Abstract
River ecosystems are exposed to a multitude of stressors, including increasing pesticide run-off driven by precipitation and irrigation. Pyrethroids are the fourth major group of insecticides in use worldwide and have extremely negative effects on aquatic fauna. In this study, we aimed to assess the effects of an acute 2 h sub-lethal exposure to different levels of the pyrethroid esfenvalerate on the swimming behaviour of two Cypriniformes species: the native Iberian barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei) and the non-native invasive bleak (Alburnus alburnus). The experimental set-up consisted of previous exposure to three esfenvalerate concentrations (control, 1.2 (low), and 2.0 (high) μg/L) before being stocked in a three-artificial-flume-channel mesocosm for behavioural trials through direct observation. Monitored behaviours included (i) routine activity, (ii) shoal cohesion, and iii) boldness. Significant differences in fish behaviour were detected for the native species (barbel), as individuals spent significantly more time holding position (i.e., resting) in the control (44.9%) than in the high esfenvalerate concentration (25.2%). Concordantly, control barbels were also found to perform more directional changes than the ones exposed to high esfenvalerate concentrations. Behavioural changes were also found for boldness, measured by the proportion of fish attempts to negotiate the upstream ramp, which were significantly higher in the control (37.4%) and in the high concentration (41.5%) compared to the low one (21.1%). Finally, regarding shoal cohesion of the barbel, it was tighter in the control (81.3%) than in the low- (70.5%) and high- (71.1%) esfenvalerate treatments. For the invasive bleak, there were no significant differences in any of the behavioural traits upon previous exposure to an increasing esfenvalerate concentration. This experimental study demonstrated that even short-term exposure to the pyrethroid esfenvalerate was sufficient to alter the behaviour of a native Cypriniformes fish species while not affecting the non-native species. This may confer greater competitive advantages to non-native fish species in the context of global changes.
Key Contribution:
Short-term exposure to the pyrethroids may be enough to impair the behaviour of a native Cypriniformes fish species while not affecting the non-native species. This gives greater competitive advantages to non-native fish species in the context of global changes.
1. Introduction
Freshwater ecosystems provide vital resources and services and are home to a great diversity of fish species, which play a crucial role in maintaining ecological health and balance [1,2]. However, the integrity of these vulnerable systems is increasingly compromised by human activities [3]. The IUCN identified “Invasive Non-Native/Non-native Species/Diseases” (33.6% of evaluated European freshwater fish species are threatened by this threat) and pollution from “Agricultural & Forestry Effluents” (24.4%) as major threats affecting European freshwater fish species, half of which are from the Cyprinidae family [4,5].
Pyrethroids are pesticides used in agriculture and urban areas to kill or control harmful insect pests [6]. The use of this type of pesticide has increased over the past decades due to its broad-spectrum effects and low toxicity to mammals and birds [7], and it is now the fourth major group of insecticides in use worldwide [8]. Esfenvalerate is one of the most commonly used pyrethroid insecticides in agriculture [9,10]. These types of organic residual pesticides can leach and enter aquatic environments through direct application or run-off [11,12]. Environmental analysis has shown that esfenvalerate concentrations in freshwater systems can amount to up to 0.76 μg/L [13,14,15]. Water contamination of this sort poses an environmental threat since the elimination rate of pyrethroids in aquatic organisms is low, and esfenvalerate has been found to have toxic effects on a wide range of aquatic organisms, particularly fish [6,16]. Exposure to esfenvalerate can cause a range of neurological, physiological, and genetic damage in fish and has been shown to accumulate in fish tissues [17,18,19]. Nonetheless, while measured concentrations of esfenvalerate are often below acute toxic levels for aquatic organisms, potential sub-lethal effects resulting in energy reallocation or behavioural and swimming activity abnormalities should be of concern because they can compromise the ecological fitness of species and ultimately may contribute to altering food webs and ecosystem dynamics [20,21]. However, addressing sub-lethal effects in the wild is very difficult, either because species require continuous behavioural observations or because affected individuals may not survive therein.
Another major global threat to freshwater fish species is the wide expansion of non-native species, especially in the Mediterranean region [4,22,23]. When such species establish self-sustaining populations, spread to new environments, and negatively interact with native species, they become invasive, leading to the decline of native fish populations, compromising the structure and dynamics of freshwater ecosystems [24], as they outcompete native species for habitat and resources [25,26]. In addition, the impacts of these pressures on freshwater fish species will be amplified by climate change and other interacting stressors present in the environment [27,28,29,30,31]. Thus, it is essential to understand the toxicological effects of sub-lethal exposure to pyrethroids on native and non-native species at an individual scale since it might potentially lead to effects on the health of fish populations [32].
Overall activity (i.e., resting, searching, and fleeing) is a significant and commonly evaluated trait in fish behavioural studies and is often related to foraging and growth [33,34]. Boldness (i.e., the tendency to leave a refuge and explore an unknown exposed environment) is another significant behavioural trait observed in fish [35,36] and is linked to responses to stimuli [37,38], predator inspection in school leaders, and predator evasion [39,40], dispersion [41,42,43], and activity [44,45,46]. Shoaling cohesion and other social behaviours are known to affect the survival of fish living in groups [47,48] by improving threat perceptions [49,50] and reducing individual risks and physical costs of movement [51,52,53]. Aggregation has other benefits, such as improved foraging efficiency [54], predator encounter dilution, and predator confusion [55,56,57]. Therefore, monitoring fish behaviour can be an incredibly relevant tool to link the impairment of individual behavioural responses to species interactions and population processes as a result of esfenvalerate exposure [12,21,32,58,59].
This paper aims to evaluate the effects of the pyrethroid pesticide esfenvalerate on freshwater fish species’ behaviour, specifically the native Iberian barbel Luciobarbus bocagei (Steindachner, 1864) and the non-native bleak Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus, 1758). The behaviour parameters observed included routine activity, boldness, and shoaling cohesion. The research on these Cypriniformes species focused on the sub-lethal impacts of toxicity caused by pesticides and the potential ecological consequences esfenvalerate might have in freshwater wild fish communities, which could help recognize the implications for the management and conservation of the vulnerable aquatic ecosystems. Specifically, we expect that exposure to increasing concentrations of esfenvalerate will (a) reduce activity in both fish species, (b) reduce shoal cohesion in both species, (c) reduce boldness in both species, and (d) the effects will be more pronounced in the native fish species than in the non-native.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pyrethroid Insecticide
In this study, we used esfenvalerate, a broad-spectrum nonselective pyrethroid insecticide, commercially acquired as Flower’s SUMIFIVE® PLUS as an oil in water emulsion (15 mL volume, formulated based on a combination of esfenvalerate 5% concentration, phenylethyl-xylene isomers, and ethyl phenylethyl-, i.e., 50 g/L, concentration). The use of pyrethroid insecticides has been increasing in the past decades [60] due to their generally low half-life periods and, consequently, low persistence in the environment. Specifically, for esfenvalerate, experiments revealed that its half-life period could range from 7.8 to 100 days in soil exposed to sunlight and 150.0 to 553.4 days in dark soil [61]. Some studies suggest that exposure to esfenvalerate can affect fish hatching and larvae viability [9], while others revealed changes in swimming behaviour in Atherinopsidae [32] and osmerids [20]. Other effects of this pyrethroid were also reported, including increased vulnerability to predation in the fathead minnow Pimephales promelas [62] and increased mortality in rainbow trout larvae Oncorhynchus mykiss [10].
2.2. Target Species and Life Stages
Representatives of native and non-native Cypriniformes were chosen for the present study: the native Iberian barbel Luciobarbus bocagei (Steindachner, 1864) (henceforth barbel), a cyprinid species endemic to the Iberian Peninsula, with a “Least Concern” status and a widespread distribution in Portuguese rivers [63], and the non-native bleak Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus, 1758), recently reclassified into the Leuciscidae family [64]. The barbel is a medium-sized species with a bottom trophic strategy; it mostly inhabits lotic environments but has the ability to live in reservoirs. The bleak is an invasive opportunist that feeds mostly on zooplankton and algae but occasionally eats fish larvae [65]. It inhabits preferably lentic environments but can spread across river networks and occupy lotic ones. It is known to hybridize with native species from the Squalius genus. A previous assessment by Miranda et al. [66] revealed that the maximum size attained by bleak did not surpass 151 mm (total length), while Masó et al. [67] reported juvenile bleak with total lengths ranging from 48 to 100 mm, sizes that can be attained by juvenile barbels [66,67,68]. Therefore, to allow for comparisons between the two species, and as both taxa do not overlap in their size range concerning specific life stages (e.g., juveniles, adults), the life stages that were used in this study included juvenile barbels and adult bleaks due to their comparable sizes and frequency of occurrence in Iberian streams. The former has been recently studied in the mesocosm facility at the School of Agriculture campus [69,70,71].
2.3. Fish Sampling and Holding Facilities
Fish sampling took place in May 2021 during two sampling events (each targeted for a different species) where a total of 36 native barbel Luciobarbus bocagei (Steindachner, 1864) and 36 non-native bleak Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus, 1758) were captured in Rivers Lizandro (barbel) and Sor (bleak) (Central Portugal), respectively. For both sampling events, a 150 m long river stretch was chosen based on habitat representativeness and accessibility. Electrofishing was carried out by means of wadable electrofishing (Hans Grassl IG-200, Schönau am Königsee, Germany), moving upstream in a zig-zag manner, following the recommendations of the European Committee of Standardization (CEN, 2003). After being sampled, fish were transported to the campus of the School of Agriculture (ISA), University of Lisbon, in a fish transport box (Hans Grassl, 190 L) filled with river water from the rivers from which fish were sampled. The box also featured a portable aeration device (ELITE, KG HAGEN Deutschland GmbH & Co., Holm, Germany) to reduce transportation stress.
At the ISA campus, individuals were kept for 48 h in a quarantine tank (800 L) featuring a High-performance Cannister Filter FX5 (Fluval, Baie-d’Urfé, QC, Canada) and PVC tubes to promote shelter for fish and hence reduce stress [71,72]. Nutrafin Aqua+ was added immediately before fish were placed in the tank to create a suitable biological media with bacteria and reduce ammonia and nitrate levels resulting from fish waste. Fish feeding (TetraPond sticks) was interrupted 24 h prior to behavioural trials. Water quality (temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen (DO)) in the acclimation tank was monitored daily with a multiparametric probe (HANNA, HI 9812-5).
2.4. Mesocosm Facility
The effects of esfenvalerate on fish swimming behaviour were assessed in the mesocosm facility located at the campus of the School of Agriculture, University of Lisbon, Portugal. Mesocosms are outdoor experimental systems that allow studying the natural environment under controlled conditions, avoiding the interference of confounding factors and incorporating natural variations (photoperiod and air temperature, for instance), hence providing a link between field surveys and highly controlled laboratory experiments [69,70].
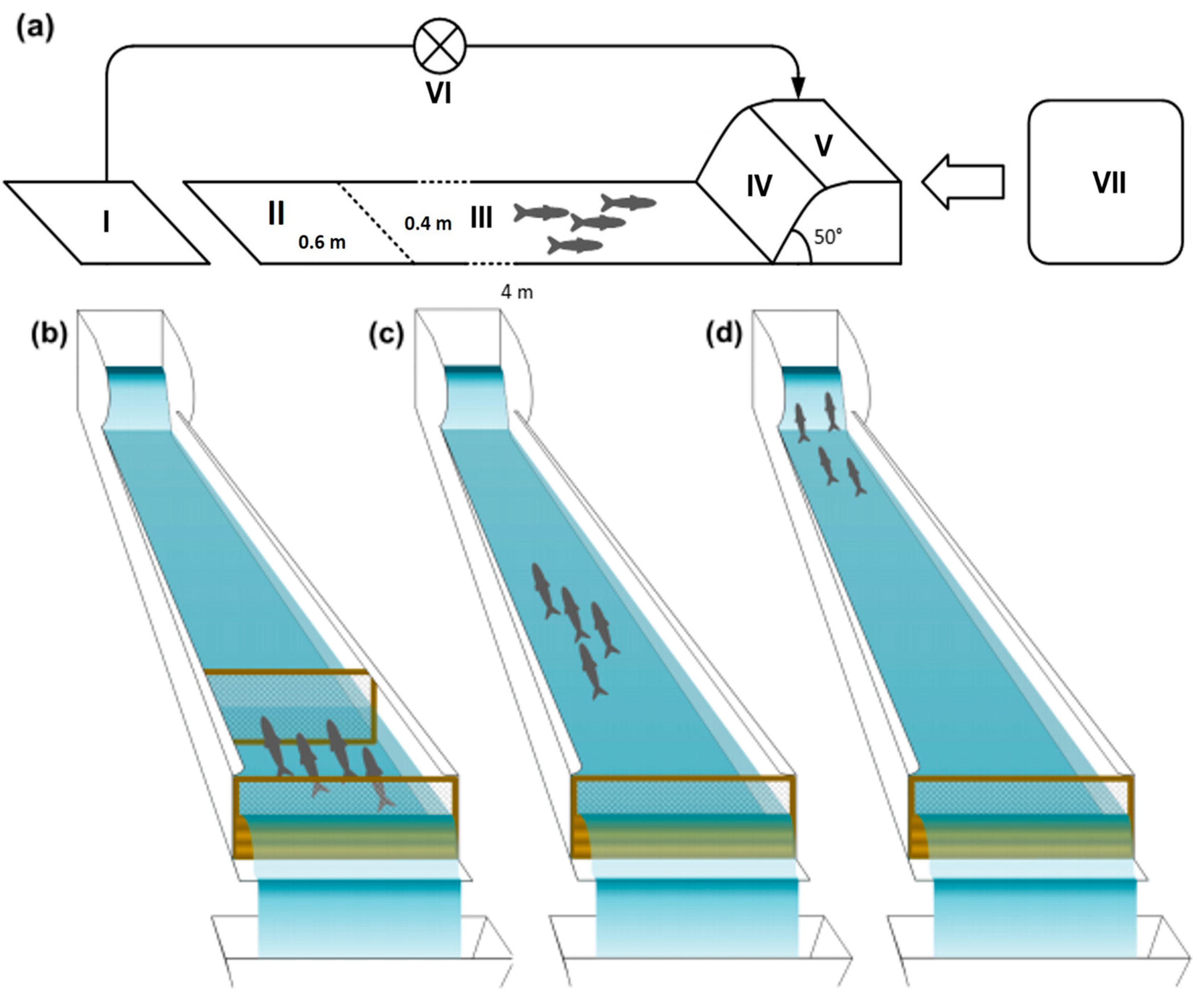
The present mesocosm facility consisted of a set of 3 tinplate-lined outdoor artificial flume channels, 0.4 m wide, 4 m long, and 0.2 m deep (Figure 1a, II and III). Each flume channel was separated from an upstream tank (70 L, Figure 1a, V) by a 47 cm long and 36 cm high ramp at a slope of 50% (Figure 1a, IV) and delimited downstream (Figure 1a, II) by a fixed mesh panel to prevent fish from dropping out of the channel. Water distribution and recirculation were achieved with a PEAD pipe system that allowed water to run from the supply tank to the upstream ones, main channels, and to 70 L downstream tanks (Figure 1a, I). The downstream tanks were connected to pumps (Kripsol OK-71 B, 0.56 kW), operating in a recirculation flow system towards the upstream tanks, allowing upholding water conditions independently of the source tank.
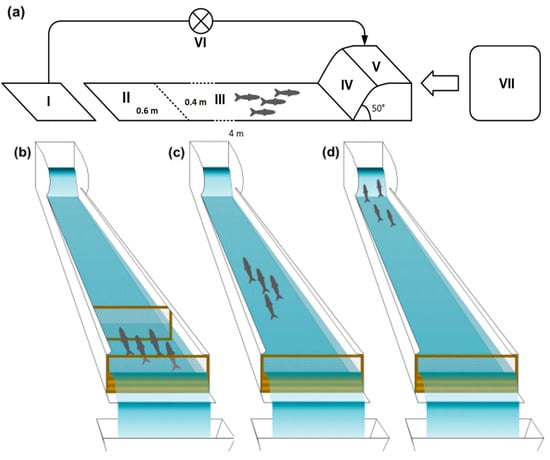
Figure 1.
Scheme of the experimental set-up in the mesocosm facility. (a) Sections composing each flume channel, operating in a recirculating system: I—downstream tank; II—acclimation section; III—flume channel; IV—ramp; V upstream tank; VI—pump Kripsol OK-71 B, 0.56 kW; VII—holding tank. (b) Acclimation phase lasting 10 min, with fish being kept in the lowermost section of each channel delimited upstream by a net; (c) free movement of the fish during 1 h trials, with one observer per channel; (d) attempts to negotiate the ramp (boldness).
2.5. Experimental Set-Up
After quarantine, fish were randomly selected into groups of 4 individuals and transferred to 50 L tanks, with natural light conditions and featuring stones for shelter to avoid stress. In these tanks, fish were exposed for 2 h to three different esfenvalerate concentrations: 0.0 μg/L (control, without the insecticide), 1.2 μg/L (low concentration), and 2.0 μg/L (high concentration) (Table 1). It should be noted that while there are no reference levels of esfenvalerate for surface water bodies in the European Union, a previous study by Floyd et al. [62] determined the effects of a short-time exposure (4 h) of low levels of esfenvalerate (ranging from 0.455 to 1.142 μg/L) in the swimming behaviour of larval fathead minnows Pimephales promelas. Similarly, in a study by DeMicco et al. [18], a concentration of either 1 μg/L deltamethrin or cypermethrin for a 6-day period post-hatching induced body spasms and uncontrolled swimming in young zebrafish Danio rerio. Considering that juvenile (and not larval) individuals were used in this study and that the period of exposure to the pyrethroid (2 h) was shorter than in previous studies using pyrethroid concentrations up to 1 μg/L [18,20,32,61], a concentration of 2.0 μg/L was adopted as the high-concentration treatment, with 1.2 μg/L being selected as the midpoint (and approximately half of the highest value) of the gradient and 0.0 μg/L as the control (no esfenvalerate). Water quality was checked with a multiparametric probe (HANNA, HI 9812-5). Each one of the 3 experimental groups had 3 replicates, with a total of 9 behavioural trials per species.

Table 1.
Fish length (TL, mm) and body mass (g) measured at the end of each trial, and physical-chemical parameters, including water temperature (°C), pH, and conductivity (mS/cm), for each of the esfenvalerate treatments administrated (control, low, and high) within each tested species (barbel and bleak) measured prior to the trials in the flume channels. Water quality was checked with a multiparametric probe (HANNA, HI 9812-5). Values shown are averages ± standard deviation.
After being exposed to each treatment, fish were transferred to the flume channels, allowing us to assess the behavioural traits in the three different treatment groups (control, low and high esfenvalerate concentrations). All behavioural trials were performed under similar weather conditions. Replicates were conducted, with these involving a school of 4 wild-caught fish of each species in the experimental unit (number of replicates = 3 schools of 4 fish per treatment, totalling 12 fish per treatment, and 72 fish overall). Following an initial acclimation period of 10 min at the lowermost section of the channels, delimited by a removable net (Figure 1a, section II, 1b), fish were allowed to move freely in the channels (Figure 1c) or attempt to negotiate the ramp (Figure 1d). Each observer (one per channel) stood still at an approximate distance of 0.5 m downstream of each channel, with a full view of it, approaching and leaving the observation points discreetly whenever necessary. This procedure was followed in previous experiments in this mesocosm facility with barbels and was considered adequate since no changes in fish behaviour were noted [69,71,73].
Monitored behavioural traits included the following: (1) activity (ecologically relevant for looking for shelter and feeding, for instance [34]), classified as “resting” (holding position), “searching”, “fleeing”, or “directional changes” (90° change in swimming direction); (2) boldness, equivalent to the total counts of fish that actively attempted to negotiate the ramp (Figure 1d), based on the idea that a novel environment is considered dangerous and suggests willingness to undertake risks [33]; and (3) shoaling cohesion, given by the ratio of the number of fish in the flume (Figure 1a, II and III) that were within one body length of each other [74]), divided by the total number of fish in the flume, excluding the ones in the upstream tank [73]. Trials lasted one hour each and consisted of the instantaneous sampling of the behavioural traits every 3 min (with the exception of boldness, which was recorded continuously). Fish were only tested once, and after each trial, they were removed from the channels, measured (TL, to the nearest mm), and later released at their previous capture locations (barbel), except for the non-native bleak, which were not returned to the river and later euthanized with an overdose of benzocaine.
2.6. Data Analyses
Data normality and homoscedasticity were tested using the Shapiro–Wilk test and F-test of variances, respectively. Both activity and boldness data were fitted into generalized linear models (GLM) with a Poisson distribution (considering the absolute frequencies of each of these behavioural traits), with treatment (esfenvalerate concentration) as a predictor. Shoaling cohesion between treatments was compared using the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by the Dunn post hoc test. All analyses were conducted in R (version 4.1.0).
3. Results
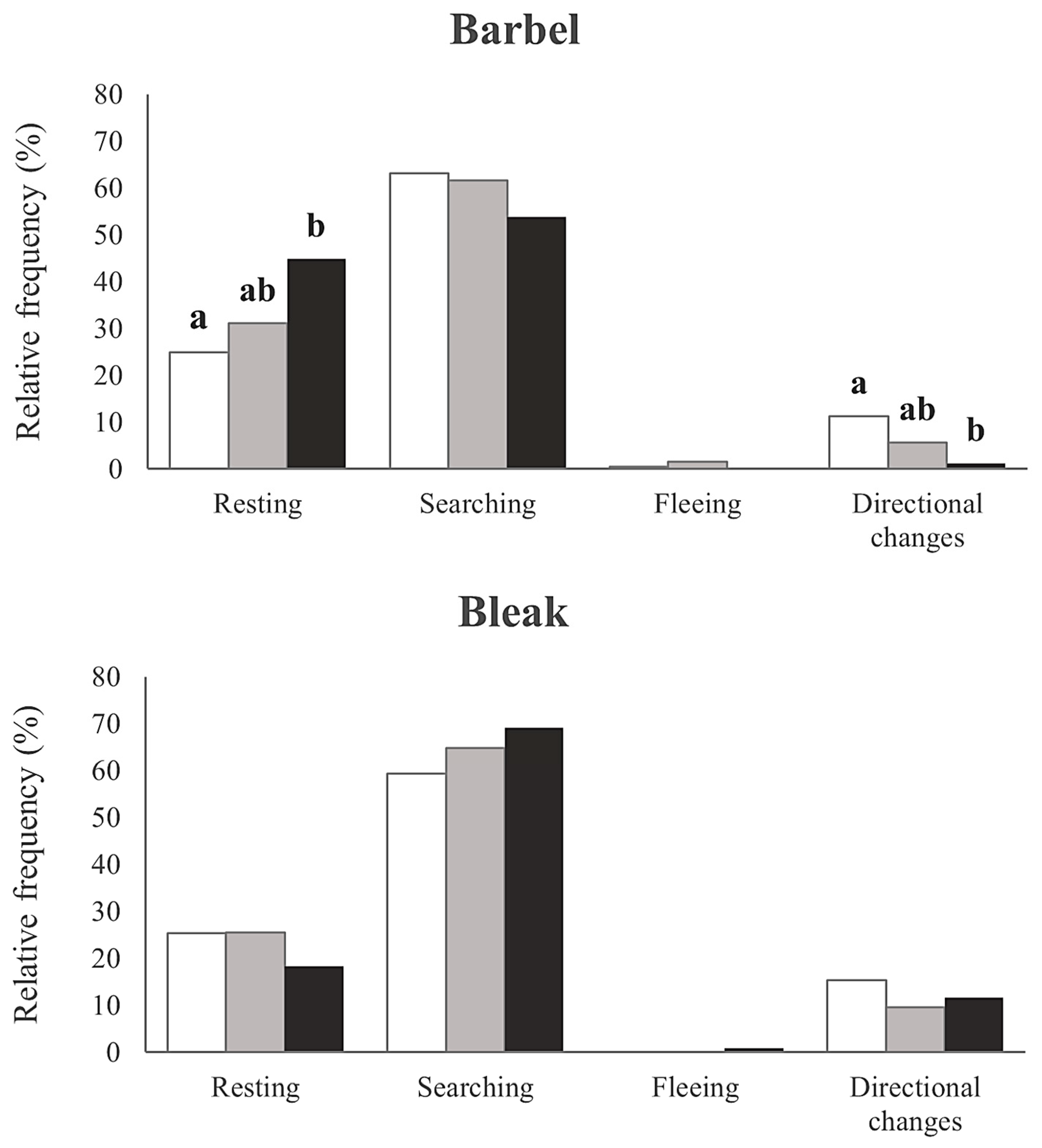
Regarding fish activity, “searching” was the most observed trait in both species, representing between 54 and 63% and 59 and 60% of all activity traits observed in the barbel and bleak, respectively, while fleeing was the least observed, accounting for 2% for both barbel and bleak (Figure 2). No significant differences between treatments were observed for the bleak for any of the traits: resting (β = −0.099, z = −0.312, p = 0.755); searching (β = −0.149, z = −1.307, p = 0.191); fleeing (β = 17.21, z = 0.005, p = 0.996); and directional changes (β = −0.475, z = −1.790, p = 0.074) (Figure 2). While “searching” and “fleeing” did not significantly differ between treatments in the barbel, the observed frequency of the two remaining activity traits significantly differed between the control and high concentration of esfenvalerate for “resting”: (β = −0.684, z = −1.073, p < 0.01) and “directional changes” (β = −2.080, z = −3.396, p < 0.01).

Figure 2.
Relative frequency (%) of activity traits (resting, searching, fleeing, and directional changes) displayed in the barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei) and bleak (Alburnus alburnus) for each concentration of esfenvalerate: control (0.0 μg/L, white fill), low (1.2 μg/L, light grey), and high (2.0 μg/L, dark grey). For each activity trait, significant differences (GLM Poisson, p < 0.05) between treatments are expressed by different letters (“a”, “b”); when treatments “share” the same letter, there are no statistical differences.
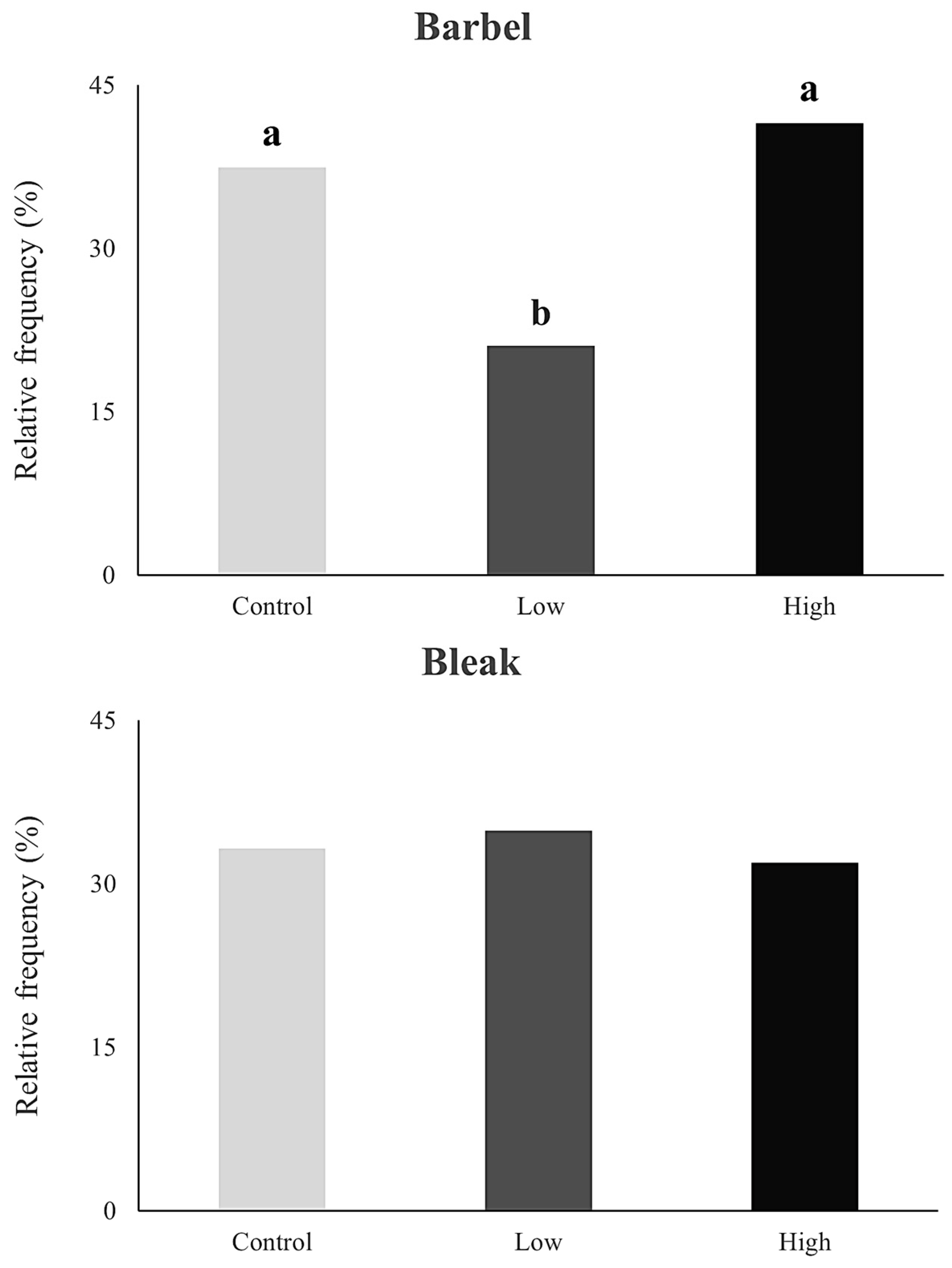
Concerning boldness, mean observed frequencies ranged between 21 and 42% in the barbel and 32 and 35% in the bleak (Figure 3). Significant differences were found for the barbel exposed to the low-esfenvalerate-concentration treatment regarding both the control (β = −0.522, z = −3.531, p < 0.01) and high-concentration treatments (β = −0.679, z = −4.728, p < 0.01), with the low concentration of esfenvalerate fish showing fewer attempts to pass the ramp (Figure 2). Similar to the activity traits, no significant differences in boldness were observed for the bleak (β = 0.049, z = 0.312, p = 0.755) (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Relative frequency (%) of boldness (measured as the number of attempts made by barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei) and bleak (Alburnus alburnus) to overcome the ramp in the flume channels) for each concentration of esfenvalerate: control (0.0 μg/L, light grey), low (1.2 μg/L, dark grey), and high (2.0 μg/L, black). Significant differences (GLM Poisson, p < 0.05) between treatments are expressed by different letters (“a” and “b”); when treatments “share” the same letter, there are no statistical differences.
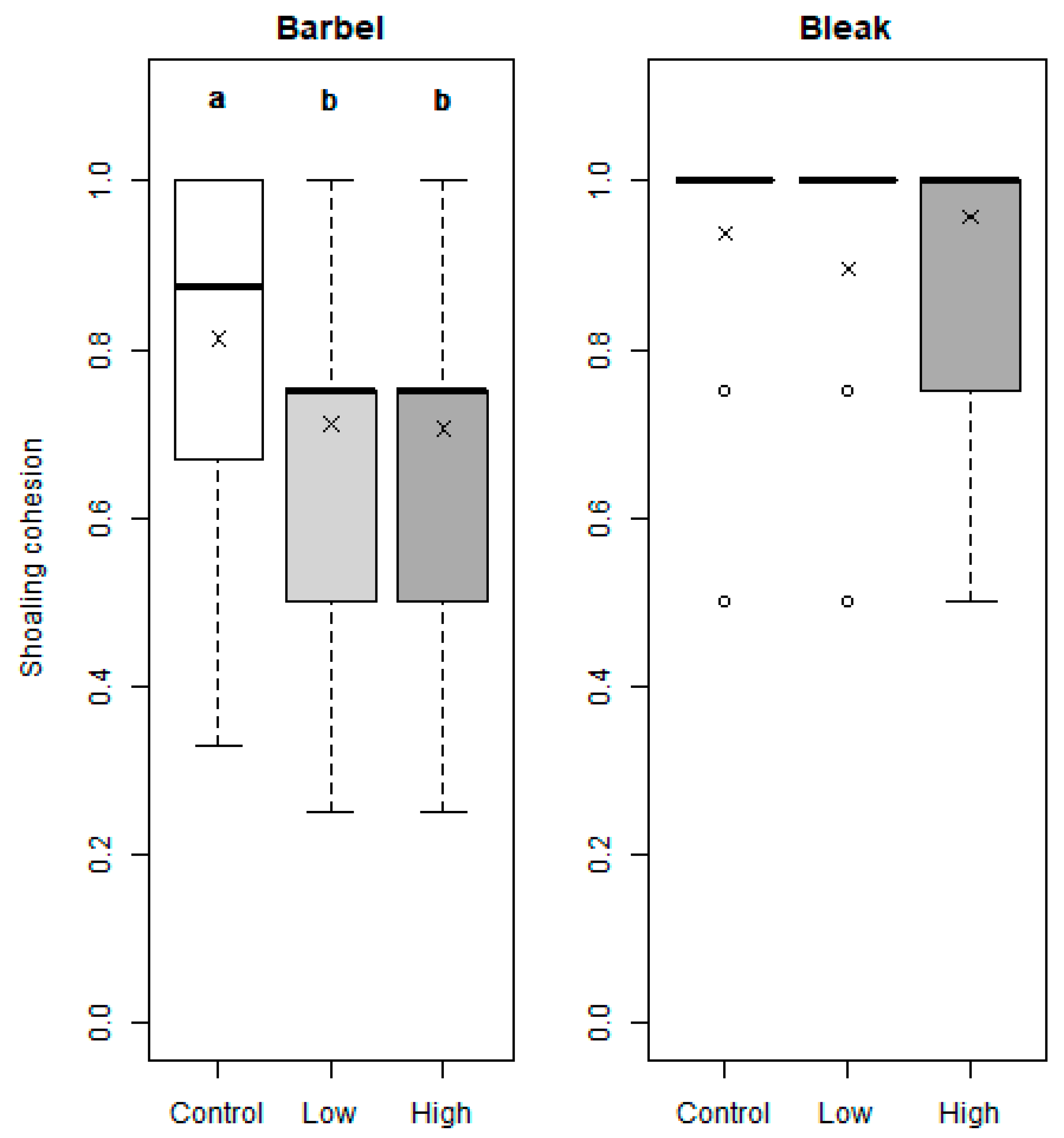
Overall, shoaling cohesion was lower in barbel (0.74 ± 0.22) when compared to the bleak (0.93 ± 0.15) (Figure 4). The barbel showed significant differences in shoal cohesion among treatments (χ2 = 7.185, df = 2, p = 0.028), specifically between the control (0.813 ± 0.207) and both low (0.705 ± 0.213; p < 0.01, Dunn post hoc) and high esfenvalerate concentrations (0.711 ± 0.211; p = 0.014, Dunn post hoc). For the bleak, there were no significant differences in shoal cohesion between the control (0.938 ± 0.142), low (0.958 ± 0.104), and high (0.896 ± 0.184) concentrations (χ2 = 3.493, df = 2, p = 0.174).

Figure 4.
Shoaling cohesion index for the barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei) and bleak (Alburnus alburnus), for each concentration of esfenvalerate: control (0.0 μg/L, white fill), low (1.2 μg/L, light grey), and high (2.0 μg/L, dark grey). Mean values and medians are represented by “×” and bold lines, respectively. For each activity trait, significant differences (Kruskal–Wallis followed by Dunn post hoc for pairwise comparisons, p < 0.05) between treatments are expressed by different letters (“a” and “b”); when treatments “share” the same letter, there are no statistical differences.
4. Discussion
Emergent stressors in rivers, such as pesticide exposure, potentiate existing threats to native aquatic fauna [6,75], which can be manifested not only in terms of direct effects, such as mortality, but also through sub-lethal effects when concentrations are below threshold values. These disturbances might have an immediate, medium-, or long-term effect on individuals and ultimately on population viability, and some effects can be measured as behavioural changes. Esfenvalerate is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide commonly used in agriculture [8,20] and is especially toxic to fish, even at lower concentrations [12,32]. This pesticide is known to cause adverse biochemical responses in organisms by blocking sodium and potassium channels, resulting in neurological damage [19]. Sub-lethal effects include reduced growth, reproductive success [76], and erratic swimming behaviour [21,77], thereby compromising the survival of aquatic species [59,62,78]. Understanding these sub-lethal effects in river systems where non-native species are also present is essential to evaluate the response of both native and non-native species, thus determining if any competitive advantage can result from different performances in native and non-native species after pesticide exposure [20]. Moreover, climate change is expected to intensify current threats to freshwater ecosystems [79], such as increasing temperatures [80,81], pollution [4,82], salinization [83,84,85], and the pressures of non-native and invasive species on native fish communities [29,86,87,88]. This work aimed to understand the behavioural effects of the three concentrations of the pyrethroid insecticide esfenvalerate on the native barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei) and the non-native invasive bleak (Alburnus alburnus) by studying routine activity, boldness, and shoaling behaviour of the fish.
The swimming behaviour of the barbel differed with different levels of esfenvalerate upon prior exposure to this pesticide. Specifically, concerning activity, the frequency of resting fish was higher in the high-esfenvalerate-exposed groups than in the control ones; concomitantly, the percentage of fish performing directional changes was lower in the high-esfenvalerate treatment as opposed to the control. These changes suggest that barbel activity is, in general, lower when exposed to higher concentrations of esfenvalerate. Similar results were found in other studies where swimming abnormalities and other significant effects on motion activity have been detected in larval fathead minnows after 4 h of exposure [20] and in juvenile bluegill after pulse exposure to 0.025 μg/L of esfenvalerate [89].
Regarding boldness, measured by the number of attempts to negotiate the ramp, significant differences were also observed for the barbel, with less bold behaviour in the low-esfenvalerate treatment than in the control and high-esfenvalerate fish groups. These results partially agree with our initial expectations of boldness reduction in fish previously exposed to a stressor when compared to control groups. This has been shown in previous experimental studies with the barbel ((wildfire ashes, heatwaves, and salinity) [69,71,73]). However, a subsequent increase in the proportion of bolder individuals in response to a higher esfenvalerate concentration (from 1.0 to 2.0 μg/L) was unexpected, as previous studies with the same species have reported that individuals decreased their bolder character and become shyer upon previous exposure to a higher concentration of stressors, such as fire ashes [69] or salinity [70]. In the present study, shy behaviour peaked at the intermediate value of the esfenvalerate concentration gradient, being minimal at both extremes, i.e., at the control (no stressor), when fish are expected to display a naturally bolder behaviour, venturing and exploring new habitats for spawning, feeding, or sheltering purposes) and at the highest concentration, when it is expected that most fish adopt a bolder, more erratic behaviour after exposure to a harmful esfenvalerate environment [90]. However, this deserves further clarification with longer-term experiments and extending the gradient of insecticide concentration. The shoaling behaviour of the barbel was significantly affected by both treatments with low and high concentrations of the stressor. This response was to be expected since previous studies with cyprinids demonstrated great effects on group behaviour caused by anthropogenic pressures; for example, when exposed to increasing salinity levels, barbel shoals were less active and more dispersed [73]. Under stressful conditions, as simulated in these experiments, barbels tended to separate from the group, as individual boldness increased in the higher concentration treatment and searched for a more favourable environment [91,92]. Individual variation in schooling and boldness behaviour may influence the dispersal of species and consequently affect spatial population dynamics [93,94,95]. Oppositely, it should be noted that the bleak’s overall behaviour seemed to be unaltered by higher concentrations of esfenvalerate. Considering searching behaviour, we could graphically observe a slight upward tendency of this swimming pattern with increasing pyrethroid concentrations inversely to the barbel’s observed behaviour. Likewise, exposure to a high concentration of insecticide showed no significant effects on the bleak’s boldness and shoaling cohesion throughout behavioural trials.
Less active and less bold fish may not be as prone to migrate in search of new habitats for refuge, feeding, and reproduction [39,96,97]. Furthermore, following exposure to esfenvalerate, less active species may lose competitive advantage to others that are not affected (or less affected) by this stressor. The bleak is a non-native species that can occur in sympatry and compete for resources with native Cypriniformes species (e.g., with the saramugo Anaecypris hispanica: [98]). The competitive disadvantage of native fish species in comparison to the bleak (and other non-native species) may be further potentiated in the face of other stressors, such as flow regulation, which can benefit non-native species with higher ecological plasticity [99].
Esfenvalerate and other pesticides are neurotoxic to fishes, and their effects on behaviour are rarely investigated relative to sub-lethal endpoints [32]. Thus, pesticides in aquatic systems are a threat to biodiversity, as impacts can cascade from individuals to populations [21,100]. Insecticides can modify food web dynamics [20] and community structure [101,102] by creating a more advantageous environment for more tolerant species, hence compromising the ability of more sensitive species to compete, deal with invasive species, or other vital behaviours, for example [103,104,105]. The barbel and other species living in seasonally harsh environmental conditions, as in Mediterranean rivers, are particularly known for their resilience to various stressors [106,107,108]; this would grant native species a competitive advantage in relation to non-natives. However, fish have different tolerances to different kinds of stressors [109,110], and the apparent tolerance, demonstrated by bleak and the impact demonstrated for barbels, clearly promotes a shift in the competitive balance between the species, favouring the non-native. In the wake of global changes, with the increasing temperatures and agriculture pressure due to climate change and human population growth, the potential effect of pesticides will be augmented by the increase in usage and a magnification effect of the concentration of pesticides in rivers under water scarcity swell.
Ultimately, behavioural impairment in fish can reflect alterations in ecological conditions and ecosystem dynamics. Thus, the behavioural responses of fish caused by exposure to pollutants such as esfenvalerate should be further researched, in addition to the interaction with other environmental stressors, to understand the true scope of the consequences of pesticide contamination for fish species. Maintaining well-structured native riparian galleries, as well as encouraging their restoration or rehabilitation when they are degraded, may, in the future, constitute an effective management measure that will certainly reduce, through filtration, the impacts arising from the increase of these substances in riverine ecosystems [111].
5. Conclusions
In this work, the swimming behaviour of a native and a non-native invasive species was assessed under mesocosms conditions, following a previous 2 h sub-lethal exposure to a concentration gradient of a widespread pyrethroid esfenvalerate. Results showed that short-term previous exposure to the pyrethroid esfenvalerate was able to significantly affect the behaviour of the native species (barbel), mainly by increasing the amount of time resting while decreasing the shoaling cohesion and boldness partially. Contrarily, no significant changes in behavioural metrics to increasing amounts of esfenvalerate were detected for the non-native invasive species (bleak). As less active and shier fish may be less prone to migrate in search of new habitats for refuge, feeding, or reproduction [39], the present findings suggest that common native species, such as the barbel, may lose competitive advantages towards other fishes that are not affected (or are less affected) by the presence of esfenvalerate. This work contributed to improving the knowledge regarding esfenvalerate effects in freshwater fish, thus providing an enhanced understanding of the effects of this pyrethroid insecticide on organisms and consequent effects at the population and ecosystem levels. Future studies should consider testing the effects of other stressors that naturally co-occur with pesticide contaminations (e.g., hypersaline conditions, warming temperatures, decreased habitat availability) to understand if their interactions have additive, antagonistic, or synergistic effects and whether they intensify the effects of pesticides in isolation. The fact that exposure to the chosen concentrations of esfenvalerate did not affect the behaviour of the non-native invasive bleak reinforces the need to further understand the tolerance of such species to this type of disturbance and to create measures that restrict the application of pesticides, which might give them competitive advantages as outlined above.
Author Contributions
T.L.: methodology, investigation, and writing—original draft; D.M.: formal analysis, data curation, and writing—original draft; I.V.: methodology, investigation, and writing—review and editing; M.O.: methodology, investigation, and writing—review and editing; P.B.: supervision, methodology, investigation, and writing—review and editing; J.M.S.: supervision, conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Tamara Leite was supported by a Ph.D. grant from the FLUVIO–River Restoration and Management program funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I. P. (FCT), Portugal (UI/BD/15052/2021). Daniel Mameri was supported by a Ph.D. scholarship from the FLUVIO—River Restoration and Management program funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. (FCT) (PD/BD/142885/2018). Paulo Branco was financed by national funds via FCT (LA/P/0092/2020). The study was partially funded by the project Dammed Fish (PTDC/CTA-AMB/4086/2021). Forest Research Centre (CEF) is a research unit funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. (FCT), Portugal (UIDB/00239/2020). The Associate Laboratory TERRA (LA/P/0092/2020) is also funded by FCT.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All proceedings involving fish sampling and handling strictly complied with the European standards (Directive 2010/63/EU) and Portuguese legislation (Decree-Law 113/7 August 2013, article 35, no. 5, transposing the European Directive for animal experimentation (Directive 2010/63/EU)). Licenses for capture, transportation, detention, and handling (no. 299/2021/CAPT and 300/2021/CAPT), as well the fishing permits (no. 38-A/2021 and no. 39/2021), were issued by the Portuguese Institute for Nature Conservation and Forests (ICNF). Fish handling and experimentation were coordinated by J. M. Santos, who holds a FELASA C certification to perform animal experimentation. All procedures were adopted to minimize fish distress.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to potential use in future works.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Institute for Nature Conservation and Forests (ICNF), which provided the necessary fishing and handling permits.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.; Naiman, R.J.; Knowler, D.J.; Le, C. Freshwater Biodiversity: Importance, Threats, Status and Conservation Challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.G.; Kottelat, M.; Smith, G.R.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; Gill, A.C. So Many Fishes, So Little Time: An Overview of Recent Ichthyological Discovery in Continental Waters. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2000, 87, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, R.F.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Pereira, V.R.; Santos, C.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Sanches, L.F. Land Use Policy Impacts of Land Use Conflicts on Riverine Ecosystems. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Duarte, G.; Segurado, P.; Branco, P. Major Threats to European Freshwater Fish Species. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Xie, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, X. Pyrethroid Bioaccumulation in Wild Fish Linked to Geographic Distribution and Feeding Habit. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lim, W.; Song, G. Mediation of Oxidative Stress Toxicity Induced by Pyrethroid Pesticides in Fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 234, 108758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brander, S.M.; Gabler, M.K.; Fowler, N.L.; Connon, R.E.; Schlenk, D. Pyrethroid Pesticides as Endocrine Disruptors: Molecular Mechanisms in Vertebrates with a Focus on Fishes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8977–8992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, I.; Geist, J.; Okihiro, M.; Rosenkranz, P.; Hinton, D.E. Effects of Dietary Exposure to the Pyrethroid Pesticide Esfenvalerate on Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M.J.; Logan, D.C.; Ahokas, J.T.; Holdway, D.A. Effects of Esfenvalerate Pulse-exposure on the Survival and Growth of Larval Australian Crimson-spotted Rainbow Fish (Melanotaenia fluviatilis). Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1995, 10, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, S.; Schulz, R. Agricultural Insecticides Threaten Surface Waters at the Global Scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5750–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Bordalo, M.D.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pestana, J.L.T. Effects of the Pyrethroid Esfenvalerate on the Oligochaete, Lumbriculus variegatus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, J.A.; Wallender, W.W.; Werner, I.; Fard, B.M.; Zalom, F.G.; Oliver, M.N.; Wilson, B.W.; Mata, M.M.; Henderson, J.D.; Deanovic, L.A.; et al. Pesticide Runoff from Orchard Floors in Davis, California, USA: A Comparative Analysis of Diazinon and Esfenvalerate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 115, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, V.E.; Cold, A. Effects of the Pyrethroid Esfenvalerate on Life-Cycle Traits and Population Dynamics of Chironomus riparius—Importance of Exposure Scenario. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.; Smith, S.; And, J.R.; Moore, M. Surface Water, Ground Water and Sediment Quality in Three Oxbow Lake Watersheds in the Mississippi Delta Agricultural Region: Pesticides. Int. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2003, 29, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Affum, A.O.; Acquaah, S.O.; Osae, S.D.; Kwaansa-Ansah, E.E. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Banned and Other Current-Use Pesticides in Surface and Groundwaters Consumed in an Agricultural Catchment Dominated by Cocoa Crops in the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Li, Z.; Zuberi, A.; Arifeen, M.Z.U.; Baig, M.M.F.A. Biomarkers of Pyrethroid Toxicity in Fish. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 945–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMicco, A.; Cooper, K.R.; Richardson, J.R.; White, L.A. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Pyrethroid Insecticides in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 113, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderlund, D.M.; Clark, J.M.; Sheets, L.P.; Mullin, L.S.; Piccirillo, V.J.; Sargent, D.; Stevens, J.T.; Weiner, M.L. Mechanisms of Pyrethroid Neurotoxicity: Implications for Cumulative Risk Assessment. Toxicology 2002, 171, 3–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.; Pfeiff, J.; Loguinov, A.V.; D’Abronzo, L.S.; Wintz, H.; Vulpe, C.D.; Werner, I. Linking Mechanistic and Behavioral Responses to Sublethal Esfenvalerate Exposure in the Endangered Delta Smelt; Hypomesus transpacificus (Fam. Osmeridae). BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.H.; Spromberg, J.A.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. A Fish of Many Scales: Extrapolating Sublethal Pesticide Exposures to the Productivity of Wild Salmon Populations. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 2004–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehage, J.S.; Sih, A. Dispersal Behavior, Boldness, and the Link to Invasiveness: A Comparison of Four Gambusia Species. Biol. Invasions 2004, 6, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliozzi, C.; Tsiamis, K.; Vigiak, O.; Deriu, I.; Gervasini, E.; Cardoso, A.C. Assessing Invasive Alien Species in European Catchments: Distribution and Impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 138677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevitch, J.; Padilla, D.K. Are Invasive Species a Major Cause of Extinctions? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, H.A.; Cleland, E.E. The Evolutionary Impact of Invasive Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5446–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçın Özdilek, Ş.; Partal, N.; Jones, R.I. An Invasive Species, Carassius gibelio, Alters the Native Fish Community through Trophic Niche Competition. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, G.; Battarbee, R.W.; Bloomfield, J.P.; Crossman, J.; Daccache, A.; Durance, I.; Elliott, J.A.; Garner, G.; Hannaford, J.; Hannah, D.M.; et al. Climate Change and Water in the UK—Past Changes and Future Prospects. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 39, 6–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, N.; Thomson, J.; Reich, P.; Stein, J. Using Species Distribution Models to Infer Potential Climate Change-Induced Range Shifts of Freshwater Fish in South-Eastern Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.; Carrizo, S.; Freyhof, J.; Cid, N.; Lengyel, S.; Scholz, M.; Kasperdius, H.; Darwall, W. Europe’s Freshwater Biodiversity under Climate Change: Distribution Shifts and Conservation Needs. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Branco, P.; Segurado, P.; Ramos, T.B.; Ferreira, T.; Neves, R.; Oliveira, R.P. De Evaluation of the Trophic Status in a Mediterranean Reservoir under Climate Change: An Integrated Modelling Approach. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarić, I.; Lennox, R.J.; Kalinkat, G.; Cvijanović, G.; Radinger, J. Susceptibility of European Freshwater Fish to Climate Change: Species Profiling Based on Life-History and Environmental Characteristics. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renick, V.C.; Anderson, T.W.; Morgan, S.G.; Cherr, G.N. Interactive Effects of Pesticide Exposure and Habitat Structure on Behavior and Predation of a Marine Larval Fish. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubenstein, T.D.; Rummer, J.L.; Nicol, S.; Parsons, D.M.; Pether, S.M.J.; Pope, S.; Smith, N.; Munday, P.L. Correlated Effects of Ocean Acidification and Warming on Behavioral and Metabolic Traits of a Large Pelagic Fish. Diversity 2018, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownscombe, J.W.; Nowell, L.; Samson, E.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Steven, J. Fishing-Related Stressors Inhibit Refuge-Seeking Behavior in Released Subadult Great Barracuda. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2014, 143, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugatkin, L.A.; Alfieri, M.S. Boldness, Behavioral Inhibition and Learning. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2003, 15, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.S.; Coleman, K.; Clark, A.B.; Biederman, L. Shy-Bold Continuum in Pumpkinseed Sunfish (Lepomis gibbosus): An Ecological Study of a Psychological Trait. J. Comp. Psychol. 1993, 107, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, Z.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Chivers, D.P. The Effects of Sub-Lethal Salinity Concentrations on the Anti-Predator Responses of Fathead Minnows. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesson, A.; Saaristo, M.; Brodin, T.; Fick, J.; Klaminder, J.; Martin, J.M.; Wong, B.B.M. Fish on Steroids: Temperature-Dependent Effects of 17Β-Trenbolone on Predator Escape, Boldness, and Exploratory Behaviors. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.F.; Gilliam, J.F.; Daley, M.J.; Le, A.N.; Skalski, G.T. Explaining Leptokurtic Movement Distributions: Intrapopulation Variation in Boldness and Exploration. Am. Nat. 2001, 158, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.; Hawlena, D.; Polo, V.; Amo, L.; Martín, J. Sources of Individual Shy-Bold Variations in Antipredator Behaviour of Male Iberian Rock Lizards. Anim. Behav. 2005, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnhagen, C.; Staffan, F. Is Boldness Affected by Group Composition in Young-of-the-Year Perch (Perca fluviatilis)? Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2005, 57, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, S.; Sadoul, B.; Gesto, M.; Joassard, L.; Chatain, B.; Geffroy, B.; Bégout, M.L. Coping Styles in European Sea Bass: The Link between Boldness, Stress Response and Neurogenesis. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 207, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, W.D.; Hale, R.; Morrongiello, J.R. Dispersal Decisions and Personality in a Freshwater Fish. Anim. Behav. 2019, 157, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budaev, S.V. Personality in the Guppy (Poecilia reticulata): A Correlational Study of Exploratory Behavior and Social Tendency. J. Comp. Psychol. 1997, 111, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budaev, S.V.; Zhuikov, A.Y. Avoidance Learning and “Personality” in the Guppy (Poecilia reticulata). J. Comp. Psychol. 1998, 112, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herde, A.; Eccard, J.A. Consistency in Boldness, Activity and Exploration at Different Stages of Life. BMC Ecol. 2013, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Donelson, M.; Fox, R.J.; Booth, D.J.; Donelson, J.M. ‘Stick with Your Own Kind, or Hang with the Locals?’ Implications of Shoaling Strategy for Tropical Reef Fish on a Range-Expansion Frontline. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemasson, B.; Tanner, C.; Woodley, C.; Threadgill, T.; Qarqish, S.; Smith, D. Motion Cues Tune Social Influence in Shoaling Fish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, A.C.; Ioannou, C.C. Turbidity Increases Risk Perception but Constrains Collective Behaviour during Foraging by Fish Shoals. Anim. Behav. 2019, 156, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romenskyy, M.; Herbert-Read, J.E.; Ioannou, C.C.; Szorkovszky, A.; Ward, A.J.W.; Sumpter, D.J.T. Quantifying the Structure and Dynamics of Fish Shoals under Predation Threat in Three Dimensions. Behav. Ecol. 2020, 31, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.J.W.; Hart, P.J.B. Foraging Benefits of Shoaling with Familiars May Be Exploited by Outsiders. Anim. Behav. 2005, 69, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Cervantes, M.; Palomera-Hernadez, V.; García, C.M. Foraging Behaviour of a Native Topminnow When Shoaling with Invaders. Aquat. Invasions 2019, 14, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, I.; Bhat, A. What Drives Mixed-Species Shoaling among Wild Zebrafish? The Roles of Predators, Food Access, Abundance of Conspecifics and Familiarity. Biol. Open 2023, 12, bio059529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paijmans, K.C.; Booth, D.J.; Wong, M.Y.L. Towards an Ultimate Explanation for Mixed-Species Shoaling. Fish Fish. 2019, 20, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.G.; Pinheiro, H.T.; Martins, A.S.; Riul, P.; Bruno, S.C.; Janzen, F.J.; Ioannou, C.C. The Anti-Predator Role of within-Nest Emergence Synchrony in Sea Turtle Hatchlings. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.; Gerlai, R. Quantification of Shoaling Behaviour in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 184, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archard, G.A.; Braithwaite, V.A. Increased Exposure to Predators Increases Both Exploration and Activity Level in Brachyrhaphis episcopi. J. Fish Biol. 2011, 78, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Rees, G.N.; Mitchell, A.M.; Watson, G.; Williams, J. The Short-Term Effects of Salinization on Anaerobic Nutrient Cycling and Microbial Community Structure in Sediment from a Freshwater Wetland. Wetlands 2006, 26, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, J.; Werner, I.; Eder, K.J.; Leutenegger, C.M. Comparisons of Tissue-Specific Transcription of Stress Response Genes with Whole Animal Endpoints of Adverse Effect in Striped Bass (Morone saxatilis) Following Treatment with Copper and Esfenvalerate. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 85, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, L.; Bassein, S.; Zalom, F.G. Almond and Stone Fruit Growers Reduce OP, Increase Pyrethroid Use in Dormant Sprays. Calif. Agric. 2000, 54, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmquist, K.; Salatas, J.; Fairbrother, A. Pyrethroid Insecticides: Use, Environmental Fate, and Ecotoxicology. In Insecticides-Advances in Integrated Pest Management; Perveen, F., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 251–278. ISBN 978-953-307-780-2. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, E.Y.; Geist, J.P.; Werner, I. Acute, Sublethal Exposure to a Pyrethoid Insecticide Alter Behavior, Growth, and Predation Risk in Larvae of the Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Alves, M.J.; Ribeiro, F.; Domingos, I.; Almeida, P.R.; da Costa, L.; Gante, H.; Filipe, A.F.; Aboim, M.A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; et al. Guia Dos Peixes de Água Doce e Migradores de Portugal Continental; Edições Afrontamento: Porto, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schönhuth, S.; Vukić, J.; Šanda, R.; Yang, L.; Mayden, R.L. Phylogenetic Relationships and Classification of the Holarctic Family Leuciscidae (Cypriniformes: Cyprinoidei). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 127, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, D.; Masó, G.; Cano-Barbacil, C.; Zamora-Marin, J.M.; Almeida, D.; Vilizzi, L.; Britton, J.R.; Cruz, A.; Fernández-Delgado, C.; González-Rojas, A.G.; et al. A Review and Meta-Analysis of the Environmental Biology of Bleak Alburnus alburnus in Its Native and Introduced Ranges, with Reflections on Its Invasiveness. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.; Oscoz, J.; Leunda, P.M.; Escala, M.C. Weight-Length Relationships of Cyprinid Fishes of the Iberian Peninsula. J. Appl. Ichtyol. 2006, 22, 297–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masó, G.; Latorre, D.; Tarkan, A.S.; Vila-Gispert, A.; Almeida, D. Inter-Population Plasticity in Growth and Reproduction of Invasive Bleak, Alburnus alburnus (Cyprinidae, Actinopterygii), in Northeastern Iberian Peninsula. Folia Zool. 2016, 65, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Ferreira, A.P.; Ferreira, M.T. Intrabasin Variations in Age and Growth of Barbus bocagei Populations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonino, G.; Branco, P.; Benedito, E.; Teresa, M.; Santos, J.M. Short-Term Effects of Wild Fire Ash Exposure on Behaviour and Hepatosomatic Condition of a Potamodromous Cyprinid Fish, the Iberian Barbel Luciobarbus bocagei ( Steindachner, 1864). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, T.; Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Canhoto, C.; Branco, P. Does Short-Term Salinization of Freshwater Alter the Behaviour of the Iberian Barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei, Steindachner 1864)? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameri, D.; Branco, P.; Ferreira, M.T.; Santos, J.M. Heatwave Effects on the Swimming Behaviour of a Mediterranean Freshwater Fish, the Iberian Barbel Luciobarbus bocagei. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammler, K.L.; Corkum, L.D. Assessment of Fish Size on Shelter Choice and Intraspecific Interactions by Round Gobies Neogobius melanostomus. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2005, 73, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, T.; Branco, P.; Ferreira, M.T.; Santos, J.M. Activity, Boldness and Schooling in Freshwater Fish Are Affected by River Salinization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manek, A.K.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Niyogi, S.; Chivers, D.P. The Interactive Effects of Multiple Stressors on Physiological Stress Responses and Club Cell Investment in Fathead Minnows. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging Threats and Persistent Conservation Challenges for Freshwater Biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, S.J.; Deng, D.; Werner, I.; Teh, F.; Hung, S.S.O. Sublethal Toxicity of Orchard Stormwater Runoff in Sacramento Splittail (Pogonichthys macrolepidotus) Larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2005, 59, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, D.J.; Shingles, A.; Taylor, E.W. Sub-Lethal Plasma Ammonia Accumulation and the Exercise Performance of Salmonids. In Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology—A Molecular and Integrative Physiology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 135, pp. 515–526. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, I.; Schneeweiss, A.; Segner, H.; Junghans, M. Environmental Risk of Pesticides for Fish in Small-and Medium-Sized Streams of Switzerland. Toxics 2012, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.; Carrizo, S.F.; Kärcher, O.; Walz, A.; David, J.N.W. Vulnerability of European Freshwater Catchments to Climate Change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3567–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevelhimer, M.; Bennett, W. Assessing Cumulative Thermal Stress in Fish during Chronic Intermittent Exposure to High Temperatures. Environ. Sci. Policy 2000, 3, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colchen, T.; Teletchea, F.; Fontaine, P.; Pasquet, A. Temperature Modifies Activity, Inter-Individual Relationships and Group Structure in a Fish. Curr. Zool. 2017, 63, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pichon, C.; Lestel, L.; Courson, E.; Merg, M.L.; Tales, E.; Belliard, J. Historical Changes in the Ecological Connectivity of the Seine River for Fish: A Focus on Physical and Chemical Barriers since the Mid-19th Century. Water 2020, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.T.P.; Hien, T.T.T.; Le Cam Tu, T.; Van Khanh, N.; Haga, Y.; Phu, T.M. Salinization Intensifies the Effects of Elevated Temperatures on Channa striata, a Common Tropical Freshwater Aquaculture Fish in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, C.L.; Shaw, C.L.; Hunsberger, K.K.; Prado, M.; Duffy, M.A. Salinization Decreases Population Densities of the Freshwater Crustacean, Daphnia dentifera. Hydrobiologia 2016, 770, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M. A Review of Recent Advances and Future Challenges in Freshwater Salinization. Limnetica 2020, 39, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, M.C. Accelerating Extinction Risk from Climate Change. Clim. Chang. 2015, 348, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebergesell, M.; Reu, B.; Stahl, U.; Freiberg, M.; Welk, E.; Kattge, J.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Peãuelas, J.; Wirth, C. Functional Resilience against Climate-Driven Extinctions—Comparing the Functional Diversity of European and North American Tree Floras. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenici, P.; Seebacher, F. The Impacts of Climate Change on the Biomechanics of Animals. Conserv. Physiol. 2020, 8, coz102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, E.E.; Dwyer, F.J.; Fairchild, J.F.; Delonay, A.J.; Zajicek, J.L. Survival of Bluegilll and Their Behavioural Responses during Continuous and Pulsed Exposures to Esfenvalerate, a Pyrethroid Insecticide. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Mathot, K.J.; Moirón, M.; Montiglio, P.O.; Wolf, M.; Dingemanse, N.J. Animal Personality and State-Behaviour Feedbacks: A Review and Guide for Empiricists. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harcourt, J.L.; Sweetman, G.; Johnstone, R.A.; Manica, A. Personality Counts: The Effect of Boldness on Shoal Choice in Three-Spined Sticklebacks. Anim. Behav. 2009, 77, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Cote, J.; Evans, M.; Fogarty, S.; Pruitt, J. Ecological Implications of Behavioural Syndromes. Ecol Lett 2012, 15, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemanse, N.J.; Réale, D. Natural Selection and Animal Personality. Behaviour 2005, 142, 1159–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Garant, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Bergeron, P.; Careau, V.; Montiglio, P.O. Personality and the Emergence of the Pace-of-Life Syndrome Concept at the Population Level. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budaev, S.V. Alternative Styles in the European Wrasse, Symphodus ocellatus: Boldness-Related Schooling Tendency. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 49, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemanse, N.J.; Wright, J.; Kazem, A.J.N.; Thomas, D.K.; Hickling, R.; Dawnay, N. Behavioural Syndromes Differ Predictably between 12 Populations of Three-Spined Stickleback. J. Anim. Ecol. 2007, 76, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemanse, N.J.; Van der Plas, F.; Wright, J.; Réale, D.; Schrama, M.; Roff, D.A.; Van der Zee, E.; Barber, I. Individual Experience and Evolutionary History of Predation Affect Expression of Heritable Variation in Fish Personality and Morphology. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, J.; Matono, P.; Barata, E.N.; Bernardo, J.M.; Costa, A.M.; Ilhéu, M. Behavioural Interactions between the Endangered Native Fish Saramugo, Anaecypris hispanica, and the Invasive Bleak, Alburnus alburnus. Limnetica 2019, 38, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matono, P.; da Silva, J.; Ilhéu, M. How Does an Invasive Cyprinid Benefit from the Hydrological Disturbance of Mediterranean Temporary Streams? Diversity 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beketov, M.A.; Kefford, B.J.; Schäfer, R.B.; Liess, M. Pesticides Reduce Regional Biodiversity of Stream Invertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11039–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleeger, J.W.; Carman, K.R.; Nisbet, R.M. Indirect Effects of Contaminants in Aquatic Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 317, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macneale, K.H.; Kiffney, P.M.; Scholz, N.L. Pesticides, Aquatic Food Webs, and the Conservation of Pacific Salmon. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.; Clobert, J. Social Personalities Influence Natal Dispersal in a Lizard. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Harris, D.J. Evolution and Behavioural Responses to Human-Induced Rapid Environmental Change. Evol. Appl. 2011, 4, 367–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.R.; Blumstein, D.T. Fitness Consequences of Personality: A Meta-Analysis. Behav. Ecol. 2008, 19, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooke, J.M. Human Impacts on Fluvial Systems in the Mediterranean Region. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, D.; García-Berthou, E.; Gascón, S.; Benejam, L.; Tornés, E.; Sala, J.; Benito, J.; Munné, A.; Solà, C.; Sabater, S. Response of Community Structure to Sustained Drought in Mediterranean Rivers. J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybowski, M.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K. Principal Threats to the Conservation of Freshwater Habitats in the Continental Biogeographical Region of Central Europe; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 28, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Segurado, P.; Ferreira, T.; Branco, P. Assessing the Effects of Multiple Stressors on Aquatic Systems across Temporal and Spatial Scales: From Measurement to Management. Water 2021, 13, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurado, P.; Santos, J.M.; Pont, D.; Melcher, A.H.; Jalon, D.G.; Hughes, R.M.; Ferreira, M.T. Estimating Species Tolerance to Human Perturbation: Expert Judgment versus Empirical Approaches. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, T.R.; Bortolozo, F.R.; Hansel, F.A.; Rasera, K.; Ferreira, M.T. Riparian Buffer Zones as Pesticide Filters of No-till Crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10618–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).