Journal Description
Sci
Sci
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all research fields published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Multidisciplinary)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
MODERHydrogen-H2: A GIS-Based Framework for Integrating Green Hydrogen into Colombia’s Energy Transition
Sci 2026, 8(2), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020037 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
The transition to green hydrogen is critical for achieving sustainable energy systems and climate goals. This study presents MODERHydrogen-H2, a comprehensive framework for assessing solar- and wind-based green hydrogen production, fossil fuel substitution, and greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction. The method integrates
[...] Read more.
The transition to green hydrogen is critical for achieving sustainable energy systems and climate goals. This study presents MODERHydrogen-H2, a comprehensive framework for assessing solar- and wind-based green hydrogen production, fossil fuel substitution, and greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction. The method integrates Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to optimize renewable energy resource allocation while adhering to sustainability criteria. Applied to four solar sites (2000 MW) in Colombia’s Magdalena–Cauca Basin and three wind projects (1700 MW) in the Caribbean Basin, the model estimates an annual production of 211,074 tons of green hydrogen by 2030. This output could displace 37,221 terajoules of fossil fuels, contributing 2.5% to the national energy matrix and reducing CO2 emissions by 10.09 million tons. MODERHydrogen-H2 demonstrates scalability and adaptability, offering a decision-support tool for global energy transition strategies. Its implementation supports affordable, reliable, and low-carbon energy systems, aligning with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) targets. The model offers a single platform from which to simulate renewable energy potential in a sustainable manner within a given geographical area, develop scenarios for modifying the energy matrix of a country or region, simulate rational and efficient water supply and demand for energy uses, including aspects of climate change, calculate green hydrogen production in a sustainable manner, and finally calculate greenhouse gas emissions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic GIS-Driven Renewable Energy Solutions: Advancing Regional Development, Rural Electrification, and Universal Energy Access)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Governing Healthcare AI in the Real World: How Fairness, Transparency, and Human Oversight Can Coexist: A Narrative Review
by
Paolo Bailo, Giulio Nittari, Giuliano Pesel, Emerenziana Basello, Tommaso Spasari and Giovanna Ricci
Sci 2026, 8(2), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020036 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly shifting from experimental pilots to mainstream clinical infrastructure, redefining how evidence, accountability, and ethics intersect in healthcare. This narrative review integrates insights from peer-reviewed studies and policy frameworks to examine seven cross-cutting aspects: bias and fairness, explainability, safety
[...] Read more.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly shifting from experimental pilots to mainstream clinical infrastructure, redefining how evidence, accountability, and ethics intersect in healthcare. This narrative review integrates insights from peer-reviewed studies and policy frameworks to examine seven cross-cutting aspects: bias and fairness, explainability, safety and quality, privacy and data protection, accountability and liability, human oversight, and procurement and deployment. Findings reveal persistent inequities driven by dataset bias and opaque design; the need for explainability tools that are validated, task-specific, and usable by clinicians; and the centrality of post-market surveillance for sustaining patient safety. Privacy-preserving methods such as federated learning and differential privacy show promise but demand rigorous validation and regulatory coherence. Emerging liability models advocate shared enterprise responsibility, while governance-by-design—embedding transparency, auditability, and equity across the AI lifecycle—appears most effective in balancing innovation with public trust. Ethical, legal, and technical safeguards must evolve together to ensure that AI augments, rather than replaces, clinical judgment and institutional accountability.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Biochemical Phenotypes in Hospitalized Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
by
Juan C. Polo, Jesus M. Angulo-Mercado, Sandra M. Coronado-Ríos, Fernando de la Vega, Edwin D. Correa and Nelson E. Arenas
Sci 2026, 8(2), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020035 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) produces systemic alterations that can be reflected in biochemical parameters beyond microbiological resolution. Early characterization of the biochemical response to treatment could provide additional criteria for following up with hospitalized patients. A retrospective observational study was conducted focusing on patients
[...] Read more.
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) produces systemic alterations that can be reflected in biochemical parameters beyond microbiological resolution. Early characterization of the biochemical response to treatment could provide additional criteria for following up with hospitalized patients. A retrospective observational study was conducted focusing on patients with pulmonary TB from a tertiary care hospital, based on biochemical parameters upon admission (“before”) and between 2 and 10 days after starting anti-tuberculosis treatment (“after”). The patients were grouped into three clusters according to the results of the clinical tests: mild (70.1%), inflammatory (26.7%), and severe (3.2%). After the start of treatment, 30% of the patients migrated toward the most biochemically compromised phenotype (Cluster 3). Sixty-one percent showed deterioration in at least one of the three key parameters; only 12.8% improved simultaneously. Significant associations were identified between unfavorable biochemical evolution and HIV (p = 0.004) or patients with public health coverage (p = 0.01). Overall, after antituberculous therapy, a reduction in CRP and leukocytes was observed (p < 0.001), and progressive anemia (ΔHb: −1.7 g/dL) and renal deterioration (ΔCr: +0.52 mg/dL) were identified. The identification of dynamic phenotypes in patients with pulmonary TB can be used to establish early risk markers and contribute to individualized clinical surveillance.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
From Ancient Aqueducts to Modern Turbines: Exploring the Impact of Nazca-Inspired Spiral Geometry on Gravitational Vortex Turbine Efficiency
by
Juliana Carvajal Guerra, Ainhoa Rubio-Clemente and Edwin Chica
Sci 2026, 8(2), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020034 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study investigates an inlet design for a gravitational vortex turbine (GVT), drawing inspiration from the ancient Nazca puquios. The puquios are ingenious subterranean aqueducts constructed by the Nazca culture (c. 100 BC–800 AD) in southern Peru, featuring spiral ojos de agua (water
[...] Read more.
This study investigates an inlet design for a gravitational vortex turbine (GVT), drawing inspiration from the ancient Nazca puquios. The puquios are ingenious subterranean aqueducts constructed by the Nazca culture (c. 100 BC–800 AD) in southern Peru, featuring spiral ojos de agua (water eyes) used to access groundwater and stabilize flow.The primary objective was to enhance vortex stability and overall GVT efficiency under low-head, low-flow operating conditions. A parametric Nazca-type inlet feeding a conical basin was defined by two controlling factors: the number of turns (N) and the inclination angle (
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Nonlinear CPG-Based Oscillator Model for Quadruped Robotic Locomotion
by
Edgar-Mario Rico-Mesa and Jesus-Antonio Hernandez-Riveros
Sci 2026, 8(2), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020033 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
In recent decades, robotic locomotion has applied different techniques to emulate central pattern generators (CPGs). The theory of CPG explains the biological functions of motor control in living organisms. This paper presents an unpublished model for coupled nonlinear oscillators. This model employs a
[...] Read more.
In recent decades, robotic locomotion has applied different techniques to emulate central pattern generators (CPGs). The theory of CPG explains the biological functions of motor control in living organisms. This paper presents an unpublished model for coupled nonlinear oscillators. This model employs a canonical nonlinear differential equation system to coordinate joint activity. The analysis, conducted under the criteria of chaos and bifurcation theory, determines that the new model is successful and without the presence of chaos. The new model is compared with other cases, including the Wilson–Cowan, Hopf, and Van Der Pol models, as well as with the operability of different robots. It highlights the new model’s advantages in terms of versatility, simplicity, and processing, as well as the comparisons of metrics of locomotion, such as support factor and symmetry index between hemibody metrics. The new model is applied to the locomotion of two quadruped robots (a crab and a dog) used in research on transitions between types of locomotion, considering both physical and computational limitations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computer Sciences, Mathematics and AI)
Open AccessArticle
Effects of a Phyto-Additive Mixture on Reproductive Performance in Male and Female Rabbits
by
Francesco Vizzarri, Ivana Spevakova, Aneta Kisova, Jaroslav Slamecka, Andrej Balazi and Lubomir Ondruska
Sci 2026, 8(2), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020032 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of phyto-additive mixture supplementation on semen quality and on some reproductive parameters after artificial insemination in rabbits. The trial run 120 days on 20 adult New Zealand white rabbit bucks that were allocated
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of phyto-additive mixture supplementation on semen quality and on some reproductive parameters after artificial insemination in rabbits. The trial run 120 days on 20 adult New Zealand white rabbit bucks that were allocated into two different groups, first was control (CON; n = 10) fed with commercial pelleted-feed and second was considered experimental group (EXP; n = 10) which received in feed a natural feed additive mixture (0.1% of dried Chlorella vulgaris powder and 0.1% of dried Laurus nobilis leaves powder). Consequently, the quality assessment of semen by the Computer Assisted Semen Analyzer (CASA) system, samples were instrumentally inseminated on rabbit does for two consecutive reproductive cycles, and productive and reproductive indexes were evaluated. Results demonstrate that while spermatozoa concentration and ejaculate volume did not differ significantly among experimental groups or between reproduction cycles, spermatozoa motility parameters were significantly enhanced in rabbits receiving the phyto-additive mixture, as evidenced by increased total motility (87.83% vs. 70.63%) and progressive motility (75.68% vs. 50.10%) compared with the control group (p < 0.01). No differences were observed in prolificacy traits during the first reproductive cycle, whereas in the second cycle the phyto-additive treatment increased the number of kits born alive per litter (12.29 vs. 10.19; p < 0.05) and improved kit growth performance at birth (79.17 vs. 66.75 g), at weaning (1085.28 vs. 963.15 g), and in average daily gain (28.75 vs. 25.61 g/day). The study provides evidence of alternative practises based on feeding programme to enhance reproductive traits in rabbit production. The goal is to provide farmers with examples of good farming practise (such as precision farming), focused on sustainability and efficiency, and a certain transfer of knowledge.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Biology Research and Life Sciences)
Open AccessArticle
Elemental Composition of Ilex paraguariensis Grown in the Brazil–Paraguay Border Region
by
Jacqueline Marques da Silva Gondim, Elaine Silva de Pádua Melo, Moisés Centenaro, Marta Aratuza Pereira Ancel and Valter Aragão do Nascimento
Sci 2026, 8(2), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020031 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
The mineral composition of Ilex paraguariensis is strongly shaped by the physicochemical characteristics and natural fertility of the soils in which it is cultivated. This study evaluated macro- and microelement concentrations in fresh leaves from fourteen rural properties in Mato Grosso do Sul,
[...] Read more.
The mineral composition of Ilex paraguariensis is strongly shaped by the physicochemical characteristics and natural fertility of the soils in which it is cultivated. This study evaluated macro- and microelement concentrations in fresh leaves from fourteen rural properties in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, and examined how soil texture, pH, organic matter content, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and aluminum saturation influence nutrient availability and foliar accumulation. Soil, leaf, and environmental data were analyzed using ANOVA, intraclass correlation coefficients, Bayes factors, and principal component analysis (PCA). Sandy and dystrophic soils with low CEC and reduced organic matter showed greater variability in micronutrient retention and favored leaching, resulting in higher fluctuations in foliar Cu, Zn, and Mn. In contrast, clayey eutrophic soils with high CEC and higher organic matter promoted greater nutrient stability and more homogeneous foliar concentrations of K, Mg, and P. PCA confirmed that differences in soil geochemistry, particularly in Se, Cr, Mn, and Zn availability, were reflected in leaf composition. Chromium remained low in leaves despite elevated soil levels, indicating restricted uptake and translocation. Overall, the results demonstrate that edaphic conditions govern the nutritional profile of I. paraguariensis, emphasizing the need for region-specific soil management to maintain leaf quality in emerging cultivation areas.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Green Hydrogen in Sustainable Agri-Food Systems: A Review of Applications in Agriculture and the Food Industry
by
Ferruccio Giametta, Ruggero Angelico, Gianluca Tanucci, Pasquale Catalano and Biagio Bianchi
Sci 2026, 8(2), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020030 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The agri-food sector is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions while facing increasing demand for food production driven by population growth. Transitioning towards sustainable and low-carbon agricultural systems is therefore critical. Green hydrogen, produced from renewable energy sources, holds significant promise
[...] Read more.
The agri-food sector is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions while facing increasing demand for food production driven by population growth. Transitioning towards sustainable and low-carbon agricultural systems is therefore critical. Green hydrogen, produced from renewable energy sources, holds significant promise as a clean energy carrier and chemical feedstock to decarbonize multiple stages of the agri-food supply chain. This systematic review is based on a structured analysis of peer-reviewed literature retrieved from Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar, covering over 120 academic publications published between 2010 and 2025. This review provides a comprehensive overview of hydrogen’s current and prospective applications across agriculture and the food industry, highlighting opportunities to reduce fossil fuel dependence and greenhouse gas emissions. In agriculture, hydrogen-powered machinery, hydrogen-rich water treatments for crop enhancement, and the use of green hydrogen for sustainable fertilizer production are explored. Innovative waste-to-hydrogen strategies contribute to circular resource utilization within farming systems. In the food industry, hydrogen supports fat hydrogenation and modified atmosphere packaging to extend product shelf life and serves as a sustainable energy source for processing operations. The analysis indicates that near-term opportunities for green hydrogen deployment are concentrated in fertilizer production, food processing, and controlled-environment agriculture, while broader adoption in agricultural machinery remains constrained by cost, storage, and infrastructure limitations. Challenges such as scalability, economic viability, and infrastructure development are also discussed. Future research should prioritize field-scale demonstrations, technology-specific life-cycle and techno-economic assessments, and policy frameworks adapted to decentralized and rural agri-food contexts. The integration of hydrogen technologies offers a promising pathway to achieve carbon-neutral, resilient, and efficient agri-food systems that align with global sustainability goals and climate commitments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Concrete Protection Against Carbonation by Traditional Coatings
by
Rui Reis, Aires Camões, Manuel Ribeiro, Raphaele Malheiro and Élia Fernandes
Sci 2026, 8(2), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020029 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In contemporary construction practice, concrete surfaces are commonly coated; however, this factor is often disregarded in durability assessments, particularly with respect to carbonation. Such omission may lead to overly conservative designs and unnecessary material consumption. This study evaluates the actual performance of traditional
[...] Read more.
In contemporary construction practice, concrete surfaces are commonly coated; however, this factor is often disregarded in durability assessments, particularly with respect to carbonation. Such omission may lead to overly conservative designs and unnecessary material consumption. This study evaluates the actual performance of traditional coatings applied to concrete, considering three types of concrete: ordinary Portland cement (OPC), high-volume fly ash (FA), and high-volume FA with a low water-to-binder ratio. The coatings investigated were mainly based on cement and hydrated lime, with the inclusion of a FA-based alternative. Accelerated carbonation tests were performed on coated and uncoated concretes, as well as on coating mortars, while a sensitivity analysis was undertaken using an empirical and semi-probabilistic model across different exposure classes to simulate real service conditions. The results demonstrate excellent performance, with coated concretes achieving on average more than 52% higher resistance compared with uncoated counterparts. These findings indicate that properly designed coatings can enable reductions in cement content while still satisfying durability requirements, thereby contributing to more sustainable reinforced concrete structures.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Compact Light-Harvesting System Based on a Glass Conical Waveguide Coupled to a Single Multimode Optical Fiber
by
Daniel Toral-Acosta, Ricardo Chapa-Garcia, Romeo Selvas-Aguilar, Juan L. López, Arturo Castillo-Guzmán and Abraham Antonio González-Roque
Sci 2026, 8(2), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020028 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This research presents a lens-based light collection system that integrates a handmade glass conical waveguide (GCW) with a single silica multimodal optical fiber (SMMF) and a concentrator Fresnel lens (FL). The GCW functions as a secondary optical element (SOE), effectively expanding the fiber’s
[...] Read more.
This research presents a lens-based light collection system that integrates a handmade glass conical waveguide (GCW) with a single silica multimodal optical fiber (SMMF) and a concentrator Fresnel lens (FL). The GCW functions as a secondary optical element (SOE), effectively expanding the fiber’s receptive area and enabling efficient coupling of concentrated light. Calibrated ray-tracing simulations confirm that the complete FL + GCW + SMMF configuration maintains low transmission losses, thereby validating efficient coupling into the SMMF. Experimental results demonstrated a maximum net optical efficiency of 41% at an FL numerical aperture (NA) of 0.08, with GCW transmission reaching 60% and splice losses to the SMMF around 34%. With a luminous flux input of 155 lumens, the system delivered up to 63 lumens at the fiber output. Importantly, the FL + GCW + SMMF configuration combines reproducible fabrication, straightforward assembly, and reliable characterization, establishing a scalable pathway for daylight harvesting. The major contribution of this work is the demonstration that a simple, manufacturable GCW can substantially expand the effective collection area of multimodal fibers while preserving low optical losses, thereby bridging practical design with efficient energy transfer for sustainable photonics applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Artificial Intelligence and Orthopaedic Prosthetic Planning: A State-of-the-Art Review and Evolving Liability Perspectives
by
Francesca Romana Guarnaccia, Federica Spadazzi, Miriam Ottaviani, Nicola Di Fazio, Gianpietro Volonnino, Lucio Di Mauro, Paola Frati and Raffaele La Russa
Sci 2026, 8(2), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020027 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and aim: Artificial intelligence (AI) is gaining increasing relevance in orthopaedic surgery, particularly in prosthetic surgery, due to its ability to support preoperative planning through advanced imaging analysis, implant size prediction, and outcome forecasting. However, recent literature shows considerable variability in employed
[...] Read more.
Background and aim: Artificial intelligence (AI) is gaining increasing relevance in orthopaedic surgery, particularly in prosthetic surgery, due to its ability to support preoperative planning through advanced imaging analysis, implant size prediction, and outcome forecasting. However, recent literature shows considerable variability in employed models, evaluated outcomes, and clinical applicability. The objective of this scoping review is to map AI applications in preoperative planning for orthopaedic arthroplasties and to assess their impact on radiographic and clinical outcomes, also discussing key ethical and medicolegal implications within both Italian and international contexts. Materials and methods: A literature review was conducted following scoping review methodology. The bibliographic search (10 September 2025) was performed in PubMed and Scopus using the query “preoperative planning WITH artificial intelligence AND prosthesis orthopaedic surgery AND outcomes”, restricted to the years 2020–2025, English-language studies, and research focused specifically on real-world AI techniques applied to preoperative planning in prosthetic surgery, reporting radiographic and/or clinical outcomes related to planning. Exclusion criteria included intra/postoperative studies, non-orthopaedic applications, robotic surgery, studies lacking clinical outcomes, case reports, and articles without full-text availability. After PRISMA screening and selection, 42 primary studies were included. Results: Of the 42 studies included, 20 focused on the hip, 19 on the knee, and 3 on the shoulder. Available evidence indicates that AI may improve templating accuracy and prosthetic component positioning, with more robust results in hip and knee arthroplasty, while applications in shoulder arthroplasty remain emerging. Nonetheless, important methodological limitations persist, including algorithm heterogeneity. Discussion: Overall, the findings suggest a promising role for AI in preoperative planning; however, the heterogeneity and variable quality of the evidence call for caution in interpretation and highlight the need for more rigorous prospective research. These considerations also carry relevant medicolegal implications, as the reliability and standardisation of AI-based tools represent essential prerequisites for their safe and conscious integration within diverse regulatory frameworks. Conclusions: AI appears to be a promising tool in the preoperative planning of orthopaedic arthroplasties, although further clinical validation and methodological standardisation are required. The evidence gathered also provides a useful foundation for addressing the associated medicolegal and regulatory implications, particularly in light of evolving Italian and European regulations and their differences from U.S. models.
Full article
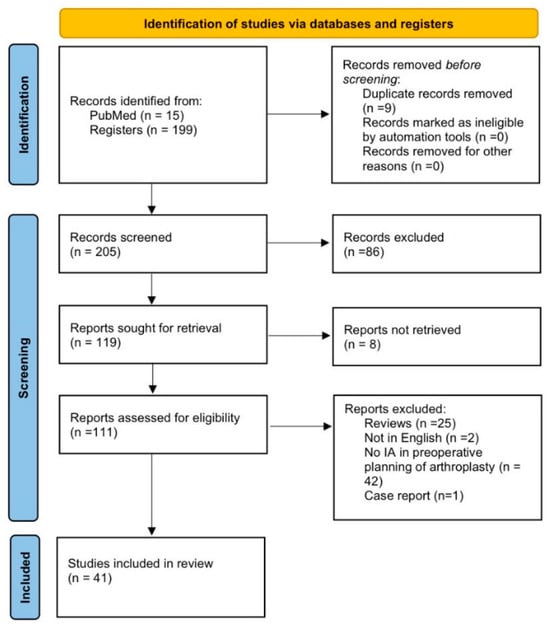
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Regional Assessment of Arsenic Accumulation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Agroecosystems of the Tejo, Almansor and Sorraia Valleys, Portugal
by
Manuela Simões, David Ferreira, Ana Coelho Marques and Ana Rita F. Coelho
Sci 2026, 8(2), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020026 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Arsenic (As) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) is considered a major environmental and food safety concern, particularly in flooded agroecosystems where reducing conditions mobilize As from soils. Portugal is one of Europe’s rice producers, especially in the Tejo, Almansor, and Sorraia
[...] Read more.
Arsenic (As) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) is considered a major environmental and food safety concern, particularly in flooded agroecosystems where reducing conditions mobilize As from soils. Portugal is one of Europe’s rice producers, especially in the Tejo, Almansor, and Sorraia valleys. As such, this study evaluates As pathways across 5000 ha of rice fields in the Tagus, Sorraia, and Almansor alluvial plains by combining soil, water, and plant analyses with a geostatistical approach. The soils exhibited consistently elevated As concentrations (mean of 18.9 mg/kg), exceeding national reference values for agricultural soils (11 mg/kg) and forming a marked east–west gradient with the highest levels in the Tagus alluvium. Geochemical analysis showed that As is strongly correlated with Fe (r = 0.686), indicating an influence of Fe-oxyhydroxides under oxidizing conditions. The irrigation waters showed low As (mean of 2.84 μg/L for surface water and 3.51 μg/L for groundwater) and predominantly low sodicity facies, suggesting that irrigation water is not the main contamination vector. In rice plants, As accumulation follows the characteristic organ hierarchy roots > stems/leaves > grains, with root concentrations reaching up to 518 mg/kg and accumulating progressively in the maturity phase. Arsenic content in harvested rice grains was 266 μg/kg (with a maximum of 413.9 μg/kg), being close to EU maximum limits when considering typical inorganic As proportions, assuming 60 to 90% inorganic fraction. Together, the findings highlight that a combined approach is essential, and identify soil geochemistry (and not irrigation water) as the primary source of As transfer in those agroecosystems, due to the flooded conditions that trigger the reductive dissolution of Fe oxides, releasing As. Additionally, the results also identified the need for targeted monitoring in areas of elevated As content in soils and support future mitigation through As speciation analysis, cultivar selection, improved fertilization strategies, and water-management practices such as Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD), to ensure the long-term food safety.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Validation of the Qualified Air System in the Pharmaceutical Industry
by
Ignacio Emilio Chica Arrieta, Vladimir Llinás Chica, Angela Patricia González Parias, Ainhoa Rubio-Clemente and Edwin Chica
Sci 2026, 8(2), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8020025 - 24 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The present study describes the ten-year (2014–2024) validation of a Class 100,000ISO 8 qualified air system used in the manufacture of non-sterile pharmaceutical dosage forms in a GMP-certified facility. The lifecycle evaluation included design, installation, qualification, continuous operation, environmental monitoring, cleaning and disinfection
[...] Read more.
The present study describes the ten-year (2014–2024) validation of a Class 100,000ISO 8 qualified air system used in the manufacture of non-sterile pharmaceutical dosage forms in a GMP-certified facility. The lifecycle evaluation included design, installation, qualification, continuous operation, environmental monitoring, cleaning and disinfection verification, and annual third-party validation. The system was assessed for critical parameters, including air renewal rates, airflow directionality, the integrity of high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and ultra-low penetration air (ULPA) filters, environmental recovery times, and non-viable particle counts. Particle monitoring focused on 0.5 μm and 1.0 μm channels within the 0.5–5 μm range specified by ISO 14644-1 for ISO 8 areas. The 0.5–1.0 μm range was prioritized because it provides higher statistical representativeness for evaluating filter performance and controlling fine particulate dispersion, which is particularly relevant in non-sterile pharmaceutical production, while larger particles (>5 μm) are more critical in aseptic processes. The influence of personnel and air exchange rates on cleanliness was also assessed during the final years of the study. Results demonstrate that continuous, systematic validation ensures the controlled environmental conditions required for pharmaceutical production and supports the sustained quality and safety of the finished products. This study provides a technical reference for engineers, pharmacists, and quality professionals involved in cleanroom design, qualification, and regulatory compliance.
Full article
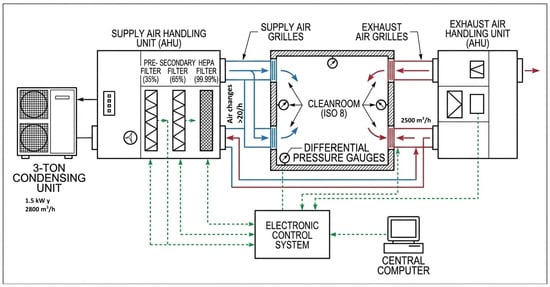
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Generative AI as a Student Research Assistant: The Relationship of Academic and Research Practices in Higher Education
by
Walery Okulicz-Kozaryn
Sci 2026, 8(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8010024 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study analyzes the observed patterns of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) use by students in higher education through the lens of the sociotechnical systems (STS) theory, focusing on the academic subsystem. The empirical basis is a survey of 2083 students (3686 responses)
[...] Read more.
This study analyzes the observed patterns of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) use by students in higher education through the lens of the sociotechnical systems (STS) theory, focusing on the academic subsystem. The empirical basis is a survey of 2083 students (3686 responses) from seven countries in Central and Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and Central Africa. Based on these data, two proxy indicators are proposed: A1, reflecting the overall academic use of Generative AI and A2, characterizing the use of Generative AI in a research context. The results show that Generative AI is widely incorporated into students’ academic activities (A1 = 79.06%), while research-oriented use remains less common (A2 = 46.66%) and varies significantly across subsamples. A joint analysis of A1 and A2, visualized as a zoned space A1–A2, reveals different configurations of academic practices: from a predominance of routine educational use to a more pronounced focus on research tasks. Cross-country comparisons show that in certain contexts (e.g., Kazakhstan and one of the Ukrainian subsamples), Generative AI is more often used in a research context, while in other cases, its use remains predominantly educational and routine. In this sense, the results indicate that Generative AI is beginning to fulfill the role of an emerging student research assistant in students’ academic life: technology has already become a familiar tool for completing educational tasks, but its use in supporting research activities remains fragmented. The proposed model and proxy indicators allow us to describe and compare current configurations of Generative AI use in the academic subsystem. The obtained results provide a basis for further research aimed at a deeper understanding of the factors determining the inclusion of Generative AI in student research practice, as well as for the development of management approaches regarding its use in higher education.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Generative AI: Advanced Technologies, Applications, and Impacts)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Association of Physical Activity with Health Indices and Healthcare Utilization
by
Anastasia Keremi, Antonia Kaltsatou, Anna Tsiakiri, Dimitrios Tsiptsios, Sotirios Botaitis, Foteini Christidi, Vasilis-Spyridon Tseriotis, Maria Voulgari, Pinelopi Vlotinou, Aspasia Serdari, Kostas Anagnostopoulos and Gregory Tripsianis
Sci 2026, 8(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8010023 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aimed to examine the association between physical activity and individuals’ health status, healthcare utilization, socio-demographic characteristics, and health behaviors in a large representative sample from Northern Greece. A cross-sectional study was conducted involving 1227 participants (47.4% males, mean age 49.94 ±
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to examine the association between physical activity and individuals’ health status, healthcare utilization, socio-demographic characteristics, and health behaviors in a large representative sample from Northern Greece. A cross-sectional study was conducted involving 1227 participants (47.4% males, mean age 49.94 ± 14.87 years) from Thrace, Greece, selected through a two-stage stratified sampling method. According to the Greek version of IPAQ, participants were classified as inactive/insufficiently active, sufficiently and highly active. Data on socio-demographic, lifestyle, and health-related variables were collected through structured interviews. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the independent effect of physical activity on subjects’ characteristics using SPSS ver. 19. Half of the participants (49.8%) were inactive/insufficiently active, 418 participants (34.1%) were sufficiently active, and 198 participants (16.1%) were highly active. In univariate analysis, smoking (p < 0.001), higher coffee consumption (p = 0.002), higher adherence to Mediterranean diet (p < 0.001), napping during the day (p = 0.017) and short sleep duration (p < 0.001) were associated with lower prevalence of high activity. In adjusted analyses, sufficiently active participants had a lower risk for bad self-rated health (aOR = 0.63), hypertension (aOR = 0.41), dyslipidemia (aOR = 0.42), diabetes (aOR = 0.53), obesity (aOR = 0.61), cardiovascular diseases (aOR = 0.43), anxiety (aOR = 0.65), depression (aOR = 0.56), daily sleepiness (aOR = 0.62), poor sleep quality (aOR = 0.71), as well as for primary (aOR = 0.54) and secondary (aOR = 0.40) healthcare utilization compared to inactive participants. Higher-intensity physical activity did not enhance these beneficial effects of sufficient activity on subjects’ characteristics. Physical inactivity significantly compromises health across multiple domains. Promoting even moderate-intensity physical activity may reduce chronic disease burden and healthcare utilization.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microstructural, Electrical, and Magnetic Characterization of Degraded Photovoltaic Cells from Desert Environments: A Preliminary Study
by
Fahima Djefaflia, Farida Khammar, Nadir Hachemi, Elfahem Sakher, Nozha El Ahlem Doghmane, Mounir Sakmeche, Houssem Eddine Doghmane, Leila Belgacem, Lala Gahramanli, Talia Tene and Cristian Vacacela Gomez
Sci 2026, 8(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8010022 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examines the functional degradation of crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells after 17 years of field exposure in the Adrar Desert, Algeria. Harsh thermal, radiative, and mechanical conditions accelerate aging, affecting electrical performance and structural stability. Monocrystalline silicon cells were extracted and analyzed
[...] Read more.
This study examines the functional degradation of crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells after 17 years of field exposure in the Adrar Desert, Algeria. Harsh thermal, radiative, and mechanical conditions accelerate aging, affecting electrical performance and structural stability. Monocrystalline silicon cells were extracted and analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), Raman spectroscopy, electrical resistivity measurements, and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM). SEM revealed microcracks, delamination, and corrosion products. EDS showed Ag, Si, O, and C signals, while Raman indicated silicon features and signatures consistent with encapsulant (EVA) degradation. The temperature-dependent resistivity displayed a dual behavior with a minimum near ~72 °C, above which resistivity increased, consistent with a transition in the dominant transport mechanisms. VSM measurements showed an overall diamagnetic response with a weak hysteresis loop suggestive of defect-related contributions. The observed aging is primarily associated with oxidation, metal migration, and encapsulant degradation. These findings motivate more robust materials and interfaces for desert climates, alongside improved thermal management and active monitoring.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Training Habits, Injury Prevalence, and Supplement Use in CrossFit Practitioners
by
José Carlos Cabrera Linares, Juan Antonio Párraga Montilla, Pedro Ángel Latorre Román, Rafael Moreno del Castillo and Mirella Pacheco González
Sci 2026, 8(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8010021 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: CrossFit® is a high-intensity functional training modality with increasing popularity, yet limited evidence describes the general profile of its practitioners. Objective: To characterize CrossFit® athletes based on their training habits, injury prevalence, and nutritional supplement use, with specific consideration given
[...] Read more.
Background: CrossFit® is a high-intensity functional training modality with increasing popularity, yet limited evidence describes the general profile of its practitioners. Objective: To characterize CrossFit® athletes based on their training habits, injury prevalence, and nutritional supplement use, with specific consideration given to sex and age. Methods: An online questionnaire was completed by 358 practitioners (182 women; mean age 35.6 ± 9.1 years) from various Spanish regions. Descriptive and comparative analyses (χ2 and ANOVA; p < 0.05) were conducted for training patterns, injury history, and supplement consumption. Results: Over half of the sample had practiced CrossFit® for more than three years, typically training 3–4 days per week in one-hour sessions. Participants primarily reported social and health-related motivations and identified as non-competitive. Overall, 42.2% experienced at least one CrossFit®-related injury, most frequently affecting the shoulder (15.6%) and lumbar spine (10.1%), largely attributed to repetitive overload. Supplement use was widespread (81.8%), with creatine (60.3%) and protein (49.4%) being the most commonly consumed. Conclusions: CrossFit® practitioners train consistently, value the social environment, and show an injury pattern similar to that of other strength-based disciplines. Supplement consumption is highly prevalent across groups. Coaches and health professionals should prioritize injury-prevention strategies, promote safe load progression, and guide responsible supplement use.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sports Science and Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cutting-Edge DoS Attack Detection in Drone Networks: Leveraging Machine Learning for Robust Security
by
Albandari Alsumayt, Naya Nagy, Shatha Alsharyofi, Resal Alahmadi, Renad Al-Rabie, Roaa Alesse, Noor Alibrahim, Amal Alahmadi, Fatemah H. Alghamedy and Zeyad Alfawaer
Sci 2026, 8(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8010020 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study aims to enhance the security of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) within the Internet of Drones (IoD) ecosystem by detecting and preventing Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. We introduce DroneDefender, a web-based intrusion detection system (IDS) that employs machine learning (ML) techniques to identify
[...] Read more.
This study aims to enhance the security of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) within the Internet of Drones (IoD) ecosystem by detecting and preventing Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. We introduce DroneDefender, a web-based intrusion detection system (IDS) that employs machine learning (ML) techniques to identify anomalous network traffic patterns associated with DoS attacks. The system is evaluated using the CIC-IDS 2018 dataset and utilizes the Random Forest algorithm, optimized with the SMOTEENN technique to tackle dataset imbalance. Our results demonstrate that DroneDefender significantly outperforms traditional IDS solutions, achieving an impressive detection accuracy of 99.93%. Key improvements include reduced latency, enhanced scalability, and a user-friendly graphical interface for network administrators. The innovative aspect of this research lies in the development of an ML-driven, web-based IDS specifically designed for IoD environments. This system provides a reliable, adaptable, and highly accurate method for safeguarding drone operations against evolving cyber threats, thereby bolstering the security and resilience of UAV applications in critical sectors such as emergency services, delivery, and surveillance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Trends and Prospects in Security, Encryption and Encoding)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Regulation of Sialidase Biosynthesis by Control Mechanism Induction in Antarctic Strain Penicillium griseofulvum P29
by
Radoslav Abrashev, Ekaterina Krumova, Penka Petrova, Rumyana Eneva, Vladislava Dishliyska, Stephan Engibarov, Yana Gocheva, Galina Stoyancheva, Jeny Miteva-Staleva, Lyudmila Yovchevska, Boryana Spasova, Vera Kolyovska and Maria Angelova
Sci 2026, 8(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8010019 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In recent years, sialidases (neuraminidases) derived from non-clinical sources have attracted considerable interest due to their potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. A deeper understanding of the mechanisms regulating sialidase synthesis could lead to more efficient enzyme production. Induction is considered
[...] Read more.
In recent years, sialidases (neuraminidases) derived from non-clinical sources have attracted considerable interest due to their potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. A deeper understanding of the mechanisms regulating sialidase synthesis could lead to more efficient enzyme production. Induction is considered a key regulatory mechanism. However, there is a lack of data on the regulation of sialidase synthesis in filamentous fungi. This study examines how regulatory mechanisms influence the production of a sialidase enzyme exhibiting high activity at low temperatures in the Antarctic fungal strain Penicillium griseofulvum P29. The inclusion of high- and low-molecular-weight substances possessing terminal non-reducing N-acetylneuramyl groups in the tests led to a marked enhancement of sialidase activity. The strongest induction response was elicited by sialic acid, followed by glycomacropeptide, milk whey, N-acetylglucosamine, N-acetylmannosamine, and colominic acid. RT-qPCR experiments demonstrated that induction occurs at the transcriptional level of the sialidase gene. Biochemical analysis elucidates the function of inducers as triggers in the de novo synthesis of the enzyme protein. To our knowledge, this is the first study to highlight the importance of regulatory mechanism induction in the synthesis of cold-active sialidases.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Experimental Evaluation of Temperature and Screw Speed Effects on the Extrusion of Recycled PP, HDPE, and PET for Sustainable Construction Applications
by
Andrés David Romero Restrepo, Mario Antonio Salom Corrales, Manuel Saba, Ramón Torres Ortega and Oscar E. Coronado-Hernández
Sci 2026, 8(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/sci8010018 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study evaluated the feasibility of using recycled plastics (PP, HDPE, and PET) for sustainable construction applications. Materials were collected, processed, and extruded following a structured methodology, and their physico-mechanical and environmental properties were assessed through standardized tests, including compression, flexural strength, water
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the feasibility of using recycled plastics (PP, HDPE, and PET) for sustainable construction applications. Materials were collected, processed, and extruded following a structured methodology, and their physico-mechanical and environmental properties were assessed through standardized tests, including compression, flexural strength, water absorption, porosity, and apparent density. Compression tests showed that increasing the processing temperature led to a reduction in the compressive strength of polypropylene (PP), while high-density polyethylene (HDPE) achieved its highest strength at the lowest temperature. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibited a similar decreasing trend with temperature. The processing speed, expressed as revolutions per minute (rpm), had little influence on PP and HDPE performance but positively affected PET, where higher rpm consistently improved compressive strength. Flexural tests revealed that higher rpm values enhanced the mechanical performance of PP and HDPE. However, for PP, an increase in processing temperature resulted in a pronounced decline in flexural strength. Overall, PP and HDPE outperformed PET, reaching compressive strengths near 10 MPa compared to values below 4 MPa for PET. In flexural tests, PP achieved 44 MPa, followed by HDPE with 25 MPa. Water absorption remained below 1% for all materials. The study is limited to physico-mechanical characterization and does not include microstructural or thermal analyses to assess crystallinity, degradation, or molecular orientation. Future research will focus on advanced thermal–chemical characterization and process optimization—particularly for PET—to improve ductility and expand the applicability of recycled plastics in construction.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Clean Technol., Energies, Sustainability, Applied Sciences, Sci
GIS-Driven Renewable Energy Solutions: Advancing Regional Development, Rural Electrification, and Universal Energy Access
Topic Editors: Javier Domínguez Bravo, Luis F. Zarzalejo, Markus BiberacherDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Cryptography, Electronics, Mathematics, Information, Sci, Entropy, JCP
Recent Developments and Applications of Image Watermarking
Topic Editors: Frederic Ros, Pedro M. B. TorresDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topic in
Molecules, Biomimetics, Chemosensors, Life, AI, Sci
Recent Advances in Chemical Artificial Intelligence
Topic Editors: Pier Luigi Gentili, Jerzy Górecki, David C Magri, Pasquale StanoDeadline: 15 October 2026
Topic in
Computers, Electronics, Entropy, Information, Mathematics, Sensors, AI, Applied Sciences, Sci, Future Internet
Addressing Security Issues Related to Modern Software
Topic Editors: Luis Javier García Villalba, Ana Lucila Sandoval OrozcoDeadline: 31 October 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sci
Generative AI: Advanced Technologies, Applications, and Impacts
Guest Editors: Claus Jacob, Paolo Bellavista, Ognjen ArandjelovićDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Sci
Enhancing Health Through Physical Activity and Sports Science: Advances in Applied Research
Guest Editors: Giovanni Esposito, Tiziana D’Isanto, Gaetano AltavillaDeadline: 20 May 2026
Special Issue in
Sci
Advanced 1D, 2D and 3D Nanomaterials
Guest Editor: Hai-Feng (Frank) JiDeadline: 31 July 2026
Special Issue in
Sci
Advances in Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
Guest Editors: Jose Navarro Pedreño, Maria K. Doula, Antonis A. ZorpasDeadline: 31 October 2026









