Abstract
Several molecules and extracts are known to have bone-specific effects. For example, the long-term use of glucocorticoids like prednisolone causes several negative effects including a loss of bone mass. Molecules like prednisolone are usually dissolved in organic solvent which are known to be toxic for zebrafish embryo in certain concentrations. Nevertheless, solvents like dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), ethanol and methanol have never been tested for specific skeletal effects during development in dose-dependency. Vitality assay, live fluorescence and bone-specific staining were used to evaluate solvents effects compared to prednisolone. DMSO, ethanol and methanol perturb osteogenesis starting from 1%, 1.5% and 3% respectively, concentrations in which vasculature, length and survival rate appear unaffected. This effect may be due to high sensitivity of the osteogenesis process to external chemical stimuli, especially in the trunk. On the contrary, the negative effect of prednisolone on skeletal development appears more specific since it is found at very low concentrations, far from any other developmental defects. The recommended solvent concentration to be used in zebrafish embryos osteogenesis assay was established in 0.5% for DMSO, 2% for methanol and 0.5% for ethanol. We recommend analyzing both head and trunk mineralization in zebrafish embryo osteogenesis assay.
Key Contribution:
This study highlights the important role of solvent concentration in osteogenesis assay in zebrafish embryo.
1. Introduction
Glucocorticoids (GC) are used in different chronic inflammatory disorders such as arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and pulmonary diseases as pharmacological therapy. Nevertheless, the long-term use of glucocorticoids, like prednisolone (PN), causes several negative effects including a loss of bone mass followed by an increasing risk of fracture in the skeleton. Based on this evidence, a specific syndrome was defined following long-term GC treatment in humans, called glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis (GIOP) [1]. The pathogenic mechanisms of GIOP are still poorly understood. It has been reported that patients treated with GC show an early, rapid bone loss followed by a chronic decrease in bone mineralization [1]. Evidence shows that GC interfere with osteoblast differentiation and behavior in vitro and in vivo [2,3].
In the last decades, Danio rerio (zebrafish) has been identified as a powerful animal model to study bone development. The use of zebrafish embryo is the animal model of choice for developmental studies on bone formation and tissue mineralization given the high similarity of bone architecture and genetics with human ones, focusing on trunk and cranial bones formation [4]. Two different types of ossification can be found in zebrafish embryo osteogenesis: the endochondral ossification which is made of a cartilaginous scaffold, and the intramembranous one made through direct ossification from mesenchymal stem cell precursors [4].
The zebrafish embryo treated with PN, proposed by Barrett et al. as model of GIOP, has shown a significant delay in early mineralization process [5]. Nevertheless, a deeper analysis of osteogenesis in comparison with embryogenesis is necessary to discriminate bone-specific alterations from general toxicity effects, even if slight. In addition, cranial bones from endochondral and intramembranous ossification should be considered separately, as well as vertebral bodies mineralization in the trunk.
Several drugs are known to have toxic effects on embryogenesis and to the point of producing different phenotypes until death [6]. Non-lethal toxicity can affect specific systems or organs during development like the nervous system or heart. In fact, the developmental and specific neurobehavioral toxicity in response to dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) was proven in embryonic zebrafish [7]. Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) reduced the survival rate of zebrafish embryos, inhibited their heart rate, introduced the presence of pericardial edema, increased the distance from sinus venous to bulbus arteriosus, and altered cardiomyocytes-endocardial distribution [8].
Molecules like PN are often soluble in organic solvent. Many solvents used to dissolve such substances, like dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), are known to be toxic for zebrafish embryo above 1% by the analysis of general development [9]. Nevertheless, DMSO was never tested for specific skeletal effects during development in dose-dependency.
The effect of ethanol (EtOH) on embryo development was studied and is known as fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD), which shows lethality above 1.5% and oxidative stress and inflammation around 1.25% [10]. In addition, the effect of EtOH was studied also on skeletal system development showing the development of cranial malformations in addition to learning and memory deficits, CNS apoptosis and alterations in reflex responses [11,12]. EtOH is commonly used to extract organic fractions from plants in drug screening experiments; EtOH-soluble fraction is also tested in zebrafish embryo to evaluate effects on liver [13].
The solvent methanol (MetOH) was never tested alone on embryonic osteogenesis but on other developmental pattern such as retinal tissue organization [14].
The present work points out the differences between survival, general development defects and specific developmental skeletal defects in solvent incubation at different concentrations. In fact, solvents are usually used to dissolve molecules or extracts in drug screening experiments. In some cases, skeletal defects may be due to a general toxic effect of the tested drug. Length and vitality of embryos should be considered together with skeletal staining to evaluate bone-specific effects during osteogenesis. The results will be helpful to identify the best concentrations of solvent for osteogenesis assay in drug screening using prednisolone as positive control. In addition, the vertebral count in the trunk will be considered as informative assay, in comparison with head staining, to evaluate specifically the mineralization process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethic Statement
This experimentation was performed in the Zebrafish Laboratory (IRCCS R. Galeazzi, GSD Foundation, Milan, Italy) according to Italian and European guidelines on research (European Directive 2010/63/EU) with ASL Varese (Italy) authorization (Prot. No. 2019/014/DVVS/0078143).
2.2. Animals
Danio rerio of a transgenic line (kdrl: GFP), which express Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) as vascular endothelium reporter, were housed in ZEBTEC© Bench Top System (Tecniplast, Buguggiate, Italy) and maintained under standard conditions such as 6.8–7.5 pH and 600–800 µS. Fish were maintained at 27–28.5 °C with a 14 light hours/day [15]. Embryos used in this experiment were obtained by single pairs of adults nine month old zebrafish.
2.3. Treatments
All embryos were checked for general health conditions, such as unfertilized eggs, mold presence and for proper cell division stage under a light stereomicroscope (SZX-ZB7 Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) as described by Kimmel et al. [16].
Ten embryos, in three independent experiments, were exposed to different solvents (DMSO, EtOH, MetOH) and PN at different concentrations starting from zero hours post fertilization (hpf) up to five days post fertilization (dpf). Embryos were maintained in E3 medium solution (5 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.33 mM CaCl2, 0.33 mM MgSO4) at 28 °C. Control (CTR) embryos were maintained in E3 medium only while treatments were performed by adding PN or the solvents to the E3 solution. Treatment concentrations were set based on previous studies for EtOH [10] and PN [5]. All the treatment solutions were changed daily up to 5 dpf. In this experiment, the following solvents has been used: EtOH (from 0% to 2%, v/v), MetOH (from 0% to 3%, v/v) and DMSO (from 0% to 2.5%, v/v). PN has been used at the concentration from 0 to 150 µM using DMSO as solvent (up to 0.5%, v/v).
2.4. Embryo Histochemistry
Osteogenesis and mortality rate were evaluated at 5 dpf. Embryos were anaesthetized with 0.01% tricaine methanesulphonate (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) E3 medium solution and fixed in 3.5% formaldehyde/0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer. A two-color acid-free staining based on the use of Alcian Blue 8GX (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and Alizarin red S (ARS, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was performed to stain cartilage and bone tissue respectively [14]. Briefly, fixed embryos were dehydrated in 50% ethanol, then stained with 0.2 mg/mL alcian blue 70% ethanol 80 mM MgCl2 solution. Embryo were bleached using 1% H2O2 1% KOH to remove pigmentation then incubated in 1 mg/mL trypsin 60% satured sodiumtetraborate solution for tissue digestion. The second staining was performed using 0.04 mg/mL alizarin red S 1% KOH solution then embryos were transferred in increasing glycerol solutions (from 10% to 60%). The mineralization rate was evaluated by counting the number of mineralized vertebral bodies (N.V.) normalized for every single embryo the length (L.) (N.V./L.). Embryos were examined under a light stereomicroscope (SZX-ZB7 Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) acquiring images using a Discovery CH30 camera (Tiesselab, Milan, Italy).
2.5. Embryo Blood Vessels Analysis
At 5 dpf, transgenic embryos (kdrl: GFP) were anaesthetized with 0.01% tricaine methanesulphonate (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) E3 medium solution and examined for blood vessels development using a fluorescence stereomicroscope (Olympus SZX-ZB7) equipped with Discovery CH30 camera (Tiesselab, Italy).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Data from embryo histochemical analysis was derived from 10 embryos for every treatment concentration. All the treatments have been repeated performing three independent experiments and obtaining comparable results. Mineralization rate data have been used to calculate the mean value expressed as mean of the means of the three independent experiments ± standard deviation versus control. Data were plotted on SigmaStat 3.5 software (San Jose, CA, USA) and subjected to Student’s t-test.
All the significance values were set at p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**) and p < 0.001 (***). The software Sigmastat 3.5 indicated that normality test and equal variance test have been passed.
3. Results
3.1. Embryo Mortality
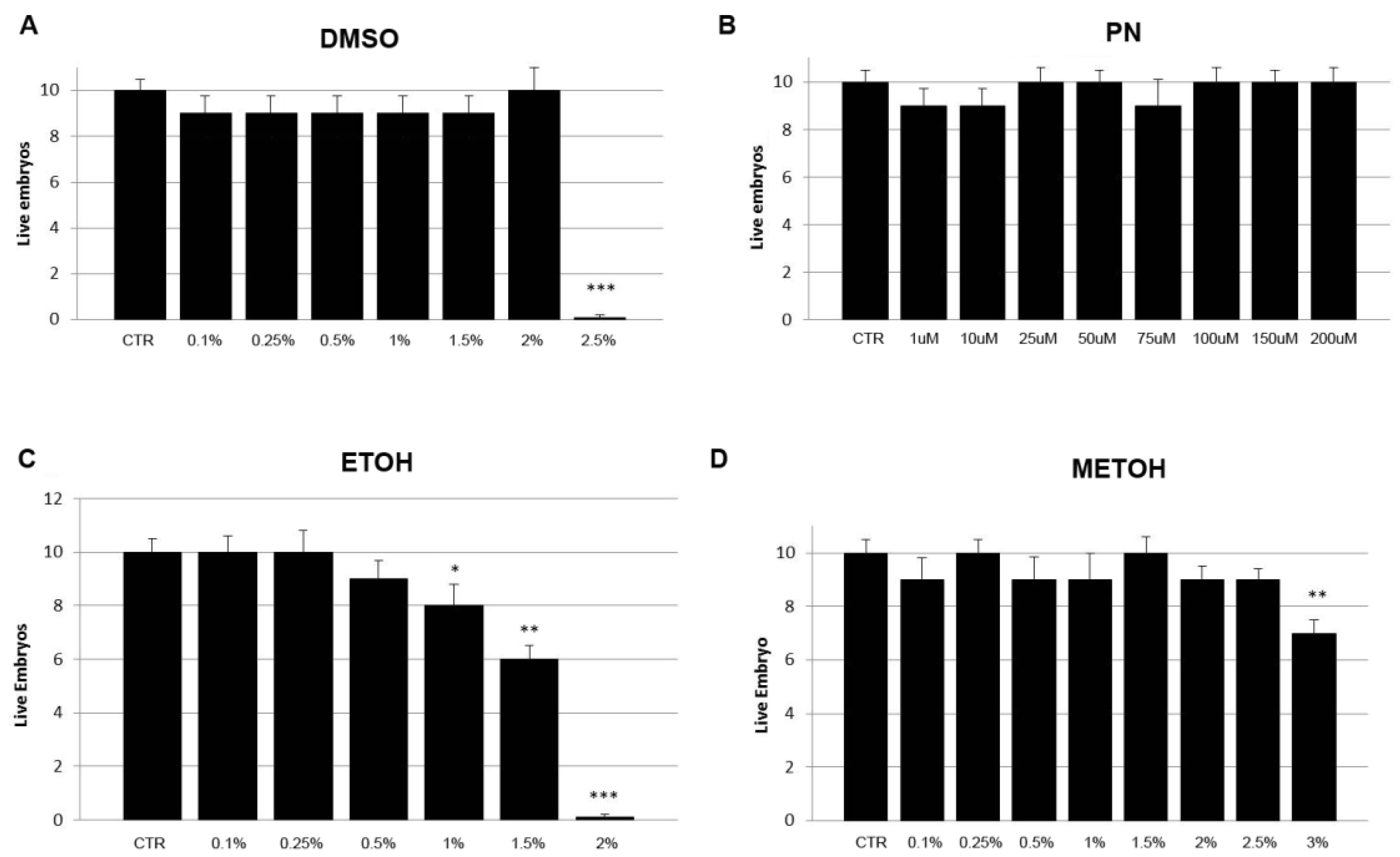
Embryos were exposed to increasing amounts of different solvents (DMSO, EtOH, MetOH) and PN from 0 hpf up to 5 dpf to verify the effects of this media on mortality rate. Moreover, DMSO at 2.5% was found suddenly lethal for 100% of embryos. EtOH was found lethal at 2% but the survival rate starts to decrease from 0.5%. MetOH shows significant, albeit minimal, toxicity at 1% whereas PN results to be safe in all concentrations tested (Figure 1). The highest concentration of DMSO, used as solvent in the PN samples, was 0.5%.
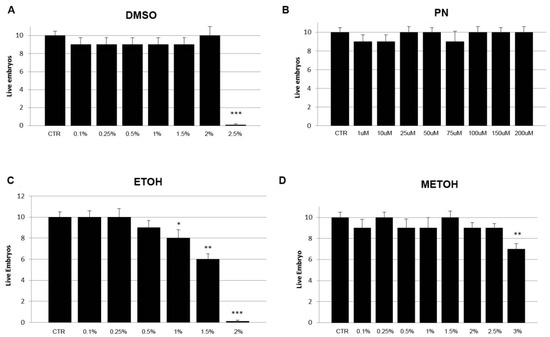
Figure 1.
Mortality rate of embryos grown under different concentrations evaluated at 5 dpf: (A) DMSO from 0 to 2.5%, (B) PN from 0 to 200 µM (in DMSO from 0 to 0.5%), (C) EtOH from 0 to 2%, (D) MetOH from 0 to 3%. Solvents show mortality at different concentration whereas PN does not (*** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05).
3.2. General Development and Lenght
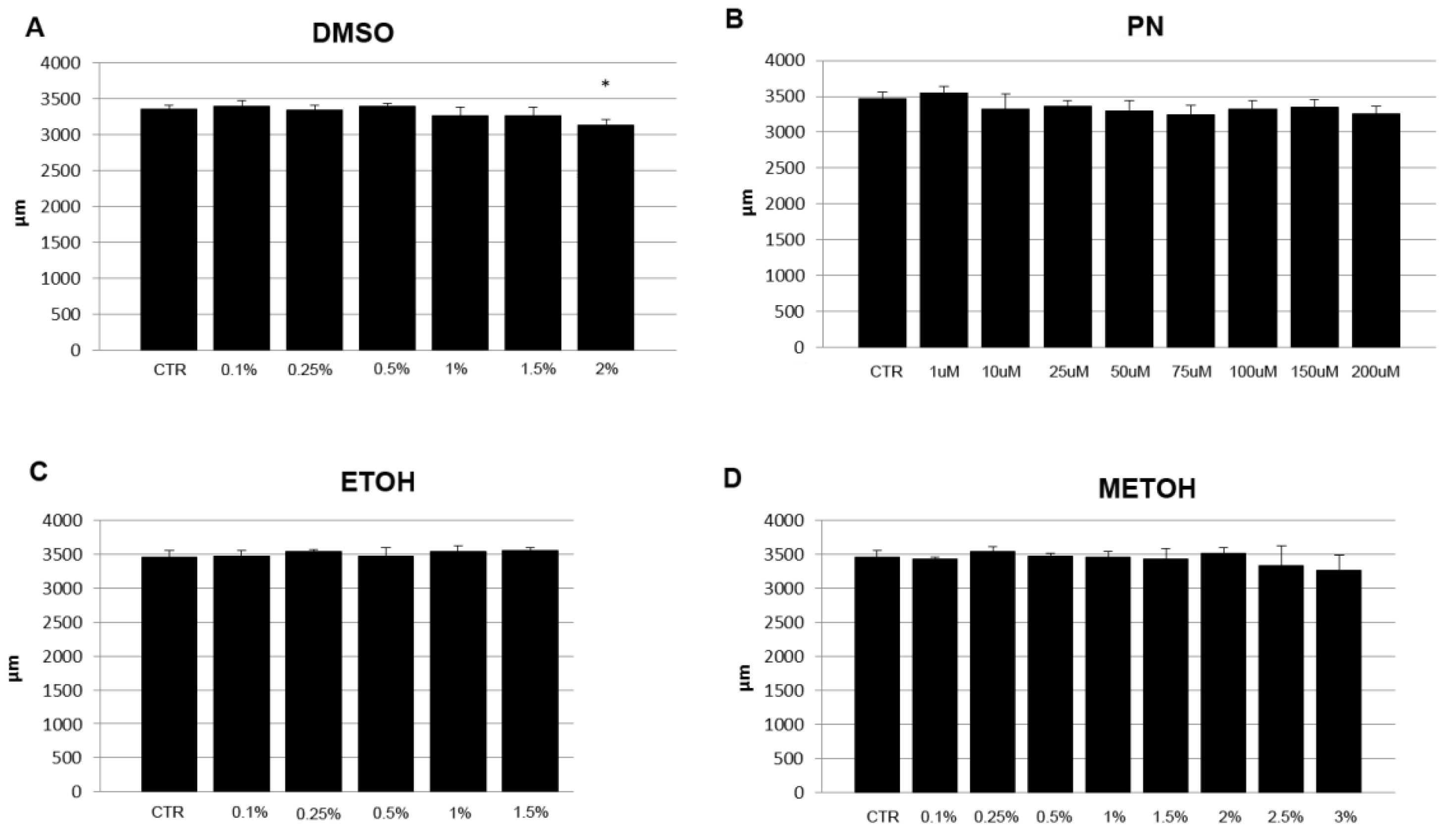
The length of vital embryos was measured to verify the effect of solvents and PN on general body growth. A slight decrease in length was found in some PN samples whereas a significant reduction can be detected only in 2% DMSO. In the same treatment, the lower concentrations (1% and 1.5% DMSO) show a small decrease of the value but not significant, as well as higher concentrations of MetOH (Figure 2).
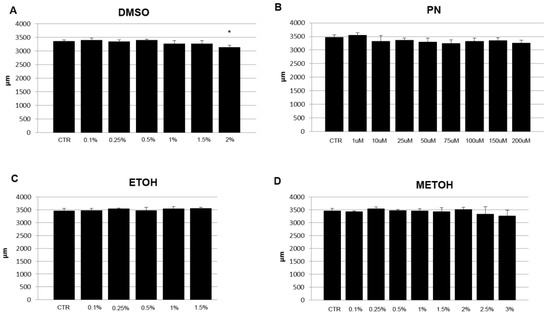
Figure 2.
Length (µm) in 5 dpf embryos grown under different concentrations of PN (in µM) (B) and, expressed in percentage %, of solvents DMSO (A), EtOH (C), MetOH (D). CTR was the untreated control (CTR). 2% DMSO had significant effect on embryo length. (* p < 0.05).
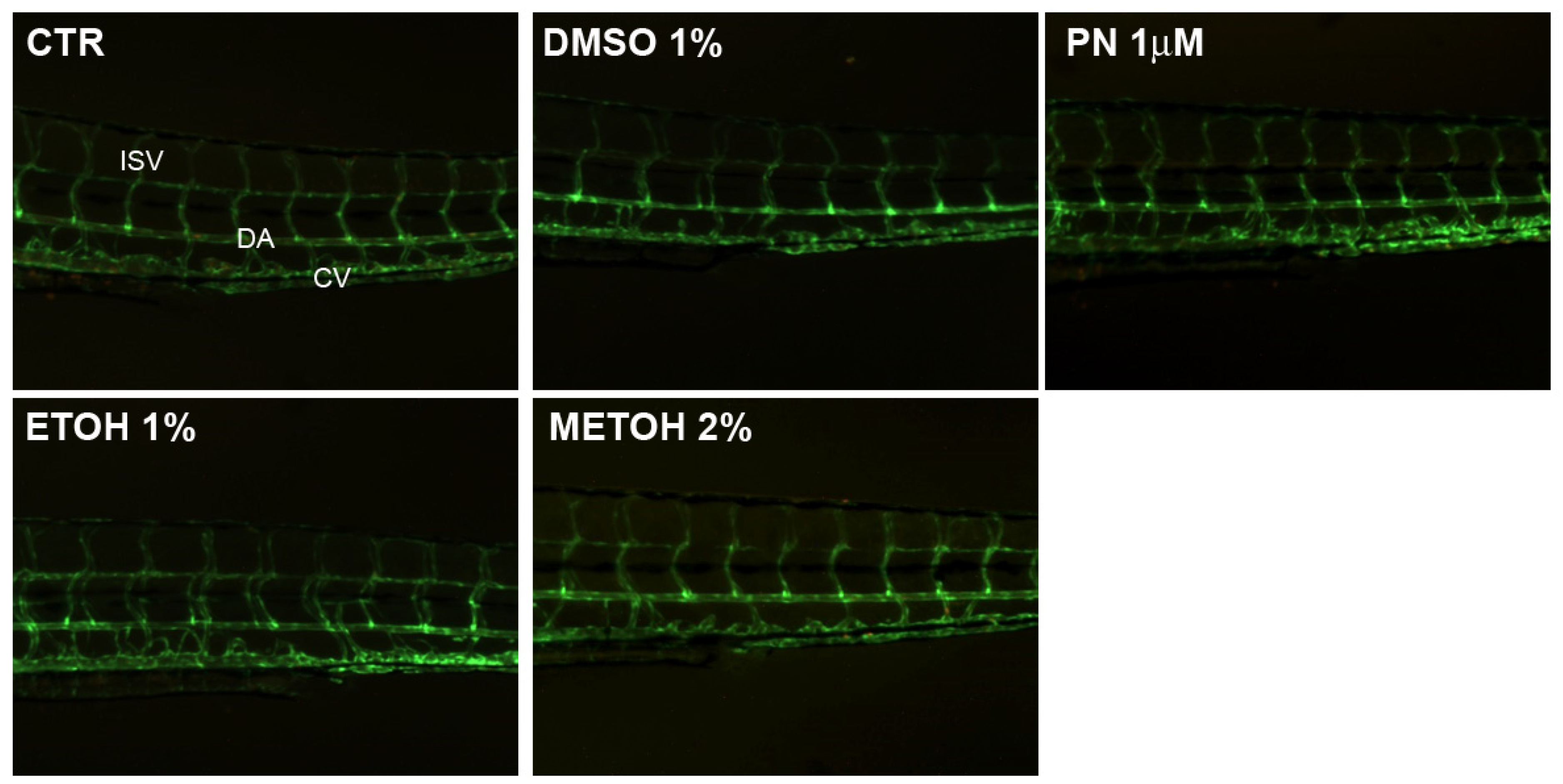
When the embryo is vital and the length is similar to the untreated control, no macroscopic alteration was detectable in non-skeletal anatomical structures as demonstrated by blood vessel pattern analysis in the trunk (Figure 3). The fluorescent pattern of vessels does not show any alteration in all conditions.
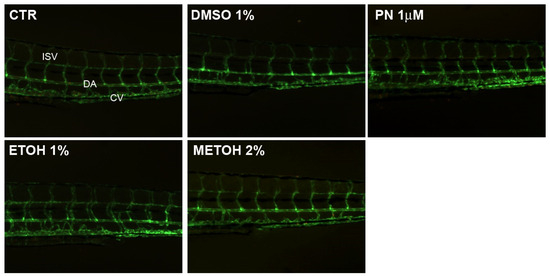
Figure 3.
Blood vessels analysis in untreated control (CTR), 1% DMSO, 10 µM PN, 1% EtOH and 2% MetOH embryos. The fluorescent pattern of vessels does not show any alteration in all the conditions. ISV = inter-segmental vessels, DA = dorsal aorta, CV = cardinal vein.
3.3. Skeletal Development
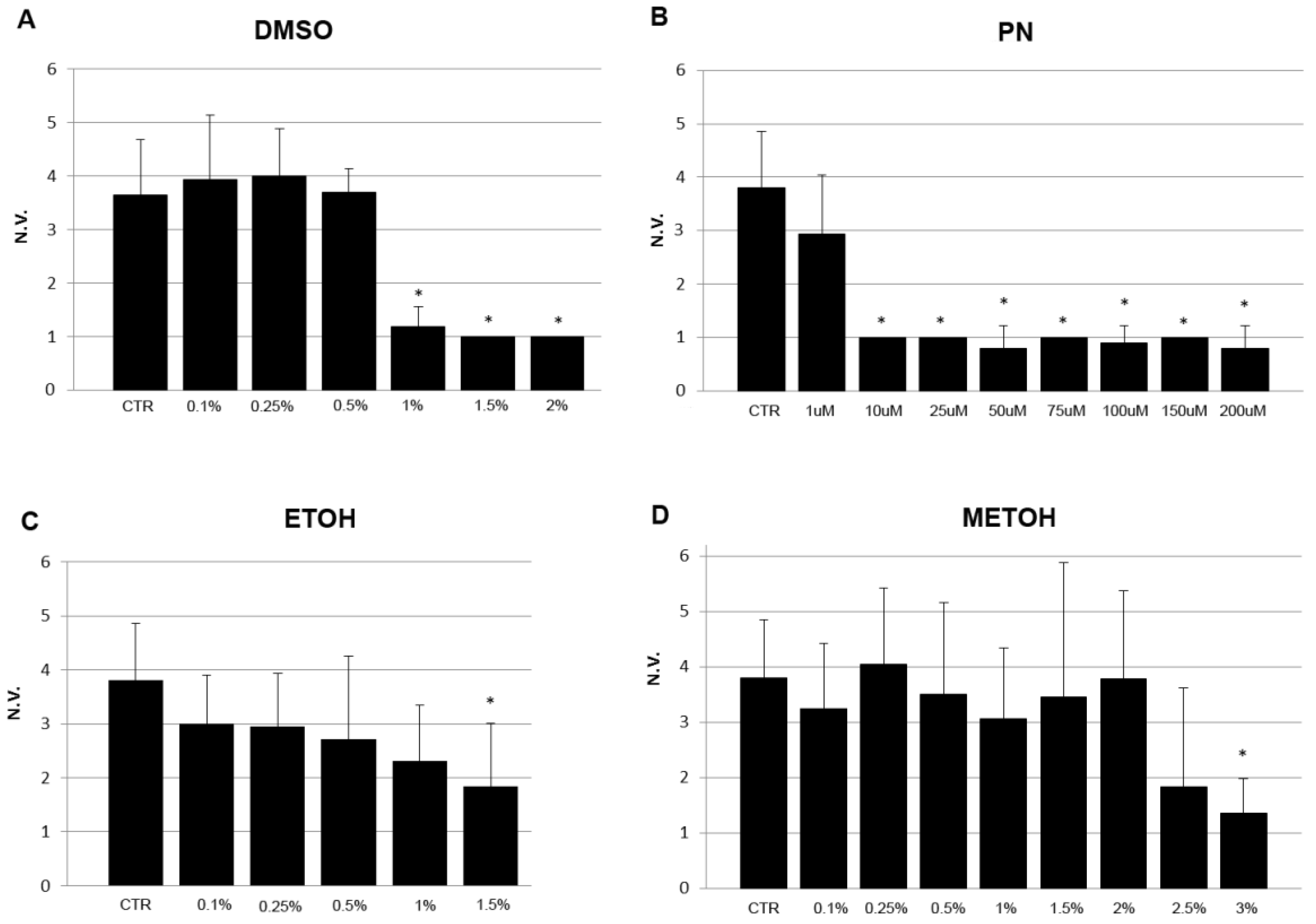
The mineralization rate in the trunk was evaluated in embryos at 5 dpf as the number of vertebral bodies positive for ARS staining. A significant inhibition of mineralization can be detected in 1% DMSO samples, 1 µM PN, 1.5% EtOH, 3% MetOH and higher (Figure 4).
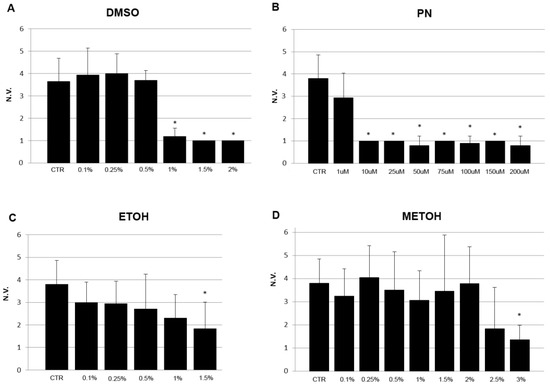
Figure 4.
Vertebral mineralization rate of 5 dpf embryos grown under no treatment (CTR) or exposed to different concentrations of solvents DMSO (A), EtOH (C), MetOH (D) and PN (B). The number of vertebral bodies (N.V.) was reduced at higher concentration of solvents but at lower concentrations in PN samples * (p < 0.05).
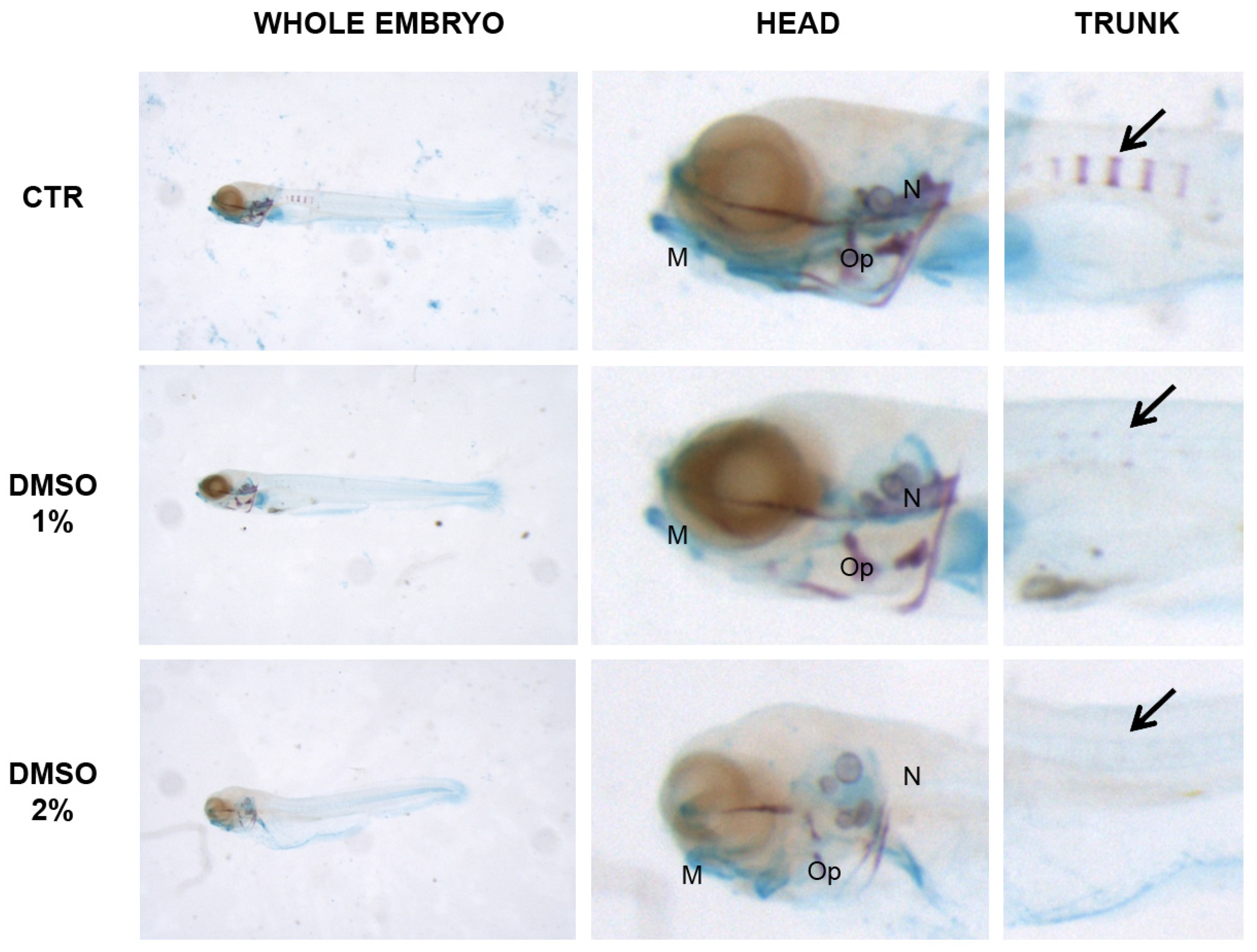
Morphological analysis of cartilage and bones in trunk versus head revealed a significant difference in the skeletal development. DMSO samples were examined in detail because DMSO is the solvent of PN and because the head staining did not reveal any alterations in other solvents. Moreover, the crucial concentrations we examined were 1% DMSO because is the first concentration with decrease of mineralized vertebral bodies and 2% DMSO because is the first concentration with decrease of length. The head mineralization in 1% DMSO samples was unaffected whereas, in the trunk, the process was inhibited. Instead, in 2% DMSO the mineralization process was affected in head as in trunk. Cartilage staining and head morphology showed severe developmental defects (Figure 5).
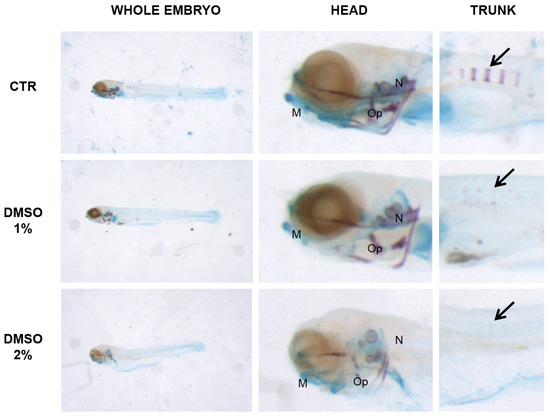
Figure 5.
Zebrafish larvae double stained with alizarin red and alcian blue: whole embryo (left panel), head (central panel) and trunk (right panel). Mineralizing structures can be visualized in purple and cartilage in blue. Black arrow indicates the mineralizing vertebral bodies in the trunk. 5 dpf embryos were grown under 1 and 2% DMSO whereas CTR was untreated. No mineralization can be detected in the trunk of both 1 and 2% DMSO. Head mineralization is defective in 2% DMSO only, where also cartilage and general morphology seems to be altered. M = Merckel’s cartilage, Op = operculum, N = notochord.
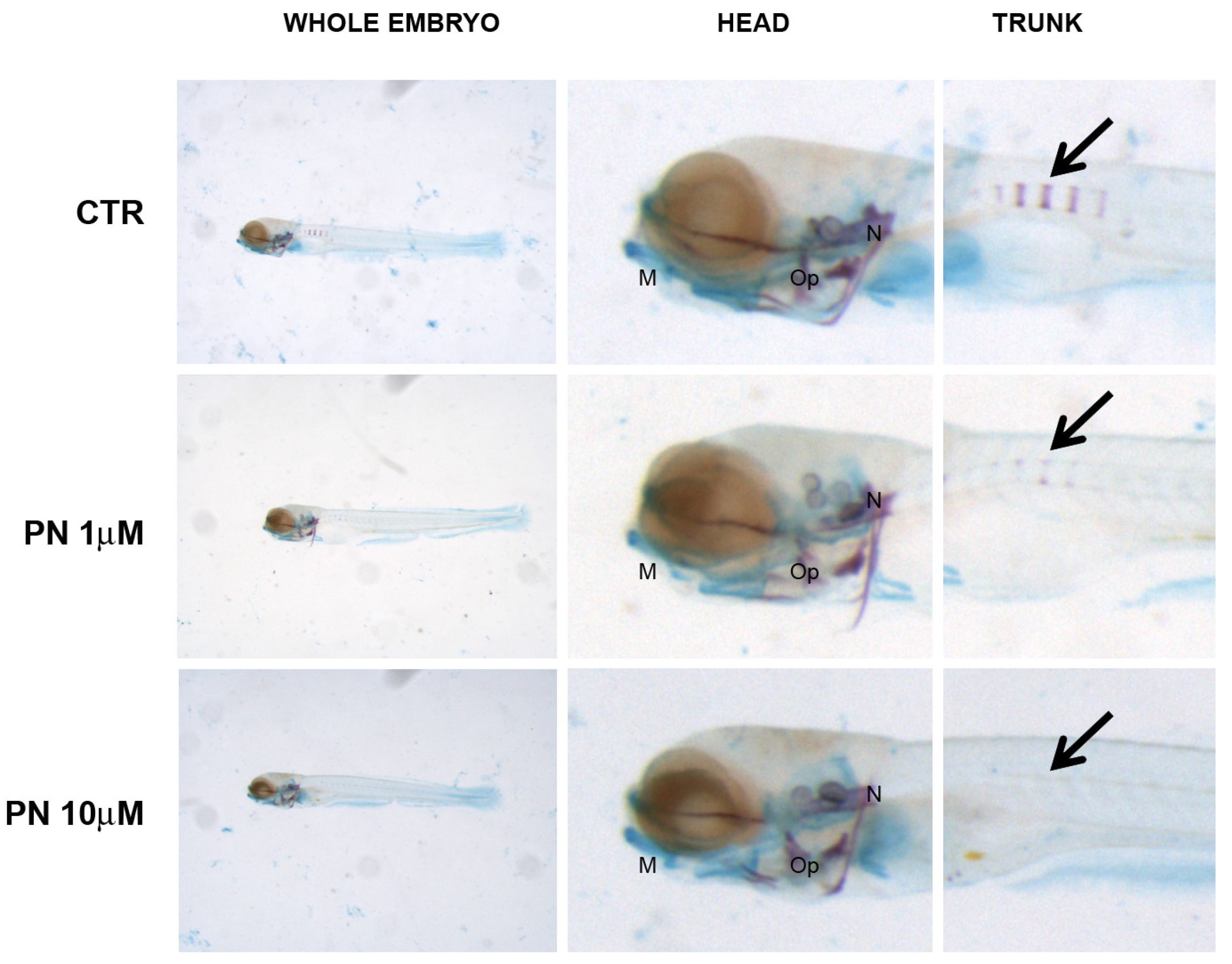
In PN samples, the head mineralization was unaffected in all the concentrations tested whereas, in the trunk, the process was strongly inhibited at 1 µM and suppressed from 10 µM up. Cartilage staining and head morphology did not prove developmental defects (Figure 6).
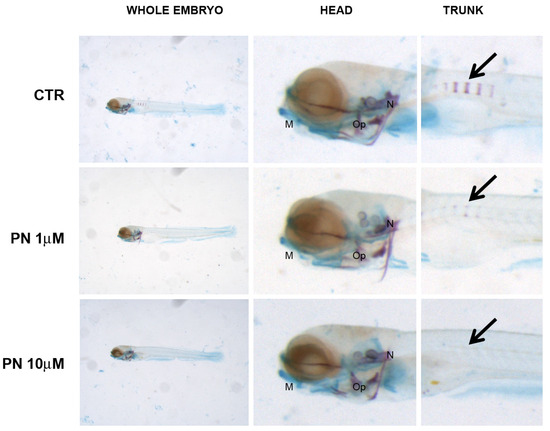
Figure 6.
Zebrafish larvae head double stained with alizarin red and alcian blue. Mineralizing structures can be visualized in purple and cartilage in blue. Black arrow indicates the mineralizing vertebral bodies in the trunk. Embryos grown in PN do not show mineralization defects in the head whereas trunk mineralization was reduced in 1 µM (middle panel) and suppressed in 10 µM (lower panel) respect to untreated controls (CTR, upper panel). Cartilage and morphology seem not to be altered. M = Merckel’s cartilage, Op = operculum, N = notochord.
4. Discussion
Zebrafish embryo is a widespread animal model to test the effects and the toxicity of molecules and drugs in large scale experiments. Zebrafish embryo is an optimum model for developmental studies on bone formation and tissue mineralization.
Skeletal development can be easily evaluated using vital staining for mineralized matrix which discriminate between cranial and trunk osteogenesis [17].
To evaluate the toxicity effects of a drug, a molecule or principle should distinguish the general toxic effects from organ-specific interferences in developmental mechanisms. Since DMSO, EtOH, and MetOH could have different effects on vitality, development and osteogenesis, we evaluated these characteristics in comparison with PN, a glucocorticoid known to inhibit embryonic osteogenesis.
DMSO has shown 100% of mortality at 2.5%, whereas at 2% all embryos were alive which suggests that the lethal threshold can be reached shortly. The embryos in 2% DMSO were alive, but the body length was significantly decreased, suggesting that general and severe developmental defects were induced. This data indicated that 1.5% DMSO seems to be safe. In effect, the canonical maximum concentration used for molecules resuspension in zebrafish embryo assay was claimed to be 1% [9]. Our data also indicated that trunk vasculature was correctly developed in 1% DMSO. Nevertheless, the analysis of mineralized vertebral bodies in the trunk proved a delayed osteogenesis even at 1% suggesting that such concentration can affect some of aspects of embryo development referred to intramembranous trunk ossification. As previously demonstrated, vertebral bodies mineralization process seems to be more sensitive to stress stimuli respect to head ossification [18]. Both processes follow intramembranous ossification but they are distinct, in timing and, probably, mechanisms [19]. In these conditions, 1% DMSO cannot be considered safe as dilution solvent at all. Consequently, 0.5% seems to be the best candidate to be claimed as maximum solvent threshold in osteogenesis assay.
Differently, EtOH has shown a 100% of mortality at 2% but a toxicity effect can be extended lower until 0.5%. Interestingly, live embryos do not show defects in length or vascular development whereas trunk ossification resulted delayed significantly at 1.5%. Nevertheless, a tendency to delay can be seen at lower concentrations, even if not significant, suggesting that some effect on trunk osteogenesis may take place. It is known that EtOH exposure may perturb bone morphogenesis [20] and the expression of BMPs and Notch [21], which are important regulators of embryo development and osteogenesis. In addition, it has been demonstrated that the lower used concentration of EtOH (0.5%) is able to promote inflammation and oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos [10]. On these bases, we can hypothesize that EtOH produces negative effects on embryos even at low concentration. For these reasons, EtOH should be avoided as a solvent in embryo experiments.
The last solvent tested, MetOH, starts to be toxic at 3% but, at this concentration, live embryos do not show defects in embryonic development as confirmed by vascular pattern analysis. Nevertheless, a delayed osteogenesis can be observed at 3% MetOH and is also suggested at 2.5% even if not significant. In conclusion, 2% MetOH or lower seems to be the safe solvent concentration for pharmacological experiments on embryos.
The use of PN showed a bone-specific effect without general toxicity effects. This molecule, resuspended in DMSO, has been used at final concentration of 0.5% and below, far from any toxic effects. PN does not have an impact on vitality and length but strongly inhibits vertebral body mineralization from 10 µM upwards. Interestingly, the inhibitory effect is more evident in the trunk than in the mineralization of the head bones, as already reported for DMSO. This is a confirmation that the two mineralization areas (head and trunk) in zebrafish embryo are organized and regulated by different cellular and molecular pathways [19]. In conclusion, compared to DMSO and other solvents, the effect of PN on skeletal development appears to be more specific since it is found at very low concentrations without any other developmental defects.
The present work points out the correct use of solvent in osteogenesis studies in zebrafish embryos. In some cases, skeletal defects may be due to a general toxic or osteotoxic effect of solvent. We found that DMSO, EtOH, and MetOH perturb osteogenesis at concentrations in which vasculature, length and survival rate appear unaffected. This effect may be due to the high sensitivity of the mineralization process to external chemical stimuli, especially in the trunk. On the contrary, the effect of PN on skeletal development appears more specific since it is found at very low concentrations without any other developmental defects.
5. Conclusions
The recommended solvent concentration to be used in osteogenesis assay in zebrafish embryos were established in 0.5% for DMSO, 2% for MetOH and 0.5% for EtOH. In addition, head and trunk mineralization should both be analyzed in zebrafish embryo osteogenesis assay.
Author Contributions
M.C. and M.M. contributed to the ideas, data analysis, data generation and manuscript preparation. G.B. contributed to supervision and funding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Italian Ministry of Health, RICERCA CORRENTE. The APC was funded by IRCCS Orthopedic Institute Galeazzi-Sant’Ambrogio.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This experimentation has been performed in the Zebrafish Laboratory (IRCCS R. Galeazzi, GSD Foundation, Milan, Italy) according to Italian and European guidelines on research (EU Directive 2010/63/EU) with ASL Varese (Italy) authorization (Prot. No. 2019/014/DVVS/0078143).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maricic, M. Update on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 37, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavassieux, P.; Pastoureau, P.; Chapuy, M.C.; Delmas, P.D.; Meunier, P.J. Glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of osteoblastic bone formation in ewes: A biochemical and histomorphometric study. Osteoporos. Int. 1993, 3, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, R.S.; Jilka, R.L.; Parfitt, A.M.; Manolagas, S.C. Inhibition of osteoblastogenesis and promotion of apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by glucocorticoids. Potential mechanisms of their deleterious effects on bone. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, N.C.; Mabee, P.M. Developmental morphology of the axial skeleton of the zebrafish, Danio rerio (Ostariophysi: Cyprinidae). Dev. Dyn. 2003, 228, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.; Chappell, C.; Quick, M.; Fleming, A. A rapid, high content, in vivo model of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimith, L.E.; Machado da Silva, V.; Costa-Silva, D.G.D.; Seregni Monteiro, L.K.; Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; André-Miral, C.; Hort, M.A. Preclinical toxicological assessment of polydatin in zebrafish model. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 47, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Lin, C.; Yang, T.; Sun, Z.; Lei, L.; Song, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, J. DDT exposure induces tremor-like behavior and neurotoxicity in developmental stages of embryonic zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Xiao, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Tao, Q.; et al. Dimethyl fumarate induces cardiac developmental toxicity in zebrafish via down-regulation of oxidative stress. Toxicology 2024, 503, 153735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyberghs, J.; Bars, C.; Ayuso, M.; Van Ginneken, C.; Foubert, K.; Van Cruchten, S. DMSO Concentrations up to 1% are Safe to be Used in the Zebrafish Embryo Developmental Toxicity Assay. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 804033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghul Kannan, S.; Latha Laxmi, I.P.; Ahmad, S.F.; Tamizhselvi, R. Embryonic ethanol exposure induces oxidative stress and inflammation in zebrafish model: A dose-dependent study. Toxicology. 2024, 506, 153876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klem, J.R.; Schwantes-An, T.H.; Abreu, M.; Suttie, M.; Gray, R.; Vo, H.; Conley, G.; Foroud, T.M.; Wetherill, L.; CIFASD; et al. Mutation in the Bone Morphogenetic Protein signaling pathway sensitize zebrafish and humans to ethanol-induced jaw malformations. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvan, M.J., 3rd; Loucks, E.; Weber, D.N.; Williams, F.E. Ethanol effects on the developing zebrafish: Neurobehavior and skeletal morphogenesis. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komakech, R.; Shim, K.S.; Yim, N.H.; Song, J.H.; Yang, S.K.; Choi, G.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.G.; Omujal, F.; Agwaya, M.; et al. In Vitro Antiosteoporosis Activity and Hepatotoxicity Evaluation in Zebrafish Larvae of Bark Extracts of Prunus jamasakura Medicinal Plant. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2020, 2020, 8582318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Jiao, J.; Weng, K.; Yu, D.; Li, R. Zebrafish methanol exposure causes patterning defects and suppressive cell proliferation in retina. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 5th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.T.; Liao, H.B.; Ye, Z.Q.; Jiang, H.S.; Li, J.X.; Ke, L.M.; Hua, J.Y.; Wei, B.; Wu, X.; Cui, L. Eurycomanone stimulates bone mineralization in zebrafish larvae and promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. J. Orthop. Translat. 2023, 40, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnovali, M.; Banfi, G.; Porta, G.; Mariotti, M. Soybean Meal-Dependent Acute Intestinal Inflammation Delays Osteogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskin, B.; Norman, J.; Bagwell, J.; Lin, A.; Adhyapok, P.; Di Talia, S.; Bagnat, M. Dynamic BMP signaling mediates notochord segmentation in zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 2574–2581.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, Y.C.M.; Meijer, J.; van der Kris, R.J.C.; de Bruijn, A.C.; Boersma, A.Y.; Gremmer, E.R.; Zwart, E.P.; Beekhof, P.K.; Slob, W.; van der Ven, L.T.M. Head skeleton malformations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) to assess adverse effects of mixtures of compounds. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 3549–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmah, S.; Muralidharan, P.; Marrs, J.A. Embryonic Ethanol Exposure Dysregulates BMP and Notch Signaling, Leading to Persistent Atrio-Ventricular Valve Defects in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).