Comparison Study of Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Different Swimming Modes of Carassius auratus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
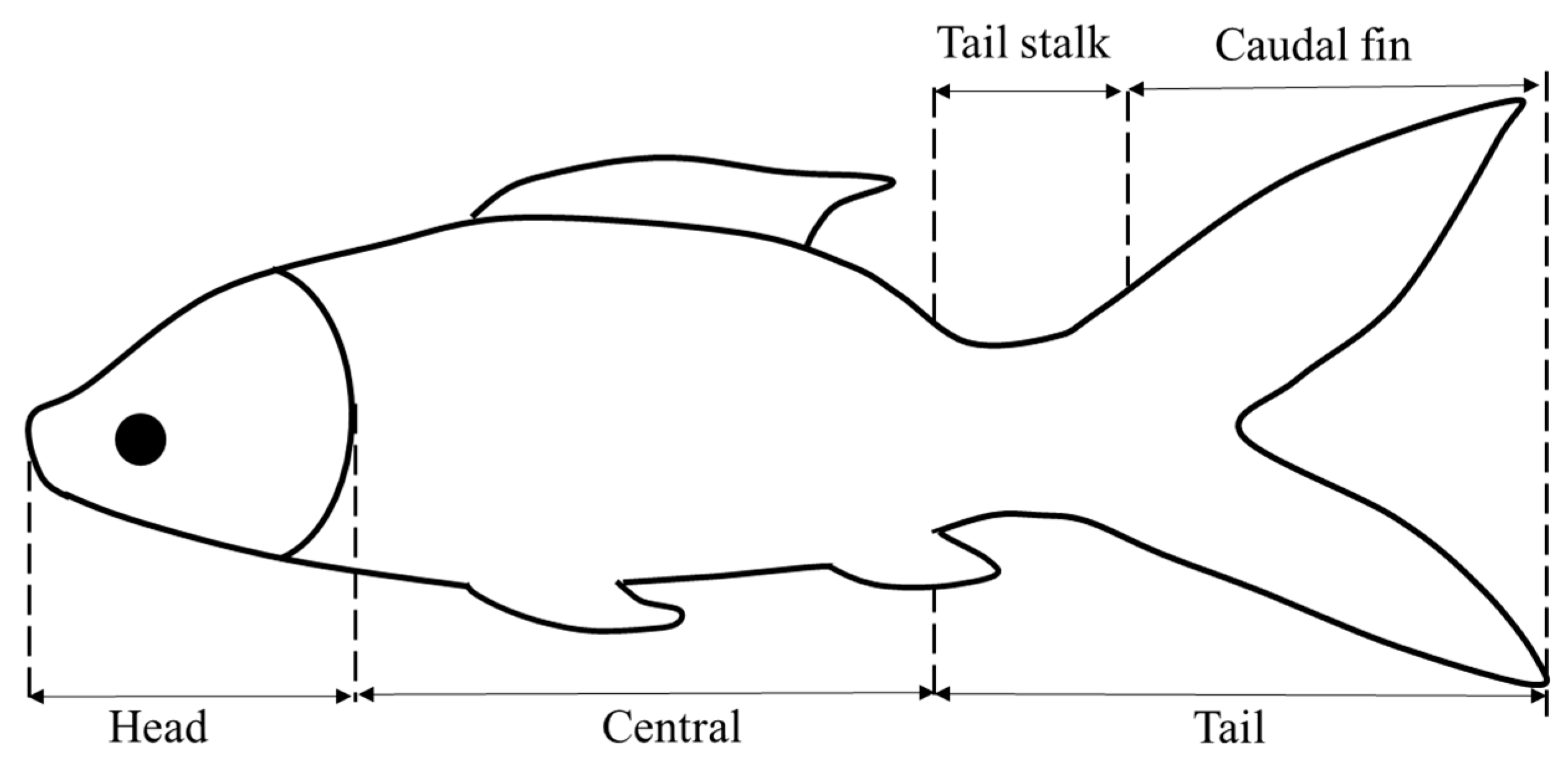
2.1. Experimental Subject Selection
2.2. Experimental Apparatus and Methods
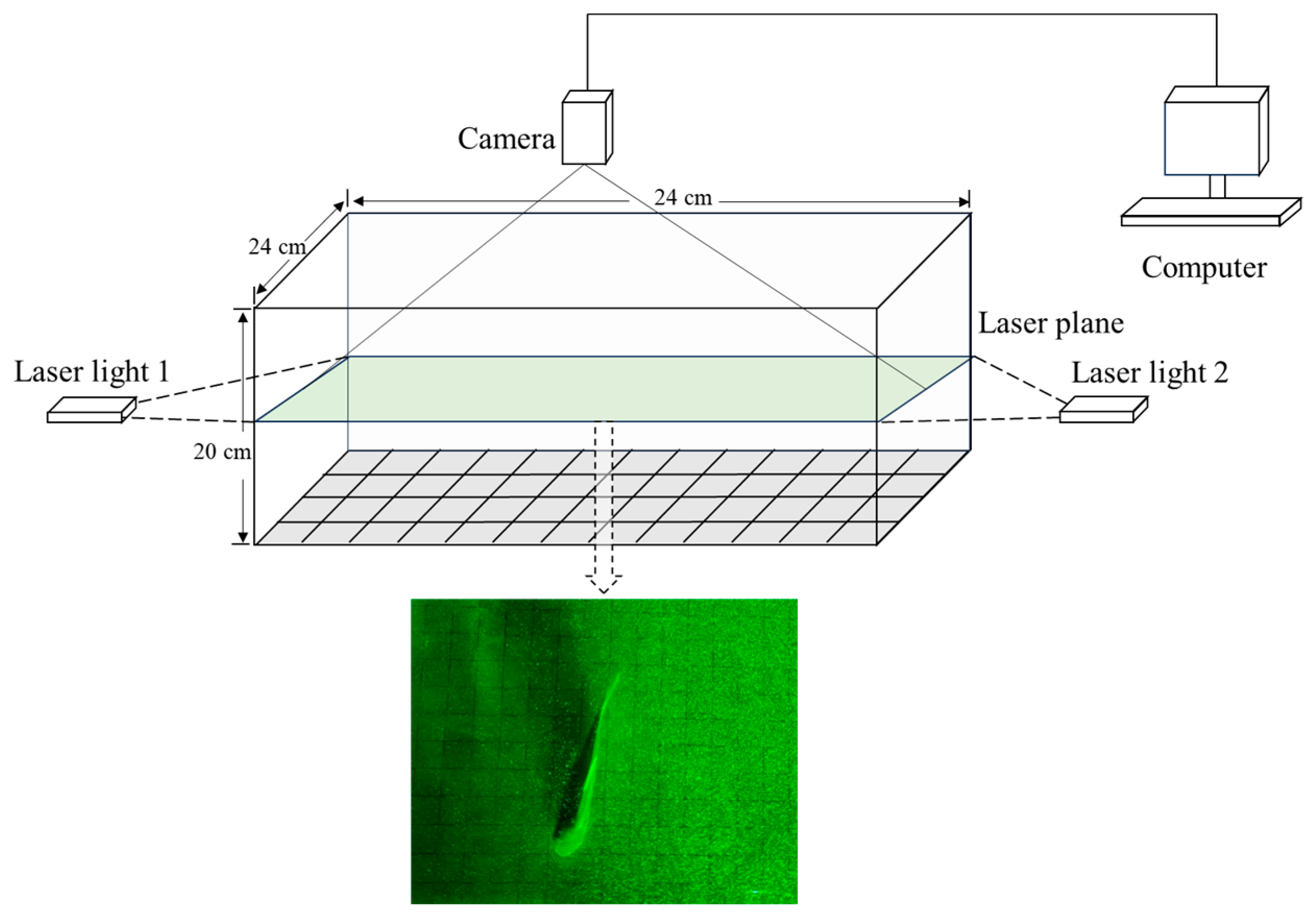
2.2.1. Experimental Apparatus
2.2.2. Experimental Methods
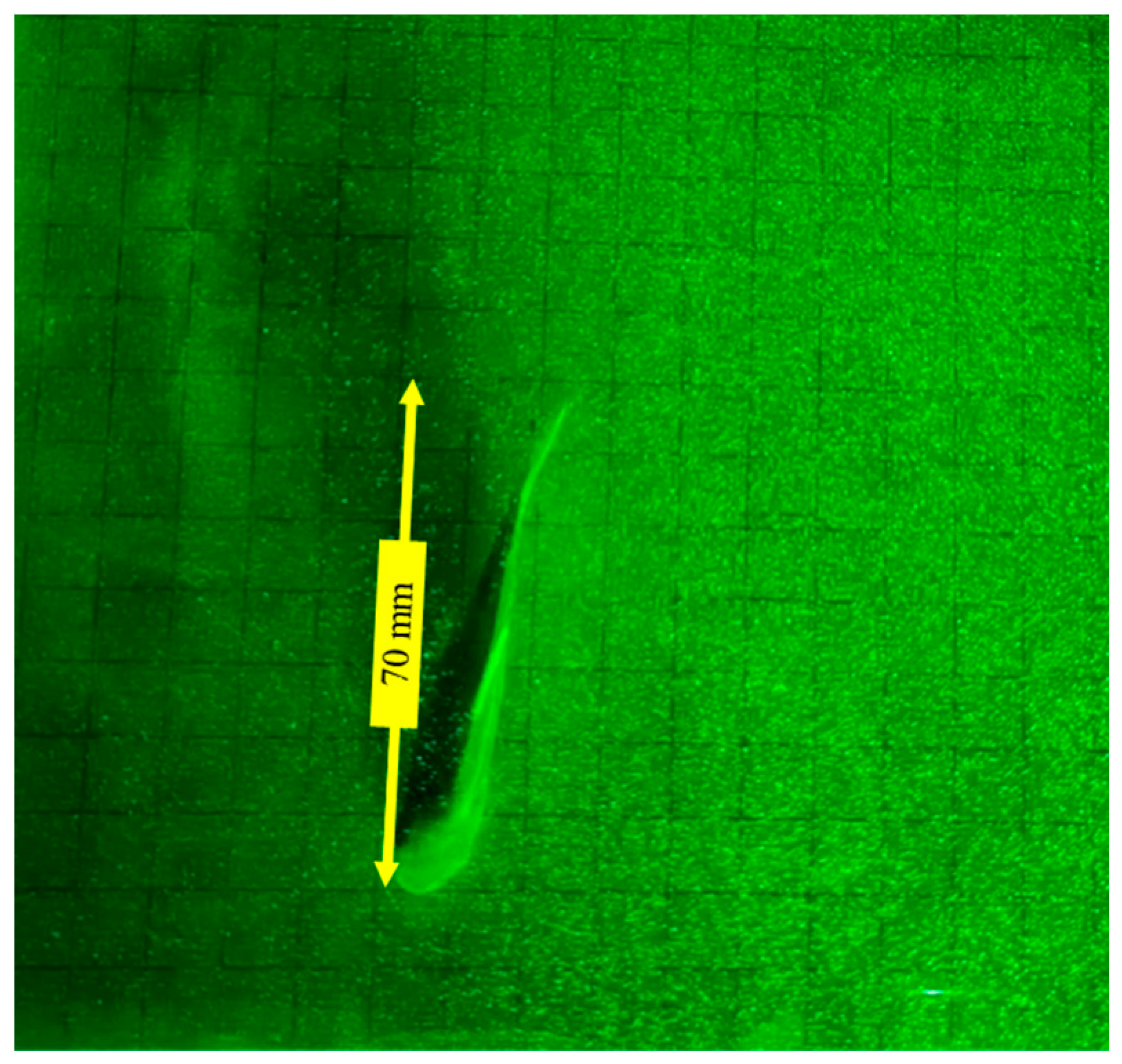
2.3. Flow-Field Measurement Techniques
2.3.1. Flow-Field Measurement Techniques
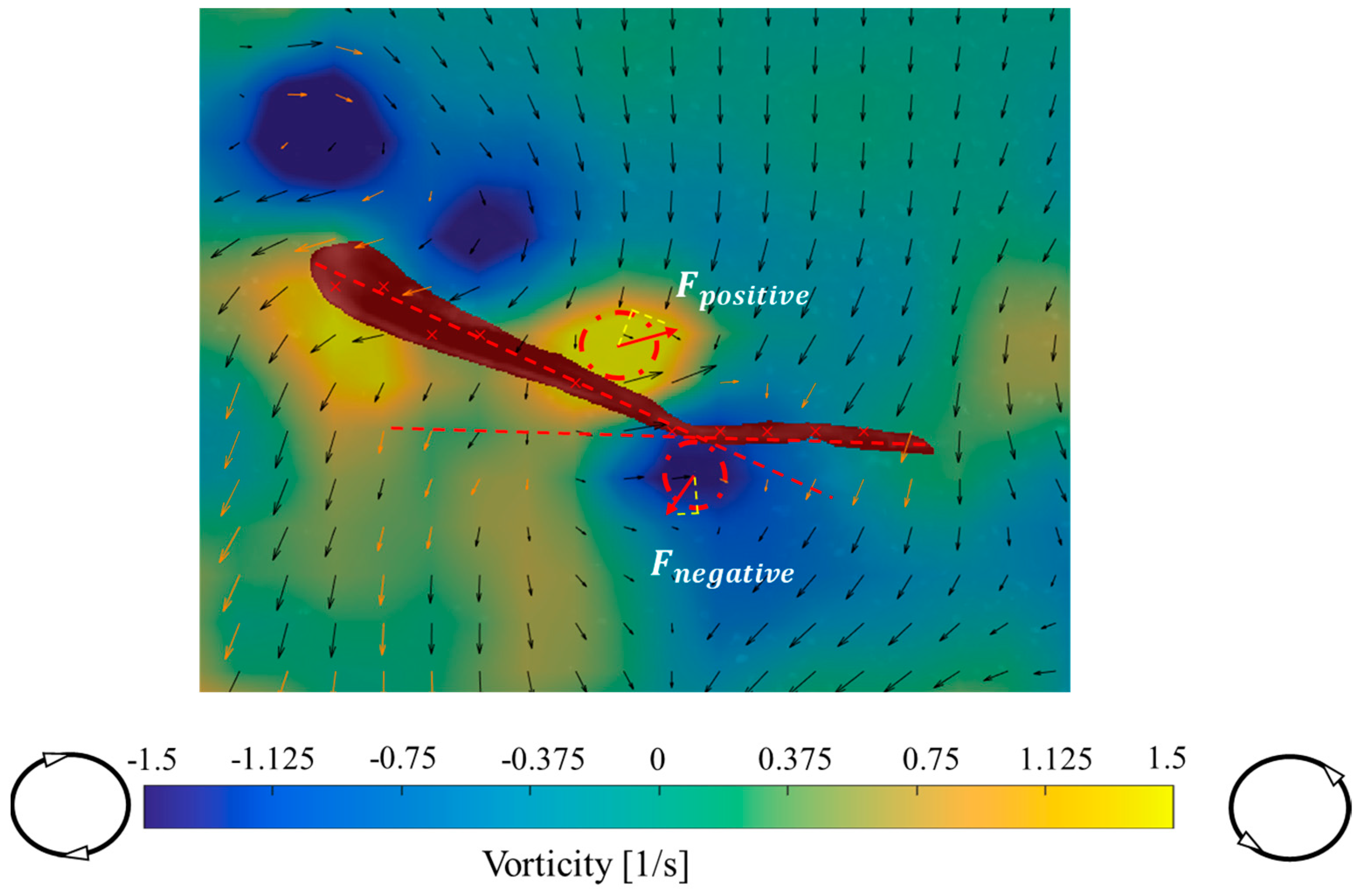
2.3.2. Vorticity and Dynamics of the Flow Field
2.4. Error Analysis
- (1)
- Reflection from the fish’s body during the experimental filming. Laser illumination on the fish’s body causes reflection, which can obscure particles around the fish, leading to measurement errors. To mitigate this, lasers were placed on both sides of the experimental aquarium, reducing the number of obscured particles and, thus, decreasing the measurement error;
- (2)
- Camera frame rate. Despite a frame rate of 120 fps, subtle changes in the fish’s contour occur between frames, leading to slight differences in the fish’s spatial coordinates from one frame to the next. These differences can introduce errors in the velocity-vector calculations during cross-correlation analysis. Therefore, this study aimed to minimize the time interval between image frames, ensuring that the selected frames adequately represent the changes in the juvenile goldfish’s various movement states;
- (3)
- Greater force exerted by the laser plane on the juvenile’s tail fork. To control the tail fork within the laser plane, the horizontal plane height was reduced. However, this adjustment may induce boundary effects on the fish’s body;
- (4)
- Particle sedimentation. Since the density of the tracer particles (1.03 g/cm3 to 1.05 g/cm3) is not identical to that of the water (1.0 g/cm3), particle sedimentation can occur at the fish’s contour when the fish body oscillates.
3. Results
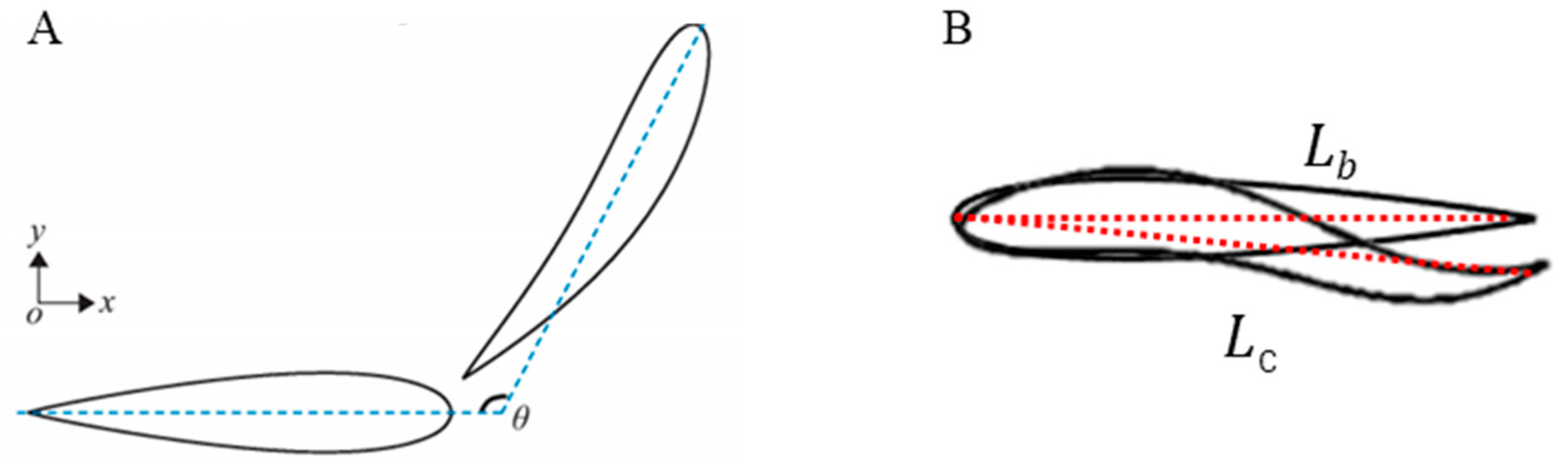
3.1. Kinematic Characteristics under Different States
- (1)
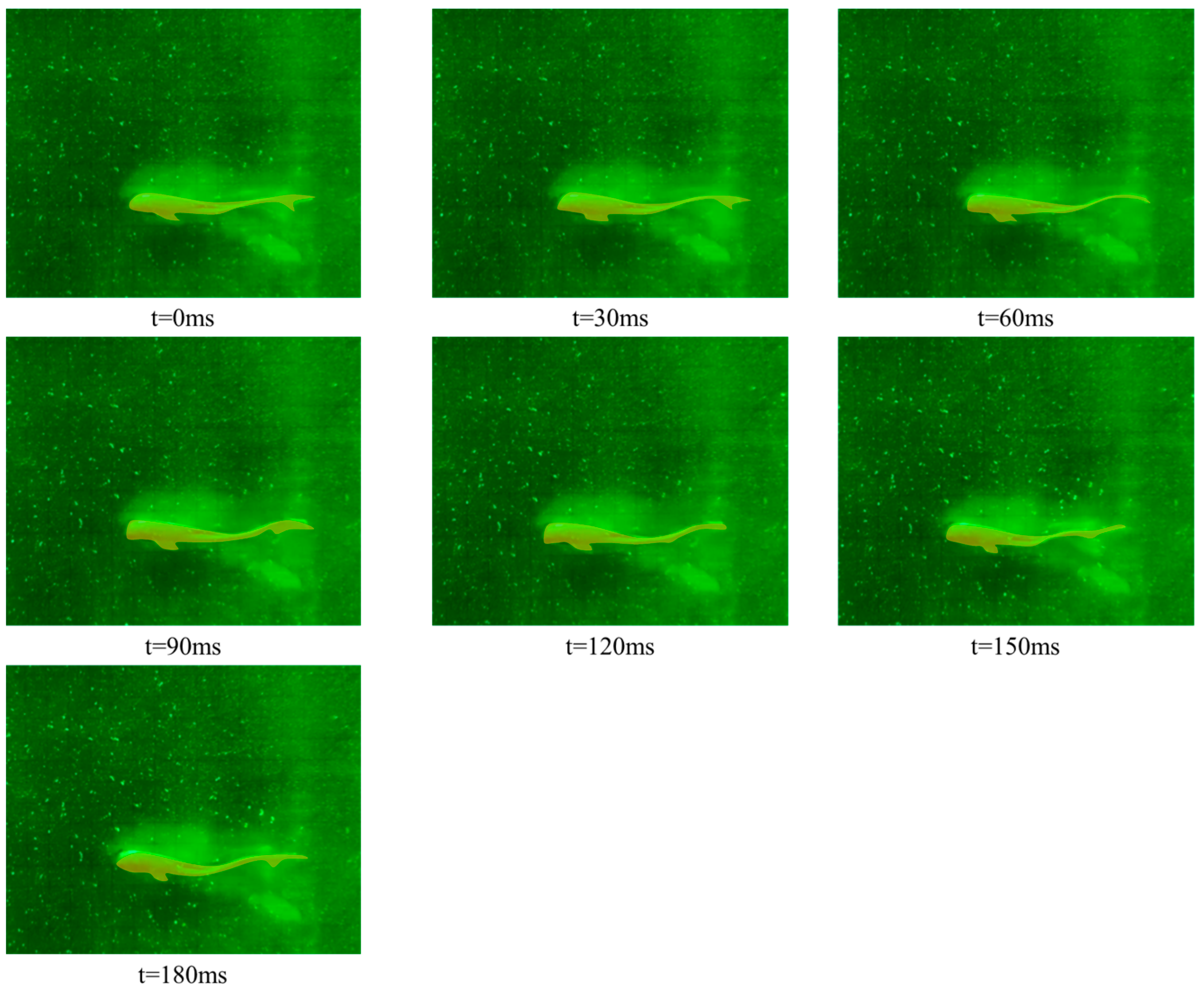
- Forward swimming condition
- (2)
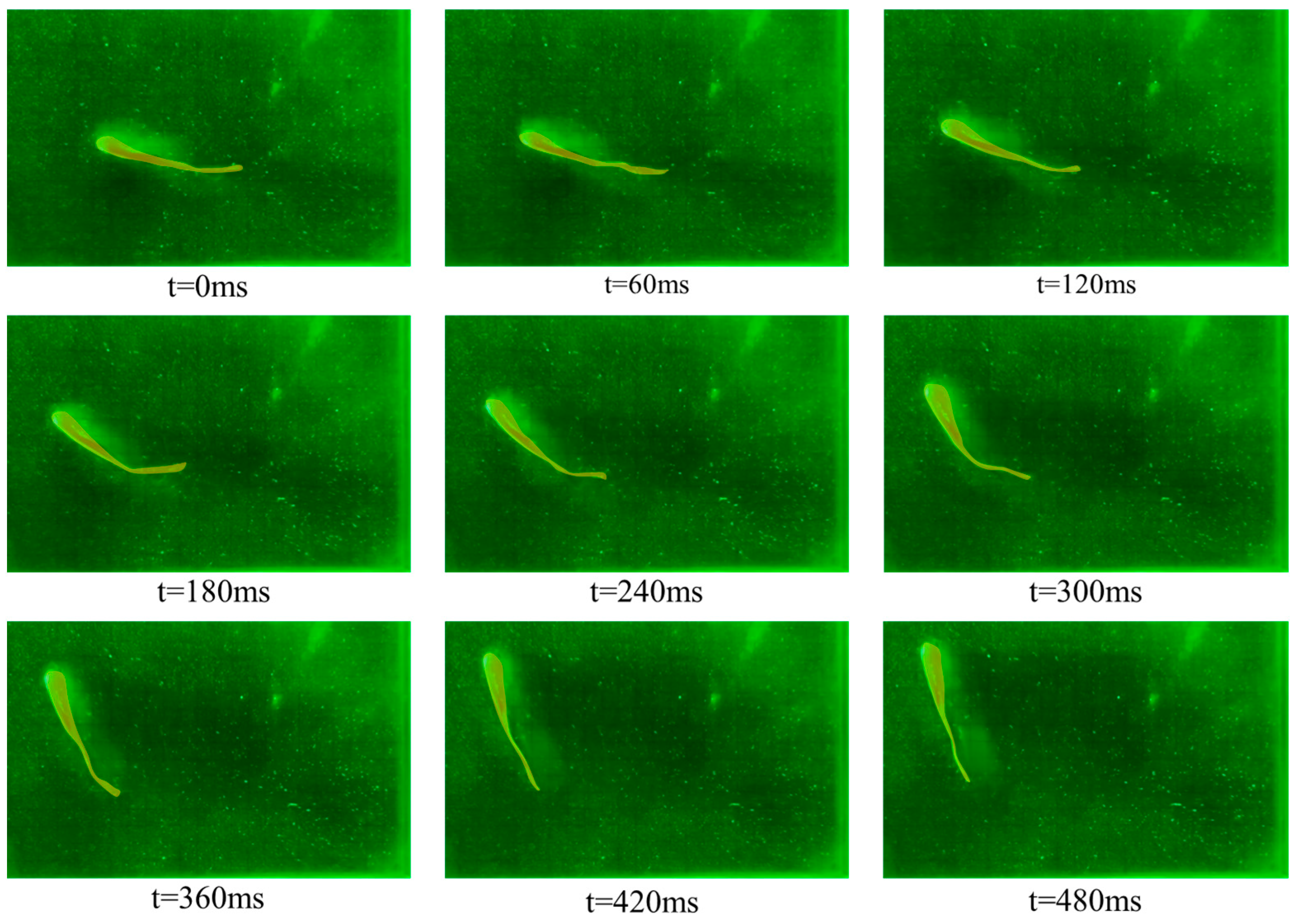
- Turning state
- (3)
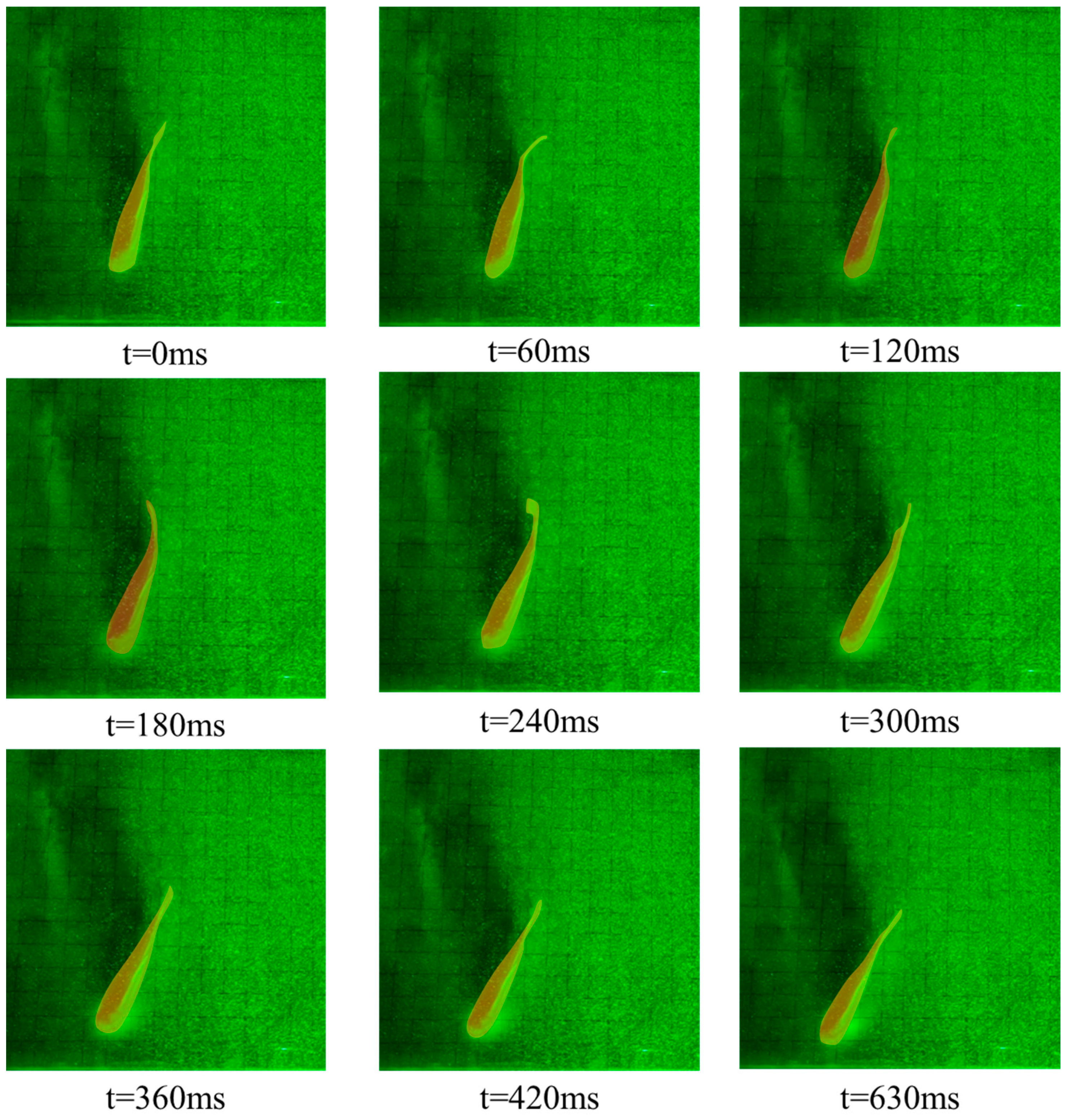
- Burst-and-coast state
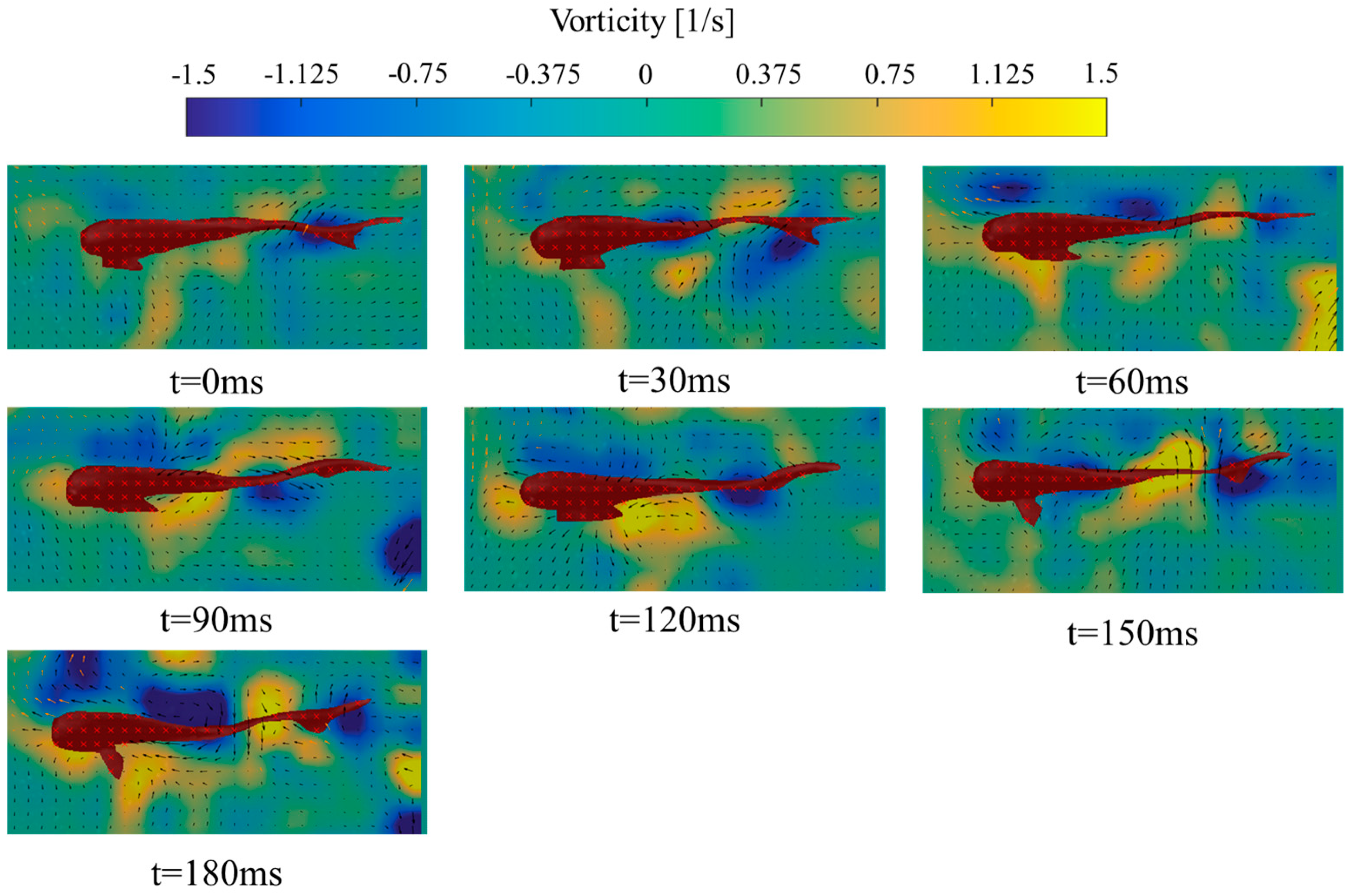
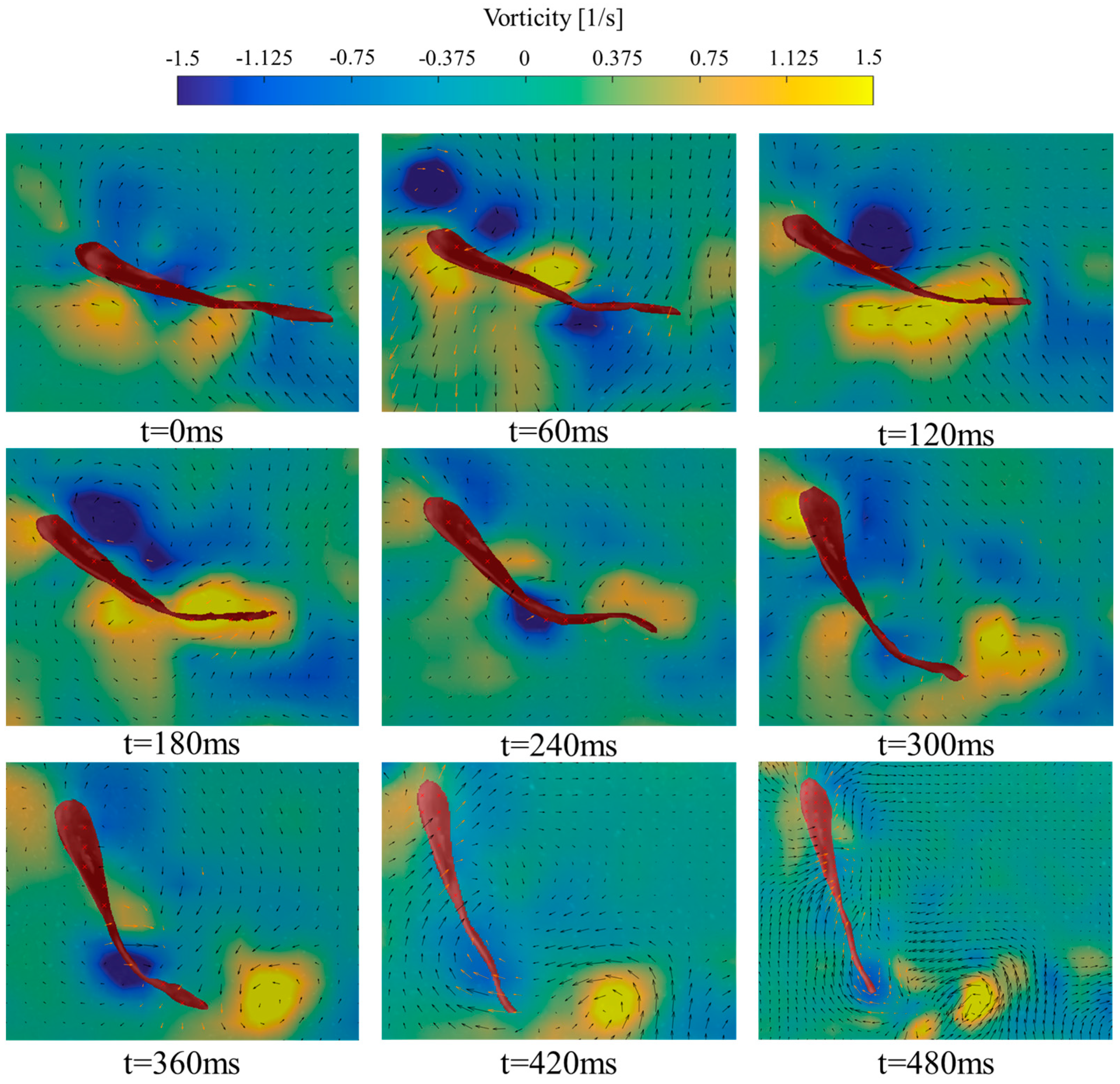
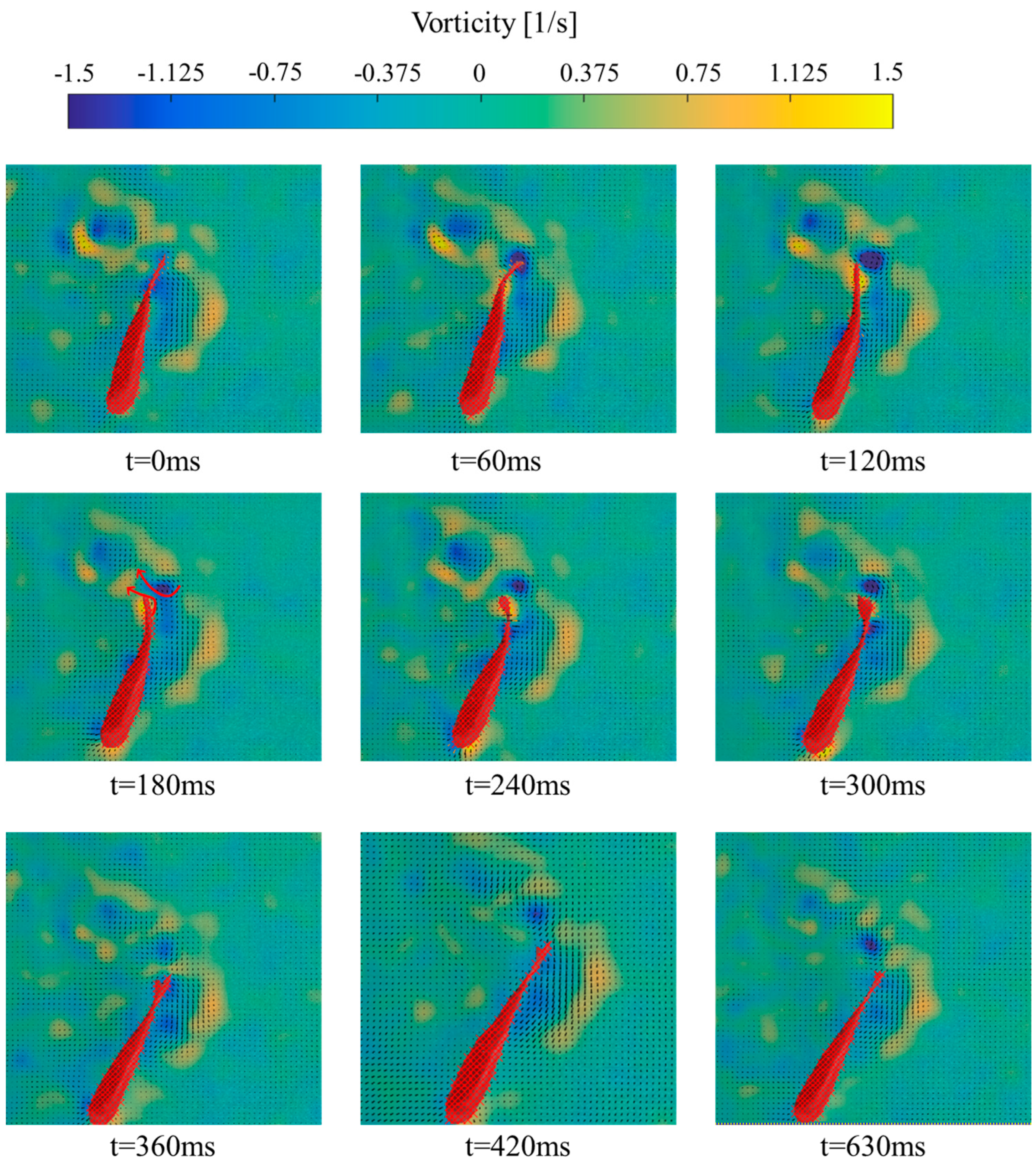
3.2. Analysis of Vorticity around the Tail under Different States
- (1)
- Forward swimming condition
- (2)
- Turning State
- (3)
- Burst-and-coast State
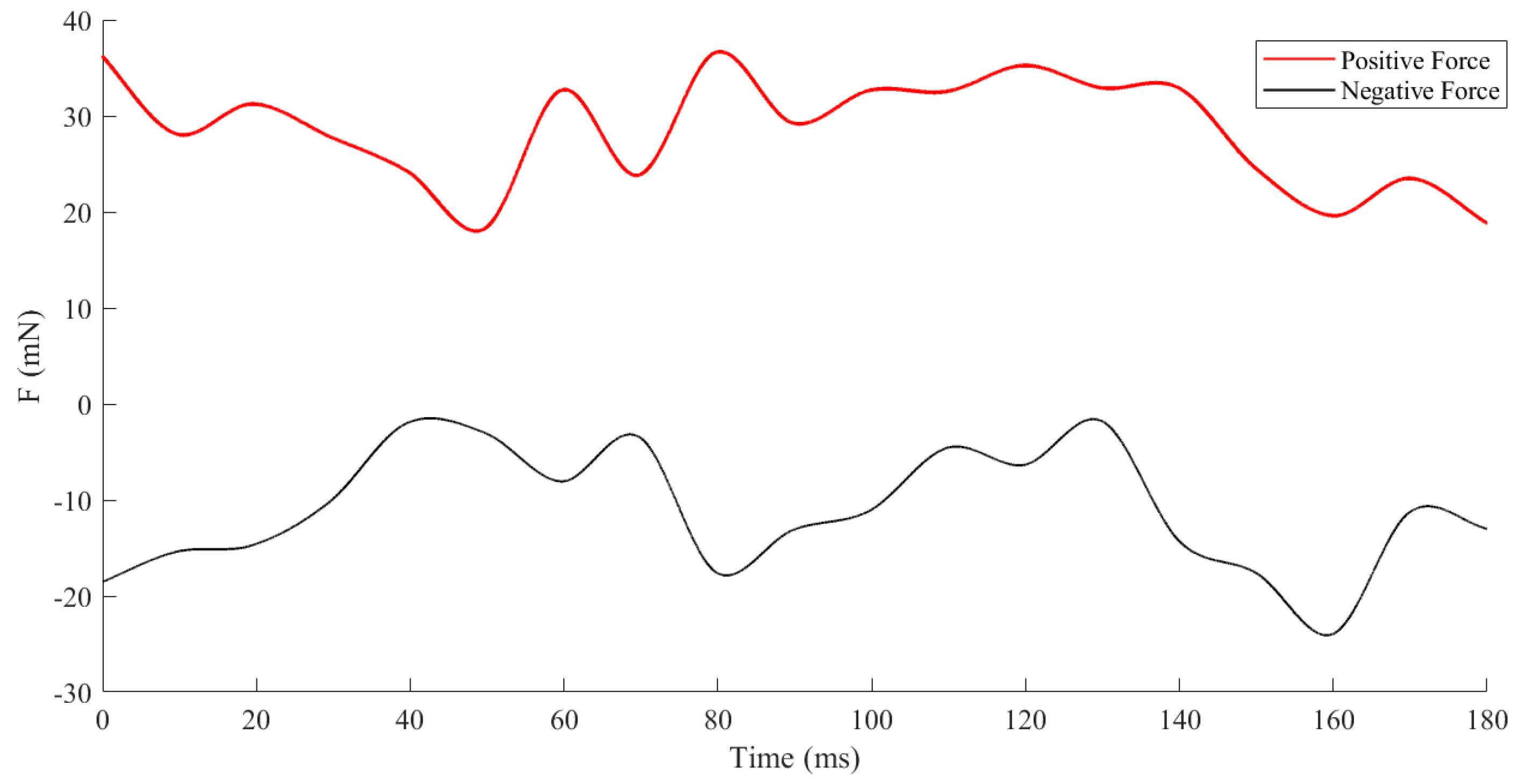
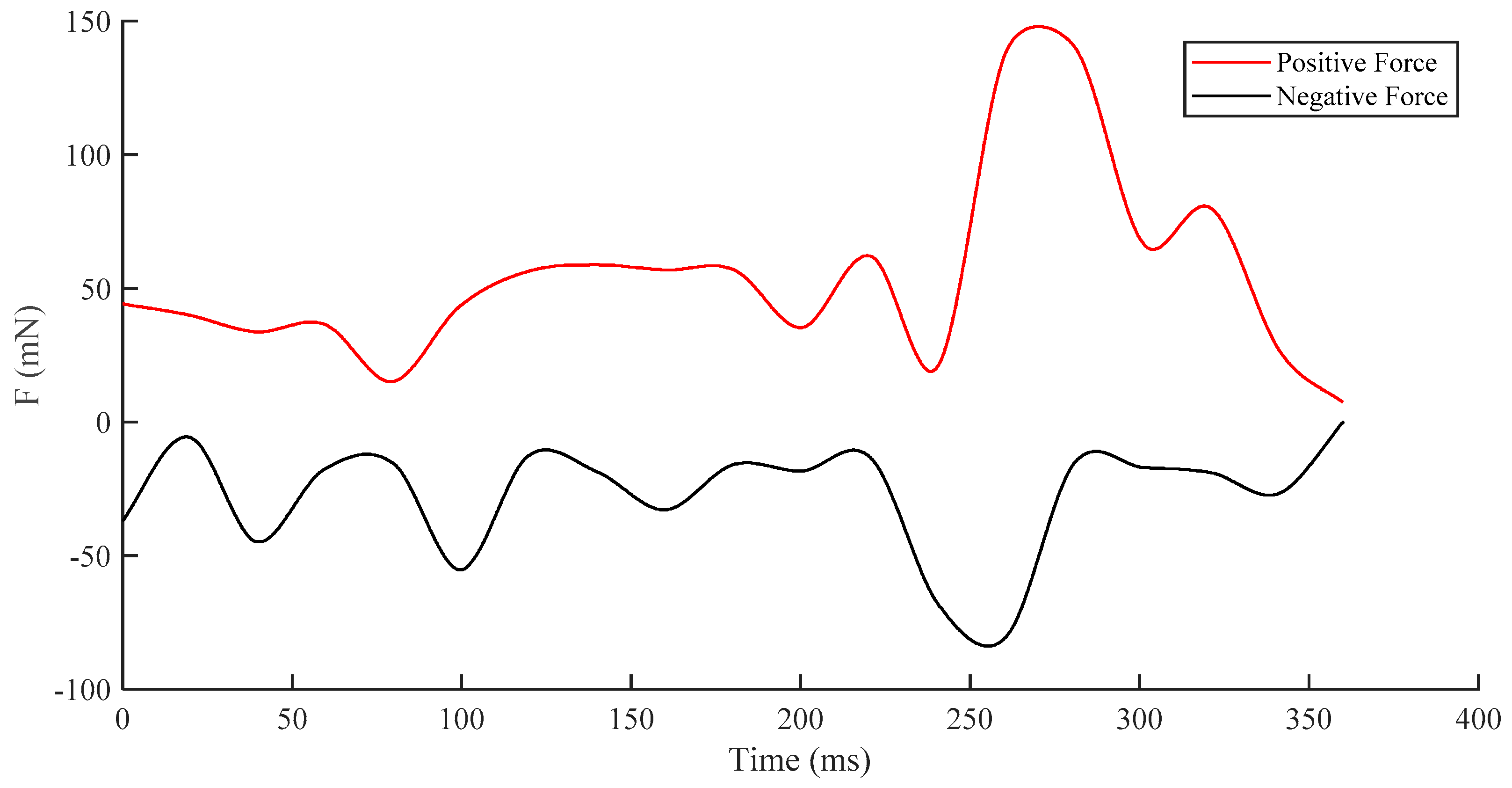
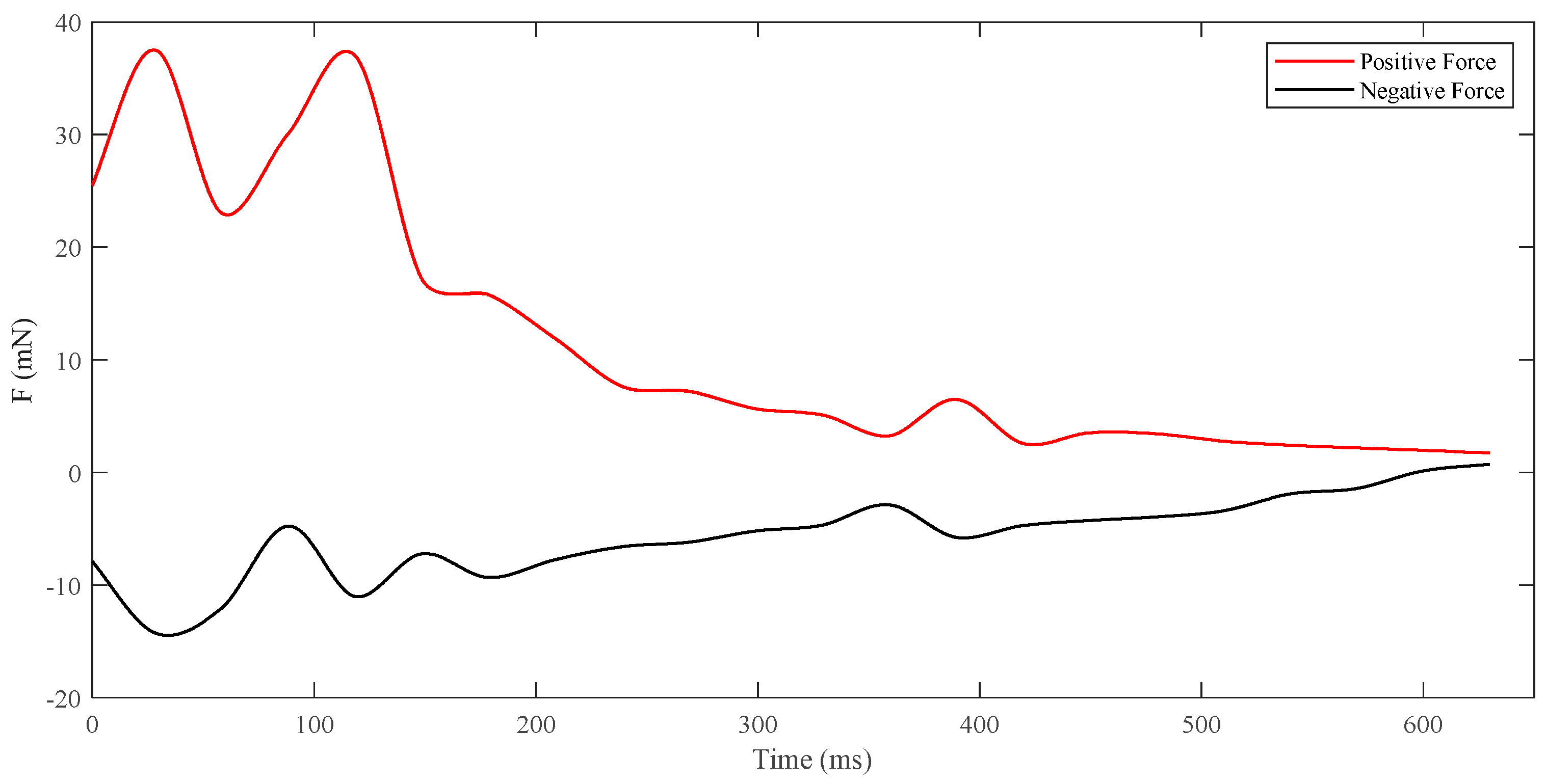
3.3. Dynamic Characteristics under Different States
- (1)
- Forward Swimming Condition
- (2)
- Turning State
- (3)
- Burst-and-coast State
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Kinematics of Goldfish under Different States
4.2. Variation of Vorticity around the Tail of Juvenile Fish under Different States
4.3. Dynamic Characteristics of the Tail of Juvenile Fish under Different States
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deen, N.G.; Westerweel, J.; Delnoij, E. Two-Phase PIV in Bubbly Flows: Status and Trends. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2002, 25, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, M.; Willert, C.; Kompenhans, J. Particle Image Velocimetry: A Practical Guide; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nauen, J.C.; Lauder, G.V. Quantification of the wake of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) using three-dimensional stereoscopic digital particle image velocimetry. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihs, D. A Hydrodynamical Analysis of Fish Turning Manoeuvres. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1972, 182, 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgang, M.J.; Anderson, J.M.; Grosenbaugh, M.A.; Yue, D.K.P.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Near-body flow dynamics in swimming fish. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 2303–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllou, M.S.; Triantafyllou, G.S.; Yue, D.K.P. Hydrodynamics of Fishlike Swimming. Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 2000, 32, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, G.; Lim, J.; Shelton, R.; Witt, C.; Anderson, E.; Tangorra, J. Robotic Models for Studying Undulatory Locomotion in Fishes. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2011, 45, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.H. Unsteady Mechanisms of Force Generation in Aquatic and Aerial Locomotion1. Am. Zool. 2015, 36, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskur, P. Side Fins Performance in Biomimetic Unmanned Underwater Vehicle. Energies 2022, 15, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytell, E.D.; Lauder, G.V. The hydrodynamics of eel swimming: I. Wake structure. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1825–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaffo, V.; Zhang, P.; Romero Cruz, S.; Porfiri, M. Zebrafish swimming in the flow: A particle image velocimetry study. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, G.V. Function of the Caudal Fin During Locomotion in Fishes: Kinematics, Flow Visualization, and Evolutionary Patterns1. Am. Zool. 2015, 40, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, J.; Lauder, G. Hydrodynamics of caudal fin locomotion by chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus (Scombridae). J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytell, E.D.; Lauder, G.V. Hydrodynamics of the escape response in bluegill sunfish, Lepomis macrochirus. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, Y.J. Research on Flow Field Characteristics of Oscillating Caudal Finbased on DPIV Technology. Master’s Thesis, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.X.; Yi, X.Z. The kinematic analysis of C-start in crucian carp (Carassius auratus). J. Exp. Mech. 2004, 19, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.F.; Jia, L.B.; Yi, X.Z. The kinematic analysis of S-start of Zebra danio (Danio rerio). J. Exp. Mech. 2007, 22, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.J.; Hu, X.; Shi, X.T.; Zhang, Y.N. Analysis on the pressure field characteristics of Schizopygopsis younghusbandi Regan tail swinging based on PIV. J. Exp. Mech. 2019, 34, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Hu, X.; Yu, Y.J.; Hong, L. Study on mechanical characteristics of grass carp juveniles based on vortocity method. J. Exp. Mech. 2020, 35, 915–924. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lan, C.A.; Yi, X.Z.; Xing, X.Z. Dynamic analysis on c-start swimming of fish-like robot. J. Harbin Ins. Techno. 2009, 41, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hanke, W.; Bleckmann, H. The hydrodynamic trails of Lepomis gibbosus (Centrarchidae), Colomesus psittacus (Tetraodontidae) and Thysochromis ansorgii (Cichlidae) investigated with scanning particle image velocimetry. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieskotten, S.; Dehnhardt, G.; Mauck, B.; Miersch, L.; Hanke, W. Hydrodynamic determination of the moving direction of an artificial fin by a harbour seal (Phoca vitulina). J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Tan, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X. Can age-0 Silver Carp cross laboratory waterfalls by leaping? Limnologica 2018, 69, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.B. Application and Development of PlV. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2019, 48, 115+119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dring, R.P. Sizing Criteria for Laser Anemometry Particles. J. Fluids Eng. 1982, 104, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hu, X.; Yang, G.D.; Long, Z.Y.; Huang, H.L.; Shi, X.T. Hydrodynamics of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) in steady swimming based on pressure field. J. Hydro Eng. 2021, 40, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, K.N.; Dabiri, J.O.; Lauder, G.V. A pressure-based force and torque prediction technique for the study of fish-like swimming. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielicke, W.; Stamhuis, E.J. PIVlab—Towards User-friendly, Affordable and Accurate Digital Particle Image Velocimetry in MATLAB. J. Open Res. Softw. 2014, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaans, R.J.M. Cross-Correlation PIV: Theory, Implementation, and Accuracy. J. Vis. 1993, 6, 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, S.M. PIV algorithms for open-channel turbulence research: Accuracy, resolution and limitations. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2011, 5, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noca, F.; Shiels, D.; Jeon, D. A Comparison of Methods for Evaluating Time-Dependent Fluid Dynamic Forces on Bodies, Using Only Velocity Fields and Their Derivatives. J. Fluid. Struct. 1999, 13, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, N.; Chen, Q. Particle image velocimetry measurement of indoor airflow field: A review of the technologies and applications. Energy Build. 2014, 69, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharnowski, S.; Kähler, C.J. Particle image velocimetry—Classical operating rules from today’s perspective. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 135, 106185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, F.; Riethmuller, M.L. Iterative multigrid approach in PIV image processing with discrete window offset. Exp. Fluids 1999, 26, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakiotakis, M.; Lane, D.M.; Davies, J.B.C. Review of fish swimming modes for aquatic locomotion. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 1999, 24, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, C.C. 1—Form, Function, and Locomotory Habits in Fish. In Fish Physiology; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978; Volume 7, pp. 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri, J.O.; Colin, S.P.; Katija, K.; Costello, J.H. A wake-based correlate of swimming performance and foraging behavior in seven co-occurring jellyfish species. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.D.; Hu, X.; Zhang, B.; Long, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Shi, X.T. Analysis of hydrodynamic characteristics of grass carpCtenopharyngodonidellus juveniles under free-swimming status basedon Particle lmage Velocimetry (PlV). J. Dalian. Ocean. Univ. 2021, 36, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.W.; Mcdonald, A.T.; Pritchard, P.J. Fox and McDonald’s Introduction to Fluid Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine, E.; Lentink, D.; Kranenbarg, S.; Müller, U.K.; van Leeuwen, J.L.; Barr, A.H.; Burdick, J.W. Automated visual tracking for studying the ontogeny of zebrafish swimming. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanyeti, O.; Liao, J.C. A kinematic model of Kármán gaiting in rainbow trout. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 4666–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandiackal, R.; Lauder, G.V. How zebrafish turn: Analysis of pressure force dynamics and mechanical work. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb223230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, O.H.; Ortega-Jiménez, V.M.; Sanford, C.P. Knifefish turning control and hydrodynamics during forward swimming. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb243498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Lauder, G.V. Function of The Heterocercal Tail In White Sturgeon: Flow Visualization During Steady Swimming And Vertical Maneuvering. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 3585–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, E.G.; Lauder, G.V. Wake Dynamics and Fluid Forces of Turning Maneuvers in Sunfish. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videler, J.J.; Müller, U.K.; Stamhuis, E.J. Aquatic vertebrate locomotion: Wakes from body waves. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanyeti, O.; Putney, J.; Yanagitsuru, Y.R.; Lauder, G.V.; Stewart, W.J.; Liao, J.C. Accelerating fishes increase propulsive efficiency by modulating vortex ring geometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13828–13833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, E.G.; Lauder, G.V. Experimental Hydrodynamics of Fish Locomotion: Functional Insights from Wake Visualization. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytell, E.D.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Williams, T.L.; Cohen, A.H.; Fauci, L.J. Interactions between internal forces, body stiffness, and fluid environment in a neuromechanical model of lamprey swimming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19832–19837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videler, J.J.; Hess, F. Fast Continuous Swimming of Two Pelagic Predators, Saithe (Pollachius Virens) and Mackerel (Scomber Scombrus): A Kinematic Analysis. J. Exp. Biol. 1984, 109, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.J. Study on the Mechanical Characteristics of Juvenile Grass Carp Tail Swinging Based-on Particle Image Velocimetry Techology. Master’s Thesis, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Flow Physics of Freely Routine Swimming of Koi carp. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hanke, W.; Brücker, C.; Bleckmann, H. The Ageing of the Low-Frequency Water Disturbances Caused by Swimming Goldfish and Its Possible Relevance to Prey Detection. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Z.; Zhu, L.; Luo, X.W. Investigation of the Flow Around a C-start Swimming Goldfish Using PlV. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2019, 40, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, R.C.; DiDomenico, R.; Nissanov, J. Flexible body dynamics of the goldfish C-start: Implications for reticulospinal command mechanisms. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2758–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Takagi, T.; Mitsunaga, Y.; Torisawa, S. Hydrodynamical effect of parallelly swimming fish using computational fluid dynamics method. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Gu, X.; Li, K.; Jiang, H. CFD Studies of the Effects of Waveform on Swimming Performance of Carangiform Fish. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Jing, D.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Kong, X. Comparison Study of Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Different Swimming Modes of Carassius auratus. Fishes 2024, 9, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090365
Zhang Y, Jing D, Huang X, Chen X, Liu B, Kong X. Comparison Study of Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Different Swimming Modes of Carassius auratus. Fishes. 2024; 9(9):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090365
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Di Jing, Xiaoshuang Huang, Xinjun Chen, Bilin Liu, and Xianghong Kong. 2024. "Comparison Study of Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Different Swimming Modes of Carassius auratus" Fishes 9, no. 9: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090365
APA StyleZhang, Y., Jing, D., Huang, X., Chen, X., Liu, B., & Kong, X. (2024). Comparison Study of Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Different Swimming Modes of Carassius auratus. Fishes, 9(9), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090365






