Co-Processing of [Fe(NH2trz)3](2ns)2 and UHMWPE into Materials Combining Spin Crossover and High Mechanical Strength
Abstract
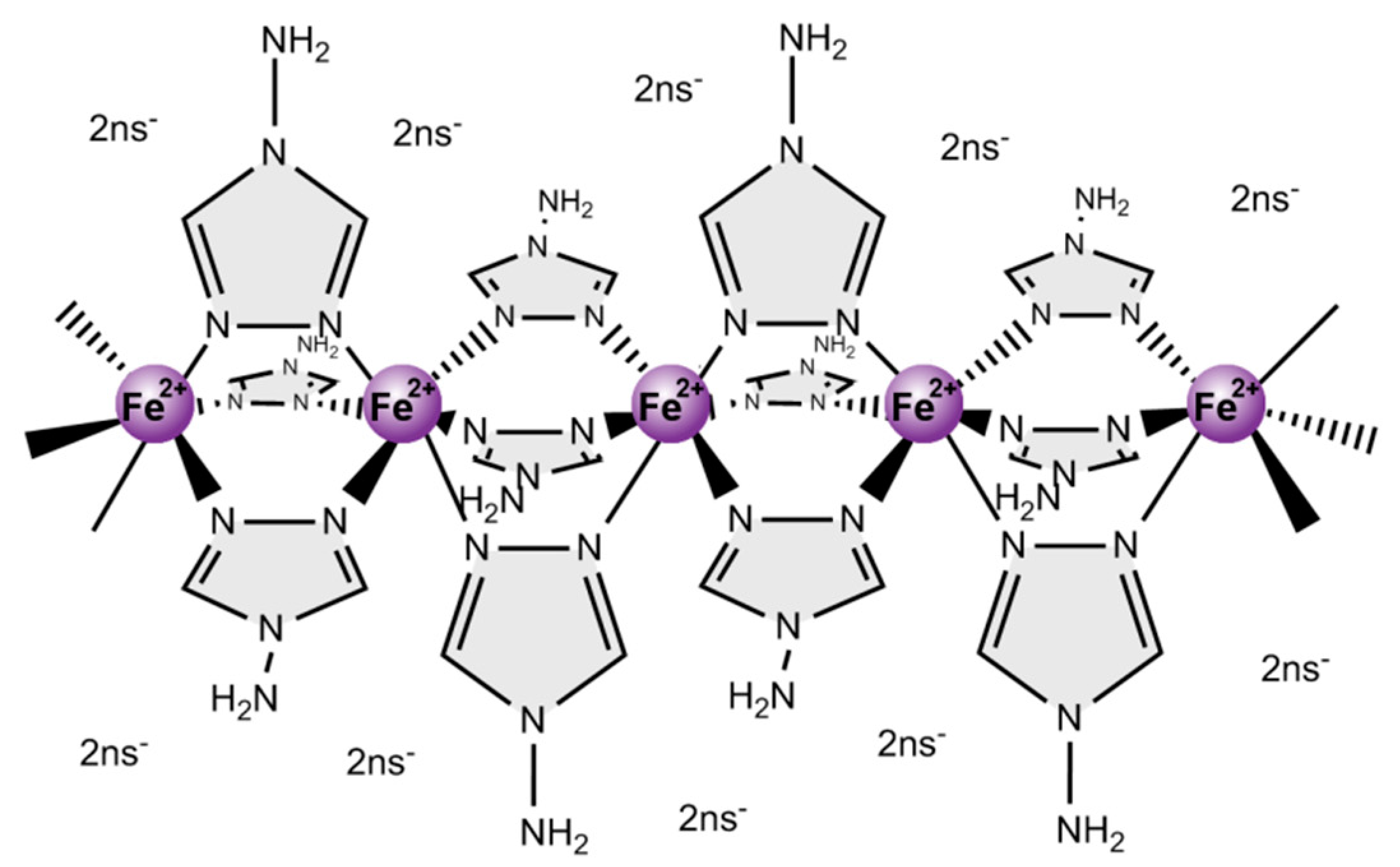
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Processing of the Blends into Ribbons and Fibers
2.3. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dîrtu, M.M.; Neuhausen, C.; Naik, A.D.; Rotaru, A.; Spinu, L.; Garcia, Y. Insights into the Origin of Cooperative Effects in the Spin Transition of [Fe(NH2trz)3](NO3)2: The Role of Supramolecular Interactions Evidenced in the Crystal Structure of [Cu(NH2trz)3](NO3)2·H2O. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5723–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosjean, A.; Daro, N.; Kauffmann, B.; Kaiba, A.; Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P. The 1-D Polymeric Structure of the [Fe(NH2trz)3](NO3)2·Nh2o (With N = 2) Spin Crossover Compound Proven by Single Crystal Investigations. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12382–12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, T.; Murakami, Y.; Kiguchi, M.; Komatsu, T.; Kojima, N. Spin-Crossover Phase Transition of a Chain Fe(II) Complex Studied by X-Ray-Absorption Fine-Structure Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 14238–14244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Koningsbruggen, P.J.; Garcia, Y.; Codjovi, E.; Lapouyade, R.; Kahn, O.; Fournès, L.; Rabardel, L. Non-Classical Feii Spin-Crossover Behaviour in Polymeric Iron(II) Compounds of Formula [Fe(NH2trz)3]X2xh2o (NH2trz=4-Amino-1,2,4-Triazole; X=Derivatives of Naphthalene Sulfonate). J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrenova, L.G.; Shakirova, O.G.; Ikorskii, V.N.; Varnek, V.A.; Sheludyakova, L.A.; Larionov, S.V. 1A 1⇄5 T2 Spin Transition in New Thermochromic Iron(II) Complexes with 1,2,4-Triazole and 4-Amino-1,2,4-Triazole. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2003, 29, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, H.; Aimé, C.; Vallée, A.; Bleuzen, A.; Schmutz, M.; Mosser, G.; Coradin, T.; Roux, C. Preserving the Spin Transition Properties of Iron-Triazole Coordination Polymers within Silica-Based Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 11542–11550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, H.; Aimé, C.; Vallée, A.; Coradin, C.; Roux, C. A Flexible Polymer-Nanoparticle Hybrid Material Containing Triazole-Based Fe(II) with Spin Crossover Properites for Magneto-Optical Applications. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushuev, M.B.; Pishchur, D.P.; Korolkov, I.V.; Vinogradova, K.A. Prototypical Iron(II) Complex with 4-Amino-1,2,4-Triazole Reinvestigated: An Unexpected Impact of Water on Spin Transition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 4056–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, K.A.; Pishchur, D.P.; Korolkov, I.V.; Bushuev, M.B. Magnetic Properties and Vapochromism of a Composite on the Base of an Iron(II) Spin Crossover Complex. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 165, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräunlich, I.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Bauer, M.; Schepper, R.; Knüsel, P.; Dshemuchadse, J.; Mezzenga, R.; Caseri, W. Polynuclear Iron(II)–Aminotriazole Spincrossover Complexes (Polymers) in Solution. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 3546–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Bräunlich, I.; Ruokolainen, J.; Bauer, M.; Schepper, R.; Smith, P.; Caseri, W.; Mezzenga, R. Gels, Xerogels and Films of Polynuclear Iron(II)–Aminotriazole Spin-Crossover Polymeric Complexes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 60842–60852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovo, G.; Bräunlich, I.; Caseri, W.R.; Stingelin, N.; Anthopoulos, T.D.; Sandeman, K.G.; Bradley, D.D.C.; Stavrinou, P.N. Room temperature dielectric bistability in solution-processed spin crossover polymer thin films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 6240–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, J.A.; Gaspar, A.B.; Muñoz, M.C. Thermal, Pressure and Light Switchable Spin-Crossover Materials. Dalton Trans. 2005, 2062–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gütlich, P.; van Koningsbruggen, P.J.; Renz, F. Recent Advances of Spin Crossover Research. Struct. Bond. 2004, 107, 27–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Hauser, A.; Spiering, H. Thermisch und optisch schaltbare Eisen(II)-Komplexe. Angew. Chem. 1994, 106, 2109–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Niel, V.; Muñoz, M.C.; Real, J.A. Spin Crossover in 1D, 2D and 3D Polymeric Fe(II) Networks. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 229–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin Crossover—An Overall Perspective. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barefield, E.K.; Busch, D.H.; Nelson, S.M. Iron, Cobalt, and Nickel Complexes having Anomalous Magnetic Moments. Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1968, 22, 457–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, H.A. Spin Transitions in Six-Coordinate Iron(II) Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1976, 18, 293–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán Mascarós, J.R.; Aromí, G.; Darawsheh, M. Polynuclear Fe(II) Complexes: Di/trinuclear molecules and coordination netwoks. C. R. Chim. 2018, 21, 1209–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, A.H.; Martin, R.L.; Ross, I.G.; White, A.H. Anomalous behaviour at the 6A1-2T2 crossover in iron (III) complexes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1964, 280, 235. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.H.; Roper, R.; Kokot, E.; Waterman, H.; Martin, R.L. The Anomalous Paramagnetism of Iron(III) NN-Dialkyldithiocarbamates. Aust. J. Chem. 1964, 17, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dîrtu, M.M.; Garcia, Y.; Nica, M.; Rotaru, A.; Linares, J.; Varret, F. Iron(II) Spin Transition 1,2,4-Triazole Chain Compounds with Novel Inorganic Fluorinated Counteranions. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 2259–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Kröber, J.; Jay, C. Spin Transition Molecular Materials for Displays and Data Recording. Adv. Mater. 1992, 4, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Jay Martinez, C. Spin-Transition Polymers: From Molecular Materials toward Memory Device. Science 1998, 279, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Ruben, M. Emerging Trends in Spin Crossover (SCO) Based Functional Materials and Devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 176–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, G.; Rat, S.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W.; Bousseksou, A. Spin Crossover Nanomaterials: From Fundamental Concepts to Devices. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 17003862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Shibata, T.; Sasaki, S.; Ohba, M.; Takahara, A.; Kunitake, T.; Kimizuka, N. Supramolecular Control of Spin-Crossover Phenomena in Lipophilic Fe(II)-1,2,4-Triazole Complexes. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 5192–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.; Hernández, R.; Nogales, A.; Roig, A.; López, D. Structure of a Spin-Crossover Fe(II)–1,2,4-Triazole Polymer Complex Dispersed in an Isotactic Polystyrene Matrix. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-W.; Lee, J.-W.; Jeong, S.-H.; Park, I.-W.; Kim, Y.-M.; Jin, J.-I. Processable Magnetic Plastics Composites—Spin Crossover of PMMA/Fe(II)-Complexes Composites. Synth. Met. 2004, 142, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallah, T.; Cavallini, M. Surfaces, Thin Films and Patterning of Spin Crossover Compounds. C. R. Chim. 2018, 21, 1270–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, L.; Catala, L. Spin-crossover Nanoparticles and Nanocomposite Materials. C. R. Chim. 2018, 21, 1230–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez-Cabrera, A.; Rapakousiou, A.; Piedrahito Bello, M.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. Spin Crossover Polymer Composites, Polymers and Related Soft Materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 419, 213396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräunlich, I.; Lienemann, S.; Mair, C.; Smith, P.; Caseri, W. Tuning the Spin-Crossover Temperature of Polynuclear Iron(II)–Triazole Complexes in Solution by Water and Preparation of Thermochromic Fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Lemstra, P.J. Ultrahigh-Strength Polyethylene Filaments by Solution Spinning/Drawing. J. Mater. Sci. 1980, 15, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, P.; Lemstra, P.J.; Pijpers, P.L.; Kiel, A.M. Ultra-drawing of high molecular weight polyethylene cast from solution, IlL Morphology and structure. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1981, 259, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perevedentsev, A.; Aksel, S.; Feldman, K.; Smith, P.; Stavrinou, P.N.; Bradley, D.D.C. Interplay between Solid State Microstructure and Photophysics for Poly(9,9-Dioctylfluorene) within Oriented Polyethylene Hosts. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaller, R.; Feldman, K.; Smith, P.; Tervoort, T.A. High-Performance Polyethylene Fibers “Al Dente”: Improved Gel-Spinning of Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene Using Vegetable Oils. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaiser, W. Kunststoffchemie für Ingenieure, 4th ed.; Hanser: Munich, Germany, 2016; pp. 249–286. ISBN 978-3-446-44638-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, A.; Sayigh, A.A. Some Fatty Acids as Phase-Change Thermal Energy Storage Materials. Renew. Energy 1994, 4, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levene, P.A.; Taylor, F.A. The Synthesis of Normal Fatty Acids from Srtearic Acid to Hexanoic Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1924, 59, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.; Suslick, K.S. One-dimensional coordination polymers: Applications to material science. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1993, 128, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batten, S.R.; Neville, S.N.; Turner, D.R. Coordination Polymers; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 273–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| λ [–] | TSCO [°C] | Tm [°C] | Thigh [°C] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43/13 | 133/115 | 222/196 |
| 10 | 43/16 | 138/116 | 223/199 |
| f [% m/m] | λ [–] | E [GPa] | σ [MPa] | ε [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 10 | 45 (9) | 790 (25) | 7 (1) |
| 0.0 | 65 | 161 (13) | 3070 (280) | 3 (1) |
| 9.1 | 10 | 33 (8) | 820 (75) | 7 (2) |
| 9.1 | 65 | 145 (25) | 2410 (160) | 3 (1) |
| 23.1 | 10 | 37 (2) | 700 (70) | 5 (1) |
| 33.3 | 10 | 17 (6) | 440 (70) | 6 (2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baumgartner, M.; Schaller, R.; Smith, P.; Weymuth, I.; Caseri, W. Co-Processing of [Fe(NH2trz)3](2ns)2 and UHMWPE into Materials Combining Spin Crossover and High Mechanical Strength. Sci 2021, 3, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010007
Baumgartner M, Schaller R, Smith P, Weymuth I, Caseri W. Co-Processing of [Fe(NH2trz)3](2ns)2 and UHMWPE into Materials Combining Spin Crossover and High Mechanical Strength. Sci. 2021; 3(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaumgartner, Manuel, Raphael Schaller, Paul Smith, Irene Weymuth, and Walter Caseri. 2021. "Co-Processing of [Fe(NH2trz)3](2ns)2 and UHMWPE into Materials Combining Spin Crossover and High Mechanical Strength" Sci 3, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010007
APA StyleBaumgartner, M., Schaller, R., Smith, P., Weymuth, I., & Caseri, W. (2021). Co-Processing of [Fe(NH2trz)3](2ns)2 and UHMWPE into Materials Combining Spin Crossover and High Mechanical Strength. Sci, 3(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010007






