Internal or External Training Load Metrics: Which Is Best for Tracking Autonomic Nervous System Recovery and Function in Collegiate American Football?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
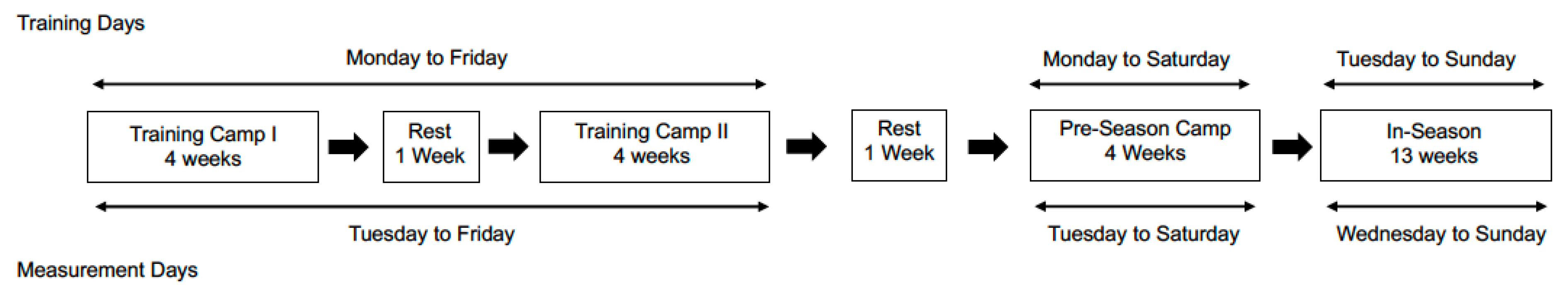
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Exercise Training Sessions
2.4. Internal Load Using WFM
2.5. HR Measurement
2.6. External Load using WFM and Catapult
2.7. ANS Recovery 24 h Post Training
Heart Rate Variability
2.8. ANS Function 24 h Post Training
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Internal Load vs. External Load on ANS Deterioration
4.2. Internal Load vs. External Load on Training Volume
4.3. Practical Implications
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foster, C.; Daines, E.; Hector, L.; Snyder, A.C.; Welsh, R. Athletic Performance in Relation to Training Load. Wis. Med. J. 1996, 95, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.I.; Bove, D.; Ward, P.; Vargas, A.; Dolan, J. Quantification of Training Load and Training Response for Improving Athletic Performance. Strength. Cond. J. 2017, 39, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaghan, E.; Wittels, H.L.; Feigenbaum, L.A.; Wishon, M.J.; Chong, S.; Wittels, E.D.; Hendricks, S.; Hecocks, D.; Bellamy, K.; Girardi, J.; et al. Exercise Cardiac Load and Autonomic Nervous System Recovery during In-Season Training: The Impact on Speed Deterioration in American Football Athletes. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittels, S.H.; Renaghan, E.; Wishon, M.J.; Wittels, H.L.; Chong, S.; Wittels, E.D.; Hendricks, S.; Hecocks, D.; Bellamy, K.; Girardi, J.; et al. Recovery of the Autonomic Nervous System Following Football Training among Division I Collegiate Football Athletes: The Influence of Intensity and Time. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manresa-Rocamora, A.; Flatt, A.A.; Casanova-Lizón, A.; Ballester-Ferrer, J.A.; Sarabia, J.M.; Vera-Garcia, F.J.; Moya-Ramón, M. Heart Rate-Based Indices to Detect Parasympathetic Hyperactivity in Functionally Overreached Athletes. A Meta-Analysis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 1164–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, M.; Bertollo, M.; Bosquet, L.; Brink, M.; Coutts, A.J.; Duffield, R.; Erlacher, D.; Halson, S.L.; Hecksteden, A.; Heidari, J.; et al. Recovery and Performance in Sport: Consensus Statement. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Alves, A.; Claudino, J.G.; Boullosa, D.; Couto, C.R.; Teixeira-Coelho, F.; Pimenta, E.M. The Relationship between Internal and External Loads as a Tool to Monitor Physical Fitness Status of Team Sport Athletes: A Systematic Review. Biol. Sport 2022, 39, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolewski, E.J. The Relationships between Internal and External Load Measures for Division I College Football Practice. Sports 2020, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, I.; Kalliokoski, K.K.; Hannukainen, J.C.; Duncker, D.J.; Nuutila, P.; Knuuti, J. Organ-Specific Physiological Responses to Acute Physical Exercise and Long-Term Training in Humans. Physiology 2014, 29, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltman, A.S.D.; Seip, R.; Schurrer, R.; Weltman, J.; Rutt, R.; Rogol, A. Percentages of Maximal Heart Rate, Heart Rate Reserve and VO2max for Determining Endurance Training Intensity in Male Runners. Int. J. Sports Med. 2008, 11, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, F.A.; Farinatti, P.D.T.V.; Midgley, A.W. Methodological and Practical Application Issues in Exercise Prescription Using the Heart Rate Reserve and Oxygen Uptake Reserve Methods. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2011, 14, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esco, M.R.; Chamberlain, N.; Flatt, A.A.; Snarr, R.L.; Bishop, P.A.; Williford, H.N. Cross-Validation of Age-Predicted Maximal Heart Rate Equations Among Female Collegiate Athletes. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittels, S.H.; Renaghan, E.; Wishon, M.J.; Wittels, H.L.; Chong, S.; Wittels, E.D.; Hendricks, S.; Hecocks, D.; Bellamy, K.; Girardi, J.; et al. A Novel Metric “Exercise Cardiac Load” Proposed to Track and Predict the Deterioration of the Autonomic Nervous System in Division I Football Athletes. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, C.; Orr, R.; O’Connor, H.; West, C. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and Microtechnology Sensors in Team Sports: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, S.J.; Macpherson, T.W.; Coutts, A.J.; Hurst, C.; Spears, I.R.; Weston, M. The Relationships Between Internal and External Measures of Training Load and Intensity in Team Sports: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.J.; Murphy, A.J.; Watsford, M.L.; Austin, D.; Rennie, M. Reliability and Validity of Sports Accelerometers during Static and Dynamic Testing. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, J.; Wishon, M.J.; Wittels, H.; Lee, S.J.; Hendricks, S.; Davila, H.; Wittels, S.H. Single Limb Electrocardiogram Using Vector Mapping: Evaluation and Validation of a Novel Medical Device. J. Electrocardiol. 2021, 67, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temme, L.A.; Wittels, H.L.; Wishon, M.J.; St. Onge, P.; McDonald, S.M.; Hecocks, D.; Wittels, S.H. Continuous Physiological Monitoring of the Combined Exposure to Hypoxia and High Cognitive Load in Military Personnel. Biology 2023, 12, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, L.J.; Ball, K.; Aughey, R.J. The Reliability of MinimaxX Accelerometers for Measuring Physical Activity in Australian Football. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2011, 6, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredt, S.D.G.T.; Chagas, M.H.; Peixoto, G.H.; Menzel, H.J.; de Andrade, A.G.P. Understanding Player Load: Meanings and Limitations. J. Hum. Kinet. 2020, 71, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speed, C.; Arneil, T.; Harle, R.; Wilson, A.; Karthikesalingam, A.; McConnell, M.; Phillips, J. Measure by Measure: Resting Heart Rate across the 24-Hour Cycle. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology the North American Society or Pacing Electrophysiology. Heart Rate Variability: Standards of Measurement, Physiological Interpretation, and Clinical Use. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, P.S.; Spodick, D.H. Recovery from Exercise at Varying Work Loads. Time Course of Responses of Heart Rate and Systolic Intervals. Br. Heart J. 1977, 39, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, M.; Foster, C.; Gastmann, U.; Keizer, H.; Steinacker, J.M. Definition, Types, Symptoms, Findings, Underlying Mechanisms, and Frequency of Overtraining and Overtraining Syndrome. In Overload, Performance Incompetence, and Regeneration in Sport; Lehmann, M., Foster, C., Gastmann, U., Keizer, H., Steinacker, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.H. Modeling Training and Overtraining. J. Sports Sci. 1997, 15, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, J.; Beckmann, J.; Bertollo, M.; Brink, M.; Kallus, W.; Robazza, C.; Kellmann, M. Multidimensional Monitoring of Recovery Status and Implications for Performance. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 14, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, J.O.C.; Coutts, A.J.; Newton, R.U.; Haff, G.G. The Current State of Subjective Training Load Monitoring: Follow-Up and Future Directions. Sports Med.-Open 2022, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.L.; Stanton, R.; Sargent, C.; Wintour, S.-A.; Scanlan, A.T. The Association Between Training Load and Performance in Team Sports: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2743–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, M.J.; Casey, D.P. Regulation of Increased Blood Flow (Hyperemia) to Muscles during Exercise: A Hierarchy of Competing Physiological Needs. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 549–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, M. Skeletal Muscle Metabolism during Exercise in Humans. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2000, 27, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccoli, G.; Amici, R. Sleep and Autonomic Nervous System. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2020, 15, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azunny, A.A.; Rahim, N.A.; Shalan, N.A.A.M. Mindfulness Meditation Improves Athletes’ Attention, Working Memory and Emotional State of Depression, Anxiety and Stress. Eur. J. Mol. Clin. Med. 2020, 7, 4028–4039. [Google Scholar]
- McDougall, S.J.; Widdop, R.E.; Lawrence, A.J. Central Autonomic Integration of Psychological Stressors: Focus on Cardiovascular Modulation. Auton. Neurosci. 2005, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Tanaka, M.; Yamaguti, K.; Kajimoto, O.; Kuratsune, H.; Watanabe, Y. Mental Fatigue Caused by Prolonged Cognitive Load Associated with Sympathetic Hyperactivity. Behav. Brain Funct. 2011, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlin, M.J.; Wilkes, D.; Elliot, C.A.; Lizamore, C.A.; Kathiravel, Y. Monitoring Training Loads and Perceived Stress in Young Elite University Athletes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean (SD) | Median (Min, Max) | |
|---|---|---|
| Training Sessions | ||
| No. of Practice Sessions | 241 | ----- |
| Duration of Practice Sessions (min) | 119.4 (43.4) | 122 (87.4, 237.3) |
| Load Metrics | ||
| Catapult External Load (a.u.) | 328.58 (113.0) | 321.5 (34.99, 800.6) |
| WFM External Load (a.u.) | 630.2 (239.2) | 610.7 (51.9, 1682.7) |
| WFM Internal Load (ECL) * | 17,110.4 (5128.6) | 17,110.3 (11,771.1, 34,362.9) |
| ANS Recovery and Function | ||
| Baseline (bpm) | 62.8 (6.8) | 62.3 (44.8, 90.5) |
| SDNN (ms) | 94.2 (18.3) | 93.8 (47.3, 189,9) |
| rMSSD (ms) | 72.9 (7.4) | 73.1 (23.8, 108.4) |
| HR Recovery (bpm) | 21.3 (5.3) | 21.4 (8.4, 46.2) |
| External Load Catapult | p-Value | External Load WFM | p-Value | Internal Load WFM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline HR | ||||||
| R2 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.19 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | 0.46 (0.30) | 0.88 (0.64) | 0.14 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.16, 1.02) | (−0.39, 2.12) | (0.11, 0.17) | |||
| HR Recovery | ||||||
| R2 | 0.07 | 0.0003 | 0.07 | 0.0003 | 0.38 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | −1.38 (0.38) | −2.94 (0.82) | 0.37 (0.02) | |||
| 95% CI | (−2.13, −0.62) | (−4.54, −1.35) | (0.34, 0.40) | |||
| HRV—SDNN | ||||||
| R2 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.19 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | −0.19 (0.15) | −0.39 (0.32) | −0.07 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.48, 0.10) | (−1.01, 0.24) | (−0.08, −0.05) | |||
| HRV—rMSSD | ||||||
| R2 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.19 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | −0.35 (0.28) | −0.71 (0.59) | −0.12 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.90, 0.20) | (−1.87, 0.45) | (−0.15, −0.10) |
| External Load Catapult | p-Value | External Load WFM | p-Value | Internal Load WFM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline HR | ||||||
| R2 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.48 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | 0.51 (0.18) | 1.04 (0.37) | 0.37 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (0.15, 0.87) | (0.30, 1.77) | (0.35, 0.40) | |||
| HR Recovery | ||||||
| R2 | 0.05 | 0.002 | 0.05 | 0.002 | 0.55 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | 0.74 (0.24) | 1.49 (0.48) | 0.58 (0.02) | |||
| 95% CI | (0.28, 1.2) | (0.54, 2.43) | (0.55, 0.61) | |||
| HRV—SDNN | ||||||
| R2 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.006 | 0.47 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | −0.25 (0.09) | −0.51 (0.18) | −0.18 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.43, −0.08) | (−0.87, −0.15) | (−0.19, −0.17) | |||
| HRV—rMSSD | ||||||
| R2 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.006 | 0.47 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | −0.47 (0.17) | −0.95 (0.34) | −0.33 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.80, −0.14) | (−1.63, −0.28) | (−0.36, −0.31) |
| External Load Catapult | p-Value | External Load WFM | p-Value | Internal Load WFM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline HR | ||||||
| R2 | 0.003 | 0.85 | 0.003 | 0.85 | 0.52 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | 0.03 (0.18) | 0.07 (0.36) | 0.40 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.32, 0.39) | (−0.64, 0.78) | (0.38, 0.42) | |||
| HR Recovery | ||||||
| R2 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.57 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | 0.76 (0.23) | 1.56 (0.47) | 0.61 (0.02) | |||
| 95% CI | (0.30, 1.21) | (0.64, 2.5) | (0.58, 0.64) | |||
| HRV—SDNN | ||||||
| R2 | 0.003 | 0.88 | 0.003 | 0.88 | 0.47 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | −0.01 (0.09) | −0.03 (0.18) | −0.18 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.19, 0.16) | (−0.38, 0.32) | (−0.19, −0.17) | |||
| HRV—rMSSD | ||||||
| R2 | 0.003 | 0.88 | 0.002 | 0.88 | 0.47 | <0.0001 |
| β coefficient (SE) | −0.03 (0.16) | −0.05 (0.33) | −0.33 (0.01) | |||
| 95% CI | (−0.35, 0.30) | (−0.70, 0.60) | (−0.36, −0.31) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renaghan, E.; Wittels, H.L.; Wittels, S.H.; Wishon, M.J.; Hecocks, D.; Wittels, E.D.; Hendricks, S.; Girardi, J.; Lee, S.J.; McDonald, S.M.; et al. Internal or External Training Load Metrics: Which Is Best for Tracking Autonomic Nervous System Recovery and Function in Collegiate American Football? J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010005
Renaghan E, Wittels HL, Wittels SH, Wishon MJ, Hecocks D, Wittels ED, Hendricks S, Girardi J, Lee SJ, McDonald SM, et al. Internal or External Training Load Metrics: Which Is Best for Tracking Autonomic Nervous System Recovery and Function in Collegiate American Football? Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2024; 9(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenaghan, Eric, Harrison L. Wittels, S. Howard Wittels, Michael Joseph Wishon, Dustin Hecocks, Eva D. Wittels, Stephanie Hendricks, Joe Girardi, Stephen J. Lee, Samantha M. McDonald, and et al. 2024. "Internal or External Training Load Metrics: Which Is Best for Tracking Autonomic Nervous System Recovery and Function in Collegiate American Football?" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 9, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010005
APA StyleRenaghan, E., Wittels, H. L., Wittels, S. H., Wishon, M. J., Hecocks, D., Wittels, E. D., Hendricks, S., Girardi, J., Lee, S. J., McDonald, S. M., & Feigenbaum, L. A. (2024). Internal or External Training Load Metrics: Which Is Best for Tracking Autonomic Nervous System Recovery and Function in Collegiate American Football? Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 9(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010005







