Bacterial Co-Infection as a Potential Threat to Farmed Flathead Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Phenotypic and Molecular Diagnosis, Histopathology, Immunity Response, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Fish Sampling and Clinical Examination
2.3. Water Quality Measures
2.4. Bacterial Strains Isolation and Identification
2.5. Molecular Identification of Bacterial Isolates
2.5.1. Bacterial DNA Extraction
2.5.2. 16S rRNA PCR, Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Antibiogram Testing
2.7. Serum Biochemical and Immune Markers
2.8. Oxidative Stress/Antioxidant Parameters
2.9. Histopathological Examination
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
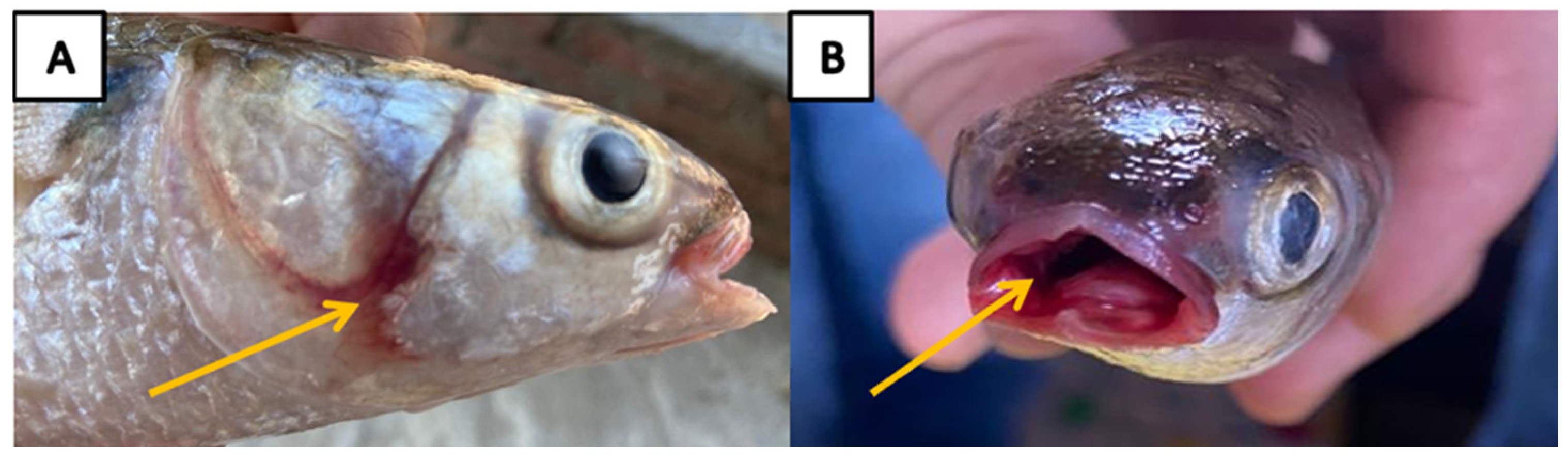
3.1. Clinical Signs and Necropsy Findings
3.2. Water Physicochemical Properties
3.3. Phenotypic Identification of Bacterial Pathogens
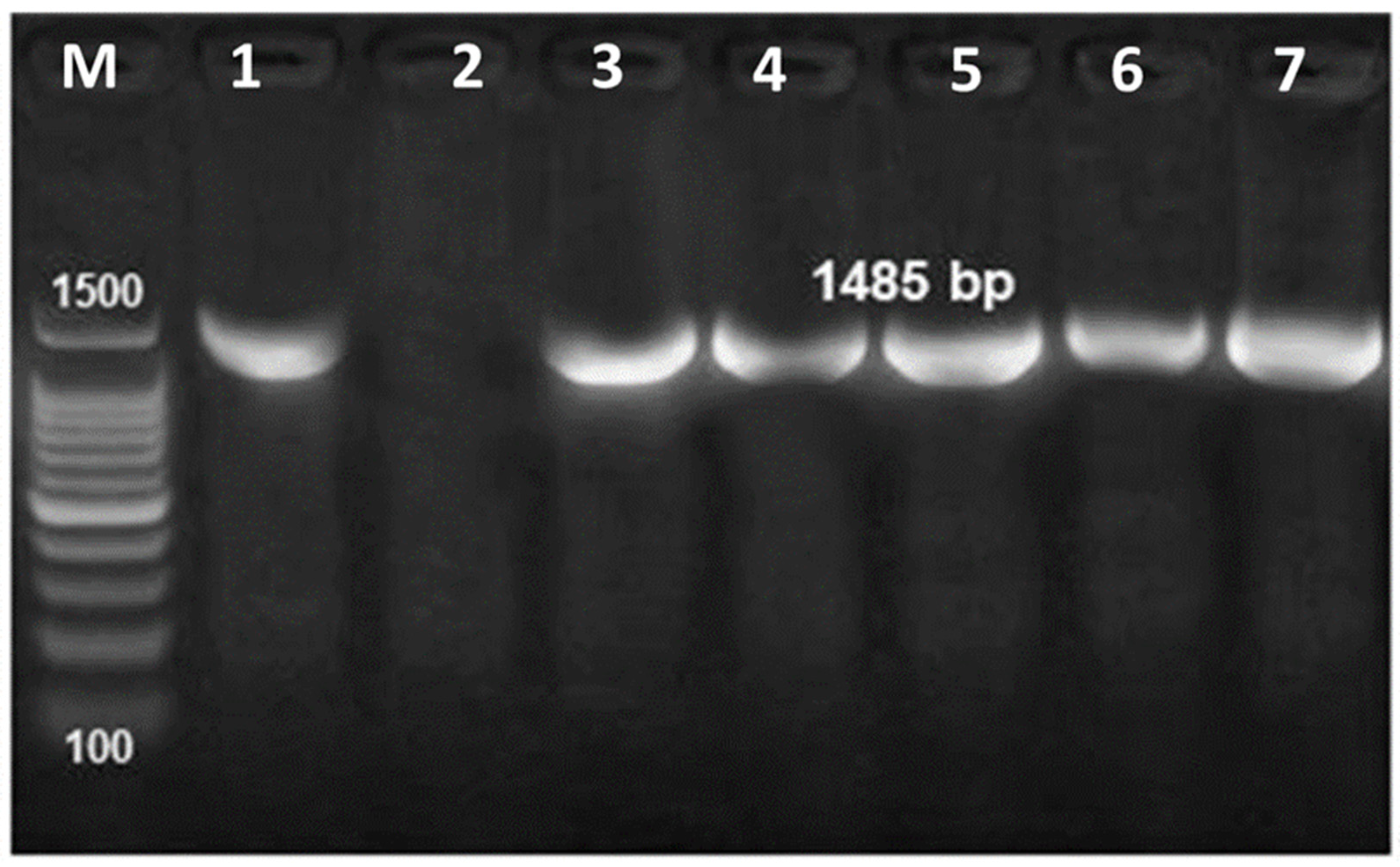
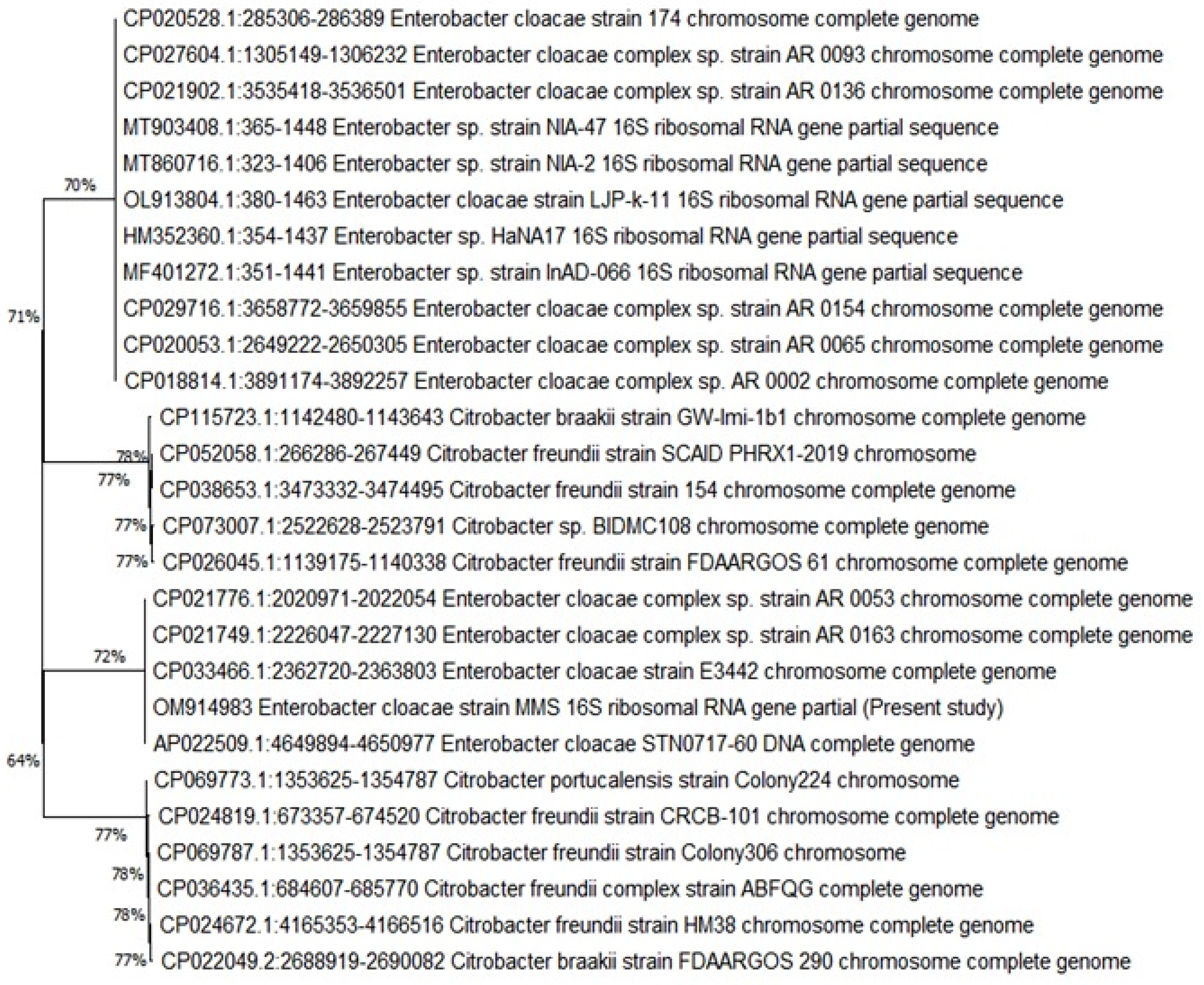
3.4. Molecular Identification of Bacterial Pathogens
3.5. Susceptibility of Pathogenic Strains to Antibiotics
3.6. Serum Biochemical and Inflammatory Findings
3.7. Oxidative Stress/Antioxidant Status
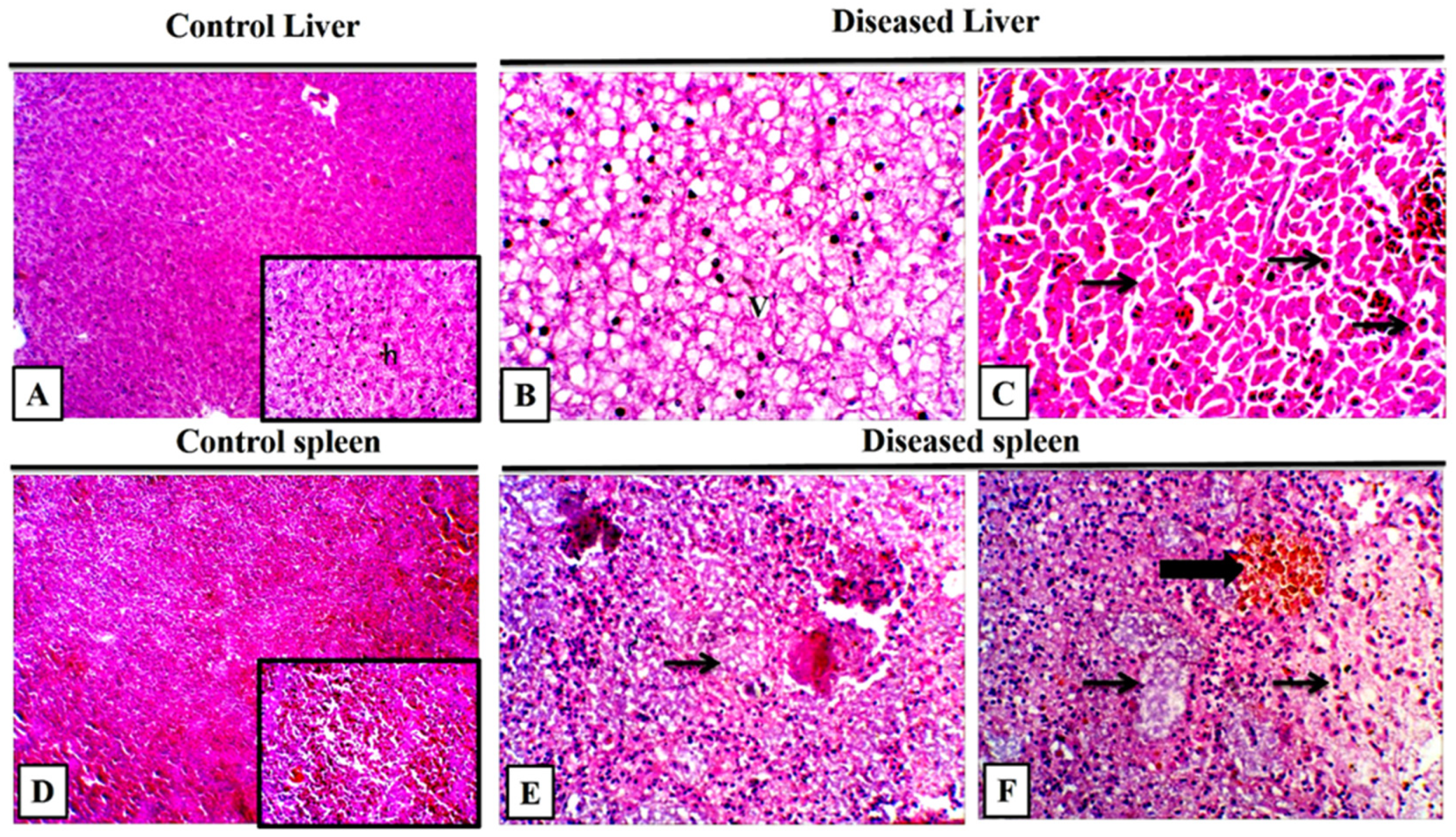
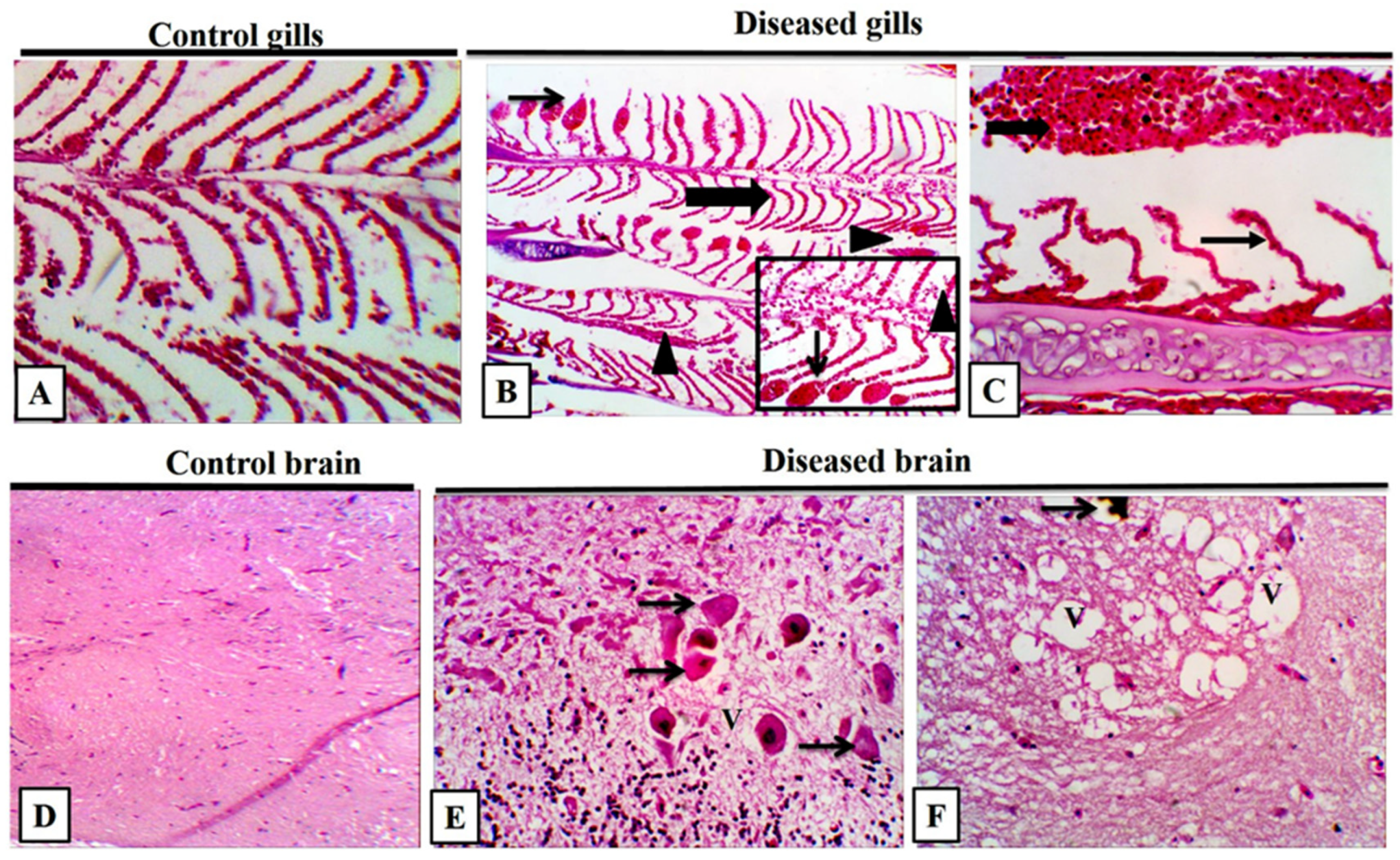
3.8. Histopathological Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GAFRD. General Authority for Fish Resources Development; GAFRD: Nasr City, Egypt, 2019.
- Soyinka, O.O. The feeding ecology of Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus) from a high brackish tropical lagoon in South-west, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 4192–4198. [Google Scholar]
- Plumber, A. Fishy Business: Assessing Egypt’s Growing Aquaculture Sector. Al Noor J. Middle East. Stud. 2019, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sukumaran, K.; Thomas, D.; Rekha, M.; Angel, J.R.J.; Bera, A.; Mandal, B.; Subburaj, R.; Thiagarajan, G.; Makesh, M.; Ambasankar, K. Reproductive maturation and induced breeding of two geographical groups of grey mullet, Mugil cephalus Linnaeus, 1758. Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-gheit, E. Some Investigations on the role of water parameters in microbial infections of fishes. Egypt. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 1, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- El-Son, M.A.; Nofal, M.I.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Co-infection of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from diseased farmed striped mullet (Mugil cephalus) in Manzala, Egypt–A case report. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Attia, M.M.; Abdelsalam, M.; Abdel-Moneam, D.A.; Zaki Ewiss, M. Ergasilus extensus and bacterial co-infection in flathead grey mullet, Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758), are associated with pathological changes and immunological gene expression alterations. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 6143–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, M.I.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Ectoparasites and bacterial co-infections causing summer mortalities among cultured fishes at Al-Manzala with special Reference to Water quality parameters. Life Sci. J. 2017, 14, 72–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2017, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ina-Salwany, M.; Al-saari, N.; Mohamad, A.; Mursidi, F.A.; Mohd-Aris, A.; Amal, M.; Kasai, H.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T.; Zamri-Saad, M. Vibriosis in fish: A review on disease development and prevention. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bouhy, Z.; El-Nobi, G.; El-Murr, A.; Abd El-Hakim, S. Study on Vibriosis in Mugil Capito in El-Dakahlia and Damitta Governorates, Egypt. Abbassa Int. J. Aquat. 2016, 9, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B. Vibrios as causal agents of zoonoses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Traoré, O.; Martikainen, O.; Siitonen, A.; Traoré, A.S.; Barro, N.; Haukka, K. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae in fish and water from a reservoir and a neighboring channel in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flach, E.J.; LeNette-Dawson, D.; Greig, D.R.; Ismail Ahmed, A.; Jenkins, C.; John, S.K.; Macgregor, S.K.; Masters, N.; Stidworthy, M.F.; Zimmerman, B. Isolation and characterisation of Vibrio cholerae from fish examined postmortem at ZSL London Zoo between 2014 and 2018. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathri, V. The Prevalence and Public Health Significance of Human Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Hawaii’s Diverse Tropical Coastal Water Environments; Water Resources Research Centre, University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tawab, A.; El-Hofy, F.; Hasb-Elnaby, G.; El-Khayat, M.; Refaey, M. Prevalence and virulence genes of vibrio and Aeromonas species isolated from Nile tilapia and mugil fish farms in Egypt. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2021, 9, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar]
- Haenen, O.; Van Zanten, E.; Jansen, R.; Roozenburg, I.; Engelsma, M.; Dijkstra, A.; Boers, S.; Voorbergen-Laarman, M.; Möller, A. Vibrio vulnificus outbreaks in Dutch eel farms since 1996: Strain diversity and impact. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 108, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.; Ibrahem, M.D.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Abu-Elala, N.M.; Abdel-moneam, D.A. Monitoring of different vibrio species affecting marine fishes in Lake Qarun and Gulf of Suez: Phenotypic and molecular characterization. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 43, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoussi, M.; Hajlaoui, H.; Noumi, E.; Zanetti, S.; Bakhrouf, A. Phenotypic and genetic diversity of Vibrio alginolyticus strains recovered from juveniles and older Sparus aurata reared in a Tunisian marine farm. Ann. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhual, N.P.; Das, B.K.; Sadique, M.; Swain, A.K.; Mishra, B.K.; Maiti, N.K.; Eknath, A.E. Molecular identification and typing of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated from black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. J. Aquac. Trop. 2010, 25, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.-y.; Yang, M.-j.; Yang, L.-f.; Chen, Z.-g.; Jiang, M.; Peng, B. Metabolic modulation of redox state confounds fish survival against Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 796–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Austin, B.; Stobie, M.; Robertson, P.; Glass, H.; Stark, J.; Mudarris, M. Vibrio alginolyticus: The cause of gill disease leading to progressive low-level mortalities among juvenile turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L., in a Scottish aquarium. J. Fish Dis. 1993, 16, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorni, A.; Paperna, I.; Gordin, H. Bacterial infections in gilt-head sea bream Sparus aurata cultured at Elat. Aquaculture 1981, 23, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balebona, M.C.; Andreu, M.J.; Bordas, M.A.; Zorrilla, I.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Borrego, J.J. Pathogenicity of Vibrio alginolyticus for cultured gilt-head sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4269–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.-K. Pathogenesis studies on Vibrio alginolyticus in the grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus, Bloch et Schneider. Microb. Pathog. 1995, 19, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhyia, A.V.; Mulloorpeedikayil, R.G.; Kollanoor, R.J.; Jeyaseelan, P.M. Molecular variations in Vibrio alginolyticus and V. harveyi in shrimp-farming systems upon stress. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalil, R.; Abd El-Latif, H. Effect of Vibrio alginolyticus on Mugil Capito. J. Arab. Aquacult. Soc. 2013, 8, 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, C.; Erken, M.; Noorian, P.; Sun, S.; McDougald, D. Environmental reservoirs and mechanisms of persistence of Vibrio cholerae. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanoi, H.; Muroga, K.; Takahashi, S. Physiological characteristics and pathogenicity of NAG Vibrio isolated from diseased ayu. Fish Pathol. 1980, 15, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiiyukia, C.; Nakajima, A.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K.; Kawakami, H.; Hashimoto, H. Vibrio cholerae non-O1 isolated from ayu fish (Plecoglossus altivelis) in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3078–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiani, S.; Naghavi, N.S.; Nazari, A. Detection of Vibrio species isolated from ornamental guppy fish in Kashan, Isfahan, Iran fish culturing pounds. Biol. J. Microorg. 2016, 4, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.T.; Nguyen, V.V.; Le, H.D.; Sangsuriya, P.; Jitrakorn, S.; Saksmerprome, V.; Senapin, S.; Rodkhum, C. Naturally concurrent infections of bacterial and viral pathogens in disease outbreaks in cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) farms. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, M.; Izhaki, I. Fish as Hosts of Vibrio cholerae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehulka, J.; Petras, P.; Marejkova, M.; Aldova, E. Vibrio cholerae non-O1/non-O139 infection in fish in the Czech Republic. Vet. Med. 2015, 60, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, G.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, S.; Deng, X.; Qiu, J.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Nordihydroguaiaretic acid reverses the antibacterial activity of colistin against MCR-1-positive bacteria in vivo/in vitro by inhibiting MCR-1 activity and injuring the bacterial cell membrane. Phytomedicine 2022, 98, 153946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simó, C.; Fornari, T.; García-Risco, M.R.; Peña-Cearra, A.; Abecia, L.; Anguita, J.; Rodríguez, H.; García-Cañas, V. Resazurin-based high-throughput screening method for the discovery of dietary phytochemicals to target microbial transformation of l-carnitine into trimethylamine, a gut metabolite associated with cardiovascular disease. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5640–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handl, J.; Nyvltova, P.; Capek, J.; Cesla, P.; Hovsepyan, A.; Avetisyan, S.; Micankova, P.; Bruckova, L.; Stankova, P.; Knotkova, K.; et al. The comparison of biological effects of bacterial and synthetic melanins in neuroblastoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 168, 113355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, E.; Elli, G.; Nurminen, N.; Oscarsson, E.; Canaviri-Paz, P.; Burri, S.; Rohrstock, A.-M.; Rahman, M.; Alsanius, B.; Molin, G.; et al. Comparative immunomodulatory effects in mice and in human dendritic cells of five bacterial strains selected for biocontrol of leafy green vegetables. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 165, 113064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonaitis, T.; Lewis, E.A.; Lourens, N.; Groot, A.; Goodman, R.E.; Mitchell, D.; Karpol, A.; Tracy, B. Subchronic feeding, allergenicity, and genotoxicity safety evaluations of single strain bacterial protein. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 162, 112878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, H.; Butt, T.M.; Coates, C.J. Nutraceutical intervention protects against bacterial and chemical-induced gastrotoxicity in a non-mammalian model, Galleria mellonella. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thillai Sekar, V.; Santiago, T.; Vijayan, K.; Alavandi, S.; Stalin Raj, V.; Rajan, J.; Sanjuktha, M.; Kalaimani, N. Involvement of Enterobacter cloacae in the mortality of the fish, Mugil cephalus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, S.G.; Lipton, A.; De los Ríos-Escalante, P.; Ibáñez-Arancibia, E. Isolation and characterization of bacterial pathogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter cloacae from the moribund fish, Etroplus maculatus. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2021, 12, 1332–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Troast, J.L. Antibodies against enteric bacteria in brown bullhead catfish (Ictalurus nebulosus, LeSueur) inhabiting contaminated waters. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 30, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, G.; Raa, J.; Olafsen, J. Isolation of Enterobacter agglomerans from dolphin fish, Coryphaena hippurus L. J. Fish Dis. 1990, 13, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldreich, E.E.; Clarke, N.A. Bacterial pollution indicators in the intestinal tract of freshwater fish. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Elala, N.M.; Abd-Elsalam, R.M.; Younis, N.A. Streptococcosis, Lactococcosis and Enterococcosis are potential threats facing cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochomis niloticus) production. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4183–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; Xu, N.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ai, X. Identification of a multi-resistant Enterobacter cloacae strain from diseased crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A.; Munn, C. Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- El-Son, M.A.; Elbahnaswy, S.; Ibrahim, I. Molecular and histopathological characterization of Photobacterium damselae in naturally and experimentally infected Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Haldar, S. Vibrio related diseases in aquaculture and development of rapid and accurate identification methods. J. Mar. Sci. Res. Dev. S 2012, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Photobacteriaceae Representatives. In Bacterial Fish Pathogens; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, L.N.; Lombardi, D.C.; Gomide, A.; Gomes, L.C. Efficacy of clove oil as anesthetic in handling and transportation of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Actinopterygii: Cichlidae) juveniles. Zoologia 2011, 28, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C. Water Quality in Ponds for Aquaculture; Agriculture Experiment Station, Auburn University: Auburn, AL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Singare, P.; Ferns, S. Study of toxic heavy metals in Mahim Creek of Mumbai. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2014, 17, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakweer, M.S.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Abdelwarith, A.A.; Younis, E.M.; Davies, S.J.; Elbahnaswy, S. Comparison of Immune Response of Litopenaeus vannamei Shrimp Naturally Infected with Vibrio Species, and after Being Fed with Florfenicol. Fishes 2023, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagacé, L.; Pitre, M.; Jacques, M.; Roy, D. Identification of the bacterial community of maple sap by using amplified ribosomal DNA (rDNA) restriction analysis and rDNA sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zidour, M.; Chevalier, M.; Belguesmia, Y.; Cudennec, B.; Grard, T.; Drider, D.; Souissi, S.; Flahaut, C. Isolation and characterization of bacteria colonizing Acartia tonsa copepod eggs and displaying antagonist effects against Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio alginolyticus and other pathogenic strains. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Fifth Informational Supplement M100-S25; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wedemeyer, G.A.; Yasutake, W.T. Clinical Methods for the Assessment of the Effects of Environmental Stress on Fish Health; Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service: Bailey’s Crossroads, VA, USA, 1977; Volume 89.
- El-Son, M.A.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Rezk, S.; Eldessouki, E.A.; Elbahnaswy, S. Dietary mixed Bacillus strains promoted the growth indices, enzymatic profile, intestinal immunity, and liver and intestinal histomorphology of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Atkinson, C.; Qiao, F.; Cianflone, K.; Chen, X.; Tomlinson, S. A complement-dependent balance between hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury and liver regeneration in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2304–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dati, F.; Lammers, M. Immunochemical methods for determination of urinary proteins (albumin and α1-microglobulin) in kidney disease. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Chem. 1989, 1, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Elbahnaswy, S.; Elshopakey, G.E. Differential gene expression and immune response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) challenged intraperitoneally with Photobacterium damselae and Aeromonas hydrophila demonstrating immunosuppression. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareghanipoora, M.; Akbary, P.; Akhlaghi, M.; Fereidouni, M. Non-specific immune responses and immune related genes expression of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, walbaum) fed Zataria multiflora boiss extract. Bull. Env. Pharmacol. 2014, 3, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran, R.; Gorantla, V.; Sun, X.; Ren, X.; Perez-Abadia, G.; Crespo, F.A.; Oliver, R.; Orhun, H.I.; Quan, E.E.; Maldonado, C. Targeting of glycosaminoglycan-cytokine interactions as a novel therapeutic approach in allotransplantation1. Transplantation 2002, 74, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.J. Fish Pathology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S. Pond Aquaculture Water Quality Management; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mustapha, S.; Mustapha, M.; Brahim, B.; Nozhal, C. Characterization of Vibrio alginolyticus Trh positive from mediterranean environment of Tamouda Bay (Morocco). World Environ. 2012, 2, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, V.; Ransangan, J. Effect of water temperature on susceptibility of culture marine fish species to vibriosis. Int. J. Res. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Yu, P.; Li, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, L. The mosaic accessory gene structures of the SXT/R391-like integrative and conjugative elements derived from Vibrio spp. isolated from aquatic products and environment in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Hak, A.; Ezzat, M.; Mohamed, G. Genotyping of Vibrio Parahemolyticus Isolated from Some Marine Fish. Suez Canal Vet. Med. J. SCVMJ 2018, 23, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, H.; Liu, M.; Actis, L.A.; Crosa, J.H. Plasmid- and chromosome-encoded siderophore anguibactin systems found in marine vibrios: Biosynthesis, transport and evolution. BioMetals 2013, 26, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Austin, B. Haemolysins in Vibrio species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K.M.; Al-Maary, K.S.; Mubarak, A.S.; Dawoud, T.M.; Moussa, I.M.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Hessain, A.M.; Orabi, A.; Fawzy, N.M. Characterization and susceptibility of streptococci and enterococci isolated from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) showing septicaemia in aquaculture and wild sites in Egypt. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.; Rahman, M.; Deb, S.C.; Alam, M.; Islam, M. Molecular identification of multiple antibiotic resistant fish pathogenic Enterococcus faecalis and their control by medicinal herbs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.; Helmy, A. Assessment of water quality of wastewaters of Bahr El-Baqar, Bilbies and El-Qalyubia drains in east delta, Egypt for irrigation purposes. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 55, 287–302. [Google Scholar]
- Elkiki, M.H. Environmental Impact of Water Reuse of Bahr El-Baqar Drain; Civil Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Port Said University: Port Said, Egypt, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Razek, N.; Shagar, G.; Ayoub, H. Investigation on mass mortality and bioaccumulation of heavy metals and fish pathogen in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Fayoum governorate. Abbassa Int. J. Aquac. 2016, 9, 336–355. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-X.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, T.-L. Distribution of Vibrio alginolyticus-like species in Shenzhen coastal waters, China. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.; Eissa, A.E.; Hanna, M.; Abou Okada, M. Identifying some pathogenic Vibrio/Photobacterium species during mass mortalities of cultured Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) from some Egyptian coastal provinces. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2013, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahran, E.; Elbahnaswy, S.; Mamdouh, A.Z.; El-Matbouli, M. Xenosteroids in aquaculture with special consideration to Lake Manzala (Northern delta lake, Egypt): Types, sources and mechanism of action. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 5962–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyad, Y.A.; Elbahnaswy, S.; Zaki, V.H. Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals in water and tissues of naturally infected Oreochromis niloticus from two polluted sites in Egypt, with reference to related oxidative stress. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 139–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kubrak, O.I.; Husak, V.V.; Rovenko, B.M.; Poigner, H.; Mazepa, M.A.; Kriews, M.; Abele, D.; Lushchak, V.I. Tissue specificity in nickel uptake and induction of oxidative stress in kidney and spleen of goldfish Carassius auratus, exposed to waterborne nickel. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 118–119, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehringer, D.B.; Finkelstein, M.E.; Coale, K.H.; Stephenson, M.; Geller, J.B. Assessing Mercury Exposure and Biomarkers in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) from a Contaminated River System in California. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.E.; Sparling, P.F.; Cornelissen, C.N. Gonococcal transferrin-binding protein 2 facilitates but is not essential for transferrin utilization. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 3162–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullen, J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1981, 3, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushlake, K.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K. Lowered phagocytosis in the blood of eels exposed to copper. Fish Pathol. 1985, 20, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sharaby, S.; Abd-Elgaber, M.; Tarabees, R.; Khalil, R.; Ali, M.; El-Ballal, S. Bacteriological and histopathological studies on Vibrio species isolated from naturally infected freshwater fish in Delta Region, Egypt. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2018, 6, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Buller, N.B. Bacteria from Fish and Other Aquatic Animals: A Practical Identification Manual; Cabi: Wallingford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, S.A.; Abou-Akkada, A.S.; El-Hoshy, S. Molecular studies on vibrio species isolated from imported frozen fish. Glob. Vet. 2014, 12, 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, F.; Gevers, D.; Thompson, C.; Dawyndt, P.; Naser, S.; Hoste, B.; Munn, C.; Swings, J. Phylogeny and molecular identification of vibrios on the basis of multilocus sequence analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5107–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ransangan, J.; Lal, T.M.; Al-Harbi, A.H. Characterization and experimental infection of Vibrio harveyi isolated from diseased Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Malays. J. Microbiol. 2012, 8, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recknagel, R.O.; Glende, E.A., Jr.; Dolak, J.A.; Waller, R.L. Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol. Ther. 1989, 43, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rostro, C.I.; Racotta, I.S.; Ibarra, A.M. Decreased genetic variation in metabolic variables of Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp after exposure to acute hypoxia. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 302, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hal, A.M.; Manal, I. Effect of Nigella sativa oil and ciprofloxacin against bacterial infection on gene expression in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) blood. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Vaucher, R.A.; Lopes, L.Q.; Vizzotto, B.S.; Raffin, R.P.; Santos, R.C.; da Veiga, M.L.; da Rocha, M.I.U.; Stefani, L.M. In vivo bactericidal effect of Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil against Aeromonas hydrophila: Silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) as an experimental model. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 98, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Wooster, G.A.; Bowser, P.R. Comparative blood chemistry and histopathology of tilapia infected with Vibrio vulnificus or Streptococcus iniae or exposed to carbon tetrachloride, gentamicin, or copper sulfate. Aquaculture 2004, 239, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ma, T.; Zhou, J.; Holland, J.W.; Gao, Q. Transcriptome analysis of the endangered Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus): Immune modulation in response to Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 169, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Gao, Z.-X.; Zhao, H.-H.; Yi, S.-K.; Chen, B.-X.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, W.-M. Transcriptome analysis and microsatellite discovery in the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) after challenge with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Asim, M.; Liang, X. Analysis of the transcriptomic profilings of Mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) infected with Flavobacterium columnare with an emphasis on immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 43, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Mu, L.; Fu, S.; Wu, L.; Han, K.; Wu, H.; Bian, X.; Wei, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, A. Expression and characterization of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) secretory and membrane-bound IgM in response to bacterial infection. Aquaculture 2019, 508, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M. C-reactive protein: A critical update. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacCarthy, E.M.; Burns, I.; Irnazarow, I.; Polwart, A.; Greenhough, T.J.; Shrive, A.K.; Hoole, D. Serum CRP-like protein profile in common carp Cyprinus carpio challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila and Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, G.J.; El-Mowafi, A.; Simko, E.; Kocal, T.E.; Ferguson, H.W.; Hayes, M.A. Plasma proteins of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) isolated by binding to lipopolysaccharide from Aeromonas salmonicida. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 120, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, C.; Ozorio, R.O.; Afonso, A.; Moraes, J.R.; Costas, B. Immune responses and gut morphology in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) fed dietary probiotic supplementation and following exposure to Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas, B.; Rêgo, P.; Simões, I.; Marques, J.; Castro-Cunha, M.; Afonso, A. Cellular and humoral immune responses of Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis (Kaup), following challenge with two Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida strains from different geographical origins. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 543–553. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Tang, Y.; Lu, F.; Luo, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J.; Li, N.; Han, Q.; Liu, F. The effect of Aeromonas hydrophila infection on the non-specific immunity of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 42, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Núñez-Díaz, J.; Fumanal, M.; Mancera, J.; Moriñigo, M.; Balebona, M. Two routes of infection with Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida are effective in the modulation of the transcription of immune related genes in Solea senegalensis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 179, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.; Mahapatra, K.D.; Saha, J.; Barat, A.; Sahoo, M.; Mohanty, B.; Gjerde, B.; Ødegård, J.; Rye, M.; Salte, R. Family association between immune parameters and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila infection in the Indian major carp, Labeo rohita. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vina, J.; Borras, C.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C. A free radical theory of frailty. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; Parmeggiani, B.; Leipnitz, G.; Verdi, C.M.; Santos, R.V.; Stefani, L.M.; Baldisserotto, B. The disturbance of antioxidant/oxidant balance in fish experimentally infected by Aeromonas caviae: Relationship with disease pathophysiology. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 122, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Guarda, N.S.; Bollick, Y.S.; Moresco, R.N.; Brusque, I.C.M.; Santos, R.C.; Baldisserotto, B. Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil nanoparticles ameliorate the hepatic antioxidant/oxidant status of silver catfish experimentally infected with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 108, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.D.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Verdi, C.M.; Santos, R.C.; Da Rocha, M.I.U.; da Veiga, M.L.; da Silva, A.S.; Baldisserotto, B. Oxidative stress and antioxidant responses in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus experimentally infected by Providencia rettgeri. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurhalyuk, N.; Tkachenko, H. Induction of oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses in the livers of sea trout, Salmo trutta L., with ulcerative dermal necrosis. Fish. Aquat. Life 2011, 19, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Baskaran, B.; Raj, M.; Mandal, A.; Shanmugam, K.; Subramanian, P.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.G.; Narayanasamy Marimuthu, P. Vibriosis Incidents in Marine Finfish Farms: Prevalence, Diagnosis of Pathogens using 16S rRNA, Histopathology, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation Against Isolated Vibrio spp. using Antibiotics and Probiotics. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 38, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupesha Sharma, S.R.; Rathore, G.; Verma, D.K.; Sadhu, N.; Philipose, K.K. Vibrio alginolyticus infection in A sian seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch) reared in open sea floating cages in India. Aquac. Res. 2012, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Water Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Dissolved oxygen (DO) (mgL−1) | 4 |
| Temperature (°C) | 33 |
| Nitrite (NO2) (mgL−1) | 0.07 |
| Un-ionized ammonia (NH3) (mgL−1) | 0.90 |
| Copper (Cu) (mgL−1) | 0.64 |
| Iron (Fe) (mgL−1) | 1.9 |
| Nickel (Ni) (mgL−1) | 0.80 |
| Cadmium (Cd) (mgL−1) | 0.09 |
| Lead (mgL−1) | 0.40 |
| Item | V. alginolyticus | V. cholerae | E. cloacae |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram staining | -ve | − | − |
| Cell morphology | Short rod with curve shaped | Short rod with curve shaped | Bacilli |
| Motility | + | + | − |
| Catalase | + | + | + |
| Growth on TCBS | Green | Green | − |
| Sorbitol (SOR) fermentation | − | − | + |
| Rhamnose (RHA) fermentation | − | − | + |
| Sucrose (SUC) fermentation | + | + | + |
| Melibiose (MEL) fermentation | − | − | + |
| Amygdalin (AMY) fermentation | + | + | + |
| Arabinose (ARA) fermentation | − | − | + |
| Cytochrome oxidase | + | + | − |
| Arginine dihydrolase | + | + | − |
| Lysine decarboxylase (LDC) | + | + | + |
| Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) | + | + | − |
| Citrate utilization | + | + | + |
| H2S production | − | − | − |
| Urease production | − | − | − |
| Tryptophane deaminase (TDA) | + | + | − |
| Indole (IND) production | + | + | − |
| Voges–Proskauer Test (VP) | − | V | + |
| Gelatine (GEL) hydrolysis | + | + | − |
| Glucose (GLU) fermentation | + | + | + |
| Mannitol (MAN) fermentation | + | + | + |
| Inositol (INO) fermentation | − | − | + |
| Antibiotic | Concentration (µg) | V. alginolyticus | V. cholera | E. cloacae |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin (AML) | 25 | 09.7 ± 0.6 (R) | 10.5 ± 1.0 (R) | 22.7 ± 1.5 (S) |
| Erythromycin (E) | 15 | 23.1 ± 1.7 (S) | 21.7 ± 1.5 (S) | 07.3 ± 0.6 (R) |
| Doxycycline (DO) | 30 | 23.3 ± 1.1 (S) | 22.3 ± 1.1 (S) | 26.0 ± 1.0 (S) |
| Florfenicol (FFC) | 30 | 20.3 ± 1.1 (S) | 21.3 ± 1.1 (S) | 24.0 ± 1.0 (S) |
| Ciprofloxacin (CIP) | 5 | 20.7 ± 1.2 (S) | 22.7 ± 1.3 (S) | 25.0 ± 1.0 (S) |
| Norfloxacin (NOR) | 10 | 10.3 ± 0.6 (R) | 10.3 ± 0.6 (R) | 26.0 ± 1.0 (S) |
| Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Healthy M. cephalus | Infected M. cephalus | Sig |
| ALT (U L−1) | 13.25 ± 1.09 | 29.04 ± 1.71 | ** |
| AST (U L−1) | 68.53 ± 2.57 | 99.1 ± 2.32 | *** |
| T. protein (g dL−1) | 5.84 ± 0.27 | 6.02 ± 0.33 | NS |
| Albumin (g dL−1) | 3.19 ± 0.12 | 2.73 ± 0.18 | NS |
| Globulin (g dL−1) | 2.65 ± 0.32 | 3.30 ± 0.29 | NS |
| IgM (mg dL−1) | 9.31 ± 0.64 | 4.98 ± 0.76 | *** |
| CRP (mg L−1) | 2.63 ± 0.41 | 7.12 ± 0.67 | ** |
| C3 (mg mL−1) | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.54 ± 0.08 | NS |
| Lysozyme (µg mL−1) | 7.82 ± 1.32 | 14.71 ± 2.19 | ** |
| Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Tissues | Healthy M. cephalus | Infected M. cephalus | Sig |
| MDA (nmol mg−1 protein) | Gills | 8.55 ± 0.94 | 12.48 ± 0.54 | *** |
| Brain | 5.24 ± 0.49 | 9.20 ± 0.56 | ** | |
| SOD (U mg−1 protein) | Gills | 116.81 ± 7.77 | 95.24 ± 4.55 | ** |
| Brain | 50.49 ± 3.64 | 32.15 ± 1.06 | ** | |
| Catalase (U mg−1 protein) | Gills | 69.11 ± 6.29 | 50.46 ± 2.27 | * |
| Brain | 31.01 ± 3.76 | 16.29 ± 1.21 | ** | |
| GSH (mg mg−1 protein) | Gills | 2.95 ± 0.51 | 1.42 ± 0.22 | ** |
| Brain | 5.89 ± 0.28 | 3.16 ± 0.14 | *** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbahnaswy, S.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Shakweer, M.S.; Eldessouki, E.A.A.; Abdelwarith, A.A.; Younis, E.M.; Davies, S.J.; El-Son, M.A.M. Bacterial Co-Infection as a Potential Threat to Farmed Flathead Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Phenotypic and Molecular Diagnosis, Histopathology, Immunity Response, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation. Fishes 2023, 8, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070357
Elbahnaswy S, Elshopakey GE, Shakweer MS, Eldessouki EAA, Abdelwarith AA, Younis EM, Davies SJ, El-Son MAM. Bacterial Co-Infection as a Potential Threat to Farmed Flathead Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Phenotypic and Molecular Diagnosis, Histopathology, Immunity Response, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation. Fishes. 2023; 8(7):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070357
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbahnaswy, Samia, Gehad E. Elshopakey, Medhat S. Shakweer, Elsayed A. A. Eldessouki, Abdelwahab A. Abdelwarith, Elsayed M. Younis, Simon J. Davies, and Mai A. M. El-Son. 2023. "Bacterial Co-Infection as a Potential Threat to Farmed Flathead Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Phenotypic and Molecular Diagnosis, Histopathology, Immunity Response, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation" Fishes 8, no. 7: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070357
APA StyleElbahnaswy, S., Elshopakey, G. E., Shakweer, M. S., Eldessouki, E. A. A., Abdelwarith, A. A., Younis, E. M., Davies, S. J., & El-Son, M. A. M. (2023). Bacterial Co-Infection as a Potential Threat to Farmed Flathead Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Phenotypic and Molecular Diagnosis, Histopathology, Immunity Response, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation. Fishes, 8(7), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070357






