Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus saprophyticus from Diseased Hybrid Sturgeon
Abstract
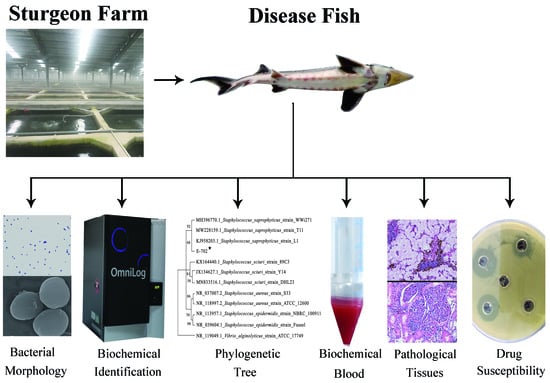
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish
2.2. Pathogen Isolation
2.3. Morphological Observation
2.4. 16S rDNA Sequence Analysis
2.5. Biochemical Identification of Bacteria
2.6. Toxicity Identification
2.7. Histopathological Observation
2.8. Analysis of Blood Parameters
2.9. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Testing
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Symptoms of Diseased Hybrid Sturgeons
3.2. Bacterial Morphological Analysis
3.3. 16S rDNA Identification
3.4. Biochemical Identification of Bacteria
3.5. Pathogenicity
3.6. Pathological Analysis
3.7. Blood Biochemical Analysis
3.8. Blood Count Analysis
3.9. Drug Sensitivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boschung, H.T.; Bailey, R.M. Acipenseriformes: AccessScience; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviar: Symbol of Luxury and Excess. 2011. Available online: http://language.chinadaily.com.cn/2011-11/01/content_14013902.htm (accessed on 1 November 2011).
- Bledsoe, G.; Bledsoe, C.; Rasco, B. Caviars and fish roe products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2003, 43, 317–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronzi, P.; Chebanov, M.; Michaels, J.; Wei, Q.; Rosenthal, H.; Gessner, J. Sturgeon meat and caviar production: Global update 2017. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2019, 3, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.; Bertoncini, T. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T39303A46914065.en (accessed on 14 September 2018).
- Jarić, I.; Bronzi, P.; Cvijanović, G.; Lenhardt, M.; Gessner, J. Paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) in Europe: An aquaculture species and a potential invader. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2019, 35, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Status and prospects of techniques in the sturgeon aquaculture industry in China. Freshw. Fish. 2017, 47, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierezan, F.; Shahin, K.; Heckman, T.; Ang, J.; Soto, E. Outbreaks of severe myositis in cultured white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus L.) associated with Streptococcus iniae. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, E.; Fast, M.; Purcell, S.; Coleman, D.; Yazdi, Z.; Kenelty, K.; Yun, S.; Camus, A. Expression of immune markers of white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) during Veronaea botryosa infection at different temperatures. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2022, 41, 100950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugetti, D.; Pastorino, P.; Menconi, V.; Pedron, C.; Prearo, M. The old and the new on viral diseases in sturgeon. Pathogens 2020, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Xue, M.; Wu, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Isolation and identification of Staphylococcus warneri from diseased Coreius guichenoti. Aquacult. Rep. 2022, 22, 100988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Xu, J.; Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Zeng, L. Histopathology and ultrastructural pathology of cyprinid herpesvirus II (CyHV-2) infection in gibel carp, Carassius auratus gibelio. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2015, 20, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, M.; Xiao, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y. Effects of dietary Enterococcus faecalis YFI-G720 on the growth, immunity, serum biochemical, intestinal morphology, intestinal microbiota, and disease resistance of crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Fishes 2022, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Ma, J.; LaPatra, S.E.; Meng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Zeng, L. Immunological responses and protection in Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus immunized with inactivated iridovirus. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, A.L.; Coyle, M.B.; Thornsberry, C.; Gerlach, E.H.; Hawkinson, R.W. Methods of measuring zones of inhibition with the Bauer-Kirby disk susceptibility test. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1979, 10, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, O.U.; Barata, M.; Fraqueza, M.J.; Worning, P.; Bartels, M.D.; Goncalves, L.; Paixão, P.; Goncalves, E.; Toscano, C.; Empel, J.; et al. Staphylococcus saprophyticus from clinical and environmental origins have distinct biofilm composition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 7, 663768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovelius, B.; Colleen, S.; Mardh, P.A. Urinary tract Infections in men caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 16, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Woo, J.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, M.N.; Yang, S.K.; Ryu, J. Clinical significance of Staphylococcus saprophyticus identified on blood culture in a tertiary care hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 56, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garduño, E.; Quez, I.M.; Beteta, A.; Said, I.; Blanco, J.; Pineda, T.S. Staphylococcus saprophyticus causing native valve endocarditis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 37, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, M.E.; Soper, D.E.; Archer, G.L. Colonization of the female genital tract with Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2975–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedman, P.; Ringertz, O.; Lindström, M.; Olsson, K. The origin of Staphylococcus saprophyticus from cattle and pigs. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 25, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, N.; Ma, A.; Wang, Y. Quorum sensing system-regulated genes affect the spoilage potential of Shewanella baltica. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Burke, C.M.; Bolch, C.; Stanley, R. Seafood spoilage microbiota and associated volatile organic compounds at different storage temperatures and packaging conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 280, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapigliati, G. Functional aspects of fish lymphocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, M.; Stanchi, K.M.C.; Erbacher, A.; Haufe, S.; Schwarze, C.P.; Handgretinger, R.; Hofbeck, M.; Kerst, G. Phagocytic activity of monocytes, their subpopulations and granulocytes during post-transplant adverse events after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Chai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, K.; Hang, J. Microscopic structures of peripheral blood cells in chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). J. Yangtze Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 12, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullaya, V.I.; Mast, Q.D.; Ven, A.; Elmoussaoui, H.; Kibiki, G.; Simonetti, E.; Jonge, M.; Ferwerda, G. Platelets modulate innate immune response against human respiratory syncytial virus in vitro. Viral Immunol. 2017, 30, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nording, H.M.; Seizer, P.; Langer, H.F. Platelets in inflammation and atherogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossaint, J.; Kühne, K.; Skupski, J.; Aken, H.V.; Looney, M.R.; Hidalgo, A.; Zarbock, A. Directed transport of neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles enables platelet-mediated innate immune response. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.; Tsai, C.; Lin, E.; Huang, C.; Lin, Y.; Lan, C.; Huang, C. Heat-killed Lactobacillus salivarius and Lactobacillus johnsonii reduce liver injury induced by alcohol in vitro and in vivo. Molecules 2016, 21, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, M.P. Physiological role of alkaline phosphatase explored in hypophosphatasia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1192, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, H. The mechanism of mineralization and the role of alkaline phosphatase in health and disease. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2010, 77, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hung, S.; Shyu, C.; Lin, C.; Liu, P.; Chang, C.; Shia, W.; Cheng, C.; Lin, S.; Tu, C. Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis infection in Bester sturgeon, a cultured hybrid of Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus, in Taiwan. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waisbren, B.A. The Sensitivity of Staphylococci to Antibiotics: A Five-Year Study of Sensitivity, Usage, and Cross Resistance in a General Hospital. AMA Arch. Intern. Med. 1958, 101, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Souza, D.; Leif, S.; Paiva, P.R.; Fernandes, R.R.; Helena, C.E.; Soares, P.M.; Dos, S.; Natacha, M.; Nunes, B. Staphylococcus saprophyticus recovered from humans, food, and recreational waters in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Int. J. Microbiol. 2017, 2017, 4287547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H. Isolation and identification of Staphylococcus saprophyticus from Acipenser schrenckii and its genomics analysis. J. Fish. Res. 2021, 43, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Reagent | Result * | Reagent | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 Negative Control | N | E1 Gelatin | B |
| A2 Dextrin | P | E2 Glycyl-L-Proline | B |
| A3 D-Maltose | P | E3 L-Alanine | B |
| A4 D-Trehalose | P | E4 L-Arginine | P |
| A5 D-Cellobiose | B | E5 L-Aspartic Acid | B |
| A6 Gentiobiose | P | E6 L-Glutamic Acid | P |
| A7 Sucrose | P | E7 L-Histidine | P |
| A8 D-Turanose | P | E8 L-Pyroglutamic Acid | B |
| A9 Stachyose | N | E9 L-Serine | P |
| A10 Positive Control | P | E10 Lincomycin | N |
| A11 PH6 | P | E11 Guanidine HCl | B |
| A12 PH5 | N | E12 Niaproof 4 | N |
| B1 D-Raffinose | N | F1 Pectin | P |
| B2 α-D-Lactose | P | F2 D-Galacturonic Acid | B |
| B3 D-Melibiose | B | F3 L-Galactonic Acid Lactone | B |
| B4 β-Methyl-D-Glucoside | P | F4 D-Gluconic Acid | P |
| B5 D-Salicin | B | F5 D-Glucuronic Acid | P |
| B6 N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine | P | F6 Glucuronamide | P |
| B7 N-Acetyl-β-D-Mannosamine | P | F7 Mucic Acid | N |
| B8 N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamine | N | F8 Quinic Acid | N |
| B9 N-Acetyl Neuraminic Acid | B | F9 D-Saccharic Acid | N |
| B10 1% NaCl | P | F10 Vancomycin | N |
| B11 4% NaCl | P | F11 Tetrazolium Violet | P |
| B12 8% NaCl | P | F12 Tetrazolium Blue | P |
| C1 α-D-Glucose | P | G1 P-Hydroxy-Phenylacetic Acid | N |
| C2 D-Mannose | P | G2 Methyl Pyruvate | P |
| C3 D-Fructose | P | G3 D-Lactic Acid Methyl Ester | P |
| C4 D-Galactose | P | G4 L-Lactic Acid | P |
| C5 3-Methyl Glucose | B | G5 Citric Acid | P |
| C6 D-Glucose | B | G6 6α-Keto-Glutaric Acid | B |
| C7 L-Fucose | B | G7 D-Malic Acid | N |
| C8 L-Rhamnose | B | G8 L-Malic Acid | P |
| C9 Inosine | B | G9 Bromo-Succinic Acid | P |
| C10 1%Sodium Lactate | B | G10 Nalidixic Acid | P |
| C11 Fusidic Acid | N | G11 Lithium Chloride | P |
| C12 D-Serine | P | G12 Potassium Tellurite | P |
| D1 D-Sorbitol | P | H1 Tween 40 | P |
| D2 D-Mannitol | P | H2 γ-Amino-Butyric Acid | P |
| D3 D-Arabitol | B | H3 α-Hydroxy-Butyric Acid | P |
| D4 Myo-lnositol | N | H4 β-Hydroxy-D, L-Butyric Acid | B |
| D5 Glycerol | P | H5 α-Keto-Butyric Acid | N |
| D6 D-Glucose-6-PO4 | B | H6 Acetoacetic Acid | P |
| D7 D-Fructose-6-PO4 | B | H7 Propionic Acid | N |
| D8 D-Aspartic Acid | N | H8 Acetic Acid | P |
| D9 D-Serine | N | H9 Formic Acid | P |
| D10 Troleandomycin | N | H10 Aztreonam | P |
| D11 Rifamycin SV | N | H11 Sodium Butyrate | P |
| D12 Minocycline | N | H12 Sodium Bromate | N |
| Group | Bacteria Concentration/(CFU·mL−1) | Injection Dose/mL | Cumulative Death Number | Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test group | 6.7 × 107 | 0.3 | 28 | 93.33% |
| 6.7 × 106 | 0.3 | 21 | 70.00% | |
| 6.7 × 105 | 0.3 | 20 | 66.67% | |
| 6.7 × 104 | 0.3 | 10 | 33.33% | |
| Control | PBS | 0.3 | 0 | 0% |
| Medicine Name | Inhibition Zone (mm) | Sensitivity | Medicine Name | Inhibition Zone (mm) | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vancomycin | 15 | I | Neomycin | 21 | S |
| Furazolidone | 17 | I | Cefazolin | 34 | S |
| Streptomycin | 18 | I | Norfloxacin | 21 | S |
| Chloramphenicol | 9 | R | Carbenicillin | 22 | S |
| Gentamicin | 16 | S | Ciprofloxacin | 23 | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xue, M.; Xiao, Z.; Jin, L.; Gao, R.; Chen, Y.; Liang, T.; Zhou, Y. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus saprophyticus from Diseased Hybrid Sturgeon. Fishes 2023, 8, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050250
Wu Y, Feng Y, Xue M, Xiao Z, Jin L, Gao R, Chen Y, Liang T, Zhou Y. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus saprophyticus from Diseased Hybrid Sturgeon. Fishes. 2023; 8(5):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050250
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yeying, Yalan Feng, Mingyang Xue, Zidong Xiao, Lijuan Jin, Ren Gao, Yahong Chen, Tianwang Liang, and Yong Zhou. 2023. "Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus saprophyticus from Diseased Hybrid Sturgeon" Fishes 8, no. 5: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050250
APA StyleWu, Y., Feng, Y., Xue, M., Xiao, Z., Jin, L., Gao, R., Chen, Y., Liang, T., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus saprophyticus from Diseased Hybrid Sturgeon. Fishes, 8(5), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050250