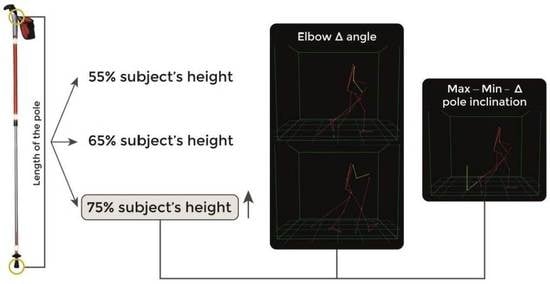
The Impact of Nordic Walking Pole Length on Gait Kinematic Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
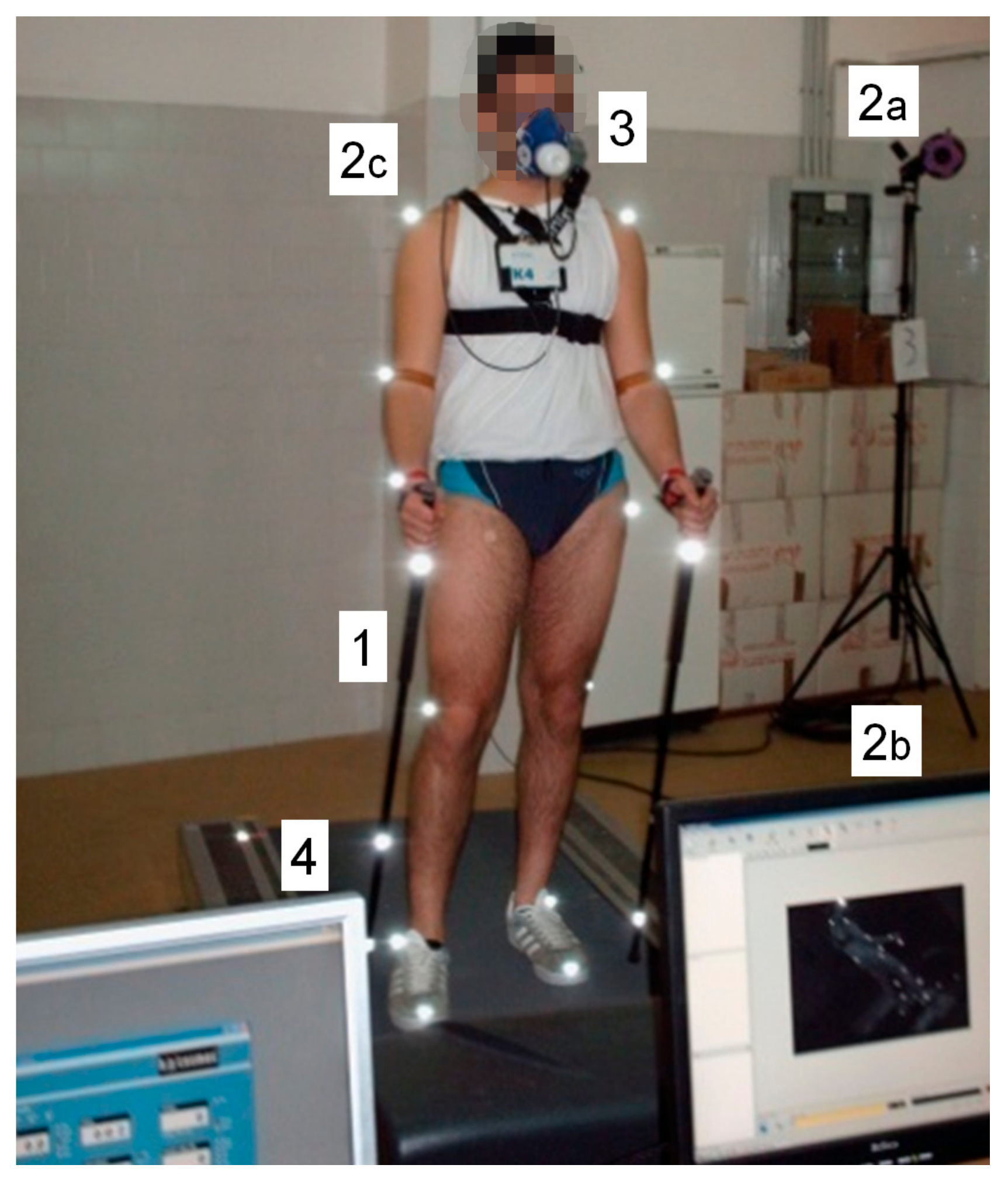
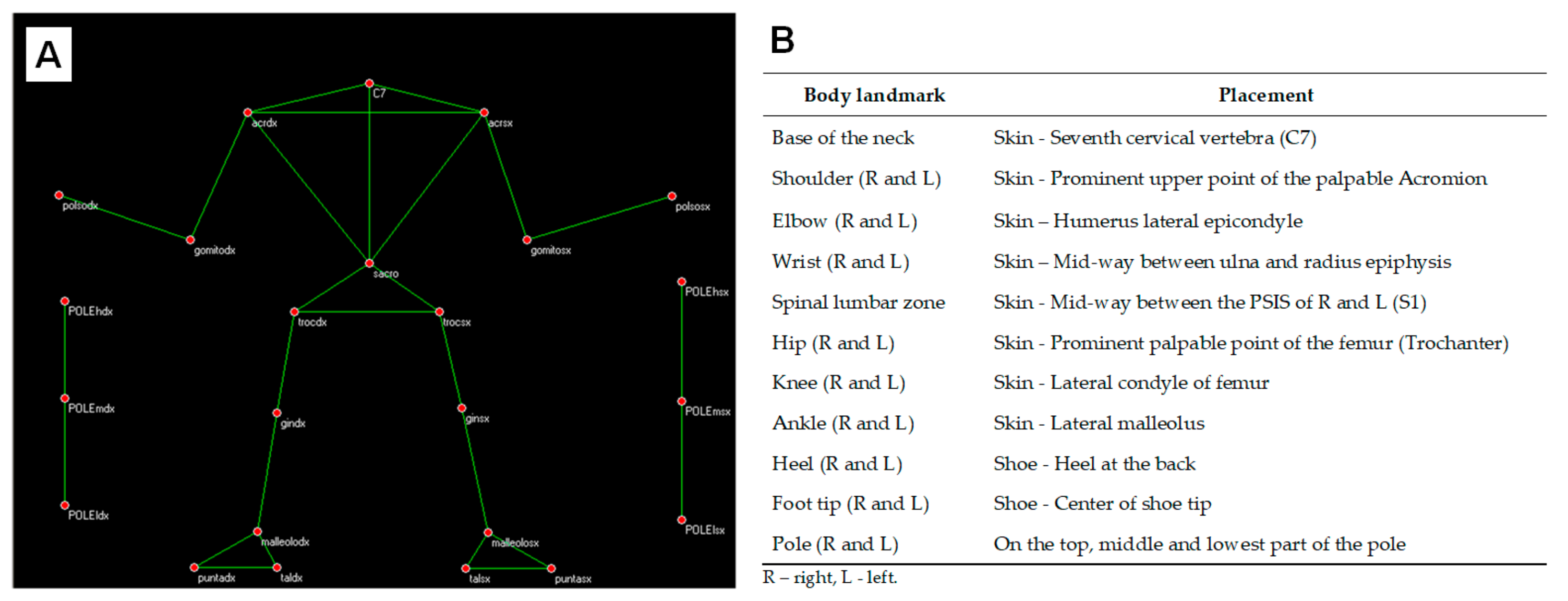
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Procedure and Data Collection
2.3.1. Kinematic Data
2.3.2. Fatigue and Metabolic Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Kinematic Differecences between NW65 and W
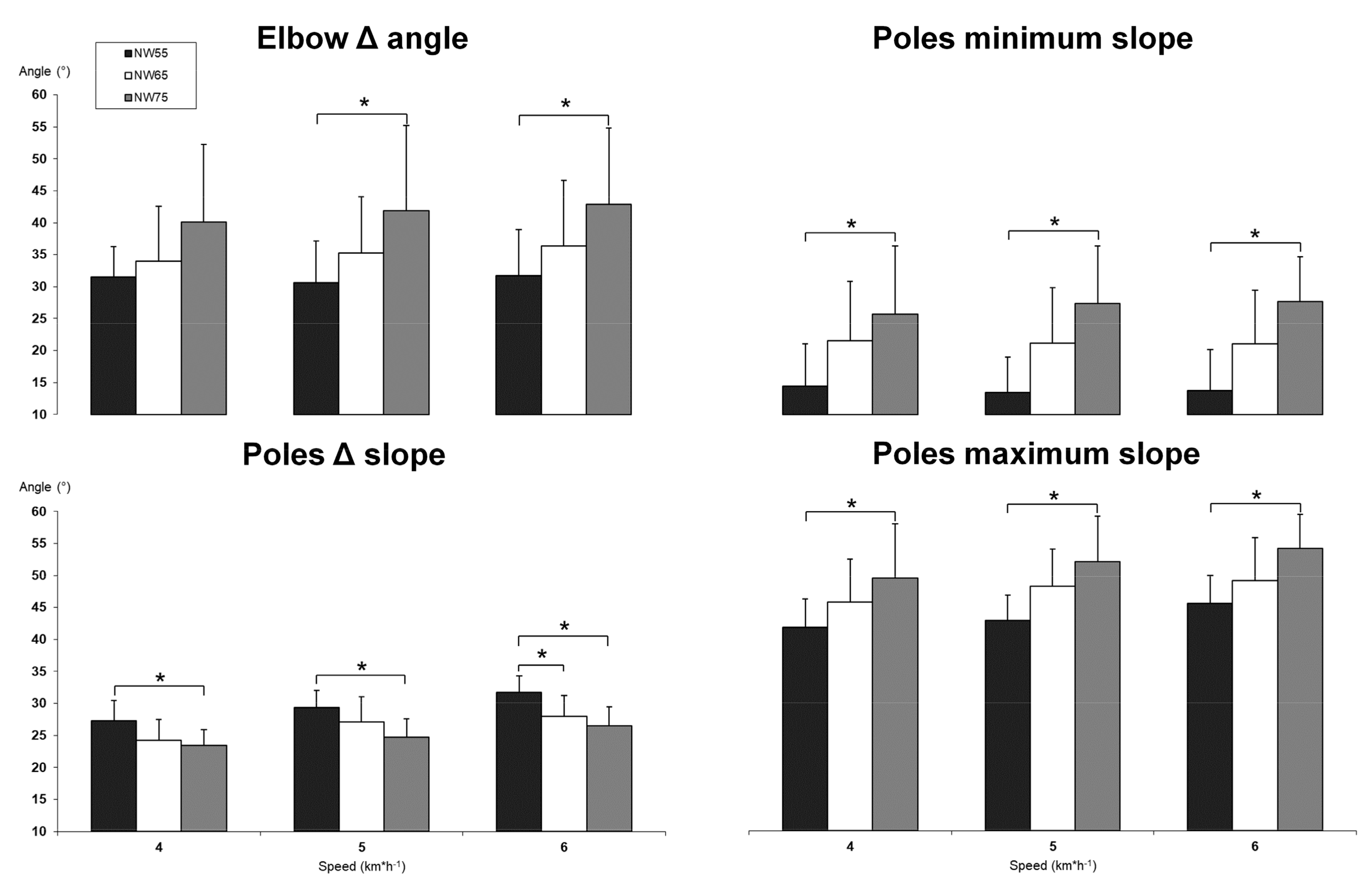
3.2. Kinematic Differecences between NW with Different Poles’ Length
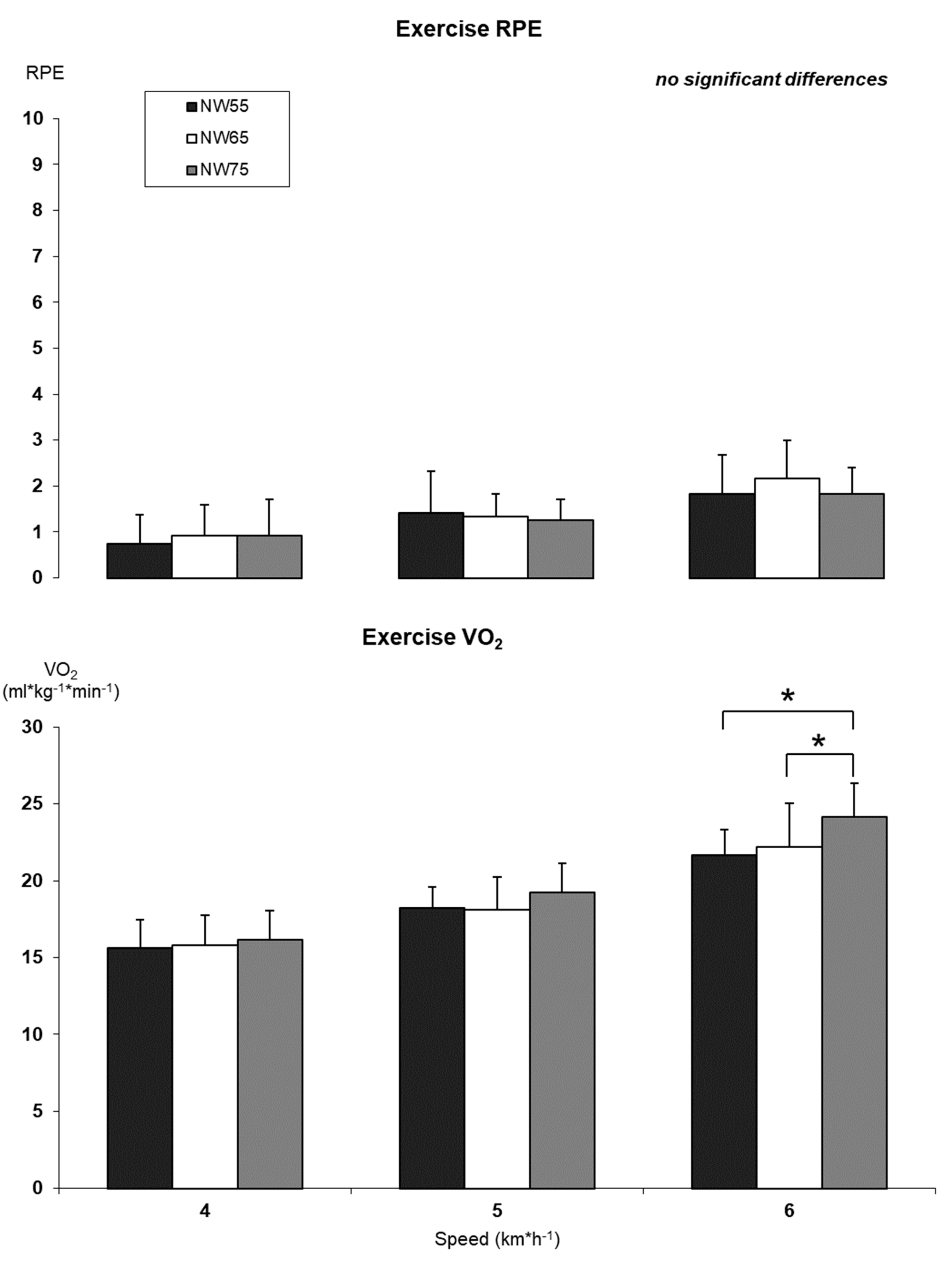
3.3. Correlations between Metabolic Data and Kinematics in NW
4. Discussion
4.1. Kinematic Differecences between NW65 and W
4.2. Characterization of NW with Different Poles’ Length
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- All the figures for the kinematic parameters described in Table 3;
- All the results for the data described into the Section 3.2. Kinematic differences between NW with different poles’ length.

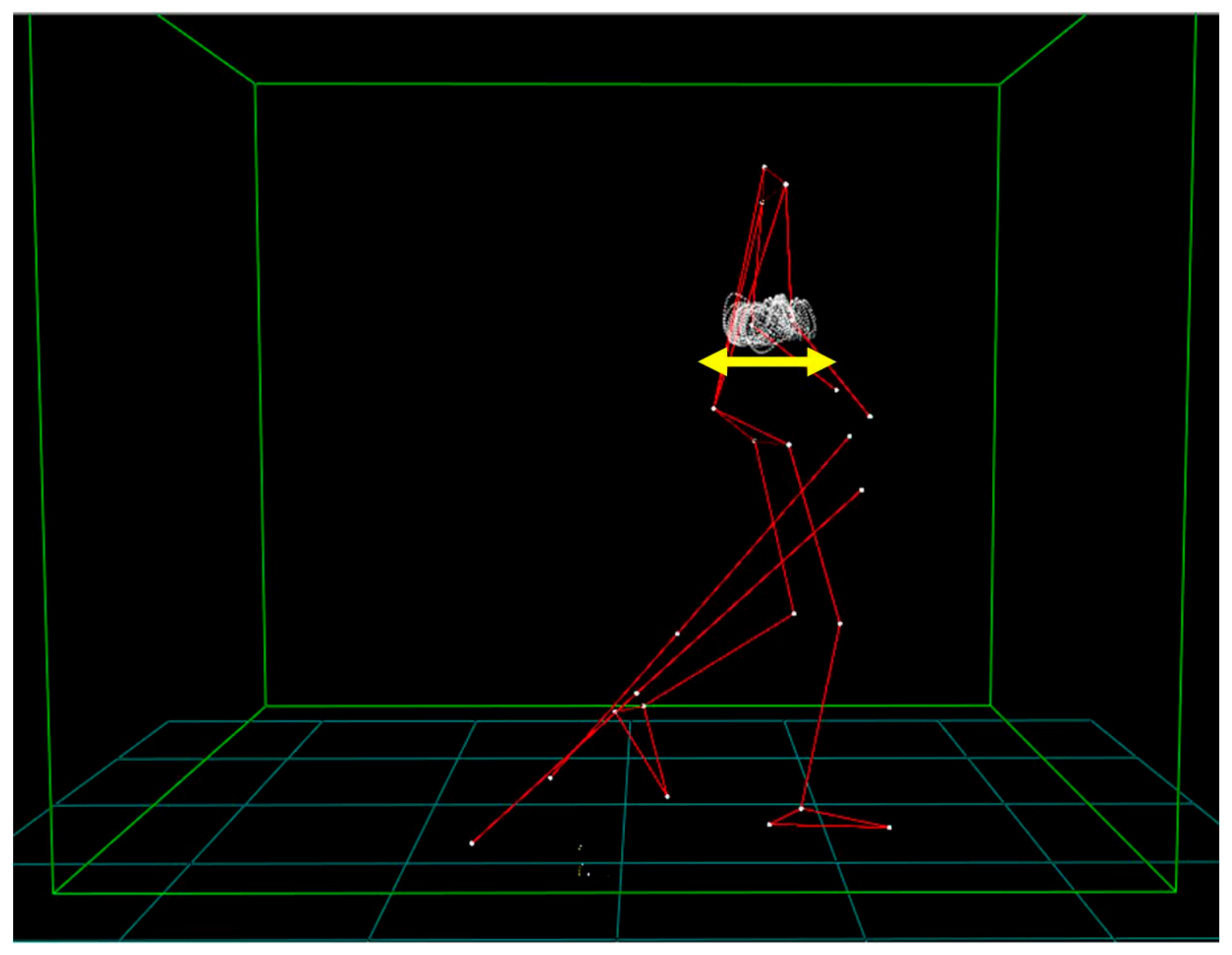
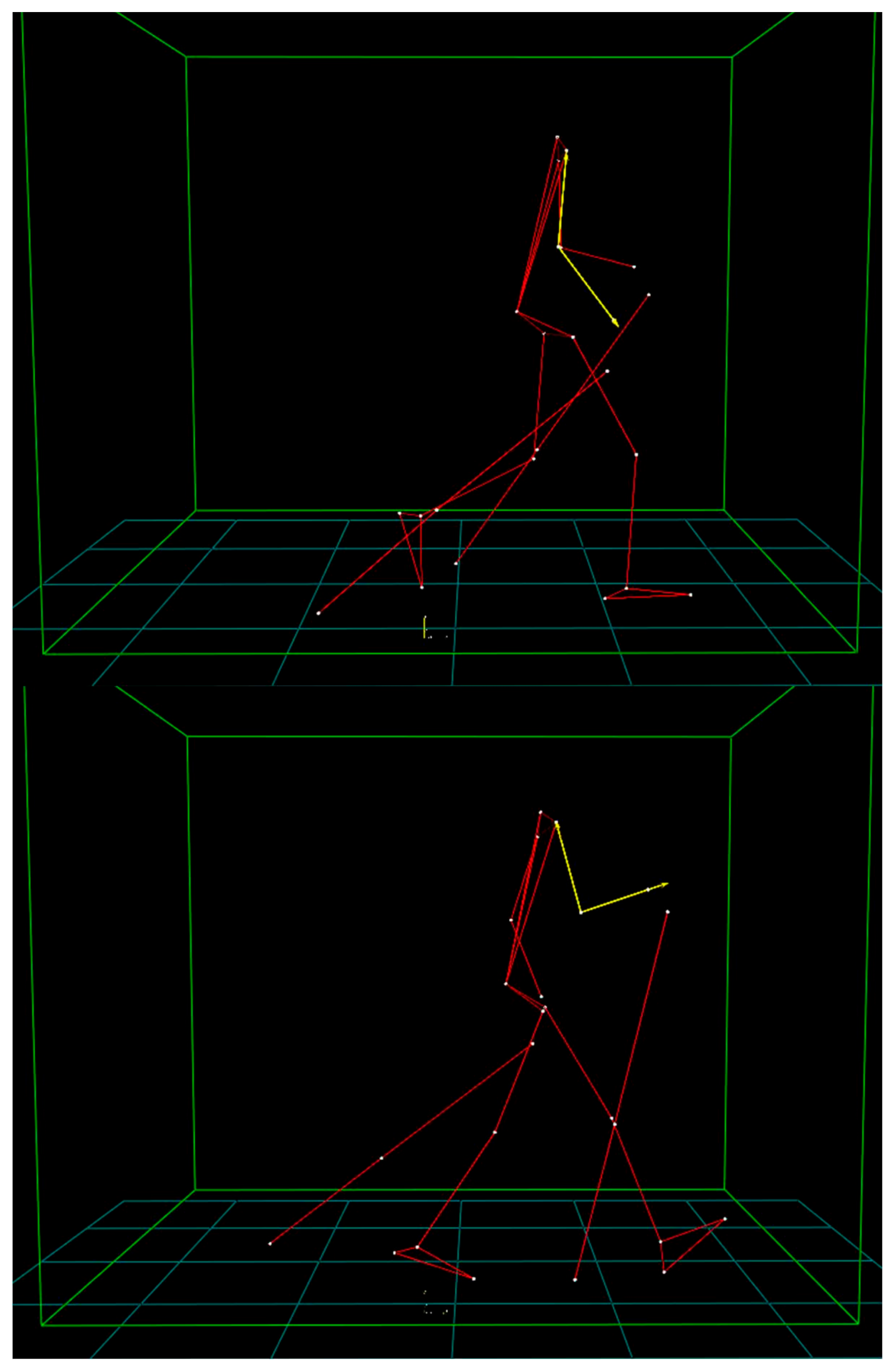
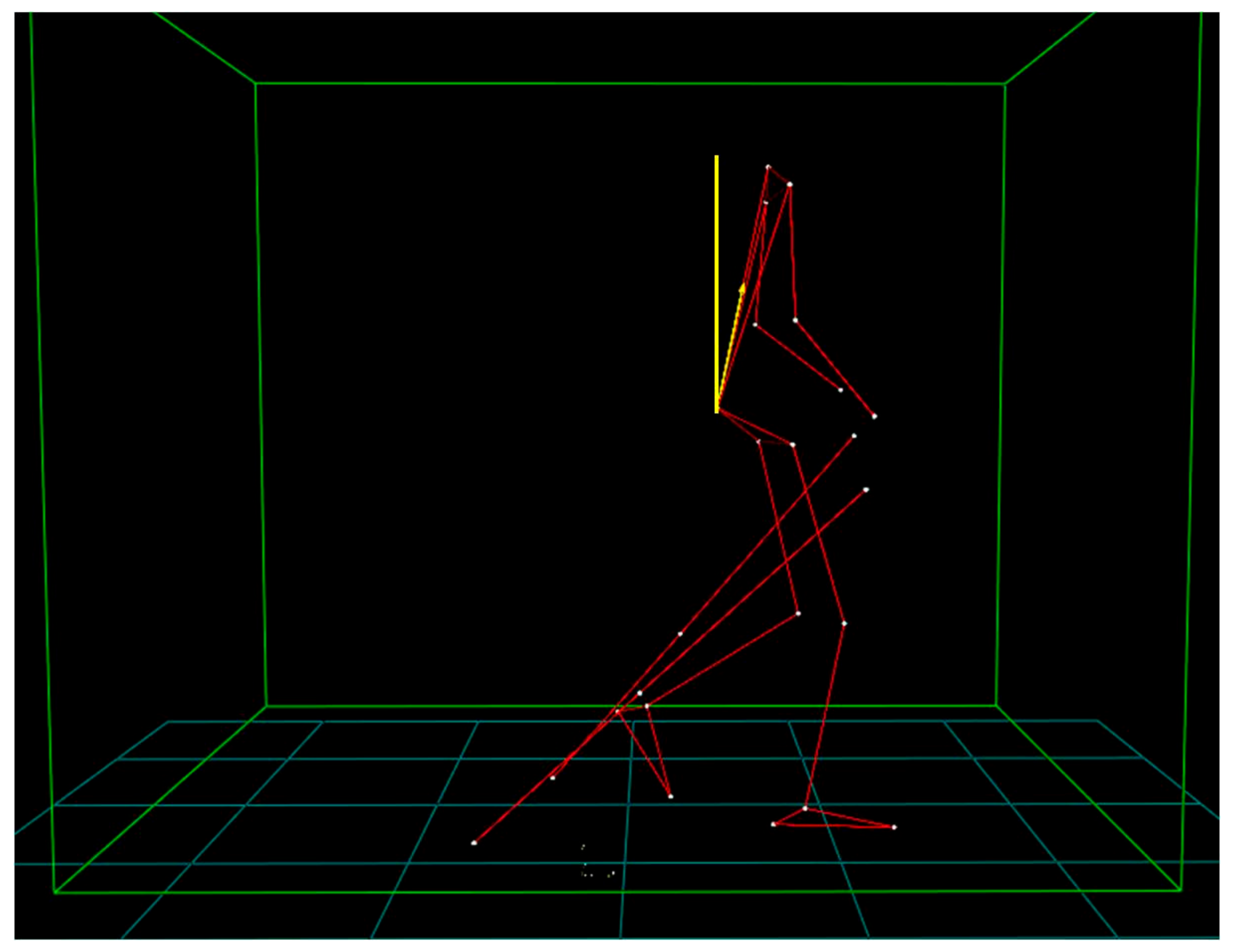

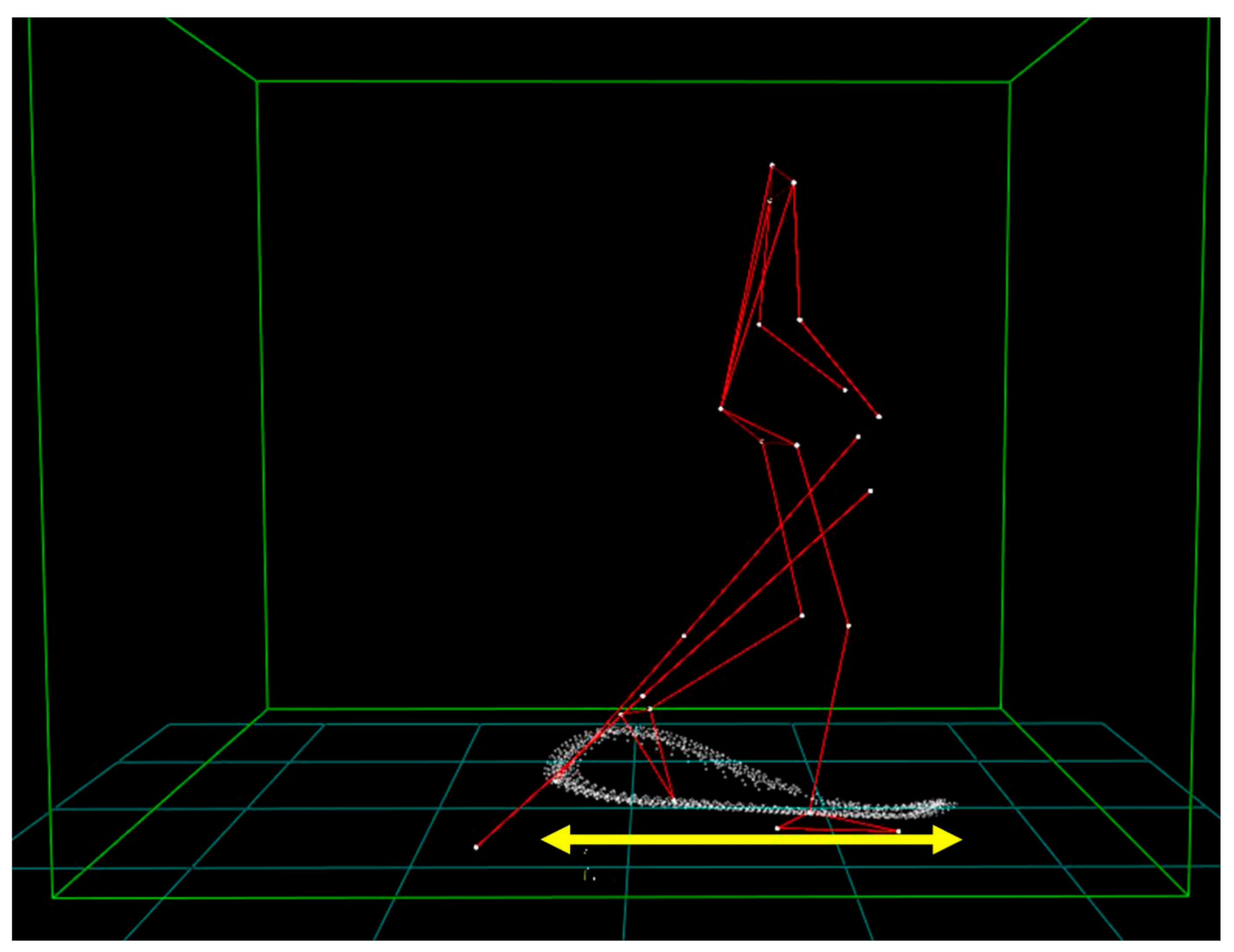
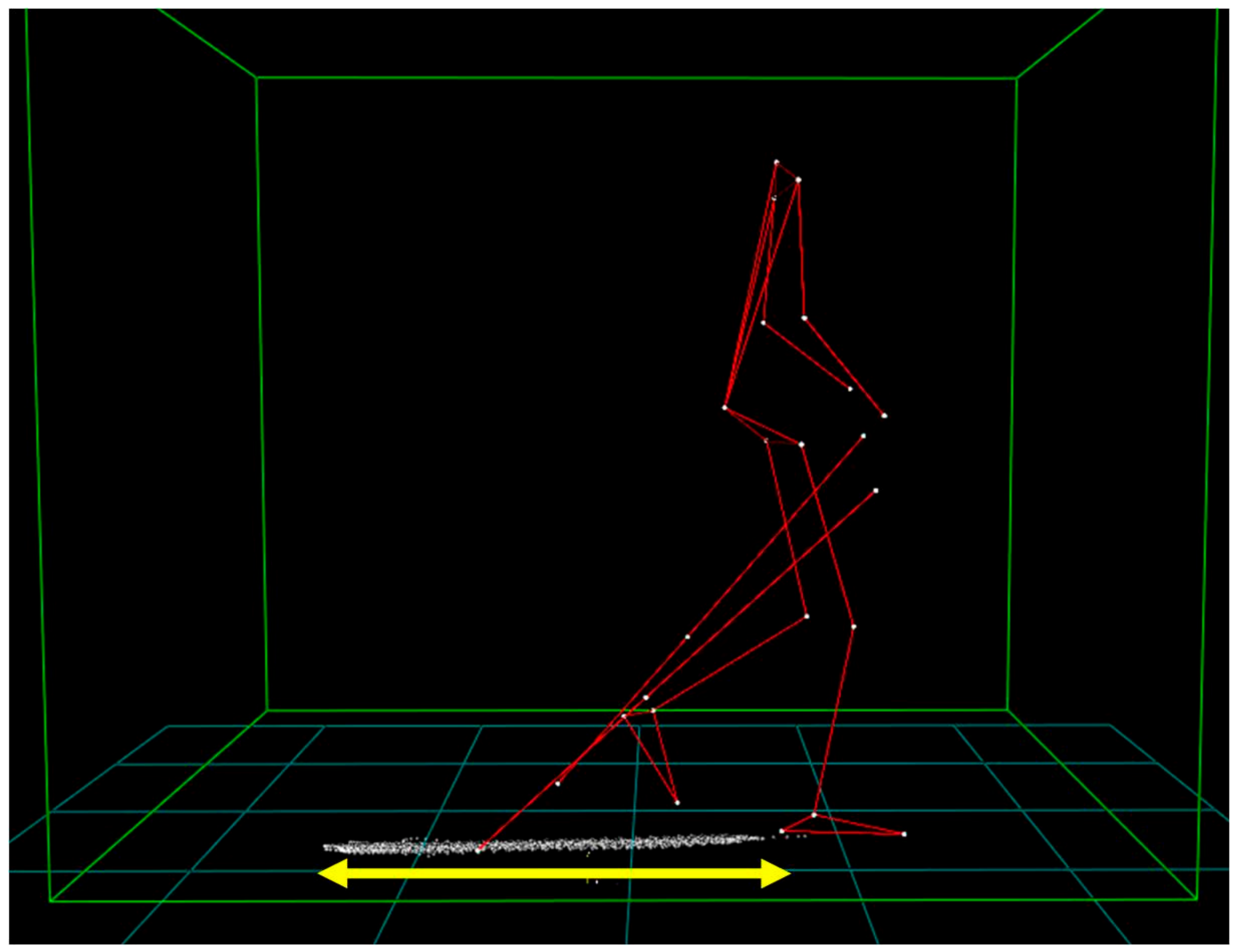

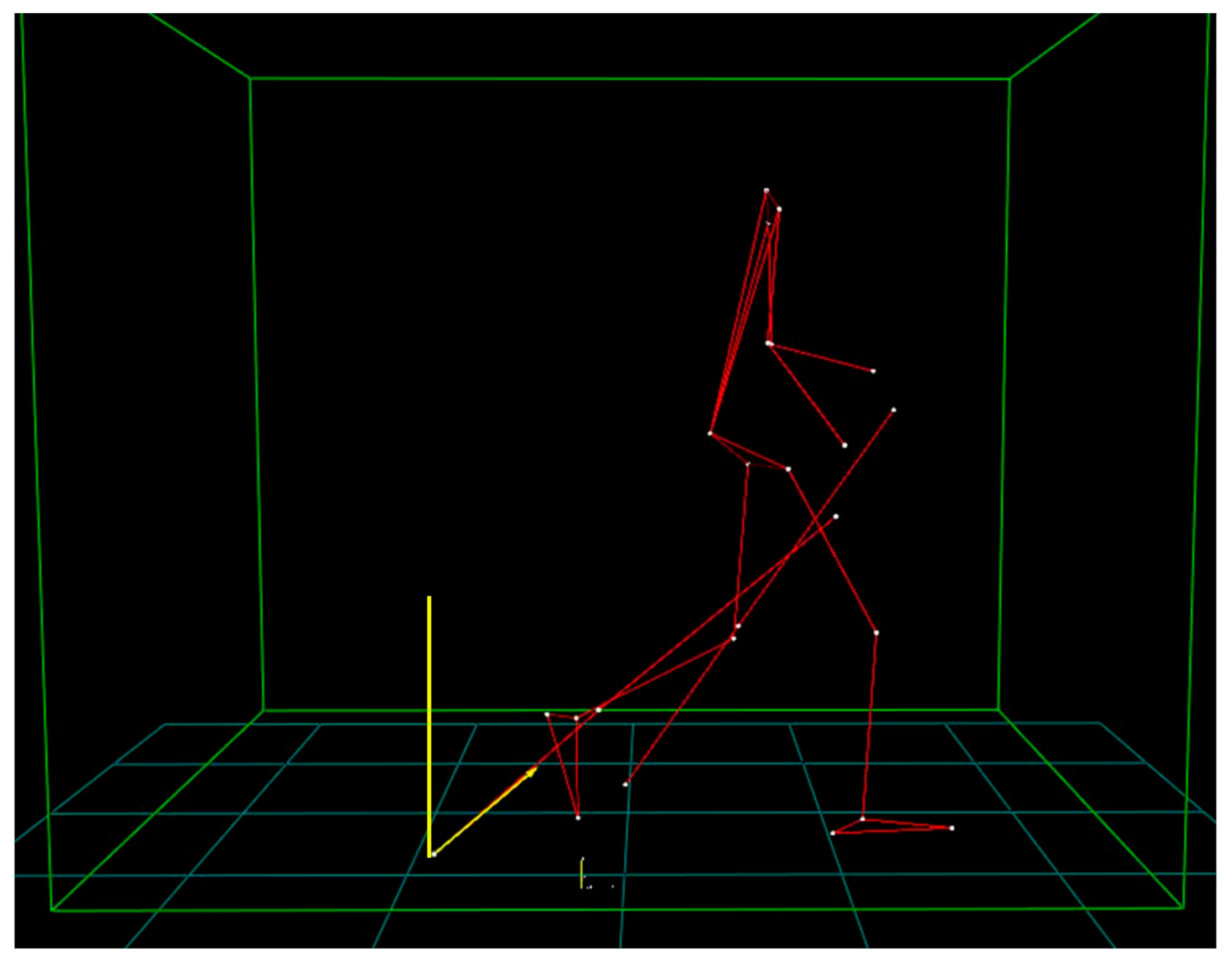
| Parameter | 4 km∗h−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NW55 Mean (SD) | NW65 Mean (SD) | NW75 Mean (SD) | p Value 55–65 | p Value 65–75 | p Value 55–75 | |
| C7 vertical acceleration peak (m∗s−2) | 3.1 (0.2) | 3.0 (0.3) | 3.1 (0.3) | 0.948 | 0.894 | 0.998 |
| C7 vertical displacement (cm) | 3.7 (0.4) | 3.5 (0.5) | 3.8 (0.5) | 0.559 | 0.322 | 0.973 |
| Elbow horizontal displacement (cm) | 10.9 (3.0) | 10.9 (4.3) | 12.2 (4.5) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.802 |
| Elbow Δ angle (°) | 31.6 (4.7) | 34.0 (8.6) | 40.1 (12.2) | 0.888 | 0.293 | 0.081 |
| Elbow advancing speed (m∗s−1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.948 | 0.855 | 0.549 |
| Spine forward slope (°) | 9.7 (3.1) | 9.3 (2.6) | 9.3 (2.6) | 0.968 | 1.000 | 0.982 |
| S1 vertical displacement (cm) | 3.2 (0.5) | 3.1 (0.6) | 3.1 (0.8) | 0.946 | 1.000 | 0.946 |
| Step length (m) | 0.68 (0.03) | 0.66 (0.04) | 0.67 (0.03) | 0.590 | 0.963 | 0.857 |
| Step frequency (Hz) | 0.82 (0.05) | 0.85 (0.08) | 0.82 (0.04) | 0.520 | 0.412 | 0.998 |
| Tip sagittal displacement (m) | 0.63 (0.04) | 0.62 (0.03) | 0.64 (0.03) | 0.913 | 0.480 | 0.853 |
| Movement frequency (Hz) | 0.82 (0.04) | 0.83 (0.04) | 0.82 (0.04) | 0.748 | 1.000 | 0.763 |
| Minimum slope (°) | 14.5 (6.6) | 21.6 (9.3) | 25.7 (10.7) | 0.176 | 0.606 | 0.013 * |
| Maximum slope (°) | 41.8 (4.4) | 45.8 (6.7) | 49.5 (4.0) | 0.411 | 0.475 | 0.028 * |
| Δ Slope (°) | 27.3 (3.2) | 24.2 (3.2) | 23.4 (2.5) | 0.054 | 0.884 | 0.010 * |
| SL/EHD ratio (cm) | 6.8 (2.6) | 7.3 (4.1) | 6.4 (3.1) | 0.979 | 0.879 | 0.985 |
| Parameter | 5 km∗h−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NW55 Mean (SD) | NW65 Mean (SD) | NW75 Mean (SD) | p Value 55–65 | p Value 65–75 | p Value 55–75 | |
| C7 vertical acceleration peak (m∗s−2) | 3.2 (0.3) | 3.3 (0.3) | 3.3 (0.4) | 1.000 | 0.962 | 0.949 |
| C7 vertical displacement (cm) | 4.7 (0.6) | 4.7 (0.7) | 4.6 (0.8) | 0.990 | 0.999 | 0.967 |
| Elbow horizontal displacement (cm) | 13.0 (3.2) | 12.7 (3.4) | 13.7 (4.0) | 0.993 | 0.870 | 0.960 |
| Elbow Δ angle (°) | 30.7 (6.5) | 35.3 (8.8) | 41.9 (13.3) | 0.599 | 0.298 | 0.027 * |
| Elbow advancing speed (m∗s−1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 1.000 | 0.558 | 0.536 |
| Spine forward slope (°) | 10.1 (3.1) | 10.0 (3.3) | 10.0 (2.7) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| S1 vertical displacement (cm) | 4.4 (0.7) | 4.5 (1.5) | 4.0 (1.1) | 0.994 | 0.761 | 0.885 |
| Step length (m) | 0.74 (0.03) | 0.74 (0.04) | 0.7 (0.03) | 0.987 | 0.721 | 0.522 |
| Step frequency (Hz) | 0.91 (0.03) | 0.91 (0.04) | 0.93 (0.04) | 0.944 | 0.848 | 0.532 |
| Tip sagittal displacement (m) | 0.68 (0.04) | 0.69 (0.05) | 0.69 (0.03) | 0.906 | 0.950 | 0.999 |
| Movement frequency (Hz) | 0.91 (0.03) | 0.91 (0.04) | 0.93 (0.04) | 0.971 | 0.499 | 0.759 |
| Minimum slope (°) | 13.5 (5.5) | 21.1 (8.8) | 27.4 (9.0) | 0.071 | 0.171 | 0.000 * |
| Maximum slope (°) | 42.9 (4.0) | 48.2 (5.8) | 52.1 (7.1) | 0.090 | 0.289 | 0.001 * |
| Δ Slope (°) | 29.4 (2.7) | 27.1 (3.9) | 24.7 (2.8) | 0.231 | 0.213 | 0.003 * |
| SL/EHD ratio (cm) | 6.0 (1.4) | 6.3 (2.0) | 5.8 (2.1) | 0.972 | 0.900 | 0.994 |
| Parameter | 6 km∗h−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NW55 Mean (SD) | NW65 Mean (SD) | NW75 Mean (SD) | p Value 55–65 | p Value 65–75 | p Value 55–75 | |
| C7 vertical acceleration peak (m∗s−2) | 3.7 (0.4) | 3.7 (0.4) | 3.7 (0.5) | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.973 |
| C7 vertical displacement (cm) | 5.8 (0.8) | 5.7 (1.0) | 5.7 (1.2) | 0.992 | 0.999 | 0.973 |
| Elbow horizontal displacement (cm) | 14.2 (3.7) | 14.1 (4.3) | 15.6 (4.4) | 1.000 | 0.752 | 0.811 |
| Elbow Δ angle (°) | 31.7 (7.21) | 36.4 (10.2) | 42.8 (12.0) | 0.602 | 0.328 | 0.031 * |
| Elbow advancing speed (m∗s−1) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.1) | 1.000 | 0.685 | 0.644 |
| Spine forward slope (°) | 11.4 (2.9) | 10.9 (2.5) | 11.3 (2.8) | 0.969 | 0.985 | 1.000 |
| S1 vertical displacement (cm) | 5.65 (0.8) | 5.49 (1.1) | 5.35 (1.6) | 0.989 | 0.970 | 0.869 |
| Step length (m) | 0.81 (0.04) | 0.80 (0.05) | 0.79 (0.04) | 0.995 | 0.822 | 0.691 |
| Step frequency (Hz) | 0.98 (0.03) | 0.99 (0.05) | 1.00 (0.04) | 0.929 | 0.966 | 0.711 |
| Tip sagittal displacement (m) | 0.73 (0.04) | 0.74 (0.06) | 0.74 (0.06) | 0.913 | 0.998 | 0.964 |
| Movement frequency (Hz) | 0.99 (0.04) | 0.99 (0.05) | 1.00 (0.04) | 1.000 | 0.963 | 0.975 |
| Minimum slope (°) | 13.7 (6.4) | 21.1 (8.4) | 27.7 (7.0) | 0.059 | 0.095 | 0.000 * |
| Maximum slope (°) | 45.5 (4.3) | 49.1 (6.8) | 54.2 (5.3) | 0.337 | 0.088 | 0.002 * |
| Δ Slope (°) | 31.7 (2.6) | 28.0 (3.2) | 26.5 (3.0) | 0.013 * | 0.500 | 0.000 * |
| SL/EHD ratio (cm) | 6.00 (1.4) | 6.38 (2.6) | 5.47 (1.7) | 0.943 | 0.579 | 0.884 |
References
- Kukkonen-Harjula, K.; Hiilloskorpi, H.; Mänttäri, A.; Pasanen, M.; Parkkari, J.; Suni, J.; Fogelholm, M.; Laukkanen, R. Self-Guided Brisk Walking Training with or without Poles: A Randomized-Controlled Trial in Middle-Aged Women. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2007, 17, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.; Henriksen, M.; Larsen, P.; Alkjaer, T. Nordic Walking Does Not Reduce the Loading of the Knee Joint. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2008, 18, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, E.A.; Smith, G. Energy Expenditure and Comfort during Nordic Walking with Different Pole Lengths. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschentscher, M.; Niederseer, D.; Niebauer, J. Health Benefits of Nordic Walking: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 44, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.J.; Krol-Warmerdam, E.M.M.; Ranke, G.M.C.; Vermeulen, H.M.; Van Der Heijden, J.; Nortier, J.W.R.; Kaptein, A.A. Stick Together: A Nordic Walking Group Intervention for Breast Cancer Survivors. J. Psychosoc. Oncol. 2015, 33, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lastra, M.A.; Torres, J.; Martínez-Lemos, I.; Ayán, C. Nordic Walking for Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Cancer Care Engl. 2019, 28, e13130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Guardia, L.; Carnevale Pellino, V.; Filipas, L.; Bonato, M.; Gallo, G.; Lovecchio, N.; Vandoni, M.; Codella, R. Nordic Walking Improves Cardiometabolic Parameters, Fitness Performance, and Quality of Life in Older Adults With Type 2 Diabetes. Endocr. Pract. 2023, 29, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, B.; Christensen, R.; Christiansen, C.; Gram, J. Effects of Nordic Walking and Exercise in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2010, 20, 355–361. [Google Scholar]
- Di Blasio, A.; Morano, T.; Napolitano, G.; Bucci, I.; Di Santo, S.; Gallina, S.; Cugusi, L.; Di Donato, F.; D′Arielli, A.; Cianchetti, E. Nordic Walking and the Isa Method for Breast Cancer Survivors: Effects on Upper Limb Circumferences and Total Body Extracellular Water—A Pilot Study. Breast Care Basel 2016, 11, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, T.; Siersma, V.; Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M.; Christensen, H.E.; Beyer, N. In Hip Osteoarthritis, Nordic Walking Is Superior to Strength Training and Home-Based Exercise for Improving Function. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2017, 27, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O′Donovan, R.; Kennedy, N. “Four Legs Instead of Two”—Perspectives on a Nordic Walking-Based Walking Programme among People with Arthritis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoletto, A.; Mauro, M.; Oppio, A.; Greco, G.; Fischetti, F.; Cataldi, S.; Toselli, S. Effects of Nordic Walking Training on Anthropometric, Body Composition and Functional Parameters in the Middle-Aged Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullo, V.; Gobbo, S.; Vendramin, B.; Duregon, F.; Cugusi, L.; Di Blasio, A.; Bocalini, D.S.; Zaccaria, M.; Bergamin, M.; Ermolao, A. Nordic Walking Can Be Incorporated in the Exercise Prescription to Increase Aerobic Capacity, Strength, and Quality of Life for Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rejuvenation Res. 2018, 21, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, C.D.; VanHeest, J.L.; Schachter, C.L. Energy expenditure during submaximal walking with Exerstriders. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 1995, 27, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.R.; Porcari, J.P.; Brice, G.; Terry, L. Acute Responses to Using Walking Poles in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. 1996, 16, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcari, J.P.; Hendrickson, T.L.; Walter, P.R.; Terry, L.; Walsko, G. The Physiological Responses to Walking with and without Power Poles on Treadmill Exercise. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1997, 68, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, T.S.; Earnest, C.P.; Morss, G.M. Field Testing of Physiological Responses Associated with Nordic Walking. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2002, 73, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, T.; Knicker, A.; Hoffman, U.; Harwig, B.; Hollmann, W.; Strüder, H.K. Physiological Responses to Nordic Walking, Walking and Jogging. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 98, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrey, S.; Fabre, N. Exertion during uphill, level and downhill walking with and without hiking poles. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2008, 7, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, M.J.; Hipp, G.R.; Wenos, D.L.; Deaton, M.L. Trekking Poles Increase Physiological Responses to Hiking without Increased Perceived Exertion. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figard-Fabre, H.; Fabre, N.; Leonardi, A.; Schena, F. Physiological and Perceptual Responses to Nordic Walking in Obese Middle-Aged Women in Comparison with the Normal Walk. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziuba, A.K.; Żurek, G.; Garrard, I.; Wierzbicka-Damska, I. Biomechanical Parameters in Lower Limbs during Natural Walking and Nordic Walking at Different Speeds. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2015, 17, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwameder, H.; Roithner, R.; Müller, E.; Niessen, W.; Raschner, C. Knee Joint Forces during Downhill Walking with Hiking Poles. J. Sport. Sci. 1999, 17, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.B.; Henriksen, M.; Aaboe, J.; Hansen, L.; Simonsen, E.B.; Alkjær, T. Is It Possible to Reduce the Knee Joint Compression Force during Level Walking with Hiking Poles? Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2011, 21, e195–e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willson, J.; Torry, M.R.; Decker, M.J.; Kernozek, T.; Steadman, J.R. Effects of Walking Poles on Lower Extremity Gait Mechanics. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2001, 33, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stief, F.; Kleindienst, F.I.; Wiemeyer, J.; Wedel, F.; Campe, S.; Krabbe, B. Inverse Dynamic Analysis of the Lower Extremities during Nordic Walking, Walking, and Running. J. Appl. Biomech. 2008, 24, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, B.; Peyré-Tartaruga, L.A.; Zoppirolli, C.; Bortolan, L.; Bacchi, E.; Figard-Fabre, H.; Schena, F. Exploring Muscle Activation during Nordic Walking: A Comparison between Conventional and Uphill Walking. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocur, P.; Pospieszna, B.; Choszczewski, D.; Michalowski, L.; Wiernicka, M.; Lewandowski, J. The Effects of Nordic Walking Training on Selected Upper-Body Muscle Groups in Female-Office Workers: A Randomized Trial. Work 2017, 56, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeterbakken, A.H.; Nordengen, S.; Andersen, V.; Fimland, M.S. Nordic Walking and Specific Strength Training for Neck- and Shoulder Pain in Office Workers: A Pilot-Study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Grattard, V.; Dinet, C.; Soares, A.V.; Decavel, P.; Sagawa, Y.J. Nordic Walking Influence on Biomechanical Parameters: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, T.; Knicker, A.; Dannöhl, R.; Strüder, H.K. Energy Cost and Pole Forces during Nordic Walking under Different Surface Conditions. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2009, 41, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, E.; Yakushi, K.; Takeda, M.; Islam, M.M.; Nakagaichi, M.; Taaffe, D.R.; Takeshima, N. Proficiency in Pole Handling during Nordic Walking Influences Exercise Effectiveness in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Yang, D.J.; Kang, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Uhm, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S. Effects of Nordic Walking and Walking on Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters and Ground Reaction Force. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 2891–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, T.; Knicker, A.; Montanarella, M.; Strüder, H.K. Mechanical and Physiological Effects of Varying Pole Weights during Nordic Walking Compared to Walking. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Is Nordic Walking|INWA. Available online: https://www.inwa-nordicwalking.com/about-us/what-is-nordic-walking/ (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Encarnación-Martínez, A.; Catalá-Vilaplana, I.; Aparicio, I.; Sanchis-Sanchis, R.; Priego-Quesada, J.I.; Jimenez-Perez, I.; Pérez-Soriano, P. Does Nordic Walking technique influence the ground reaction forces? Gait Posture 2023, 101, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padulo, J.; Chamari, K.; Ardigò, L.P. Walking and Running on Treadmill: The Standard Criteria for Kinematics Studies. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardigò, L.P.; Buglione, A.; Russo, L.; Cular, D.; Esposito, F.; Doria, C.; Padulo, J. Marathon Shoes vs. Track Spikes: A Crossover Pilot Study on Metabolic Demand at Different Speeds in Experienced Runners. Res. Sport. Med. 2023, 31, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.; Montagnani, E.; Pietrantuono, D.; D’Angona, F.; Fratini, T.; Di Giminiani, R.; Palermi, S.; Ceccarini, F.; Migliaccio, G.M.; Lupu, E.; et al. Self-Myofascial Release of the Foot Plantar Surface: The Effects of a Single Exercise Session on the Posterior Muscular Chain Flexibility after One Hour. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardigò, L.P.; Palermi, S.; Padulo, J.; Dhahbi, W.; Russo, L.; Linetti, S.; Cular, D.; Tomljanovic, M. External Responsiveness of the SuperOpTM Device to Assess Recovery After Exercise: A Pilot Study. Front. Sport. Act. Living 2020, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomeñuka, N.A.; Oliveira, H.B.; Silva, E.S.; Costa, R.R.; Kanitz, A.C.; Liedtke, G.V.; Schuch, F.B.; Peyré-Tartaruga, L.A. Effects of Nordic walking training on quality of life, balance and functional mobility in elderly: A randomized clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leardini, A.; Sawacha, Z.; Paolini, G.; Ingrosso, S.; Nativo, R.; Benedetti, M.G. A New Anatomically Based Protocol for Gait Analysis in Children. Gait Posture 2007, 26, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibella, F.; Frosio, I.; Schena, F.; Borghese, N.A. 3D Analysis of the Body Center of Mass in Rock Climbing. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2007, 26, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Benedetti, M.G.; Pavan, E.; Frigo, C.; Bettinelli, D.; Rabuffetti, M.; Crenna, P.; Leardini, A. Quantitative Comparison of Five Current Protocols in Gait Analysis. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinley, J.L.; Baker, R.; Wolfe, R.; Morris, M.E. The Reliability of Three-Dimensional Kinematic Gait Measurements: A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.; Leardini, A.; Cavazza, S.; Ferraresi, G.; Marchi, P.; Zanaga, E.; Benedetti, M.G. Repeatability of a New Protocol for Gait Analysis in Adult Subjects. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giminiani, R.; Di Lorenzo, D.; La Greca, S.; Russo, L.; Masedu, F.; Totaro, R.; Padua, E. Angle-Angle Diagrams in the Assessment of Locomotion in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis: A Preliminary Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.; Di Capua, R.; Arnone, B.; Borrelli, M.; Coppola, R.; Esposito, F.; Padulo, J. Shoes and Insoles: The Influence on Motor Tasks Related to Walking Gait Variability and Stability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.; Florhaug, J.A.; Franklin, J.; Gottschall, L.; Hrovatin, L.A.; Parker, S.; Doleshal, P.; Dodge, C. A new approach to monitoring exercise training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2001, 15, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Boccia, G.; Zoppirolli, C.; Bortolan, L.; Schena, F.; Pellegrini, B. Shared and Task-Specific Muscle Synergies of Nordic Walking and Conventional Walking. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2018, 28, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanuszkiewicz, J.M.; WoŹniewski, M.; Malicka, I. The Influence of Nordic Walking on Isokinetic Trunk Muscle Endurance and Sagittal Spinal Curvatures in Women after Breast Cancer Treatment. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2020, 22, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanuszkiewicz, J.; Woźniewski, M.; Malicka, I. The Influence of Nordic Walking on Isokinetic Trunk Muscle Endurance and Sagittal Spinal Curvatures in Women after Breast Cancer Treatment: Age-Specific Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyré-Tartaruga, L.A.; Boccia, G.; Feijó Martins, V.; Zoppirolli, C.; Bortolan, L.; Pellegrini, B. Margins of Stability and Trunk Coordination during Nordic Walking. J. Biomech. 2022, 134, 111001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Soriano, P.; Llana-Belloch, S.; Encarnación-Martínez, A.; Martínez-Nova, A.; Morey-Klapsing, G. Nordic Walking Practice Might Improve Plantar Pressure Distribution. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2011, 82, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippi, R.; Di Blasio, A.; Aiello, C.; Fanelli, C.; Bullo, V.; Gobbo, S.; Cugusi, L.; Bergamin, M. Effects of a Supervised Nordic Walking Program on Obese Adults with and without Type 2 Diabetes: The C.U.R.I.A.Mo. Centre Experience. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugusi, L.; Solla, P.; Serpe, R.; Carzedda, T.; Piras, L.; Oggianu, M.; Gabba, S.; Di Blasio, A.; Bergamin, M.; Cannas, A.; et al. Effects of a Nordic Walking Program on Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms, Functional Performance and Body Composition in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbo, S.; Bullo, V.; Roma, E.; Duregon, F.; Bocalini, D.S.; Rica, R.L.; Di Blasio, A.; Cugusi, L.; Vendramin, B.; Bergamo, M.; et al. Nordic Walking Promoted Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese People: A Systematic Review for Future Exercise Prescription. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2019, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasio, A.; Rinaldi, M.; Morano, T.; Izzicupo, P.; Dell’Aquila, S.; Grossi, S.; Russo, L.; Bergamin, M.; Gobbo, S.; Viscioni, G.; et al. Effects of Acupuncture and Nordic Walking Practice, and Their Interaction, on Bodily Fluids Distribution of Breast Cancer Survivors. Hum. Mov. 2022, 24, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Condition | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed (km∗h−1) | Speed (km∗h−1) | Speed (km∗h−1) | Speed (km∗h−1) | |||||||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| W | X | X | X | |||||||||
| NW55 | X | X | X | |||||||||
| NW65 | X | X | X | |||||||||
| NW75 | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Parameter | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Upper body | C7 vertical acceleration peak (m∗s−2) | Peak vertical acceleration after the push off phase of the foot on the ground |
| C7 vertical displacement (cm) | Vertical displacement of the marker on C7 from the lowest to the highest point for each step | |
| Elbow horizontal displacement (cm) | Maximal horizontal displacement of the elbow on the sagittal plane for each step | |
| Elbow Δ angle (°) | Angular displacement of the elbow from the maximum flexion to the maximum extended position | |
| Elbow advancing speed (m∗s−1) | Speed of the elbow during the forward movement from back to front | |
| Spine forward slope (°) | Slope of the spine calculated by the inclination of the S1-C7 segment from the vertical position | |
| S1 vertical displacement (cm) | Vertical displacement of the marker on S1 from the lowest to the highest point for each step | |
| Lower body | Step length (m) | Horizontal displacement of feet |
| Step frequency (Hz) | Number of steps per second | |
| Poles | Tip sagittal displacement (m) | Horizontal displacement of the pole tip |
| Movement frequency (Hz) | Number of pole pushes per second | |
| Minimum slope (°) | Minimum inclination of the pole | |
| Maximum slope (°) | Maximum inclination of the pole | |
| Δ Slope (°) | Angular displacement of the pole from the maximum to the minimum inclination of the pole |
| Parameter | 4 km∗h−1 | 5 km∗h−1 | 6 km∗h−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NW Mean (SD) | W Mean (SD) | p Value | NW Mean (SD) | W Mean (SD) | p Value | NW Mean (SD) | W Mean (SD) | p Value | |
| C7 vertical acceleration peak (m∗s−2) | 3.0 (0.3) | 3.0 (0.3) | 0.805 | 3.3 (0.3) | 3.1 (0.3) | 0.127 | 3.7 (0.4) | 3.5 (0.4) | 0.002 * |
| C7 vertical displacement (cm) | 3.5 (0.5) | 3.2 (0.5) | 0.010 * | 4.7 (0.7) | 4.0 (0.7) | 0.000 * | 5.7 (1.0) | 5.1 (0.8) | 0.007 * |
| Elbow horizontal displacement (cm) | 10.9 (4.3) | 15.9 (2.9) | 0.002 * | 12.7 (3.4) | 17.4 (2.9) | 0.001 * | 14.1 (4.3) | 18.3 (3.3) | 0.001 * |
| Elbow Δ angle (°) | 34.0 (8.6) | 22.1 (6.5) | 0.005 * | 35.3 (8.8) | 29.8 (5.7) | 0.141 | 36.4 (10.3) | 36.5 (6.9) | 0.970 |
| Elbow advancing speed (m∗s−1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.003 * | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.001 * | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.1) | 0.000 * |
| Spine forward slope (°) | 9.3 (2.6) | 8.7 (2.1) | 0.109 | 10.0 (3.3) | 9.1 (2.3) | 0.032 * | 10.9 (2.5) | 10.1 (2.1) | 0.067 |
| S1 vertical displacement (cm) | 3.1 (0.6) | 2.7 (0.6) | 0.001 * | 4.5 (1.5) | 3.7 (0.8) | 0.033 * | 5.5 (1.1) | 4.9 (0.9) | 0.020 * |
| Step length (m) | 0.66 (0.04) | 0.64 (0.03) | 0.036 * | 0.74 (0.04) | 0.71 (0.04) | 0.000 * | 0.80 (0.05) | 0.77 (0.04) | 0.006 * |
| Step frequency (Hz) | 0.85 (0.08) | 0.86 (0.03) | 0.750 | 0.91 (0.04) | 0.95 (0.03) | 0.004 * | 0.99 (0.05) | 1.02 (0.03) | 0.010 * |
| SL/EHD ratio (cm) | 7.3 (4.1) | 4.12 (0.8) | 0.023 * | 6.3 (2.0) | 4.2 (0.7) | 0.004 * | 6.4 (2.5) | 4.4 (0.8) | 0.005 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, L.; Belli, G.; Di Blasio, A.; Lupu, E.; Larion, A.; Fischetti, F.; Montagnani, E.; Di Biase Arrivabene, P.; De Angelis, M. The Impact of Nordic Walking Pole Length on Gait Kinematic Parameters. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020050
Russo L, Belli G, Di Blasio A, Lupu E, Larion A, Fischetti F, Montagnani E, Di Biase Arrivabene P, De Angelis M. The Impact of Nordic Walking Pole Length on Gait Kinematic Parameters. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2023; 8(2):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Luca, Guido Belli, Andrea Di Blasio, Elena Lupu, Alin Larion, Francesco Fischetti, Eleonora Montagnani, Pierfrancesco Di Biase Arrivabene, and Marco De Angelis. 2023. "The Impact of Nordic Walking Pole Length on Gait Kinematic Parameters" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 8, no. 2: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020050
APA StyleRusso, L., Belli, G., Di Blasio, A., Lupu, E., Larion, A., Fischetti, F., Montagnani, E., Di Biase Arrivabene, P., & De Angelis, M. (2023). The Impact of Nordic Walking Pole Length on Gait Kinematic Parameters. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 8(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020050