Analysis of Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of (Fe,Co) Co-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized under UV Light
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation
3. Characterization Techniques
4. Results
4.1. Structural Studies
4.2. Optical Properties
4.2.1. Absorption
4.2.2. Band Gap
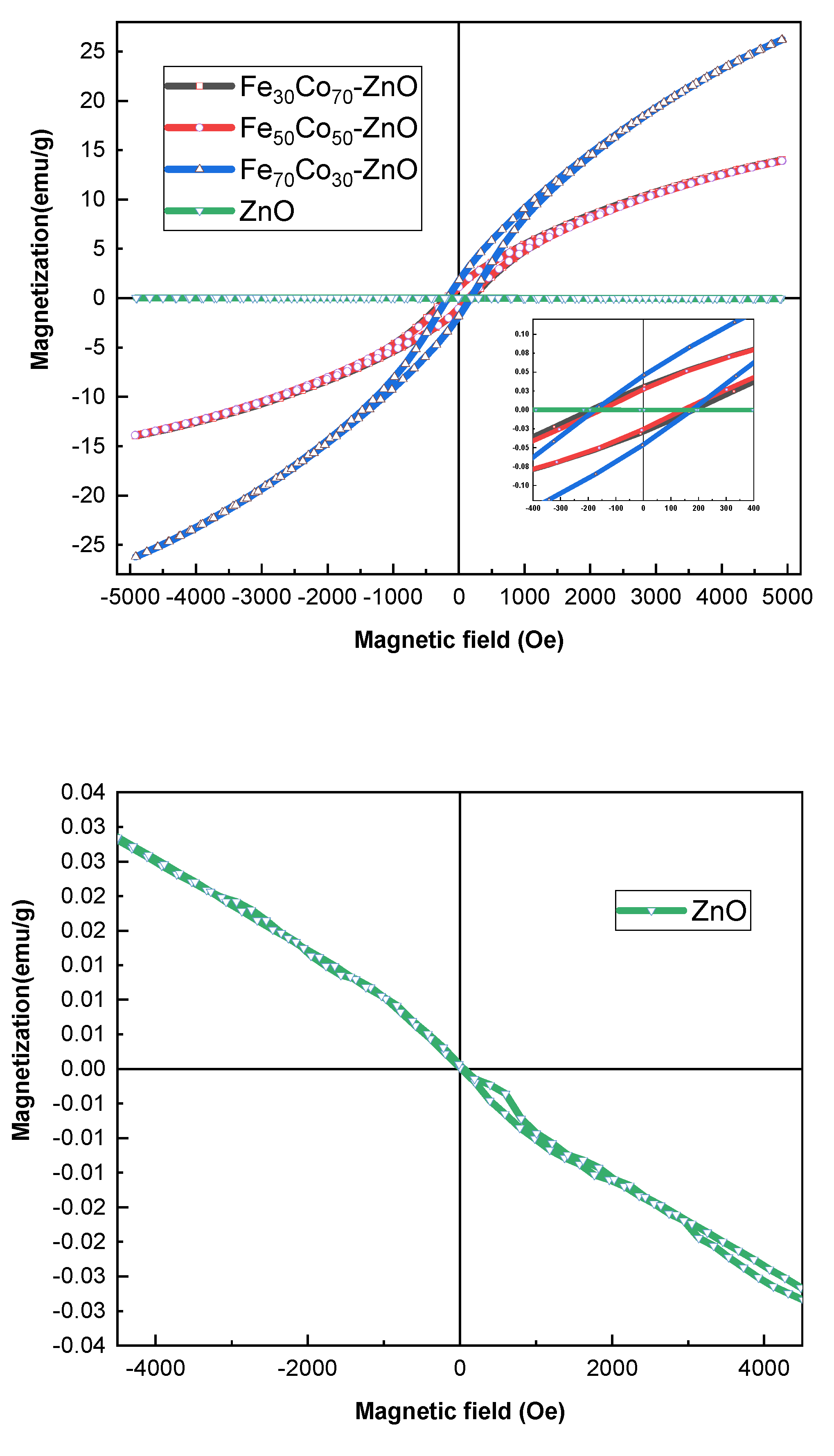
4.2.3. Magnetic Properties
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakraborty, D.; Gayen, R.; Hussain, S.; Bhar, R.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Pal, A.K. ZnO/Ti Thin Film: Synthesis, Characterization and Methane Gas Sensing Property. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 390, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, D.; Yin, G.; Huang, Z.; Li, L.; Liao, X.; Chen, X.; Yao, Y.; Hao, B. Cellular Compatibility of Biomineralized ZnO Nanoparticles Based on Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Systems. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13206–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Pan, L.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, T.; Zhu, G.; Chen, T.; Lu, T.; Sun, Z.; Sun, C. UV-assisted photocatalytic synthesis of ZnO–reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity in reduction of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 183, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Xiao, L.; Gong, F.; Luo, M.; Wang, F.; Jia, Y.; Chang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; et al. Light-Driven WSe2 -ZnO Junction Field-Effect Transistors for High-Performance Photodetection. Adv. Sci. 2019, 7, 1901637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Al-Dossary, O.; Kumar, G.; Umar, A. Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for NO2 Gas–Sensor Applications: A Review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 7, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kang, B.-H.; Jeong, H.-M.; Kim, S.-W.; Xu, B.; Kang, S.-W. Quantum dot light emitting diodes using size-controlled ZnO NPs. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, H.; Benzarti, Z.; Rhouma, F.I.H.; Sanguino, P.; Guermazi, S.; Khirouni, K.; Vieira, M.T. Enhancing the electrical and dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles through Fe doping for electric storage applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 1536–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Das, D. Investigation on Fe-doped ZnO nanostructures prepared by a chemical route. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 171, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.L.; Abuçafy, M.P.; Manaia, E.B.; Junior, J.A.O.; Chiari-Andréo, B.G.; Pietro, R.C.R.; Chiavacci, L.A. Relationship Between Structure And Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: An Overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9395–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, R.S.C. Nanaostructured ZnO, ZnO-TiO2 And ZnO-Nb2O5 As Solid State Humidity Sensor. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2012, 3, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J.J.; Barrero, C.A.; Punnoose, A. Understanding the role of iron in the magnetism of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 15284–15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Damonte, L. Study of Co and Fe-doped ZnO milled nanopowders. Powder Technol. 2015, 286, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Cui, Y.; Wan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. MOF-derived magnetic-dielectric balanced Co@ZnO@N-doped carbon composite materials for strong microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 190, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerdj, I.; Jagličić, Z.; Arčon, D.; Niederberger, M. Co-Doped ZnO nanoparticles: Minireview. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowicz, J.; Chudoba, T.; Majcher, A.; Łojkowski, W. 12. Microwaves applied to hydrothermal synthesis of nanoparticles. In Microwave Chemistry; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivill, M.; Pearton, S.J.; Rawal, S.; Leu, L.; Sadik, P.; Das, R.; Hebard, A.F.; Chisholm, M.; Budai, J.D.; Norton, D.P. Structure and magnetism of cobalt-doped ZnO thin films. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowicz, J.; Chudoba, T.; Gierlotka, S.; Sobczak, K.; Lojkowski, W. Size Control of Cobalt-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Obtained in Microwave Solvothermal Synthesis. Crystals 2018, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kafle, B.; Acharya, S.; Thapa, S.; Poudel, S. Structural and optical properties of Fe-doped ZnO transparent thin films. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasulu, T.; Saritha, K.; Reddy, K.R. Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped ZnO thin films deposited by chemical spray pyrolysis. Mod. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, J. Preparation and Characterization of (Al, Fe) Codoped ZnO Films Prepared by Sol–Gel. Coatings 2021, 11, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, H.; Benzarti, Z.; Sanguino, P.; Hadouch, Y.; Mezzane, D.; Khirouni, K.; Abdelmoula, N.; Khemakhem, H. Improving the optical, electrical and dielectric characteristics of ZnO nanoparticles through (Fe + Al) addition for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghoul, J.; Kraini, M.; El Mir, L. Synthesis of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles by Sol-gel method and its characterization. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, G.-H.; Dang, Z.-M. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanorods prepared by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 576, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J.J.; Osorio, J.; Barrero, C.A.; Hanna, C.; Punnoose, A. Magnetic properties of Fe doped, Co doped, and Fe+Co co-doped ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17C308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romeiro, F.C.; Marinho, J.Z.; Lemos, S.C.; de Moura, A.P.; Freire, P.G.; da Silva, L.F.; Longo, E.; Munoz, R.A.; Lima, R.C. Rapid synthesis of Co, Ni co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Optical and electrochemical properties. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 230, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, C.; Ren, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X.; Pan, C. Present Perspectives of Advanced Characterization Techniques in TiO2-Based Photocatalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23265–23286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafle, B.P. Introduction to nanomaterials and application of UV-Visible spectroscopy for their characterization. Chem. Anal. Mater. Charact. Spectrophotom. 2019, 147–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklein, A.; Multian, V.; Kuz’Micheva, G.; Linnik, R.; Lisnyak, V.; Popov, A.; Gayvoronsky, V.Y. Nonlinear optical response of bulk ZnO crystals with different content of intrinsic defects. Opt. Mater. 2018, 84, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskaleva, A.; Blagoev, B.S.; Terziyska, P.T.; Mehandzhiev, V.; Tzvetkov, P.; Kovacheva, D.; Avramova, I.; Spassov, D.; Ivanova, T.; Gesheva, K. Structural, morphological and optical properties of atomic layer deposited transition metal (Co, Ni or Fe)- doped ZnO layers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 7162–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekar, G.; Singaevsky, A.; Kolomys, O.; Strelchuk, V.; Lytvyn, P.; Osipyonok, M.; Vasin, I.; Skoryk, M. Magnetic and optical properties of printed ZnO:Co polycrystalline layers. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 135, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doğan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.P.P.; Hudiara, I.S.; Panday, S.; Rana, S.B. Effect of Ni Doping on Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Fe-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2015, 28, 3685–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Li, Y.; Li, W.-X.; Yu, Z.-R.; Li, J.-M.; Hu, Y.-M.; Zhu, M.-Y.; Jin, H.-M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.-B.; et al. Structural, ferromagnetic, and optical properties of Fe and Al co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles synthesized under high magnetic field. Adv. Manuf. 2019, 7, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumal, B.; Protasova, S.G.; Mazilkin, A.A.; Tietze, T.; Goering, E.; Schütz, G.; Straumal, P.; Baretzky, B. Ferromagnetic behaviour of Fe-doped ZnO nanograined films. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.M.; Thakur, P.K.; Tanemura, M.; Hihara, T.; Ganesan, V.; Soga, T.; Chae, K.H.; Jayavel, R.; Jimbo, T. Intrinsic ferromagnetism and magnetic anisotropy in Gd-doped ZnO thin films synthesized by pulsed spray pyrolysis method. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 053904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | Type of Nanostructure | Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe-doped ZnO | Spin coating | [18] |
| 2 | Fe-doped ZnO | Chemical spray pyrolysis | [19] |
| 3 | (Al, Fe) co-doped ZnO | Sol-gel method | [20] |
| 4 | (Al, Fe) co-doped ZnO | Co-precipitation process | [21] |
| 5 | Co-doped ZnO | Pulsed-laser deposition (PLD) | [16] |
| 6 | Fe- and Co-doped ZnO | Mechanical milling | [12] |
| 7 | Co-doped ZnO | Sol-gel method | [22] |
| 8 | Co-doped ZnO | Hydrothermal method | [23] |
| 9 | Fe- and Co-doped ZnO | Sol-gel method | [24] |
| 10 | Fe- and Co-doped ZnO | Ultrasonication probe under UV radiation | This work |
| Samples | Grain Size (nm) | a = b (Å) | c (Å) | c/a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 21.4 ± 0.3 | 3.2299 | 5.1789 | 1.6034 |
| (Fe30Co70)ZnO | 25.2 ± 0.8 | 3.2365 | 5.1991 | 1.6064 |
| (Fe50Co50) ZnO | 24.2 ± 0.5 | 3.2353 | 5.1893 | 1.6039 |
| (Fe70Co30) ZnO | 23.5 ± 0.1 | 3.2355 | 5.1842 | 1.6023 |
| Urbach Energy (eV) | Band Gap (eV) | Absorption Wavelength (nm) | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.319 | 3.221 | 385.1 | ZnO |
| 0.095 | 3.293 | 376.9 | Fe30Co70ZnO |
| 0.1757 | 3.230 | 383.9 | Fe50Co50ZnO |
| 0.922 | 3.131 | 396.2 | Fe70Co30ZnO |
| Sample | Hc (Oe) | Mr (emu/g) | Ms (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 20.98 | 3.06 × 10−4 | 3.43 × 10−2 |
| (Fe30Co70)ZnO | 137.71 | 1.24 | 14 |
| (Fe50Co50)ZnO | 140.01 | 1.12 | 13.92 |
| (Fe70Co30)ZnO | 151.25 | 1.80 | 26.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madkhali, N. Analysis of Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of (Fe,Co) Co-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized under UV Light. Condens. Matter 2022, 7, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7040063
Madkhali N. Analysis of Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of (Fe,Co) Co-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized under UV Light. Condensed Matter. 2022; 7(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadkhali, Nawal. 2022. "Analysis of Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of (Fe,Co) Co-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized under UV Light" Condensed Matter 7, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7040063
APA StyleMadkhali, N. (2022). Analysis of Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of (Fe,Co) Co-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized under UV Light. Condensed Matter, 7(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7040063






