The Colours of Octopus: Using Spectral Data to Measure Octopus Camouflage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
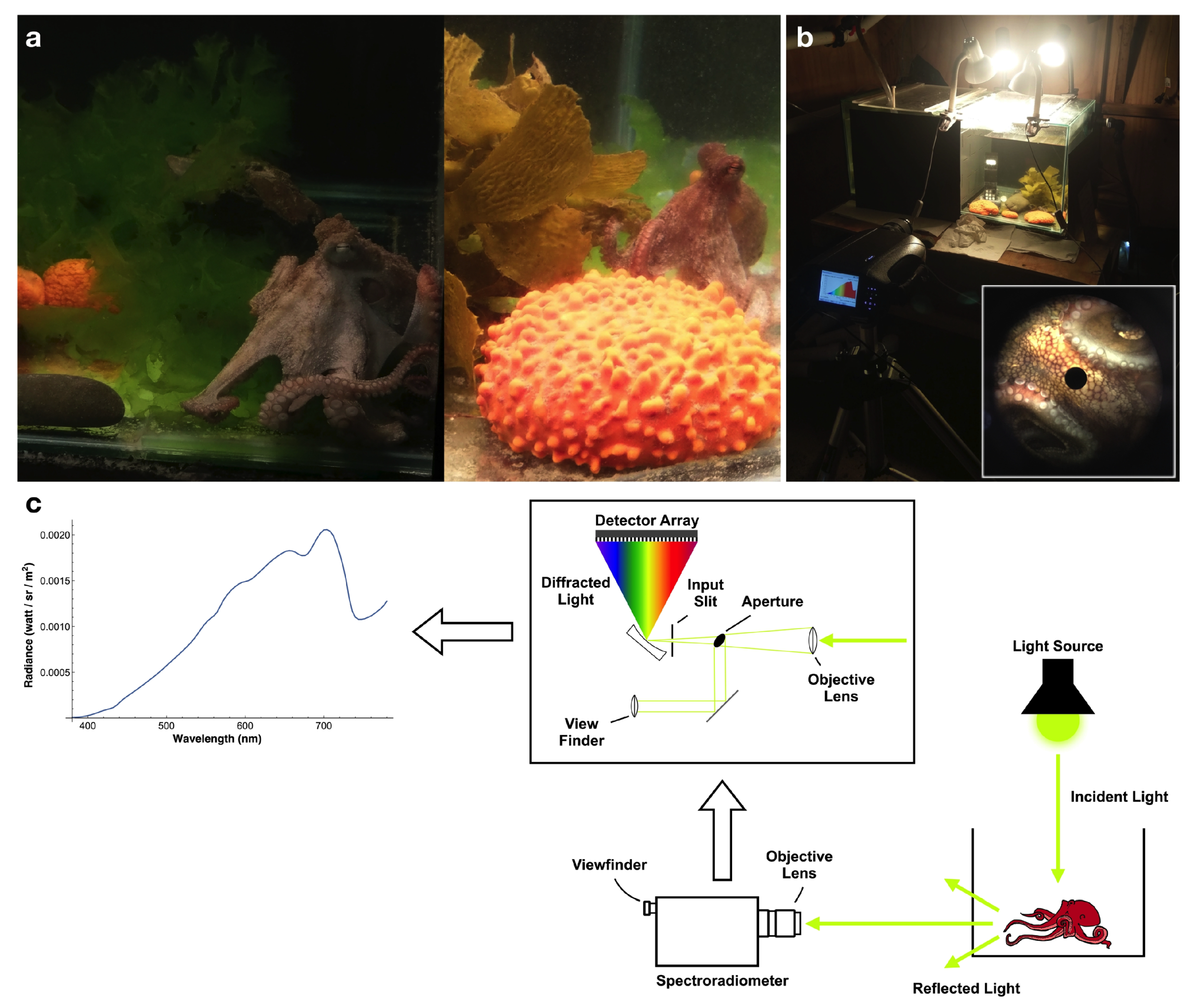
2.1. Experimental Setup and Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Analysis of Spectra Similarity
2.2.2. Comparison between Octopus and Background Spectra
2.2.3. Modelling of Colours
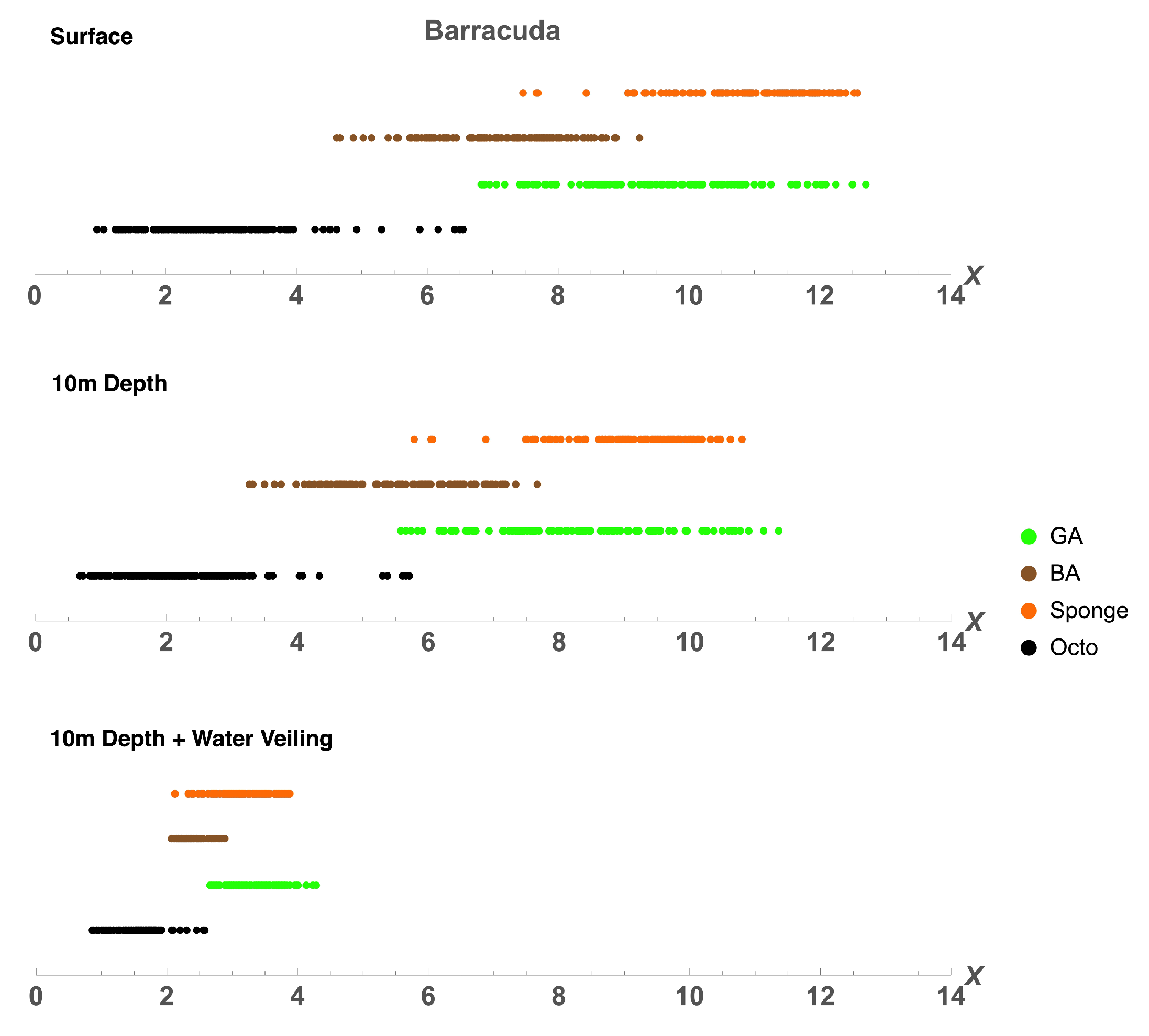
3. Results
3.1. Reflectance Spectra
3.2. Octopus in the Eyes of Different Animals
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Chromaticity | The aspect of colour that remains invariant when the intensity of a light stimulus changes. Chromaticity of a colour is shown in chromaticity diagrams. |
| Colour | A set of signals elicited by a light stimulus in the nervous system of an animal. We quantify colour as a set of photoreceptor quantum catches (the number of absorbed photons). |
| Colour-Matching | Colours are matched if an animal cannot discriminate between them. We assume that colour discrimination is set by noise, which includes both fluctuations of number of absorbed quanta of light and neural noise. |
| Lightness | Achromatic aspect of colour relative to that of illumination. Lightness can be mediated either by a signal of a single photoreceptor spectral type or by a weighted sum of several spectral types of photoreceptors. Lightness of a reflecting surface is quantified as a ratio of a photoreceptor quantum catch (or the weighted sum) corresponding to this surface to that of the ideal white reflector. |
| Reflectance Spectrum | The ratio of the spectrum of light reflected from a surface to that of a surface that reflects 100% of light at all wavelengths (ideal white surface) and illuminated by the light having the same spectral composition and intensity. We often use the term `spectrum’ instead of `reflectance spectrum’ where it is clear from context that the reflectance spectrum is discussed. |
| Saturation | Aspect of colour that indicates how different the colour is from grey. We characterise saturation as the distance of a colour locus from an achromatic point in the Receptor Noise Limited Chromatic Diagram [36]. It is important to note that it is not known if animals perceive saturation as a distinct aspect of colour. |
References
- Hanlon, R.T. Cephalopod Dynamic Camouflage. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R400–R404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, R.T.; Forsythe, J.W.; Joneschild, D.E. Crypsis, conspicuousness, mimicry and polyphenism as antipredator defences of foraging octopuses on Indo-Pacific coral reefs, with a method of quantifying crypsis from video tapes. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1999, 66, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, R.T.; Chiao, C.C.; Mäthger, L.M.; Barbosa, A.; Buresch, K.C.; Chubb, C. Cephalopod dynamic camouflage: Bridging the continuum between background matching and disruptive coloration. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, R.T.; Shashar, N. Aspects of the Sensory Ecology of Cephalopods. In Sensory Processing in Aquatic Environments, 1st ed.; Collin, S.P., Marshall, N.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Chapter 14; pp. 266–282. [Google Scholar]
- Mäthger, L.M.; Hanlon, R.T. Malleable skin coloration in cephalopods: Selective reflectance, transmission and absorbance of light by chromatophores and iridophores. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 329, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kito, Y.; Narita, K.; Seidou, M.; Michinomae, M.; Yoshihara, K.; Partridge, J.C.; Herring, P.J. A blue sensitive visual pigment based on 4-hydroxyretinal is found widely in mesopelagic cephalopods. In Structures and Functions of Retinal Proteins; Rigaud, J.L., Ed.; Colloques INSERM/John Libbey Eurotext Ltd.: Montrogue, France, 1992; Volume 221, pp. 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, S.; Seidou, M.; Horiuchi, S.; Uchiyama, I.; Kito, Y. Adaptation of a Deep-sea Cephalopod to the Photic Environment. Evidence for Three Visual Pigments. J. Gen. Physiol. 1988, 92, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michinomae, M.; Masuda, H.; Seidou, M.; Kito, Y. Structural Basis for Wavelength Discrimination in the Banked Retina of the Firefly Squid Watasenia Scintillans. J. Exp. Biol. 1994, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidou, M.; Sugahara, M.; Uchiyama, H.; Hiraki, K.; Hamanaka, T.; Michinomae, M.; Yoshihara, K.; Kito, Y. On the three visual pigments in the retina of the firefly squid, Watasenia scintillans. J. Comp. Physiol. A Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 1990, 166, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.K.; Brown, P.S. Visual pigments of the octopus and cuttlefish. Nature 1958, 182, 1288–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, J.B. Evidence that Octopus is Colour Blind. J. Exp. Biol. 1977, 70, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaynak, D.; Allen, J.J.; Mäthger, L.M.; Chiao, C.C.; Hanlon, R.T. Quantification of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) camouflage: A study of color and luminance using in situ spectrometry. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2013, 199, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiao, C.C.; Kenneth Wickiser, J.; Allen, J.J.; Genter, B.; Hanlon, R.T. Hyperspectral imaging of cuttlefish camouflage indicates good color match in the eyes of fish predators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9148–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäthger, L.M.; Chiao, C.C.; Barbosa, A.; Hanlon, R.T. Color matching on natural substrates in cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2008, 194, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froesch, D.; Messenger, J.B. On leucophores and the chromatic unit of Octopus vulgaris. J. Zool. 1978, 186, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, R.T.; Messenger, J.B. Adaptive Coloration in Young Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis L.): The Morphology and Development of Body Patterns and their Relation to Behaviour. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1988, 320, 437–487. [Google Scholar]
- Messenger, J.B. The eyes and skin of Octopus: Compensating for sensory deficiencies. Endeavour 1979, 3, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josef, N.; Amodio, P.; Fiorito, G.; Shashar, N. Camouflaging in a complex environment-octopuses use specific features of their surroundings for background matching. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäthger, L.M.; Shashar, N.; Hanlon, R.T. Do cephalopods communicate using polarized light reflections from their skin? J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, A.; Sanders, G.D. Body Patterns of Octopus vulgaris and Maturation of the Response to Disturbance. Anim. Behav. 1971, 19, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.J. Habitat selection and shelter use by Octopus tetricus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 150, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, S. Heller’s Barracuda, Sphyraena Helleri. In Fishes of Australia. 2018. Available online: http://fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/2553 (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Bray, D.J.; Schultz, S. Sphyraena Novaehollandiae. In Fishes of Australia. 2019. Available online: http://fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/2550 (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Pierce, S.J.; Pardo, S.A.; Bennett, M.B. Reproduction of the blue-spotted maskray Neotrygon kuhlii (Myliobatoidei: Dasyatidae) in south-east Queensland, Australia. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 1291–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, S.M. Neotrygon Kuhlii (Müller & Henle, 1841): Blue-spotted Stingray. In FishBass. Froese, R., Pauly, D., Eds.; 2019. Available online: https://www.fishbase.in/summary/Dasyatis-kuhlii.html (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- OBIS. Neotrygon kuhlii (Müller & Henle, 1841). In Ocean Biogeographic Information System; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://obis.org/taxon/398330 (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Heithaus, M. Species Fact Sheet—Rays. In Shark Bay Ecosystem Research Project; Florida International University: Miami, FL, USA, 2018; Available online: http://faculty.fiu.edu/{~{}}heithaus/SBERP/pdfs/species/raysfs.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Bray, D.J.; Red Bass, Lutjanus bohar (Forsskål 1775). In Fishes of Australia. 2018. Available online: http://fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/551 (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Luna, S.M. Lutjanus Bohar (Forsskål, 1775): Two-spot Red Snapper. In FishBass. Froese, R., Pauly, D., Eds.; 2019. Available online: https://www.fishbase.in/summary/Lutjanus-bohar.html (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- OBIS. Lutjanus bohar (Forsskål, 1775). In Ocean Biogeographic Information System; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://obis.org/taxon/218479 (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- OBIS. Puffinus pacificus (Gmelin, 1789). In Ocean Biogeographic Information System; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://obis.org/taxon/212634 (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Szabo, M. Wedge-tailed Shearwater—Puffinus Pacificus (Gmelin, 1789). In New Zealand Birds. Miskelly, C., Ed.; 2013. Available online: http://nzbirdsonline.org.nz/species/wedge-tailed-shearwater (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Burger, A.E. Diving Depths of Shearwaters. Auk Ornithol. Adv. 2001, 118, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, M.; Osorio, D. Receptor Noise as a Determinant of Colour Thresholds. Proc. R. Soc. B 1998, 265, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, S. How to measure color using spectrometers and calibrated photographs. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobyev, M.; Marshall, N.J.; Osorio, D.; Hempel de Ibarra, N.; Menzel, R. Colourful Objects Through Animal Eyes. Color Res. Appl. 2001, 26, S214–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiao, C.C.; Osorio, D.; Vorobyev, M.; Cronin, T.W. Characterization of natural illuminants in forests and the use of digital video data to reconstruct illuminant spectra. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2000, 17, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govardovskii, V.I.; Fyhrquist, N.; Reuter, T.; Kuzmin, D.G.; Donner, K. In search of the visual pigment template. Vis. Neurosci. 2000, 17, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.S.; Vorobyev, M. Modelling oil droplet absorption spectra and spectral sensitivities of bird cone photoreceptors. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2005, 191, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, H.M.; Schaefer, V.; Vorobyev, M. Are fruit colors adapted to consumer vision and birds equally efficient in detecting colorful signals? Am. Nat. 2007, 169, S159–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.J.; Vorobyev, M. The design of color signals and color vision in fishes. In Sensory Processing in Aquatic Environments; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Chapter 10; pp. 194–222. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen, S. The Optics of Life: A Biologist’s Guide to Light in Nature; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012; p. 346. [Google Scholar]
- Wyszecki, G.; Stiles, W.S. Color Science: Concepts and Methods, Quantitative Data and Formulae; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1982; p. 950. [Google Scholar]
- Kelber, A.; Vorobyev, M.; Osorio, D. Animal colour vision - Behavioural tests and physiological concepts. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2003, 78, 81–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, D.; Vorobyev, M. Colour Vision as an Adaptation to Frugivory in Primates. Proc. R. Soc. B 1996, 263, 593–599. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, N.J.; Vorobyev, M.; Siebeck, U.E. What Does a Reef Fish See When It Sees a Reef Fish? Eating ’Nemo’ ©. In Communication in Fishes, 1st ed.; Ladich, F., Collin, S.P., Moller, P., Kapoor, B., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, UK, 2006; Chapter 14; pp. 393–422. [Google Scholar]
- McComb, D.M.; Frank, T.M.; Hueter, R.E.; Kajiura, S.M. Temporal Resolution and Spectral Sensitivity of the Visual System of Three Coastal Shark Species from Different Light Environments. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2010, 83, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theiss, S.M.; Lisney, T.J.; Collin, S.P.; Hart, N.S. Colour vision and visual ecology of the blue-spotted maskray, Dasyatis kuhlii Müller & Henle, 1814. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2007, 193, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lythgoe, J.N.; Muntz, W.; Partridge, J.C.; Shand, J.; Williams, D.M. The ecology of the visual pigments of snappers (Lutjanidae) on the Great Barrier Reef. J. Comp. Physiol. A Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 1994, 174, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebeck, U.E.; Marshall, N.J. Ocular media transmission of coral reef fish - Can coral reef fish see ultraviolet light? Vis. Res. 2001, 41, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.S. Microspectrophotometry of visual pigments and oil droplets in a marine bird, the wedge-tailed shearwater Puffinus pacificus: Topographic variations in photoreceptor spectral characteristics. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, P.; Lind, O.; Kelber, A. Chromatic and achromatic vision: Parameter choice and limitations for reliable model predictions. Behav. Ecol. 2018, 29, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, S.Z.; Kosyakov, A.; Chang, B.S. Spectral Tuning of Killer Whale (Orcinus orca) Rhodopsin: Evidence for Positive Selection and Functional Adaptation in a Cetacean Visual Pigment. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasick, J.I.; Robinson, P.R. Mechanism of Spectral Tuning in the Dolphin Visual Pigments. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebel, U.; König, G.; Schmid, A. Spectral Sensitivity in Two Species of Pinnipeds (Phoca vitulina and Otaria flavescens). Mar. Mammal Sci. 2006, 22, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, J.G.; Talas, L.; Baddeley, R.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Scott-Samuel, N.E. Optimizing colour for camouflage and visibility using deep learning: The effects of the environment and the observer’s visual system. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håstad, O.; Victorsson, J.; Ödeen, A. Differences in color vision make passerines less conspicuous in the eyes of their predators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6391–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, T.W. Quantifying camouflage and conspicuousness using visual salience. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuart-Fox, D.; Moussalli, A. Camouflage, communication and thermoregulation: Lessons from colour changing organisms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, M.; Debut, M.; Gomez, D.; Casas, J. Specific color sensitivities of prey and predator explain camouflage in different visual systems. Behav. Ecol. 2005, 16, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilts, B.D.; Michielsen, K.; Kuipers, J.; De Raedt, H.; Stavenga, D.G. Brilliant camouflage: Photonic crystals in the diamond weevil, Entimus imperialis. Proc. R. Soc. B 2012, 279, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, J.W.; Hanlon, R.T. Foraging and associated behavior by Octopus cyanea Gray, 1849 on a coral atoll, French Polynesia. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 209, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, J.B. Reflecting elements in cephalopod skin and their importance for camouflage. J. Zool. 1974, 174, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, R.C.; Flores, A.A.; Stevens, M. Camouflage through colour change: Mechanisms, adaptive value and ecological significance. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wente, W.H.; Phillips, J.B. Fixed Green and Brown Color Morphs and a Novel Color-Changing Morph of the Pacific Tree Frog Hyla regilla. Am. Nat. 2003, 162, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langridge, K.V. Cuttlefish use startle displays, but not against large predators. Anim. Behav. 2009, 77, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langridge, K.V.; Broom, M.; Osorio, D. Selective signalling by cuttlefish to predators. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R1044–R1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, M.D.; Finn, J.; Tregenza, T. Dynamic mimicry in an Indo-Malayan octopus. Proc. R. Soc. B 2001, 268, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart-Fox, D.; Whiting, M.J.; Moussalli, A. Camouflage and colour change: Antipredator responses to bird and snake predators across multiple populations in a dwarf chameleon. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 88, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart-Fox, D.; Moussalli, A.; Whiting, M.J. Predator-specific camouflage in chameleons. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.J.; Messenger, J.B. Colour-blind camouflage. Nature 1996, 382, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Richardson, C.; Lengagne, T.; Derex, M.; Plenet, S.; Joly, P.; Léna, J.P.; Théry, M. Support for a role of colour vision in mate choice in the nocturnal European treefrog (Hyla arborea). Behaviour 2010, 147, 1753–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.B.; Douglass, J.K.; Phillips, J.B.; Baube, C.L. Scotopic spectral sensitivity of the optomotor response in the green treefrog Hyla cinerea. J. Exp. Zool. 1993, 267, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.I.; Dyck, J. Adaptation of the Tree Frog, Hyla cinerea, to Colored Backgrounds, and the Role of the Three Chromatophore Types. J. Exp. Zool. 1978, 205, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, A.C.N.; Kuzirian, A.M.; Hanlon, R.T.; Cronin, T.W. Visual phototransduction components in cephalopod chromatophores suggest dermal photoreception. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäthger, L.M.; Roberts, S.B.; Hanlon, R.T. Evidence for distributed light sensing in the skin of cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.D.; Oakley, T.H. Eye-independent, light-activated chromatophore expansion (LACE) and expression of phototransduction genes in the skin of Octopus bimaculoides. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, A.L.; Stubbs, C.W. Spectral discrimination in color blind animals via chromatic aberration and pupil shape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 8206–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Land, M.F. Optics and Vision in Invertebrates. In Handbook of Sensory Physiology; Autrum, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; Volume Voume VII/6B, Chapter 4; pp. 471–592. [Google Scholar]
- Jagger, W.S.; Sands, P.J. A wide-angle gradient index optical model of the crystalline lens and eye of the octopus. Vis. Res. 1999, 39, 2841–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, A.L.; Stubbs, C.W. Reply to Gagnon et al. - All color vision is more difficult in turbid water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, Y.L.; Osorio, D.C.; Wardill, T.J.; Marshall, N.J.; Chung, W.S.; Temple, S.E. Can chromatic aberration enable color vision in natural environments? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6908–E6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.S.; Theiss, S.M.; Harahush, B.K.; Collin, S.P. Microspectrophotometric evidence for cone monochromacy in sharks. Naturwissenschaften 2011, 98, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Tang, M.Y.; Yan, H.Y. A comparative study on the visual adaptations of four species of moray eel. Vis. Res. 2011, 51, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, R.T.; Watson, A.C.; Barbosa, A. A “Mimic Octopus” in the Atlantic: Flatfish Mimicry and Camouflage by Macrotritopus defilippi. Biol. Bull. 2010, 218, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Species | Spectral Sensitivity | OMT | Oil Droplets | Source | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | C | Y | Y | R | R | |||||||
| Heller’s barracuda (Sphyraena helleri) | — | — | 455 | 531 | [41,46] | |||||||
| Blue-spotted stingray (Neotrygon kuhlii) | — | 476 | 498 | 552 | 412 | [47,48] | ||||||
| Two-spotted red snapper (Lutjanus bohar) | — | 424 | 494 | 518 | 386 | [49,50] | ||||||
| Wedge-tailed shearwater (Puffinus pacificus) | 406 | 472 | 539 | 601 | 335 | 445 | 460 | 506 | 528 | 562 | 586 | [39,51] |
| Distance () to Octopus Eigenvector | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCs | Green Algae | Brown Algae | Sponge | |
| Non-Normalised | 1 PC | 0.533 | 0.269 | 0.542 |
| 2 PCs | 0.897 | 1 | 0.701 | |
| 3 PCs | 0.662 | 0.738 | 0.698 | |
| Normalised | 1 PC | 0.932 | 0.999 | 0.574 |
| 2 PCs | 0.623 | 0.733 | 0.706 | |
| 3 PCs | 0.804 | 0.875 | 0.592 | |
| Distance to Octopus Subspace | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Algae | Brown Algae | Sponge | |
| Non-Normalised | 4.14 | 3.111 | 4.206 |
| Normalised | 6.764 | 4.084 | 7.378 |
| Distance to Octopus Subspace () | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Algae | Brown Algae | Sponge | |
| Barracuda | 4.018 | 3.127 | 5.812 |
| Barracuda 10m | 3.726 | 2.606 | 5.317 |
| Barracuda 10m + V | 3.757 | 2.32 | 3.383 |
| Ray | 5.51 | 3.246 | 6.522 |
| Ray 10m | 5.515 | 3.222 | 6.398 |
| Ray 10m + V | 4.189 | 2.35 | 4.534 |
| Snapper | 4.029 | 3.187 | 6.371 |
| Snapper 10m | 4.316 | 3.088 | 6.336 |
| Snapper 10m + V | 3.76 | 2.402 | 4.01 |
| Bird | 7.124 | 3.172 | 7.085 |
| Bird 10m | 7.55 | 3.779 | 7.040 |
| Bird 10m + V | 5.292 | 2.785 | 4.663 |
| Colour-Match % | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Algae | Brown Algae | Sponge | |||||||
| Threshold | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Barracuda | 1.563 ± 0.9 | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 5.729 ± 1.68 | 9.896 ± 2.16 | 23.958 ± 3.08 | 0 | 1.042 ± 0.73 | 2.083 ± 1.03 |
| Barracuda 10m | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 3.646 ± 1.35 | 16.667 ± 2.69 | 38.542 ± 3.51 | 69.792 ± 3.31 | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 3.125 ± 1.26 |
| Barracuda 10m + V | 3.125 ± 1.26 | 40.104 ± 3.54 | 92.708 ± 1.88 | 58.333 ± 3.56 | 94.792 ± 1.6 | 100 | 48.958 ± 3.61 | 93.229 ± 1.81 | 100 |
| Ray | 0 | 5.208 ± 1.6 | 17.188 ± 2.72 | 6.25 ± 1.75 | 10.938 ± 2.25 | 15.104 ± 2.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ray 10m | 2.083 ± 1.03 | 4.688 ± 1.53 | 10.938 ± 2.25 | 4.688 ± 1.53 | 10.938 ± 2.25 | 21.875 ± 2.98 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ray 10m + V | 17.708 ± 2.75 | 78.125 ± 2.98 | 93.75 ± 1.75 | 43.229 ± 3.58 | 86.458 ± 2.47 | 96.354 ± 1.35 | 4.688 ± 1.53 | 57.292 ± 3.57 | 89.063 ± 2.25 |
| Snapper | 0 | 1.042 ± 0.73 | 2.083 ± 1.03 | 5.729 ± 1.68 | 12.5 ± 2.39 | 23.958 ± 3.08 | 0 | 0.521 ± 0.52 | 3.125 ± 1.26 |
| Snapper 10m | 0 | 0 | 1.042 ± 0.73 | 5.729 ± 1.68 | 13.542 ± 2.47 | 27.083 ± 3.21 | 0 | 2.6 04 ± 1.15 | 4.167 ± 1.44 |
| Snapper 10m + V | 3.646 ± 1.35 | 90.625 ± 2.1 | 100 | 89.063 ± 2.25 | 100 | 100 | 84.896 ± 2.58 | 100 | 100 |
| Bird | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.042 ± 0.73 | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 7.292 ± 1.88 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bird 10m | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.521 ± 0.52 | 2.083 ± 1.03 | 4.167 ± 1.44 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bird 10m + V | 0.521 ± 0.52 | 2.604 ± 1.15 | 4.688 ± 1.53 | 6.25 ± 1.75 | 34.375 ± 3.43 | 59.375 ± 3.54 | 0 | 0 | 2.083 ± 1.03 |
| Octopus Colourmatch Intersection Ratio | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Algae | |||||||||||||
| Barracuda | Ray | Snapper | Bird | ||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | ||
| Barracuda | Surface | 0 | 0.8 | 1 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 10m | 0.8 | 1 | 1 | – | 0 | 0.286 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 10m + V | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 948 | 1 | 0.167 | 0.065 | 0.051 | ||||
| Ray | Surface | – | 0.4 | 0.152 | – | 0.2 | 0.121 | – | 0 | 0 | |||
| 10m | 1 | 0.556 | 0.333 | – | 0 | 0.095 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 10m + V | 0.176 | 0.513 | 0.989 | 0.206 | 0.82 | 1 | 0.029 | 0.033 | 0.05 | ||||
| Snapper | Surface | – | 1 | 1 | – | 1 | 1 | – | 0 | 0 | |||
| 10m | – | – | 1 | – | – | 1 | – | – | 0 | ||||
| 10m + V | 0.857 | 0.42 | 0.927 | 1 | 0.707 | 0.938 | 0.143 | 0.029 | 0.047 | ||||
| Bird | Surface | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| 10m | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||
| 10m + V | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Brown Algae | |||||||||||||
| Barracuda | Surface | 0.909 | 1 | 0.609 | 1 | 0.895 | 0.8 91 | 0.182 | 0.263 | 0.304 | |||
| 10m | 0.281 | 0.284 | 0.313 | 0.344 | 0.351 | 0.388 | 0.031 | 0.054 | 0.06 | ||||
| 10m + V | 0.714 | 0.912 | 0.964 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.107 | 0.363 | 0.594 | ||||
| Ray | Surface | 0.833 | 0.905 | 0.966 | 0.833 | 0.81 | 0.828 | 0.167 | 0.238 | 0.483 | |||
| 10m | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.762 | 0.111 | 0.19 | 0.19 | ||||
| 10m + V | 0.964 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.145 | 0.398 | 0.616 | ||||
| Snapper | Surface | 1 | 0.708 | 0.891 | 0.909 | 0.708 | 0.522 | 0.182 | 0.208 | 0.304 | |||
| 10m | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.818 | 0.818 | 0.615 | 0.091 | 0.154 | 0.154 | ||||
| 10m + V | 0.655 | 0.948 | 1 | 0.485 | 0.865 | 0.964 | 0.07 | 0.344 | 0.594 | ||||
| Bird | Surface | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 10m | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 10m + V | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Sponge | |||||||||||||
| Barracuda | Surface | – | 0 | 0 | – | 0.5 | 1 | – | 0 | 0 | |||
| 10m | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 10m + V | 0.096 | 0.615 | 0.891 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.021 | ||||
| Ray | Surface | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| 10m | – | – | – | 0 | – | – | 0 | – | – | ||||
| 10m + V | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.023 | ||||
| Snapper | Surface | – | 1 | 0.667 | – | 0 | 0 | – | 0 | 0 | |||
| 10m | – | 1 | 0.75 | – | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 10m + V | 0.577 | 0.932 | 1 | 0.055 | 0.573 | 0.891 | 0 | 0 | 0.021 | ||||
| Bird | Surface | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| 10m | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||
| 10m + V | – | – | 1 | – | – | 1 | – | – | 1 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nahmad-Rohen, L.; Qureshi, Y.H.; Vorobyev, M. The Colours of Octopus: Using Spectral Data to Measure Octopus Camouflage. Vision 2022, 6, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040059
Nahmad-Rohen L, Qureshi YH, Vorobyev M. The Colours of Octopus: Using Spectral Data to Measure Octopus Camouflage. Vision. 2022; 6(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleNahmad-Rohen, Luis, Yusuf H. Qureshi, and Misha Vorobyev. 2022. "The Colours of Octopus: Using Spectral Data to Measure Octopus Camouflage" Vision 6, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040059
APA StyleNahmad-Rohen, L., Qureshi, Y. H., & Vorobyev, M. (2022). The Colours of Octopus: Using Spectral Data to Measure Octopus Camouflage. Vision, 6(4), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040059






