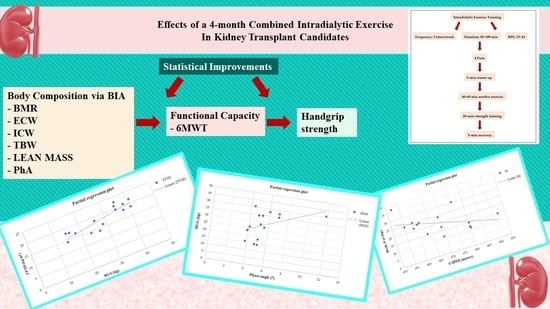
Effects of a Combined Intradialytic Exercise Training Program on Functional Capacity and Body Composition in Kidney Transplant Candidates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Six-Minute Walking Test
2.5. 10-Repetition Sit-to-Stand Test
2.6. Handgrip Strength Test
2.7. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
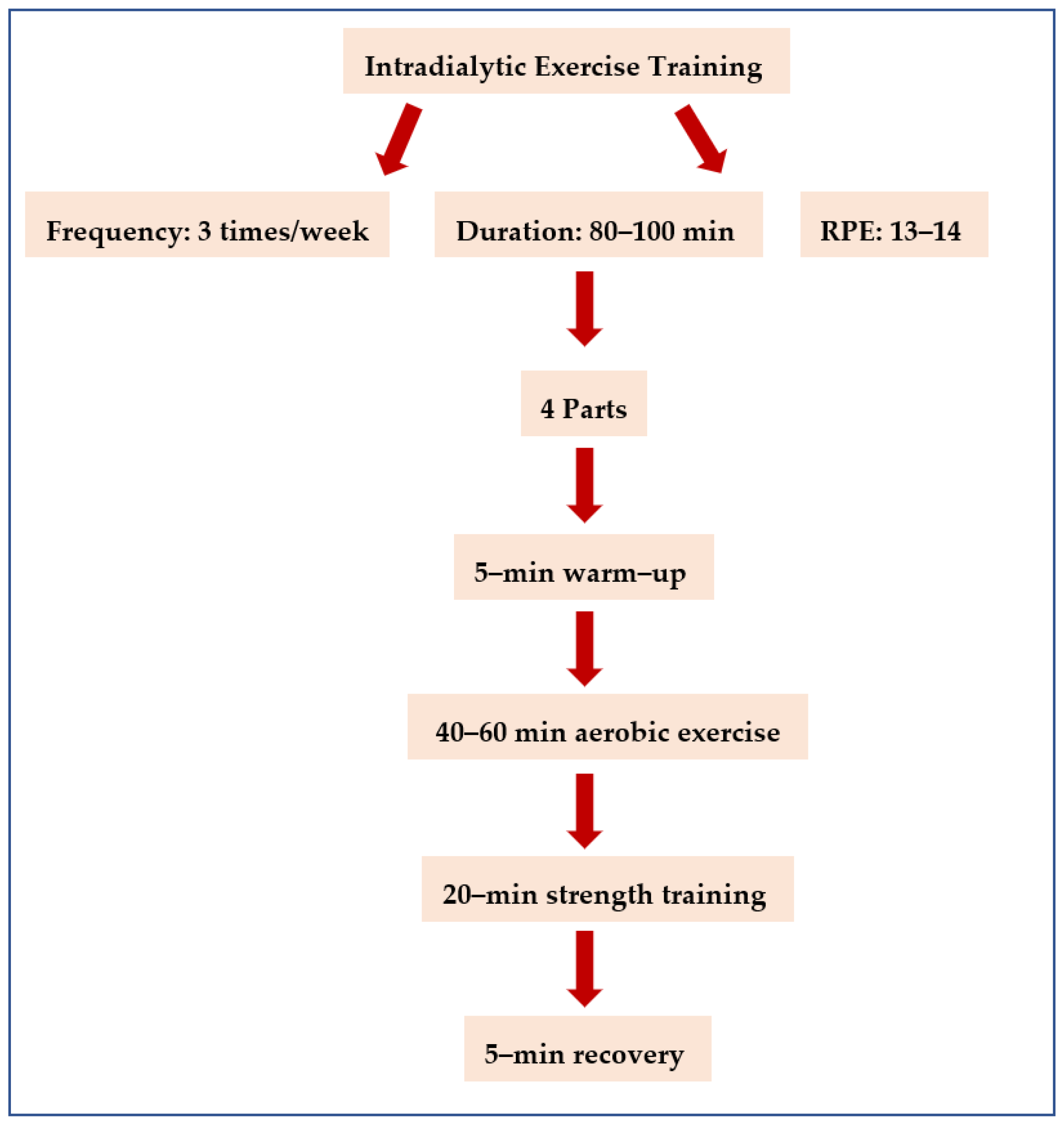
2.8. Intradialytic Exercise Program
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, R.; Kanso, A.; Sedor, J.R. Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Complications. Prim. Care Clin. Off. Pract. 2008, 35, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araujo, A.M.; Orcy, R.B.; Feter, N.; Weymar, M.K.; Cardoso, R.K.; Bohlke, M.; Rombaldi, A.J. Effects of intradialytic exercise on functional capacity in patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Res. Sports Med. 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Cuppari, L.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kaysen, G.; Mitch, W.E.; Price, S.R.; Wanner, C.; Wang, A.Y.; et al. Etiology of the Protein-Energy Wasting Syndrome in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Statement From the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM). J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, S.J.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Hwang, H.J. Relationship between Stage of Chronic Kidney Disease and Sarcopenia in Korean Aged 40 Years and Older Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES IV-2, 3, and V-1, 2), 2008–2011. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.C.; Shapiro, B.B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Porszasz, J.; Bross, R.; Feroze, U.; Upreti, R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D. Daily physical activity and physical function in adult maintenance hemodialysis patients. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Bhave, N.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Dietrich, X.; Eckard, A.; Eggers, P.W.; et al. US Renal Data System 2017 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmadakis, G.; Bevington, A.; Smith, A.; Clapp, E.; Viana, J.; Bishop, N.; Feehally, J. Physical Exercise in Patients with Severe Kidney Disease. Nephron. Clin. Pr. 2010, 115, c7–c16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masajtis-Zagajewska, A.; Muras, K.; Nowicki, M. Effects of a Structured Physical Activity Program on Habitual Physical Activity and Body Composition in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 17, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, K.; Nishida, Y.; Moriyama, Y.; Yabe, H.; Taoka, M.; Sato, T. Investigation of Factors Affecting the Six-Minute Walk Test Results in Hemodialysis Patients. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2014, 18, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Ortí, E.; Martínez-Olmos, F.J. Test-Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change Scores for Sit-to-Stand-to-Sit Tests, the Six-Minute Walk Test, the One-Leg Heel-Rise Test, and Handgrip Strength in People Undergoing Hemodialysis. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Lee, D.H.; Min, J.; Jeon, J.Y. Handgrip Strength as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Undergoing Dialysis: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Ren. Nutr. 2019, 29, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Schulzke, J.D.; Pirlich, M. Hand grip strength: Outcome predictor and marker of nutritional status. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.R.; Alvestrand, A.; Danielsson, A.; Divino-Filho, J.C.; Gutierrez, A.; Lindholm, B.; Bergström, J. Factors predicting malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leal, V.O.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Farage, N.E.; Aranha, L.N.; Fouque, D.; Anjos, L.A.; Mafra, D. Handgrip strength and its dialysis determinants in hemodialysis patients. Nutrition 2011, 27, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilloway, T.; Ashby, D.R.; Hickson, M.; Temple, A.; Johansson, L.R. Handgrip Strength Index: A Novel Parameter which quantifies clinical weakness in people on haemodialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, V.O.; Mafra, D.; Fouque, D.; Anjos, L.A. Use of handgrip strength in the assessment of the muscle function of chronic kidney disease patients on dialysis: A systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.H.; Do, J.Y.; Kim, J.C. Impedance-derived phase angle is associated with muscle mass, strength, quality of life, and clinical outcomes in maintenance hemodialysis patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.A.; March, D.S.; Wilkinson, T.J.; Billany, R.E.; Bishop, N.C.; Castle, E.M.; Chilcot, J.; Davies, M.D.; Graham-Brown, M.P.M.; Greenwood, S.A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline exercise and lifestyle in chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K. Intradialytic Exercise is Medicine for Hemodialysis Patients. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2016, 15, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Mohamed, A.; Davenport, A. A pilot study investigating the effect of pedalling exercise during dialysis on 6-min walking test and hand grip and pinch strength. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 42, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuguero-Ortiz, A.; Gomez, M.; Arias-Guillén, M.; Ojeda, R.; Fontseré, N.; Rodas, L.; Broseta, J.J.; Vera, M.; Hernandez-Sanchez, S.; Maduell, F. Impact and safety outcomes of an intradialytic physical exercise program. Nefrología 2021, 41, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellberg, M.; Höglund, P.; Svensson, P.; Clyne, N. Randomized Controlled Trial of Exercise in CKD—The RENEXC Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhee, S.Y.; Song, J.K.; Hong, S.C.; Choi, J.W.; Jeon, H.J.; Shin, D.H.; Ji, E.H.; Choi, E.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, A.; et al. Intradialytic exercise improves physical function and reduces intradialytic hypotension and depression in hemodialysis patients. Korean J. Int. Med. 2019, 34, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BBasile, C.; Vernaglione, L.; Lomonte, C.; Bellizzi, V.; Libutti, P.; Teutonico, A.; Di Iorio, B. Comparison of alternative methods for scaling dialysis dose. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakaloudi, D.R.; Siargkas, A.; Poulia, K.A.; Dounousi, E.; Chourdakis, M. The Effect of Exercise on Nutritional Status and Body Composition in Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passauer, J.; Petrov, H.; Schleser, A.; Leicht, J.; Pucalka, K. Evaluation of clinical dry weight assessment in haemodialysis patients using bioimpedance spectroscopy: A cross-sectional study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehmet, H.; Yang, A.W.H.; Robinson, S.R. What is the optimal chair stand test protocol for older adults? A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter-Kroker, A.; Kroker, A.; Mattiucci-Guehlke, M.; Glaab, T. A practical guide to bioelectrical impedance analysis using the example of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, M.R.; Barbieri, M.; Fava, I.; Desiderio, M.; Coppola, C.; Marfella, R.; Paolisso, G. Sarcopenia in Elderly Diabetic Patients: Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollie, J.M.; Harris-Love, M.O.; Patel, S.S.; Argani, S. Chronic kidney disease: Considerations for monitoring skeletal muscle health and prescribing resistance exercise. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 11, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidou, E.; Koukouvou, G.; Kouidi, E.; Deligiannis, A.; Tourkantonis, A. Exercise training in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis: Comparison of three rehabilitation programs. J. Rehabil. Med. 2002, 34, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; McAdams-DeMarco, M.; Bennett, P.N.; Wilund, K. Advances in exercise therapy in predialysis chronic kidney disease, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and kidney transplantation. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, T. Let’s programme exercise during haemodialysis (intradialytic exercise) into the care plan for patients, regardless of age. Br. J. Sport Med 2016, 50, 1357–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ou, S. Efficacy and safety of intradialytic exercise in haemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e020633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohl, L.D.M.; Signori, L.U.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Silva, A.M.V.; Moreira, P.R.; Dipp, T.; Sbruzzi, G.; Lukrafka, J.L.; Plentz, R.D.M. Prognostic value of the six-minute walk test in end-stage renal disease life expectancy: A prospective cohort study. Clinics 2012, 67, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiwe, S.; Jacobson, S.H. Exercise Training in Adults With CKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.; Aragoncillo, I.; Moreno, J.; Vega, A.; Abad, S.; García-Prieto, A.; Macias, N.; Hernandez, A.; Godino, M.T.; Luño, J. Exercise training during hemodialysis sessions: Physical and biochemical benefits. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2020, 24, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frih, B.; Jaafar, H.; Mkacher, W.; ben Salah, Z.; Hammami, M.; Frih, A. The Effect of Interdialytic Combined Resistance and Aerobic Exercise Training on Health Related Outcomes in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients: The Tunisian Randomized Controlled Study. Front Physiol. 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaal, A.A.M.; Abdulaziz, E.M. Effect of exercise therapy on physical performance and functional balance in patients on maintenance renal hemodialysis: Randomized controlled study. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2019, 15, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.M.M.; Figueiredo, P.H.S.; Silva, A.C.R.; Campos, P.C.; Gonçalves, G.T.; Freitas, J.d.P.C.; Junior, F.A.d.S.; Santos, J.M.; Alves, F.L.; Rodrigues, V.G.B.; et al. Determining factors of functioning in hemodialysis patients using the international classification of functioning, disability and health. BMC Nephrol 2022, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, R.M.; Syddall, H.E.; Cooper, R.; Kuh, D.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. Global variation in grip strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis of normative data. Age Ageing 2016, 45, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delanaye, P.; Quinonez, K.; Buckinx, F.; Krzesinski, J.M.; Bruyère, O. Hand grip strength measurement in haemodialysis patients: Before or after the session? Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 11, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matos, C.M.; Silva, L.F.; Santana, L.D.; Santos, L.S.; Protásio, B.M.; Rocha, M.T.; Ferreira, V.L.; Azevedo, M.F.; Martins, M.T.S.; Lopes, G.B.; et al. Handgrip Strength at Baseline and Mortality Risk in a Cohort of Women and Men on Hemodialysis: A 4-Year Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2014, 24, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.F.; Matos, C.M.; Lopes, G.B.; Martins, M.T.S.; Martins, M.S.; Arias, L.U.; Pisoni, R.L.; Lopes, A.A. Handgrip Strength as a Simple Indicator of Possible Malnutrition and Inflammation in Men and Women on Maintenance Hemodialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, R.; Kamitani, T.; Roshanravan, B.; Fukuma, S.; Joki, N.; Fukagawa, M. Decline in the Functional Status and Mortality in Patients on Hemodialysis: Results from the Japan Dialysis Outcome and Practice Patterns Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2019, 29, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D. Frailty and Protein-Energy Wasting in Elderly Patients with End Stage Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leavey, S.F.; McCullough, K.; Hecking, E.; Goodkin, D.; Port, F.K.; Young, E.W. Body mass index and mortality in ‘healthier’ as compared with ‘sicker’ haemodialysis patients: Results from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Abbott, K.C.; Salahudeen, A.K.; Kilpatrick, R.D.; Horwich, T.B. Survival advantages of obesity in dialysis patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suhardjono Umami, V.; Tedjasukmana, D.; Setiati, S. The effect of intradialytic exercise twice a week on the physical capacity, inflammation, and nutritional status of dialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Hemodial. Int. 2019, 23, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M.; Ogawa, M.; Kondo, H.; Suga, K.; Takahashi, T.; Itoh, H.; Tabata, Y. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle as a determinant of protein-energy wasting and frailty in maintenance hemodialysis patients: Retrospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajek, M.; Sember, V.; Čuk, I.; Šimenko, J.; Pajek, J. Comparison of Body Composition Monitor and InBody 720 Bioimpedance Devices for Body Composition Estimation in Hemodialysis Patients and Healthy Controls. Symmetry 2021, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrin, M.Y.; Morel, H. Body fluid volumes measurements by impedance: A review of bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and bioimpedance analysis (BIA) methods. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mager, J.R.; Sibley, S.D.; Beckman, T.R.; Kellogg, T.A.; Earthman, C.P. Multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis and bioimpedance spectroscopy for monitoring fluid and body cell mass changes after gastric bypass surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogiatzaki, E.; Michou, V.; Liakopoulos, V.; Roumeliotis, A.; Roumeliotis, S.; Kouidi, E.; Deligiannis, A. The effect of a 6-month intradialytic exercise program on hemodialysis adequacy and body composition: A randomized controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, C.; Marinho, S.; Lobo, J.C.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Barros, A.F.; Jacobson, L.V.; da Nobrega, A.C.L.; Rosa, M.L.G. Effects of resistance exercise training on acyl-ghrelin and obestatin levels in hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Yin, L.X. Effects of intradialytic resistance exercise on systemic inflammation in maintenance hemodialysis patients with sarcopenia: A randomized controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Alemañy, G.; Valdez-Ortiz, R.; Olvera-Soto, G.; Gomez-Guerrero, I.; Aguire-Esquivel, G.; Cantu-Quintanilla, G.; Lopez-Alvarenga, J.C.; Miranda-Alatriste, P.; Espinosa-Cuevas, A. The effects of resistance exercise and oral nutritional supplementation during hemodialysis on indicators of nutritional status and quality of life. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlini, L.M.; Alves, F.D.; Ceretta, L.B.; Perry, I.S.; Souza, G.C.; Clausell, N.O. Phase angle and mortality: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selberg, O.; Selberg, D. Norms and correlates of bioimpedance phase angle in healthy human subjects, hospitalized patients, and patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 86, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group A | Group Β | p/ES | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 15 | 14 | p = 0.87 (0.006) |
| Age (years) | 53.26 ± 9.48 | 54.50 ± 9.95 | p = 0.73 (0.05) |
| Height (cm) | 1.70 ± 0.07 | 1.68 ± 0.08 | p = 0.37 (0.45) |
| Dry weight (kg) | 78.96 ± 17.56 | 80.47 ± 21.73 | p = 0.67 (0.30) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.63 ± 4.19 | 28.69 ± 6.49 | p = 0.42 (0.18) |
| HD vintage (years) | 95.41 ± 77.22 | 96.67 ± 70.13 | p = 0.77 (0.03) |
| Dialysis access | |||
| 10 | 8 | p = 0.45 (0.28) |
| 5 | 6 | p = 0.87 (0.007) |
| Comorbidities | |||
| 2 | 1 | p = 0.89 (0.006) |
| 11 | 12 | p = 0.91 (0.01) |
| 3 | 2 | p = 0.89 (0.009) |
| 2 | 1 | p = 0.92 (0.02) |
| 4 | 2 | p = 0.76 (0.04) |
| 1 | 0 | p = 0.88 (0.008) |
| 1 | 2 | p = 0.81 (0.007) |
| Ht (%) | 36.2 ± 4.0 | 35.9 ± 4.1 | p = 0.55 (0.23) |
| Hb (mg/dL) | 12.3 ± 1.2 | 12.3 ± 1.1 | p = 0.81 (0.008) |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 106.1 ± 30.9 | 107.0 ± 31.1 | p = 0.65 (0.27) |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 11.2 ± 2.5 | 11.4 ± 2.1 | p = 0.94 (0.02) |
| URR (%) | 74.9 ± 3.2 | 75.0 ± 3.4 | p = 0.70 (0.03) |
| Kt/V | 1.25 ± 0.0 | 1.27 ± 0.1 | p = 0.58 (0.17) |
| Group A | Group B | A vs. B Group | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 4-Months | p (ES) | Δ (CI) | Baseline | After 4-Months | p (ES) | Δ (CI) | Pre p (ES) | Δp | Post p (ES) | Δp | |
| Handgrip Strength (kg) | 26.59 ± 9.23 | 28.61 ± 9.58 | p < 0.05 (1.41) | −2.01 (1.25/2.89) | 26.26 ± 6.55 | 26.00 ± 6.62 | p = 0.08 (1.39) | −0.26 (−0.12/0.64) | p = 0.12 (0.01) | p = 0.32 | p = 0.07 (0.03) | p = 0.32 |
| 10-STS (sec) | 22.40 ± 5.50 | 24.80 ± 6.33 | p < 0.05 (0.41) | 2.40 (1.42/3.43) | 22.07 ± 2.99 | 20.42 ± 3.73 | p < 0.05 (1.73) | 0.5 (−1.45/0.45) | p = 0.18 (0.02) | p = 0.46 | p < 0.05 (0.14) | p = 0.05 |
| 6-MWD (m) | 427.07 ± 7.66 | 468.16 ± 11.39 | p < 0.05 (1.69) | −19.76 (−44.80/−2.39) | 420.55 ± 13.17 | 408.54 ± 10.85 | p = 0.16 (0.39) | 12.01 (7.98/16.04) | p = 0.08 (0.09) | p = 0.51 | p = 0.06 (0.10) | p = 0.04 |
| Group A | Group B | A vs. B Group | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 4-Months | p (ES) | Δ (CI) | Baseline | After 4-Months | p (ES) | Δ (CI) | Pre p (ES) | Δp | Post p (ES) | Δp | |
| BF (kg) | 21.61 ± 6.62 | 20.52 ± 7.39 | p = 0.01 (0.52) | −1.09 (−2.40/0.04) | 28.57 ± 12.21 | 28.82 ± 12.68 | p = 0.51 (0.17) | 0.26 (−0.59/1.12) | p = 0.15 (0.12) | p = 0.37 | p < 0.05 (0.14) | p = 0.15 |
| BFMI (kg/m2) | 7.12 ± 2.09 | 6.65 ± 2.06 | p = 0.03 (0.68) | −1.09 (−2.40/0.04) | 9.41 ± 3.15 | 9.57 ± 3.38 | p = 0.43 (0.27) | 0.16 (−0.17/0.50) | p = 0.06 (0.16) | p = 0.09 | p = 0.12 (0.22) | p = 0.07 |
| FFMI (kg/m2) | 18.54 ± 2.60 | 19.08 ± 2.63 | p = 0.05 (0.60) | 0.13 (0.08/1.10) | 18.47 ± 2.94 | 18.47 ± 2.66 | p = 0.51 (0.01) | 0.007 (−0.33/0.35) | p = 0.87 (0.00) | p = 0.32 | p = 0.85 (0.01) | p = 0.31 |
| BCM (kg) | 33.16 ± 6.51 | 34.10 ± 6.07 | p = 0.11 (0.53) | 1.39 (−0.11/1.99) | 31.97 ± 7.30 | 31.09 ± 7.59 | p = 0.96 (0.46) | −0.88 (−1.99/0.21) | p = 0.90 (0.008) | p = 0.30 | p = 0.44 (0.04) | p = 0.26 |
| BMR (kcal) | 1713.80 ± 291.41 | 1754.53 ± 282.43 | p < 0.05 (0.70) | 40.73 (11.01/−76.41) | 1583.07 ± 278.22 | 1571.21 ± 275.63 | p = 0.57 (0.42) | −11.85 (−27.94/4.23) | p = 0.97 (0.05) | p = 0.06 | p = 0.90 (0.10) | p = 0.01 |
| BMR/BW (kcal/kg) | 21.95 ± 1.77 | 22.47 ± 2.00 | p = 0.06 (0.79) | 0.52 (0.17/0.94) | 20.13 ± 2.28 | 19.87 ± 2.27 | p = 0.13 (0.41) | −0.25 (−0.61/0.10) | p = 0.47 (0.17) | p = 0.16 | p = 0.54 (0.28) | p = 0.01 |
| ECW (lt) | 17.66 ± 2.65 | 18.30 ± 2.91 | p = 0.01 (0.52) | 0.64 (−0.03/1.41) | 17.10 ± 2.91 | 17.57 ± 2.67 | p = 0.15 (0.42) | 0.47 (−0.18/1.14) | p = 0.94 (0.01) | p = 0.12 | p = 0.45 (0.01) | p = 0.10 |
| ICW (lt) | 23.00 ± 4.15 | 23.87 ± 4.23 | p = 0.01 (0.72) | 0.87 (0.16/1.60) | 22.39 ± 5.10 | 22.81 ± 4.86 | p = 0.14 (0.45) | 0.42 (−0.11/0.95) | p = 0.75 (0.05) | p = 0.15 | p = 0.96 (0.01) | p = 0.12 |
| TBW (lt) | 41.10 ± 6.88 | 42.80 ± 7.00 | p = 0.01 (0.68) | 1.7 (0.37/3.28) | 39.22 ± 7.20 | 40.03 ± 7.18 | p = 0.11 (0.44) | 0.81 (−0.05/1.68) | p = 0.84 (0.01) | p = 0.08 | p = 0.70 (0.03) | p = 0.06 |
| LEAN (kg) | 56.96 ± 11.26 | 58.53 ± 11.15 | p = 0.01 (0.68) | 1.56 (0.34/3.03) | 51.92 ± 11.36 | 51.87 ± 10.62 | p = 0.32 (0.53) | −0.05 (−0.97/0.85) | p = 0.99 (0.02) | p = 0.28 | p = 0.94 (0.04) | p = 0.25 |
| DRY LEAN (kg) | 15.88 ± 5.11 | 15.73 ± 5.06 | p = 0.29 (0.28) | −0.14 (−0.47/0.13) | 12.71 ± 4.75 | 11.91 ± 4.88 | p = 0.89 (0.28) | −0.14 (−2.60/0.43) | p = 0.71 (0.05) | p = 0.18 | p = 0.58 (0.09) | p = 0.01 |
| PhA (0) | 4.94 ± 0.77 | 5.60 ± 1.96 | p = 0.04 (0.42) | 0.65 (−0.33/1.14) | 5.29 ± 2.18 | 5.18 ± 2.41 | p = 0.14 (0.28) | −0.10 (−1.85/0.42) | p = 0.21 (0.10) | p = 0.80 | p = 0.22 (0.14) | p = 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michou, V.; Davioti, M.; Syrakou, N.; Liakopoulos, V.; Deligiannis, A.; Kouidi, E. Effects of a Combined Intradialytic Exercise Training Program on Functional Capacity and Body Composition in Kidney Transplant Candidates. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010009
Michou V, Davioti M, Syrakou N, Liakopoulos V, Deligiannis A, Kouidi E. Effects of a Combined Intradialytic Exercise Training Program on Functional Capacity and Body Composition in Kidney Transplant Candidates. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2023; 8(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichou, Vasiliki, Michaela Davioti, Niki Syrakou, Vasilios Liakopoulos, Asterios Deligiannis, and Evangelia Kouidi. 2023. "Effects of a Combined Intradialytic Exercise Training Program on Functional Capacity and Body Composition in Kidney Transplant Candidates" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 8, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010009
APA StyleMichou, V., Davioti, M., Syrakou, N., Liakopoulos, V., Deligiannis, A., & Kouidi, E. (2023). Effects of a Combined Intradialytic Exercise Training Program on Functional Capacity and Body Composition in Kidney Transplant Candidates. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 8(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010009