin supplement influence on growth, immunity, antioxidant status, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2017, 475, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musthafa, M.S.; Ali, A.R.J.; Kumar, M.S.A.; Paray, B.A.; Al-Sadoon, M.K.; Balasundaram, C.; Harikrishnan, R. Effect of Cucurbita mixta (L.) seed meal enrichment diet on growth, immune response and disease resistance in Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 68, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musthafa, M.S.; Asgari, S.M.; Kurian, A.; Elumalai, P.; Ali, A.R.J.; Paray, B.A.; Al-Sadoon, M.K. Protective efficacy of Mucuna pruriens (L.) seed meal enriched diet on growth performance, innate immunity, and disease resistance in Oreochromis mossambicus against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 75, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, E.; El-Gawad, E.A.A.; Risha, E. Dietary Withania sominefera root confers protective and immunotherapeutic effects against Aeromonas hydrophila infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 80, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laith, A.; Mazlan, A.; Effendy, A.; Ambak, M.; Nurhafizah, W.; Alia, A.; Jabar, A.; Najiah, M. Effect of Excoecaria agallocha on non-specific immune responses and disease resistance of Oreochromis niloticus against Streptococcus agalactiae. Res. Veter- Sci. 2017, 112, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omitoyin, B.O.; Ajani, E.K.; Orisasona, O.; Bassey, H.E.; Kareem, K.O.; Osho, F.E. Effect of guava Psidium guajava (L.) aqueous extract diet on growth performance, intestinal morphology, immune response and survival of Oreochromis niloticus challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbokane, E.; Moyo, N. A preliminary investigation into the potential effect of Artemisia afra on growth and disease resistance in sub-adults of Oreochromis mossambicus. Aquaculture 2018, 482, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, S.F.; Nordin, M.L.; Osman, A.Y.; Hamdan, R.H.; Shaari, R.; Arshad, M.M.; Aziz, A.R. The Effect of Matricaria chamomilla L. on the Growth Performance of Red Hybrid Tilapia. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2017, 10, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njagi, G.W.; Lee, S.; Won, S.; Hong, J.; Hamidoghli, A.; Bai, S.C. Effects of dietary Yucca meal on growth, haematology, non-specific immune responses and disease resistance of juvenile Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 4399–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrok, M.A.E.; Wahdan, A. The immune modulatory effect of oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) essential oil on Tilapia zillii following intraperitoneal infection with Vibrio anguillarum. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.T.D.S.; Pereira, U.D.P.; de Oliveira, H.M.; Brasil, E.M.; Pereira, S.A.; Chagas, E.C.; Jesus, G.F.A.; Cardoso, L.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Martins, M.L. Hemato-immunological and zootechnical parameters of Nile tilapia fed essential oil of Mentha piperita after challenge with Streptococcus agalactiae. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamam, M.S.A.; Pantami, H.A.; Azam, A.A.; Shaari, K.; Min, C.C.; Ismail, I.S. The immunostimulant effects of Isochrysis galbana supplemented diet on the spleen of red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) evaluated by nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics. Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 1154558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkatatny, N.M.; El Nahas, A.F.; Helal, M.A.; Fahmy, H.A.; Tanekhy, M. The impacts of seasonal variation on the immune status of Nile tilapia larvae and their response to different immunostimulants feed additives. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 96, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owatari, M.S.; da Silva, L.R.; Ferreira, G.B.; Rodhermel, J.C.B.; de Andrade, J.I.A.; Dartora, A.; Jatobá, A. Body yield, growth performance, and haematological evaluation of Nile tilapia fed a diet supplemented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2022, 293, 115453. [Google Scholar]
- Essa, M.A.; El-Serafy, S.S.; El-Ezabi, M.M.; Daboor, S.M.; Esmael, N.A.; Lall, S.P. Effect of different dietary probiotics on growth, feed utilization and digestive enzymes activities of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. Arab. Aquac. Soc. 2010, 5, 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, K.; Banerjee, S.; Moon, U.M.; Khan, H.A.; Dutta, D. Evaluation of gut associated extracellular enzyme-producing and pathogen inhibitory microbial community as potential probiotics in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Int. J. Aquac. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G.; Ray, A.K. Bacterial symbiosis in the fish gut and its role in health and metabolism. Symbiosis 2017, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Ringø, E.; Ghosh, K. Extracellular tannase-producing bacteria detected in the digestive tracts of freshwater fishes (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae and Cichlidae). Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2016, 46, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Flores, M.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Olvera-Novoa, M.A. Effect of the inclusion of a bacterial mix (Streptococcus faecium and Lactobacillus acidophilus), and the yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) on growth, feed utilization and intestinal enzymatic activity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Fis. Aquac. 2010, 2, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; Ahmed, Y.A.-G.; Ghareeb, A.A.-A.; Mohamed, M.F. Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2008, 25, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samat, N.A.; Yusoff, F.M.; Rasdi, N.W.; Karim, M. The Efficacy of Moina micrura Enriched with Probiotic Bacillus pocheonensis in Enhancing Survival and Disease Resistance of Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) Larvae. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Harikrishnan, R.; Soltani, M.; Ghosh, K. The Effect of Gut Microbiota and Probiotics on Metabolism in Fish and Shrimp. Animals 2022, 12, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Ponzoni, R.W.; Vijayakumar, S.; Raj, T.S. Establishment of a satellite nucleus of the gift strain at Rajiv Gandhi, Center for aquaculture (RGCA) to support tilapia production in India (37–41). Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA). 2011. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=QW2016000355 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Henriksson, P.J.G.; Troell, M.; Banks, L.K.; Belton, B.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Klinger, D.H.; Pelletier, N.; Phillips, M.J.; Tran, N. Interventions for improving the productivity and environmental performance of global aquaculture for future food security. One Earth 2021, 4, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Barange, M.; Subasinghe, R.; Pinstrup-Andersen, P.; Merino, G.; Hemre, G.-I.; Williams, M. Feeding 9 billion by 2050—Putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| S. No | Antibiotic | Target Disease/Causative Organisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oxytetracycline | Francisellosis, motile Aeromonas septicemia, and Streptococcosis | [190] |
| 2 | Florfenicol | Aeromonas salmonicida, Aeromonas hydrophila, Flavobacterium psychrophilum, Yersinia ruckeri, and Vibrio anguillarum | [191] |
| 3 | Azithromycin | Aeromonas spp., Pseudomonas fluorescens, Vibrio anguillarum, Flavobacterium columnare, Edwardsiella tarda, Streptococcus spp., and Enterococcus spp. | [192] |
| 4 | Sulfamethoxazole | Alphaproteobacteria, cyanobacteria, Fusobacteria, and unclassified–P-proteobacteria | [193] |
| 5 | Erythromycin | Streptococcosis | [194] |
| S. No | Immunostimulant | Organism | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Turmeric (Curcuma longa) | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Enhances growth, immunity, and antioxidant status | [204] |
| 2 | Pumpkin seed meal (Cucurbita mixta) | Mossambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) | Enhances growth, immune, and disease resistance activity | [205] |
| 3 | Velvet bean (Mucuna pruriens) | Mossambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) | Enhances innate immunity and growth performance | [206] |
| 4 | Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Provides an immuno-therapeutic effect | [207] |
| 5 | Mangrove (Excoecaria agallocha) | Red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Enhances non-specific immune responses and disease resistance | [208] |
| 6 | Guava (Psidium guajava) | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Enhances growth, nutrient utilization, and immune system | [209] |
| 7 | African wormwood (Artemisia afra) | Mossambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) | Enhances growth and disease resistance | [210] |
| 8 | Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Enhances growth and immune parameters | [211] |
| 9 | Spanish dagger (Yucca schidigera) | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Enhances growth, hematology, nonspecific immune responses, and disease resistance | [212] |
| 10 | Oregano (Origanum vulgare) | Red belly tilapia (Coptodon zillii) | Enhances innate immunity | [213] |
| 11 | Peppermint (Mentha piperita) | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Enhances hemato-immunological parameters | [214] |
| S. No. | Governing Body/Funding Agencies | Project | Target Fish Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | NFDB | Brackish water cage culture for sustainable aquaculture in coastal regions of India | Milk Fish (Chanos chanos), Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer), grey mullet (Mugil cephalus), pearlspot (Etroplus suratensis), Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), silver pompano (Trachinotus blochii) |
| Demonstration of azolla production for tilapia feed supplement in Madhavaram, TNJFU Campus, Tamil Nadu | GIFT Tilapia | ||
| Backyard Recirculatory Aquaculture System | Monosex tilapia, Pangasius valenciennes | ||
| 2. | RGCA working in association with (WFC) to enhance the genetic strains of tilapia. | Establishment of a satellite nucleus of the GIFT strain at RGCA to support tilapia production in India: Phase I (2011–2016) Establishment of a satellite nucleus of the GIFT strain at RGCA, India: Phase II (2019–2023) | GIFT Tilapia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arumugam, M.; Jayaraman, S.; Sridhar, A.; Venkatasamy, V.; Brown, P.B.; Abdul Kari, Z.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Ramasamy, T. Recent Advances in Tilapia Production for Sustainable Developments in Indian Aquaculture and Its Economic Benefits. Fishes 2023, 8, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040176
Arumugam M, Jayaraman S, Sridhar A, Venkatasamy V, Brown PB, Abdul Kari Z, Tellez-Isaias G, Ramasamy T. Recent Advances in Tilapia Production for Sustainable Developments in Indian Aquaculture and Its Economic Benefits. Fishes. 2023; 8(4):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040176
Chicago/Turabian StyleArumugam, Manikandan, Sudharshini Jayaraman, Arun Sridhar, Vignesh Venkatasamy, Paul B. Brown, Zulhisyam Abdul Kari, Guillermo Tellez-Isaias, and Thirumurugan Ramasamy. 2023. "Recent Advances in Tilapia Production for Sustainable Developments in Indian Aquaculture and Its Economic Benefits" Fishes 8, no. 4: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040176
APA StyleArumugam, M., Jayaraman, S., Sridhar, A., Venkatasamy, V., Brown, P. B., Abdul Kari, Z., Tellez-Isaias, G., & Ramasamy, T. (2023). Recent Advances in Tilapia Production for Sustainable Developments in Indian Aquaculture and Its Economic Benefits. Fishes, 8(4), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040176









