Morphological Comparison of the Chesapeake Logperch Percina bimaculata with the Logperch Percina c. caprodes and Percina c. semifasciata in Pennsylvania
Abstract
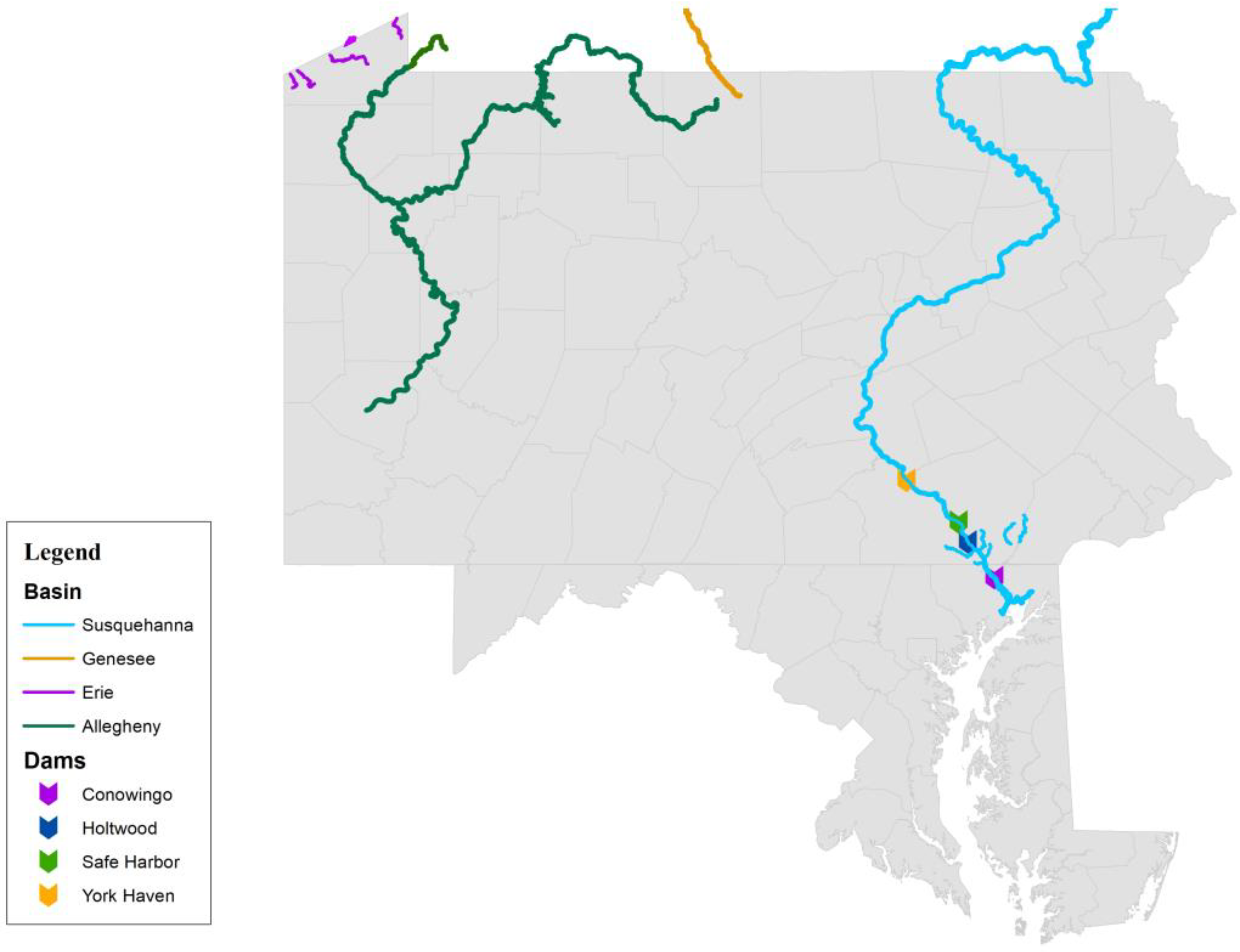
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haldeman, S.S. Description of two new species of the genus Perca, from the Susquehanna River. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phil. 1842, 8, 330. [Google Scholar]
- Haldeman, S.S. Percina bimaculata, n. sp. from the Susquehanna River. Proc. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 1844, 1, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Page, L.M.; Burr, B.M. Field Guide to Freshwater Fishes of North America North of Mexico, 2nd ed.; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- DeKay, J.E. Natural history of New York. In Part 1. Zoology. Reptiles and Fishes. Part 4–Fishes; Appleton and Co. and Wilby and Putnam: Albany, NY, USA, 1842; 415p. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.A.; Page, L.M. Variation in western logperches (Pisces: Percidae), with description of a new subspecies from the Ozarks. Copeia 1981, 1981, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J. Rescued from synonomy: A redescription of Percina bimaculata Haldeman and a molecular phylogenetic analysis of logperch darters (Percidae: Etheostomatinae). Bull. Peabody Mus. Nat. Hist. 2008, 49, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.E.; Burkhead, N.M. Freshwaters Fishes of Virginia; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.S. The darters of Maryland. Md. Conserv. 1977, 53, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.S.; Platnia, S.P.; Norden, A.W.; Gilbert, C.R.; Franz, R. Endangered, threatened, and extirpated freshwater fishes of Maryland. In Threatened and Endangered Plants and Animals of Maryland, Annapolis; Norden, A.W., Forester, D.C., Fenwick, G.H., Eds.; Maryland Department of Natural Resources: Annapolis, MD, USA, 1984; pp. 287–328. [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer, J.R., Jr.; Criswell, R.W.; Fischer, D.P. The Fishes of Pennsylvania; Cichlid Press: El Paso TX, USA, 2016; 556p. [Google Scholar]
- Freedman, J.A.; Stecko, T.D.; Lorson, B.D.; Stauffer, J.R., Jr. Development and efficacy of an electrified benthic trawl for sampling large-river fish assemblages. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2009, 29, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, A.F.; Stauffer, J.R., Jr. Revised diagnosis of Metriaclima with description of a new species (Teleostei: Cichlidae) from Lake Malaŵi National Park, Africa. Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2006, 7, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Humphries, J.M.; Bookstein, F.L.; Chernoff, B.; Smith, G.R.; Elder, R.L.; Poss, S.G. Multivariate discrimination by shape in relation to size. Syst. Zool. 1981, 30, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, J.R., Jr.; Bowers, N.J.; Kellogg, K.A.; McKaye, K.R. A revision of the blue-black Pseudotropheus zebra (Teleostei: Cichlidae) complex from Lake Malawi, Africa, with a description of a new genus and ten new species. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1997, 148, 189–230. [Google Scholar]
- Abbe, C., Jr. The Physiography of Garrett County. In Garrett County; Geological Survey: Maryland, MD, USA, 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Hocutt, C.H.; Jenkins, R.E.; Stauffer, J.R., Jr. Zoogeography of the fishes of the Central Appalachians and Central Atlantic Coastal Plain. In The Zoogeography of North American Freshwater Fishes; Hocutt, C.H., Wiley, E.O., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 161–211. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, B. Geographic history of the Potomac River. In The Potomac River Basin; United States Geological Survey Water Supp. and Irrigation Pap. No. 192; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1907; pp. 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, H.D. Drainage evolution in the southern Appalachians. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 1939, 50, 1323–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.D. The Subspecies and Races of the Cyprinid Fish Campostoma anomalum (Rafinesque) in Eastern United States. Ph.D. Dissertation, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, P.J. The distribution and probable post-glacial dispersal of the percid fish, Etheostoma b. blennioides in the Potomac River. Copeia 1965, 1965, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, J.R., Jr.; Hocutt, C.H.; Lee, D.S. The zoogeography of the freshwater fishes of the Potomac River Basin. In The Freshwater Potomac: Aquatic Communities and Environmental Stresses; Flynn, K.C., Mason, W.T., Eds.; Commission of the Potomac River Basin: Rockville, MD, USA, 1978; pp. 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, B.A. Percina kathae, a new logperch endemic to the Mobile Basin in Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, and Tennessee (Percidae, Eheostomatini). Occ. Pap. Mus. Nat. Sci. Louisiana State Univ. 1997, 73, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, B.A. Percina austroperca: A new species of logperch (Percidae, subgenus Percina) from the Choctawhatchee and Escambia rivers in Alabama and Florida. Occ. Pap. Mus. Nat. Sci. Louisiana State Univ. 1995, 69, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J.; Bossu, C.M.; Bradburd, G.S.; Carlson, R.L.; Harrington, R.C.; Hollingsworth, P.R., Jr.; Keck, B.P.; Etnier, D.A. Phylogeny and termporal diversification of darters (Percidae: Eheostomatinae). Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 565–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rube, P.J. Fish distribution in Gatineau Park, Quebec, in relation to postglacial dispersal, man’s influence, and euthrophication. Can. Field Nat. 1975, 89, 389–399. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, B.A. Percina caprodes (Rafinesque), logperch. In Atlas of North American Freshwater Fishes; Lee, D.S., Gilbert, C.R., Hocutt, C.H., Jenkins, R.E., McAllister, D.E., Stauffer, J.R., Jr., Eds.; North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1980; pp. 719–720. [Google Scholar]
- Denoncourt, R.F.; Hocutt, C.H.; Stauffer, J.R., Jr. Additions to the Pennsylvania ichthyofauna of the Susquehanna River drainage. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1975, 127, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, R.E.; Lachner, E.A.; Schwartz, F.J. Fishes of the central Appalachian Drainages: Their distribution and dispersal. In The Distributional History of the Biota of the Southern Appalachians Part III; Holt, P.C., Ed.; Research Division Monograph 4; Virginia Polytechnic Institute, State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Collette, B.B.; Knapp, L.W. Catalog of type specimens of the darters (Pisces, Percidae, Etheostomatini). Proc. United States Natl. Mus. 1967, 119, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, L.W. Systematic Studies of the Rainbow Darter, Etheostoma caeruleum Storer, and the Subgenus Hadropterus (Pices, Percidae). Ph.D. Dissertation, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Esmond, E.F.; Stauffer, J.R., Jr. Taxometric comparison of the Atlantic Slope and Ohio River populations of Etheostoma caeruleum Storer. Am. Mid. Nat. 1983, 109, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.; Kornfield, I. Retention of an ancestral polymorhism in the mbuna species flock (Pisces: Cichlidae) of Lake Malawi. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer, J.R., Jr.; LoVullo, T.J.; McKaye, K.R. Three new sand-dwelling cichlids from Lake Malawi, Africa, with a discussion of the status of the genus Copidachromis (Teleostei: Cichlidae). Copeia 1993, 1993, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Interior Federal Regi. Available online: https://www.fws.gov/sites/default/files/federal_register_documents/2022-24633.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2023).




| Octoraro Creek (n = 19) | Susquehanna River (n = 27) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max |
| Standard length | 80.8 | 55.3 | 166.2 | 69.5 | 51.2 | 90.0 |
| Head length | 21.2 | 15.4 | 29.5 | 18.2 | 13.7 | 23.8 |
| Percent head length (%) | ||||||
| Snout length | 33.7 | 30.4 | 37.1 | 32.7 | 29.4 | 36.5 |
| Postorbital head length | 47.4 | 43.7 | 49.1 | 47.3 | 43.0 | 50.6 |
| Horizontal eye diameter | 21.5 | 18.9 | 24.3 | 22.9 | 20.3 | 24.7 |
| Vertical eye diameter | 21.2 | 18.6 | 24.7 | 22.4 | 19.5 | 25.0 |
| Head depth | 53.4 | 49.3 | 58.6 | 53.5 | 45.8 | 64.1 |
| Percent standard length (%) | ||||||
| Head length | 26.3 | 24.9 | 28.1 | 26.3 | 24.6 | 28.3 |
| Snout to first dorsal fin origin | 32.5 | 30.8 | 34.1 | 32.8 | 31.8 | 34.7 |
| Snout to pelvic fin origin | 30.8 | 28.8 | 33.4 | 20.2 | 27.7 | 33.1 |
| First dorsal fin base length | 31.4 | 29.2 | 33.8 | 31.4 | 29.2 | 33.2 |
| Second dorsal fin base length | 21.7 | 19.7 | 23.0 | 21.5 | 19.5 | 23.5 |
| Ant. dorsal fin to ant. anal fin | 35.3 | 33.3 | 38.0 | 35.3 | 32.0 | 37.4 |
| Post. second dorsal to ventral caudal fin | 32.8 | 31.4 | 34.4 | 32.4 | 30.4 | 34.3 |
| Posterior anal fin to dorsal caudal | 17.7 | 16.2 | 19.7 | 17.6 | 15.5 | 19.1 |
| Posterior dorsal fin to pelvic fin origin | 37.6 | 34.4 | 43.1 | 37.3 | 32.3 | 39.3 |
| Caudal peduncle length | 20.1 | 18.0 | 21.7 | 20.6 | 18.5 | 24.0 |
| Least caudal peduncle depth | 8.7 | 8.0 | 9.6 | 8.7 | 7.9 | 9.7 |
| Meristics | Mode | Min | Max | Mode | Min | Max |
| Dorsal fin spines | 13 | 12 | 15 | 13/14 | 13 | 15 |
| Dorsal fin rays | 15 | 14 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 16 |
| Anal fin rays | 11 | 10 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 12 |
| Pectoral fin rays | 14 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 15 |
| Pelvic fin rays | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
| Lateral line scales | 75/76 | 70 | 82 | 76 | 67 | 80 |
| Pored scales posterior to the lateral line | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Lake Erie Drainage (n = 21) | Mississippi River Drainage (n = 7) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max |
| Standard length | 94.7 | 72.2 | 120.6 | 95.8 | 80.9 | 115.4 |
| Head length | 25.0 | 19.0 | 32.1 | 24.3 | 21.3 | 27.5 |
| Percent head length (%) | ||||||
| Snout length | 33.0 | 29.4 | 35.5 | 32.3 | 30.5 | 35.3 |
| Postorbital head length | 46.7 | 44.3 | 49.0 | 48.3 | 47.0 | 49.2 |
| Horizontal eye diameter | 22.3 | 20.3 | 25.4 | 22.7 | 20.3 | 23.9 |
| Vertical eye diameter | 21.1 | 18.7 | 24.0 | 22.0 | 21.0 | 22.7 |
| Head depth | 51.6 | 44.7 | 57.3 | 52.9 | 49.6 | 56.7 |
| Percent standard length (%) | ||||||
| Head length | 26.4 | 24.9 | 27.6 | 25.5 | 23.8 | 26.3 |
| Snout to first dorsal fin origin | 32.3 | 30.9 | 33.8 | 31.3 | 29.3 | 33.0 |
| Snout to pelvic fin origin | 30.8 | 27.0 | 34.4 | 29.9 | 27.9 | 31.6 |
| First dorsal fin base length | 29.7 | 26.2 | 32.3 | 31.4 | 30.2 | 32.7 |
| Second dorsal fin base length | 20.5 | 17.7 | 22.8 | 22.0 | 20.8 | 23.4 |
| Ant. dorsal fin to ant. anal fin | 36.5 | 33.5 | 39.1 | 36.4 | 34.4 | 39.0 |
| Post. second dorsal to ventral caudal fin | 18.4 | 16.7 | 19.8 | 19.0 | 17.2 | 20.5 |
| Posterior anal fin to dorsal caudal | 23.9 | 21.6 | 25.9 | 24.1 | 23.2 | 25.0 |
| Posterior dorsal fin to pelvic fin origin | 55.4 | 53.3 | 60.0 | 55.6 | 53.1 | 58.1 |
| Caudal peduncle length | 22.8 | 17.8 | 24.6 | 22.4 | 21.6 | 23.6 |
| Least caudal peduncle depth | 7.7 | 7.1 | 9.2 | 7.6 | 7.1 | 8.5 |
| Meristics | Mode | Min | Max | Mode | Min | Max |
| Dorsal fin spines | 14 | 13 | 15 | 14/15 | 13 | 15 |
| Dorsal fin rays | 14 | 15 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| Anal fin rays | 7 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
| Pectoral fin rays | 12 | 10 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 14 |
| Pelvic fin rays | 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
| Lateral line scales | 80 | 75 | 85 | 79 | 77 | 87 |
| Pored scales posterior to the lateral line | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Allegheny River (n = 44) | Genesee River (n = 7) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max |
| Standard length | 99.6 | 72.0 | 126.3 | 93.7 | 91.6 | 96.0 |
| Head length | 23.4 | 18.5 | 32.0 | 23.8 | 22.8 | 24.9 |
| Percent head length (%) | ||||||
| Snout length | 33.2 | 28.0 | 37.1 | 34.9 | 32.8 | 37.2 |
| Postorbital head length | 47.1 | 41.2 | 51.2 | 47.2 | 45.4 | 48.5 |
| Horizontal eye diameter | 22.3 | 19.2 | 26.7 | 20.2 | 19.4 | 21.1 |
| Vertical eye diameter | 21.1 | 18.9 | 24.6 | 21.2 | 18.8 | 24.8 |
| Head depth | 49.2 | 38.7 | 56.5 | 49.1 | 44.3 | 52.2 |
| Percent standard length (%) | ||||||
| Head length | 25.9 | 24.3 | 28.0 | 25.3 | 24.3 | 27.1 |
| Snout to first dorsal fin origin | 31.1 | 28.6 | 34.5 | 31.7 | 30.8 | 32.4 |
| Snout to pelvic-fin origin | 29.8 | 27.4 | 33.2 | 28.0 | 26.9 | 28.8 |
| First dorsal fin base length | 31.4 | 28.6 | 34.5 | 31.9 | 30.9 | 33.3 |
| Second dorsal fin base length | 22.5 | 18.8 | 24.7 | 23.9 | 23.0 | 24.9 |
| Ant. dorsal fin to ant. anal fin | 36.0 | 32.5 | 39.3 | 35.5 | 33.9 | 37.7 |
| Post. second dorsal to ventral caudal fin | 23.6 | 20.4 | 26.2 | 17.8 | 16.8 | 18.7 |
| Posterior anal fin to dorsal caudal | 18.2 | 14.5 | 19.9 | 24.1 | 23.5 | 24.7 |
| Posterior dorsal fin to pelvic fin origin | 55.8 | 50.0 | 59.7 | 57.3 | 55.7 | 58.3 |
| Caudal peduncle length | 22.5 | 18.5 | 24.9 | 23.3 | 21.4 | 24.7 |
| Least caudal peduncle depth | 7.6 | 6.9 | 8.5 | 7.3 | 6.9 | 7.8 |
| Meristics | Mode | Min | Max | Mode | Min | Max |
| Dorsal fin spines | 15 | 13 | 16 | 14 | 13 | 16 |
| Dorsal fin rays | 15 | 14 | 17 | 15 | 14 | 17 |
| Anal fin rays | 7 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Pectoral fin rays | 13 | 11 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 13 |
| Pelvic fin rays | 7 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Lateral line scales | 87 | 81 | 90 | 86 | 85 | 89 |
| Pored scales posterior to the lateral line | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stauffer, J.R., Jr.; Freedman, J.A.; Fischer, D.P.; Criswell, R.W. Morphological Comparison of the Chesapeake Logperch Percina bimaculata with the Logperch Percina c. caprodes and Percina c. semifasciata in Pennsylvania. Fishes 2023, 8, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060288
Stauffer JR Jr., Freedman JA, Fischer DP, Criswell RW. Morphological Comparison of the Chesapeake Logperch Percina bimaculata with the Logperch Percina c. caprodes and Percina c. semifasciata in Pennsylvania. Fishes. 2023; 8(6):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060288
Chicago/Turabian StyleStauffer, Jay R., Jr., Jonathan A. Freedman, Douglas P. Fischer, and Robert W. Criswell. 2023. "Morphological Comparison of the Chesapeake Logperch Percina bimaculata with the Logperch Percina c. caprodes and Percina c. semifasciata in Pennsylvania" Fishes 8, no. 6: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060288
APA StyleStauffer, J. R., Jr., Freedman, J. A., Fischer, D. P., & Criswell, R. W. (2023). Morphological Comparison of the Chesapeake Logperch Percina bimaculata with the Logperch Percina c. caprodes and Percina c. semifasciata in Pennsylvania. Fishes, 8(6), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060288






