Aquaculture in Zambia: The Current Status, Challenges, Opportunities and Adaptable Lessons Learnt from China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods Section
3. Results and Discussion
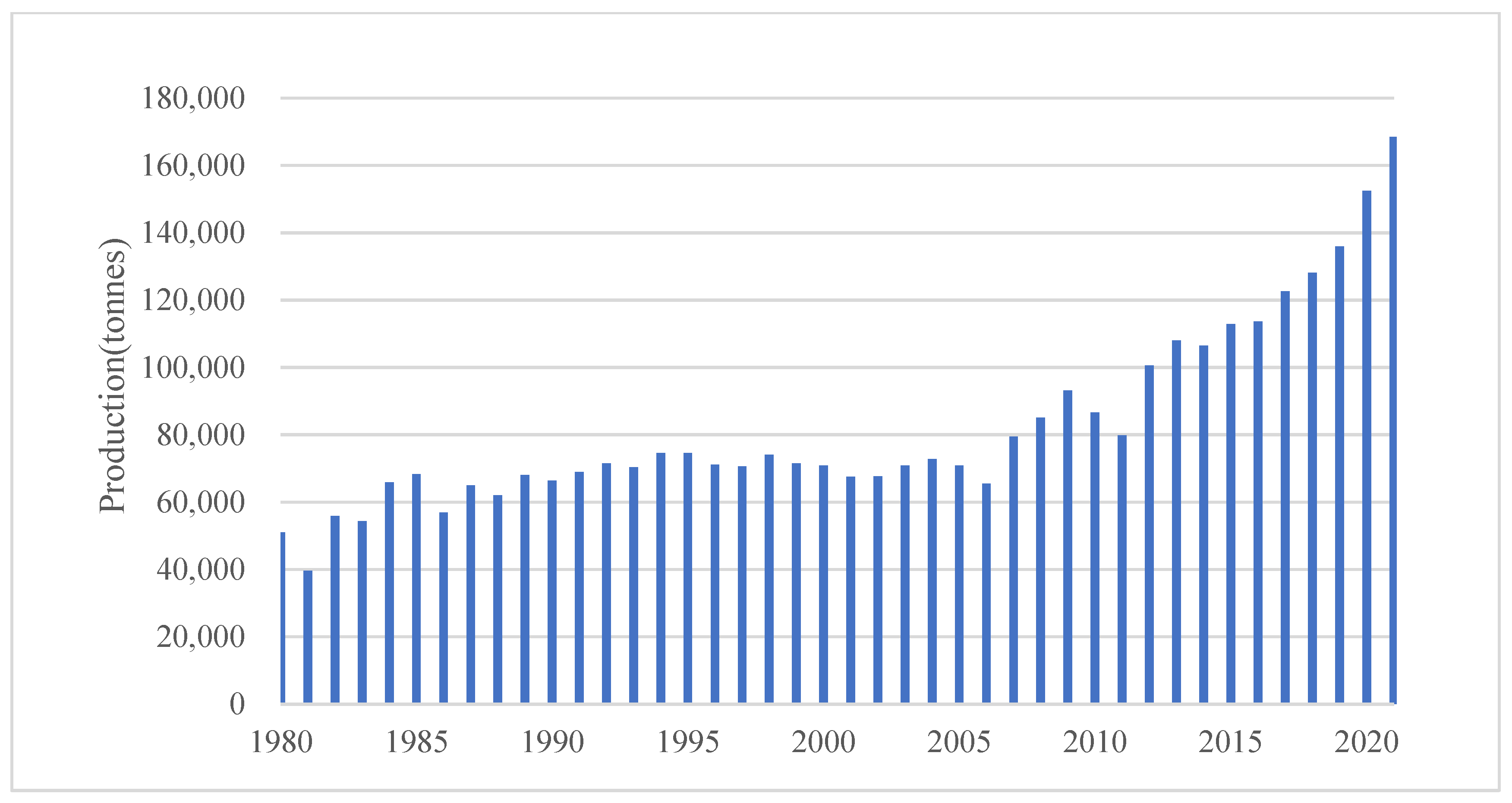
3.1. Overall Status of Fisheries in Zambia
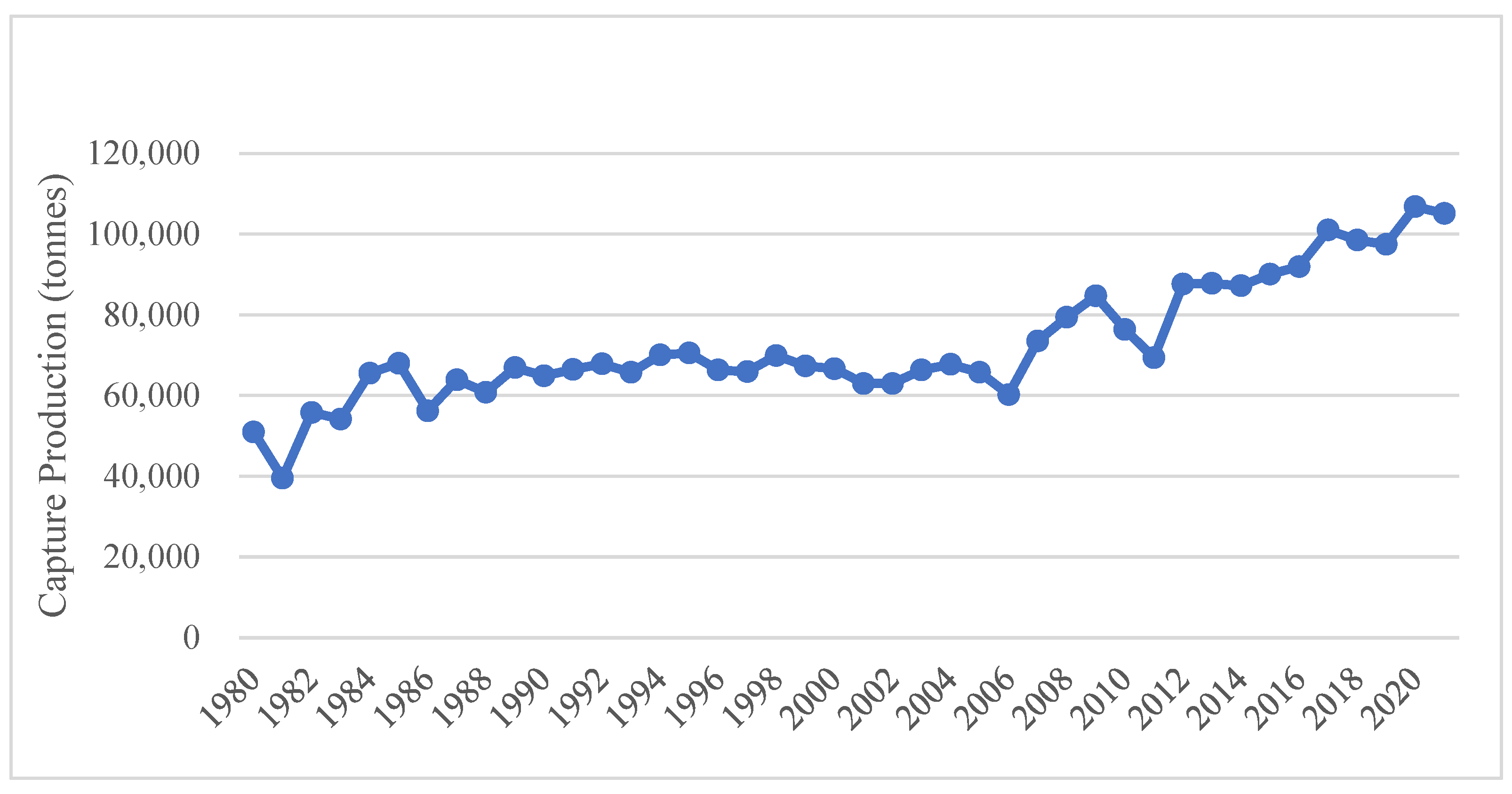
3.2. Capture Fisheries
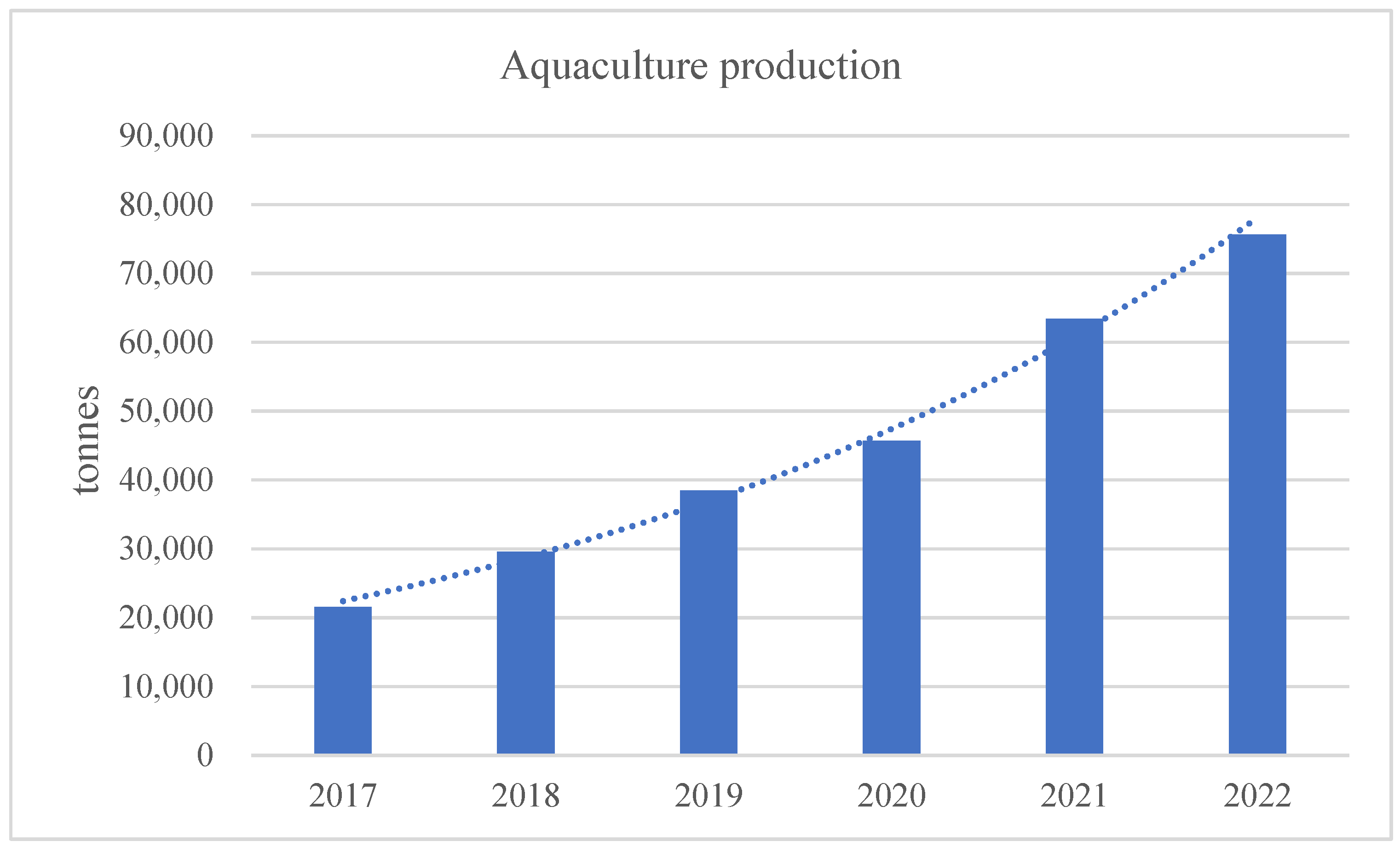
3.3. Aquaculture
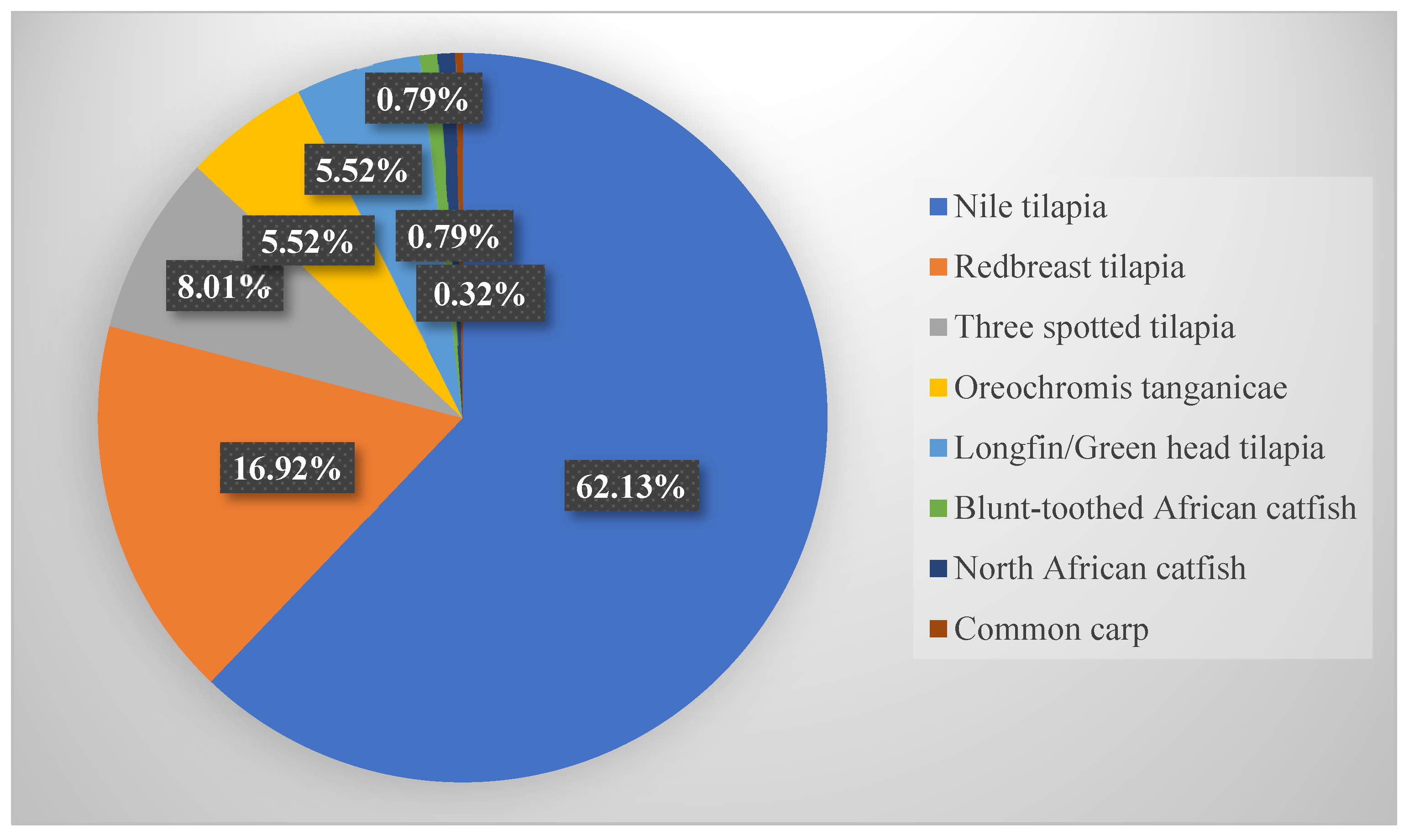
3.3.1. Cultured Species
3.3.2. Aquaculture Production Systems
3.4. Governance
3.5. Challenges Analysis of Aquaculture Development in Zambia
3.5.1. Fish Seed Diversity and Quality
3.5.2. Fish Feed Accessibility and Affordability
3.5.3. Post-Harvest Fish Losses
3.5.4. Fish Marketing Mechanism
3.5.5. Fishery Management
4. Opportunities to Boost Aquaculture Production in Zambia through Adaptable Lessons from China
4.1. Sound Policy Formulation and Appropriate Implementation
4.2. Government Support to S&T with Step-to-Step Goals
4.3. Improvements in Production Systems That Best Suit Local Conditions
4.4. Species Improvement and Diversification with Long-Term Breeding Programs
4.5. Creation of Environment to Promote Private Investments and Better Invlove Smallholders
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finegold, C. The Importance of Fisheries and Aquaculture to Development; The Royal Swedish Academy of Agriculture and Forestry: Stockholm, Sweden, 2009; pp. 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Scientists to Global Policymakers: Treat Fish as Food to Help Solve World Hunger. Available online: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/01/210119122051.htm (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoola, S.O. Sustainable fish production in Africa. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2010, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Subasinghe, R.; Soto, D.; Jia, J.S. Global aquaculture and its role in sustainable development. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 154, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudenda, H.G. Assessment of National Aquaculture Policies and Programmes in Zambia; Institute of Policy Studies: Lusaka, Zambia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nsonga, A.; Simbotwe, M. Challenges and Emerging Opportunities for Aquaculture Development in Zambia. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2014, 2, 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.N.; Galli, G.; Zhou, X.W. Zambia—WAPI factsheet on Aquaculture Growth Potential; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, A.; Hassan, R.; Mendelsohn, R.; Benhin, J. Climate Change and Agriculture in Africa: Impact Assessment and adaptation Strategies; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kasali, G. Climate Change and Health in Zambia. Lusaka, Zambia: CLACC Working Paper; IIED: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hasimuna, O.J.; Maulu, S.; Monde, C.; Mweemba, M. Cage Aquaculture Production in Zambia: Assessment of Opportunities and Challenges on Lake Kariba, Siavonga District. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Munganga, B.; Hasimuna, O.; Hambiya, L.; Seemani, B. A Review of the Science and Technology Developments in Zambia’s Aquaculture Industry. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock. The 2017/2018 Livestock and Aquaculture Census Main Report; Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock and Central Statistics Office: Lusaka, Zambia, 2021.
- Musumali, M.M.; Heck, S.; Husken, S.M.C.; Wishart, M. Fisheries in Zambia: An Undervalued Contributor to Poverty Reduction; World Fish Center: Penang, Malaysia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fishery and Aquaculture Country Profiles. Zambia, 2021. Country Profile Fact Sheets. Fisheries and Aquaculture Division. Rome. Updated 7 February 2022; Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/knowledgebase/82 (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Kaminski, A.M.; Little, D.C.; Middleton, L.; Syapwaya, M.; Lundeba, M.; Johnson, J.; Huchzermeyer, C.; Thilsted, S.H. The Role of Aquaculture and Capture Fisheries in Meeting Food and Nutrition Security: Testing a Nutrition-Sensitive Pond Polyculture Intervention in Rural Zambia. Foods 2022, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Chu, L.; Chan, C.Y.; Genschick, S.; Phillips, M.J.; Kefi, A.S. Fish Supply and Demand for Food Security in Sub-Saharan Africa: An Analysis of the Zambian Fish Sector. Mar. Policy 2019, 99, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shula, A.K.; Mofya-Mukuka, R. The Fisheries Sector in Zambia: Status, Management, and Challenges. Indaba Agricultural Policy Research Institute Technical Paper; Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock: Lusaka, Zambia, 2015; p. 3.
- Department of Fisheries (DoF), Zambia. Fisheries and Aquaculture Statistics: Annual Report; Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock: Chilanga, Zambia, 2021.
- Avadí, A.; Cole, S.M.; Kruijssen, F.; Dabat, M.H.; Mungule, C.M. How to Enhance the Sustainability and Inclusiveness of Smallholder Aquaculture Production Systems in Zambia? Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genschick, S.; Kaminski, A.M.; Kefi, A.S.; Cole, S.M. Aquaculture in Zambia: An Overview and Evaluation of the Sector’s Responsiveness to the Needs of the Poor. Penang, Malaysia: CGIAR Research Program on Fish Agri-Food Systems and Lusaka, Zambia; Department of Fisheries: Lusaka, Zambia, 2017; Working Paper: FISH-2017-08. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski, A.M.; Genschick, S.; Kefi, A.S.; Kruijssen, F. Commercialization and Upgrading in the Aquaculture Value Chain in Zambia. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiita, R.K.; Trinh, T.Q.; Sakala, M.E.; Chungu, P.; Malambo, T.; Hampuwo, B.; Mwema, C.; Benzie, J.A.H. Performance of Oreochromis Niloticus and Oreochromis Andersonii in Controlled Laboratory Conditions in Zambia. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sector Profile. Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries. Agric. Livest. Fish. 2010, 1, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Utsugi, K.; Mazingaliwa, K. Field Guide to Zambian Fishes, Planktons and Aquaculture; Japan International Co-operation Agency (JICA): Tokyo, Japan, 2002; p. 41.
- Widjaja, S.; Long, T.; Wirajuda, H. Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated Fishing and Associated Drivers; World Resources Institute: Washington, USA, 2020; Available online: www.oceanpanel.org/iuu-fishing-and-associated-drivers (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Petit, P.; Shipton, T. IUU Fishing on Lake Tanganyika. Implementation of a Regional Fisheries Strategy for The Eastern-Southern Africa and India Ocean Region. REPORT/RAPPORT; Indian Ocean Commission: Port Louis, Mauritius, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haambiya, L.; Kaunda, E.; Likongwe, J.; Kambewa, D.; Muyangali, K. Local-Scale Governance: A Review of the Zambian Approach to Fisheries Management. JAST-B 2015, 5, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G.; Gislason, H.; Graham, K.; Hill, L.; Jin, X.; Koranteng, K.; Manickchand-Heileman, S.; Payá, I.; Sainsbury, K.; Sanchez, F.; et al. Impact of Fishing on Size Composition and Diversity of Demersal Fish Communities. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Blanchard, J.L. Fish Abundance with No Fishing: Predictions Based on Macroecological Theory. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.; Tran, N.; Pethiyagoda, S.; Crissman, C.C.; Sulser, T.B.; Phillips, M.J. Prospects and Challenges of Fish for Food Security in Africa. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasimuna, O.J.; Maulu, S.; Nawanzi, K.; Lundu, B.; Mphande, J.; Phiri, C.J.; Kikamba, E.; Siankwilimba, E.; Siavwapa, S.; Chibesa, M. Integrated Agriculture-Aquaculture as an Alternative to Improving Small-Scale Fish Production in Zambia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1161121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture Statistics: Annual Report (Draft); Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock: Chilanga, Zambia, 2023.
- Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock of the Republic of Zambia (MFL). National Fisheries and Aquaculture Policy (NFAP); Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock: Lusaka, Zambia, 2023.
- Department of Fisheries (DoF), Zambia. Fisheries and Aquaculture Statistics: Annual Report; Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock: Chilanga, Zambia, 2019.
- Department of Fisheries (DoF), Zambia. Fisheries and Aquaculture Statistics: Annual Report; Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock: Chilanga, Zambia, 2018.
- Department of Fisheries (DoF), Zambia. Fisheries and Aquaculture Statistics: Annual Report; Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock: Chilanga, Zambia, 2020.
- Mphande, J.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Kikamba, E.; Maulu, S.; Nawanzi, K.; Phiri, D.; Siavwapa, S. Application of anaesthetics in fish hatcheries to promote broodstock and fish seed welfare in Zambia. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2211845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musuka, C.; Mainza, R. Extent of Small-Scale Fish Farming in Three Districts of Lusaka Province. Int. J. Aquac. 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namonje-Kapembwa, T.; Samboko, P. Assessing the Profitability of Small-Scale Aquaculture Fish Production in Zambia; Indaba Agricultural Policy Research Institute (IAPRI): Lusaka, Zambia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, K.J.; Siriwardena, S.; Hasan, M.R. Impact of Rising Feed Ingredient Prices on Aquafeeds and Aquaculture Production; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- Kord, M.I.; Srour, T.M.; Omar, E.A.; Farag, A.A.; Nour, A.A.M.; Khalil, H.S. The immunostimulatory effects of commercial feed additives on growth performance, non-specific immune response, antioxidants assay, and intestinal morphometry of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 627499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nölle, N.; Genschick, S.; Schwadorf, K.; Hrenn, H.; Brandner, S.; Biesalski, H.K. Fish as a Source of (Micro)Nutrients to Combat Hidden Hunger in Zambia. Food. Sec. 2020, 12, 1385–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Monde, C.; Mweemba, M. An Assessment of Post-Harvest Fish Losses and Preservation Practices in Siavonga District, Southern Zambia. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 23, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.; Fang, S.; Fanzo, J. A Global View of Aquaculture Policy. Food Policy 2023, 116, 102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, K. Lake Tanganyika: Results and Experiences of the UNDP/GEF Conservation Initiative (RAF/92/G32) in Burundi, D.R. Congo, Tanzania, and Zambia; Lake Tanganyika Biodiversity Project: Burundi, South Africa, 2001; p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Maulu, S.; Musuka, C. Assessing the Abundance and Distribution of Tilapia Species in Lake Kariba. Int. J. Fish. Aquac. Sci. (IJFAS) IRPH 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. China Fishery Economic Statistical Bulletin 2022 (CFESB); Fisheries and Fisheries Administration Bureau: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Jiao, B. Aquaculture Industry in China: Current State, Challenges, and Outlook. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2011, 19, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, M.; Raux, P.; Massa, F.; Fezzardi, D.; Pérez Agúndez, J.A. Why Not? Decrypting Social Attitudes toward European Aquaculture: An Updated Policy Perspective for an Old Problem. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzer, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Costello, C.; Gaichas, S.; Nies, T.; Peñas, E.; Sainsbury, K.; Shen, C.; Szuwalski, C.; et al. Advancing Multispecies Fishery Management in China: Lessons from International Experience. Aquac. Fish. 2023, 8, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, W.; Tourgee, A.; Wu, C.; Fujita, R. How to Achieve Conservation Outcomes at Scale: An Evaluation of Scaling Principles. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 3, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. The Thirteenth Five-Year Plan for National Fisheries Development (2016–2020); Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. The 14th Five-Year Plan for National Fisheries Development; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Wang, P.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Y. Aquaculture extension system in China: Development, challenges, and prospects. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.D.; Han, G.; Kong, W.L.; Li, M.L.; Fang, H. Research on the development strategy for fisheries science and technology innovation alliance in China. J. Ocean. Univ. China (Soc. Sci.) 2016, 3, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.W. New features and new countermeasures of current fishery technology extension. Shandong Ind. Tech. 2019, 1, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Guan, C.; Jia, Y. Development of the different aquaculture models for marine fishes. Open J. Fish. Res. 2018, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.F.; Tang, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; De Silva, S.S. (Eds.) Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Shan, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; et al. A Revisit to Fishmeal Usage and Associated Consequences in Chinese Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Haambiya, L.H.; Monde, C.; Musuka, C.G.; Makorwa, T.H.; Munganga, B.P.; Phiri, K.J.; Nsekanabo, J.D. Climate Change Effects on Aquaculture Production: Sustainability Implications, Mitigation, and Adaptations. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 609097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghe, R.P.; Phillips, M.J. Small-scale aquaculture: Organization, clusters and business. FAO Aquac. Newsl. 2010, 45, 37–39. [Google Scholar]


| Systems | No. of Farmers | No. of Ponds/Dams | No. of Cages | Area (m2)/Area (ha) | Volume (m3)/Area (ha) | No. of Production Cycles | Total Fish Produced (MT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small scale Ponds | 13,565 | 11,693.92 | / | 7016.35 | / | 1.5 | 32,977.36 |
| Commercial Land-Based | 33 | 3828.08 | / | / | / | 1.5 | 10,718.06 |
| Small scale Cages | 636 | / | 190 | / | 82,987.96 | 1.5 | 5073.44 |
| Commercial (cages) | 13 | 2945.95 | 263 | / | 294,230.04 | 2 | 14,586.14 |
| Total | 14,247 | 15,522 | 453 | 9962.30 | 377,218 | / | 63,418.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Maulu, S.; Hua, F.; Chama, M.K.H.; Xu, P. Aquaculture in Zambia: The Current Status, Challenges, Opportunities and Adaptable Lessons Learnt from China. Fishes 2024, 9, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010014
Zhang L, Maulu S, Hua F, Chama MKH, Xu P. Aquaculture in Zambia: The Current Status, Challenges, Opportunities and Adaptable Lessons Learnt from China. Fishes. 2024; 9(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lin, Sahya Maulu, Fenglei Hua, Majory K. H. Chama, and Pao Xu. 2024. "Aquaculture in Zambia: The Current Status, Challenges, Opportunities and Adaptable Lessons Learnt from China" Fishes 9, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010014
APA StyleZhang, L., Maulu, S., Hua, F., Chama, M. K. H., & Xu, P. (2024). Aquaculture in Zambia: The Current Status, Challenges, Opportunities and Adaptable Lessons Learnt from China. Fishes, 9(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010014







