Abstract
Nasoalveolar molding of the cleft lip, nose, and alveolar palate has been a successful strategy for the restoration of oronasal function and appearance, but it has some drawbacks. The temporary implant that is inserted before surgical reconstruction is a large appliance requiring numerous adjustments, it can irritate delicate soft tissues, and interfere with the infant’s ability to nurse or feed. In the early post-operative period and for months after cleft lip repair, patients wear standardized silicone stents that come in multiple sizes, but require significant sculpting to fit the unique cleft deformity. Three-dimensional (3D) printing offers the potential of highly personalized and patient-specific treatment. We developed a method that produces a customized 3D printed stent that matches the contours and unique features of each patient and permits modification and adjustments in size and shape as the patient ages. With 3D scanning technology, the device can be designed at the first visit to create an appliance that can be worn sequentially with minimal trauma, does not impede feeding, and a prosthesis that will improve compliance. The device will be worn intraorally to help shape the alveolus, lip, and nose before surgical repair. Furthermore, the stent can be doped with drugs as each patient’s case warrants.
1. Introduction
Recent advances in biofabrication and bioprinting (e.g., microcontact printing, inkjet printing, and three-dimensional (3D) printing) are enabling anywhere on-demand and patient-specific medical treatment [1,2,3]. Developed in the early 1990’s by Sachs et al., 3D printing technology was originally developed as a powder-based fabrication method for quick tool design and production using ceramics and various metals [4,5]. The standard typical printing operation produces a 3D model that is based on a digital file through a layer-by-layer process that has the potential of producing almost any shape, internal geometry or external architecture [6,7]. 3D printing is most well-known for creating plastic prototypes, objects, and structures, rapidly, cheaply, and with a high degree of accuracy. Developments over the last ten years have shown that 3D printing has found its place in medicine, bio-, and nanotechnology, thus paving the way for the rapid printing of medicine, artificial devices and prosthetics, and even human tissue [8,9,10]. Currently, there is an intense research effort focused on the application of 3D printing and bioprinting for the development of blood vessels [8,9,10], bioengineered tissues [11,12], and the production of functional biomedical materials and devices for dental and orthopedic applications [13,14,15,16]. The advantages offered by 3D printing include fast and accurate fabrication of structures with complex 3D features, high reproducibility, ease of manufacture, and the ability to produce customized medical devices [6,7,16].
Cleft lip and palate (CLP) is the second most common congenital birth defect in the United States (U.S.), trailing only the incidence of Down syndrome [17,18,19]. It is estimated that nearly 7000 infants are born with orofacial clefts in the U.S. annually [17]. During early facial development, body tissues and special cells (neural crest cells) from each side of the head grow toward the center of the face and unite together to form our facial features, lips, nose, and mouth, etc. [17,18,19,20]. Congenital defects result when the baby’s lip or mouth do not form properly during pregnancy. Cleft lip (CL), cleft lip and palate (CLP), and the rare cleft palate (CP) are separate clinical defects and are among the most common congenital birth defects of the head and face [18,20,21]. A baby can have a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both a cleft lip and cleft palate. When a cleft lip is present, there is a separation or a space within the upper lip, which can vary from a subtle notch or groove to a wide gap [21,22,23]. This separation can also involve the roof of the mouth or palate [21]. A CL occurs when the tissue of the future lip does not unite completely before birth resulting in an opening in the upper lip that varies in size and severity. CLs can be unilateral or bilateral and often children with a CL also can have a CP wherein the roof of the mouth does not fuse completely [20,22,24]. CLP is also associated with significant psychological and socioeconomic effects on the patient and family, including a decreased quality of life [25,26]. It is also associated with increased mortality from many causes, including suicide [21], as well as substantial patient healthcare costs [22].
Pre-surgical orthopedic treatments are often used as a means for guiding future surgical repair and refer to all the techniques prior to the cleft lip repair [18,19,20,27]. These include parental finger massage of the prolabium, tape pressure on the labial segments, intraoral device fixation, or nasoalveolar molding [24,27]. However, due to the use of treatment modalities, timing of intervention, and the lack of normative data and long-term clinical studies, there is some controversy regarding the use of pre-surgical orthopedics [23]. Despite this, the use of pre-surgical orthopedics is widely employed in cleft lip/palate therapy designed to promote improved surgical and esthetic results.
Nasoalveolar molding (NAM) of the cleft lip, nose, and alveolar palate for the restoration of function has been a successful pre-surgical treatment strategy, but it has some drawbacks [23,24]. The removable appliance (RA) inserted before surgical reconstruction is a large and bulky appliance. It typically requires numerous adjustments that irritate delicate soft tissues and can interfere with the infant’s ability to nurse or feed. During the early post-operative period, and for months after CL repair, patients wear prefabricated and standardized silicone stents that do not directly address the child’s unique cleft deformity.
Fused depositional modeling (FDM) has seen a significant increase in its use in the fabrication of biomedical applications [25,26]. The most commonly used biocompatible materials that are used for implantable constructs include polylactic acid (PLA), polyglycolic acid (PGLA), polycaprolactone (PCL), and blends of polyethylene glycol (PEG). These are being as blends and in composites to produce new and innovative biomedical devices, including prosthetics [28,29], implants [14,15,30], and scaffolding for regenerative medicine [30,31,32]. 3D printing offers the potential for a more customized and patient-specific treatment [33].
Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polyester with a low melting point of around 60 °C, and has received a great deal of attention for use as an implantable biomaterial and as a long term implantable device, owing to its rate of degradation [25]. Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic that is derived from renewable resources, such as cornstarch, tapioca roots, or sugarcane and is widely employed in various biomedical devices [26]. We used these thermoplastics in developing a novel three-dimensional (3D) printing method designed for infection prophylaxis, cancer remediation, and disease prevention [14,15,16]. This method enables the printing of a single bead, or beads within a string, as disks in filament forms, catheters, medical mesh, or other desired shapes [14,15].
We applied this method for the design of a personalized solution for CL/CLP patients. In our design, emphasis was placed on developing a construct that matches the contour and unique features of the cleft patient and permits modification and adjustments in size and contour as the patient ages. The construct would be worn intraorally to help shape the alveolus with an external membrane to shape the lip and nose prior to surgical repair. The construct would have two forms, a porous or mesh form, composed of multiple polymers in layers, and whose properties can be mechanically enhanced or made bioactive through the inclusion of drugs or other bioactive substances.
We used a method to scan or manually render nasal stents into computer-aided design files, and we used solid works to fabricate a wide range of hard and soft polymers including PLA, Flex-PLA, and PCL. Material characterization studies confirmed that specific single polymer filaments or blends could be fabricated with the desired material characteristics: conformability, easy to extrude with no clogging, printable into desired shapes and structures, and bioactive. A modular concept to print multiple materials into a single nasal stent of various designs was also demonstrated using a layered design concept. Nasal stents were printed with mesh and porous surfaces and anti-bacterial growth inhibition studies were used to show that filaments and stent constructs were bioactive as clear zones of bacterial inhibition in both as compared to the controls. Ultimately, this presentation demonstrates that it is possible to customize both physical and bioactive properties of nasal stents using 3D printing, and this proof of concept shows a novel area of future research in cleft surgery.
2. Materials
All of the treatment compounds used in this study were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The polylactic acid (PLA) pellets used for the printing media were obtained from NatureWorks, LLC (Minnetonka, MN, USA). For bacterial culture, E. coli vitroids Escherichia coli ATCC® 11775 Vitroids™ 1000 CFU and gentamicin sulfate (GS) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich, bacterial culture supplies 100 mm Mueller Hinton agar plates, and Mueller Hinton liquid broth 1 L were purchased from Fischer Scientific (Hampton, NH, USA). Petri dishes plates and other lab plastics were purchased from MidSci, St. Louis, MO, USA. KJLC 705 silicone oil was used as a base for coating the pellets before extrusion and was purchased from Kurt J. Lesker Company (Jefferson Hills, PA, USA). Our 3D printing system was comprised of an ExtrusionBot extruder (ExtrusionBot, LLC, Phoenix, AZ, USA) and a MakerBot 2X 3D printer (Brooklyn, NY, USA).
2.1. Polylactic Acid (PLA) Pellet Preparation
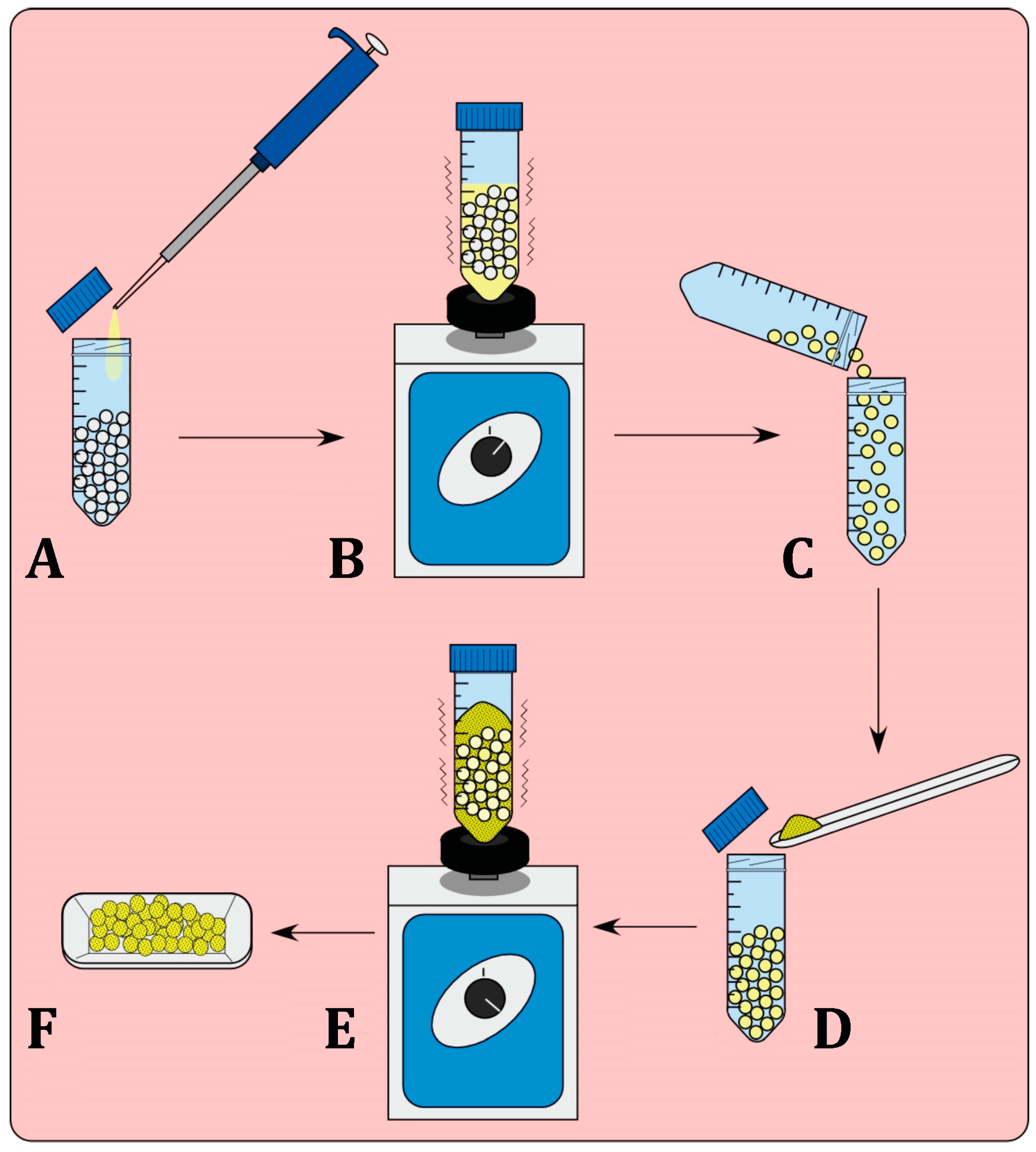
Batches of PLA pellets (20 g) were added to a 50-mL sterile plastic tube and KJLC 705 silicone oil (20 μL) was then added and the tube was vortexed to assure that the pellets were consistently coated. Pellets were removed and were placed in a new 50 mL sterile plastic tube to ensure minimal loss of the applied oil surface coating. To make a 1% or 2.5% coatings, respectively, 200 or 500 mg of GS was then added to the pellets and subsequently vortexed (Figure 1).
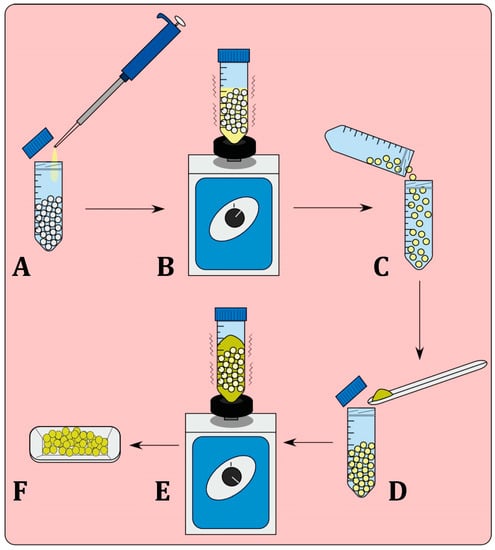
Figure 1.
Process of bead coating with bioactive additives. Pellets are first coated in the silicone oil (A) and vortexed (B) to ensure complete coating of the pellets. The pellets must be placed in a new container (C) as losses of additive material will occur on the surface of the container. Introduction of the additive (D) and the bead mixture is again vortexed (E), to allow for complete coating of the pellets, (F) Coated pellets.
2.2. Filament Extrusion
The ExtrusionBot filament extruder was used for filament creation. It consisted of a vertical column and a hopper that was directly connected to a melt chamber containing an auger housed within a heated pipe. The metal die used for extrusion point had a bore diameter of 1.75 mm. The extrusion temperature is adjusted through a control panel and the melt temperature used for PLA pellets was 170 °C, with slight variations in extrusion temperature depending on ambient temperature and humidity conditions. For the extrusion GS doped filaments, a temperature of 175 °C was used. We established in a previous study the stability of GS during the extrusion and printing processes [14,17].
2.3. 3D Printing
Once the filaments were extruded, 5 mm disks were 3D printed on the MakerBot 2X at 220 °C. Layer printing height was set to 300 µm resolution with a 100% fill. The SolidWorks computer software modeling program (Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Corporation Waltham, MA, USA) was used to design the 3D print files. The resulting generated STL file was used to dictate the construct dimensions to the printer through MakerWare (MakerBot® MakerWare™, 2.4.1, MakerBot, New York, NY, USA).
2.4. Imaging
A S4800 Field Emission Scanning Emission Microscope (SEM), HITACHI (Schaumburg, IL, USA) was used to image the filaments at 35×, 2 k×, and 15 k× magnifications. Bacterial plates and cultures were photodocumented using with a Canon ZR80 camera (Canon, Tokyo, Japan). For documentation of the growth inhibition zone that was obtained during the agar diffusion test, a caliper was used to measure the size of the inhibition field at three different locations for each filament or disc.
2.5. Bacterial Cultures
Samples were tested for antimicrobial activity using two methods, an agar diffusion assay and liquid nutrient broth test. Negative controls were also tested for antibiotic activity. A set of positive controls was used and included antibiotic powders. Plain PLA samples and heated antibiotic powders were used as negative controls. E. coli vitroids were used to raise bacterial colonies and one colony was picked to make the 0.5 McFarland standard bacterial suspensions.
3. Results
3.1. Scanning Emission Microscope (SEM) Analysis
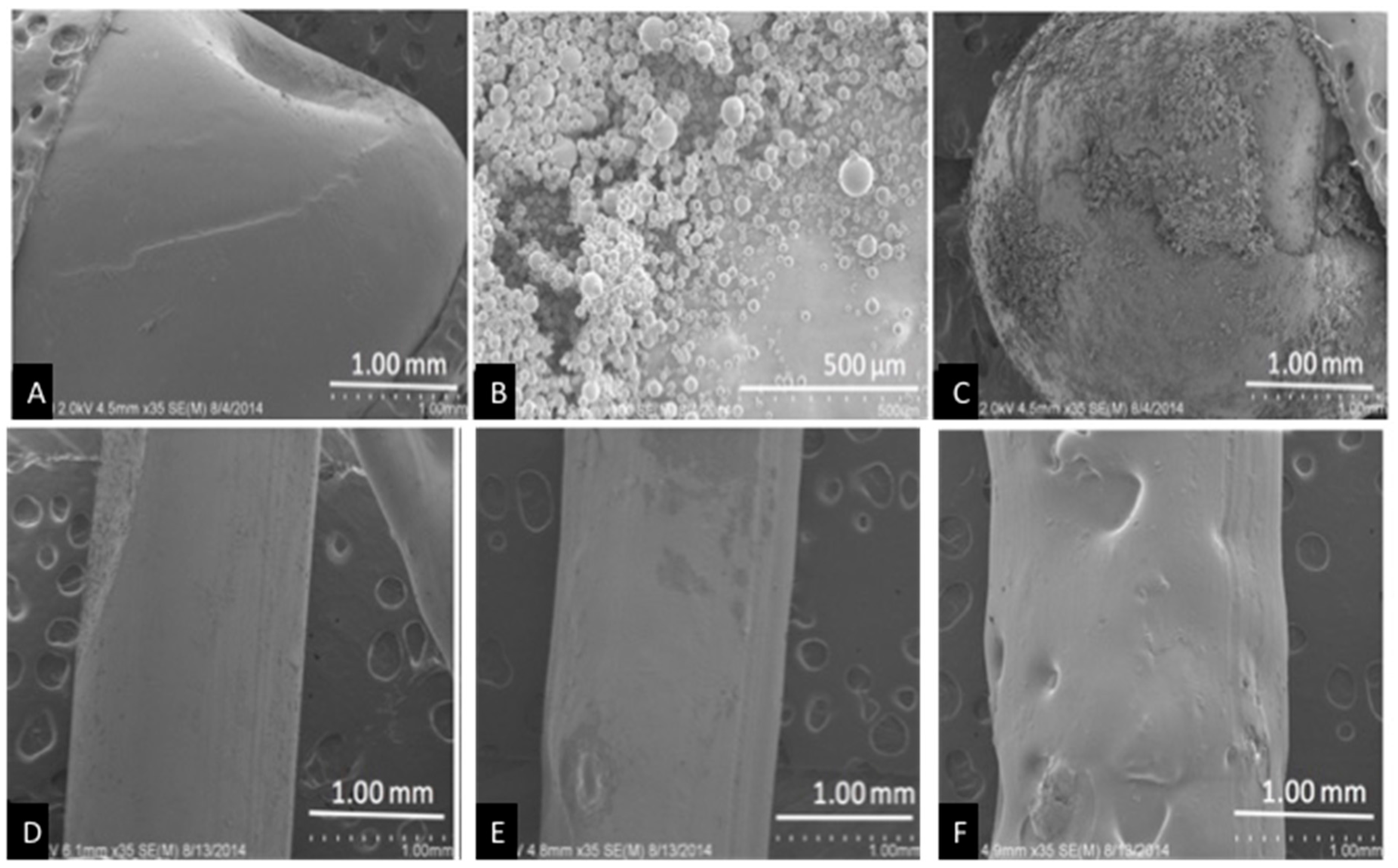
Control pellets had a smooth surface while coated beads showed a deposit of GS covering the bead surface (Figure 2A). The entire bead is not covered and this is most likely due to processing the bead for SEM (Figure 2C). The extruded control filament also has a smooth surface, while the GS extruded filaments had a rough surface (1% GS, Figure 2E) and increased GS addition produced a rough filament with pits and depressions observed across its surface (2.5% GS, Figure 2F).
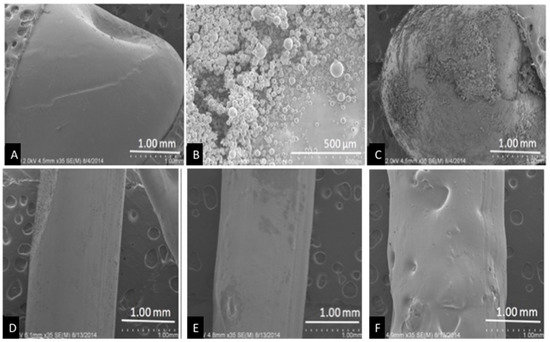
Figure 2.
SEM pellets and filaments. (A) Control pellet; (B) gentamicin sulfate (GS) powder; (C) 1 wt % GS-polylactic acid (PLA) pellet; (D) Control filament; (E) 1 wt % GS-PLA filament; and, (F) 5 wt % GS-PLA filament.
3.2. Device Fabrication
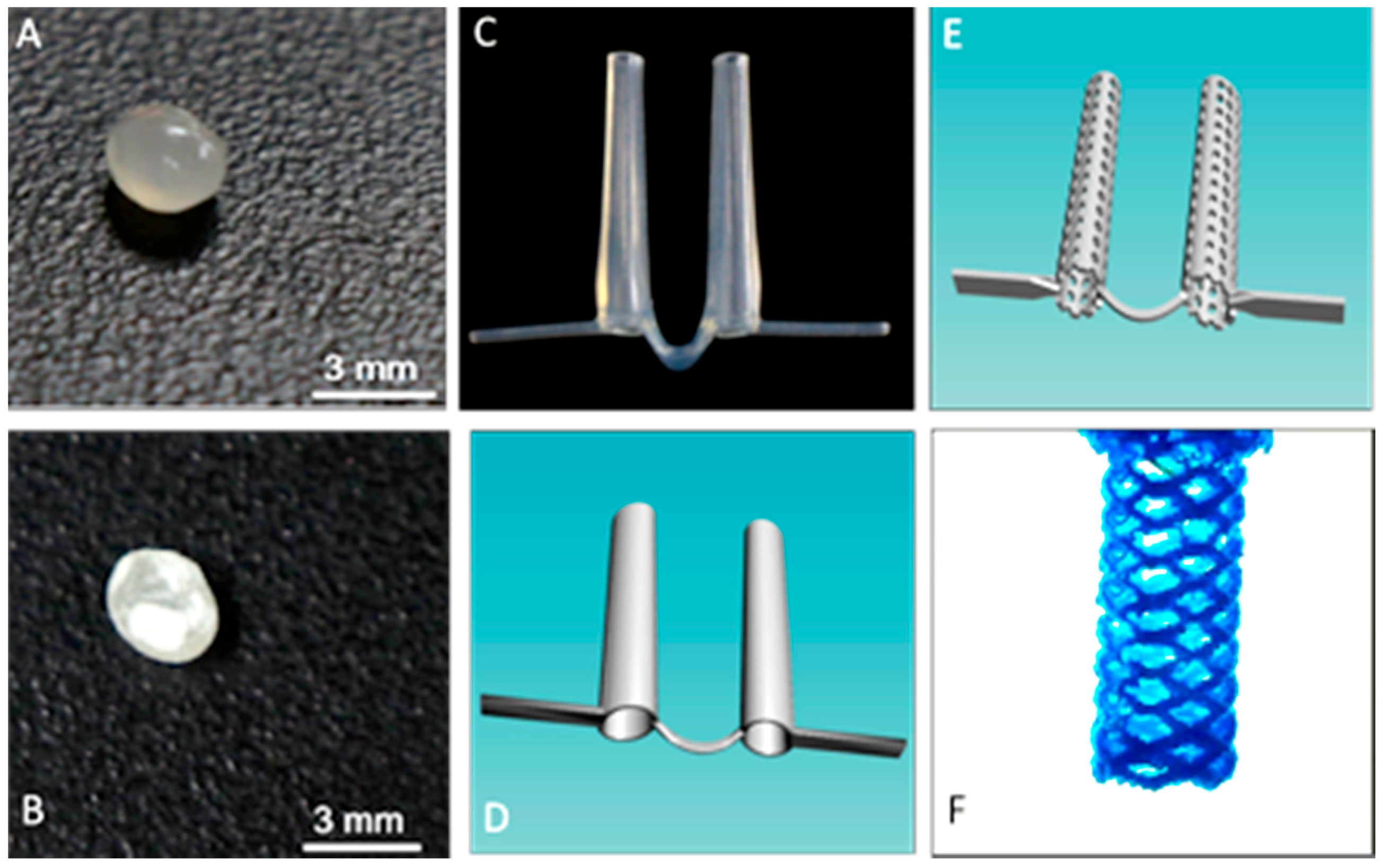
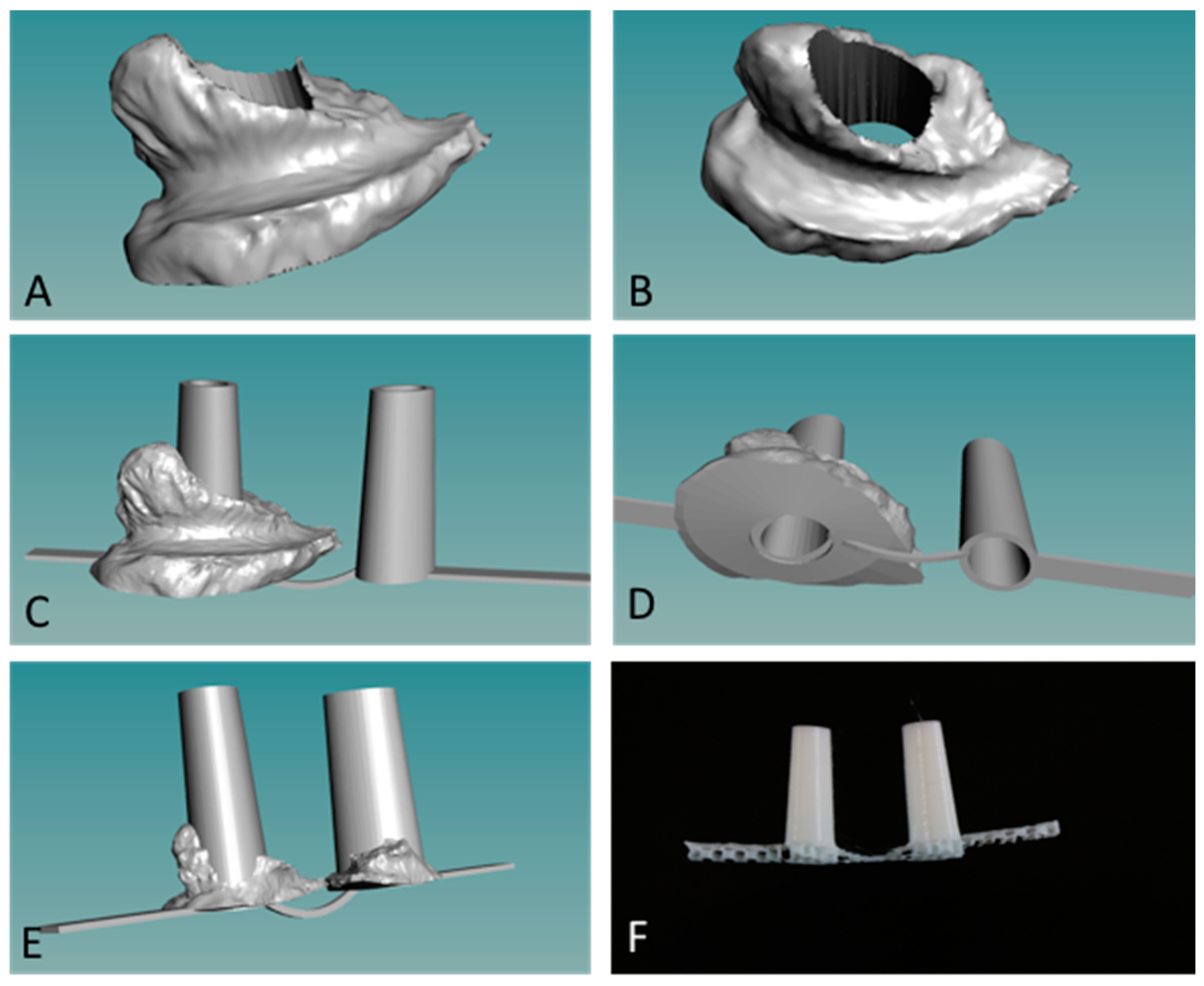
We used a novel powder bead formulation method in developing the custom polymers used with a new grade of biomedical extruder (see Figure 1) [14,16]. Customized powder-coated pellets are extruded to form the required filaments. The design process begins with 3D scanned images of the oral cleft/defect that is used as a guide to fabricate a hard and compliant, but inert material, replacing the soft medical grade silicone impression, thus eliminating the airway risk during silicone impression taking (Figure 3 and Figure 4). 3D scanned images of currently used stents (Figure 3C,D) can be taken and used to design the customized stent to be fabricated via 3D printing as either solid, porous, or mesh forms, and with different thermoplastics or polymer composites (Figure 3E,F). Further customization can be done using the 3D scanned CAD file and 3D scanned images of the oral cleft/defect (Figure 4A,B). The 3D nasal mold image can be rendered with the 3D scanned stent and the stent shaped into compliance using the CAD software (Figure 4C,D). Finally, using the final drawn stent as a guide, a 3D printed hard and compliant but inert material can be fabricated to replace the soft medical grade silicone impression currently used (Figure 4E,F).
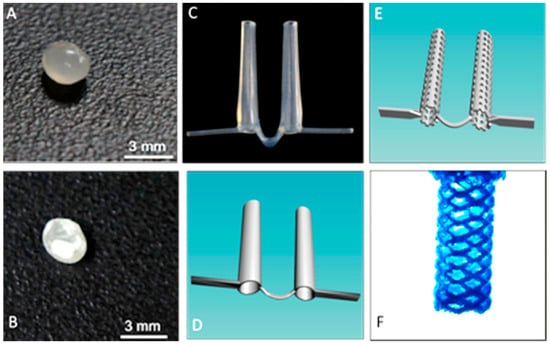
Figure 3.
Fabrication process for the production of customize stents. (A) Control PLA pellet; (B) GS coated PLA pellet; (C) picture of a currently used pre-fabricated stent; and, (D) pre-fabricated stent scanned into a digital template; (E) CAD designed porous stent; (F) CAD designed porous stent mesh framed stent.
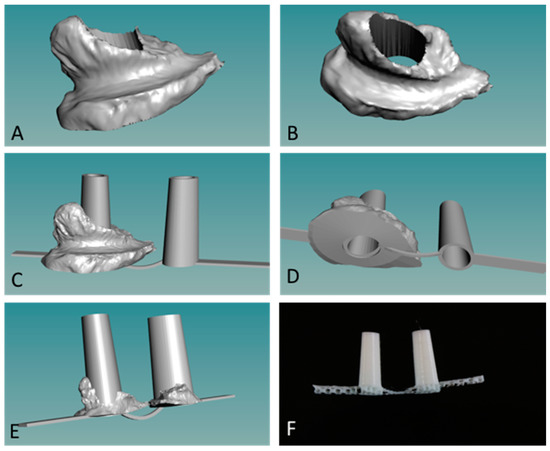
Figure 4.
Customization of nasal stents. (A,B) Images of 3D scanned nasal molds from subject X; (C,D) Scanned nasal mold is used as guide to render a CAD designed and compliant nasal stent; (E) 3D CAD image of customized stent; (F) three-dimensional (3D) printed and patient-specific stent. Smoothing before implantation is the final step.
3.3. Growth Inhibition Studies
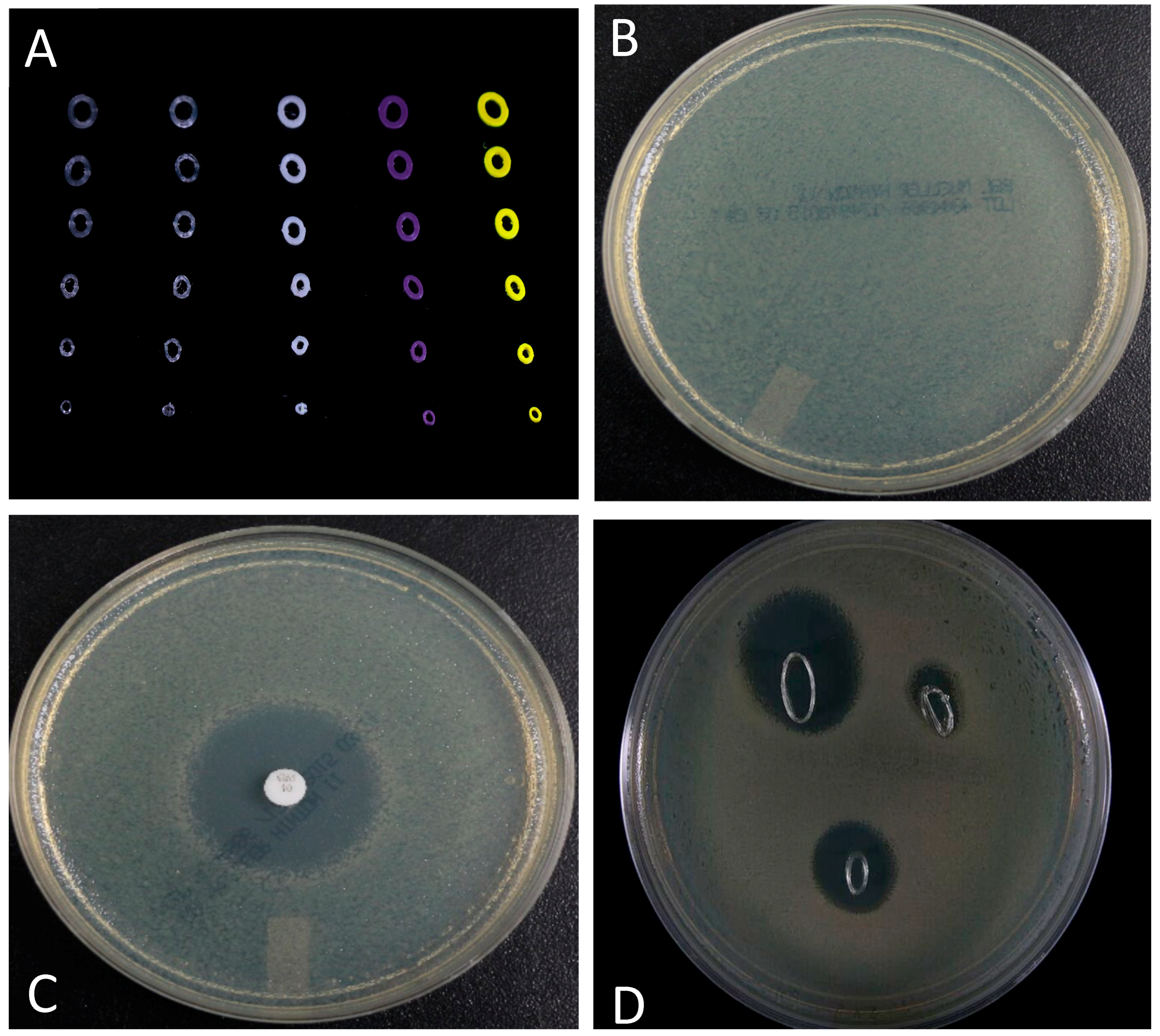
A pilot study designed to show that customized stents could also be fabricated with bioactive factors (e.g., antibiotics) showed promising results. Figure 4 shows the results of growth inhibition studies using cross-sectioned stents. Cross-section GS doped stents showed pronounced zones of inhibition that were comparable to a GS doped control disk (Figure 5C,D).
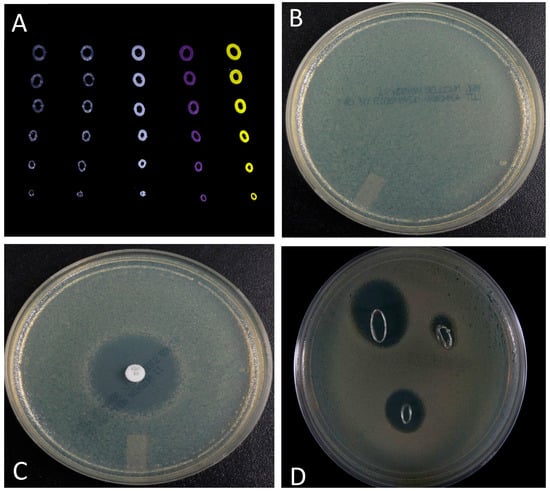
Figure 5.
Growth inhibition studies. (A) Image of different types of cross-sectioned nasal stents; (B) Confluent plate of cultured E. coli; (C). GS control disk showed a pronounced zone of inhibition; and, (D) Cross-sectioned GS doped nasal stents (varying in overall diameter) also showed pronounced zones of bacterial growth inhibition.
4. Discussion
Cleft lip/palate repair is a complicated surgical procedure as multiple anatomic structures are involved and whose altered form as presented can occur with varying severity [20,24,27]. Each case presents a new challenge to the surgeon as each patient presents a novel clinical condition: unilateral versus bilateral, narrow clefts versus wide clefts, and syndromic patients versus non-syndromic patients [33]. Reconstruction of normal form and function must also be unique to ensure a successful restoration of functional and cosmetic appearance [25]. In the immediate postoperative period, the goals of wound care include preventing infection and removing obstacles to epithelialization. Proper postoperative wound management after cleft lip closure is recognized as fundamental to repair [33]. Improper wound care can result in reduced cosmetic and functional outcomes [24,27].
Current methods in handling maxillofacial defects, such as CLP, are not robust and are highly dependent on the surgeon’s skills and the patients’ capacity for regenerating lost tissues [18,19,27]. The ability to create 3D devices and scaffolds that are patient-specific and tunable holds great promise in the surgical repair of orofacial and maxillofacial defects. In this study, we used a 3D printing method that fabricates customized and antibiotic thermoplastic filaments for 3D printing [14,15,16]. 3D printed stents were successfully fabricated into antibiotic, porous, and mesh forms, and whose properties can be mechanically enhanced or modified. As FDM uses a layer-by-layer approach, the printed stent has the antibiotic distributed throughout the device and should assist in preventing infection leading to tissue repair and regeneration [14,15].
Advances in 3D printing are enabling on-demand, integrated 3D planning, and printing for personalized surgery and patient specific medical and dental devices [14,30,34]. Our design has the potential to eliminate the repetitive adjustments required of currently used nasal stents, the use of noxious materials in their fabrication, and irritation to the oral mucosa, gingival tissue, or nasal mucosa [35]. Our method aides in patient compliance by producing customized 3D printed removable appliances that match the contour and unique features of the cleft patient, feeding is not impeded, and easy modification and adjustments in size and contour prior can be made before surgical correction. Pre-surgical appliances will be designed to be worn intra-orally and will work to shape the alveolus, the lip and nose through an external membrane. The process will lower clinical risks, allowing the surgeons to provide patient-specific treatment, increase positive outcomes, and potentially permit earlier intervention. An earlier surgical response may lead to enhanced self-esteem often hindered by self-recognized facial differences.
Our technology has significant potential for use in a range of biomedical applications as a tunable drug delivery system with a capacity for sustained release of an array of bioactive agents. We anticipate that this method will provide a means for improving treatment modalities for patients affected by numerous dental and craniofacial pathologic conditions, such as cleft lip and palate, hemi-facial microsomia, osteonecrosis, congenital/acquired loss of alveolar bone and/or teeth, and avulsive trauma. We have shown the technical and clinical viability of our composites through several in vitro basic and clinical measures, and their potential use in a range of biomedical applications as a tunable drug delivery system with a sustained release capacity for an array of bioactive agents.
Custom-designed 3D printed scaffolds can be used to reconstruct the developmental defects by tissue engineering and regenerative medicine techniques, significantly enhancing pre-prosthetic surgeries [36]. Polymers, ceramics, natural and synthetic bioplastics, proteins, biomolecules, living cells, and growth factors incorporated during the the 3D printing of bioactive scaffolds [37,38]. In current 3D printing applications, there are a range of material limitations, ranging from heat resistance to strength. The addition of clay nanoparticles, such has halloysite, could be used to modify polymer material properties and so improve adhesion, tensile, compressive, thermal, and other properties [39]. Finally, the use of HNTs as a nanocontainer to incorporate drugs or bioactive factors, singly or in multiples, provides a significant capability to 3D printed polymer-based devices [39,40].
Current work is directed towards further customizing the fabrication process by using designer filaments with tailored material properties that are formed by the combination of halloysite with PLC, PLA, or PEKK, a thermoplastic with high heat and mechanical load resistance.
5. Conclusions
We successfully 3D printed stents for CLP repair in porous or mesh forms and composed of multiple polymers in layers and whose properties can be mechanically enhanced or made bioactive. With 3D scanning technology, the device will permit the improved alignment of the cleft segments, reduce cleft aperture, prevent post-surgical infection, and increase patient compliance, leading to positive post-operative outcomes. In preparation for future surgical restoration, a bioactive appliance/BMP-2 carrier is being developed using the same printing method that may eliminate bone grafting and additional surgical procedures, permit earlier intervention, thus reducing the wait time until full reconstruction is achieved.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially funded by the Louisiana Governor’s Biotechnology Initiative, The Lagniappe Ladies Fund and a Louisiana Board of Regents Prototype/Proof-of-Concept grant.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript. Karthik Tappa, Uday Jammalamadaka, and Jeffery Weisman conducted the design and fabrication of the nasal stents. David Mills and Jennifer Woerner conceived of the concept and supervised conducting of the experiments. All authors contributed to data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sachs, E.M.; Haggerty, J.S.; Cima, M.J.; Williams, P.A. Three-dimensional printing techniques. Patent US5340656 A, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jijotiya, D.; Verma, P.L. A survey of performance based advanced rapid prototyping techniques. Sch. J. Eng. Tech. 2013, 1, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Derby, B. Printing and prototyping of tissues and scaffolds. Science 2012, 338, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, W.; Stansbury, J.W.; Idacavageca, M.J. 3D printing with polymers, challenges among expanding options and opportunities. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee, A.; Atala, A. Printing technologies for medical applications. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayhurst, C. 3D printing and medical devices. Biomed. Instrum. Tech. 2014, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayavenkataraman, S.; Fuh, J.T.H.; Wen, F.; Lu, W.F. 3D printing and 3D bioprinting in pediatrics. Bioengineering 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Montgomery, M.; Chamberlain, M.D.; Ogawa, S.; Korolj, A.; Pahnke, A.; Wells, L.A.; Masse, S.; Kim, J.; Reis, L.; et al. Biodegradable scaffold with built-in vasculature for organ-n-a-chip engineering and direct surgical anastomosis. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Yu, Y. Bioprinting towards organ fabrication, challenges and future trends. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Hockaday, L.A.; Kang, K.H.; Butcher, J.T. 3D bioprinting of heterogeneous aortic valve conduits with alginate/gelatin hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Vahabzadeh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Bone tissue engineering using 3D printing. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.P.; Qu, X.; Soman, P.; Hribar, K.; Lee, J.W.; Chen, S.; He, S. Rapid fabrication of complex 3D extracellular microenvironments by dynamic optical projection stereolithography. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4266–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisman, J.; Nicholson, C.; Tappa, K.; Jammalamadaka, U.; Wilson, C.; Mills, D.K. Antibiotic and chemotherapeutic enhanced 3D printer filaments and constructs for biomedical applications. Inter. J. Nanomed. 2014, 10, 357–370. [Google Scholar]
- Landers, R.; Mülhaupt, R. Desktop manufacturing of complex objects, prototypes and biomedical scaffolds by means of computer-assisted design combined with computer-guided 3D plotting of polymers and reactive oligomers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2000, 282, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, D.H.; Weisman, J.A.; Jammalamadaka, U.; Tappa, K.; Alexander, S.; Griffen, F. Three-dimensional printing of bioactive hernia meshes, in vitro proof of principle. Surgery 2017, 161, 1479–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, S.E.; Mai, C.T.; Canfield, M.A.; Richard, R.; Yang, Y.; Meyer, M. Updated national birth estimates prevalence for selected birth defects in the US. Birth Defect Res. 2010, 88, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkoukani, M.A.; Chen, M.; Vong, A. Cleft lip—A comprehensive review. Front. Pediatr. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossey, P.A.; Little, J.; Munger, R.G.; Dixon, M.J.; Shaw, W.C. Cleft lip and palate. Lancet 2009, 374, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enlow, D.H. Facial Growth, 3rd ed.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.G. Plastic Surgery, Cleft Lip and Palate and Craniofacial Anomalies; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, M.J.; Marazita, M.L.; Beaty, T.H.; Murray, J.C. Cleft lip and palate, synthesizing genetic and environmental influences. Nat. Rev. Genet 2011, 12, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.R.; Alonso, N. Protocols in cleft lip and palate treatment, systematic review. Plast. Surg. Int. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehby, G.L.; Cassell, C.H. The impact of orofacial clefts on quality of life and healthcare use and costs. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, S.; Das, S. Mechanical and microstructural properties of polycaprolactone scaffolds with one-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional orthogonally oriented porous architectures produced by selective laser sintering. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, G.; Gauthier, M. Poly(lactic acid)-based biomaterials, synthesis, modification and applications. In Biomedical Science, Engineering and Technology; Ghista, D.N., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-307-471-9. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, R.D.; Dubé, R.; Therriault, D. Three-dimensional printing of multifunctional nanocomposites, manufacturing techniques and applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5794–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, C.W. Presurgical orthopedics. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. 1996, 4, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, N.; Simpson, D.; Spence, W.D.; Ion, W. A preliminary investigation into the development of 3—D printing of prosthetic sockets. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2015, 42, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zopf, D.A.; Hollister, S.J.; Nelson, M.E.; Ohye, R.G.; Green, G.E. Bioresorbable airway splint created with a three—Dimensional printer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2043–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Luca, A.; Longoni, A.; Criscenti, G.; Lorenzo-Moldero, I.; Klein-Gunnewiek, M.; Vancso, J.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Mota, C.; Moroni, L. Surface energy and stiffness discrete gradients in additive manufactured scaffolds for osteochondral regeneration. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jariwala, S.H.; Lewis, G.S.; Bushman, Z.J.; Adair, J.H.; Donahue, H.J. 3D printing of personalized artificial bone scaffolds. 3D Print Addit. Manuf. 2015, 1, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahoma, A. Complete cleft palate, A new scheme of treatment. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2006, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Grayson, B.H.; Shetye, P.R. Presurgical nasoalveolar moulding treatment in cleft lip and palate patients. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2009, 42, S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, T.A.; Bueno, R.A.; Alkhalefah, G.K.; Langhals, N.B.; Urbanchek, M.G.; Cederna, P.S. Innovations in prosthetic interfaces for the upper extremity. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zein, I.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Tan, K.C.; Teoh, S.H. Fused deposition modeling of novel scaffold architectures for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, H.N.; Wu, B.M. Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials. J. Biol. Eng. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Vacant, J. Advances in tissue engineering. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdllayev, E.; Lvov, L. Functional polymer clay nanotube composites with sustained release of chemical agents. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1690–1719. [Google Scholar]
- Weisman, J.; Jammalamadaka, U.; Tappa, K.; Mills, D.K. Doped halloysite nanotubes for use in the 3D printing of medical devices. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnik, S.; Mills, D.K. Nanoenhanced hydrogel system with sustained release capabilities. J. BioMed Mater. Res. 2015, 103, 2416–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).