Abstract
In the present study, Curcuma longa (CL) hydrolate and the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum (LP) were provided as dietary supplements to Nile tilapia. One hundred ninety-two juvenile tilapias (2.25 ± 0.14 g and 4.5 ± 0.10 cm) were distributed in sixteen experimental units, and four experimental groups were established: CL [CUR]: fish fed a diet supplemented with CL hydrolate at 2.5%; probiotic [PRO]: a diet supplemented with LP; LP + CL [COMB]: diet supplemented with the LP strain cultivated in media supplemented with 2.5% CL hydrolate; and control [CTRL]: diet without supplementation. After 70 days, the final average weight was significantly greater in the PRO group (33.26 ± 1.12 g) than in the CTRL and CUR groups, whereas the specific growth rate was significantly greater in the PRO and COMB groups than in the CTRL and CUR groups. Feed conversion decreased significantly in the PRO group (1.03 ± 0.11). Dietary supplementation did not change the body composition of tilapia. Leukocyte and lymphocyte counts were greater in the PRO treatment than in the CTRL group. Compared with those in the CTRL group, total serum protein was significantly increased in the PRO group. Immunoglobulins were higher in the COMB and PRO groups. In the experimental challenge, all the fish in the treated groups presented lower cumulative mortality rates. The combination of LP and CL improved the growth parameters of Nile tilapia.
Key Contribution:
Lactobacillus plantarum + Curcuma longa hydrolate reduced feed conversion. L. plantarum + C. longa hydrolate improved immunoglobulin levels. L. plantarum increased total plasma protein.
1. Introduction
Phytotherapeutics, such as essential oils and their bioactive compounds, are products obtained from plants and are used for curative, prophylactic, or adjuvant nutraceutical purposes in the prevention and treatment of diseases [1,2,3]. Historically, plants and their derivatives have been used to treat different diseases in humans and animals [4] and control bacterial and parasitic infections in the aquaculture industry [1,5].
In aquaculture, many products derived from plants have already been identified as authentic therapeutic agents for use in fish farming owing to their medicinal, antioxidant, antifungal, antibacterial, and immunostimulant properties [6,7]. Among them, Lippia origanoides stands out as an antiparasitic agent for Colossoma macropomum [5]. Psidium guajava leaf extract minimized the toxicity effects of cypermethrin on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) [8]. Punica granatum peel mitigated the adverse effects of silver nanoparticles on Nile tilapia welfare [9]. Aloe vera induced immune gene expression in Oncorhynchus mykiss [10]. Allium sativum was found to prevent monogenean infection [11]. Zingiber officinale improved the immune response of the Asian sea bass Lates calcarifer against Vibrio harveyi [12] and enhanced the growth and immune response of fish against Streptococcus agalactiae [13]. Ocimum gratissimum increases the growth and immune response of Lophiosilurus alexandri and serves as an anesthetic agent [14]. Silybum marianum acted as a hepatic protector and immunomodulator in Nile tilapia during S. agalactiae infection [15], and Curcuma longa hydrolate was found to improve the immune response and survival of fish [16,17].
The hydrolate is a byproduct of the distillation process in the extraction of essential oils. During this process, some volatile and bioactive elements of the original plant not present in the oil are captured by the water vapor that passes through the vegetable mass. This occurs because some plant compounds are hydrophilic and only have an affinity for water [16].
Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae), known in Brazil as açafrão-da-terra [18], is a perennial plant widely cultivated in tropical regions of Asia [4]. It is a plant with a small stem and large and oblong leaves with oval, elliptical, or piriform rhizomes that are occasionally branched and brownish-yellow. Turmeric is the component from which the predominant yellow color of dry C. longa powder originates. Indian Turmeric or Haridra, Yellow Ginger, Kyoo, or Ukon are just a few names. Turmeric is commonly used in Indian culture as a home therapy in the treatment of human diseases [4,19,20].
Nile tilapia was the top four species produced in 2022, with around 5.3 million tonnes [21]. In tilapia farming, bacterial diseases, one of the main weaknesses of the production sector, which are caused, for example, by the bacteria of the genus Streptococcus [22] and Aeromonas [23], are preventable with the use of probiotics [24]. In addition, probiotics, which are beneficial microorganisms that cohabit with the diverse microbial community of the host’s digestive tract [25], can also improve fish appetite, leading to greater growth performance and optimizing feed conversion [25,26,27]. Among probiotic microorganisms, Lactobacillus plantarum has already demonstrated beneficial effects on the immunocompetence and growth parameters of Nile tilapia [28,29,30].
According to Yue et al. [31], polysaccharides contained in bioactive plant ingredients can be degraded into absorbable metabolites by bacteria that colonize the intestine. Consequently, the intestinal microbiota plays a vital role in the catabolism of these polysaccharides. In addition, polysaccharides can modulate the composition and activities of the intestinal microbiota, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the colonization of pathogenic bacteria.
In recent decades, the growing individualized use of phytotherapeutics and probiotics, driven by scientific discovery, has become an alternative to the chemical products and antibiotics frequently used in aquaculture, aiming at sustainability in fish production [24,27,32,33,34]. However, little is known about the crosstalk between phytotherapeutics and probiotics when combined with dietary supplementation and the possible effects of such cross-actions on Nile tilapia.
Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of the phytobiotic Curcuma longa hydrolate and the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum, which are provided as dietary supplements to Nile tilapia.
2. Materials and Methods
This research was approved by the National Council for the Control of Animal Experimentation (CONCEA) under protocol number 263/2018. All the fish used in the biological analyses were previously anesthetized with eugenol (50 mg L−1) and euthanized by spinal cord transection. Following the guidelines of the Ethics Committee on Animal Use (CEUA) and aiming at the principles of “reduction, replacement and refinement” in the use of animals in scientific and academic centers, the present research used a minimal, but adequate, number of animals per experimental procedure to minimize animal discomfort.
2.1. In Vitro Assay to Test the Dosage of Curcuma longa Hydrolate in Probiotic Culture Medium
C. longa hydrolate was included in the final growth phase of L. plantarum. For this purpose, Man Rogosa Sharpe (MRS) culture media were prepared with five different concentrations of vehicle (Table 1). L. plantarum was sown in an MRS tube and incubated at 35 °C for 24 h. After incubation, the number of colony-forming units per mL (CFU mL−1) of each concentration was estimated through a serial dilution (factor of 1:10) in MRS agar culture medium, which was performed in triplicate.

Table 1.
Vehicle volume used to cultivate Lactobacillus plantarum.
The inhibitory capacity against Pseudomonas sp. Streptococcus sp., Aeromonas hydrophila, and A. veronii was verified. For this purpose, L. plantarum was cultivated on MRS agar, as shown in Table 1. The different treatments were evaluated for their inhibitory effects via the disc agar diffusion technique, as described by Jatobá et al. [28]. The bacteria grown in different vehicles were seeded in a Petri dish containing MRS agar and incubated at 35 °C for 24 h. After this period, discs 1 cm in diameter were removed from these MRS plates with L. plantarum, which were superimposed on the surface of the same newly sown pathogenic bacteria and incubated at 30 °C for 24 h. Antagonistic activity was expressed as the diameter (mm) of the zone of inhibition around the agar discs superimposed in triplicate.
2.2. In Vivo Experimental Design
In total, 192 Nile tilapia with initial average weight and length of 2.25 ± 0.14 g and 4.5 ± 0.10 cm were distributed in 16 experimental units (12 fish per unit), with a useful volume of 800 L, which were arranged in a recirculation aquaculture system equipped with physical and biological filtration, ultraviolet sterilizers, constant aeration, and central water heating.
The experiment was a completely randomized design with four groups in quadruplicate. The groups were fish fed (1) Curcuma longa (CUR), a diet supplemented with 2.5% C. longa hydrolate according to Pereira et al. (2020); (2) probiotic (PRO), a diet supplemented with L. plantarum; (3) L. plantarum + C. longa (COMB), a diet supplemented with L. plantarum cultivated with 2.5% C. longa hydrolate as a vehicle; or (4) control (CTRL), a diet without supplementation.
The experimental diet (Supplementary File S1) was sprayed with PRO, CUR, COMB, or distilled water (CTRL). PRO and COMB were previously grown in MRS culture media at a rate of 100 mL kg feed−1. Subsequently, it was stored in a drying oven at 24 to 35 °C. Next, the feed was dried in an oven for 24 h at 35 °C. For the CUR group, the commercial diet was supplemented with 2.5% C. longa hydrolate, according to the protocols established by Pereira et al. [16], and the control feed was sprayed with distilled water (100 mL kg feed−1). To quantify the lactic acid bacteria content in the feed, serial dilutions (1:10) were carried out. The final count of lactic acid bacteria in the PRO and COMB groups was greater than 1 × 108 CFU g feed−1.
The fish were fed four times a day with 6% biomass, and weekly biometrics were performed to monitor growth and adjust feeding management. After 70 days, at the end of the growth performance period, the final weight, specific growth rate (SGR) = (lnFinal weight − lnInitial weight)/(cultivation days) × 100), feed conversion rate (FCR) = (consumed feed/weight gain), survival rate (%) = [(number of animals at the end/number of animals at the beginning) × 100], yield (g m−3) = [(final biomass − initial biomass)/(experimental unit volume)], hepatosomatic index (HIS %) = [(liver weight/fish body weight) × 100], and viscerosomatic index (VSI %) = [(viscera weight/fish body weight) × 100] were evaluated. In addition, the carcasses of the fish were used to determine moisture, ash, lipid, and crude protein contents following the methodologies of the AOAC [35].
Water quality variables were measured throughout the experimental period and included dissolved oxygen at 5.12 ± 0.76 mg L−1 and a temperature of 29.01 ± 2.59 °C (YSI PRO20 Oximeter), ammonia at 0.11 ± 0.09 mg L−1, nitrite below 0.10 mg L−1, nitrate below 0.20 ± 0.12 mg L−1, alkalinity at 101.2 mg CaCO2 L−1 and pH at 6.86 ± 0.21. Dissolved oxygen and temperature were checked twice daily, and the other variables were checked once weekly. The experimental units were siphoned twice weekly to remove excess organic solids accumulated at the bottom of the boxes.
2.3. Hematoimmunological Analysis
For hematological analysis, blood from 20 fish from each treatment (five fish per experimental unit) was collected via puncture of the caudal vessel with insulin syringes coated with the anticoagulant solution HEMSTB (EDTA K2 15 g dL−1) for the preparation of blood smears in duplicate, and the following hematological analyses were performed: determination of hematocrit via the standard microhematocrit method [36]; glucose (G-TECH free®, Accumed-Glicomed, Duque de Caxias, RJ, Brazil); total hemocyte count via a Neubauer hemocytometer; and hemoglobin concentration [37]. Hematimetric absolute rates of the mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) were also obtained [38]. Blood smear slides were stained with May Grunwald–Giemsa stain (MGG) [39] for total and differential leukocyte counts according to Ishikawa et al. [40].
For immunological analyses, blood was collected without anticoagulant for serum withdrawal. The blood was kept in Eppendorf tubes for 1 h at 25 °C until coagulation and subsequently centrifuged at 1400× g for 15 min for serum withdrawal and stored at −20 °C for immunological analyses. The serum antimicrobial titer was determined against A. hydrophila in a 96-well flat-bottom microplate [41]. The inoculum of A. hydrophila was grown in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth at 28 °C for 24 h and prepared in poor broth (PB) culture medium at a concentration of 1 × 105 CFU mL−1. The serum was diluted 1:3 in PB in the first well (50 μL of plasma:100 μL of PB solution) and was serially diluted by a factor of 1:2 for the other wells. For the positive and white controls, saline solution was diluted in PB in a manner similar to that used for the serum. Finally, 20 μL of A. hydrophila was added to the wells with diluted serum and a positive control. The microplates were incubated at 28 °C for 24 h. The growth of the microorganisms was determined in a microplate reader at a wavelength of 550 nm. The plasma antimicrobial titer was the reciprocal of the last dilution that showed bactericidal activity, i.e., evidence of total inhibition of microbial growth.
Blood serum protein was measured via a commercial total protein kit. The total immunoglobulin (Ig) concentration was measured according to the method described by Amar et al. [42]. This protocol involves mixing 50 µL of the serum with 50 µL of 12% polyethylene glycol solution (PEG, 10,000 MW, Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO, USA) and incubating the mixture at 25 °C for two hours to precipitate the immunoglobulin molecules. The immunoglobulin precipitate was removed by centrifugation (5000× g at 4 °C for 10 min), and the supernatant was removed. The amount of total protein was also measured with a commercial kit, in which bovine serum albumin was used to construct a standard curve. The concentration of total immunoglobulin was expressed in mg mL−1 and calculated as GI (mg mL−1) = total whey protein − PEG-treated protein.
2.4. Experimental Infection of Aeromonas
After 70 days of growth (fish weight above 28.03 ± 3.44 g), two experimental infections were carried out against A. hydrophila and A. veronii, two pathogens that cause large losses in tilapia farming [23]. Both infections were completely randomized designs with the same four groups described above in triplicate.
For the A. hydrophila challenge, 60 juvenile Nile tilapia were distributed in 15 polyethylene boxes (40 L) equipped with a biological filter and thermostat. These parameters were measured daily: dissolved oxygen above 5.52 mg L−1 and a temperature of 28.54 ± 0.23 °C (YSI PRO20 Oximeter); ammonia, 0.04 NH3 mg L−1; and pH, 6.93 ± 0.06.
For the challenge, 1 × 107 CFU mL−1, approximately 1.5 × 105 CFU g−1, was administered by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection such that each fish received 100 μL of the bacterial mixture. The inoculum cultivated in BHI for 24 h at 30 °C was centrifuged for 30 min at 1800× g. The supernatant was discarded, and the sediment was resuspended in a 0.65% sterile saline solution at a concentration of 1 × 107 CFU mL−1.
For infection of A. veronii, another batch of 60 fish was used, and the process described above was repeated. All the parameters were measured daily: dissolved oxygen above 5.64 mg L−1 and a temperature of 28.23 ± 0.19 °C (YSI PRO20 Oximeter); ammonia below 0.04 NH3 mg L−1; and a pH of 6.94 ± 0.07. After both challenges, the fish were observed for nine days to obtain the mortality rate, and the percentage of deaths and cumulative mortality were calculated. Mortality was checked every 8 h, and dead fish were immediately removed from the tank.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The data were subjected to the Kolmogorov‒Smirnov test to determine normality, and Levene’s test was used to verify homoscedasticity. The data obtained met the prerequisites of normality and homoscedasticity, and one-way ANOVA and significant differences among treatments were analyzed via the Student‒Newman‒Keuls (SNK) test. The vehicle concentrations were subjected to second-order polynomial regression. All tests were conducted at a 5% level of significance.
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Assay
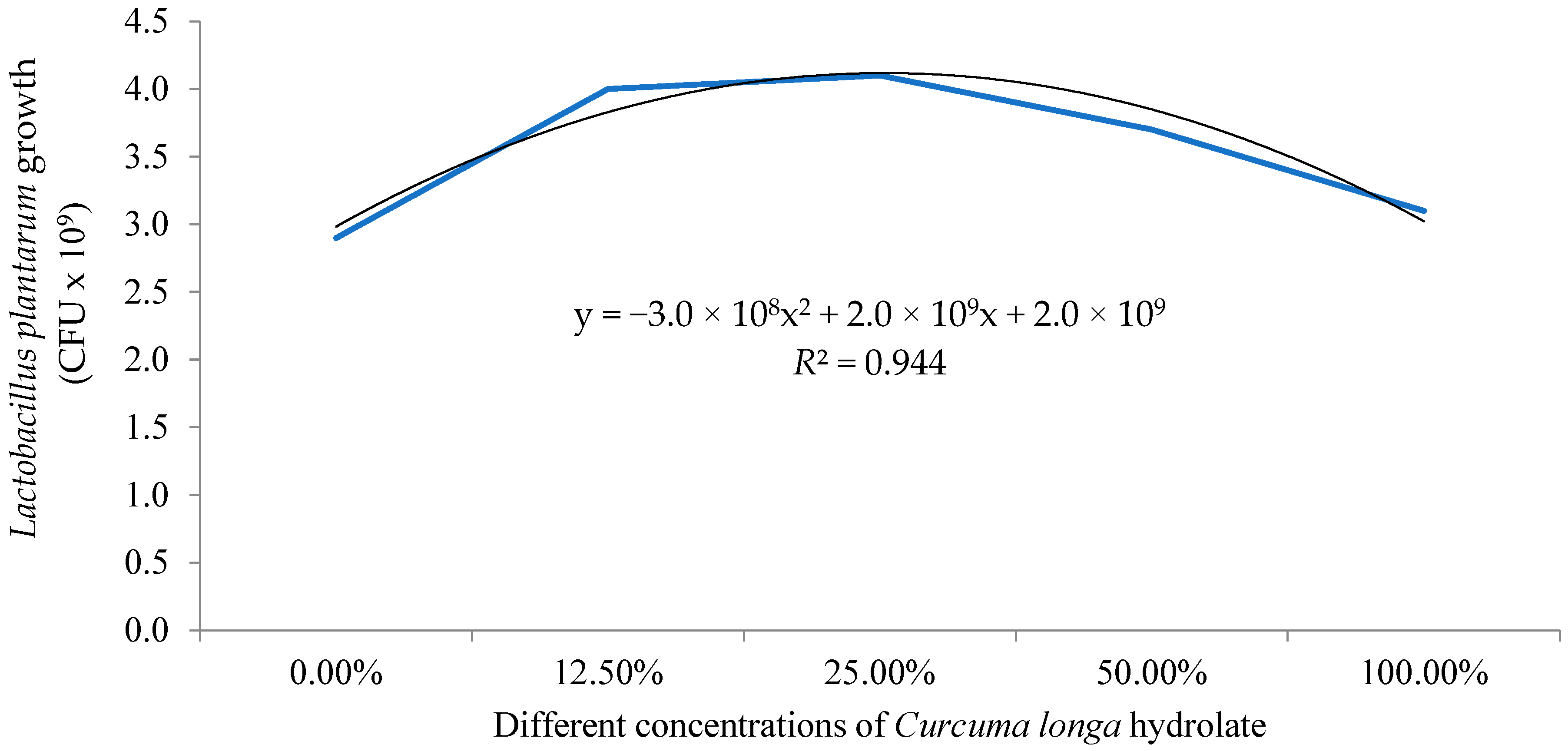
The in vitro results revealed greater growth of L. plantarum when cultivated in 2.5% C. longa hydrolate as a vehicle (Figure 1). The inhibition halo was significantly (p < 0.05) reduced against S. agalactiae when L. plantarum was cultivated in culture media supplemented with 10.0% C. longa hydrolate (Table 2).
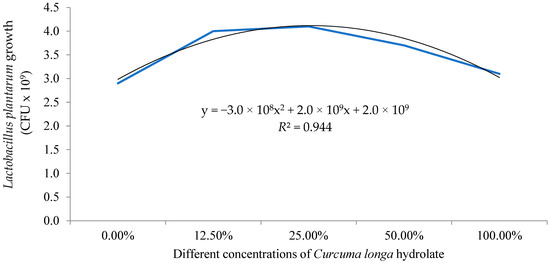
Figure 1.
Growth curve of Lactobacillus plantarum cultivated with different concentrations of C. longa hydrolate as a vehicle. The vehicle concentrations were subjected to second-order polynomial regression.

Table 2.
Inhibition halo (mm) of Lactobacillus plantarum cultivated under different concentrations of Curcuma longa hydrolate as a vehicle against pathogenic bacteria.
3.2. In Vivo Assay
3.2.1. Growth Performance
The average final weight of the fish in the PRO treatment group was greater (p < 0.05) (33.26 ± 1.12 g), whereas those in the CUR and COMB groups did not differ from those in the control group. The specific growth rate was significantly (p < 0.05) greater in the fish from the PRO (1.64 ± 0.01% day−1) and COMB (1.61 ± 0.04% day−1) groups than in those from the CUR and CTRL groups. Feed conversion was significantly (p < 0.05) lower for the fish in the PRO and COMB groups. The lowest survival rate (83.33 ± 5.56%) and lowest yield (345.42 ± 24.44 g m−3) were observed in the CTRL group (Table 3). The body indices did not significantly differ (p > 0.05) among the treatments (Table 4).

Table 3.
Growth performance (mean ± standard deviation) for Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) reared in RAS, fed a diet supplemented with Curcuma longa hydrolate and probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum in combination or alone.

Table 4.
Whole-body composition analysis of Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) reared in RAS, fed a diet supplemented with Curcuma longa hydrolate and probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum in a combined or isolated way.
3.2.2. Hematoimmunological Analyses
According to the hemogram, the number of total leukocytes and lymphocytes in the fish from the PRO group was significantly greater (p < 0.05) than that in the CTRL group; however, this increase was equal to that in the other treatment groups. The other hematological indices did not significantly differ (p > 0.05) among the treatments (Table 5).

Table 5.
Hematological parameters (mean ± standard deviation) for Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) reared in RAS, fed a diet supplemented with Curcuma longa hydrolate and probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum in a combined or isolated way.
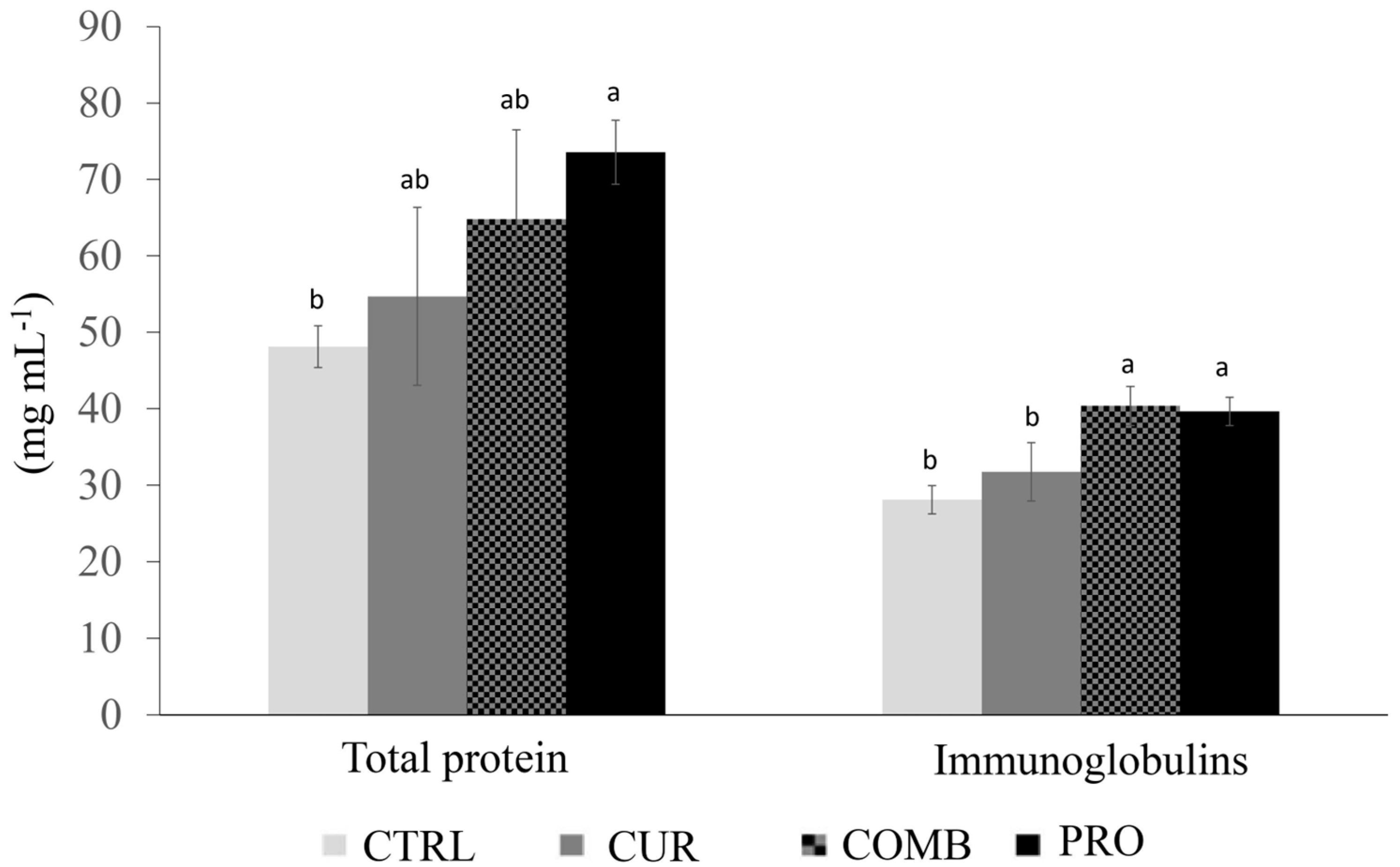
Compared with the fish in the CTRL group (48.12 mg mL−1), the fish in the PRO treatment group presented a significant increase (p < 0.05) in total plasma protein (73.55 mg mL−1), whereas the CUR (54.69 mg mL−1) and COMB (64.76 mg mL−1) groups did not differ from the PRO or the CTRL groups. However, significantly greater (p < 0.05) immunoglobulin concentrations were detected in the fish in the COMB (40.34 mg mL−1) and PRO (39.64 mg mL−1) groups than in the CUR (31.74 mg mL−1) and CTRL (28.09 mg mL−1) groups (Figure 2). The MIC and agglutination titer did not significantly differ (p > 0.05) among the treatments (Table 5).
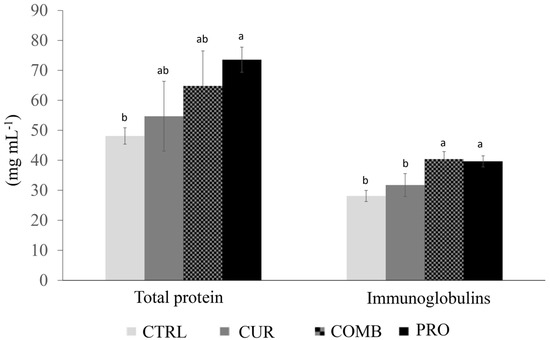
Figure 2.
Total serum protein and immunoglobulins (mean ± standard deviation) of Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) reared in a recirculating aquaculture system and fed a diet supplemented with Curcuma longa hydrolate and the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum, either in combination or alone. CTRL = control group; CUR = C. longa hydrolate in an isolated way; PRO = L. plantarum probiotic in an isolated way; and COMB = C. longa hydrolate and probiotic L. plantarum in a combined way. Different letters indicate significant differences according to ANOVA and SNK (p < 0.05).
3.2.3. Experimental Challenge
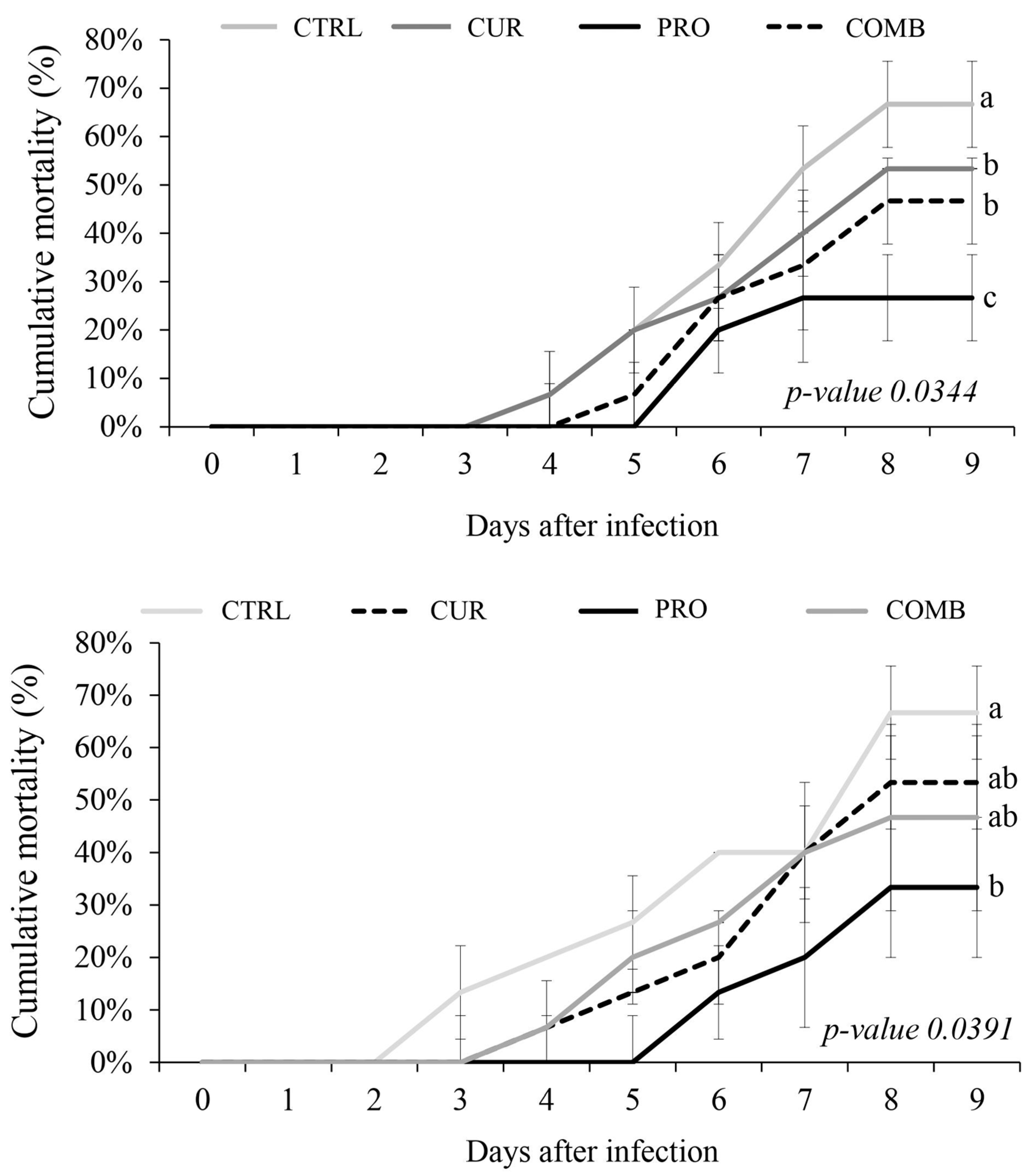
Among the evaluated groups, the PRO treatment group presented the lowest cumulative mortality, followed by the CUR and COMB groups, with the highest cumulative mortality recorded in the CTRL group (Figure 3).
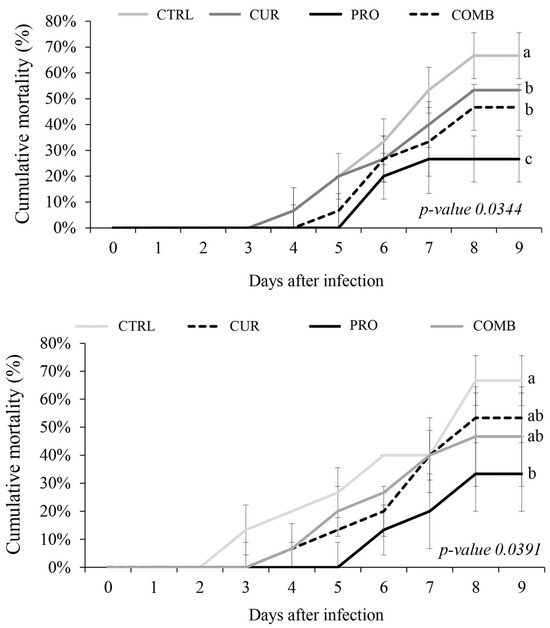
Figure 3.
Cumulative mortality of Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) fed a diet supplemented with Curcuma longa hydrolate and the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum, either in combination or alone: experimental challenge with Aeromonas hydrophila (above); experimental challenge with A. veronii (below). Different letters indicate significant differences according to ANOVA and SNK (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Functional diets are increasingly gaining prominence in the aquafeed industry. For example, Nigella sativa exhibited hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects against silver nanoparticle toxicity [43], while papaya extract, Carica papaya, alleviated endocrine disruption and hepatic DNA damage and counteracted the subchronic toxicity of chlorpyrifos [44] in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). This can be attributed to their ability to promote health and prevent disease owing to the wide range of scientifically tested bioactive substances with proven efficacy for inclusion in fish diets [3,7,34,44].
Among supplemental feeds, phytotherapeutics [1] and probiotics [45] stand out because of their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties [24,32]. In the present study, a novel dietary plan for Nile tilapia was formulated based on diets enriched with bioactive components derived from Curcuma longa, highlighting the combined dietary effects of L. plantarum + C. longa.
C. longa is a plant that has bioactive compounds such as curcumin, a powerful antioxidant that fights free radicals, safeguarding cells and tissues from oxidative harm. It also possesses anti-inflammatory characteristics that can lower cytokine production [18,20]. Similarly, L. plantarum is recognized for its antioxidant properties and other advantageous substances that promote intestinal health in aquacultured fish [24].
Phytotherapeutics can influence the microbiota by helping to strengthen and balance the intestinal flora [31]. Some compounds found in plants, such as the polyphenols ar-turmerone, α-tumerone, and α-curcumene, present in C. longa hydrolate [17], have shown beneficial effects [16,17,18,19,20,46,47,48].
Some herbal products are natural sources of prebiotics, which are substances used as substrates for probiotic bacteria, favoring their multiplication in the intestine to increase the diversity of beneficial bacteria and protect against the growth of harmful bacteria [1]. In addition, a clean, pathogen-free, and more stable water environment, such as the recirculation system used in this research, is a fundamental strategy for improving fish health.
Su et al. [49] reported the potential for combined therapy with herbal medicines and probiotics in microbial infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. At that time, researchers reported that the combination of green tea extract and probiotics significantly reduced the viable count of both pathogens at 4 h and at 24 h, suggesting a possible synergistic effect between the two products. Indeed, in the present study, the addition of 25% and 100% C. longa hydrolate to the culture medium promoted the greatest in vitro growth of the probiotic bacterium L. plantarum and inhibited the in vitro growth of the pathogenic bacterium S. agalactiae, corroborating the studies cited above.
The effects of the probiotic L. plantarum have already been reported in other studies since it has been widely tested and used as a probiotic for Nile tilapia in different life stages and culture environments, promoting growth and improving innate immunity [28,29,30,50]. In the present study, the highest daily specific growth rates were observed in the fish from the groups in which the probiotic was present.
In clear water RAS, the specific growth rate (SGR) of Nile tilapia (initial weight of 0.85 ± 0.08 g) fed with feed containing 2.5% C. longa hydrolate was equal to that of the control group, reaching 2.21 ± 0.05% day−1 after 40 days of cultivation [17]. These results corroborate the findings of the present research, in which the SGRs of the CUR and CTRL groups remained the same.
Combining probiotics and phytotherapeutics results in a synergistic effect in which probiotics balance the intestinal microbiota, whereas phytotherapeutics provide bioactive compounds that promote the regulation of physiological functions that, in turn, improve the absorption of nutrients, improve growth, and strengthen the immune system [51]. Indeed, in the present study, improvements were observed in the zootechnical performance of Nile tilapia fed L. plantarum cultivated in a culture medium supplemented with C. longa (L. plantarum + C. longa). However, the effects were the same as those for the PRO group, and when used alone, C. longa hydrolate presented indices similar to those of the control group. The present study demonstrated that the probiotic L. plantarum was responsible for the improved growth performance of tilapia, given that probiotic supplementation alone increased the average final weight, SGR, and feed conversion compared with those of the CUR group.
Despite high variability in the microbiota of fish, lactic acid bacteria (LAB), such as L. plantarum, are sometimes abundant in the gut, especially in freshwater fish. Fortunately, most LAB are harmless, and some strains have been reported to have beneficial health effects by boosting the immune system in fish, along with pathogen antagonism, another key feature of candidate bacteria used as probiotics [52,53,54]. These characteristics were confirmed in the present study when we performed hematoimmunological analyses. A significant increase in plasma protein levels was observed in the blood of the fish in the groups treated with either probiotics or C. longa hydrolate alone, as well as L. plantarum + C. longa, indicating that both probiotics and phytotherapeutics caused these changes. Indeed, phytotherapeutics may also be used to improve hematoimmunological variables in fish. Abdel-Tawwab and Hamed [8] reported that dietary guava (Psidium guajava) leaf extract significantly enhanced hematobiochemical and immunity variables in cypermethrin-intoxicated Nile tilapia, significantly minimizing the negative impacts caused by synthetic pyrethroid insecticide. The increase in plasma protein in the present study is an important indicator of the health status of the fish, revealing that tilapia in these groups were better prepared to trigger an immune response to pathogens.
On the other hand, Santos et al. [45] reported significant reductions in immunoglobulin concentrations in Nile tilapia after an experimental challenge, demonstrating that infectious processes promote considerable reductions in this blood component. In contrast, Moraes et al. [27] did not observe changes in immunoglobulins in juvenile tilapia when the fish were fed diets supplemented with probiotic additives containing Bacillus spp. or Saccharomyces cerevisiae microencapsulated. In the present study, the level of immunoglobulins was altered in the PRO and L. plantarum + C. longa groups. However, in the group of fish receiving C. longa alone, the immunoglobulin concentration was the same as that in the control group, suggesting that the probiotic caused changes in immunoglobulin levels.
Leukocytes are fundamental cells for the immune defense of animals [38]. Even without coming into contact with the host’s blood system, lactic acid bacteria can interact directly with immune cells through specialized cells of the intestinal epithelium, such as M cells, and induce the activation and multiplication of the cells responsible for defense [55]. In the present study, dietary supplementation with the probiotic L. plantarum may have induced greater production or release of total leukocytes and circulating lymphocytes, which may suggest a nonspecific response to infections [28].
Recently, Pereira et al. [16] tested different concentrations of Curcuma longa hydrolate (0.0%, 2.5%, 7.5%, and 10.0%) in the diet of juvenile Nile tilapia (7.45 ± 0.38 g). Pereira et al. [17] demonstrated that dietary supplementation with 2.5% C. longa hydrolate improved the immune response and survival and promoted beneficial changes in the intestinal microbial community of tilapia fingerlings (0.85 ± 0.08 g). Furthermore, the major compounds of C. longa hydrolate are ar-turmerone, α-tumerone, and α-curcumene, representing approximately 93.50% purity. Lee [47] reported that ar-turmerone and arachidonic acid effectively inhibited platelet aggregation induced by collagen (IC50, 14.4 µM and IC50, 43.6 μM, respectively). However, ar-turmerone had no effect on platelet activation factor or thrombin-induced platelet aggregation, suggesting that it could be useful as a lead compound to inhibit platelet aggregation. In the blood count of the present study, we observed that the group that received C. longa alone in the diet presented, in absolute number, a smaller number of thrombocytes, but the difference was not significant. Furthermore, the COMB group showed no significant improvement beyond that of either the probiotic L. plantarum or C. longa alone since no possible synergistic effects were observed in the hematology analyses.
Experimental challenges that use the intraperitoneal route for infections can be aggressive, offering few opportunities for fish to recover after exposure to the pathogen and causing severe damage to organs responsible for vital functions, such as the brain, liver, and spleen [56]. When juvenile tilapias were challenged with A. hydrophila, Moraes et al. [27] reported that treatments supplemented with probiotics resulted in lower cumulative mortality during the experimental challenge. Similarly, Santos et al. [45] reported lower mortality rates for juvenile tilapia fed the probiotic Bacillus spp. or 0.1% benzoic acid alone. However, when Bacillus was combined with 0.1% benzoic acid, no synergistic effects were observed during the experimental challenge.
Many isoprenoids and phenolic compounds with antioxidant properties and molecular interactions that affect inflammatory processes have been discovered in C. longa [48]. Ferreira et al. [46] verified that a fraction consisting of ar-turmerone isolated from C. longa neutralized the hemorrhagic activity present in Bothrops jararaca venom and inhibited the proliferation and natural killer activity of human lymphocytes. Devi et al. [57] also verified the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of partially purified herbal extracts against ornamental fish pathogens. At that time, researchers revealed that turmeric extract exhibited significant antibacterial activity and greater antioxidant properties and phenol content, among which the highest presence of ar-turmerone (42.85%) was revealed. The authors also suggested that partially purified turmeric extract improved the hematobiochemical profile and survival rate of Pseudochromis dilectus against Proteus mirabilis.
These characteristics attributed to ar-turmerone may have influenced the survival of fish in the C. longa and L. plantarum + C. longa groups during experimental challenge with A. hydrophila. Since the genus Aeromonas causes severe hemorrhage, this condition may have been alleviated in the affected fish, considering the lower mortality rates observed relative to those in the control group. However, the lowest cumulative mortality in both challenges was attributed to the group that received the probiotic alone.
Probiotics are considered effective alternatives to chemotherapy [58,59]. However, the effectiveness of probiotics can be contradictory; therefore, it is important to search for alternatives to improve their effectiveness [51]. According to Yue et al. [31], some polysaccharides present in natural products derived from plants can be catabolized with difficulty, and the intestinal microbiota plays a fundamental role in the degradation of these polysaccharides. Therefore, it is necessary to further investigate the mode of combined action between L. plantarum and other plant-derived products that may exhibit synergistic action and thus enhance the efficacy of this probiotic. Nonetheless, it is worth mentioning that C. longa can be considered a medicine for the treatment of inflammation, microbial infections, biliary disorders, and liver disorders, including antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, hepatoprotective, and immunostimulant activities in animals [19].
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated the effects of supplementing Nile tilapia diets with L. plantarum and C. longa hydrolate. The results show that both probiotic L. plantarum and phytobiotic C. longa improved the growth performance of Nile tilapia in a recirculating aquaculture system. While L. plantarum alone showed better results, the combination of L. plantarum and C. longa was also effective. All additives enhanced the innate immune resistance of juvenile tilapia, reducing mortality rates under experimental conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes9120503/s1, Supplementary file S1 Composition of experimental diet before inclusion of feed additives.
Author Contributions
A.J.—experimental execution, conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, data curation, visualization; G.F.A.J.—conceptualization, project administration; S.A.P.D.—hematoimmunological analysis, data curation, microbiological count; M.d.O.P.—experimental execution, investigation, data curation; D.D.S.—experimental execution, investigation, data curation; J.L.P.M.—conceptualization, supervision; M.S.O.—experimental execution, data curation, manuscript review, final writing; supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was approved by the National Council for the Control of Animal Experimentation (CONCEA) under protocol number 263/2018, and it was performed in the Aquaculture Laboratory (LAq) of IFc-Araquari—IFCA. All the fish used in the biological analyses were previously anesthetized with eugenol (50 mg L−1) and euthanized by spinal cord transection. Following the guidelines of the Ethics Committee on Animal Use (CEUA) and aiming at the principles of “reduction, replacement and refinement” in the use of animals in scientific and academic centers, the present research used a minimal, but adequate, number of animals per experimental procedure to minimize animal discomfort.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data related to this research are available upon prior request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for grant to Adolfo Jatobá (308661/2023-0); and the company Presence–Brazil for providing diets used in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Elumalai, P.; Kurian, A.; Lakshmi, S.; Faggio, C.; Esteban, M.A.; Ringø, E. Herbal immunomodulators in aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyavani, J.; Sibiya, A.; Sivakamavalli, J.; Divya, M.; Preetham, E.; Vaseeharan, B.; Faggio, C. Phytotherapy and combined nanoformulations as a promising disease management in aquaculture: A review. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Hamed, H.S.; Monier, M.N.; Amen, R.M. The ameliorative effects of dietary rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) against growth retardation, oxidative stress, and immunosuppression induced by waterborne lead toxicity in Nile tilapia fingerlings. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammon, H.P.; Wahl, M.A. Pharmacology of Curcuma longa. Planta Med. 1991, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, B.V.; Cardoso, A.C.F.; Campos, R.R.; Gonçalves, B.B.; Santos, G.G.; Chaves, F.C.M.; Chagas, E.C.; Tavares-Dias, M. Antiparasitic, physiological and histological effects of the essential oil of Lippia origanoides (Verbenaceae) in native freshwater fish Colossoma macropomum. Aquaculture 2017, 469, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, H.S.; El-Sayed, Y.S. Antioxidant activities of Moringa oleifera leaf extract against pendimethalin-induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Elabd, H.; Mahboub, H.H.; Assayed, M.E.M.; Hamed, H.S.; Elsayyad, A.; Mohamed, E.M. The protective efficacy of dual dietary rosemary plus cinnamon mix against lead nitrate-induced immune suppression, genotoxicity, and oxidant/antioxidant status in Nile tilapia fingerlings. Aquac. Int. 2023, 32, 4009–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Hamed, H.S. Antagonistic effects of dietary guava (Psidium guajava) leaves extract on growth, hemato-biochemical, and immunity response of cypermethrin-intoxicated Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, fingerlings. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, H.S.; Abdel-Tawwab, M. Dietary pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel mitigated the adverse effects of silver nanoparticles on the performance, haemato-biochemical, antioxidant, and immune responses of Nile tilapia fingerlings. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanuzzo, F.S.; Urbinati, E.C.; Rise, M.L.; Hall, J.R.; Nash, G.W.; Gamperl, A.K. Aeromonas salmonicida induced immune gene expression in Aloe vera fed steelhead trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquaculture 2015, 435, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militz, T.A.; Southgate, P.C.; Carton, A.G.; Hutson, K.S. Dietary supplementation of garlic (Allium sativum) to prevent monogenean infection in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2013, 408, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpur, A.D.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Bolong, A.M.A. Nutritional effects of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) on immune response of Asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch) and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi. Aquaculture 2013, 400, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, A.; Pereira, S.A.; Owatari, M.S.; Chagas, E.C.; Chaves, F.C.M.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Martins, M.L. Effect of dietary essential oils of clove basil and ginger on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) following challenge with Streptococcus agalactiae. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaventura, T.P.; Souza, C.F.; Ferreira, A.L.; Favero, G.C.; Baldissera, M.D.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Baldisserotto, B.; Luz, R.K. Essential oil of Ocimum gratissimum (Linnaeus, 1753) as anesthetic for Lophiosilurus alexandri: Induction, recovery, hematology, biochemistry and oxidative stress. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owatari, M.S.; Jesus GF, A.; Brum, A.; Pereira, S.A.; Lehmann, N.B.; Pereira, U.P.; Martins, M.L.; Mouriño, J.L.P. Sylimarin as hepatic protector and immunomodulator in Nile tilapia during Streptococcus agalactiae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.O.; Moraes, A.V.; Rodhermel, J.C.B.; Hess, J.D.; Alves, L.; Chaaban, A.; Jatobá, A. Supplementation of Curcuma longa hydrolate improves immunomodulatory response in Nile tilapia reared in a recirculation aquaculture system. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2020, 72, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.O.; Hess, J.D.; Rodhermel, J.C.B.; Farias, D.R.; Schleder, D.D.; Alves, L.; Bertoldi, F.C.; Chaban, A.; Andrade, J.I.A.; Jatobá, A. Curcuma longa hydrolate improves Nile tilapia survival in a recirculation rearing system, maintaining the animal homeostasis and modulating the gut microbial community. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2021, 93, e20210088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, J.P.; Tedesco, L.; Melo, A.D.C.; Frasson, A.C.; França, V.F.; Sato, S.W.; Lovato, E.C.W. Curcuma longa L., o açafrão da terra, e seus benefícios medicinais. Arq. Ciênc. Saúde UNIPAR 2016, 20, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Omosa, L.K.; Midiwo, J.O.; Kuete, V. Curcuma longa. In Medicinal Spices and Vegetables from Africa; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Jyotirmayee, B.; Mahalik, G. A review on selected pharmacological activities of Curcuma longa L. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 1377–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, C.M.; Samai, H.; Labrie, L. Streptococcus agalactiae serotype IV in farmed tilapia. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares-Dias, M.; Martins, M.L. An overall estimation of losses caused by diseases in the Brazilian fish farms. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Jiang, B.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, W. Screening and effects of intestinal probiotics on growth performance, gut health, immunity, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalactiae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 151, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatesoupe, F.J. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Al-Harbi, A.H.; Austin, B. Developments in the use of probiotics for disease control in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.V.; Owatari, M.S.; Silva, E.; Pereira, M.O.; Piola, M.; Ramos, C.; Farias, D.R.; Schleder, D.D.; Jesus, G.F.A.; Jatobá, A. Effects of microencapsulated probiotics-supplemented diet on growth, non-specific immunity, intestinal health and resistance of juvenile Nile tilapia challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 287, 115286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, A.; Vieira, F.D.N.; Buglione Neto, C.; Silva, B.C.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Jerônimo, G.T.; Dotta, G.; Martins, M.L. Utilização de bactérias ácido-lácticas isoladas do trato intestinal de tilápia-do-nilo como probiótico. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2008, 43, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, A.; Vieira, F.D.N.; Buglione-Neto, C.C.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Silva, B.C.; Seiftter, W.Q.; Andreatta, E.R. Diet supplemented with probiotic for Nile tilapia in polyculture system with marine shrimp. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, A.; Pereira, M.O.; Vieira, L.M.; Bitencourt, M.; Rodrigues, E.; Fachini, F.A.; Moraes, A.V. Action time and feed frequency of Lactobacillus plantarum for Nile tilapia. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2018, 70, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Zong, G.; Tao, R.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Y. Crosstalk between traditional Chinese medicine-derived polysaccharides and the gut microbiota: A new perspective to understand traditional Chinese medicine. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 4125–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, H.S.; Amen, R.M.; Elelemi, A.H.; Mahboub, H.H.; Elabd, H.; Abdelfattah, A.M.; Abdel Moniem, H.; El-Beltagy, M.A.; Alkafafy, M.; Yassin, E.M.M.; et al. Effect of dietary Moringa oleifera leaves nanoparticles on growth performance, physiological, immunological responses, and liver antioxidant biomarkers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity. Fishes 2022, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, H.; Mahboub, H.H.; Salem, S.M.; Abdelwahab, A.M.; Alwutayd, K.M.; Shaalan, M.; Ismail, S.H.; Abdelfattah, A.M.; Khalid, A.; Mansour, A.T.; et al. Nano-curcumin/chitosan modulates growth, biochemical, immune, and antioxidative profiles, and the expression of related genes in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fishes 2023, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, M.N.; Shaheen, A.A.; Hamed, H.S. Potential role of dietary parsley and/or parsley nanoparticles against zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity induced physiological, and histological alterations in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Goldenfarb, P.B.; Bowyer, F.P.; Hall, E.; Brosious, E. Reproducibility in the hematology laboratory: The microhematocrit determination. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1971, 56, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaxhall, P.C.; Daisley, K.W. Routine haematological methods for use with fish blood. J. Fish Biol. 1973, 5, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paiva, M.J.T.R.; Pádua, S.B.; Tavares-Dias, M.; Egami, M.I. Métodos Para Análise Hematológica em Peixes; Editora da Universidade Estadual de Maringá-EDUEM: Maringá, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, G. Corante pancrômico para hematologia e citologia clínica. Nova combinação dos componentes do May-Grünwald e do Giemsa num só corante de emprego rápido. Mem. Inst. Butantan 1947, 20, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, N.M.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T.; Lombardi, J.V. Total leukocyte counts methods in fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Arch. Vet. Sci. 2008, 13, 54–63. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11449/70526 (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Silva, B.C.; Martins, M.L.; Jatobá, A.; Buglione Neto, C.C.; Vieira, F.N.; Pereira, G.V.; Jerônimo, G.T.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Mouriño, J.L.P. Hematological and immunological responses of Nile tilapia after polyvalent vaccine administration by different routes. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2009, 29, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, E.C.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Okamoto, N.; Watanabe, T. Effects of dietary β carotene on the immune response of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrawes, N.G.; Nour, A.A.A.; Shaheen, A.A.; Hamed, H.S. Effect of Nigella sativa enriched diet on biochemical variables and antioxidant damage caused by silver nanoparticles toxicity in the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.T.; Hamed, H.S.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Mohamed, W.F. Modulatory effect of papaya extract against chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress, immune suppression, endocrine disruption, and DNA damage in female Clarias gariepinus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.G.; Libanori, M.C.M.; Pereira, S.A.; Ferrarezi, J.V.S.; Ferreira, M.B.; Soligo, T.A.; Yamashita, E.; Martins, M.L.; Mouriño, J.L.P. Probiotic mix of Bacillus spp. and benzoic organic acid as growth promoter against Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2023, 566, 739212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Henriques, O.B.; Andreoni, A.A.; Vital, G.R.; Campos, M.M.; Habermehl, G.G.; Moraes, V.L. Antivenom and biological effects of ar-turmerone isolated from Curcuma longa (Zingiberaceae). Toxicon 1992, 30, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S. Antiplatelet property of Curcuma longa L. rhizome-derived ar-turmerone. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E. Multitargeted bioactive materials of plants in the Curcuma genus and related compounds: Recent advances. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2016, 47, 111–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Henriksson, A.; Nilsson, C.; Mitchell, H. Synergistic effect of green tea extract and probiotics on the pathogenic bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, A.; Mouriño, J.L.P. Lactobacillus plantarum effect on intestinal tract of Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings. Ciênc. Anim. Bras. 2015, 16, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomba, A.; Nemcová, R.; Mudroňová, D.; Guba, P. The possibilities of potentiating the efficacy of probiotics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Gatesoupe, F.J. Lactic acid bacteria in fish: A review. Aquaculture 1998, 160, 177–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; González, M.; Murado, M.A. Effects of lactic acid bacteria cultures on pathogenic microbiota from fish. Aquaculture 2005, 245, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ghosh, K.; Doan, H.V.; Beck, B.R.; Song, S.K. Lactic acid bacteria in finfish—An update. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S. Probiotics to enhance anti-infective defences in the gastrointestinal tract. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17, 755–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owatari, M.S.; Cardoso, L.; Pereira, S.A.; Pereira, U.P.; Tachibana, L.; Martins, M.L.; Mouriño, J.L.P. Laboratory-controlled challenges of streptococcosis in Nile tilapia using the oral route (infected-feed) for infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, K.N.; Dhayanithi, N.B.; Kumar, T.T.A.; Balasundaram, C.; Harikrishnan, R. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of partially purified herbal extracts against bacterial fish pathogens. Aquaculture 2016, 458, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Van Doan, H. Probiotic application for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, S.; Tyagi, A.; Singh, R. Probiotic supplementation as an emerging alternative to chemical therapeutics in finfish aquaculture: A Review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 15, 1151–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).