Visual Background Choice and Light Environment Affect Male Guppy Visual Contrast
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
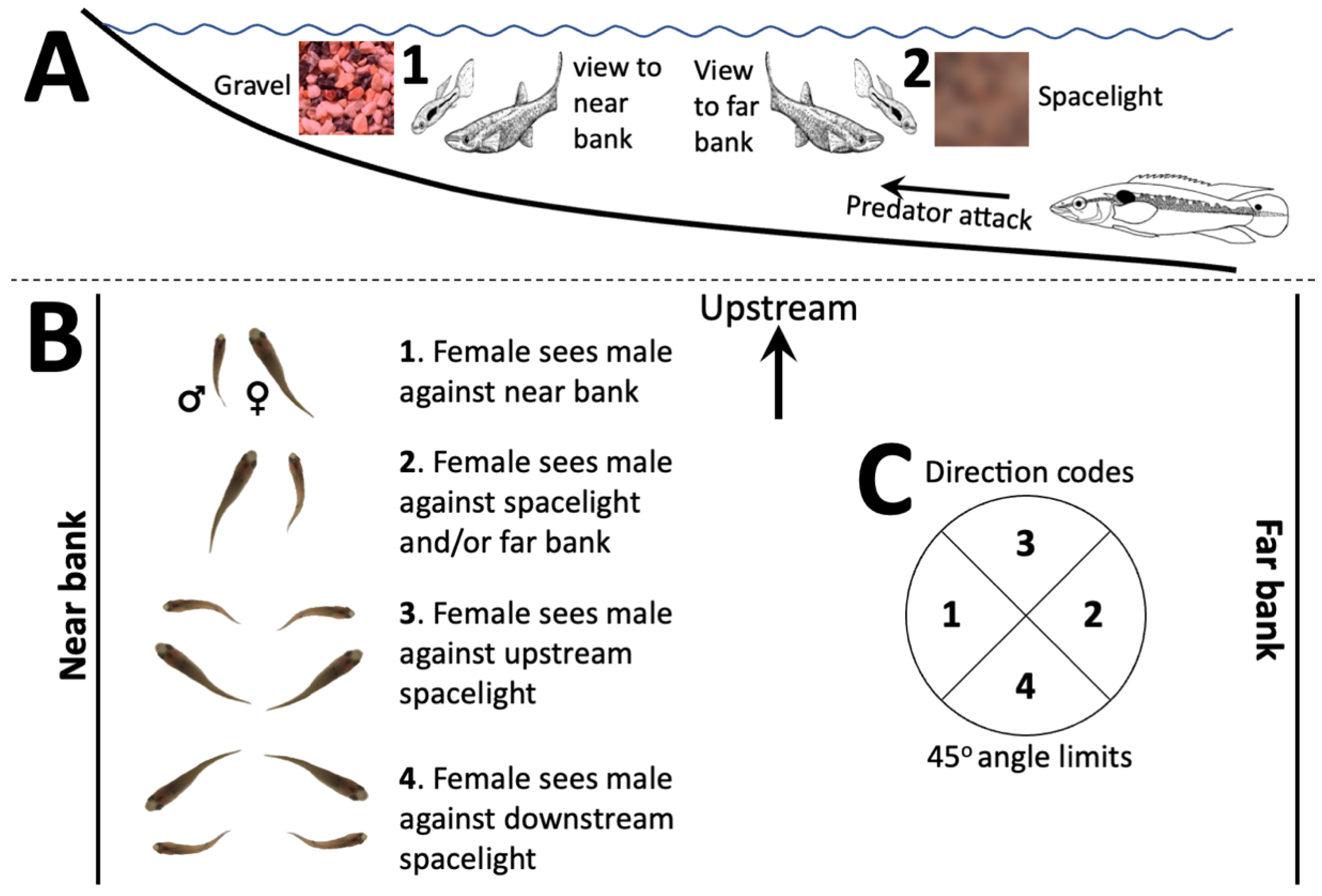
2.1. Orientation during Courtship
2.2. Light Measurements
2.3. Guppy Color Patch Reflectance Spectra
2.4. Guppy Visual Contrast Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Displays and Display Direction
3.2. Display Conditions
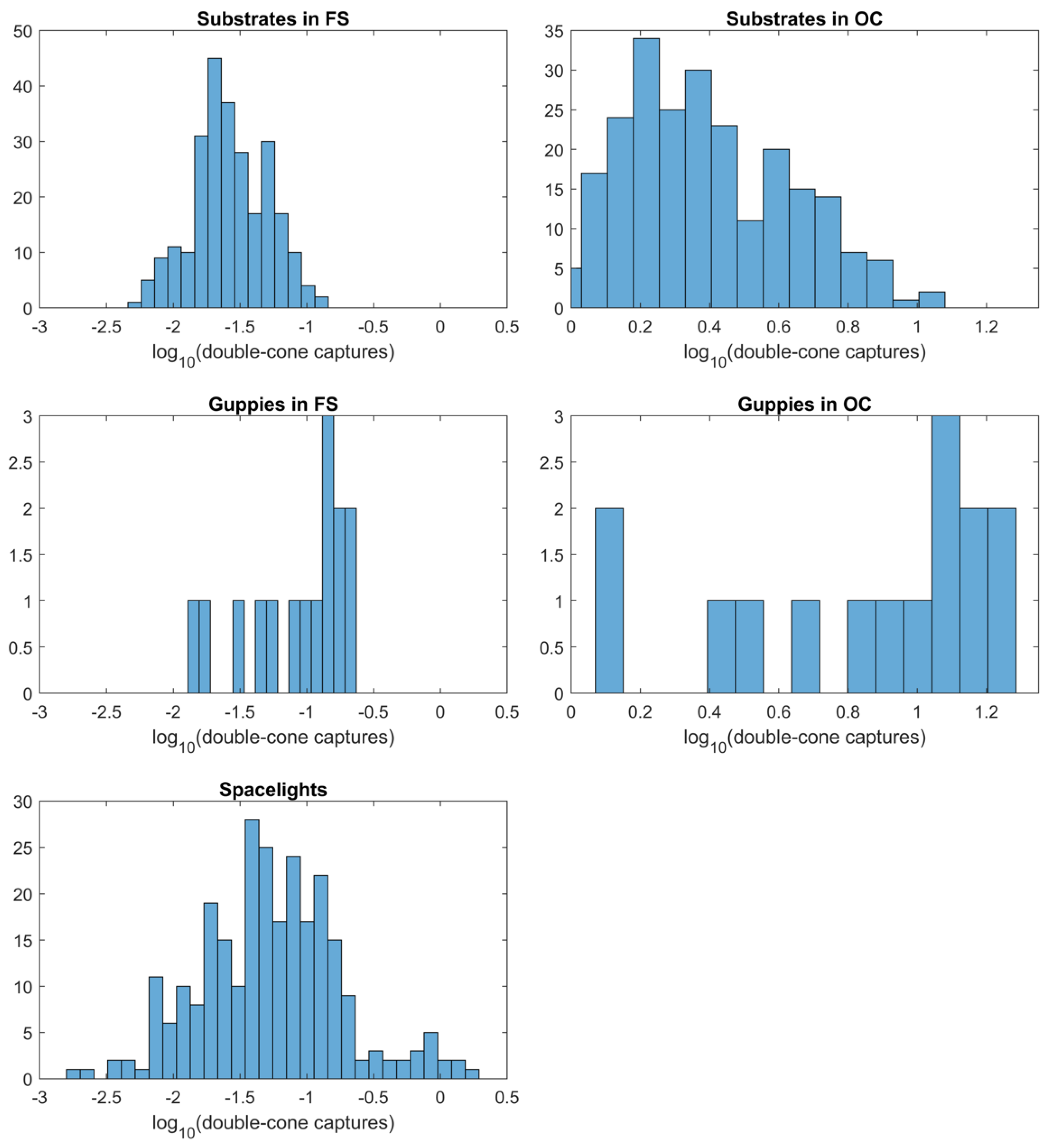
3.3. Visual Contrast
3.4. Tests of Contrast with the Visual Backgrounds (Substrates or Spacelights)
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brock, C.D.; Cummings, M.E.; Bolnick, D.I. Phenotypic plasticity drives a depth gradient in male conspicuousness in threespine stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Evolution 2017, 71, 2022–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.L.; Endler, J.A. Variable Environmental Effects on a Multicomponent Sexually Selected Trait. Am. Nat. 2015, 185, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.L.; Endler, J.A. Male courtship decisions are influenced by light environment and female receptivity. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.; Fleishman, L.J. Differences in visual signal design and detectability between alloatric populations of Anolis lizards. Am. Nat. 2004, 163, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetz, G.W.; Clark, D.L.; Roberts, J.A.; Rector, M. Effect of visual background complexity and light level on the detection of visual signals of male Schizocosa ocreata wolf spiders by female conspecifics. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2011, 65, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Sanabria-Fernández, A.; Baños-Villalba, A.; Edelaar, P. Experimental evidence that matching habitat choice drives local adaptation in a wild population. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2020, 287, 20200721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A.; Théry, M. Interacting effects of lek placement, display behavior, ambient light and color patterns in three neotropical forest-dwelling birds. Am. Nat. 1996, 148, 421–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindl, M.; Winkler, H. Vertical lek placement of forest-dwelling manakin species (Aves, Pipridae) is associated with vertical gradients of ambient light. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 80, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.; Fleishman, L.J. Evidence for habitat partitioning based on adaptation to environmental light in a pair of sympatric lizard species. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2001, 269, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameri, D.; van Kammen, C.; Groothuis, T.G.G.; Seehausen, O.; Maan, M.E. Visual adaptation and microhabitat choice in Lake Victoria cichlid fish. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 101876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schultz, T.D.; Anderson, C.N.; Symes, L.B. The conspicuousness of color cues in male pond damselflies depends on ambient light and visual system. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christy, J.H.; Baum, J.; Backwell, P.R. Attractiveness of sand hoods built by courting male fiddler crabs, Uca musica: Test of a sensory trap hypothesis. Anim. Behav. 2003, 66, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M.E.; Jordão, J.M.; Cronin, T.W.; Oliveira, R.F. Visual ecology of the fiddler crab, Uca tangeri: Effects of sex, viewer and background on conspicuousness. Anim. Behav. 2008, 75, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlund, M.; Östlund-Nilsson, S. The artistic three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteous aculeatus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2003, 53, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, J.A.C.; Endler, J. Modification of the visual background increases the conspicuousness of golden-collared manakin displays. Behav. Ecol. 2004, 15, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.E.; Vogel-Ghibely, N.; Butterworth, N.J. Flies Exploit Predictable Perspectives and Backgrounds to Enhance Iridescent Signal Salience and Mating Success. Am. Nat. 2020, 195, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Shim, K.C.; Brock, C.D. Female stickleback prefer shallow males: Sexual selection on nest microhabitat. Evolution 2015, 69, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, C.D.; Rennison, D.; Veen, T.; Bolnick, D.I. Opsin expression predicts male nuptial color in threespine stickleback. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 80, 7094–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, A.E. Sex, Color and Mate Choice in Guppies; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Waterbolk, H.; Brouwer, R.; Baerends, G. Ethological Studies On Lebistes Reticulatus (Peters). Behaviour 1955, 8, 249–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A. Natural selection on color patterns in Poecilia reticulata. Evolution 1980, 34, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A. A predator’s view of animal color patterns. Evol. Biol. 1978, 11, 319–364. [Google Scholar]
- Long, K.D. Variation in Mating Behavior of the Guppy, Poecilia Reticulata, as a Function of Environmental Irradiance, Visual Acuity, and Perception of Male Color Patterns. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kranz, A.M.; Cole, G.L.; Singh, P.; Endler, J.A. Colour pattern component phenotypic divergence can be predicted by the light environment. J. Evol. Biol. 2018, 31, 1459–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.D.; Rosenqvist, G. Changes in male guppy courting distance in response to a fluctuating light environment. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1998, 44, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, R.D. The Optical System of Fishes. In The Visual System of Fish; Douglas, R., Djamgoz, M., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1990; pp. 45–61. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, R.H.; Hawryshyn, C.W. Behavioral studies of fish vision: An analysis of visual capabilities. In The Visual System of Fish; Douglas, R., Djamgoz, M., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1990; pp. 373–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lythgoe, J. The Ecology of Vision; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, T.J.; Heatherly, T.N.; El-Sabaawi, R.W.; Zandonà, E.; Marshall, M.C.; Flecker, A.S.; Pringle, C.M.; Reznick, D.N.; Thomas, S.A. Flow, nutrients, and light availability influence Neotropical epilithon biomass and stoichiometry. Freshw. Sci. 2012, 31, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A. Predation, light intensity, and courtship behavior in Poecilia reticulata. Anim. Behav. 1987, 35, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J. The Color of Light in Forests and Its Implications. Ecol. Monogr. 1993, 63, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardia, K.V.; Jupp, P.E. Directional Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mielke, P.W., Jr.; Berry, K.J. Permutation Methods: A Distance Function Approach; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Endler, J.A. On the measurement and classification of color in studies of animal color patterns. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 1990, 41, 315–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobyev, M.; Osorio, D. Receptor noise as a determinant of color thresholds. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A.; Mielke, P.W., Jr. Comparing entire color patterns as birds see them. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 2005, 86, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.J.; Herberstein, M.E.; Fleishman, L.J.; Endler, J.A.; Bennett, A.T.D.; Dyer, A.G.; Hart, N.S.; Marshall, J.; Whiting, M.J. An Integrative Framework for the Appraisal of Coloration in Nature. Am. Nat. 2015, 185, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibeaux, A.; Cole, G.L.; Endler, J.A. The relative importance of local and global visual contrast in mate choice. Anim. Behav. 2019, 154, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A.; Gaburro, J.; Kelley, L. Visual effects in great bowerbird sexual displays and their implications for signal design. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2014, 281, 20140235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A.; Cole, G.L.; Kranz, A.M. Boundary strength analysis: Combining colour pattern geometry and coloured patch visual properties for use in predicting behaviour and fitness. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 2334–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, C.P.; Troscianko, J.; Endler, J.A.; Marshall, N.J.; Cheney, K.L. Quantitative color pattern analysis (QCPA): A comprehensive framework for the analysis of color patterns in nature. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleishman, L.J.; Perez, C.W.; Yeo, A.I.; Cummings, K.J.; Dick, S.; Almonte, E. Perceptual distance between colored stimuli in the lizard Anolis sagrei: Comparing visual system models to empirical results. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2016, 70, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, M.; Merilaita, S. Prey concealment: Visual background complexity and prey contrast distribution. Behav. Ecol. 2009, 21, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, M.; Merilaita, S. Prey pattern regularity and background complexity affect detectability of background-matching prey. Behav. Ecol. 2011, 23, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.; Giesel, M.; Gegenfurtner, K.R. Chromatic discrimination of natural objects. J. Vis. 2008, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, C.; Green, N.F.; Hamilton, N.; Endler, J.A.; Osorio, D.C.; Marshall, N.J.; Cheney, K.L. Does conspicuousness scale linearly with colour distance? A test using reef fish. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pas, S.F.T.; Koenderink, J.J. Visual Discrimination of Spectral Distributions. Perception 2004, 33, 1483–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, R.T.; Liley, N.R. A sexual pheromone in the guppy, Poecilia reticulata (Peters). Can. J. Zoo. 1979, 57, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Fiore, P.; Stapley, J.; Watt, P.J. Mating effort and female receptivity: How do male guppies decide when to invest in sex? Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2010, 64, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Light Environment | SG * Small Gaps | EL Early | FS Forest Shade | OC Cloudy | Total | χ2 1:1 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caigual | 2 | 1 | 18 | 61 | 82 | 23.41 | 0 |
| Taylor | 3 | 0 | 73 | 52 | 128 | 3.53 | 0.06 |
| Total | 5 | 1 | 91 | 113 | 210 | 2.37 | 0.123 |
| Caigual | Taylor | Both Pooled | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | p for χ2 | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | p for χ2 | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | p for χ2 |
| D1 | 5 | 13 | 8 | 15 | 0.1058 | 30 | 20 | 13 | 21 | 0.073 | 35 | 33 | 21 | 36 | 0.2008 |
| D2 | 6 | 9 | 11 | 22 | 0.01 | 18 | 38 | 23 | 19 | 0.015 | 24 | 47 | 34 | 41 | 0.0454 |
| D3 | 8 | 12 | 2 | 5 | 0.044 | 13 | 28 | 14 | 21 | 0.053 | 21 | 40 | 16 | 26 | 0.006 |
| D4 | 14 | 20 | 2 | 17 | 0 | 21 | 33 | 9 | 36 | 0 | 35 | 53 | 11 | 53 | <0.0001 |
| Forest Shade (FS) | Cloudy (OC) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | Observed Mean ∆S or Difference δ | Permutation Test p | Supplemental Figure | Observed Mean ∆S or Difference δ | Permutation Test p | Supplemental Figure |
| Chromatic ∆S Guppy-Spacelight | 13.2 | <0.00001 | Figure S11 | 12.9 | <0.00001 | Figure S11 |
| Chromatic ∆S Guppy-Substrate | 5.98 | <0.00001 | Figure S11 | 5.98 | <0.00001 | Figure S11 |
| Chromatic δ | +7.25 | <0.00001 | Figure S14 | +6.92 | <0.00001 | Figure S14 |
| Achromatic ∆S Guppy-Spacelight | 12.6 | 0.73 | Figure S16 | 48.8 | <0.00001 | Figure S16 |
| Achromatic ∆S Guppy Substrate | 13.7 | <0.00001 | Figure S16 | 13.7 | <0.00001 | Figure S16 |
| Achromatic δ | −1.04 | <0.00001 | Figure S18 | +5.1 | <0.00001 | Figure S18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Endler, J.A.; Raggay, D.-M.; Maerowitz-McMahan, S.; Reznick, D.N.; Fuller, R.C. Visual Background Choice and Light Environment Affect Male Guppy Visual Contrast. Vision 2022, 6, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6030056
Endler JA, Raggay D-M, Maerowitz-McMahan S, Reznick DN, Fuller RC. Visual Background Choice and Light Environment Affect Male Guppy Visual Contrast. Vision. 2022; 6(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleEndler, John A., Dara-Marie Raggay, Solomon Maerowitz-McMahan, David N. Reznick, and Rebecca C. Fuller. 2022. "Visual Background Choice and Light Environment Affect Male Guppy Visual Contrast" Vision 6, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6030056
APA StyleEndler, J. A., Raggay, D.-M., Maerowitz-McMahan, S., Reznick, D. N., & Fuller, R. C. (2022). Visual Background Choice and Light Environment Affect Male Guppy Visual Contrast. Vision, 6(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6030056





