Journal Description
Inventions
Inventions
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal published bimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Inspec, Ei Compendex and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Multidisciplinary) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Engineering)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
1.9 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Potential Recovery and Recycling of Condensate Water from Atlas Copco ZR315 FF Industrial Air Compressors
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010010 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
This research examines the feasibility of recovering and recycling condensate water, a waste byproduct generated by Atlas Copco ZR315 FF industrial air compressors utilizing oil-free rotary screw technology with integrated dryers. Given the growing severity of global water scarcity, finding alternative water sources
[...] Read more.
This research examines the feasibility of recovering and recycling condensate water, a waste byproduct generated by Atlas Copco ZR315 FF industrial air compressors utilizing oil-free rotary screw technology with integrated dryers. Given the growing severity of global water scarcity, finding alternative water sources is essential for sustainable industrial practices. This study specifically evaluates the potential of capturing and treating compressed air condensate as a viable method for water recovery. The investigation analyzes both the quantity and quality of condensate water produced by the ZR315 FF unit. It contrasts this recovery approach with traditional water production methods, such as desalination and atmospheric water generation (AWG) via dehumidification. The findings demonstrate that recovering condensate water from industrial air compressors is a cost-effective and energy-efficient substitute for conventional water production, especially in water-stressed areas like Morocco. The results show a significant opportunity to reduce industrial water usage and provide a sustainable source of process water. This research therefore supports the application of circular economy principles in industrial water management and offers practical solutions for overcoming water scarcity challenges within manufacturing environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Energy and Thermal/Fluidic Science)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Electric Bus Charging and Fleet Sizing Incorporating Traffic Congestion Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
by
Hai Yan, Xinyu Sui, Ning Chen and Shuo Pan
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010009 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Amid the increasing demand to reduce carbon emissions, replacing diesel buses with electric buses has become a key development direction in public transportation. However, a significant challenge in this transition lies in developing efficient charging strategies and accurately determining the required fleet size,
[...] Read more.
Amid the increasing demand to reduce carbon emissions, replacing diesel buses with electric buses has become a key development direction in public transportation. However, a significant challenge in this transition lies in developing efficient charging strategies and accurately determining the required fleet size, as existing research often fails to adequately account for the impact of real-time traffic congestion on energy consumption. To address this gap, in this study, an optimized charging strategy is proposed, and the necessary fleet size is calculated using a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approach, which integrates actual route characteristics and dynamic traffic congestion patterns into an electric bus operation model. Modeling is conducted based on Beijing Bus Route 400 to ensure the practical applicability of the proposed method. The results demonstrate that the proposed DRL method ensures operational completion while minimizing charging time, with the algorithm showing rapid and stable convergence. In the multi-route scenarios investigated in this study, the DRL-based charging strategy requires 40% more electric buses, with this figure decreasing to 24% when fast-charging technology is adopted. This study provides bus companies with valuable electric bus procurement and route operation references.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies and Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable and Intelligent Transportation Systems: Second Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reinforcement Learning-Based Handover Algorithm for 5G/6G AI-RAN
by
Ildar A. Safiullin, Ivan P. Ashaev, Alexey A. Korobkov, Artur K. Gaysin and Adel F. Nadeev
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010008 - 10 Jan 2026
Abstract
The increasing number of Base Stations (BSs) and connected devices, coupled with their mobility, poses significant challenges and makes mobility management even more pressing. Therefore, advanced handover (HO) management technologies are required to address this issue. This paper focuses on the ping-pong HO
[...] Read more.
The increasing number of Base Stations (BSs) and connected devices, coupled with their mobility, poses significant challenges and makes mobility management even more pressing. Therefore, advanced handover (HO) management technologies are required to address this issue. This paper focuses on the ping-pong HO problem. To address this issue, we propose an algorithm using Reinforcement Learning (RL) based on the Double Deep Q-Network (DDQN). The novelty of our approach is to assign specialized RL agents to users based on their mobility patterns. The use of specialized RL agents simplifies the learning process. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is demonstrated in tests on the ns-3 platform due to its ability to replicate real-world scenarios. To compare the results of the proposed approach, the baseline handover algorithm based on Events A2 and A4 is used. The results show that the proposed approach reduces the number of HO by more than four times on average, resulting in a more stable data rate and increasing it up to two times in the best case.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Electrical Engineering/Energy/Communications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Integrating Additive Manufacturing into Dental Production: Innovations, Applications and Challenges
by
Maryna Yeromina, Jan Duplak, Jozef Torok, Darina Duplakova and Monika Torokova
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010007 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
Additive manufacturing (AM) has emerged as a key enabling technology in contemporary dental manufacturing, driven by its capacity for customization, geometric complexity, and seamless integration with digital design workflows. This article presents a technology-oriented narrative review of additive manufacturing in dental implant production,
[...] Read more.
Additive manufacturing (AM) has emerged as a key enabling technology in contemporary dental manufacturing, driven by its capacity for customization, geometric complexity, and seamless integration with digital design workflows. This article presents a technology-oriented narrative review of additive manufacturing in dental implant production, focusing on dominant processing routes, material systems, and emerging research trends rather than a systematic or critical appraisal of the literature. An indicative descriptive analysis of publications indexed in the Web of Science and Scopus databases between 2014 and 2024 was used to contextualize the technological development of the field and identify major research directions. Emphasis was placed on metal powder bed fusion technologies, specifically Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), which enable the fabrication of titanium implants with controlled porosity and enhanced osseointegration. Ceramic AM approaches, including SLA, DLP, and PBF, are discussed in relation to their potential for aesthetic dental restorations and customized prosthetic components. The publication trend overview indicates a growing interest in ceramic AM after 2020, an increasing focus on hybrid and functionally graded materials, and persistent challenges related to standardization and the availability of long-term clinical evidence. Key technological limitations—including manufacturing accuracy, material stability, validated metrology, and process reproducibility—are highlighted alongside emerging directions such as artificial intelligence-assisted workflows, nanostructured surface modifications, and concepts enabling accelerated or immediate clinical use of additively manufactured dental restorations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Advanced Manufacturing)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
visionMC: A Low-Cost AI System Using Facial Recognition and Voice Interaction to Optimize Primary Care Workflows
by
Marius Cioca and Adriana Lavinia Cioca
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010006 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
This pilot study evaluated the visionMC system, a low-cost artificial intelligence system integrating HOG-based facial recognition and voice notifications, for workflow optimization in a family medicine practice. Implemented on a Raspberry Pi 4, the system was tested over two weeks with 50 patients.
[...] Read more.
This pilot study evaluated the visionMC system, a low-cost artificial intelligence system integrating HOG-based facial recognition and voice notifications, for workflow optimization in a family medicine practice. Implemented on a Raspberry Pi 4, the system was tested over two weeks with 50 patients. It achieved 85% recognition accuracy and an average detection time of 3.4 s. Compared with baseline, patient waiting times showed a substantial reduction in waiting time and administrative workload, and the administrative workload decreased by 5–7 min per patient. A satisfaction survey (N = 35) indicated high acceptance, with all scores above 4.5/5, particularly for usefulness and waiting time reduction. These results suggest that visionMC can improve efficiency and enhance patient experience with minimal financial and technical requirements. Larger multicenter studies are warranted to confirm scalability and generalizability. visionMC demonstrates that effective AI integration in small practices is feasible with minimal resources, supporting scalable digital health transformation. Beyond biometric identification, the system’s primary contribution is streamlining practice management by instantly displaying the arriving patient and enabling rapid chart preparation. Personalized greetings enhance patient experience, while email alerts on motion events provide a secondary security benefit. These combined effects drove the observed reductions in waiting and administrative times.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Design, Modeling and Computing Methods)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Heat Transfer Enhancement and Flow Resistance Characteristics in a Tube with Alternating Corrugated-Smooth Segments
by
Junwen Cheng, Jiahao Zhu, Xin Wen, Haodong Yu, Wei Lin, Zuqiang Xin and Jiuyang Yu
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010005 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
To mitigate the inherent high flow resistance of conventional corrugated tubes, a novel design with alternating clockwise/counterclockwise corrugated segments separated by smooth sections is proposed. A 3D numerical model was developed to systematically evaluate the thermal-hydraulic performance of the novel tube against smooth
[...] Read more.
To mitigate the inherent high flow resistance of conventional corrugated tubes, a novel design with alternating clockwise/counterclockwise corrugated segments separated by smooth sections is proposed. A 3D numerical model was developed to systematically evaluate the thermal-hydraulic performance of the novel tube against smooth and conventional corrugated tubes, with simulations conducted at Reynolds number (Re) = 9952–35,827. Results show both corrugated configurations enhanced heat transfer significantly relative to the smooth tube: the conventional tube had the highest Nusselt number (Nu) (1.76–1.79 times that of the smooth tube), while the novel tube achieved Nu = 1.61–1.65 times that of the smooth tube. Notably, the novel tube reduced flow resistance substantially—at Re = 35,827, its friction factor (f) was only 65.2% of the conventional tube’s. Parametric studies revealed that more corrugated segments improved heat transfer but increased pressure drop: the 72-12 configuration exhibited the best heat transfer, while the 72-2 configuration reduced f by 40.7%. The novel tube showed superior overall performance (Performance Evaluation Criterion (PEC) > 1.24 for all Re), as corrugated segments generated periodic vortices to disrupt the thermal boundary layer, while smooth segments enabled flow redevelopment and pressure recovery. This study provides valuable guidance for designing high-efficiency, low-resistance heat exchange elements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations and Inventions in Two-Phase Flow and Heat Transfer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessPatent Summary
Screw-Type Shredder for Solid Photopolymer Resin in Microgravity Environments
by
Iulian Vlăducă and Emilia Georgiana Prisăcariu
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010004 - 2 Jan 2026
Abstract
The invention concerns a screw-driven shredder for solid photopolymer resin, designed for both terrestrial use and prospective deployment in microgravity environments. The system addresses the need for efficient recycling of cured photopolymer waste generated by stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing—a process not yet implemented
[...] Read more.
The invention concerns a screw-driven shredder for solid photopolymer resin, designed for both terrestrial use and prospective deployment in microgravity environments. The system addresses the need for efficient recycling of cured photopolymer waste generated by stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing—a process not yet implemented in orbit, but envisioned as part of future closed-loop additive manufacturing systems aboard space stations or lunar habitats. The proposed device is a compact, hermetically sealed mechanical unit composed of ten subassemblies, featuring two counter-rotating screw shafts equipped with carbide milling inserts arranged helically to achieve uniform and controlled fragmentation of solid SLA residues. The shredding process is supported by a pressurized inert fluid circuit, utilizing carbon dioxide (CO2) as a cryogenic working medium to enhance cutting efficiency, reduce heat accumulation, and ensure particle evacuation under microgravity conditions. Studies indicate that CO2-assisted cooling can reduce tool-tip temperature by 10–30 °C, cutting forces by 5–15%, and electrical power consumption by 5–12% while extending tool life by up to 50%. This invention thus provides a key component for a future in situ photopolymer recycling loop in space while also offering a high-efficiency shredding solution for Earth-based photopolymer waste management in additive manufacturing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Advanced Manufacturing)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Distributed, Energy-Autonomous Multi-Sensor IoT System for Monitoring and Reducing Water Losses in Distribution Networks
by
Juan Arquero-Gallego, Carlos Gilarranz-Casado, Vicente Garcia-Alcántara and José Álvarez
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010003 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
Water resources are fundamental for human development in every possible sense; from natural development, since they are the main biological factor necessary for the development of life, to economic development, since they are essential for a large number of productive systems, especially in
[...] Read more.
Water resources are fundamental for human development in every possible sense; from natural development, since they are the main biological factor necessary for the development of life, to economic development, since they are essential for a large number of productive systems, especially in the primary and secondary sectors. This makes them a resource which, although at first glance may seem unlimited, is critical since their scarcity and unavailability compromise the whole of human development, greatly limiting productive and economic activity and, ultimately, social welfare. The current development of IoT technology, on the other hand, provides tools to face this problem in a technical way, allowing the adoption of distributed and automated solutions that, together with the knowledge provided by disciplines such as agricultural and alimentary engineering, make viable the development of a system that allows us to monitor and control water distribution networks (WDNs). Next, the situations that involve the mentioned problem will be detailed and different aspects will be proposed in which the implementation of the presented system is intended to have a direct impact.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Electrical Engineering/Energy/Communications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Three-Dimensional Visualization System for Tea Production Lines Based on Digital Twins
by
Honghao Liu, Guoliang Ma and Kaixing Zhang
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010002 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
Current traditional tea processing production lines suffer from issues such as fragmented data and low levels of intelligence. This paper proposes a three-dimensional visualization system for tea processing production lines based on digital twins. Firstly, the system’s overall framework and functional architecture were
[...] Read more.
Current traditional tea processing production lines suffer from issues such as fragmented data and low levels of intelligence. This paper proposes a three-dimensional visualization system for tea processing production lines based on digital twins. Firstly, the system’s overall framework and functional architecture were established. Secondly, multi-source heterogeneous data from the production line was collected and managed through a driver architecture, enabling the construction and mapping of the digital twin information model. Thirdly, referencing the actual environment of a green tea processing line, scene-specific lighting models and rendering techniques were employed to recreate a virtual green tea processing environment. During this process, lighting optimization enhanced the realism of the system’s scenes. Finally, employing data-driven methodologies, the system dynamically simulates the operational states of various production line equipment and the morphological changes in tea leaves. This achieves comprehensive three-dimensional visualization and all-round monitoring of the tea processing production line. Experimental validation confirms the feasibility of this visualized 3D system, injecting fresh impetus into advancing intelligent tea production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Advanced Manufacturing)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Extreme Strengthening of Nickel by Ultralow Additions of SiC Nanoparticles: Synergy of Microstructure Control and Interfacial Reactions During Spark Plasma Sintering
by
Leonid Agureev, Svetlana Savushkina and Artem Ashmarin
Inventions 2026, 11(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions11010001 - 29 Dec 2025
Abstract
Ni–ySiC system (where y = 0.001, 0.005, and 0.015 wt.%) composite materials with enhanced mechanical properties have been fabricated and comprehensively investigated. The composites were synthesized using a combined technology involving preliminary mechanical activation of powder components in a planetary mill followed by
[...] Read more.
Ni–ySiC system (where y = 0.001, 0.005, and 0.015 wt.%) composite materials with enhanced mechanical properties have been fabricated and comprehensively investigated. The composites were synthesized using a combined technology involving preliminary mechanical activation of powder components in a planetary mill followed by consolidation via spark plasma sintering (SPS) at 850 °C. The microstructure and phase composition were studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The physico-mechanical properties were evaluated by density measurements (hydrostatic weighing), three-point bending tests (25 °C and 400 °C), and Young’s modulus measurement using an ultrasonic method (25–750 °C). It was found that the introduction of ultralow amounts of SiC nanoparticles (0.001 wt.%) leads to an extreme increase in flexural strength: by 115% at 20 °C (up to 1130 MPa) and by 86% at 400 °C (up to 976 MPa) compared to pure nickel. Microstructural analysis revealed the formation of an ultrafine-grained structure (0.15–0.4 µm) with the presence of pyrolytic carbon and probable nickel silicide interlayers at the grain boundaries. Thermodynamic and kinetic modeling, including the calculation of chemical potentials and diffusion coefficients, confirmed the possibility of reactions at the Ni/SiC interface with the formation of nickel silicides (Ni2Si, NiSi) and free carbon. The scientific novelty of the work lies in establishing a synergistic strengthening mechanism combining the Hall–Petch, Orowan (dispersion), and solid solution strengthening effects, and in demonstrating the property extremum at an ultralow content of the dispersed phase (0.001 wt.%), explained from the standpoint of quantum-chemical analysis of phase stability. The obtained results are of practical importance for the development of high-strength and thermally stable nickel composites, promising for application in aerospace engineering.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Applied Chemistry and Physics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Adaptive Concurrent Multiscale Approach Based on the Phase-Field Cohesive Zone Model for the Failure Analysis of Masonry Structures
by
Fabrizio Greco, Francesco Fabbrocino, Lorenzo Leonetti, Arturo Pascuzzo and Girolamo Sgambitterra
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 111; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060111 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
Simulating damage phenomena in masonry structures remains a significant challenge because of the intricate and heterogeneous nature of this material. An accurate evaluation of fracture behavior is essential for assessing the bearing capacity of these structures, thereby mitigating dramatic failures. This paper proposes
[...] Read more.
Simulating damage phenomena in masonry structures remains a significant challenge because of the intricate and heterogeneous nature of this material. An accurate evaluation of fracture behavior is essential for assessing the bearing capacity of these structures, thereby mitigating dramatic failures. This paper proposes an innovative adaptive concurrent multiscale model for evaluating the bearing capacity of in-plane masonry structures under in-plane loadings. Developed within a Finite Element (FE) set, the proposed model employs a domain decomposition scheme to solve a combination of fine- and coarse-scale sub-models concurrently. In regions requiring less detail, the masonry is represented by homogeneous linear elastic macro-elements. The material properties for these macro-elements are derived through a first-order computational homogenization strategy. Conversely, in areas with higher resolution needs, the masonry is modeled by accurately depicting individual brick units and mortar joints. To capture strain localization effectively in these finer regions, a Phase Field Cohesive Zone Model (PF-CZM) formulation is employed as the fracture model. The adaptive nature derives from the fact that at the beginning of the analysis, the model is entirely composed of coarse regions. As nonlinear phenomena develop, these regions are progressively deactivated and replaced by finer regions. An activation criterion identifies damage-prone regions of the domain, thereby triggering the transition from macro to micro scales. The proposed model’s validity was assessed through multiscale numerical simulations applied to a targeted case study, with the results compared to those from a direct numerical simulation. The results confirm the effectiveness and accuracy of this innovative approach for analyzing masonry failure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Numerical Approaches to Simulate Crack Propagation Mechanisms in Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Study of Neuroevolution and Deep Reinforcement Learning for Voltage Regulation in Power Systems
by
Adrián Alarcón Becerra, Vinícius Albernaz Lacerda, Roberto Rocca, Ana Patricia Talayero Navales and Andrés Llombart Estopiñán
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 110; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060110 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
The regulation of voltage in transmission networks is becoming increasingly complex due to the dynamic behavior of modern power systems and the growing penetration of renewable generation. This study presents a comparative analysis of three artificial intelligence approaches—Deep Q-Learning (DQL), Genetic Algorithms (GAs),
[...] Read more.
The regulation of voltage in transmission networks is becoming increasingly complex due to the dynamic behavior of modern power systems and the growing penetration of renewable generation. This study presents a comparative analysis of three artificial intelligence approaches—Deep Q-Learning (DQL), Genetic Algorithms (GAs), and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)—for training agents capable of performing autonomous voltage control. A unified neural architecture was implemented and tested on the IEEE 30-bus system, where the agent was tasked with adjusting reactive power set points and transformer tap positions to maintain voltages within secure operating limits under a range of load conditions and contingencies. The experiments were carried out using the GridCal simulation environment, and performance was assessed through multiple indicators, including convergence rate, action efficiency, and cumulative reward. Quantitative results demonstrate that PSO achieved 3% higher cumulative rewards compared to GA and 5% higher than DQL, while requiring 8% fewer actions to stabilize the system. GA showed intermediate performance with 6% faster initial convergence than DQL but 4% more variable results than PSO. DQL demonstrated consistent learning progression throughout training, though it required approximately 12% more episodes to achieve similar performance levels. The quasi-dynamic validation confirmed PSO’s advantages over conventional AVR-based strategies, achieving voltage stabilization approximately 15% faster. These findings underscore the potential of neuroevolutionary algorithms as competitive alternatives for advanced voltage regulation in smart grids and point to promising research avenues such as topology optimization, hybrid metaheuristics, and federated learning for scalable deployment in distributed power systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Distribution Renewable Energy Integration and Grid Modernization)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Innovative Solar Still Desalination: Effects of Fans, Lenses, and Porous Materials on Thermal Performance Under Renewable Energy Integration
by
Karim Choubani and Mohamed Ben Rabha
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 109; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060109 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
Global freshwater scarcity continues to escalate due to pollution, climate change, and population growth, making innovative sustainable desalination technologies increasingly vital. Solar stills offer a simple and eco-friendly method for freshwater production by utilizing renewable energy, yet their low productivity remains a major
[...] Read more.
Global freshwater scarcity continues to escalate due to pollution, climate change, and population growth, making innovative sustainable desalination technologies increasingly vital. Solar stills offer a simple and eco-friendly method for freshwater production by utilizing renewable energy, yet their low productivity remains a major limitation. This study experimentally evaluates and quantifies several established enhancement techniques under real climatic conditions to improve evaporation and condensation efficiency. The integration of porous materials, such as black rocks, significantly improves thermal energy storage and management by retaining absorbed heat during the daytime and releasing it gradually, resulting in an average 30% increase in daily distillate production (SD = 6 mL). Additionally, forced convection using small fans enhances humid air removal and evaporation rates, increasing the average yield by approximately 11.4% (SD = 2 mL). Optical concentration through lenses intensifies solar irradiation on the evaporation surface, achieving the highest performance with an average 50% improvement in water output (SD = 5 mL). The incorporation of Phase Change Materials (PCM) is further proposed to extend thermal stability during off-sunshine hours, with materials selected based on a melting point range of 38–45 °C. To minimize nocturnal heat loss, future designs may integrate radiative cooling materials for passive night-time condensation support, by applying a radiative cooling coating to the condenser plate to enhance passive heat rejection to the sky. Overall, the validated combined use of renewable energy-driven desalination, thermal storage media, and advanced strategies presents a practical pathway toward high-efficiency solar stills suitable for sustainable buildings and decentralized water supply systems in arid regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Energy and Thermal/Fluidic Science)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Invention for Controlled Plant Cutting Growth: Chamber Design Enabling Data Collection for AI Tasks
by
Jesús Gerardo Ávila-Sánchez, Manuel de Jesús López-Martínez, Valeria Maeda-Gutiérrez, Francisco E. López-Monteagudo, Celina L. Castañeda-Miranda, Manuel Rivera-Escobedo, Sven Verlienden, Genaro M. Soto-Zarazua and Carlos A. Olvera-Olvera
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 108; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060108 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
The Cutting Development Chamber (CDC) design is presented as an innovative solution to crucial human challenges, such as food and plant medicinal production. Unlike conventional propagation chambers, the CDC is a much more comprehensive research tool, specifically designed to optimize plant reproduction from
[...] Read more.
The Cutting Development Chamber (CDC) design is presented as an innovative solution to crucial human challenges, such as food and plant medicinal production. Unlike conventional propagation chambers, the CDC is a much more comprehensive research tool, specifically designed to optimize plant reproduction from cuttings. It maintains precise control over humidity, temperature, and lighting, which are essential parameters for plant development, thus maximizing the success rate, even in difficult-to-propagate species. Its modular design is one of its main strengths, allowing users to adapt the chamber to their specific needs, whether for research studies or for larger-scale propagation. The most distinctive feature of this chamber is its ability to collect detailed, labeled data, such as images of plant growth and environmental parameters that can be used in artificial intelligence tasks, which differentiate it from chambers that are solely used for propagation. A study that validated and calibrated the chamber design using cuttings of various species demonstrated its effectiveness through descriptive statistics, confirming that CDC is a powerful tool for research and optimization of plant growth. In validation experiments (Aloysia citrodora and Stevia rebaudiana), the system generated 6579 labeled images and 67,919 environmental records, providing a robust dataset that confirmed stable control of temperature and humidity while documenting cutting development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Inventions and Innovation in Smart Sensing Technologies for Agriculture: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quantifying Innovation: Intellectual Property Data as Indicators of Technology Maturity of Metal–Organic-Frameworks and Inorganic Nanoparticles
by
Umberto Maria Matera, Matteo Faccenda, Yolanda Pérez, Darina Francesca Picchi, Lorenzo Rossi, Sergio Larreina and Patricia Horcajada
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060107 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
The increasing significance of intellectual property (IP) in recent decades highlights its crucial role in driving innovation and shaping competitive strategies. While many studies have attempted to evaluate the technological level of specific sectors or companies, few offer a standardized and scalable approach
[...] Read more.
The increasing significance of intellectual property (IP) in recent decades highlights its crucial role in driving innovation and shaping competitive strategies. While many studies have attempted to evaluate the technological level of specific sectors or companies, few offer a standardized and scalable approach for cross-domain comparison. This study proposes a patent-based framework to comparatively evaluate technological maturity across different fields using a concise set of intellectual property (IP) indicators. The selected metrics, renewal trends, family size, grant rate, and citation patterns, capture legal, economic, and technological dimensions of innovation without requiring field-specific calibration. We apply this approach to two representative nanomedical technologies, Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and inorganic nanoparticles (iNPs), within the domain of cancer therapy. Our analysis highlights distinct trajectories: MOFs show increasing patent activity and sustained short-term citation growth, consistent with an emerging field; iNPs exhibit signs of stabilization and declining citation intensity, suggesting greater maturity. These findings demonstrate the utility of standardized IP indicators for mapping innovation dynamics across domains. The proposed framework offers a replicable tool for strategic technology assessment, with potential applications in research prioritization, technology forecasting, and early-stage investment analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Biotechnology and Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Impact of Digital Twins on Real Practices in Manufacturing Industries
by
Muhammad Qamar Khan, Muhammad Abbas Haider Alvi, Hafiza Hifza Nawaz and Muhammad Umar
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 106; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060106 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
In the era of Industry 5.0, the digital revolution stands as the paramount tool for achieving efficiency and elevating the standards of quality and quantity. This study delves deeply into the invaluable applications of digital twins within real production settings, highlighting their transformative
[...] Read more.
In the era of Industry 5.0, the digital revolution stands as the paramount tool for achieving efficiency and elevating the standards of quality and quantity. This study delves deeply into the invaluable applications of digital twins within real production settings, highlighting their transformative potential across a multitude of industries. Focusing particularly on textiles, machinery, and electronics manufacturing, the authors illustrate how digital twins enhance productivity, anticipate challenges, bolster the food supply chain, refine healthcare services, and propel sustainability initiatives within each sector. Through concrete examples, we demonstrate how digital twins can markedly decrease waste, energy consumption, and production downtime, all while elevating product quality and enabling virtualization. By virtually simulating physical systems, numerous operational issues can be mitigated, underscoring the pivotal role of digital twins in fostering hyper-personalization, sustainability, and resilience the foundational tenets of Industry 5.0. Nevertheless, this evaluation acknowledges the inherent challenges associated with the widespread adoption of digital twins, including concerns regarding data infrastructure, cybersecurity, and workforce adaptation. By presenting a balanced assessment of both the advantages and disadvantages, this review aims to guide future research and development endeavors, paving the way for the successful integration of this revolutionary technology as we journey toward Industry 5.0.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Design, Modeling and Computing Methods)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review of Heat and Energy Recovery Possibilities Within CO2 Refrigeration Systems
by
Cornel Constantin Pavel, Valentin Apostol, Horatiu Pop, Tudor Prisecaru, Claudia Ionita and Adrian Chiriac
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 105; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060105 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
The paper identifies and describes the possibilities for heat and mechanical energy recovery within refrigeration systems using CO2 as a working fluid, employed in commercial and industrial applications. The heat and mechanical energy recovery methods that can be utilized for beneficial purposes
[...] Read more.
The paper identifies and describes the possibilities for heat and mechanical energy recovery within refrigeration systems using CO2 as a working fluid, employed in commercial and industrial applications. The heat and mechanical energy recovery methods that can be utilized for beneficial purposes are taken into consideration. These methods could increase the energy efficiency of the refrigeration system or the building in which it operates. This paper summarizes various configurations and recovery methods and critically compares and evaluates them (COP improvements, exergy performance, and system integration complexity) based on the data available in the literature. As a result, the internal heat exchangers can be used as a superheater, in which case the COP can increase to 35%. If the internal heat exchanger is used as a subcooler, it could lead to a COP increase of 17% compared to a CO2 refrigeration system without subcooling for an evaporating temperature of −10 °C and the temperature of the gas cooler outlet of 30 °C. The heat and mechanical energy recovery possibilities are presented using the available scientific literature.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Energy and Thermal/Fluidic Science)
►▼
Show Figures
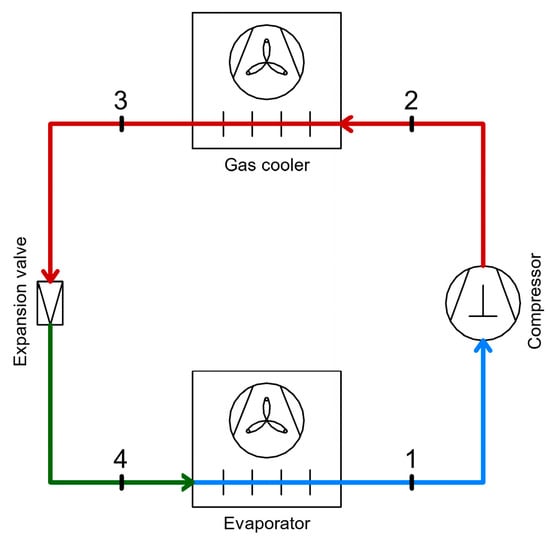
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Analysis of the Near-Wake Flow Field of Two Closely Spaced Wind Turbines with Passive Flow Control Ducts
by
Maytham M. Abid and Marc Marín-Genescà
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 104; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060104 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
The growing demand for renewable energy in space-constrained environments highlights the need for compact, high-efficiency wind energy systems. Conventional bare wind turbine (BWT) arrays suffer from severe wake interactions and performance degradation when operated in tandem or closely spaced configurations. To address these
[...] Read more.
The growing demand for renewable energy in space-constrained environments highlights the need for compact, high-efficiency wind energy systems. Conventional bare wind turbine (BWT) arrays suffer from severe wake interactions and performance degradation when operated in tandem or closely spaced configurations. To address these limitations, this study investigates the aerodynamic performance and near-wake dynamics of a novel multi-ducted wind turbine (MDWT) system that integrates passive flow-control technique (PFCT) into an innovative fixed-duct design. The objective is to evaluate how tandem ducted arrangements with this integrated mechanism influence wake recovery, vortex dynamics, and power generation compared with multi-bare wind turbine (MBWT) system. A numerical approach is employed using the Unsteady Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes (URANS) formulation with the k–ω SST turbulence model, validated against experimental data. The analysis focuses on two identical, fixed-orientation ducts arranged in tandem without lateral offset, tested under three spacing configurations. The results reveal that the ducted system accelerates the near-wake flow and displaces velocity-deficit regions downward due to the passive flow-control sheets, producing stronger inflow fluctuations and enhanced turbulence mixing. These effects improve wake recovery and mitigate energy losses behind the first turbine. Quantitatively, the MDWT array achieves total power outputs 1.99, 1.90, and 1.81 times greater than those of the MBWT array for Configurations No. 1, No. 2, and No. 3, respectively. In particular, the second duct in Configuration No. 1 demonstrates a 3.46-fold increase in power coefficient compared with its bare counterpart. These substantial gains arise because the upstream duct–PFCT assembly generates a favorable pressure gradient that entrains ambient air into the wake, while coherent tip vortices and redirected shear flows enhance mixing and channel high-momentum fluid toward the downstream rotor plane. The consistent performance across spacings further confirms that duct-induced flow acceleration and organized vortex structures dominate over natural wake recovery effects, maintaining efficient energy transfer between turbines. The study concludes that closely spaced MDWT systems provide a compact and modular solution for maximizing energy extraction in constrained environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advancements and Challenges in Marine Renewable Energy and Marine Structures)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
ROboMC: A Portable Multimodal System for eHealth Training and Scalable AI-Assisted Education
by
Marius Cioca and Adriana-Lavinia Cioca
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 103; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060103 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
AI-based educational chatbots can expand access to learning, but many remain limited to text-only interfaces and fixed infrastructures, while purely generative responses raise concerns of reliability and consistency. In this context, we present ROboMC, a portable and multimodal system that combines a validated
[...] Read more.
AI-based educational chatbots can expand access to learning, but many remain limited to text-only interfaces and fixed infrastructures, while purely generative responses raise concerns of reliability and consistency. In this context, we present ROboMC, a portable and multimodal system that combines a validated knowledge base with generative responses (OpenAI) and voice–text interaction, designed to enable both text and voice interaction, ensuring reliability and flexibility in diverse educational scenarios. The system, developed in Django, integrates two response pipelines: local search using normalized keywords and fuzzy matching in the LocalQuestion database, and fallback to the generative model GPT-3.5-Turbo (OpenAI, San Francisco, CA, USA) with a prompt adapted exclusively for Romanian and an explicit disclaimer. All interactions are logged in AutomaticQuestion for later analysis, supported by a semantic encoder (SentenceTransformer—paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2’, Hugging Face Inc., New York, NY, USA) that ensures search tolerance to variations in phrasing. Voice interaction is managed through gTTS (Google LLC, Mountain View, CA, USA) with integrated audio playback, while portability is achieved through deployment on a Raspberry Pi 4B (Raspberry Pi Foundation, Cambridge, UK) with microphone, speaker, and battery power. Voice input is enabled through a cloud-based speech-to-text component (Google Web Speech API accessed via the Python SpeechRecognition library, (Anthony Zhang, open-source project, USA) using the Google Web Speech API (Google LLC, Mountain View, CA, USA; language = “ro-RO”)), allowing users to interact by speaking. Preliminary tests showed average latencies of 120–180 ms for validated responses on laptop and 250–350 ms on Raspberry Pi, respectively, 2.5–3.5 s on laptop and 4–6 s on Raspberry Pi for generative responses, timings considered acceptable for real educational scenarios. A small-scale usability study (N ≈ 35) indicated good acceptability (SUS ~80/100), with participants valuing the balance between validated and generative responses, the voice integration, and the hardware portability. Although system validation was carried out in the eHealth context, its architecture allows extension to any educational field: depending on the content introduced into the validated database, ROboMC can be adapted to medicine, engineering, social sciences, or other disciplines, relying on ChatGPT only when no clear match is found in the local base, making it a scalable and interdisciplinary solution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Design, Modeling and Computing Methods)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Time-Series Forecasting Patents in Mexico Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models
by
Juan-Carlos Gonzalez-Islas, Ernesto Bolaños-Rodriguez, Omar-Arturo Dominguez-Ramirez, Aldo Márquez-Grajales, Víctor-Hugo Guadarrama-Atrizco and Elba-Mariana Pedraza-Amador
Inventions 2025, 10(6), 102; https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060102 - 10 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Patenting is essential for protecting intellectual property, fostering technological innovation, and maintaining competitive advantages in the global market. In Mexico, strategic planning in science, technology, and innovation requires reliable forecasting tools. This study evaluates computational models for predicting applied and granted patents between
[...] Read more.
Patenting is essential for protecting intellectual property, fostering technological innovation, and maintaining competitive advantages in the global market. In Mexico, strategic planning in science, technology, and innovation requires reliable forecasting tools. This study evaluates computational models for predicting applied and granted patents between 1990 and 2024, including statistical (ARIMA), machine learning (Regression Trees, Random Forests, and Support Vector Machines), and deep learning (Long Short-Term Memory, LSTM) approaches. The workflow involves historical data acquisition, exploratory analysis, decomposition, model selection, forecasting, and evaluation using the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), the determination coefficient (
(This article belongs to the Section Inventions and Innovation in Design, Modeling and Computing Methods)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Future Internet, IoT, Technologies, Inventions, Sensors, Vehicles
Next-Generation IoT and Smart Systems for Communication and Sensing
Topic Editors: Dinh-Thuan Do, Vitor Fialho, Luis Pires, Francisco Rego, Ricardo Santos, Vasco VelezDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topic in
Electronics, Energies, Eng, Machines, Vehicles, Designs, Batteries, Inventions
Next-Generation EV Motor Systems: Integrated Design and AI-Driven Optimization
Topic Editors: Kan Akatsu, Minh Cao TaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
JMSE, Sustainability, Energies, Inventions, Processes
Advancements and Challenges in Marine Renewable Energy and Marine Structures
Topic Editors: Tiago Fazeres Ferradosa, Mario López Gallego, Paulo Jorge Rosa-Santos, Dawei Guan, Daniel ClementeDeadline: 30 September 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Inventions
Innovative Research and Applications in Hydrodynamics and Flow Control, 3rd Edition
Guest Editors: Peng Du, Haibao Hu, Xiaopeng ChenDeadline: 29 January 2026
Special Issue in
Inventions
Innovations in Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Integrating Smart Systems, Advanced Materials, and Ergonomics for Next-Generation PPE
Guest Editor: Regan WattsDeadline: 30 January 2026
Special Issue in
Inventions
Innovations and Inventions in Two-Phase Flow and Heat Transfer
Guest Editor: Shyy Woei ChangDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
Inventions
Advances in XR-Based Teleoperation and Robot Manipulation
Guest Editor: Seungnam YuDeadline: 20 February 2026











