Enhancing Indoor Culture of Weather Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) and Caipira Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in a Decoupled FLOCponics System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
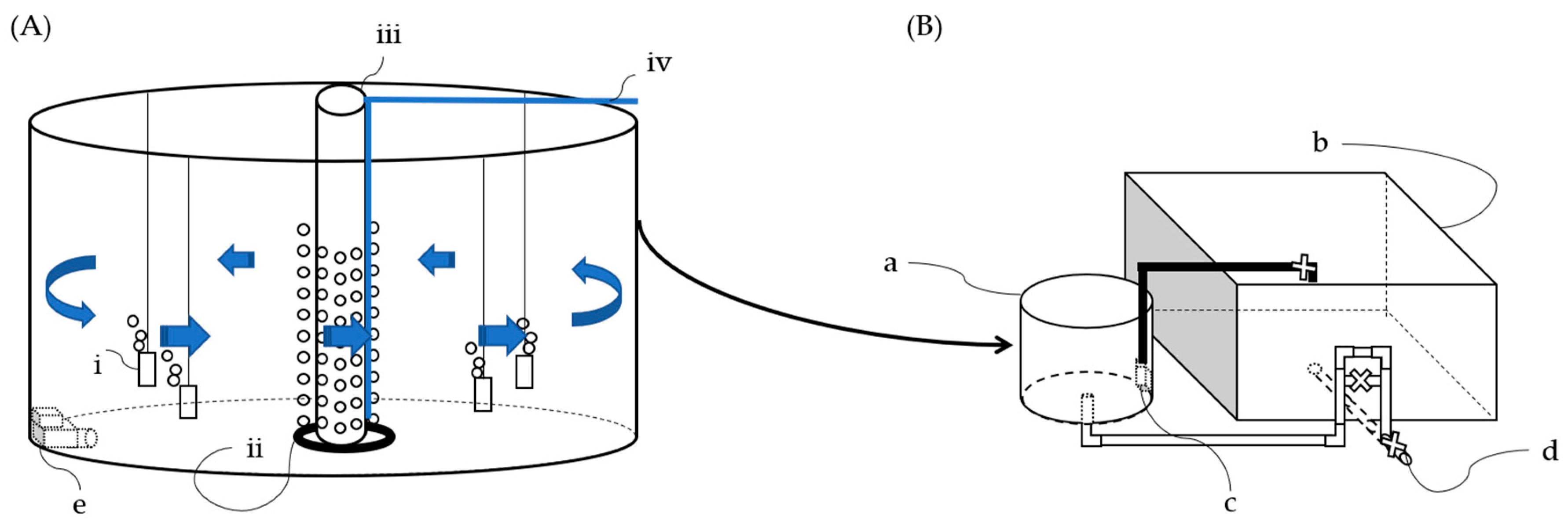
2.1. Aquaponics System Based on Biofloc Technology—FLOCponics (FP) Design
2.2. Fish and Crop
2.3. Preparing the BFT Rearing Water
Carbon (C) in molasses = 50%
Feed crude protein (CP) (%) = 40%
Amount of nitrogen (N) in the feed:
= 0.090 (kg) × 0.40 (CP%) × 0.155 (amount of N in CP)
= 0.00558
C/N ratio in the feed:
= 0.090 × 0.5 (C = in the Feed)/0.00558 (kg)
= 7.76:1.
Amount of C needed for 15:1
= (0.090 × 0.5 + molasses × 2)/0.00558 = 15
Molasses = (15 × 0.00558) − 0.090 × 0.5
= 0.0387 kg ≒ 39 g
2.4. Measurements of Water Quality
2.5. Growth Performance and Production of Fish and Crops
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance of M. anguillicaudatus
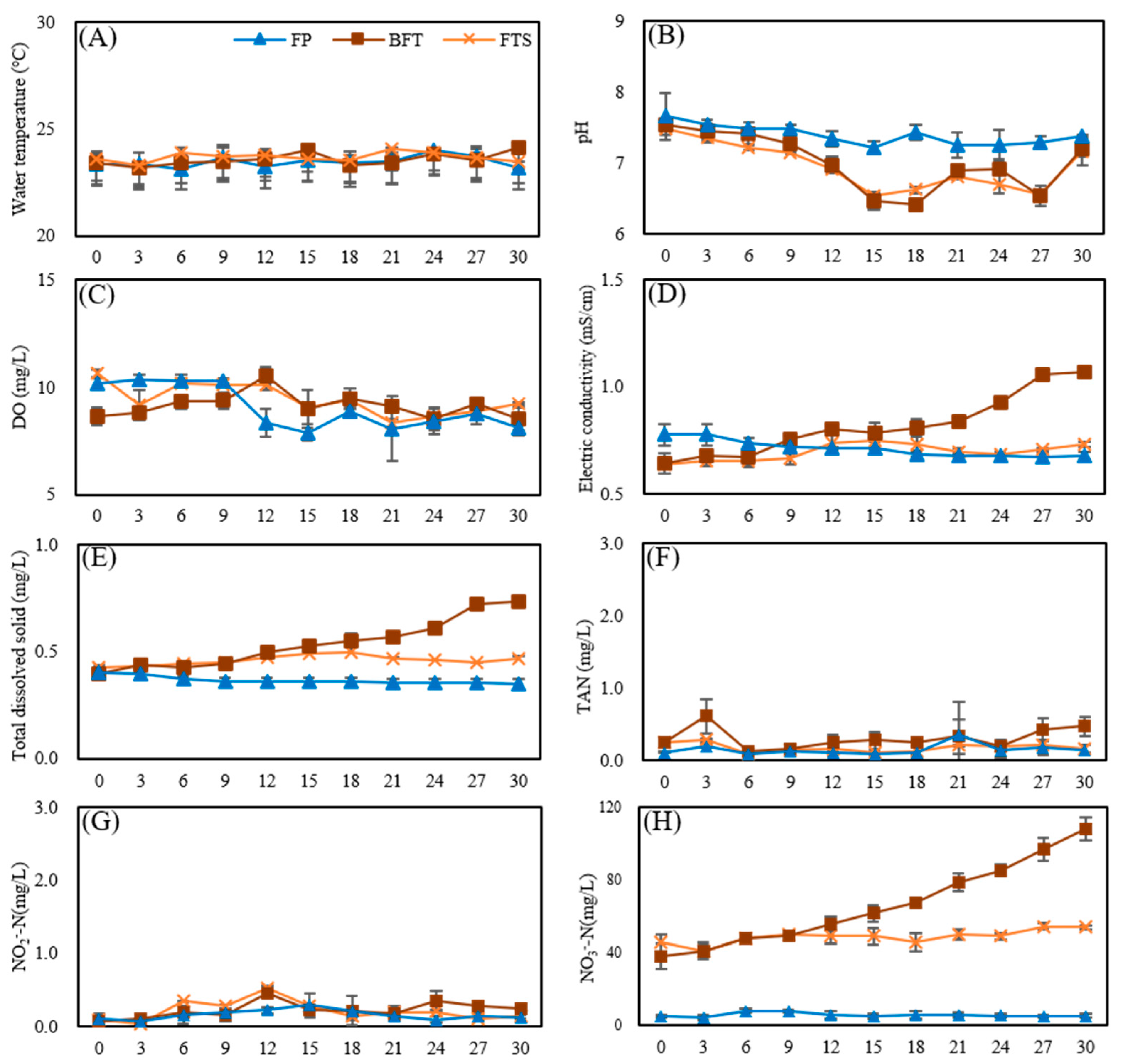
3.2. Water Quality Analysis in FP, BFT, and FTS
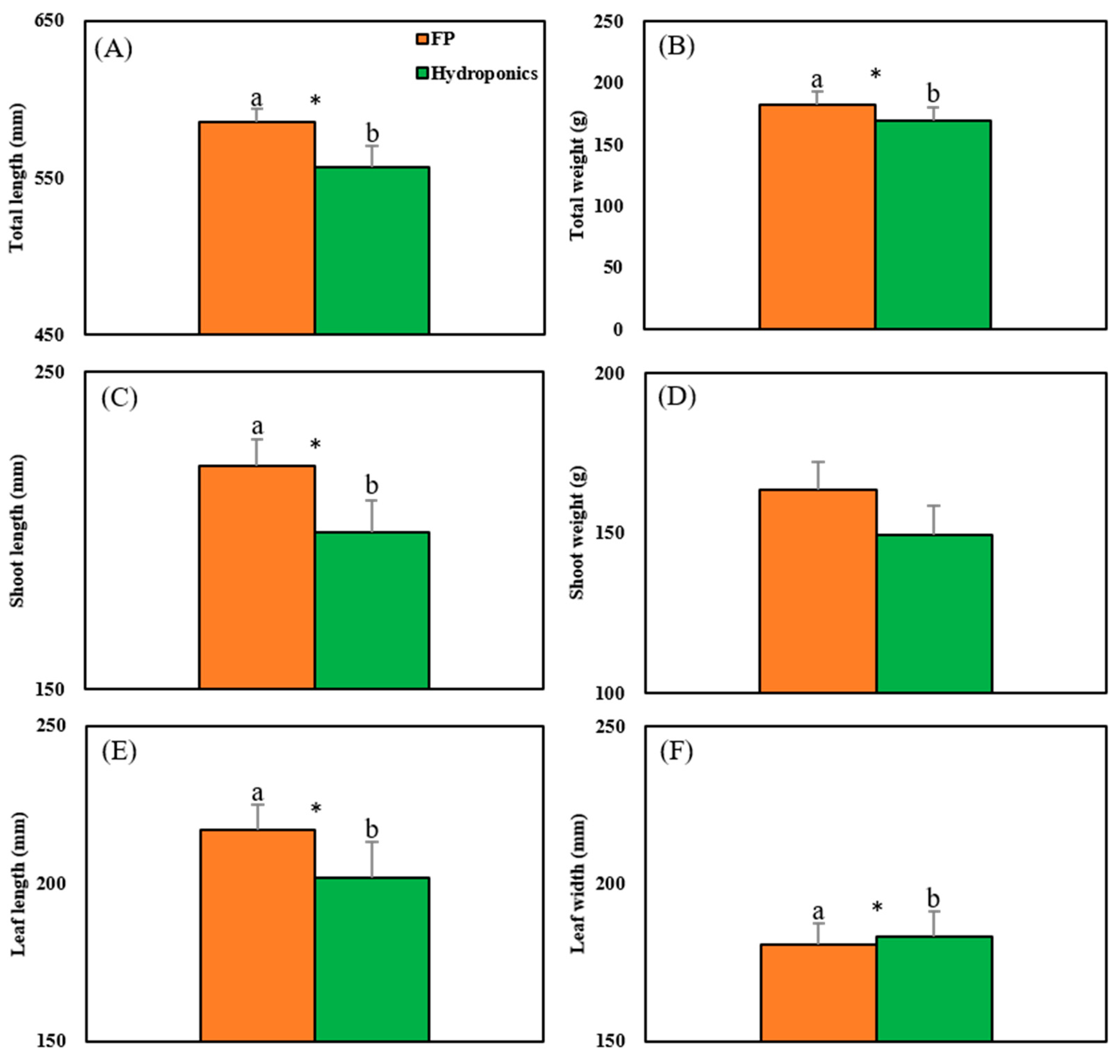
3.3. Production of Caipira Lettuce
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.K. Studies on the nutritional value of Loach Misgurnus mizolepis. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 1985, 14, 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, K.S.; Lim, S.G.; Im, J.H.; Han, H.G.; Soh, H.Y.; Cheong, C.J. Effect of fertilizer addition on water quality and fingerling production of loach (Misgurnus naguillicaudatus) in natural outdoor ponds. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.K.; Han, M.S..; Cho, K.J.; Nam, H.K.; NA, Y.E.; Kim, M.R.; Kim, M.H.; Choe, L.J. Effet of Agricultural Practices on Mudfish Population in Paddy Fields; The Korean Society of Environmental Agriculture: Suwon-si, Republic of Korea, 2013; p. 273. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Lim, S.G.; Bang, I.C.; Choi, J.; Lee, S.M. Optimal dietary protein and lipid levels for growth of juvenile muddy loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Korean J. Fish. Aquac. Sci. 2013, 46, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Kim, M.S.; Seok, Y.S.; Park, S.D.; Lee, H.H. Characterization and DNA Structure Analysis of Replication Origin of Misgurnus mizolepis. Korean J. Fish. Aquac. Sci. 1996, 9, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.S.; Kim, B.S.; Im, J.H.; Park, H.M.; Nam, Y.K.; Jeong, C.H.; Kim, D.S. Improved Early survival in backcrosses of male mud loach (Misgurnus mizolepis) X cyprinid loach (M. anguillicaudatus) hybrids to female cyprinid loach. J. Aqua. 1997, 10, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.S.; Song, Y.J.; Kwon, S.I.; Eo, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.H. Monthly change of the length-weight relationship of the loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) population in paddy fields by farming practices. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2018, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.B.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, S.S.; Lim, M.S.; Park, R.K. Studies on the rice-fish farming in rice paddy field 1. Studies on loach culture in rice paddy field. Res. Rept. RDA(R) 1991, 33, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Longo, S.B.; Clark, B.; York, R.; Jorgenson, A.K. Aquaculture and the displacement of fisheries captures. Conser. Biol. 2019, 33, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, C.E.; McNevin, A.A.; Clay, J.; Johnson, H.M. Certification issues for some common aquaculture species. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2005, 13, 231–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.R.; Sohn, S.G.; Choi, H.S.; Cheong, C.J.; Lee, Y.S. Acute toxicity of Ammonia and Nitrite for Fry Loach. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Technol. 2016, 17, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, K.R.; Cho, J.Y. Reuse of hydroponic waste solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 16, 9569–9577. [Google Scholar]
- Bondarczuk, K.; Markowicz, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. The urgent need for risk assessment on the antibiotic resistance spread via sewage sludge land application. Environ. Int. 2016, 87, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijn, J. The potential for integrated biological treatment systems in recirculating fish culture—A review. Aquaculture 1996, 139, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1999, 176, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diver, S. Aquaponics-Integration of Hydroponic with Aquaculture; National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service: Butte, MT, USA, 2006; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- De Schryver, P.; Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. The basics of bio-flocs technology: The added value for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2008, 277, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Morris, T.C.; Samocha, T.M. Effects of C/N ratio on biofloc development, water quality, and performance of Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles in a biofloc-based, high-density, zero-exchange, outdoor tank system. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Babitha, M.B.; Verma, A.K.; Maqsood, M. Biofloc technology: An emerging avenue in aquatic animal healthcare and nutrition. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betanzo-Torres, E.A.; Pinar-Alvarez, M.A.; Sierra-Carmona, C.G.; Santamaria, L.E.G.; Loeza-Mejia, C.I.; Marin-Muniz, J.L.; Herazo, L.C.S. Proposal of Ecotechnologies for Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Production in Mexico: Economic, Environmental, and Social Implications. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; He, Y.L.; Zhang, X.F. Nitrogen removal capability through simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by Bacillus sp. LY. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.L.S.; Cavalcante, D.D.H.; Carvalho, F.C.T.; Vieira, R.H.S.D.F.; Sa, M.V.D.C.; Sousa, O.V. Aquatic microbiota diversity in the culture of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) using bioflocs or periphyton: Virulence factors and biofilm formation. Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2016, 38, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, R.; Konig, B.; Villarroel, M.; Komives, T.; Jijakli, M.H. Strategic Points in aquaponics. Water 2017, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, U.; Pribbernow, M.; Xu, L.; Appelbaum, S.; Palm, H.W. Basil (Ocimum basilicum) cultivation in decoupled aquaponics with three hydro-components (Grow pipes, Raft, Gravel) and African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) production in northern Germany. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seginer, I.; Halachmi, I. Optimal stocking in intensive aquaculture under sinusoidal temperature, price and marketing conditions. Aquac. Eng. 2008, 39, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Toapanta, E.; Fisher, P.; Gómez, C. Growth rate and nutrient uptake of basil in small-scale hydroponics. HortScience 2020, 55, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.A.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Choe, J.R.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.S. Effect on Eel Anguilla japonica and crop growth by the development of a biofloc technology (BFT) Aquaponics System. Korean J. Fish. Aqua. Sci. 2021, 54, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, S.M.; David, L.H.; Garcia, F.; Portella, M.C.; Keesman, K.J. Sustainability assessment of FLOCponics compared to stand-alone hydroponics and biofloc systems using enerfy synthesis. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, J.A.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.H. Assessment of water quality parameters during a course of applying biofloc technology (BFT). J Fish. Mar. Sci. 2020, 32, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Azim, M.E.; Little, D.C.; Bron, J.E. Microbial protein production in activated suspension tanks manipulating C:N ratio in feed and the implications for fish culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3590–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, R.B.; Figueras, M.J. Molecular detection and characterization of furunculosis and other Aeromonas fish infections. In Health and Environment in Aquaculture; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2012; pp. 97–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Biofloc Production Systems for Aquaculture; Publication No. 4503; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center (SRAC): Stoneville, MS, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology-A Practical Guide Book, 3rd ed.; The World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Fuentes, J.A.; Hernández-Vergara, M.P.; Pérez-Rostro, C.I.; Fogel, I. C:N ratios affect nitrogen removal and nitrogen removal and production of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus raised in a biofloc system under high density cultivation. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Small-Scale Aquaponics Food Production Integrated Fish and Plant Farming; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, N.N.; Hwang, J.A.; Kim, H.S. A study on growth performance and water quality of far eastern catfish (Silurus asotus) using biofloc technology (BFT) aquaculture. J. Fish. Mar. Sci. Edu. 2021, 33, 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Bakar, N.S.; Mohd Nasir, N.; Lananan, F.; Abdul Hamid, S.H.; Lam, S.S.; Jusoh, A. Optimization of C/N ratios for nutrient removal in aquaculture system culturing African catfish, (Clarias gariepinus) utilizing Bioflocs technology. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriani, Y.; Dhahiyat, Y.; Zahidah, Z.; Zidni, I. The effect of stocking density ratio of fish on water plant productivity in aquaponics culture system. Nusant. Biosci. 2017, 9, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zokaeifar, H.; Balcazar, J.L.; Saad, C.R.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Sijam, K.; Arshad, A.; Nejat, N. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, digestive enzymes, immune gene expression and disease resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, S.M.; Mohamed, M.F.; John, G. Effect of probiotics on the survival, growth and challenge infection in Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathia, C.M.; del Carmen, M.D.M.; Aida, H.P.; Jorge, C.M.; Felix, A.G.J.; Amadeo, B.M.J. Effect of two probiotics on bacterial community composition from biofloc system and their impact on survival and growth of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 525–533. [Google Scholar]
- Portz, D.E.; Woodley, C.M.; Cech, J.J. Stress-associated impacts of short-term holding on fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2006, 16, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, C.; Wu, F. Effect of biofloc technology on growth, digestive enzyme activity, hemotology, and immune response of genetically improved famed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2015, 448, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares-Dias, M.; Mariano, W.S. Aquicultura No Brasil: Novas Perspectvias; Pedro & João Editores: São Carlos, SP, Brasil, 2015; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, W.G.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Abreu, P.C.; Brandao, H.; Krummenauer, D. Rearing of the pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) in BFT system with different photoperiods: Effects on the microbial community, water quality and zootechnical performance. Aquaculture 2019, 508, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshisundaram, M.; Sugantham, F.; Muthukuma, C.; Chandrasekar, M.S. Metagenomic characterization of biofloc in the grow-out culture of genetically improved farmed tilapia (GIFT). Aquac. Res. 2020, 52, 4249–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisano, H.; Barbosa, P.T.L.; Hayd, L.A.; Mattioli, C.C. Comparative study of growth, feed efficiency, and hematological and recirculating aquaculture system. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J.E. Ten guidelines for aquaponics systems. 10th Anniversary Issue. Aquaponics J. 2007, 46, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Goddek, S.; Schmautz, Z.; Scott, B.; Delaide, B.; Keesman, K.J.; Wuertz, S.; Junge, R. The effect of anaerobic and aerobic fish sludge supernatant on hydroponic lettuce. Agronomy 2015, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.S.; Ferrarezi, R.S. Valuation of vegetable crops produced in the UVI commercial aquaponics system. Aquac. Rep. 2017, 7, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lee, J.W.; Chandran, K.; Kim, S.P.; Botto, A.C.; Khanal, S.K. Effect of plant species on nitrogen recovery in aquaponics. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 188, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, C.E.; Massaut, L. Risks associated with the use of chemicals in pond aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 1999, 20, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkiew, S.; Hu, Z.; Chandran, K.; Woo-Lee, J.; Khanal, S.K. Nitrogen transformations in aquaponic systems: A review. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 76, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S.B.; Salie, K.; Stander, H.B. A growth comparison among three commercial tilapia species in a biofloc system. Aqua. Int. 2016, 24, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Little, D.C. The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: Water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2008, 283, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaide, B.; Goddek, S.; Gott, J.; Soyeurt, H.; Jijakli, M.H. Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. Sucrine) growth performance in complemented aquaponic solution outperforms hydroponics. Water 2016, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Systems | † FP | ‡ BFT | § FTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 IBW (g) | 1.27 ± 0.360 NS | 1.27 ± 0.360 | 1.27 ± 0.360 |
| 2 FBW (g) | 1.99 ± 0.734 a | 1.69 ± 0.329 ab | 1.52 ± 0.432 b |
| 3 ITW (kg) | 3.0 NS | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| 4 FTW (kg) | 4.5 ± 0.11 a | 3.3 ± 0.12 ab | 2.5 ± 0.04 b |
| 5 ITL (mm) | 65.4 ± 6.78 NS | 65.4 ± 6.78 | 65.4 ± 6.78 |
| 6 FTL (mm) | 74.0 ± 7.84 NS | 74.2 ± 3.67 | 72.4 ± 5.38 |
| 7 WGR (%) | 51.11 ± 3.69 a | 24.00 ± 4.16 b | −15.56 ± 1.35 c |
| 8 SGR (%/day) | 1.62 ± 0.07 a | 1.03 ± 0.08 b | 0.65 ± 0.11 c |
| 9 FCR | 1.65 ± 0.12 a | 3.57 ± 0.58 b | −5.43 ± 0.46 c |
| 10 SR (%) | 91.06 ± 2.64 a | 82.12 ± 10.98 ab | 66.75 ± 2.75 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Hwang, J.-a.; Choe, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, H. Enhancing Indoor Culture of Weather Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) and Caipira Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in a Decoupled FLOCponics System. Fishes 2024, 9, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050150
Park J, Hwang J-a, Choe J, Lee D, Kim H. Enhancing Indoor Culture of Weather Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) and Caipira Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in a Decoupled FLOCponics System. Fishes. 2024; 9(5):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050150
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Junseong, Ju-ae Hwang, Jongryeol Choe, Donggil Lee, and Hyeongsu Kim. 2024. "Enhancing Indoor Culture of Weather Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) and Caipira Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in a Decoupled FLOCponics System" Fishes 9, no. 5: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050150
APA StylePark, J., Hwang, J.-a., Choe, J., Lee, D., & Kim, H. (2024). Enhancing Indoor Culture of Weather Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) and Caipira Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in a Decoupled FLOCponics System. Fishes, 9(5), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050150






