GNSS (GPS) Monitoring of Dynamic Deflections of Bridges: Structural Constraints and Metrological Limitations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Constraints in Dynamic Deflections of Bridges
2.1. Evidence from Regulations and Codes
2.2. Evidence from Field Data
2.3. Modal Frequencies, Resonance, and Deflections
3. Bridge Type, SNR and Multipath in Geodetic Deflection Measurements
3.1. Typical GPS/GNSS Accuracies
3.2. Long, Flexible Bridges
3.3. Short, Stiff Bridges
3.4. The Threat of Dynamic Multipath
4. Reported Large Deflections of Stiff, Structurally Healthy Bridges
5. Discussion
5.1. Contrasts between Observations and Structural Predictions
5.2. Searching the Source of the Error in the GNSS Data
6. Strategy for Reliable Bridge Monitoring
7. Conclusions and Summary
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Billah, K.Y.; Scanlan, R.H. Resonance, Tacoma Narrows Bridge failure, and undergraduate physics textbooks. Am. J. Phys. 1991, 59, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallard, P.; Fitzpatrick, A.J.; Flint, A.; Le Bourva, S.; Low, A.; Ridsdill Smith, R.M.; Willford, M. The London Millennium Footbridge. Struct. Eng. 2001, 79, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, G.; Brownjohn, J.M.W.; Taylor, C.A. Measurements of static and dynamic displacement from visual monitoring of the Humber Bridge. Eng. Struct. 1993, 15, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashkenazi, V.; Dodson, A.H.; Moore, T.; Roberts, G. Real Time OTF GPS Monitoring of the Humber Bridge. Surv. World 1996, 4, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cantieni, R. Dynamic load testing of highway bridges. In Transportation Research Record; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; Volume 950, pp. 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Moreu, F.; Jo, H.; Li, J.; Kim, R.E. Dynamic assessment of timber railroad bridges using displacements. J. Bridge Eng. 2015, 20, 4014114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryba, L. Vibration of Solids and Structures under Moving Loads, 3rd ed.; Academia Prague: Prague, Czech Republic, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ayati, A.A.; Steiros, K.; Miller, M.A.; Duvvuri, S.; Hultmark, M. A double-multiple streamtube model for vertical axis wind turbines of arbitrary rotor loading. Wind Eng. Sci. 2019, 4, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AASHTO. Guide Specifications for Design of Pedestrian Bridges; American Association of State, Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Dodson, A.; Roberts, G. Detecting bridge dynamics with GPS and triaxial accelerometers. Eng. Struct. 2007, 29, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownjohn, J.M.; Koo, K.-Y.; Scullion, A.; List, D. Operational deformations in long-span bridges. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2015, 11, 556–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, E.J.; Koo, K.-Y.; Brownjohn, J.; Worden, K. Long-term monitoring and data analysis of the Tamar Bridge. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S.C. Measurement of the dynamic displacements and of the modal frequencies of a short-span pedestrian bridge using GPS and an accelerometer. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S.C. Three-dimensional dynamic deflections and natural frequencies of a stiff footbridge based on measurements of collocated sensors. Struct. Control. Heal. Monit. 2014, 21, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S. Dynamic Deflections of a Stiff Footbridge Using 100-Hz GNSS and Accelerometer Data. J. Surv. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psimoulis, P.; Stiros, S. Measuring deflections of a short-span railway bridge using a Robotic Total Station (RTS). J. Bridge Eng. 2013, 18, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiros, S.; Psimoulis, P.; Moschas, F.; Saltogianni, V.; Tsantopoulos, E.; Triantafyllidis, P. Multi-sensor measurement of dynamic deflections and structural health monitoring of flexible and stiff bridges. Bridg. Struct. 2019, 15, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, A.; Brunner, F.K. Analysis of bridge deformations using continuous GPS measurements. In Proceedings of the INGEO2002, 2nd Conference of Engineering Surveying; Kopacik, A., Kyrinovic, P., Eds.; Slovak University of Technology: Bratislava, Czech Republic, 2002; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X. Real-time Deformation Monitoring of Bridges Using GPS/Accelerometers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, H.; Ammann, W.J.; Deischl, F.; Eisenmann, J.; Floegl, I.; Hirsch, G.H.; Steinbeisser, L. Vibration Problems in Structures, Practical Guidelines; Birkauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 1997; 234p. [Google Scholar]
- Häggström, J.; Bagge, N.; Nilimaa, J.; Sas, G.; Blanksvärd, T.; Täljsten, B.; Carolin, A. Testing Bridges to Failure Experiences. In Proceedings of the 39th IABSE Symposium—Engineering the Future, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–23 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kafle, B.; Zhang, L.; Mendis, P.; Herath, N.; Maizuar, M.; Duffield, C.; Thompson, R.G. Monitoring the Dynamic Behavior of The Merlynston Creek Bridge Using Interferometric Radar Sensors and Finite Element Modeling. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2017, 9, 1750003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, C.; Bernardini, G. An interferometric radar for non-contact measurement of deflections on civil engineering structures: Laboratory and full-scale tests. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2010, 65, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekidis, V.; Tsakiri, M.; Makra, K.; Karakostas, C.; Klimis, N.; Sous, I. Evaluation of dynamic response and local soil effects of the Evripos cable-stayed bridge using multi-sensor monitoring systems. Eng. Geol. 2005, 79, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschas, F.; Avallone, A.; Saltogianni, V.; Stiros, S. Strong-motion displacement waveforms using 10Hz PPP-GPS: An assessment based on free oscillation experiments. Earthq. Eng. Struct Dyn. 2014, 43, 1853–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, N. Dynamic analysis of railway bridge under high-speed trains. Comput. Struct. 2005, 83, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.W.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.; Cosser, E. Multipath Mitigation for Bridge Deformation Monitoring. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2002, 1, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S.C. Dynamic multipath in structural bridge monitoring: An experimental approach. GPS Solut. 2013, 18, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.B.; Hurlebus, S.; Kang, Y.J. Summary Review of GPS Technology for Structural Health Monitoring. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, E.G.; Gaxiola-Camacho, R.; Bennett, R.; Guzman-Acevedo, M.; Gaxiola-Camacho, I. Structural evaluation of dynamic and semi-static displacements of the Juarez Bridge using GPS technology. Measurement 2017, 110, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapid Decay of a Timber Footbridge and Changes in Its Modal Frequencies Derived from Multiannual Lateral Deflection Measurements. Available online: https://ascelibrary.org/doi/suppl/10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000629/suppl_file/Supplemental_Data_BE.1943-5592.0000629_Stiros.mp4 (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Fradelos, Y.; Thalla, O.; Biliani, I.; Stiros, S. Study of lateral displacements and natural frequency of a pedestrian bridge using low-cost cameras. Sensors 2020, 20, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Brownjohn, J.M.W. Review of machine-vision based methodologies for displacement measurement in civil structures. J. Civ. Struct. Heal. Monit. 2018, 8, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mas, D.; Espinosa, J.; Roig, A.B.; Ferrer, B.; Perez, J.; Illueca, C. Measurement of wide frequency range structural microvibrations with a pocket digital camera and sub-pixel techniques. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, D.; Calçada, R.; Ferreira, J.; Martins, T. Non-contact measurement of the dynamic displacement of railway bridges using an advanced video-based system. Eng. Struct. 2014, 75, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, E.; Purasinghe, R.; Feng, M.Q. Multi-output modal identification of landmark suspension bridges with distributed smartphone data: Golden Gate Bridge. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2576. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.-H.; Tang, D.-H.; Teng, J.; Said, S.; Rohrmann, R.G. Structural Health Monitoring of a Prestressed Concrete Bridge Based on Statistical Pattern Recognition of Continuous Dynamic Measurements over 14 years. Sensors 2018, 18, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
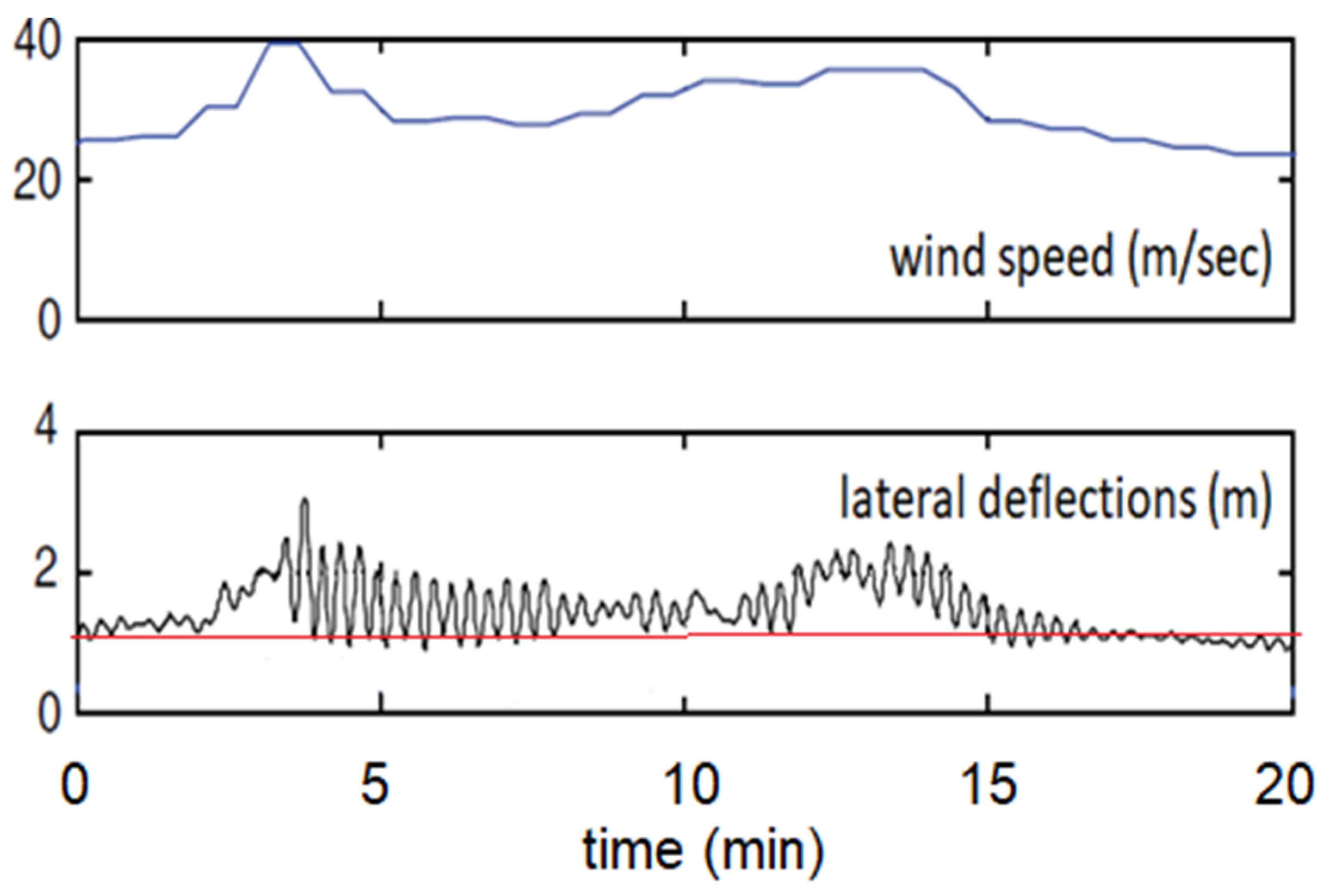
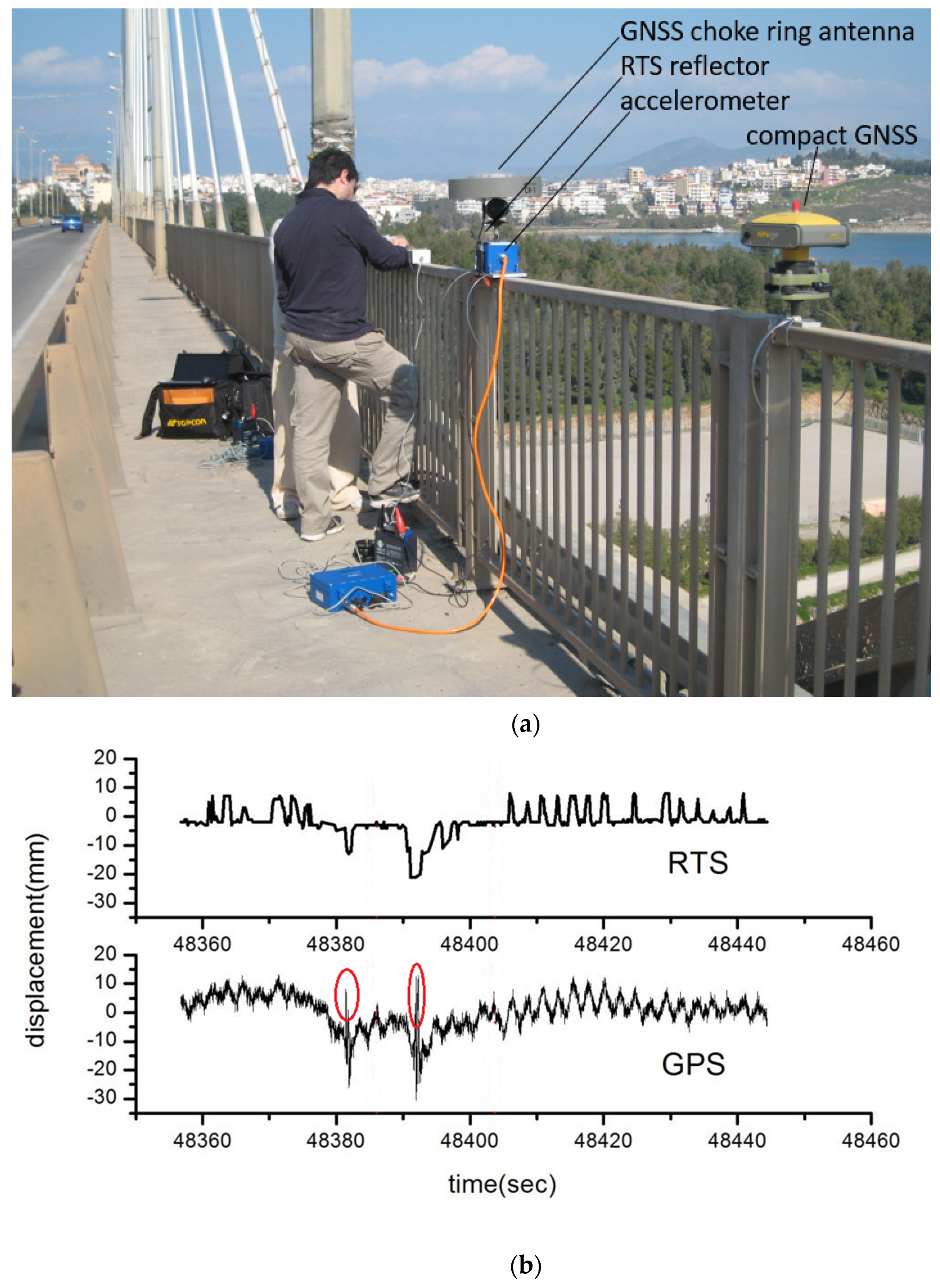



| Bridge | Span (L) (m) | Vertical Deflection (d), (mm) | Type of Measurement | Loading | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| timber deck train bridge | 24 | <4 | LVDT | passing train | [6] |
| motorway multi-span pre-stressed RC bridge | ~20 | <3 | Radar interferometry | cars and trucks | [22] |
| Historic metallic train bridge (GR) | 30 | 6 | robotic total station (RTS) | passing train | [16] |
| Pedestrian metallic, three-span truss bridge (GR) | 41 | <6 | robotic total station (RTS) | coordinated jumping to resonance | [14] |
| three-span RC bridge | 62 | <3 | Radar interferometry | traffic | [23] |
| five-span pre-stressed motorway bridge | 24 | ~300 (at failure) | LVDT | bent to failure | [21] |
| Mode 1 | Mode 2 | Mode 11 |
|---|---|---|
| f1 = 0.36 Hz | f2 = 0.39 Hz | f3 = 0.94 Hz |
| excited by traffic | excited by traffic | excited by earthquakes |
| Measurement session | 1 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 19 | |
| Max deflection(cm) | midspan | 4 | 9 | 21 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 5 |
| pier | 5 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | |
| session | 2 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 20 | |
| Max deflection(cm) | midspan | 24 | 9 | 14 | 5 | 7 | 18 | 8 |
| pier | 13 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 8 | |
| session | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | |
| Max deflection(cm) | midspan | 25 | 20 | 11 | 4 | 5 | 13 | 7 |
| pier | 12 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stiros, S.C. GNSS (GPS) Monitoring of Dynamic Deflections of Bridges: Structural Constraints and Metrological Limitations. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures6020023
Stiros SC. GNSS (GPS) Monitoring of Dynamic Deflections of Bridges: Structural Constraints and Metrological Limitations. Infrastructures. 2021; 6(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures6020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleStiros, Stathis C. 2021. "GNSS (GPS) Monitoring of Dynamic Deflections of Bridges: Structural Constraints and Metrological Limitations" Infrastructures 6, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures6020023
APA StyleStiros, S. C. (2021). GNSS (GPS) Monitoring of Dynamic Deflections of Bridges: Structural Constraints and Metrological Limitations. Infrastructures, 6(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures6020023






