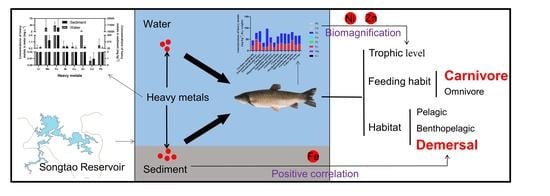
Feeding Habit-Specific Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Fish in a Tropical Reservoir in Southern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
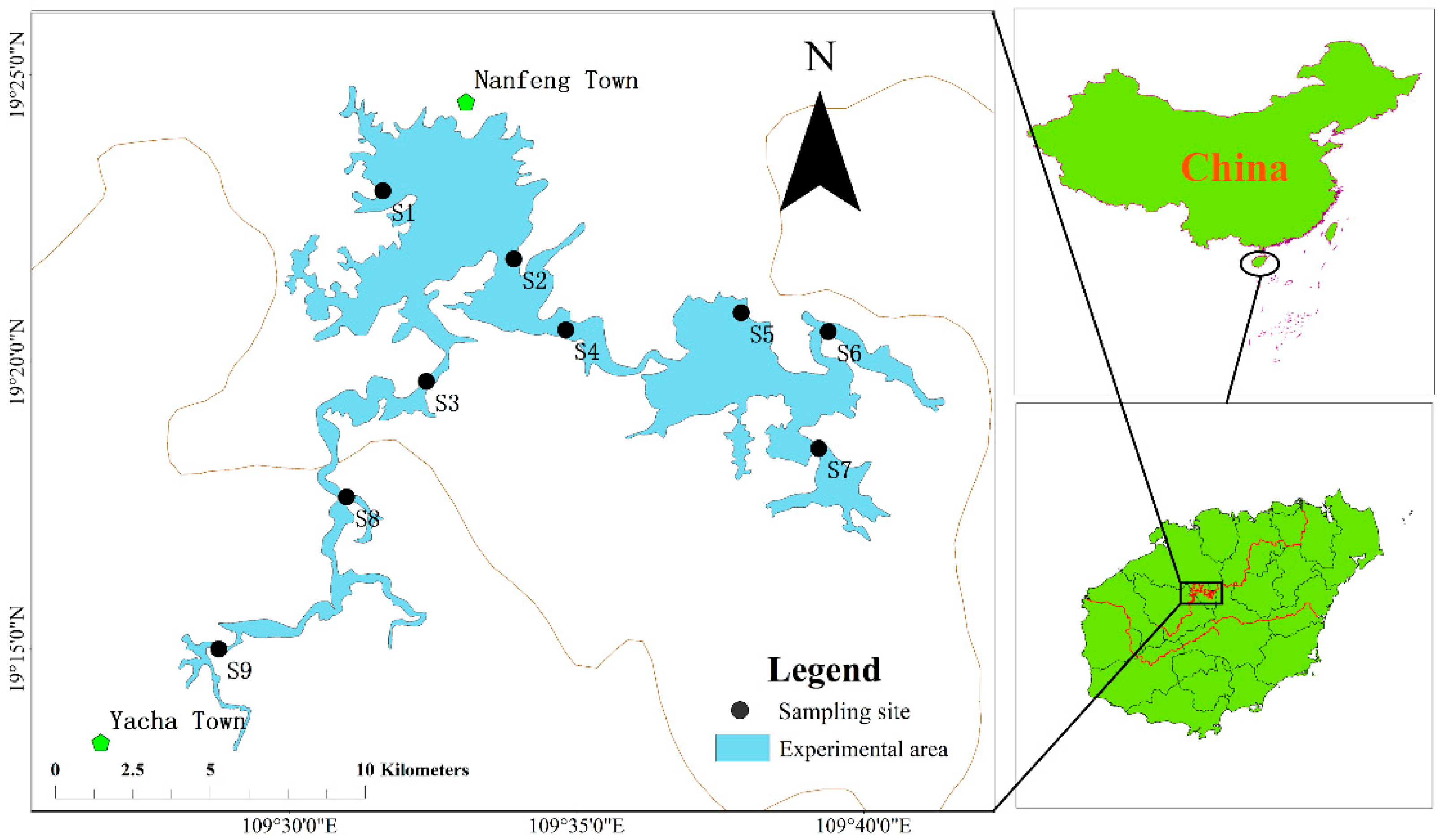
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Determination of Metals
2.4. Analyses of Stable Isotope (δ13C and δ15N)
2.5. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
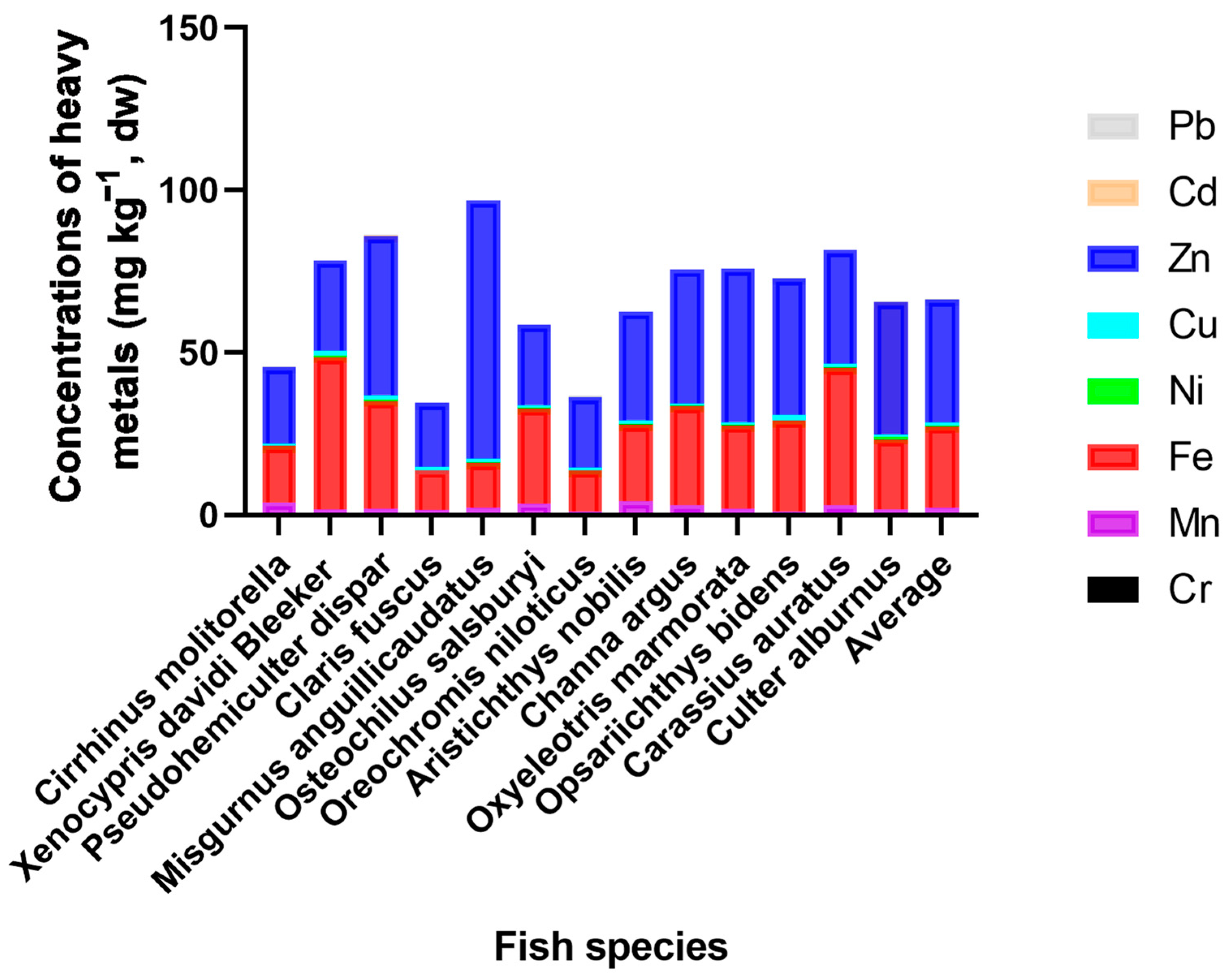
3.1. The Contents of Metals among Fish
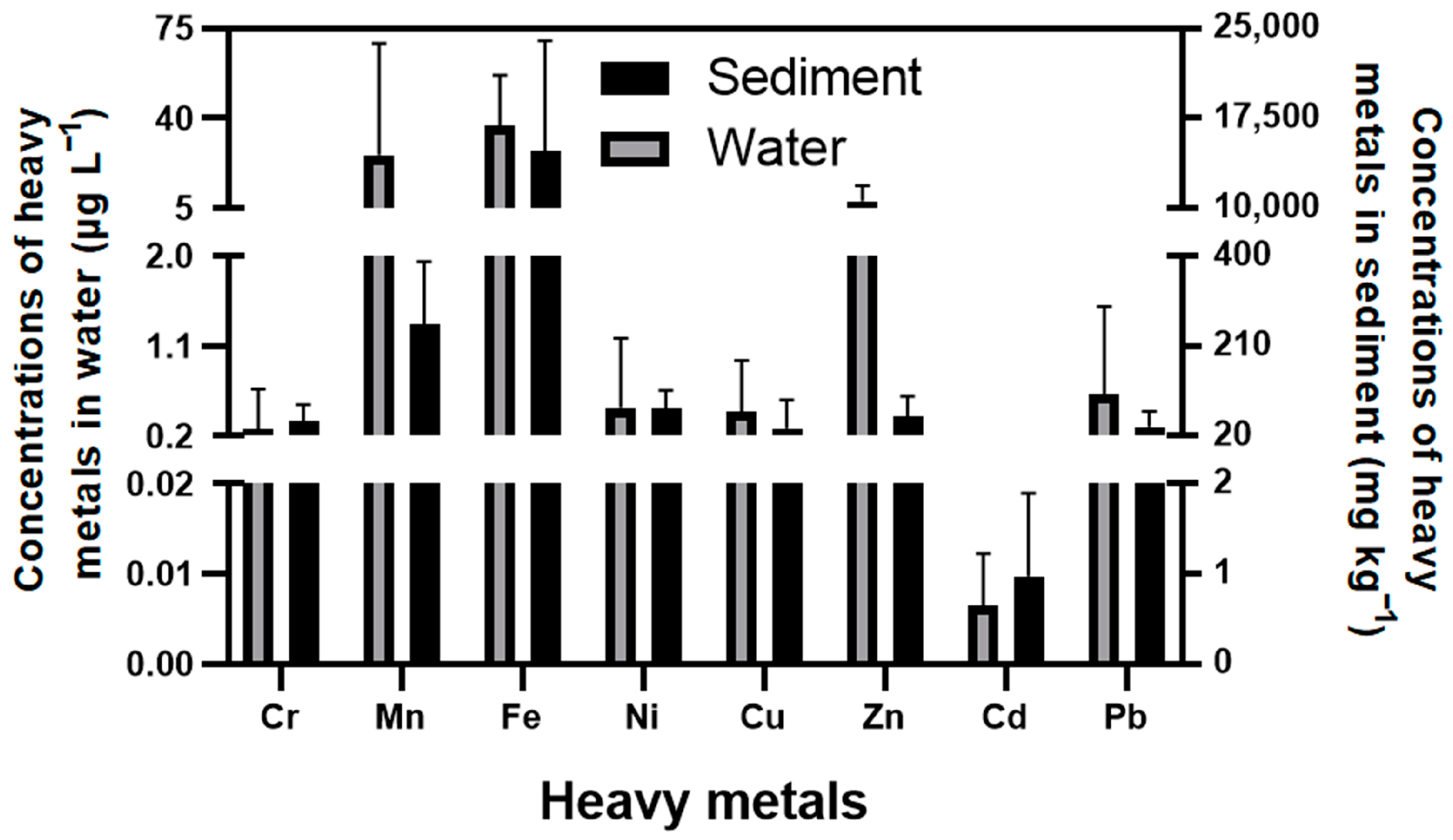
3.2. The Content of Metals in the Environment
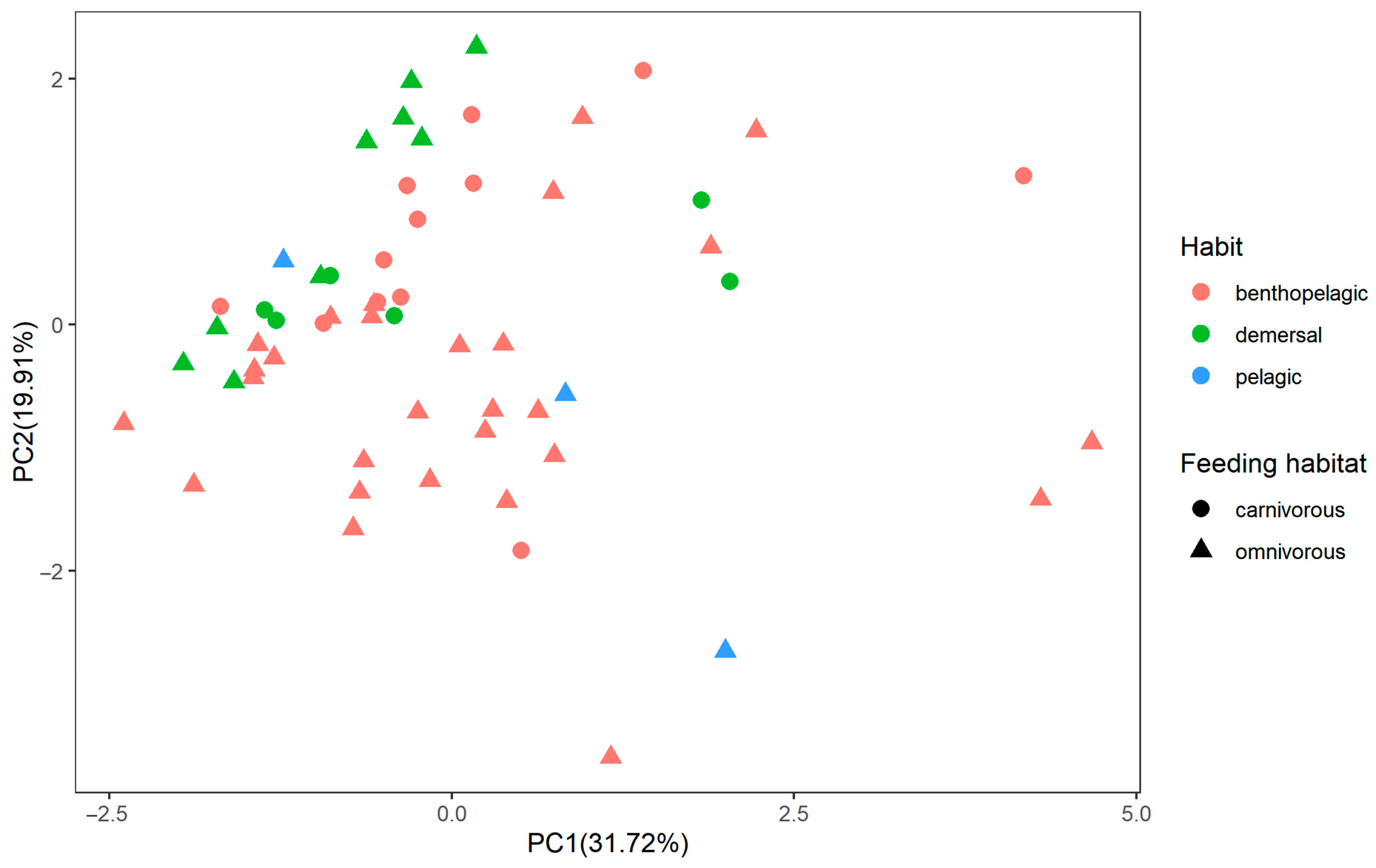
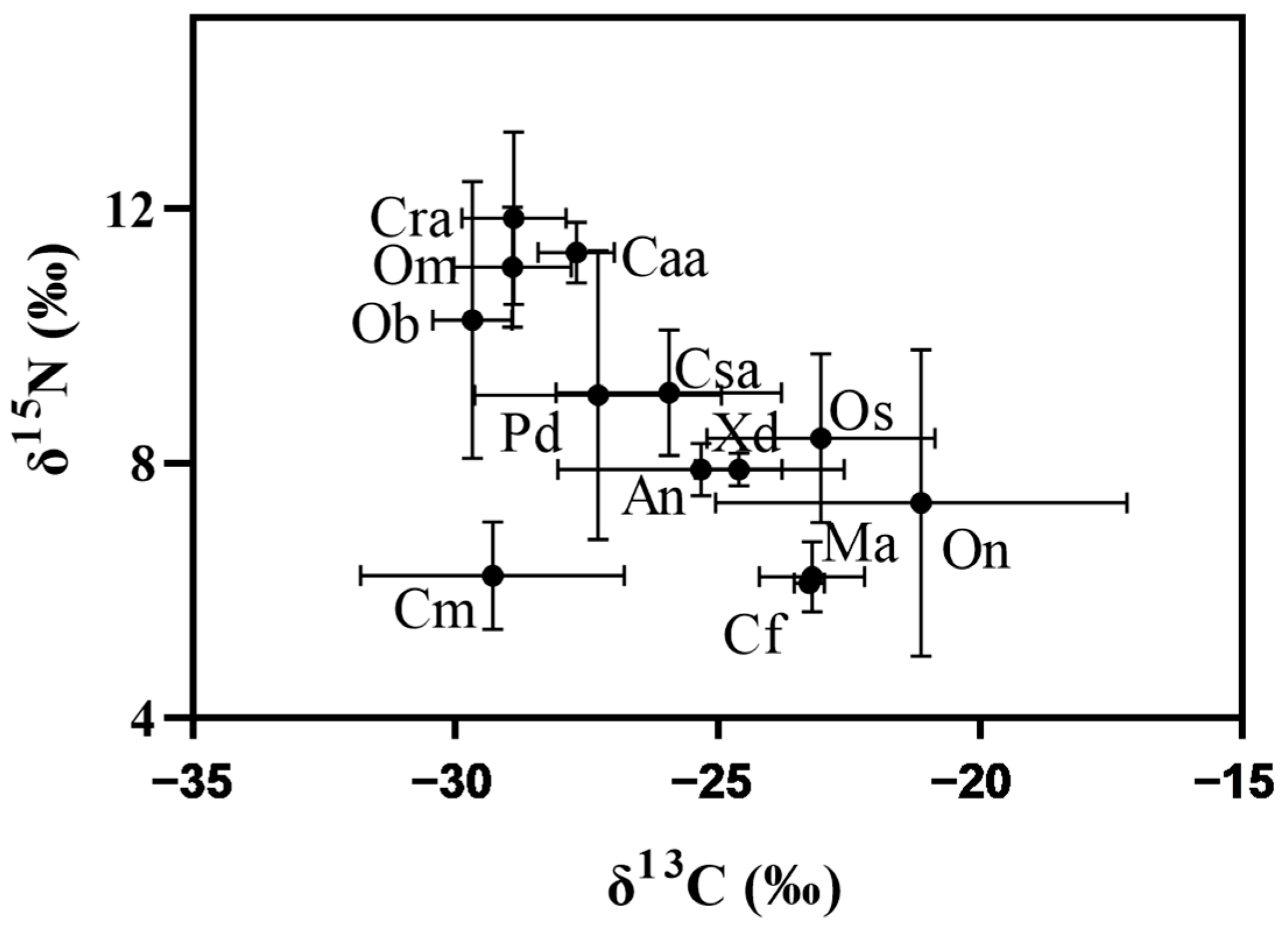
3.3. Values of the Stable Isotope
3.4. The EDI and THQ of Metals
4. Discussion
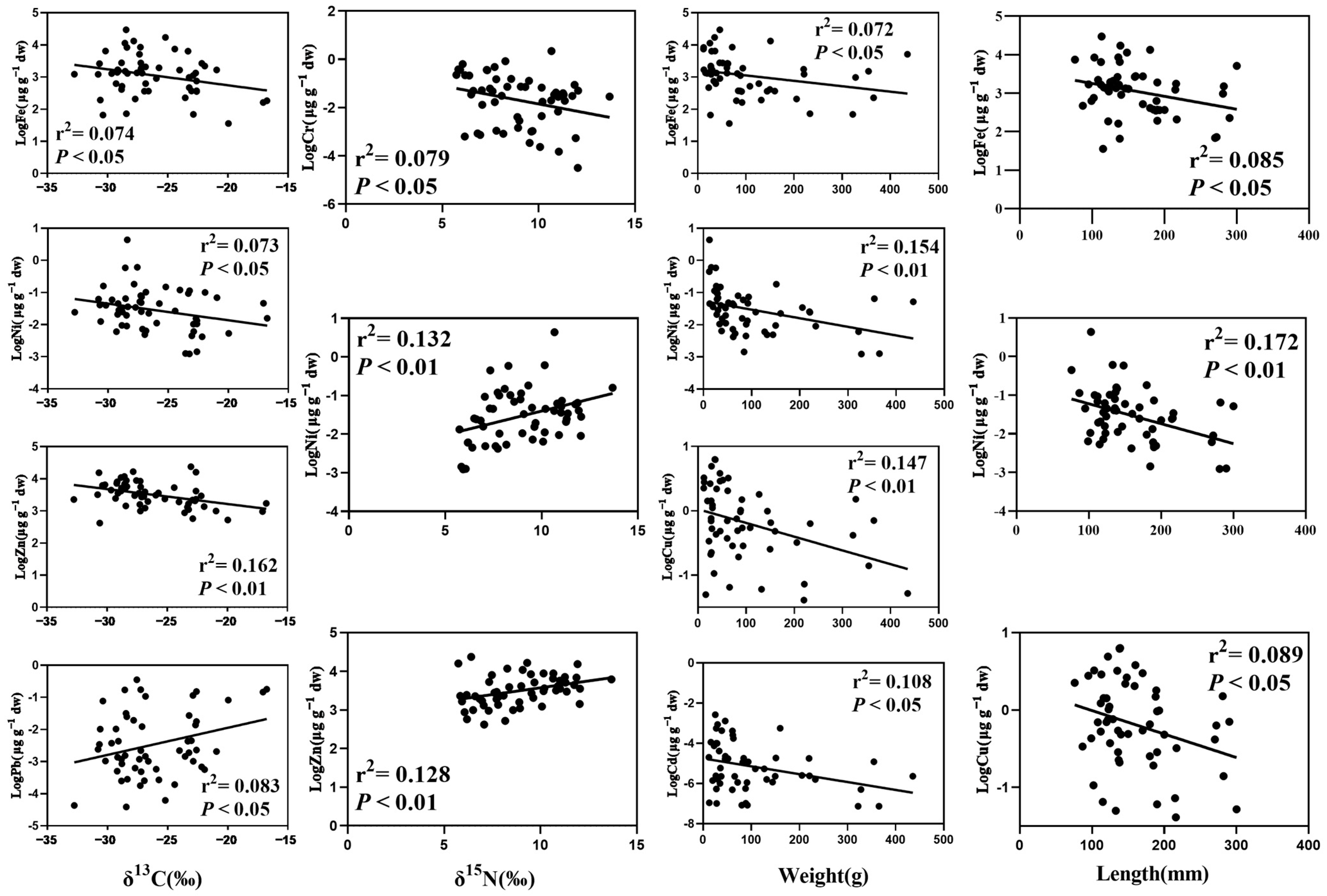
4.1. Variation of Metal Contents in Fish
4.2. The Feeding Habit and Living Habitat Had Great Significance on Heavy Metal Contents in Fish
4.3. The Biological Dilution of Metals in Fish
4.4. The Human Health Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grizzetti, B.; Lanzanova, D.; Liquete, C.; Reynaud, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Assessing water ecosystem services for water resource management. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 61, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, H.S.; Atlabachew, M. Review of characterization, factors, impacts, and solutions of Lake eutrophication: Lesson for lake Tana, Ethiopia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14233–14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tang, X.; Guo, W.; Lin, L.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal distribution dynamics of heavy metals in water, sediment, and zoobenthos in mainstream sections of the middle and lower Changjiang River. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 714, 136779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, J.P.; Ernest, D.W.; Kagley, A.N. A comparison of the non-essential elements cadmium, mercury, and lead found in fish and sediment from Alaska and California. Sci. Total. Environ. 2005, 339, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Fu, J. Trace elements in fish from Taihu Lake, China: Levels, associated risks, and trophic transfer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 90, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, S.; Ahmad, K. Heavy metal contamination in water and fish of the Hunza River and its tributaries in Gilgit–Baltistan: Evaluation of potential risks and provenance. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, R.; Imran, U.; Ullah, A.; Ullman, J.L.; Weidhaas, J. Health risks associated with accumulation of heavy metals in fish of Keenjhar Lake, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24162–24172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanbakhsh, M.; Javid, A.Z.; Hadi, M.; Fard, N.J.H. Heavy metals risk assessment in fish species (Johnius Belangerii (C) and Cynoglossus Arel) in Musa Estuary, Persian Gulf. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, N.; Nayeem, J.; Deb, N.; Hossain, S.; Kibria, M. Heavy metals contamination: Possible health risk assessment in highly consumed fish species and water of Karnafuli River Estuary, Bangladesh. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2021, 13, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Khan, M.A.; Ghosh, P. Assessment of variations in metal concentrations of the Ganges River water by using multivariate statistical techniques. Limnologica 2022, 95, 125989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yin, D.; Feng, X.; Wang, D. Bioaccumulation characteristics of mercury in fish in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243 Pt A, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.W.; Xiao, L.J.; Han, B.P. Seasonal dynamics of cyanobacteria assemblage in tropical large reservoirs, South China-using Dashahe and Gaozhou Reservoirs as examples. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 2027–2034. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Wang, M.H.; Lin, Z.W.; Xing, Q.; Li, Y.F.; Zheng, J.; Ren, M.Z. The pesticides concentrations of aquatic organism in Songtao Reservoir and their health risks via ingestion. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2016, 4, 114–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wada, E.; Terazaki, M.; Kabaya, Y.; Nemoto, T. 15N and 13C abundances in the Antartic Ocean with emphasis on the biogeochemical structure of the food web. Deep. Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1987, 34, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergin, M.; Saydam, C.; Baştürk, Ö.; Erdem, E.; Yörük, R. Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments from the two coastal inlets (Golden Horn Estuary and İzmit Bay) of the northeastern Sea of Marmara. Chem. Geol. 1991, 91, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, C.; Ikenaka, Y.; Nakayama, S.M.; Mizukawa, H.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Watanuki, Y.; Fukuwaka, M.; Ishizuka, M. Contamination status and accumulation characteristics of heavy metals and arsenic in five seabird species from the central Bering Sea. J. Veter-Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, Z.; Da, C. Distribution of heavy metals, stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) and risk assessment of fish from the Yellow River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, N.; Zaman, M.R. Evaluation of possible health risks of heavy metals by consumption of foodstuffs available in the central market of Rajshahi City, Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3867–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezemonye, L.I.; Adebayo, P.O.; Enuneku, A.A.; Tongo, I.; Ogbomida, E. Potential health risk consequences of heavy metal concentrations in surface water, shrimp (Macrobrachium macrobrachion) and fish (Brycinus longipinnis) from Benin River, Nigeria. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSY (China Statistical Yearbook). National Bureau of Statistics PRC; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IRIS. Integrated Risk Information System Online Database; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Ge, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Da, C. Occurrence, potential health risk of heavy metals in aquatic organisms from Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JECFA (Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives). Evaluations of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Fang, B.B.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, W.L.; Chang, W.J.; Du, M.Y.; Zhang, M. The spatio-temporal distribution of heavy metals in the surface water and sediment of the Lake Taihu Basin and assessment of their potential ecological risks. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2017, 33, 215–224. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, G.J.; Zhou, C.C.; Liu, R.Q. Temporal-spatial distribution and pollution assessment of dissolved heavy metals in Chaohu Lake. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 738–747. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, S. Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, and fish from Dongting Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34076–34090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Du, L. Tissue-specific distribution and bioaccumulation pattern of trace metals in fish species from the heavily sediment-laden Yellow River, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 128050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Ghosh, P.; Sakthivel, T.; Khan, A.M. Stable isotopic analysis of long-whiskered catfish (Sperata aor) otoliths for characterization of their habitat and relationship with water temperature in the Ganges River. Curr. Chin. Sci. 2023, 3, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Recommended Dietary Allowances, 10th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; Volume 2.
- USEPA. Risk-Based Concentration Table; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/reg3hwmd/risk/human/index.htm (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Anan, Y.; Kunito, T.; Tanabe, S.; Mitrofanov, I.; Aubrey, D.G. Trace element accumulation in fishes collected from coastal waters of the Caspian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Gui, D.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y. Risk for Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) and human health related to the heavy metal levels in fish from the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, A.B.; Sangün, M.K.; Yağlıoğlu, D.; Turan, C. Metals (major, essential to non-essential) composition of the different tissues of three demersal fish species from İskenderun Bay, Turkey. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fish of Dongting Lake, China: Effects of feeding habits, habitat preferences and body size. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, K.A.; Agusa, T.; Kubota, R.; Mochizuki, H.; Ramu, K.; Nishida, S.; Ohta, S.; Yeh, H.-M.; Subramanian, A.; Tanabe, S. Trace elements and stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) in fish from deep-waters of the Sulu Sea and the Celebes Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jitar, O.; Teodosiu, C.; Oros, A.; Gabriel, P.; Mircea, N. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in marine organisms from the Romanian sector of the Black Sea. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Xu, X.; Shi, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Q.; Shou, L. Heavy metal concentrations in tissues of marine fish and crab collected from the middle coast of Zhejiang Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Lam, K.S.P. Heavy metals (As, Hg and V) and stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) in fish from Yellow River Estuary, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 613–614, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Zhao, K.; Ding, W.; Li, J.; Liang, P.; Wu, S.; Wong, M. The level of mercury contamination in mariculture sites at the estuary of Pearl River and the potential health risk. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in freshwater fish in the central and eastern North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1 | |||||||
| Mn | 0.024 | 1 | ||||||
| Fe | 0.188 | 0.420 ** | 1 | |||||
| Ni | 0.250 | 0.239 | 0.495 ** | 1 | ||||
| Cu | 0.138 | −0.079 | 0.383 ** | 0.015 | 1 | |||
| Zn | 0.251 | 0.161 | 0.376 ** | 0.244 | 0.396 ** | 1 | ||
| Cd | −0.112 | 0.589 ** | 0.404 ** | 0.346 ** | −0.028 | 0.077 | 1 | |
| Pb | −0.167 | 0.111 | −0.063 | 0.198 | −0.139 | −0.132 | 0.185 | 1 |
| Water | Sediment | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | |
| This study | 0.27 | 25.73 | 37.12 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 7.81 | 0.01 | 0.62 | 51.73 | 255.31 | 14730.20 | 77.24 | 36.71 | 62.13 | 0.98 | 39.73 |
| Taihu lake [24] | 0.88 | - | - | - | 3.21 | 10.96 | 3.29 | 0.019 | 81.21 | - | - | 38.65 | 26.47 | 79.21 | NA | 33.02 |
| Chaohu Lake [25] | 1.63 | - | - | 1.92 | 4.55 | 20.67 | - | 2.08 | 11.89 | - | - | 14.96 | 8.93 | 103.26 | 0.63 | 26.77 |
| Dongting lake [26] | 0.62 | - | - | 2.50 | 20.91 | 1.49 | 88.97 | - | - | 41.65 | 45.46 | 322.6 | 2.87 | 57.96 | ||
| Yellow River [27] | 0.46 | 0.79 | 22.3 | 3.94 | 1.94 | 1.93 | 0.02 | 0.39 | 43.8 | 371 | 20500 | 22.1 | 16.3 | 44.7 | 0.15 | 10.8 |
| Omnivore | Carnivore | Pelagic | Benthopelagic | Demersal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment | Water | Sediment | |
| Total | −0.118 | 0.358 * | 0.033 | 0.087 | −0.025 | −0.745 | −0.110 | 0.463 ** | 0.042 | 0.368 |
| Cr | 0.024 | −0.135 | −0.224 | 0.082 | −0.427 | −0.450 | −0.161 | −0.113 | 0.203 | −0.141 |
| Mn | 0.104 | 0.104 | −0.164 | 0.466 | −0.456 | 0.934 | 0.172 | 0.365 * | −0.355 | −0.178 |
| Fe | −0.075 | 0.236 | 0.302 | 0.084 | 0.435 | −0.436 | −0.090 | 0.327 * | 0.394 | 0.557 * |
| Ni | −0.039 | −0.009 | 0.027 | −0.080 | −0.766 | −1.000 * | 0.053 | 0.186 | −0.004 | −0.094 |
| Cu | −0.214 | −0.225 | −0.204 | 0.626 * | 0.982 | −0.583 | −0.312 | −0.011 | 0.243 | 0.011 |
| Zn | 0.2 | 0.147 | 0.293 | 0.164 | −0.686 | −0.975 | 0.296 | 0.242 | 0.296 | 0.129 |
| Cd | −0.052 | 0.002 | 0.123 | 0.539 * | −0.85 | −0.969 | 0.090 | −0.032 | −0.344 | 0.397 |
| Pb | −0.036 | −0.006 | 0.127 | 0.140 | −0.877 | −0.681 | 0.046 | 0.083 | 0.049 | −0.23 |
| Heavy Metal Element | Estimated Daily Intake (EDI) (μg kg−1 bw day−1) | Permissible Tolerable Daily Intake (PTDI) (μg kg−1 bw day−1) | Oral Reference Dose (RfD) (μg kg−1 bw day−1) | Target Hazard Quotient (THQ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.027 | 2.86 a | 1500 d | 0.00002 |
| (0.008–0.062) | ||||
| Mn | 0.221 | 28.57 a | 140 e | 0.00158 |
| (0.061–1.163) | ||||
| Fe | 2.431 | 800 b | 700 d | 0.00347 |
| (0.998–6.513) | ||||
| Ni | 0.0262 | 4.26 c | 20 d | 0.00131 |
| (0.006–0.067) | ||||
| Cu | 0.098 | 500 b | 40 d | 0.00244 |
| (0.036–0.325) | ||||
| Zn | 3.622 | 857.14 c | 300 d | 0.01207 |
| (1.629–9.464) | ||||
| Cd | 0.001 | 0.828 b | 1 d | 0.00101 |
| (0.0001–0.0037) | ||||
| Pb | 0.016 | 3.57 b | 4 d | 0.00407 |
| (0.003–0.071) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, D.; Feng, H.; Zou, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, P.; Ji, Y.; Lek, S.; Guo, Z.; Fu, Q. Feeding Habit-Specific Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Fish in a Tropical Reservoir in Southern China. Fishes 2023, 8, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040211
Wu D, Feng H, Zou Y, Xiao J, Zhang P, Ji Y, Lek S, Guo Z, Fu Q. Feeding Habit-Specific Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Fish in a Tropical Reservoir in Southern China. Fishes. 2023; 8(4):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040211
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Di, Hao Feng, Ying Zou, Juan Xiao, Pengfei Zhang, Yuxiang Ji, Sovan Lek, Zhiqiang Guo, and Qiongyao Fu. 2023. "Feeding Habit-Specific Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Fish in a Tropical Reservoir in Southern China" Fishes 8, no. 4: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040211
APA StyleWu, D., Feng, H., Zou, Y., Xiao, J., Zhang, P., Ji, Y., Lek, S., Guo, Z., & Fu, Q. (2023). Feeding Habit-Specific Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Fish in a Tropical Reservoir in Southern China. Fishes, 8(4), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040211