Abstract
In the region of King William Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high Arctic, populations of salmonids including Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus), cisco (Coregonus autumnalis and C. sardinella) as well as lake whitefish (C. clupeaformis) are diadromous, overwintering in freshwater and transitioning to saline waters following ice melt. Since these fish were sampled at the same time and from the same traditional fishing sites, comparison of their skin structures, as revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing, has allowed an assessment of influences on wild fish bacterial communities. Arctic char skin microbiota underwent turnover in different seasonal habitats, but these striking differences in dispersion and diversity metrics, as well as prominent taxa involving primarily Proteobacteria and Firmicutes, were less apparent in the sympatric salmonids. Not only do these results refute the hypothesis that skin communities, for the most part, reflect water microbiota, but they also indicate that differential recruitment of bacteria is influenced by the host genome and physiology. In comparison to the well-adapted Arctic char, lake whitefish at the northern edge of their range may be particularly vulnerable, and we suggest the use of skin microbiomes as a supplemental tool to monitor a sustainable Indigenous salmonid harvest during this period of change in the high Arctic.
Keywords:
Arctic char; Salvelinus alpinus; Coregonus spp.; lake whitefish; cisco; microbiomes; Arctic; Nunavut; diadromy Key Contribution:
Skin-associated microbial communities of high Arctic salmonids are not simply dependent on water communities, reflecting host genome and physiology. Arctic char skin-associated microbial communities undergo striking changes in response to changing seasonal habitat and water salinity compared to lake whitefish, possibly suggesting lake whitefish maladaptation and vulnerability.
1. Introduction
Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) have a circumpolar distribution and represent the northernmost fish species on Earth [1]. At high latitudes, populations can be diadromous with seasonal migration to escape sub-zero temperatures in the sea by overwintering in freshwater lakes and rivers, with a return to saline waters to feed in the spring. Another salmonid, the closely related lake whitefish (Coregonus clupeaformis), is commonly found in freshwater lakes and rivers all year. Nonetheless, members of the Coregonus species complex (CSC) including lake whitefish and cisco (Arctic cisco, Coregonus autumnalis, and sardine cisco, Coregonus sardinella), are sympatric with Arctic char in the high Arctic, on King William Island and at adjacent mainland fishing sites in Nunavut, Canada. This region includes the northern extent of the lake whitefish range [2]. Here, as well as in the James-Hudson Bay area and the Yukon River, CSC can also be diadromous [3,4,5]. Indeed, traditional Indigenous knowledge shared by community members, or Inuit Qaujimajatuqangit (IQ), teaches that CSC in this region follow the annual migration of Arctic char and can be fished swimming upriver within days of the peak char autumn “run”. Such migration demands that these fish species physiologically and behaviorally adjust to seasonal environmental changes, but less known are any changes to their skin-associated microbiota. Here, we track migration-associated changes to skin microbiota in these sympatric salmonids to determine if these communities are influenced by environmental or host-specific factors.
Skin shares microbial species with the surrounding water. Indeed, most of the microbiota differences between distinct populations of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) could be attributed to their host waters [6,7,8]. As well, analyses of Atlantic salmon and Arctic char populations revealed that variations in water salinity could impact skin structure [7,9,10,11]. However, other abiotic and biotic factors may also influence fish microbiomes [12,13,14,15]. Immune health could play a role, with mucosal-associated skin lymph tissue, a mucous complex of immunoglobulins, antimicrobial peptides, mucins, and commensal bacteria, being critical to innate immunity [16,17]. Indeed, teleosts appear to promote the association of symbiotic bacteria, likely to help maintain skin immune function stability, with any disruption possibly resulting in dysbiosis, or the loss of beneficial microbes and an increased pathogen abundance that could culminate in an inflammatory response [15,16,18,19,20,21]. It is likely important that salmonids maintain immune function homeostasis and symbiotic skin bacteria during changes due to seasonal migration, and we suggest that such turnover could be orchestrated by the host.
Despite its importance to fish health, little is known about the drivers that influence skin microbiomes. Experimental work presents conflicting results. For example, skin microbiota in Atlantic salmon and catfish, Silurus glanis, were not prominently shaped by the host [7,22]. However, species differences were reported to have the largest influence on skin microbiota among three factors investigated in six different Gulf of Mexico teleosts [23]. Host influence on skin consortia was also shown in hybrids produced by crosses between domestic and wild brook char, Salvelinus fontinalis, and indicated that certain bacterial genera were influenced by three quantitative trait loci [24]. In non-human land mammals, skin microbiota appears to be most influenced by the host species, with geographical habitat being less influential [25]. The latter findings argue that the ecology of the bacterial community is inexorably woven into the phylogenetic history of the host, a process dubbed phylosymbiosis [25,26,27].
As noted, in the region of the Arctic under study, Arctic char and CSC are migratory and are fished from the same traditional sites. Therefore, these salmonids present a unique opportunity to compare skin microbial communities in wild sympatric species sampled from freshwater and sea fishing sites. Such investigation should allow insight into abiotic influences on the bacterial communities, provide a baseline for microbial populations in the face of anthropogenic change, and also illuminate any even minor host-specific genotype influences in salmonids that diverged ~50 million years ago [28]. Such monitoring can positively contribute to fish population health surveillance and be useful for future management of sustainable Arctic fishery ventures, in addition to informing local Inuit of skin bacteria that could be of some concern when consuming raw fish.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Fish, and Water Sampling
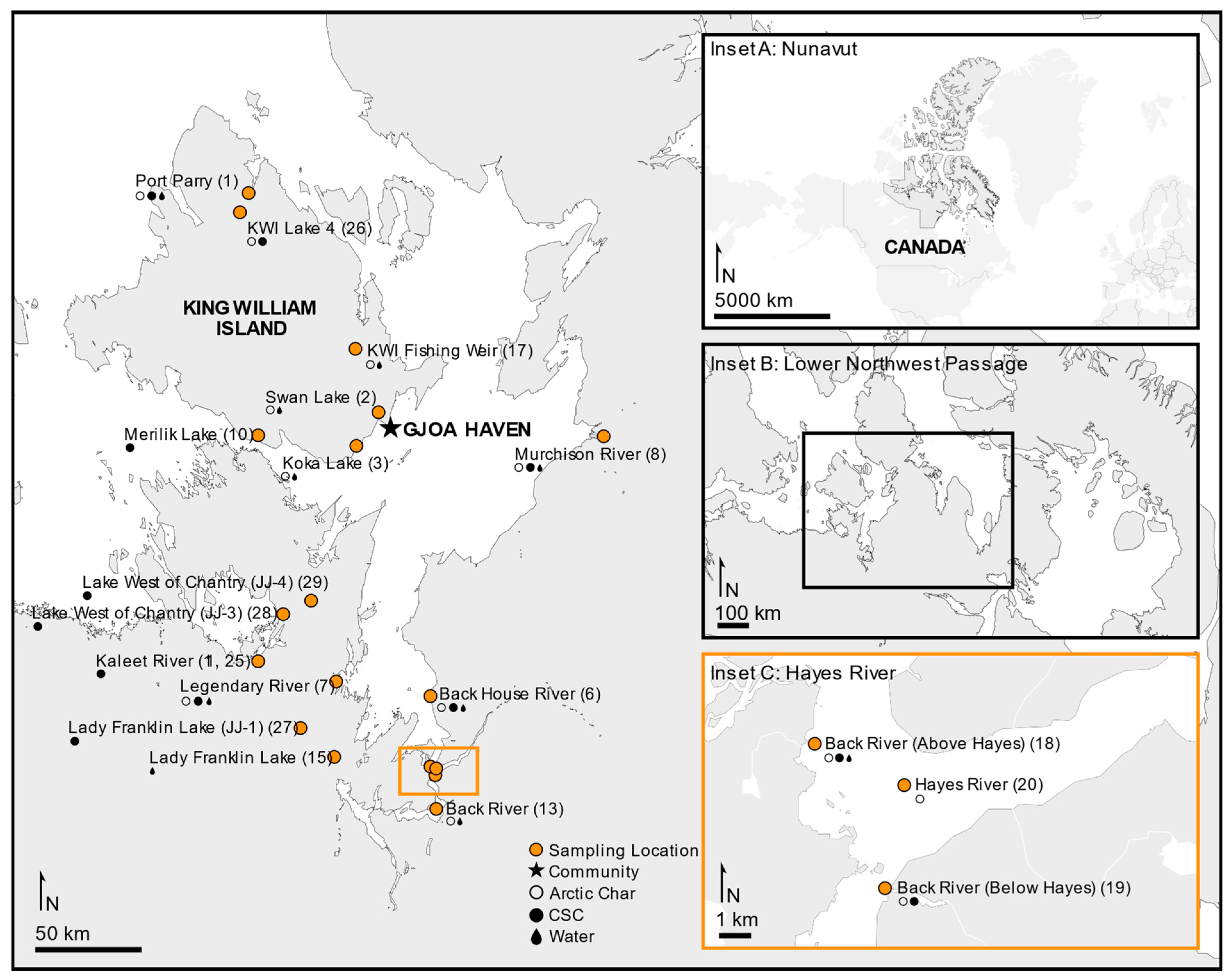
Fishing sites in the Kitikmeot region of Nunavut (NU) were located within 400 km of King William Island (KWI) and the community of Gjoa Haven, including the saline water bodies of Rasmussen Basin and Chantrey Inlet. Freshwater sites included six lakes and rivers, including a traditional stone weir river site (Figure 1). The subsistence fishing locations were chosen based on IQ sharing by local Inuit elders in association with the Hunters and Trappers Association of Gjoa Haven, NU. Licenses to fish for scientific purposes were obtained in accordance with section 52 of the general fishery regulations of the Fisheries Act, Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO), and water was sampled as permitted by the Nunavut Impact Review Board. Animal care permits were issued by the Freshwater Institute Animal Care Committee of DFO (S-18/19-1045-NU and FWI-ACC AUP-2018-63).
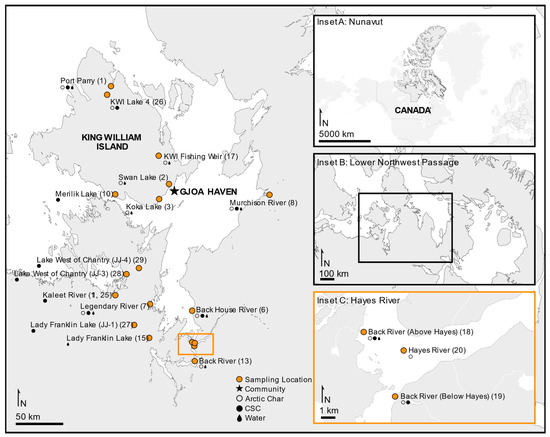
Figure 1.
Study area of the lower Northwest Passage located in the Kitikmeot region within the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Sampling sites are shown indicating where fished Arctic char (open circles), members of the Coregonus species complex (CSC; closed circles) or water (dark drop) was collected. Map produced using ArcGIS Online and Affinity Designer.
Fish samples were aseptically collected from net and traditionally spear-harvested Arctic char and CSC. The majority of fish were humanely euthanized according to standard procedures with a blow to the head, while traditionally spear-harvested fish were killed according to traditional Inuit fishing practices. Each sampled fish was assigned a unique barcode [29]. Skin mucous samples were taken along the left lateral line of each fish using a sterile scalpel or cotton-tipped swab, stored in sterile barcode-labeled 5 mL tubes, frozen, packed into coolers with frozen freezer packs and shipped by plane [11]. Because of the distance to the laboratory, shipping coolers were kept in walk-in freezers during overnight layovers, and the skin samples were subsequently stored in −20 °C freezers. Once the aseptic skin samples were obtained at the fishing sites, the fish were weighed, measured for fork length (mm), and dissected to obtain otoliths, which were subsequently dried and used for age analysis as previously described [30,31].
Water samples were taken from as many fishing sites as was logistically possible (Figure 1), with up to 2 L of water filtered through sterile 0.22 μm filters (Pall) in triplicate. The filters were then frozen and transported in insulated containers at −20 °C, then stored at −80 °C. Additional water samples were collected in 50 mL plastic tubes, shipped with the skin samples but stored at −80 °C upon arrival at the laboratory. The water samples were thawed and assessed for specific conductivity using a conductivity meter (Traceable Fisherbrand, Fisher Scientific, Hampton, NH, USA).
2.2. Fish Condition and Growth Curve Calculations
Fulton’s condition factor was calculated according to Barnham and Baxter as:
where mass (or weight, W) was measured in g and length (L) in mm [32]. Otolith age data were extrapolated for 12 Arctic char, four lake whitefish, and two ciscos, using a size-at-age key [33]. Growth curves were calculated as previously described by dividing the mean fork-length (FL), measured in mm, by age for fish aged 3–28 (Arctic char), 4–43 (lake whitefish) and 2–27 years (cisco species) and log10 transformed to construct plots [11]. A standard incremental annual growth curve was constructed by line of best fit, and deviations from these standards were calculated as percent relative differences where the mean growth standard is determined as the value of FL·Age−1, predicted by the calculated mean annual incremental growth curve at the specified age of the fish as previously described [11].
2.3. DNA Extractions and Sequencing
DNA was extracted from skin mucosal samples using the NucleoSpin Soil Extraction Kit (Machery-Nagel GmbH, Düren, Germany) with modifications including a final elution with double-distilled sterile water (ddH2O) as previously described [11]. DNA extracts were diluted to ~50 ng μL−1, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification was performed using primers 8F and 1406R to generate the V1–V9 region of the bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene and then subsequently re-amplified using the V4–V5 region using primers 515F-Y and 926R [34,35]. Skin-derived Illumina libraries were sequenced on a MiSeq instrument (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). For water samples, the 16S rRNA gene V4–V5 region was amplified from each water sample as previously described and sequenced using a MiSeq instrument [36,37].
A total of 682 skin and 50 water samples, in addition to controls, were analyzed using Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology 2 (QIIME2) (version 2020.6) managed by automated exploration of microbial diversity (AXIOME3) [38,39]. DADA2 (version 2020.6) was used to remove primer sequences and chimeras, dereplicate, and denoise reads [40]. Taxonomy was assigned to amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) using a naive Bayesian classifier pre-trained with the SILVA database (release 138) [41]. The prevalence method in Decontam was used to identify contaminants using a threshold of 0.5 as described previously [42,43]. Beta diversity was assessed using PCoA ordination with a Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix, and alpha diversity using Chao1 and Shannon index metrics. Diversity analysis was conducted using phyloseq (version 1.40.0) in Rstudio (version 2022.2.03) running R (version 4.2.0) [44]. Skin and water sequences obtained have been made available in the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) database under accession number PRJEB48811.
2.4. Statistical Analyses, Data Availability, and Efforts to Reduce Environmental Impact
Beta diversity between groups was tested through both PERMDISP and PERMANOVA using the adonis2 functions in the vegan R package (version 2.6.2) and the pairwise Adonis function from the corresponding package (version 0.4) using 10,000 permutations [45,46,47,48]. As noted, alpha diversity was determined using the Chao1 and Shannon index as a measure of taxonomic abundance and diversity, respectively. One-way ANOVAs with post-hoc Tukey’s honest significant difference tests were performed to determine significant differences in means between factor groups with a 95% confidence threshold. Compact letter displays representing statistically significant groupings were generated using the R package multcompView (version 0.1.8). Bubble plots for taxonomic visualization were generated using ggplot2 (version 3.3.6) [49]. Similarity percentages (SIMPER) analyses were conducted using Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrices in PAST (Paleontological Statistics) (version 4.08) [50]. Core microbiomes were determined using the microbiome package in R (version 1.18.0) with phyloseq and thresholds of 0.001 and prevalence of 50% [51].
Fish samples and otoliths have been archived for future access, and fish sample metadata is available in the Polar Data Catalogue (PDC) as open access (PDC#312992; NA profile of IOS 19115:2003, uploaded 5 February 2020, doi: 10.21963/12992). Measures were taken by the authors to reduce the environmental impact of research activities as well as to include Indigenous community members. These efforts included the hiring of local Inuit fishers, employing community youth to prepare samples, and making the fish available to the local “food bank” and other community programs. Furthermore, the coordination of multiple investigations encouraged southern visitors to volunteer for social science projects and enabled the bulk purchase of reagents to share among other research groups. Additionally, supplies and samples were shipped as personal baggage to reduce packaging and costs.
3. Results
3.1. Condition Factors and Annual Incremental Growth
The use of extrapolated age data for ~2.5% of the salmonids allowed the calculation of the mean annual incremental growth for 377 Arctic char, 188 lake whitefish, and 136 cisco, for which measurements were available. Annual incremental growth of individual fish was plotted against the standard curves (Figure S1), which allowed the calculation of relative differences from the standard growth curves and showed an average percent deviation of 3.7% (standard deviation, SD = 19) for Arctic char, 0.8% (SD = 10.5) for lake whitefish and 2.4% (SD = 15.5) for the two cisco species. There were no statistical differences in deviations for any of the salmonid groupings from different freshwater sites, indicating that there was no phenotype divergence that might suggest resource polymorphism within the taxa.
Arctic char condition factor (K) was significantly higher at the grouped saline fishing sites compared to all freshwater habitats (p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA; Figure S2). As previously reported, there was no significant difference in the condition factor for cisco between different seasonal habitats, and in lake whitefish the condition factor was significantly higher when caught in freshwater than in saline environments (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA; Figure S2; [43]).
3.2. Arctic Char Skin Microbiome
A total of 441 Arctic char skin samples from fresh (n = 317) and saline (n = 124) waters were analyzed, including those obtained representing the change in seasonal habitats: autumn saline water (n = 124), autumn freshwater (n = 106), winter freshwater (n = 63), and spring freshwater (n = 148) (Figure 1). Across all seasonal habitats, Arctic char skin microbiomes were dominated by Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Firmicutes, and Actinobacteriota (Figure S3).
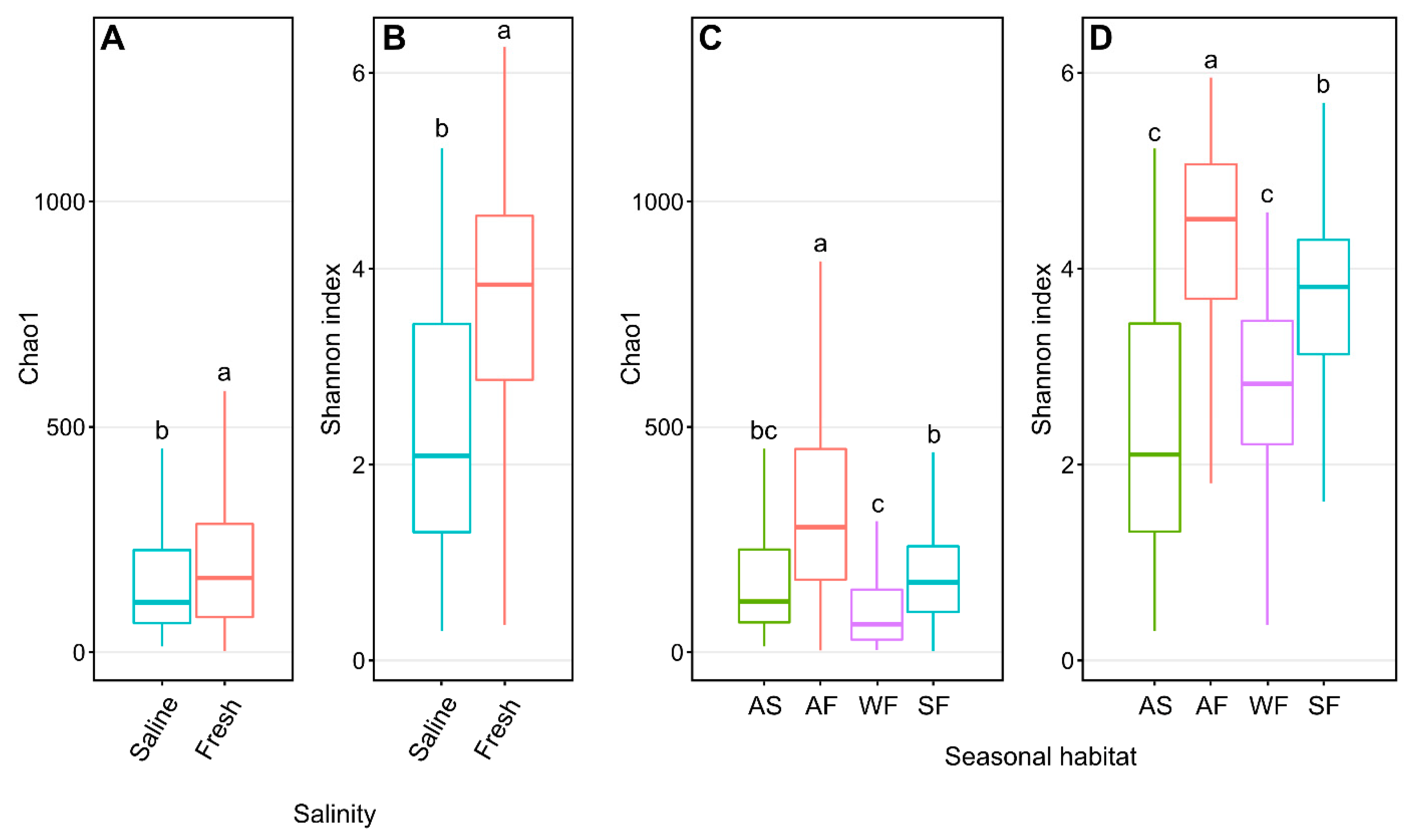
Freshwater Arctic char skin samples had significantly higher (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA) Shannon diversity than samples from saline waters (Figure 2A), with species richness likewise significantly higher (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA) in freshwater-caught samples (Figure 2B). When considering seasonal habitats along with water conditions, autumn freshwater-caught Arctic char had significantly greater (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) Shannon diversity (Figure 2C) and species richness (Figure 2D) than all other seasonal habitats.
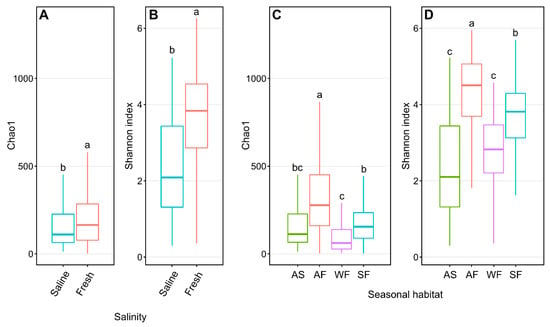
Figure 2.
Alpha diversity metrics of Chao1 and Shannon entropy assessments of Arctic char skin community richness and diversity, respectively. Plots show differences between samples obtained from saline water (S; n = 124) and freshwater (F; n = 317) (A,B) and different seasonal habitats (C,D) including samples obtained from autumn saline water (AS; n = 124), autumn fresh water (AF; n = 106), winter fresh water (WF; n = 63), and spring fresh water (SF; n = 148). Different lower-case letters within the graphs display significantly different (p < 0.001) groupings as determined by one-way ANOVA.
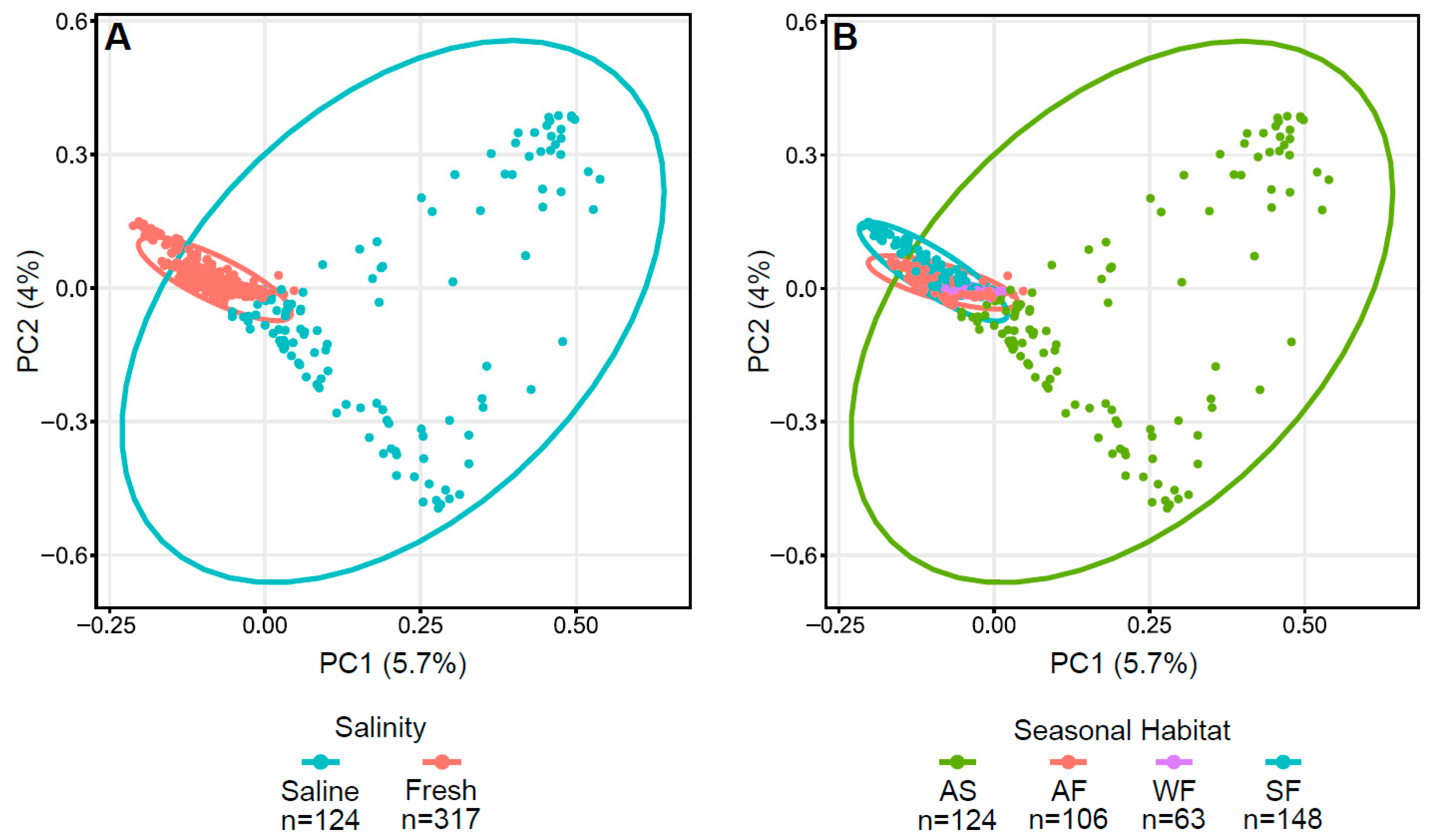
Bray–Curtis dissimilarity plots of Arctic char skin highlight the differences between fresh and saline waters, as well as autumn saline and other seasonal habitats (Figure 3) with significance verified using both PERMDISP (p < 0.001) and PERMANOVA (p < 0.001). Indeed, accounting for seasonality, autumn freshwater communities were significantly different from all others using both PERMDISP (p < 0.05) and PERMANOVA (p = 0.001).
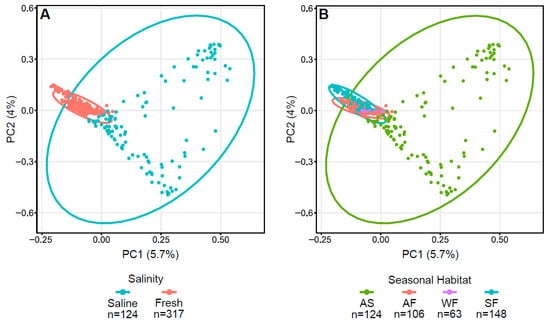
Figure 3.
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plots displaying dissimilarities in Arctic char skin samples using Bray–Curtis or beta diversity calculations. PCoA plots with (A) saline and freshwater environments and (B) seasonal habitats of autumn saline water (AS), autumn fresh water (AF), winter fresh water (WF), spring fresh water (SF). Number of fish samples per group (n) are indicated below the graphs.
Similarity percentages (SIMPER) analyses were performed to determine which ASVs were key to the differences between the saline and freshwater and seasonal habitat communities (Table S1). Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Firmicutes were the primary contributors to the distinctiveness of saline and freshwater communities. Photobacterium (Proteobacteria) and Tychonema (Cyanobacteria) consistently contributed the most to microbiota dissimilarity, at 9.7% and 5% between saline and freshwater and between autumn saline and autumn fresh conditions, respectively. In contrast, the same genera had a much lower average relative abundance in freshwater, consisting of 0.05% and 0.04%, 0.008% and 0%, 0%, and 0.0003% in autumn fresh, winter fresh, and spring freshwater habitats, respectively (Table S1). More diverse taxa were responsible for dissimilarity between the different freshwater seasonal habitats, including Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Planctomycetota, Verrucomicrobiota, and Actinobacteriota. When comparing autumn to winter freshwater, Staphylococcus (Firmicutes) contributed the most to dissimilarity, at 3.7%, with Escherichia-Shigella (Proteobacteria) second, at 3.4%. Staphylococcus, at 3.8%, was again the greatest contributor to dissimilarity in the transition from winter to spring freshwater, and Escherichia-Shigella, at 3.5% dissimilarity, was noted when the autumn and spring freshwaters were compared.
ASVs present in ≥50% of skin samples and >0.1% relative abundance are defined as representing core taxa, but when considering every seasonal habitat, this criterion was not satisfied for a single ASV. However, when only skin samples from saline fishing sites were considered, there were six core taxa identified (Table S2). Four belong to Cyanobacteria (Rivularia, Phormidesmis, Synechococcus sp., Tychonema, and Cyanobium) and two to Gammaproteobacteria (Psychrobacter and Photobacterium). No core bacteria were noted from all freshwater-caught char, but if these were classified as to seasonal habitat, eight taxa were identified from autumn freshwater-caught fish, including two Gammaproteobacteria (Polynucleobacter and Rhodoferax), two Verrucomicrobiae, (Chthoniobacter and Luteolibacter), one Planctomycetota (a Gemmataceae), one Cyanobacterim (Cyanobium), and two Actinomycetota (a Sporichthyaceae and an Acidimicrobiia). With a prolonged stay in freshwater, the core skin microbiomes of winter and spring-caught fish were reduced to single genera, the kleptoplastic or photosynthetic-associated taxa Formanifera (Planoglabratella opercularis) and Gammaproteobacteria (Rhodoferax), respectively.
3.3. Influence of Surrounding Water on Arctic Char Skin Communities
Water samples were dominated by Proteobacteria, Actinobacteriota, Bacteroidota, and Cyanobacteria for both saline and freshwater sites (Figure S4), as previously reported from coastal waters [52,53]. Alpha diversity metrics (Figure S5) and PCoA plots of the water taxa from different seasonal habitats (Figure S6) showed no distinct groupings for saline and fresh waters. Two of the prominent water phyla, the Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria (average relative abundances of 35% and 31% in fresh and saline, respectively, for Proteobacteria and 12% and 15% in fresh and saline, respectively, for Cyanobacteria), were also found on Arctic char skin (Figure S3). However, they had a different relative abundance on the skin (46% and 43% in fresh and saline skin samples, respectively, for Proteobacteria and 32% and 13% in fresh and saline, respectively, for Cyanobacteria), suggesting colonization bias. Notably, the relative abundance of Actinobacteriota decreased in spring freshwater compared to other water samples, but there was no significant change in the Arctic char skin community, reflecting that change in the fishing site waters. Likewise, the relative abundance of skin-associated Cyanobacteria decreased in spring freshwater habitats, but water microbiomes did not change with respect to this taxon. Bacteroidota also decreased in relative abundance on char caught in autumn saline and winter freshwater habitats, whereas water samples showed that phyla were reasonably consistent in these fished waters. Overall, individual taxa from the water communities are undoubtedly recruited from the water to Arctic char skin, but fish genomes and physiology appear to influence the relative bacterial abundance.
3.4. CSC Skin Microbiomes, Fishing Sites, and Water Microbiota
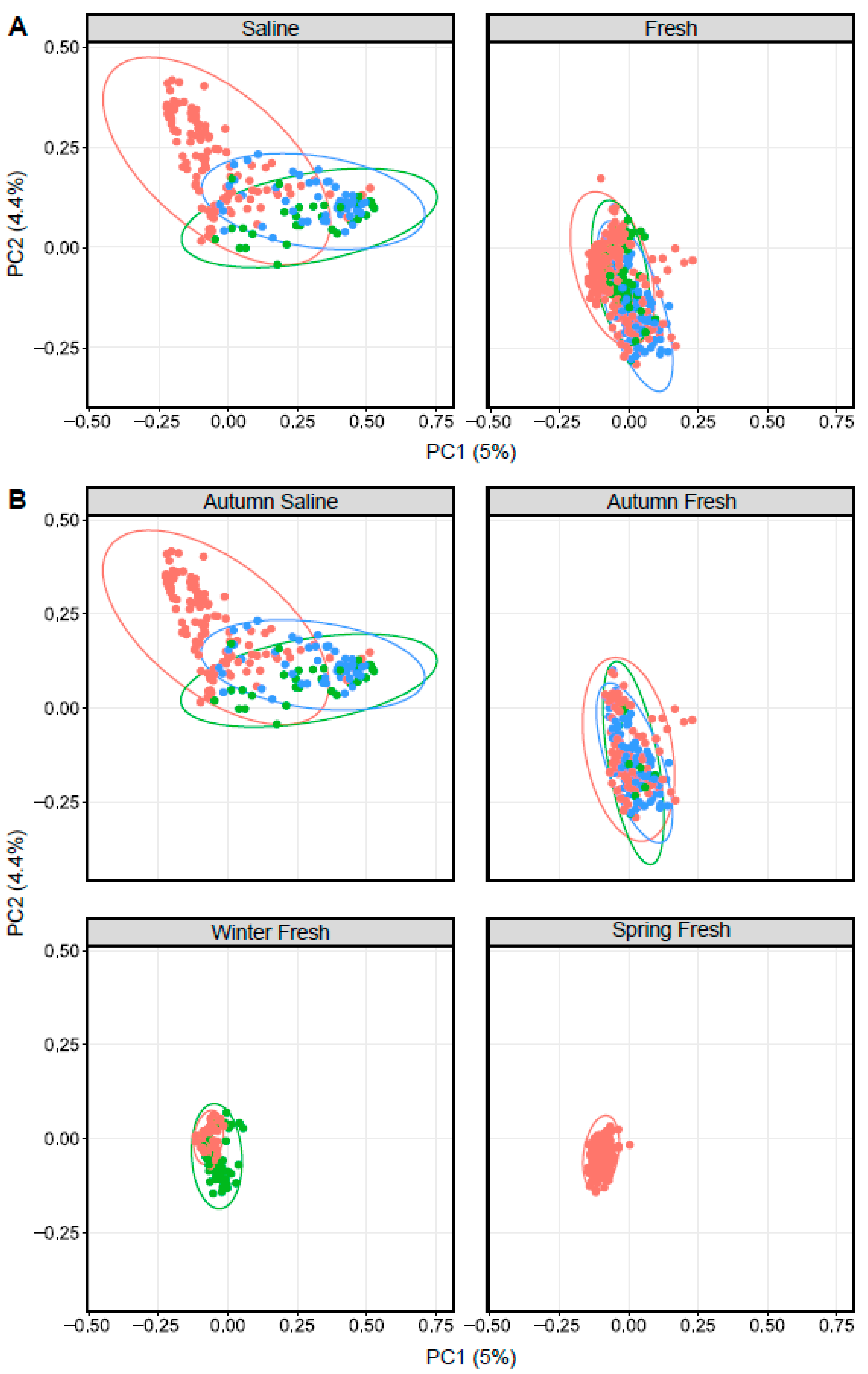
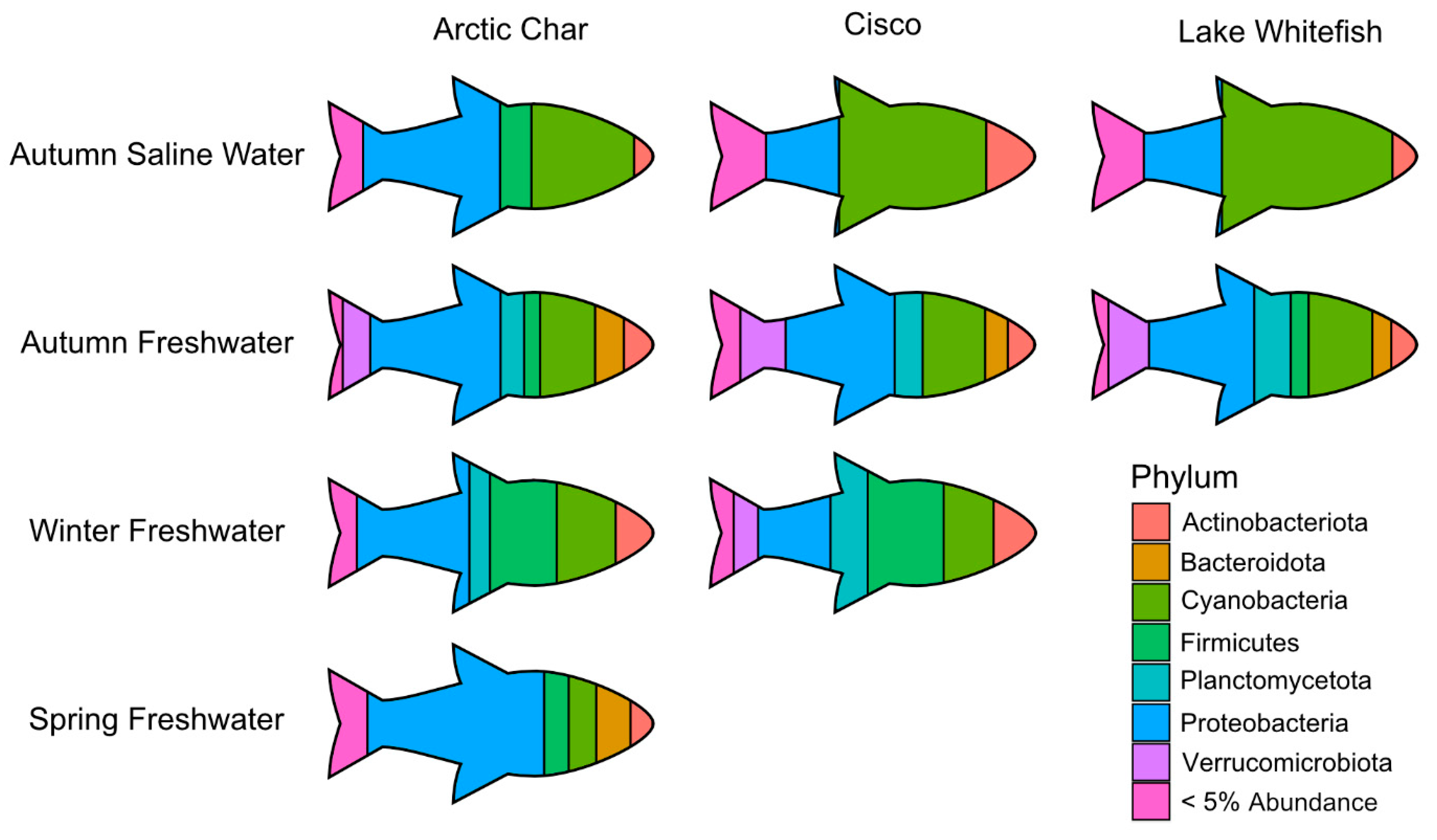
Similar to Arctic char, ordination based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity showed distinct groupings between lake whitefish (n = 140) as well as cisco (n = 101) caught in fresh and saline waters (Figure 4). As in Arctic char, CSC skin communities did not simply reflect the surrounding water microbiota (Figure 5 and Figure S4). For example, CSC skin showed a lower average relative abundance of Bacteroidota (3%) compared to water samples (29%) across all seasonal habitats. Firmicutes was relatively abundant in CSC skin, whereas this phylum represented less than 1% in water collected across all seasonal habitats. Cyanobacteria made up a higher average relative abundance on CSC skin (27%) compared to water samples (13%) with CSC skin having 46% relative abundance in the sea compared to 15% in saline water alone. Therefore, after environmental exposure to bacterial communities, there appears to be differential microbial recruitment on the CSC skin.
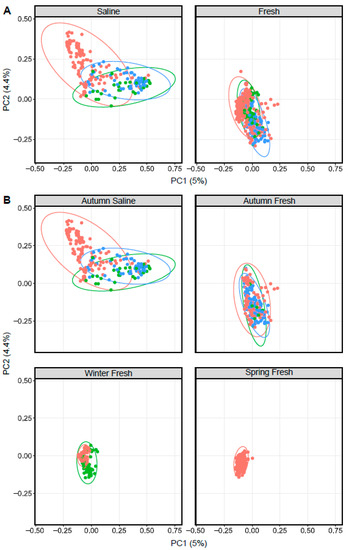
Figure 4.
Principal coordinate analysis plots displaying dissimilarity using Bray–Curtis distances between Arctic char (red dots), cisco (bright green) and lake whitefish (blue) in (A) saline and freshwater, as well as (B) different seasonal habitats as indicated above each graph.
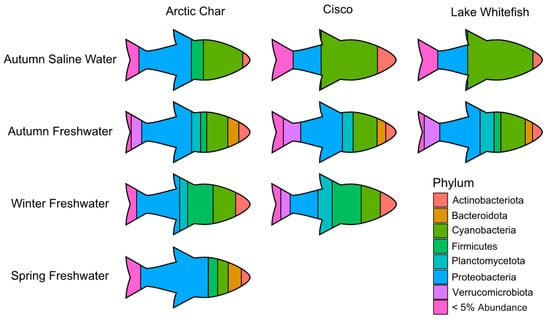
Figure 5.
A pictograph showing abundant skin-associated microbiota in the high Arctic salmonids under study and across seasonal gradients. For simplicity, only the most prominent phyla are shown at their average relative abundance in Arctic char, cisco and lake whitefish. Phyla comprising < 5% average relative abundance are grouped together and only those seasonal habitats with sufficient number of caught fish are shown.
3.5. Impact of Fish Host on Skin Microbiomes
Across all seasonal habitats, skin from all three salmonids showed a large relative abundance of Proteobacteria. However, in autumn saline waters, cisco and lake whitefish skin microbiomes were dominated by Cyanobacteria, in contrast to a 50% lesser abundance of that taxa in Arctic char (Figure 5). As the different salmonids swam up freshwater rivers in the autumn, the skin communities became more similar, but diverged again during the winter when cisco contained relatively more Verrucomicrobiota and Planctomycetota, compared to Arctic char with average relative abundance of Planctomycetota and Verrucomicrobiota at least doubling (6% to 12% and 3% to 8%, respectively). By the time spring arrived, Arctic char skin microbiota showed the highest relative abundance of Proteobacteria among all characterized skin-associated microbiomes.
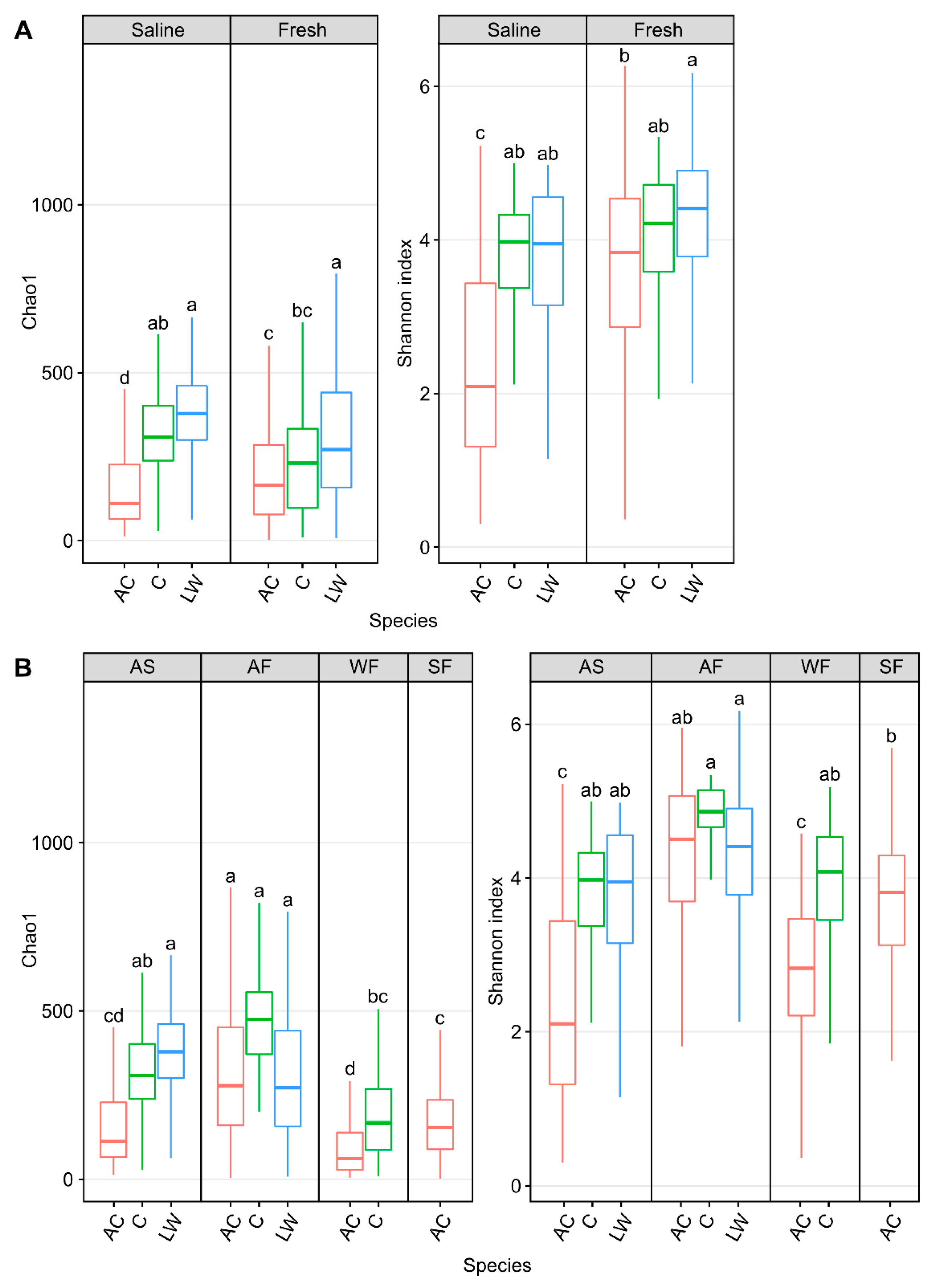
When these high Arctic sympatric salmonids were compared, skin alpha diversity, Chao1, in ocean-caught Arctic char was significantly (Chao1: p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA) lower than in both cisco and lake whitefish (Figure 6A). Community diversity in these chars were also lower than in freshwater samples (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA). Likewise, Arctic char skin community diversity was significantly lower (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA) than in lake whitefish and cisco under saline conditions and also significantly lower than in lake whitefish in freshwater samples. Overall, skin communities from Arctic char showed significantly decreased (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA) community abundance and diversity in autumn saline and winter fresh habitats. Notably, taxa changes along migratory routes, as seen by the shifts between seasonal habitats, were more pronounced in Arctic char compared to cisco and lake whitefish.
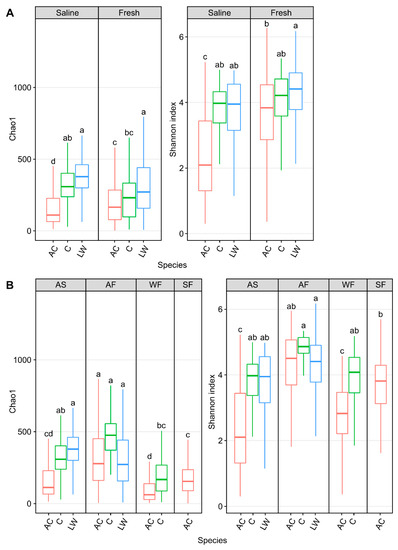
Figure 6.
Alpha diversity metrics, Chao1 and Shannon diversity, measuring skin microbial community abundance and diversity, respectively, of Arctic char (AC) and Coregonus species complex cisco (C) as well as lake whitefish (LW) in (A) saline and freshwater and (B) in different seasonal habitats (abbreviated as described in Figure 3 and situated above each graph). Lower case letters within each individual graph display significantly different (p < 0.001) groupings as determined by one-way ANOVA. It should be noted that data from lake whitefish and cisco (Hamilton et al., 2023 [43]) are presented here for comparison with the Arctic char calculated diversity.
Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrices comparing Arctic char and CSC skin communities in fish caught in waters of different salinities and seasonal habitat showed significant centroid differences (p < 0.001, PERMDISP and p < 0.005, PERMANOVA; Figure 4). Considering only seasonal habitat, Arctic char was consistently significantly different in diversity metrics than either cisco or lake whitefish. For example, in autumn saline and freshwater habitats as well as in winter freshwater habitats, Arctic char were significantly different (PERMDISP; p < 0.001, p < 0.05 and p < 0.005, respectively, and PERMANOVA; p < 0.005, p < 0.01, and p < 0.005, respectively).
4. Discussion
4.1. Skin Microbiota in Related Migrating Salmonids
Salmonoid skin epithelia are protected by a layer of mucus, which presumably acts to defend against pathogens, osmotic and mechanical stress, environmental perturbations as well as to conserve energy by reducing drag [12,54]. These secreted glycosylated mucins presumably foster colonization, particularly by biofilm-formers that are recruited from the surrounding waters, with fish benefits including protection against freeze-thaw, the sequestering of metals in oligotrophic environments and the production of antimicrobial metabolites to reduce pathogen colonization [7,55,56,57,58,59]. Although there are some differences in pathogen adhesion to different mucins [54], we are unaware of any differences in mucin chemistry in closely related salmonids. Thus, we hypothesized that related and sympatric Arctic char and CSC, fished from the same waters, would have the same or very similar communities. Indeed, the surrounding water microbiota has been argued to have the biggest influence on the teleost microbiome [7,58,60,61,62,63]. However, our hypothesis was not correct; even though water microbiota appeared to be relatively similar and overlapping, independent of salinity and seasonal change, the skin microbiota of the different salmonids changed (Figures S3 and S4). Only a portion of the water taxa were recovered on the skin, and depending on the seasonal habitat, there were some distinct fish skin communities (Figure 5). This strongly argues that wild salmonid hosts exert an important role on skin microbiome establishment.
As indicated, water samples had generally similar microbiota, but there was a decrease in Shannon diversity and species richness in winter- and spring-collected waters. Significantly, despite a similar diversity in autumn-sampled waters, independent of salinity, diversity of Arctic char skin communities in different autumn environmental habitats was not the same. For example, six taxa were classified as core community members in ocean-caught char, but none of these could be consistently identified at freshwater sites. Arctic char skin diversity increased after entry to freshwater, both as assessed by Shannon metrics, species richness and by PCoA plots, and this shift was also apparent when comparing the two autumn seasonal habitats (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4). In comparison, few core taxa were identified in CSC samples. In addition, there were no significant differences in the diversity of lake whitefish skin communities obtained from ocean and freshwater fishing sites (Figure 4; [43]). Indeed, our initial expectation that core microbiota would be shared among the different salmonids and between environments was not corroborated; distinct differences between Arctic char and CSC, cisco and most notably, lake whitefish, were observed.
Both Arctic char and cisco skin communities were relatively abundant in ASVs representing Actinobacteria, which are likely psychrophilic and commensal, with previous reports in rainbow trout gut microbiota [64,65,66]. Core taxa in ocean Arctic char skin communities also included Proteobacteria, represented by the low-temperature-tolerant Psychrobacter and Photobacterium. Both of these are known to form biofilms, and Photobacterium was one of the drivers of overall seasonal dissimilarity, with an average relative abundance ~400–1500-fold greater in ocean-caught fish than in freshwater samples. All three groups of ocean-caught salmonids were colonized by Cyanobacteria, which is not surprising considering that these primary producers, many of which are tolerant to low temperatures, synthesize bio-reactive compounds and can form multi-taxa biofilms [57,59,67,68]. Together, this phylum made up ~32% and ~25% of the ASVs in Arctic char and CSC, respectively. Nevertheless, of the five cyanobacteria found as part of the core in Arctic char sampled from saline fishing sites, only one, Cyanobium, was regularly found in cisco. Lake whitefish carried both Cyanobium and Planktothrix, with the latter genus not a core taxon in autumn saline-caught Arctic char or cisco. This may be cause for some concern, since some of these species produce microcystins that are associated with whitefish toxicity [43,69].
According to IQ, lake whitefish and cisco follow Arctic char upriver and indeed, nets and spears pulled from these waters frequently contained char and CSC. This autumn migration was associated with a partial turnover of skin taxa in these salmonids. As noted, diversity and species richness increased in Arctic char during this run but not in CSC. In Arctic char, Cyanobium was retained during the swim upriver, but turnover resulted in replacement by autumn freshwater taxa, including Luteolibacter and planktonic Polynucleobacter and Rhodoferax that all associate with biofilms [70,71,72,73]. A few taxa overlapped in the sympatric salmonids, and although not consistent enough to be part of a core, Luteolibacter and Chthoniobacter, the latter a genus previously reported in ice-covered lakes, were the most frequent ASVs in communities from autumn freshwater-caught lake whitefish and in cisco, a ASV corresponding to Candidatus Bacilloplasma, which was previously identified as part of the Atlantic salmon microbiome, predominated [74,75]. Fewer fish were obtained in the winter and spring from lines set under the ice, but in overwintering Arctic char there was a loss of Shannon diversity and species richness associated with these seasonal habitats, which in this case, was also seen in the water communities. The number of relatively consistent distinct core skin bacteria declined so much that the Arctic char skin was represented by a single genus in each of these under ice habitats.
4.2. Adaptation to Environmental Conditions, a Changing Climate, and Fisheries Management
The three salmonids shared a common ancestor ~50 million years ago in the ice-free Eocene Arctic Ocean. Arctic char retained their circumpolar distribution after the last glaciation, but ancestral CSC colonized North American lakes and are currently extending their northern range [1,2,28,76]. Thus, Arctic char should be well adapted to high Arctic conditions, and cisco may also be so, since they frequently seasonally migrate throughout their range. In contrast, diadromy is not frequent in lake whitefish worldwide. However, at their northern limits, this behaviour may be mandated by the low resources in high Arctic lakes [1,3,77,78,79]. Migration to and from oligotrophic lakes and the sea requires that their skin, a major component of their immune system [80,81], is safeguarded with commensal bacteria that form biofilms. Certain microbes from the water column appear to join as a core part of the consortium depending on water salinity, with the salmonid skin facilitating the proliferation of specific microbiota from the water column as shown here and supported by previous findings [24]. As Arctic char swim upriver in the autumn there is a transient increase in microbiota diversity, which is associated with a turnover of members of the skin community, presumably increasing fitness by recruiting beneficial taxa from the water. For example, Photobacterium represented more than 19% of the taxa in Arctic char caught in saline waters, and since species within this bacterial genus produce antibacterial compounds, these could inhibit the growth of competing bacteria [82]. Wild Arctic char appear to have developed a symbiotic relationship with this taxon, as suggested by its prevalence in both skin- and intestine-associated microbiomes in the autumn saline seasonal habitat (Figure S1; [83]). Cyanobium sp. with antibacterial and antiviral properties likely also contributes to this role, and in this case is part of the autumn saline core bacteria in all three salmonids.
As indicated, diadromous Arctic char are well adapted to their environment. These salmonids showed a higher condition (K) at the start of their autumn migration before swimming upriver, while cisco showed no condition differences between these seasonal habitats. In contrast, lake whitefish may not be as well adapted, since they had a significantly lower average condition upon their return from summer feeding compared to migrating freshwater-caught fish. Certain lake whitefish year classes were absent in the otolith data set, suggesting that there may have been lower recruitment in certain year classes, and in contrast to an increase in diversity that accompanied the autumn habitat transition seen in Arctic char, mean community richness did not increase in lake whitefish. It has been suggested that a shift in microbiota can assist fish to cope with hypotonic stress [84], and thus this difference may also reflect the fitness cost to lake whitefish at the edge of their range. In addition, the presence of possibly microcystin-producing Planktothrix as a core taxon only in lake whitefish may be cause for concern. Taken together, it is migratory lake whitefish, and not Arctic char or cisco, which may be less able to cope with climate change. We therefore recommend that these populations be targeted for future monitoring using this baseline data.
Diadromous Arctic char present with cisco and lake whitefish at traditional fishing sites have been harvested by Indigenous peoples throughout their oral history and, we hope, well into the future. As noted, the additional stress associated with climate change may be particularly challenging for migratory lake whitefish with biotic and abiotic stresses telegraphed to the skin consortium, offering a new tool to monitor the health of fish populations, in addition to enumeration and condition calculations. It is not known if any members of the skin consortium pose a risk to humans, but since Inuit frequently consume raw fish, knowledge of the timing of pathogen risk could help inform fishers to mitigate potential human health risks. For example, since skin microbiomes may be more stable in the autumn saline environment and therefore less susceptible to disease, community members might consider choosing to fish the autumn “runs” closer to the river outflow rather than upriver, where the microbiota is more likely to be in a transition state. To recapitulate, we have shown that distinct differences between sympatric salmonid skin-associated communities reflect salmonid genomic differences that help drive differential colonization. Such analysis, it is hoped, will contribute to future sustainable management of Arctic fisheries, particularly under increasing intergovernmental claims and commercial interests in the region, whilst maintaining Indigenous fishing rights and the interests and health of local communities.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes8040214/s1, All supplemental information including Table S1: SIMPER analyses; Table S2: core microbiomes; Figure S1: growth curves; Figure S2: condition factors; Figure S3: all skin microbiota phyla; Figure S4: all water microbiota phyla; Figure S5: alpha diversity of water microbiomes; Figure S6: beta diversity of water microbiomes.
Author Contributions
Sample processing was done by E.F.H., sequencing was performed by C.W.G., J.D.N. and K.E., data analysis by J.D.N., C.W.G., E.F.H., K.E., J.M.C. and C.L.J., figures made by C.L.J., study design by V.K.W., initial draft written by V.K.W. and C.L.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the “Towards a Sustainable Fishery for Nunavummiut” project, a large-scale Genome Canada project funded by the Government of Canada through Genome Canada and the Ontario Genomics Institute (OGI-096), as well as associated and in-kind support from the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation, CanNor, Nunavut Arctic College, and the Government of Nunavut. Important additional funding was provided by the Northern Scientific Training Program (Polar Knowledge Canada) and Queen’s University to EH, and a Discovery Grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (Canada) to VKW.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Freshwater Institute Animal Care Committee of the Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada (S-18/19-1045-NU and FWI-ACC AUP-2018-63).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is openly available in the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) database under accession number PRJEB48811 at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/view/PRJEB48811 (uploaded on 1 September 2022).
Acknowledgments
We thank the residents of Gjoa Haven, Nunavut, the Gjoa Haven Hunters and Trappers Association, community fishers, and youth for identifying fishing sites, for their invaluable IQ, as well as sampling expertise and preparation. Geraint Element and Peter van Coverden de Groot facilitated the collection and shipping of many samples to the laboratory, and GIS services consultant, Eric Daechsel, made the initial map. Kristy Moniz is thanked for general laboratory assistance, with age and growth interpretation assistance from Bronte McPhedran, Jordan Balson and Kate Brouwer. We are grateful to Stephan Schott and his social science team as well as W. Leggett, L. Harris, and K. Hedges for supporting our efforts to investigate Arctic fish.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Klemetsen, A.; Amundsen, P.A.; Dempson, J.B.; Jonsson, B.; Jonsson, N.; O’Connell, M.F.; Mortensen, E. Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar L., Brown Trout Salmo trutta L. and Arctic Charr Salvelinus alpinus (L.): A Review of Aspects of Their Life Histories. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2003, 12, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, W.B.; Crossman, E.J. Freshwater Fishes of Canada. Fish. Res. Board Can. Bull. 1973, 184, 966. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, R.; Dodson, J.J.; Power, G. Life History Variations of Anadromous Cisco (Coregonus artedii), Lake Whitefish (C. clupeaformis), and Round Whitefish (Prosopium cylindraceum) Populations of Eastern James–Hudson Bay. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.; Bickford, N.; Severin, K. Otolith Trace Element Chemistry as an Indicator of Anadromy in Yukon River Drainage Coregonine Fishes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2007, 136, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, I.; Das, P.; McPhedran, B.E.; Casselman, J.M.; Moniz, K.L.; van Coeverden de Groot, P.; Chen, C.Y.; Walker, V.K. Correlation of Mercury Occurrence with Age, Elemental Composition, and Life History in Sea-Run Food Fish from the Canadian Arctic Archipelago’s Lower Northwest Passage. Foods 2021, 10, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sun, G.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Intestinal Microbiota of Healthy and Unhealthy Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar L. in a Recirculating Aquaculture System. J. Ocean Limnol. 2018, 36, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.M.U.; Consuegra, S.; Hitchings, M.; de Leaniz, C.G. Interpopulation Variation in the Atlantic Salmon Microbiome Reflects Environmental and Genetic Diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00691-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvain, F.É.; Holland, A.; Bouslama, S.; Audet-Gilbert, É.; Lavoie, C.; Val, A.L.; Derome, N. Fish Skin and Gut Microbiomes Show Contrasting Signatures of Host Species and Habitat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00789-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, J.; Kiron, V. Transition from Freshwater to Seawater Reshapes the Skin-Associated Microbiota of Atlantic Salmon. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler, C.E.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A. Seawater Transfer Alters the Intestinal Microbiota Profiles of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.F.; Element, G.; van Coeverden de Groot, P.; Engel, K.; Neufeld, J.D.; Shah, V.; Walker, V.K. Anadromous Arctic Char Microbiomes: Bioprospecting in the High Arctic. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Danilowicz, B.S.; Meijer, W.G. The Diversity of Bacterial Communities Associated with Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueneman, J.G.; Parfrey, L.W.; Woodhams, D.C.; Archer, H.M.; Knight, R.; McKenzie, V.J. The Amphibian Skin-Associated Microbiome across Species, Space and Life History Stages. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apprill, A. Marine Animal Microbiomes: Toward Understanding Host–Microbiome Interactions in a Changing Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Wong, M.K.-S.; Hyodo, S.; Goto, S.; Hamasaki, K. Temperature Modulation Alters the Gut and Skin Microbial Profiles of Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1027621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Parra, D.; Gomez, D.; Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.A.; Von Gersdorff Jorgensen, L.; LaPatra, S.E.; Sunyer, J.O. Teleost Skin, an Ancient Mucosal Surface That Elicits Gut-Like Immune Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13097–13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.Á.; Cerezuela, R. Fish Mucosal Immunity: Skin. In Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Beck, B.H., Peatman, E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharschmidt, T.C.; Fischbach, M.A. What Lives on Our Skin: Ecology, Genomics and Therapeutic Opportunities of the Skin Microbiome. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2013, 10, e83–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenerman, P.; Ogg, G. Killer T Cells Show Their Kinder Side. Nature 2018, 555, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, J.L.; Harrison, O.J.; Han, S.J.; Byrd, A.L.; Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Villarino, A.V.; Sen, S.K.; Shaik, J.; Smelkinson, M.; Tamoutounour, S.; et al. Non-classical Immunity Controls Microbiota Impact on Skin Immunity and Tissue Repair. Cell 2018, 172, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, J.A.; Zhang, L.J.; Williams, M.R.; Gangoiti, J.A.; Huang, C.M.; Gallo, R.L. Inhibition of HDAC8 and HDAC9 by Microbial Short-Chain Fatty Acids Breaks Immune Tolerance of the Epidermis to TLR Ligands. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, eaah4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; Paz-Vinas, I.; Veyssière, C.; Santoul, F.; Loot, G.; Ferriol, J.; Boulêtreau, S. Environmental Conditions and Neutral Processes Shape the Skin Microbiome of European Catfish (Silurus glanis) Populations of Southwestern France. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A.M.; Tao, Z.; Bullard, S.A.; Arias, C.R. Diversity of the Skin Microbiota of Fishes: Evidence for Host Species Specificity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, S.; Sauvage, C.; Bernatchez, L.; Audet, C.; Derome, N. Interindividual Variations of the Fish Skin Microbiota: Host Genetics Basis of Mutualism? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.A.; Müller, K.M.; Weese, J.S.; Neufeld, J.D. Comprehensive Skin Microbiome Analysis Reveals the Uniqueness of Human Skin and Evidence for Phylosymbiosis within the Class Mammalia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5786–E5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.W.; Kohl, K.D.; Brucker, R.M.; van Opstal, E.J.; Bordenstein, S.R. Phylosymbiosis: Relationships and Functional Effects of Microbial Communities across Host Evolutionary History. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e2000225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.; Salinas, I. Under Pressure: Interactions between Commensal Microbiota and the Teleost Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crête-Lafrenière, A.; Weir, L.K.; Bernatchez, L. Framing the Salmonidae family phylogenetic portrait: A more complete picture from increased taxon sampling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lougheed, D.R.; Lougheed, S.C.; Moniz, K.; Walker, V.K.; Colautti, R.I. baRcodeR: An Open-Source R Package for Sample Labelling. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.E.; Casselman, J.M.; Jones, C.M. Bomb Radiocarbon Chronologies in the Arctic, with Implications for the Age Validation of Lake Trout (Salvelinus namaycush) and Other Arctic Species. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casselman, J.M.; Jones, C.M.; Campana, S.E. Bomb Radiocarbon Age Validation for the Long-Lived, Unexploited Arctic Fish Species Coregonus clupeaformis. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnham, C.; Baxter, A. Condition Factor, K, for Salmonid Fish. Fisheries Notes. Nat. Resour. Environ. 1998, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Isermann, D.A.; Knight, C.T. A Computer Program for Age-Length Keys Incorporating Age Assignment to Individual Fish. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2005, 25, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every Base Matters: Assessing Small Subunit rRNA Primers for Marine Microbiomes with Mock Communities, Time Series and Global Field Samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quince, C.; Lanzen, A.; Davenport, R.J.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Removing Noise from Pyrosequenced Amplicons. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, J.; Yergeau, E.; Fortin, N.; Cobanli, S.; Elias, M.; King, T.L.; Greer, C.W. Chemical Dispersants Enhance the Activity of Oil-and Gas Condensate-Degrading Marine Bacteria. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2793–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobanli, S.E.; Wohlgeschaffen, G.; Ryther, C.; MacDonald, J.; Gladwell, A.; Watts, T.; Greer, C.W.; Elias, M.; Wasserscheid, J.; Robinson, B.; et al. Microbial Community Response to Simulated Diluted Bitumen Spills in Coastal Seawater and Implications for Oil Spill Response. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2022, 98, fiac033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.; Doxey, A.C.; Neufeld, J.D. AXIOME3: Automation, Extension, and Integration of Microbial Ecology. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A Comprehensive Online Resource for Quality Checked and Aligned Ribosomal RNA Sequence Data Compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.M.; Proctor, D.M.; Holmes, S.P.; Relman, D.A.; Callahan, B.J. Simple Statistical Identification and Removal of Contaminant Sequences in Marker-Gene and Metagenomics Data. Microbiome 2018, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.F.; Juurakko, C.L.; Engel, K.; de Groot, P.J.C.; Casselman, J.M.; Greer, C.W.; Neufeld, J.D.; Walker, V.K. Characterization of Skin- and Intestine Microbial Communities in Migrating High Arctic Lake Whitefish and Cisco. bioRxiv. 2023. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.03.08.531621v1 (accessed on 12 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J. A New Method for Non-Parametric Multivariate Analysis of Variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Distance-Based Tests for Homogeneity of Multivariate Dispersion. Biometrics 2006, 62, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, B.H.; Anderson, M.J. Fitting Multivariate Models to Community Data: A Comment on Distance-Based Redundancy Analysis. Ecology 2001, 82, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizu, P.M. PairwiseAdonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using Adonis, R Package Version 0.4. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Wickham, H. Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (ggplot2); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S. Microbiome R Package. Bioconductor 2017. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/microbiome.html (accessed on 12 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wawrik, B.; Liu, Z. Different Bacterial Communities Involved in Peptide Decomposition between Normoxic and Hypoxic Coastal Waters. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.; Lian, E.; Liu, D.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R. Bacterial and Protistan Community Variation across the Changjiang Estuary to the Ocean with Multiple Environmental Gradients. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padra, J.T.; Murugan, A.V.; Sundell, K.; Sundh, H.; Benktander, J.; Lindén, S.K. Fish Pathogen Binding to Mucins from Atlantic Salmon and Arctic Char Differs in Avidity and Specificity and Is Modulated by Fluid Velocity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Kan, F.W.K.; She, Y.M.; Walker, V.K. Biofilm, Ice Recrystallization Inhibition and Freeze-Thaw Protection in an Epiphyte Community. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2012, 48, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; De La Fuente, L.; Arias, C.R. Biofilm Formation by the Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium columnare: Development and Parameters Affecting Surface Attachment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5633–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmas, N.A.; Barker, G.; Anesio, A.M.; Sánchez-Baracaldo, P. Genomic Mechanisms for Cold Tolerance and Production of Exopolysaccharides in the Arctic Cyanobacterium Phormidesmis Priestleyi BC1401. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.M.U.; Rodriguez-Barreto, D.; Castaldo, G.; Gough, P.; Consuegra, S.; de Leaniz, C.G. Environmental Plasticity and Colonisation History in the Atlantic Salmon Microbiome: A Translocation Experiment. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliara, P.; De Benedetto, G.E.; Francavilla, M.; Barca, A.; Caroppo, C. Bioactive Potential of Two Marine Picocyanobacteria Belonging to Cyanobium and Synechococcus Genera. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, S.; Bernatchez, L.; Audet, C.; Derôme, N. Network Analysis Highlights Complex Interactions between Pathogen, Host and Commensal Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarello, M.; Villeger, S.; Bouvier, C.; Bettarel, Y.; Bouvier, T. High Diversity of Skin-Associated Bacterial Communities of Marine Fishes Is Promoted by Their High Variability among Body Parts, Individuals and Species. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost Microbiomes: The State of the Art in Their Characterization, Manipulation and Importance in Aquaculture and Fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øygarden, E.T. Influence of Genetic Background and Environmental Factors on the Skin and Gut Microbiota of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Fry. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2017. Available online: https://ntnuopen.ntnu.no/ntnu-xmlui/handle/11250/2454377 (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Guardabassi, L.; Dalsgaard, A.; Olsen, J.E. Phenotypic Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Acinetobacter spp. Isolated from Aquatic Sources. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 87, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, K.; Christner, B.; Staley, J. Diversity of Psychrophilic Bacteria from Sea Ice and Glacial Ice Communities. In Extremophiles Handbook; Horikoshi, K., Ed.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2011; pp. 794–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Yu, Y.; Su, J.; Xu, Z. Alterations of the Mucosal Immune Response and Microbial Community of the Skin upon Viral Infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, B.; Hoeger, S.J.; O’Brien, E.; Dietrich, D.R. Oral Toxicity of the Microcystin-Containing Cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens in European Whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 79, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, S.I.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Romeu, M.J.; Morais, J.; Jong, E.D.; Sjollema, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Mergulhão, F.J. Unveiling the Antifouling Performance of Different Marine Surfaces and Their Effect on the Development and Structure of Cyanobacterial Biofilms. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancrace, C.; Barny, M.A.; Ueoka, R.; Calteau, A.; Scalvenzi, T.; Pédron, J.; Humbert, J.-F.; Gugger, M. Insights into the Planktothrix Genus: Genomic and Metabolic Comparison of Benthic and Planktic Strains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W.; Jezberová, J.; Koll, U.; Saueressig-Beckm, T.; Schmidt, J. Complete Ecological Isolation and Cryptic Diversity in Polynucleobacter Bacteria Not Resolved by 16S rRNA Gene Sequences. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1642–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Meng, F. New Insights into the Spatial Variability of Biofilm Communities and Potentially Negative Bacterial Groups in Hydraulic Concrete Structures. Water Res. 2017, 123, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, F.; Acuña, V.; Sabater, S. Multiple Stressors Determine Community Structure and Estimated Function of River Biofilm Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, E00291-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, G.; Luo, X.; Rauan, A.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Yu, H.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q. A Hydroponic Plants and Biofilm Combined Treatment System Efficiently Purified Wastewater from Cold Flowing Water Aquaculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, I.B.; Lovejoy, C.; Vincent, W.F. Changes in the Community Structure of Under-Ice and Open-Water Microbiomes in Urban Lakes Exposed to Road Salts. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 660719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.M.U.; Consuegra, S.; de Leaniz, C.G. Early Life Stress Causes Persistent Impacts on the Microbiome of Atlantic Salmon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, J.J.; Greenwood, D.R. Life at the Top of the Greenhouse Eocene World—A Review of the Eocene Flora and Vertebrate Fauna from Canada’s High Arctic. Bulletin 2012, 124, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, H.K.; Kidd, K.A.; Reist, J.D. Effects of Partially Anadromous Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus) Populations on Ecology of Coastal Arctic Lakes. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corush, J.B. Evolutionary Patterns of Diadromy in Fishes: More than a Transitional State between Marine and Freshwater. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laske, S.M.; Amundsen, P.A.; Christoffersen, K.S.; Erkinaro, J.; Guðbergsson, G.; Hayden, B.; Kahilainen, K.K.; Klemetsen, A.; Knudsen, R.; L’Abée-Lund, J.H.; et al. Circumpolar Patterns of Arctic Freshwater Fish Biodiversity: A Baseline for Monitoring. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosvitin Plays a Critical Role in the Immunity of Zebrafish Embryos via Acting as a Pattern Recognition Receptor and an Antimicrobial Effector. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22653–22664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, E.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Slawinska, A. Innate Immune Responses of Skin Mucosa in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Fed a Diet Supplemented with Galactooligosaccharides. Animals 2020, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansson, M.; Nielsen, A.; Kjærulff, L.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Wietz, M.; Ingmer, H.; Gram, L.; Larsen, T.O. Inhibition of Virulence Gene Expression in Staphylococcus aureus by Novel Depsipeptides from a Marine Photobacterium. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2537–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Element, G.; Engel, K.; Neufeld, J.D.; Casselman, J.M.; van Coeverden de Groot, P.; Greer, C.W.; Walker, V.K. Seasonal Habitat Drives Intestinal Microbiome Composition in Anadromous Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus). Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 3112–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Lin, X.; Tam, N.; Ho, J.C.H.; Wong, M.K.-S.; Gu, J.; Chan, T.F.; Tse, W.K.F. Osmotic Stress Induces Gut Microbiota Community Shift in Fish. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3784–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).