Distribution and Management of Residual Antibiotics in the Litopenaeus vannamei Shrimp Farming Environment: Recommendations for Effective Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aquaculture Pond
2.2. Breeding Feed
2.3. Chemical Reagents
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Extraction Method
2.6. Test Method
2.6.1. Liquid Chromatography Conditions
2.6.2. Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.7. Data Analysis
2.8. Model Construction
- (1)
- Total amount of an antibiotic in the feed (Equation (2):
- (2)
- Total net residue of an antibiotic in the water (Equation (3)):
- (3)
- Total amount of antibiotic residues in the surface sediments (Equation (4)):
- (4)
- Total amount of antibiotic residues in the shrimp (Equation (5)):
2.9. Estimation of Antibiotic Addition
3. Results and Discussion
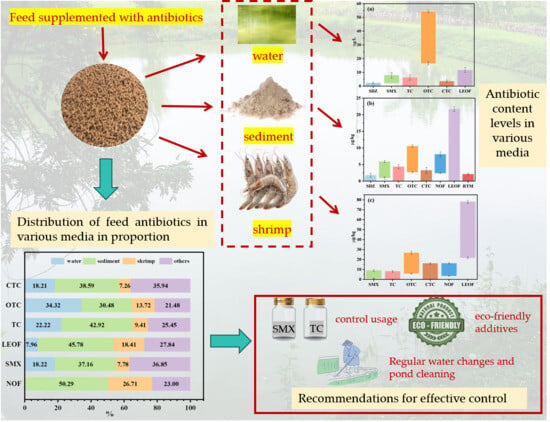
3.1. Residual Antibiotics in Various Media in the Aquaculture Pond
3.2. Distribution of Antibiotics in Various Media
3.3. Estimation of the Amount of Available Antibiotics Added to the Aquaculture Feed
3.4. Recommendations for Shrimp Farming Management
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.-R.; Liu, S.-S.; Zhou, G.-J.; Sun, K.-F.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.-G. Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: Occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Pei, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Zeng, W.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in mariculture farms, estuaries and the coast of the Beibu Gulf, China: Bioconcentration and diet safety of seafood. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, R.; Pan, C.; Sun, Y.; Mai, B.; Li, Q.X. Antibiotics and Food Safety in Aquaculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11908–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, W.Y.; Chen, Z.; Leung, H.M.; Leung, A.O.W. Application of veterinary antibiotics in China’s aquaculture industry and their potential human health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8978–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulijwa, R.; Rupia, E.J.; Alfaro, A.C. Antibiotic use in aquaculture, policies and regulation, health and environmental risks: A review of the top 15 major producers. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Naylor, R.; Henriksson, P.; Leadbitter, D.; Metian, M.; Troell, M.; Zhang, W. China’s aquaculture and the world’s wild fisheries. Science 2015, 347, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, K.; Konishi, Y.; Harada, K.; Okihashi, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Do, M.H.N.; Thi Bui, L.; Duc Nguyen, T.; Do Nguyen, P.; Thi Khong, D.; et al. Monitoring of Antibiotic Residues in Aquatic Products in Urban and Rural Areas of Vietnam. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6133–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.M.; Abdel-Rahman, G.N.; Salem, S.H.; Fouzy, A.S.M. Incidence, stability and risk assessment for sulfonamides and tetracyclines in aqua-cultured Nile Tilapia fish of Egypt. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X.-Z. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.-V.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chao, W.-L.; Yeh, S.-L.; Kuo, D.-L.; Yang, C.-W. Effects of sulfamethoxazole and sulfamethoxazole-degrading bacteria on water quality and microbial communities in milkfish ponds. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, O.E.; Kruse, H.; Grave, K.; Collignon, P.; Karunasagar, I.; Angulo, F.J. Human Health Consequences of Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Aquaculture. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrizo, J.C.; Griboff, J.; Bonansea, R.I.; Nimptsch, J.; Valdés, M.E.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Amé, M.V. Different antibiotic profiles in wild and farmed Chilean salmonids. Which is the main source for antibiotic in fish? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.D.M.; Ziora, Z.M.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Quinolone antibiotics. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1719–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Wei, Z.; Zhiming, X.; Yang, L.; Xia, F. Trace analysis and identification of 33 sulfonamides and sulfonamide potentiators in eggs by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-high field orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4452–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okocha, R.C.; Olatoye, I.O.; Adedeji, O.B. Food safety impacts of antimicrobial use and their residues in aquaculture. Public Health Rev. 2018, 39, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.-G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, N.; Anwar, Z.; Waiho, K.; Shi, C.; Mu, C.; Wang, C.; Qingyang, W. A review on aquaculture adaptation for fish treatment from antibiotic to vaccine prophylaxis. Aquac. Int. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchi, T.; Maor, Y.; Tadmor, G.; Shenker, M.; Chefetz, B. Irrigation of Root Vegetables with Treated Wastewater: Evaluating Uptake of Pharmaceuticals and the Associated Human Health Risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9325–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; Le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I.; et al. Review of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Gokulan, K.; Piñeiro, S.A.; Williams, K.M.; Yuan, Z.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Khare, S. Effects of Acute and Chronic Exposure to Residual Level Erythromycin on Human Intestinal Epithelium Cell Permeability and Cytotoxicity. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part II. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, Q.H.; Nguyen, T.B.T.; Nguyen, T.L.A.; Do, T.T.T.; Dao, T.H.T.; Padungtod, P. Antibiotics use in fish and shrimp farms in Vietnam. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, C.; Fan, L.; Qiu, L.; Wu, W.; Meng, S.; Hu, G.; Kamira, B.; Chen, J. Occurrence of antibiotics and their impacts to primary productivity in fishponds around Tai Lake, China. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsbury, M.V.; Hamoutene, D.; Kraska, P.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Page, F.; Coyle, T.; Sutherland, T.; Gibb, O.; Mckindsey, C.W.; Hartog, F.; et al. Relationship between in feed drugs, antibiotics and organic enrichment in marine sediments at Canadian Atlantic salmon aquaculture sites. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiang, E.L.; Lee, C.W.; Takada, H.; Seki, K.; Takei, A.; Suzuki, S.; Wang, A.; Bong, C.W. Antibiotic residues from aquaculture farms and their ecological risks in Southeast Asia: A case Study from Malaysia. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2021, 7, 1926337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, J.; Leston, S.; Freitas, A.; Barbosa, J.; Rema, P.; Dias, J.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Pardal, M.Â.; Ramos, F. Tissue depletion of five antibiotic residues in farmed European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 2019, 498, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gaya, B.; García-Bueno, N.; Buelow, E.; Marin, A.; Rico, A. Effects of aquaculture waste feeds and antibiotics on marine benthic ecosystems in the Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Xiao, Y. Sources, distribution and dynamics of antibiotics in Litopenaeus vannamei farming environment. Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Li, D.; Sui, J.; Kong, J.; Meng, X.; Luan, S. Prediction of meat yield in the Pacific whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2023, 577, 739914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhong, P.; Yi, J.-Q.; Xu, A.-X.; Lin, W.-Y.; Guo, Z.-C.; Wang, C.-G.; Sun, C.-B.; Chan, S. Potential role for microRNA in facilitating physiological adaptation to hypoxia in the Pacific whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmström, K.; Gräslund, S.; Wahlström, A.; Poungshompoo, S.; Bengtsson, B.-E.; Kautsky, N. Antibiotic use in shrimp farming and implications for environmental impacts and human health. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadas, S.; Zakaria, Z.; Shariff, M.; Bhassu, S.; Karim, M.; Natrah, I. Methodologies and standards for monitoring antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in shrimp aquaculture. Aquaculture 2024, 579, 740216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, N.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Peng, N. Enrofloxacin-induced transfer of multiple-antibiotic resistance genes and emergence of novel resistant bacteria in red swamp crayfish guts and pond sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniyappan, V.; Nagalingam, A.K.; Ranganathan, H.P.; Kandhikuppam, K.B.; Kothandam, H.P.; Vasu, S. Antibiotics in South Indian coastal sea and farmed prawns (Penaeus monodon). Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2013, 6, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, A.; Jacobs, R.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Tello, A. A probabilistic approach to assess antibiotic resistance development risks in environmental compartments and its application to an intensive aquaculture production scenario. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Yu, T.; Yang, Y.; Yu, S.; Wu, J.; Lin, R.; Li, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhu, C. Co-occurrence of Antibiotic and Heavy Metal Resistance and Sequence Type Diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Isolated from Penaeus vannamei at Freshwater Farms, Seawater Farms, and Markets in Zhejiang Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadella, R.K.; Panda, S.K.; Madhusudana Rao, B.; Pani Prasad, K.; Raman, R.P.; Mothadaka, M.P. Antibiotic Resistance of Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Isolated from Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Aquaculture Ponds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the PRC. Pollution-Free Food—Rules for Application of Fishery Medicine; The Ministry of Agriculture of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Mao, L.; Tao, H. Effect of Vegetable Growth on Content and Composition of Antibiotics in Litopenaeus vannamei Pond Sediments in Crop/Aquacultural Rotation Process. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, Z.; Nie, X.; Yang, Y.; Pan, D.; Leung, A.O.W.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, K. Residues of fluoroquinolones in marine aquaculture environment of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2012, 34, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Yuan, J.; Liu, M.; Gu, Z. Assessment of water quality and phytoplankton community of Limpenaeus vannamei pond in intertidal zone of Hangzhou Bay, China. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 11, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M.; Szpunar, J.; Lobinski, R.; Edirisinghe, E.M.R.K.B. Determination of Multi-Class Antibiotics Residues in Farmed Fish and Shrimp from Sri Lanka by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Fishes 2023, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, distribution and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in the Haihe River in China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J. Progress in the gut microbiota in exploring shrimp disease pathogenesis and incidence. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7343–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Lu, J.; Xuan, L.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Sediment prokaryotic assembly, methane cycling, and ammonia oxidation potentials in response to increasing antibiotic pollution at shrimp aquafarm. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhuan, R. Degradation of antibiotics by advanced oxidation processes: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 135023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eheneden, I.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J. Antibiotic removal by microalgae-bacteria consortium: Metabolic pathways and microbial responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yezli, S.; Li, H. Antibiotic resistance amongst healthcare-associated pathogens in China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-R.; Huang, C.-H. Transformation kinetics and pathways of tetracycline antibiotics with manganese oxide. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J. Environmental fate of tetracycline antibiotics: Degradation pathway mechanisms, challenges, and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Luo, Y.; He, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, B.; Pan, X. Algal organic matter accelerates the photodegradation of tetracycline: Mechanisms, degradation pathways and product toxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pacheco, C.V.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; López-Peñalver, J. Tetracycline removal from waters by integrated technologies based on ozonation and biodegradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.-R.; Diao, Z.-H.; Sun, K.-F.; Hao, Q.-W.; Liu, S.-S.; Ying, G.-G. Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.C.; Kwakkel, R.P.; Soede, J.; Williams, B.A.; Verstegen, M.W.A. Effect of a Chinese herb medicine formulation, as an alternative for antibiotics, on performance of broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2004, 45, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagawany, M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Farag, M.R.; Sachan, S.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K. The use of probiotics as eco-friendly alternatives for antibiotics in poultry nutrition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10611–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Aquaculture Pond | Pond Age (Year) | Breeding Mode | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | Single culture of Litopenaeus vannamei | Track and study a breeding cycle |
| 2 | 5 | Single culture of Litopenaeus vannamei | Track and study a breeding cycle |
| 3 | 7 | Single culture of Litopenaeus vannamei | Track and study a breeding cycle |
| Correlation | Feed | Sediment | Shrimp | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | 1 | 0.953 ** | 0.851 * | 0.398 |
| Sediment | 0.953 ** | 1 | 0.676 | 0.303 |
| Shrimp | 0.851 * | 0.676 | 1 | 0.671 |
| Water | 0.398 | 0.303 | 0.671 | 1 |
| SMX | NOF | LEOF | TC | OTC | CTC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gf | 32.89 | 19.44 | 132.36 | 28.12 | 60.49 | 23.91 |
| Gw | 5.99 | 0.00 | 10.54 | 6.25 | 20.76 | 4.35 |
| Gs | 12.22 | 9.77 | 60.60 | 12.07 | 18.44 | 9.23 |
| GP,v | 2.56 | 5.19 | 24.37 | 2.65 | 8.30 | 1.74 |
| Gothers | 12.12 | 4.47 | 36.85 | 7.16 | 12.99 | 8.59 |
| Residual Concentration in Aquatic Products * (μg/kg, Calculated by Fresh Weight) | Distribution Proportion in Aquatic Products (%) | Daily Feed Addition (μg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMX | 100 | 7.78 | 527.68 |
| TC | 100 | 9.41 | 509.81 |
| OTC | 100 | 13.72 | 162.54 |
| CTC | 100 | 12.44 | 429.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Xie, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Yu, H. Distribution and Management of Residual Antibiotics in the Litopenaeus vannamei Shrimp Farming Environment: Recommendations for Effective Control. Fishes 2024, 9, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030084
Li F, Xie S, Wang M, Chen L, Yu H. Distribution and Management of Residual Antibiotics in the Litopenaeus vannamei Shrimp Farming Environment: Recommendations for Effective Control. Fishes. 2024; 9(3):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030084
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Feipeng, Siyu Xie, Mingzhu Wang, Ling Chen, and Haixiang Yu. 2024. "Distribution and Management of Residual Antibiotics in the Litopenaeus vannamei Shrimp Farming Environment: Recommendations for Effective Control" Fishes 9, no. 3: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030084
APA StyleLi, F., Xie, S., Wang, M., Chen, L., & Yu, H. (2024). Distribution and Management of Residual Antibiotics in the Litopenaeus vannamei Shrimp Farming Environment: Recommendations for Effective Control. Fishes, 9(3), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030084