Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Tissue Distribution of Butachlor in the Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
2.2. Determination of the Oxidative Stress-Related Parameters
2.3. Butachlor Residue Test
2.4. Calculation of the Median Lethal Concentration (LC50) and the Safe Concentration (SC)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity of Butachlor in Juvenile E. sinensis Crabs
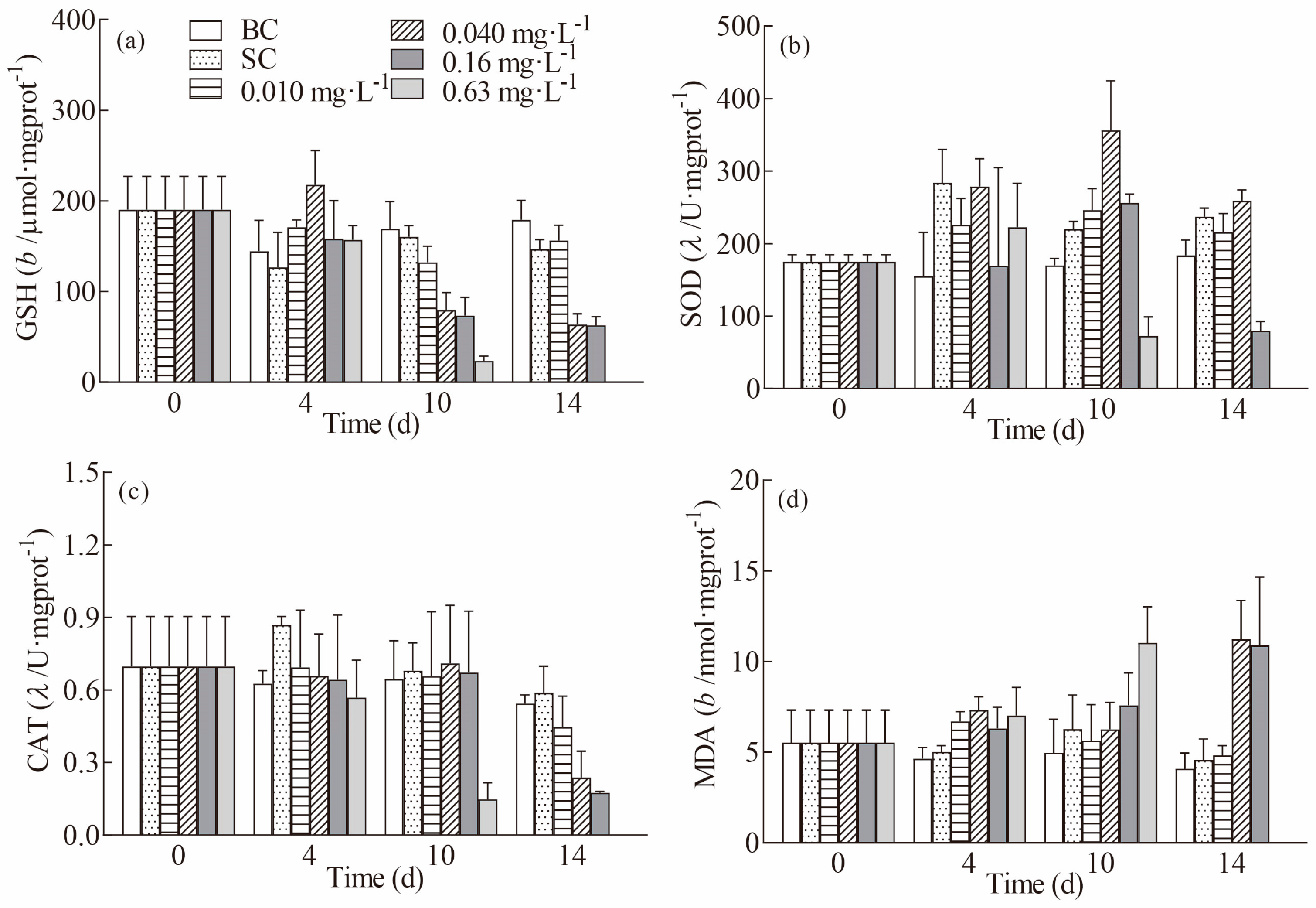
3.2. Effects of Butachlor on Oxidative Stress-Related Parameters in the Gills of Juvenile E. sinensis Crabs
3.3. Effects of Butachlor on Oxidative Stress-Related Parameters in the Hepatopancreas of Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crabs
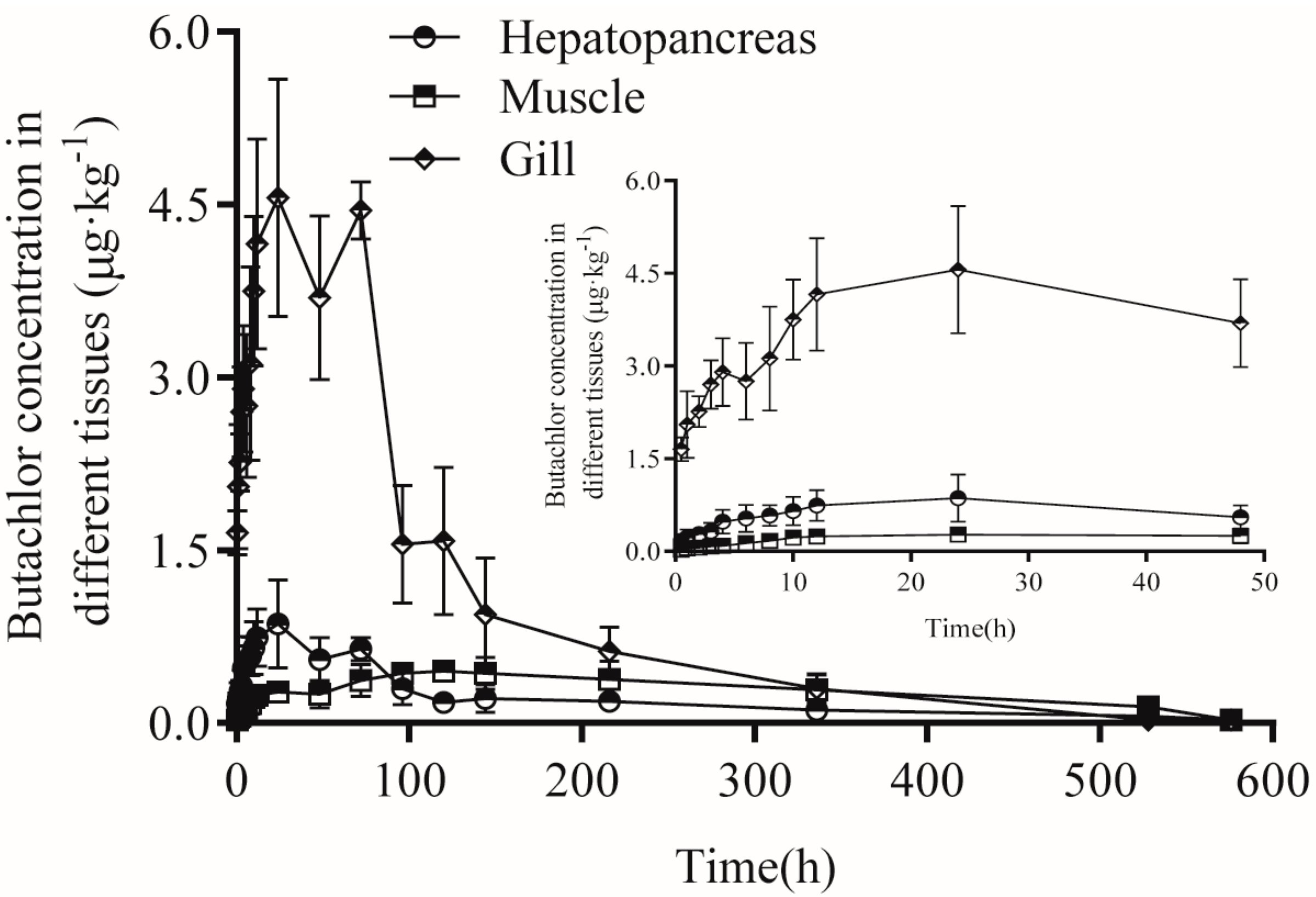
3.4. Residues of Butachlor in Different Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S. China Rural Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, F.P. Agriculture, pesticides, food security and food safety. Environ. Sci. Policy 2006, 9, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, O.M.; Basheer, A.A.; Khattab, R.A.; Ali, I. Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.S.; Coupe, R.H.; Foreman, W.T.; Capel, P.D. Pesticides in Mississippi air and rain: A comparison between 1995 and 2007. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, U.; Lorenz, S.; Hörmann, G.; Stähler, M.; Neubauer, L.; Fohrer, N. Multiple pesticides in lentic small water bodies: Exposure, ecotoxicological risk, and contamination origin. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 816, 151504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyohemba, R.L.; Pillay, L.; Humphries, M.S. Herbicide residues in sediments from Lake St Lucia (iSimangaliso World Heritage Site, South Africa) and its catchment areas: Occurrence and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, C.; Lambright, C.; Mann, P.; Price, M.; Cooper, R.L.; Ostby, J.; Gray, L.E. Administration of potentially antiandrogenic pesticides (procymidone, linuron, iprodione, chlozolinate, p, p′-DDE, and ketoconazole) and toxic substances (dibutyl-and diethylhexyl phthalate, PCB 169, and ethane dimethane sulphonate) during sexual differentiation produces diverse profiles of reproductive malformations in the male rat. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1999, 15, 94–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mostafalou, S.; Abdollahi, M. Pesticides and human chronic diseases: Evidences, mechanisms, and perspectives. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 268, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meftaul, I.M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Dharmarajan, R.; Annamalai, P.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Parven, A.; Megharaj, M. Controversies over human health and ecological impacts of glyphosate: Is it to be banned in modern agriculture? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.L.; Holland, P.T.; James, T.K.; McNaughton, D.E.; Rahman, A. Persistence and leaching of the herbicides acetochlor and terbuthylazine in an allophanic soil: Comparisons of field results with PRZM-3 predictions. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghersa, F.; Pessah, S.; Duarte, A.; Ferraro, D. Theory and Practice for Environmental Risk Assessment: Understanding the Trade-Off Between the Benefits and Risks Behind Herbicide Use as Tool for Designing Sustainable Weed Management Systems. Decis. Supp. Syst. Weed. Manag. 2020, 8, 161–189. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.J.; Dang, Z.J.; Yang, L.K. Report on the Development of China’s rice-fishery integrated planting and breeding industry in China. Chin. Fish 2023, 566, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, X.Z.; Dong, Y.Z.; Xu, D.Y.; Huang, Z.Q. Effects of imidacloprid on the oxidative stress, detoxification and gut microbiota of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.M.; Lin, W.C.; Shi, C.; Li, R.H.; Mu, C.K.; Wang, C.L.; Ye, Y.F. Accumulation, detoxification, and toxicity of dibutyl phthalate in the swimming crab. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, W.J.; Qian, X.B.; Ji, J.; Ning, X.H.; Zhu, F.; Yin, S.W.; Zhang, K. Effects of hypoxia and reoxygenation on apoptosis, oxidative stress, immune response and gut microbiota of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 260, 106556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Q.; Zhao, Z.G.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, R.; Guo, K.; Yang, Y.H. Immune and intestinal microbiota responses to heat stress in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Wu, Y.; Wu, L.; Bai, Y.Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.F. The effects of ammonia stress exposure on protein degradation, immune response, degradation of nitrogen-containing compounds and energy metabolism of Chinese mitten crab. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 6053–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Z.; Song, Y.M.; Zhang, C.; Pang, Y.Y.; Song, X.Z.; Wu, M.Y.; Cheng, Y.X. Effects of the glyphosate-based herbicide roundup on the survival, immune response, digestive activities and gut microbiota of the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 214, 105243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, F.; Trausch, G.; Devos, L.S. Effects of atrazine on osmoregulation in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 132, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.S.; Liu, Y.W.; Li, Y.W.; Yi, J.N.; Yang, B.J.; Li, Y.L.; Ouyang, Z.X.; Liu, B.X.; Shang, P.; Mehmood, K.; et al. The potential risks of herbicide butachlor to immunotoxicity via induction of autophagy and apoptosis in the spleen. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.L.; Shutes, B.; Niu, T.T. Effect of butachlor on microcystis aeruginosa: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 449, 131042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Lei, M.J.; Jing, L.D.; Xia, F.; Yan, M.X.; Liu, J.T.; Wu, Y.H.; Wu, Y.L.; Wu, C.X. Effects of herbicide butachlor application on the growth of periphytic biofilms and nitrogen loss in paddy systems. Pedosphere 2024, 34, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvani, G.; Jumawan, J.C. Butachlor at environmentally relevant concentrations induces partial feminization in male Luzon wart frog Fejervarya vittigera Wiegmann, 1834. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.D.; Wang, J.S.; Li, M.H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Jia, A.Q. 1NMR based metabolomics approach to study the toxic effects of herbicide butachlor on goldfish (Carassius auratus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, M.; Kim, J.Y.; Hur, K.J.; Ramesh, M.; Hur, J.H. Responses of the freshwater fish Cyprinus carpio exposed to different concentrations of butachlor and oxadiazon. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 11, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Swain, H.S.; Roy, S.; Das, B.K.; Upadhyay, A.; Ramteke, M.H.; Kumar, V.; Kole, R.K.; Banerjee, H. Integrated biomarker approach strongly explaining in vivo sub-lethal acute toxicity of butachlor on Labeo rohita. Comp. Biochem. Phys. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 261, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, M.H.; Zhu, G.N. Effects of butachlor on reproduction and hormone levels in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, M.A.; Ateeq, B.; Ali, M.N.; Sabir, R.; Ahmad, W. Studies on lethal concentrations and toxicity stress of some xenobiotics on aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Lv, L.; Yu, Y.J.; Yang, G.L.; Xu, Z.L.; Wang, Q.; Cai, L.M. Single and joint toxic effects of five selected pesticides on the early life stages of zebrafish (Denio rerio). Chemosphere 2017, 170, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.Q.; Niu, L.L.; Liu, W.P.; Xu, C. Embryonic exposure to butachlor in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Endocrine disruption, developmental toxicity and immunotoxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 89, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.H.; Lv, L.; Peng, J.; Li, J.P.; Xiong, Z.T.; Chen, D.Q.; He, L. Multi-residue method for the determination of organofluorine pesticides in fish tissue by liquid chromatography triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. Food. Chem. 2016, 207, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Wu, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.X.; Qin, D.L. Toxicity of mefenacet on the juvenile Eriocheir sinensis. Chin. Fishery. Qual. Stand. 2021, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tilak, K.S.; Veeraiah, K.; Thathaji, R.B.; Butchiram, M.S. Toxicity studies of butachlor to the freshwater fish Channa punctata (Bloch). J. Environ. Biol. 2007, 28, 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Nwani, C.D.; Ama, U.I.; Okoh, F.; Oji, U.O.; Ogbonyealu, R.C.; Ibiam, A.A.; Udu-Ibiam, O. Acute toxicity of the chloroacetanilide herbicide butachlor and its effects on the behavior of the freshwater fish Tilapia zillii. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 499–503. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlin, C. The Pesticide Manual, 15th ed.; British Crop Protection Council: Cambridge, UK, 1994; pp. 855–857. [Google Scholar]
- Hedayati, A.; Gerami, M.H. Acute toxicity of butachlor to caspian kutum (Rutilus frisii Kutum Kamensky, 1991). J. Environ. Treat. Tech. 2014, 2, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 31270.21-2014; Guidelines on Environmental Safety Assessment for Chemical Pesticides—Part 21: Macro-crustacean Toxicity Test. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (MOA): Beijing, China, 2014.
- Hong, Y.H.; Yang, X.Z.; Yan, G.W.; Huang YZuo, F.; Shen, Y.X.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, Y. Effects of glyphosate on immune responses and haemocyte DNA damage of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 71, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Song, W.H.; Li, W.K.; Fu, L.J.; Yao, X.F.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J. Acute toxicity of three pesticides to juvenile Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Chin. J. Fish 2013, 26, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.H.; Wu, S.G.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, Y.H.; An, X.H.; Cai, L.M.; Zhao, X.P. Effect of acetochlor on transcription of genes associated with oxidative stress, apoptosis, immunotoxicity and endocrine disruption in the early life stage of zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramboo, S.M.; Yousuf, A.R.; Akbar, S. Oxidative stress-inducing potential of butachlor in a freshwater fish, Cyprinus carpio (L). Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2011, 93, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Yu, H.X.; Wang, X.R. Bioaccumulation and ROS generation in liver of freshwater fish, goldfish Carassius auratus under HC Orange No. 1 exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2007, 22, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Yum, S.; Park, H.S.; Lee, T.K.; Ryu, J.C. Effects of heavy metals on antioxidants and stress-responsive gene expression in Javanese medaka (Oryzias javanicus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Xu, L.; Zhao, X.F.; Lai, Q.L.; Zhou, X.Y. Control efficacy of oxadiargly·simetryn·butachlor 50% EC against weeds in rice transplanting field. World Pest. 2021, 43, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Z.; Yu, X.W.; Sun, N.B.; Shi, X.L.; Niu, C.; Shi, A.Y.; Cheng, Y.X. Glyphosate-based herbicide causes spermatogenesis disorder andspermatozoa damage of the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) by affecting testes characteristic enzymes, antioxidant capacities and inducing apoptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 447, 116086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.G.; Fang, Y.C.; Liu, J.N.; Chen, A.Q.; Cheng, Y.X.; Wang, Y.J. Moderate acidification mitigates the toxic effects of phenanthrene on the mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, L.N.; Chen, Q.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liao, X.Q.; Li, Z.X.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, X.J. Marine pollutant Phenanthrene (PHE) exposure causes immunosuppression of hemocytes in crustacean species, Scylla paramamosain. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 275, 109761. [Google Scholar]

| Items | Average Number of Death/Mortality Rate (%) (n = 10) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | ||||||
| Number | Rate (%) | Number | Rate (%) | Number | Rate (%) | Number | Rate (%) | ||
| Butachlor concentration (mg/L) | Blank control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ethanol control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.58 | 5.00 ± 5.77 b | 1.00 ± 0.82 | 10.00 ± 8.17 b | 1.50 ± 0.58 | 15.00 ± 5.77 b | 2.00 ± 0.82 | 20.00 ± 8.17 b | |
| 0.04 | 1.00 ± 0.82 | 10.00 ± 8.17 b | 1.25 ± 0.96 | 12.50 ± 9.57 b | 1.75 ± 0.50 | 17.50 ± 5.00 b | 3.50 ± 0.58 | 35.00 ± 5.77 b | |
| 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.82 | 10.00 ± 8.17 ab | 1.25 ± 0.96 | 17.50 ± 5.00 b | 1.75 ± 0.50 | 37.50 ± 5.00 b | 3.50 ± 0.58 | 47.50 ± 9.57 b | |
| 0.63 | 1.75 ± 0.50 | 17.50 ± 5.00 b | 2.25 ± 0.96 | 22.50 ± 9.57 b | 4.50 ± 1.29 | 45.00 ± 12.91 b | 6.25 ± 0.96 | 62.50 ± 9.57 b | |
| 2.51 | 2.50 ± 0.58 | 25.00 ± 5.77 b | 4.50 ± 1.29 | 45.00 ± 12.9 b | 8.00 ± 0.82 | 80.00 ± 8.17 a | 9.50 ± 0.58 | 95.00 ± 5.77 a | |
| 10 | 4.50 ± 1.29 | 45.00 ± 12.91 a | 6.50 ± 0.58 | 65.00 ± 5.77 a | 10.00 | 100.00 a | 10.00 | 100 a | |
| LC50/(mg/L) | 5.31 | 2.11 | 0.47 | 0.18 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Hao, Q.; Gao, L.; Qin, D.; Huang, X. Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Tissue Distribution of Butachlor in the Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fishes 2024, 9, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050177
Wu S, Wang P, Zhang Y, Huang L, Hao Q, Gao L, Qin D, Huang X. Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Tissue Distribution of Butachlor in the Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fishes. 2024; 9(5):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050177
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Song, Peng Wang, Ying Zhang, Li Huang, Qirui Hao, Lei Gao, Dongli Qin, and Xiaoli Huang. 2024. "Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Tissue Distribution of Butachlor in the Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis)" Fishes 9, no. 5: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050177
APA StyleWu, S., Wang, P., Zhang, Y., Huang, L., Hao, Q., Gao, L., Qin, D., & Huang, X. (2024). Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Tissue Distribution of Butachlor in the Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fishes, 9(5), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050177






