Abstract
Serendipitous learning, characterized by the discovery of new insights and unexpected connections, is recognized as a valuable educational experience that stimulates critical thinking and self-regulated learning. While there have been limited efforts to develop serendipity-oriented recommender systems in education, these systems often fall short in supporting learners’ agency, that is, the sense of ownership and control over their learning journey. In this paper, we introduce an Interactive Evolutionary Computation (IEC)-driven recommender system designed to empower learners by granting them control over their learning experiences while offering recommendations that are both novel and unexpected yet aligned with their interests. Our proposed system leverages an Interactive Genetic Algorithm in conjunction with Knowledge Graphs to dynamically recommend learning content, with a focus on the history of scientific discoveries. We conducted both numerical simulations and experimental evaluations to assess the effectiveness of our content optimization algorithm and the impact of our approach on inducing serendipity in informal learning environments. The results indicate that a significant number of participants found certain recommended learning materials to be engaging and surprising, providing evidence that our system has the potential to facilitate serendipitous learning experiences within informal learning contexts.
1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been a notable emergence of recommender systems, sophisticated information-filtering tools designed to predict user preferences and deliver highly relevant content or items within an extensive array of options [1]. These systems have gained substantial traction in commercial sectors such as e-commerce (e.g., Amazon) and media-streaming platforms (e.g., Netflix and Spotify).
In the realm of technology-enhanced education, where a wealth of digital learning resources is readily available, the application of recommender systems has garnered increased attention as a promising approach to assist learners in navigating a plethora of suitable educational materials [2]. The two predominant techniques employed in the development of recommender systems are collaborative filtering [3] and content-based filtering [4]. Collaborative recommenders rely on the assessment of user–item similarities to provide recommendations, while content-based recommenders create user profiles based on the characteristics of previously accessed items [5]. Both methods, when applied to education, exhibit limitations, giving rise to the “serendipity problem” [6], which pertains to the risk of either overgeneralization (in collaborative recommenders) or overspecialization (in content-based recommenders). These issues can result in a dearth of novel and unexpected content, inadvertently confining learners to what is often referred to as a “filter bubble” [7,8].
This study employed a multi-faceted research and investigation methodology to develop and evaluate a serendipity-oriented recommendation system for informal learning. The overall research design encompassed three main phases: system development, simulation studies, and experimental evaluation. In the system development phase, we leveraged Interactive Genetic Algorithms and knowledge graphs to create a recommender system capable of generating novel and unexpected learning paths. The simulation studies aimed to validate the effectiveness of the content optimization algorithm and fine-tune system parameters. Finally, the experimental evaluation involved user studies to assess the system’s ability to induce serendipity and enhance learner motivation in informal learning contexts. This methodology allowed us to systematically investigate the proposed system’s technical feasibility, algorithmic performance, and user experience outcomes.
The term “serendipity”, first introduced by Horace Walpole in the 18th century, encapsulates the idea of making unforeseen discoveries through accidents and sagacity, as opposed to intentional pursuit [9]. While there have been noteworthy efforts to devise serendipity-oriented recommender systems in education [10,11,12], these systems have frequently fallen short of supporting learners’ agency, which entails learners taking charge of their own learning process.
In the present paper, we propose an innovative solution: an Interactive Evolutionary Computation (IEC)-driven recommender system. This system not only empowers learners to assume control and responsibility for their learning journeys but also guides them toward novel and unexpected learning resources that are pertinent to their areas of interest. Our proposed approach leverages Interactive Genetic Algorithms and Knowledge Graphs to dynamically generate personalized learning content.
The subsequent sections of this paper are structured as follows: Section 2 offers a concise review of pertinent research on serendipity, recommender systems, and interactive evolutionary computation. Section 3 provides a detailed exposition of our proposed system, elucidating its capacity to address the limitations of conventional methods. The technical soundness of our content recommendation algorithm is assessed through a simulation study in Section 4. Section 5 presents a comprehensive account of experimental evaluations, encompassing methodologies, outcomes, and their far-reaching implications. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper.
This paper invites readers to embark on an academic exploration of educational recommender systems, where the convergence of serendipity and learner empowerment promises to reshape the landscape of personalized learning experiences.
2. Background
2.1. Serendipity, Importance of Agency, and Informal Learning
The term “serendipity” was coined by Horace Walpole in 1754, inspired by the Persian fairy tale “The Three Princes of Serendip” that was published in 1557 by Michele Tramezzino [13]. Serendip is the old Persian name for Sri Lanka, and the tale depicts the story of three princes who made many discoveries of things they were not initially in quest of, by accidents and sagacity. Hence, the most common definition of serendipity requires the concept to include three components which are relevance, novelty, and unexpectedness [14]. Interestingly, serendipity is commonly applied to inventions or findings made by “chance” rather than intent. The invention of the microwave oven and the discoveries of penicillin and gelignite are a few examples of achievements often associated with serendipity. In the same vein, Kuhn argued that most scientific breakthroughs are unpredictable as they are not in accord with the current set of practices and beliefs [15]. As suggested by Stoskopf, serendipitous discoveries are of significant value in the advancement of science and often present the foundation for important intellectual leaps of understanding [16]. Moreover, researchers have claimed that serendipitous items might help broaden people’s preferences [17] and increase satisfaction [18].
The concept of serendipity has long intrigued scholars across various domains. In the context of education, serendipity is defined as the phenomenon of learners making unplanned discoveries that expand their knowledge horizons. While serendipity is highly valued in the learning process, it often remains elusive in traditional educational settings. Educational environments that prioritize structured curricula and predefined learning pathways can inadvertently stifle the serendipitous aspect of learning. The term “serendipitous learning” has been used to refer to learning through gaining new insights, discovering interesting aspects, and recognizing new relations, which occurs by chance or as a by-product of other activities [19,20]. However, as stated by Pasteur, “chance favors only the prepared minded”; therefore, serendipitous encounters also owe to the open-minded attitude of the seekers, their curiosity, and their perspicacity. In the same vein, in the field of academia, Yaqub [21] argues that serendipity goes beyond happy accidents and identifies astute observation, controlled sloppiness, collaborative action, etc., as examples of factors that could lead to serendipitous findings. In other words, the seeker’s agency (i.e., proactive attitude towards the information-seeking activity) is an important prerequisite that should be fulfilled in order to make serendipitous discoveries possible.
In learning settings, agency is defined by Brennan as the “learner’s ability to define and pursue learning behavior” [22]. It is often associated with self-directed learning, which involves learners taking the initiative to diagnose their needs, formulate their goals, implement appropriate learning strategies, and evaluate learning outcomes [23]. In other terms, agency “accounts for the individual’s personal control and responsibility over his or her learning” [24].
Assuming that learners show agency when they determine, influence, and personalize their learning paths [25,26], recommender systems, that rather than providing a predefined learning path, allow learners to explore the learning resources and negotiate and create meaningful learning paths for themselves, which may increase the chances of inducing serendipity in the context of technology-enhanced learning.
The importance of serendipity in informal learning can be grounded in several theoretical perspectives. Self-determination theory (SDT) posits that intrinsic motivation, which is crucial for sustained engagement in informal learning, is fostered by the satisfaction of three basic psychological needs: autonomy, competence, and relatedness [27]. Serendipitous discovery aligns with the need for autonomy, as it empowers learners to explore and learn based on their own interests and curiosity. The experience of serendipity can also enhance perceived competence, as learners feel capable of making valuable discoveries on their own [28].
Moreover, constructivist learning theories emphasize the role of active exploration, experimentation, and personal meaning-making in the learning process [29]. Serendipitous encounters with new information and ideas can stimulate learners to construct their own knowledge by integrating novel insights with their existing understanding. This process of knowledge construction is particularly relevant in informal learning settings, where learners have greater control over their learning goals and trajectories [30].
However, it is important to acknowledge that the benefits of serendipity in informal learning may vary depending on individual learner characteristics, such as prior knowledge, learning style, and openness to experience [31].
Unlike previous studies that treat serendipity as purely chance encounters, our work uniquely contributes a structured approach to facilitating serendipitous learning while maintaining learner agency. By explicitly supporting the three key elements—internal factors, external factors, and exploratory behavior—our approach provides a comprehensive framework for designing serendipity-oriented learning environments. This represents a significant advancement over existing systems that typically focus on only one or two of these elements.
2.2. Learning-Support-Oriented Recommender Systems
The integration of recommender systems in education has garnered substantial interest in recent years. These systems hold the potential to alleviate the challenges posed by the vast and often overwhelming landscape of digital learning resources. However, the conventional approaches of collaborative and content-based filtering have inherent limitations when applied to education, particularly in terms of serendipity.
The role of recommender systems is twofold: predicting user’s preferences, and recommending resources accordingly [32]. In the context of technology-enhanced education, recommender systems hold the potential of assisting learners in carrying out a learning activity, viewing content, taking a course, joining a community, contacting a user, etc. [33].
Recent learning-support-oriented recommender systems have employed diverse algorithmic strategies to provide personalized content recommendations. In formal learning environments, such as learning management systems (LMSs) and intelligent tutoring systems (ITSs), recommender systems primarily aim to support learners in achieving predefined learning objectives and completing structured curricula [34,35]. These systems often employ collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, or hybrid approaches to recommend learning resources, tasks, or peer interactions that align with learners’ knowledge levels, skills, and performance goals [36]. Given the risk of overspecialization and overgeneralization of information using such techniques, it might be desirable to carefully consider which algorithm should be employed for a particular context. Interestingly, Lemire combined inferences rules with collaborative filtering to provide context-aware recommendations [37].
In contrast, recommender systems for informal learning environments, such as personal learning environments and social learning platforms, prioritize learner autonomy, exploration, and serendipitous discovery [38]. These systems focus on recommending diverse and engaging learning resources that cater to learners’ individual interests, preferences, and learning styles [39]. Techniques such as context-aware recommendation, social recommendation, and knowledge-based recommendation are commonly used to support self-directed and curiosity-driven learning in informal settings [34].
However, the principles and techniques for content recommendation in formal and informal learning environments are not entirely disparate. Both contexts can benefit from personalized, adaptive, and explainable recommendations that align with learners’ needs and goals. Nonetheless, the emphasis on structure, assessment, and domain-specific knowledge in formal settings, versus the focus on flexibility, exploration, and cross-disciplinary discovery in informal settings, necessitates distinct recommendation strategies and evaluation criteria. In a review of recommender systems used in education [40], Deschênes established that, in most cases, systems aimed at finding good items and suggesting learning activities, while a few others were dedicated to finding suitable peers. Moreover, it was established that most previous studies were targeting support of students in formal learning contexts. Therefore, it was suggested that from an agency point of view, it would be beneficial to conduct research with learners in less formal settings. In the same vein, in order to support the agency of learners, previous research suggested that personal recommender systems in learning support environments could be used to guide learners in choosing suitable learning activities to follow [41]. To this end, Fazeli, for instance, proposed a graph-based approach that uses graph-walking to improve performance on educational datasets [42].
When it comes to evaluating the effects of recommender systems on learning, most previous studies tended to limit the measurements to learners’ grades [43]. Since educational success is not limited to academic achievement, it might be interesting to carry out studies that consider aspects such as learners’ engagement and their subjective opinions of the system features, as part of involving learners themselves in the design process.
While existing recommender systems have made progress in supporting formal learning environments, our approach distinctively addresses the challenges of informal learning contexts. Unlike previous systems that prioritize either personalization or discovery, our work introduces a novel balance between these competing needs. By combining interactive evaluation with dynamic path generation, we overcome the limitations of both collaborative and content-based filtering approaches in supporting serendipitous discovery.
2.3. Interactive Evolutionary Computation
Interactive Evolutionary Computation (IEC) is a generic term, which refers to a group of optimization techniques or algorithms that use subjective human evaluation instead of a numerical fitness function to perform searches [44]. According to Sun [45], these algorithms combine a traditional evolution mechanism with a user’s intelligent evaluation, where the user assigns an individual’s fitness rather than a function that is difficult or even impossible to explicitly express. Given such characteristics, IEC techniques have been widely adopted to solve optimization problems where the fitness function cannot be assumed or appropriately represented in the form of a mathematical function. This is often the case when the result of optimization should fit a particular user preference (for example, taste of coffee or color set of the user interface). IEC techniques have also been successfully applied in many fields, such as face identification [46], fashion design [47], music composition [48], and hearing aid fitting [49]. In a typical scenario of IEC, a small number of solutions (e.g., a population of ten solutions) are shown to a human user who is supposed to assign one of a pre-specified set of ranks (e.g., 1: very bad, 2: bad, 3: average, 4: good, 5: very good) to each solution in the population. Other implementations of IEC also include pair-wise comparison-based IEC models [50] or single-item evaluation-based IEC models [51].
Interestingly, original implementations of IEC-based recommender systems were also proposed in the literature. For example, Oku and Hattori proposed an IEC-driven fusion-based recommender system in which new item recommendation was performed by combining the features of two items previously selected by the user. It was reported that by repeating such an interactive recommendation process, the system was able to help users make serendipitous discoveries in an exploratory manner [5]. Nevertheless, the proposed system appeared to not sufficiently support users’ proactive exploration of the environment (agency), which has been highlighted as an important prerequisite to induce serendipity. Over the years, IEC has emerged as a promising paradigm for addressing the challenges associated with traditional recommender systems in education. IEC methods, particularly Interactive Genetic Algorithms (IGAs), provide a means to actively involve learners in the recommendation process. These algorithms enable users to provide feedback and iteratively refine recommendations, fostering a sense of agency and control over their learning journey. Moreover, IEC methods can dynamically adapt to learners’ evolving preferences and promote serendipity by introducing unexpected but relevant learning resources.
In contrast to previous applications of IEC in educational technology, our work makes three key contributions: (1) the novel combination of IGA with Knowledge Graphs for learning path optimization, (2) explicit support for serendipitous discovery through balanced exploration and exploitation, and (3) integration of user agency in the evolutionary process. This unique approach addresses the limitations of existing recommender systems while maintaining the benefits of interactive optimization.
The review above highlights several gaps in existing research: insufficient support for learner agency in recommender systems, limited consideration of serendipity in informal learning contexts, and inadequate integration of user preferences in path optimization. Our work addresses these gaps through a novel combination of interactive Evolutionary Computation, Knowledge Graphs, and user-centered design principles. This approach uniquely supports serendipitous discovery while maintaining learner agency and ensuring content relevance—a balance not achieved in previous systems.
3. Research Goal and Approach
3.1. Problem Statement and Research Goals
When analyzing existing studies in technology-enhanced learning, several limitations became apparent. Current recommender systems primarily target formal learning settings, inadequately support learners’ agency, and predominantly assess effectiveness based on learners’ grades. Yet, informal learning, which is often self-directed and dependent on individual preferences [52], could greatly benefit from serendipity-oriented recommender systems.
Many existing recommender systems for learning support employ techniques that may inadvertently confine learners to “filter bubbles”, effectively channeling them down specific paths based on machine-learned stereotypes. In contrast, serendipitous experiences have been acknowledged as valuable for personal learning [53], underscoring the positive impact of unexpected realizations and hidden connections on learning processes [20,54].
Therefore, our research aimed to develop a serendipity-oriented recommender system that achieved the following:
- Targets support of learning in informal environments.
- Facilitates learners’ agency through interactive exploration.
- Incorporates a recommendation algorithm capable of mitigating the limitations of collaborative and content-based filtering approaches.
- Actively engages learners in the recommendation refinement process by actively gathering their preferences.
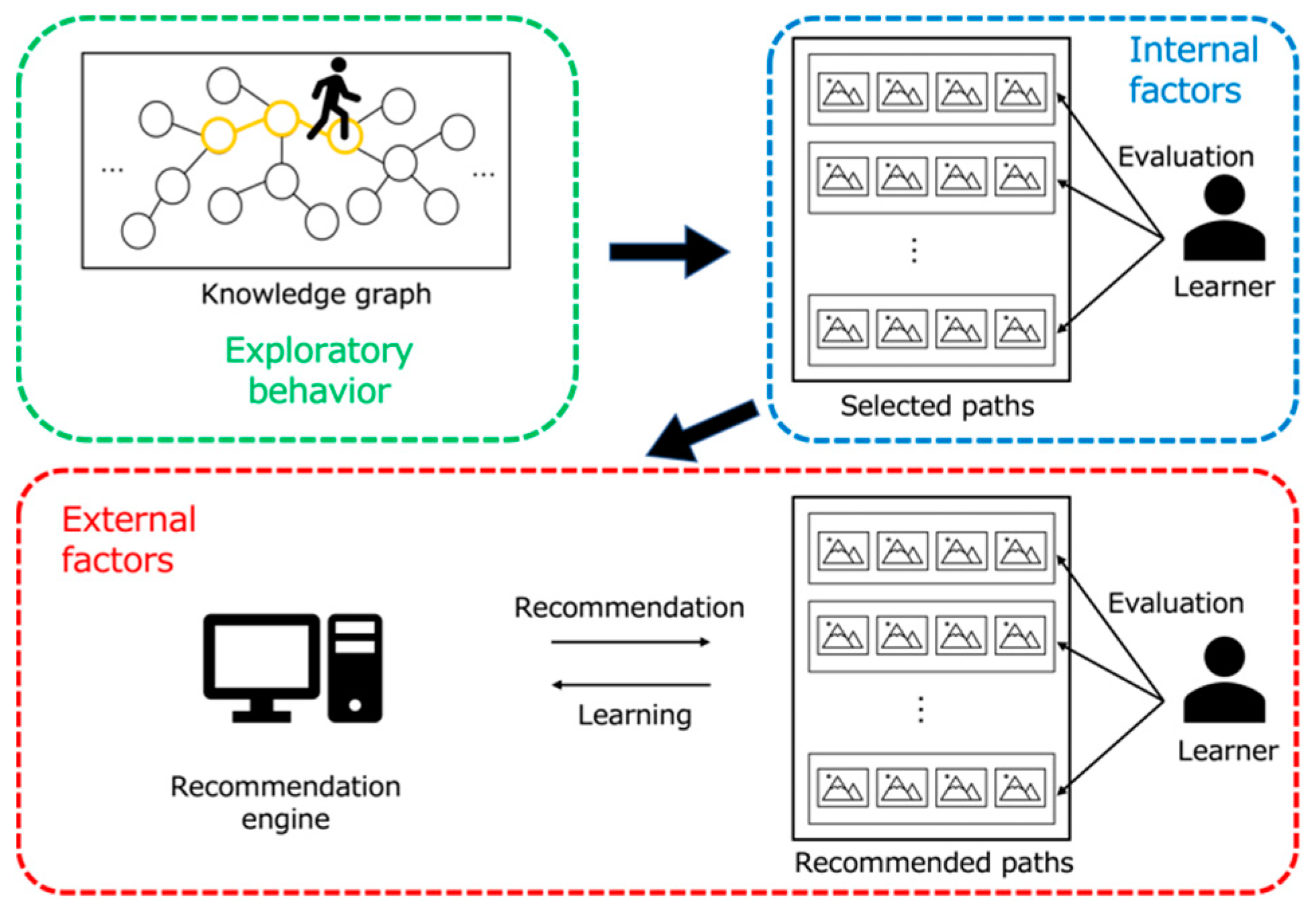
To the best of our knowledge, this study represents the first attempt to propose a recommender system that encompasses all of these essential requirements. Furthermore, we posit that three crucial elements are necessary to induce serendipity among learners: (i) external factors presented by the system, (ii) internal factors in the form of user preferences, (iii) exploratory behavior, facilitated through support for learners’ agency.
In this paper, we particularly emphasize the significance of the third element, “exploratory behavior”, in providing serendipitous recommendations to learners, as it has not received adequate consideration in prior related studies.
3.2. System Architecture
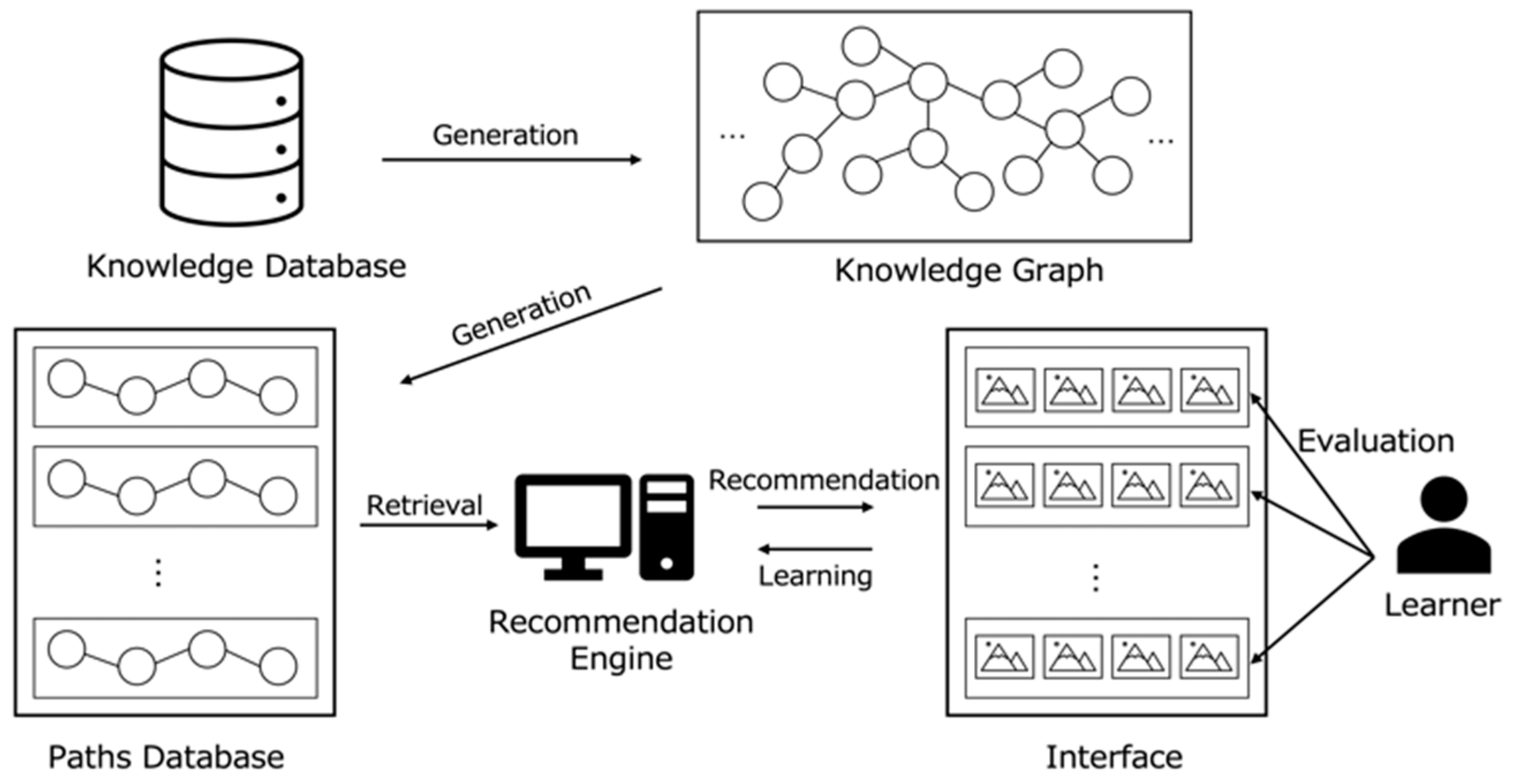
Our proposed system, illustrated in Figure 1, combines Interactive Evolutionary Computation (IEC), specifically an Interactive Genetic Algorithm (IGA), with Knowledge Graphs to create dynamic learning experiences.
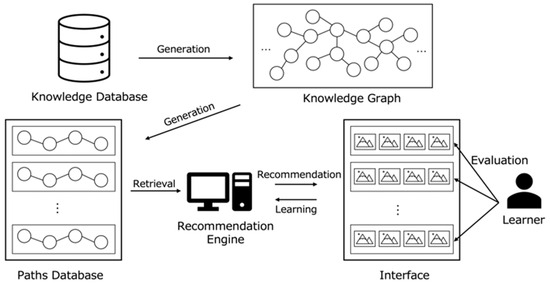
Figure 1.
Overview of proposed system.
This technical approach was carefully chosen to address the unique challenges of supporting serendipitous learning. Knowledge Graphs provide the structured representation needed to maintain meaningful connections between scientific concepts, while ensuring educational relevance even in unexpected discoveries. Interactive Genetic Algorithms (IGAs), a variant of IEC, enable controlled exploration of this structure while naturally supporting user agency through interactive evaluation, allowing learners to guide the evolution of recommendations. This combination uniquely addresses the challenge of facilitating serendipitous discovery while maintaining learning coherence, a balance difficult to achieve with conventional recommendation approaches.
Learning content takes the form of “learning paths”, which encompass interconnected concepts accessible through a dedicated interface.
The system operates in two main phases:
- Initial Exploration (Phase 1): Users explore and select paths from a diverse initial set extracted from the Knowledge Graph.
- Optimization (Phase 2): An Interactive Genetic Algorithm (IGA) generates new candidate paths by applying crossover and mutation operations to highly-rated paths.
When the IGA generates a path, two scenarios are possible:
- If an exact match exists in the database, that path is presented.
- If no exact match exists, the system retrieves the most similar path using Dynamic Time Warping (DTW).
This approach enables novel and unexpected path discovery while ensuring content coherence and relevance.
In more concrete terms, in our system, learning content takes the form of “learning paths”, which encompass interconnected concepts and are accessible to learners through a dedicated interface. For this study, our knowledge database comprises learning content, including scientific discoveries and inventions, interlinked in a quantitatively expressible manner, as elaborated in subsequent sections.
The path database is initially populated with a diverse set of paths extracted from the Knowledge Graph, providing a starting point for recommendations before any user interaction occurs. In Phase 1, the user explores and selects paths of interest from this initial set. Then, in Phase 2, the Interactive Genetic Algorithm (IGA) generates new candidate paths by applying crossover and mutation operations to the paths rated highly by the user in Phase 1. These IGA-generated paths may not match paths in the database exactly.
If an IGA-generated path has an exact match in the database, that existing path is directly presented to the user. However, if there is no exact match, the system retrieves the most similar path from the database using Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) and presents it to the user instead. This allows novel and unexpected paths to be presented, either as direct IGA outputs that happen to already exist in the database or as the nearest matches to novel IGA outputs. The database thus serves as both a source of initial paths and a constraint on the final outputs, while still enabling the IGA to generate novel paths personalized to the user’s interests.
Further insights into the user interface and the procedural intricacies of the system can be found in Section 5 (Experimental Evaluation).
3.3. Knowledge Graph Construction
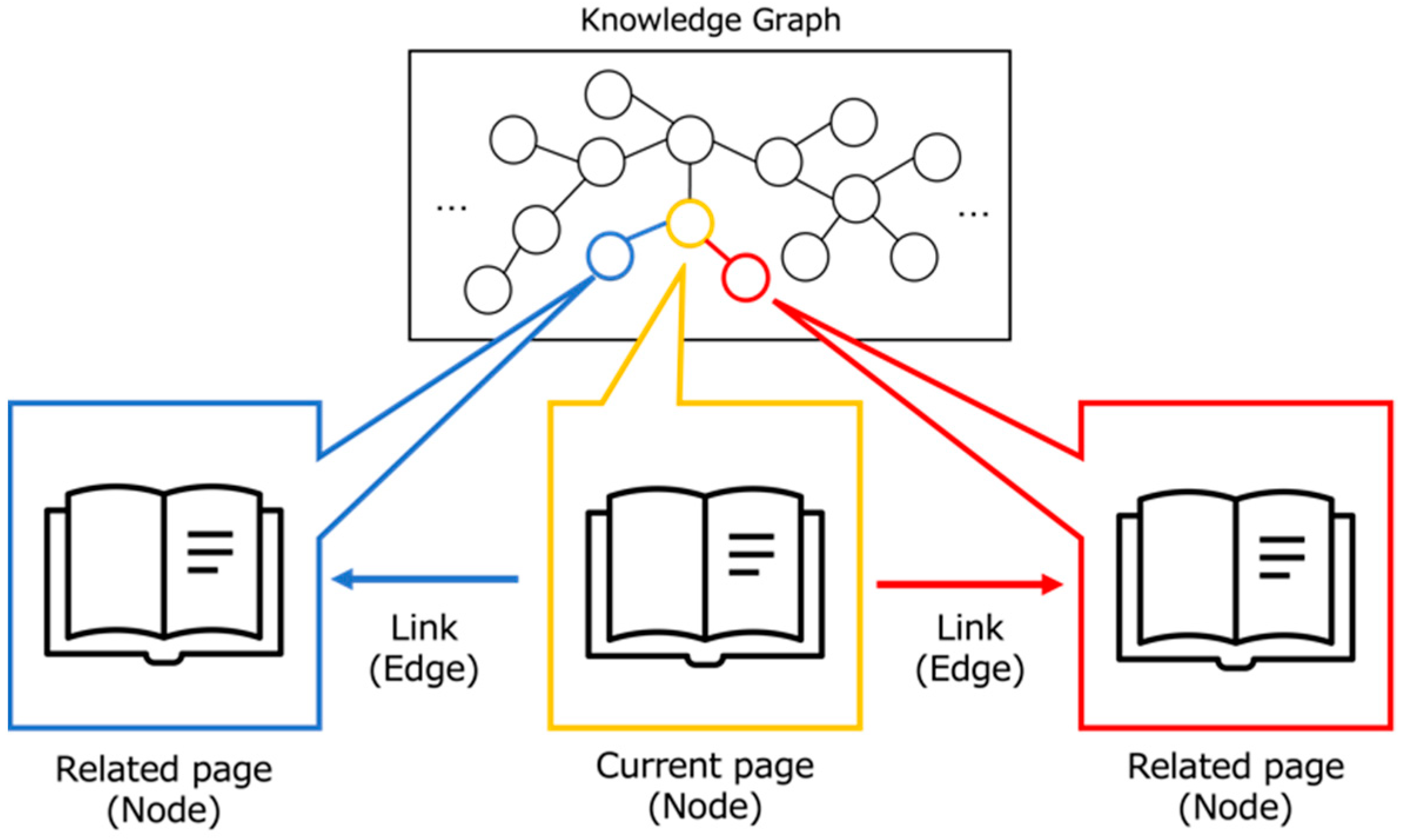
Our system’s knowledge base is built from Science: The Definitive Visual Guide [55], which chronicles scientific and technological evolution chronologically. The book’s inherent structure of interconnected discoveries naturally lends itself to Knowledge Graph representation, as illustrated in Figure 2.
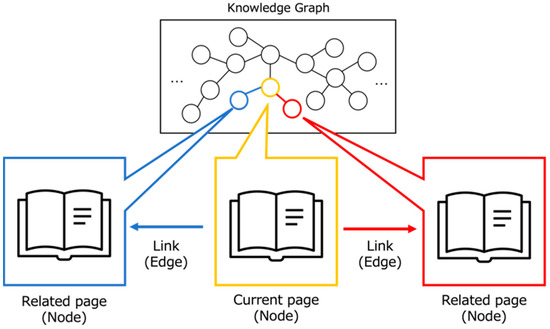
Figure 2.
Structure of Knowledge Graph.
The Knowledge Graph represents major discoveries and inventions as nodes, with edges depicting their relationships. These relationships include the following:
- Temporal connections (“preceded by”, “followed by”).
- Causal links (“led to”, “influenced by”).
- Hierarchical associations (“part of”, “subfield of”).
For practical implementation, each node represents a book page, with edges defined by explicit relationships between pages. While nodes do not capture every detail from the source material, they preserve essential connections and chronological progression.
Learning paths are generated as fixed-length sequences of four nodes and three edges, constructed by traversing the Knowledge Graph according to defined relationships. These paths are stored in a database that supports the system’s recommendation and optimization processes.
3.4. Knowledge Graph Parameters
In general, a Knowledge Graph G = {E, R, F} is a collection of entities E, R, and facts F [56]. A fact is a triple (, , ) ∈ F that denotes a link ∈ R between the head ∈ E and the tail ∈ E of the triple. In the proposed system, the relationship between nodes and edges is also represented using the common (, , ) triples. Note that and represent two different nodes in the Knowledge Graph, while represents an edge linking these nodes. In the following lines, we will explain how these triples are defined in the context of this study.
First of all, we express as a collection of the three parameters vectors , , and .
represents the main contents of a page, and is expressed as in Equation (2), where is the page number of the node, is the discipline (i.e., scientific field), and is the era of the node contents. The page number and the era are set correspondingly to the contents of the book. The discipline refers to one of the disciplines shown in Table 1 and is assigned according to the main contents of each page. These disciplines were taken from the list of disciplines in the Appendix section of the book [55]. Since the disciplines were not explicitly indicated on each page of the book, we manually carried out the labeling of the disciplines based on the main contents of each page. Table 2 shows the list of eras covered by the learning contents as presented in the book by the authors.

Table 1.
List of disciplines.

Table 2.
List of eras and corresponding pages.
represents the related pages labeled as page BEFORE (=B) in the book. In other terms, it refers to the related pages older than the current page. is defined as in Equation (3) according to the number of older related pages NB, and each BEFORE page is defined by Equation (4).
is defined similarly to and represents the related pages labeled as page AFTER (=A) in the book, as shown in (5). Note that NA stands for the number of related pages coming after the current page while each of these pages is defined as in (6).
Next, which also represents a content node, similarly to above is defined as follows. Let denote the page number, denote the discipline, and the era. t is expressed as in (7).
Finally, consists of the association of the following three vectors: , , and , as shown in Equation (8).
expresses the relation between the main contents of node and the main contents of node in terms of the difference between discipline and era parameters, as shown in (9).
is defined as the difference between node and in terms of three parameters: pages number, discipline, and era, as shown in Equations (10) and (11). Note that here = 0 if = (i ∈ NB).
Similarly, is defined as the difference between node and in terms of three parameters: pages number, discipline, and era, as shown in Equations (12) and (13). Here as well, = 0 if = (j ∈ NA).
Based on the proposed knowledge graph model, our key idea is to let an edge capture differences in terms of discipline, era, and page number between two given nodes, and . In addition, by expressing era and page number as time series parameters and adopting a similarity scale for the discipline parameter, we aim to quantitatively express the degree of relevance or divergence between two nodes (i.e., learning content).
Consequently, we represent each path as a 20-dimensional vector with normalized values for each parameter. When ( = 0) ∪ (Aj = 0) holds, each parameter is replaced and normalized by the following values:
Note that to compute the differences between disciplines in the Knowledge Graph, each discipline is assigned a numerical code (e.g., Astronomy = 1, Biology = 2, Chemistry = 3). The absolute difference between these codes is then calculated as the disciplinary difference. For example, |Astronomy − Biology| = |1 − 2| = 1. Larger differences indicate more dissimilar disciplines.
This approach treats disciplines as ordered on a simple scale from 1 to 7. Future work could explore more sophisticated measures of disciplinary similarity, such as using an explicit hierarchy or knowledge-based measures.
3.5. Path Optimization Using Interactive Genetic Algorithm
Path optimization here refers to the generation of new paths of interest to the user by the system. Let N be the number of paths generated from the Knowledge Graph G described in the previous section, and (k ∈ N) be a path arbitrarily retrieved from the path database. In this study, each has a fixed length and is composed of four nodes h1, h2, h3, and h4 (h1, h2, h3, h4 ∈ ) and three edges , , and (, , ∈ ).
Considering that the edges , , and are defined as in (8), which is the vector representing the whole path (i.e., ), is expressed as the sum of , , and as shown in (16).
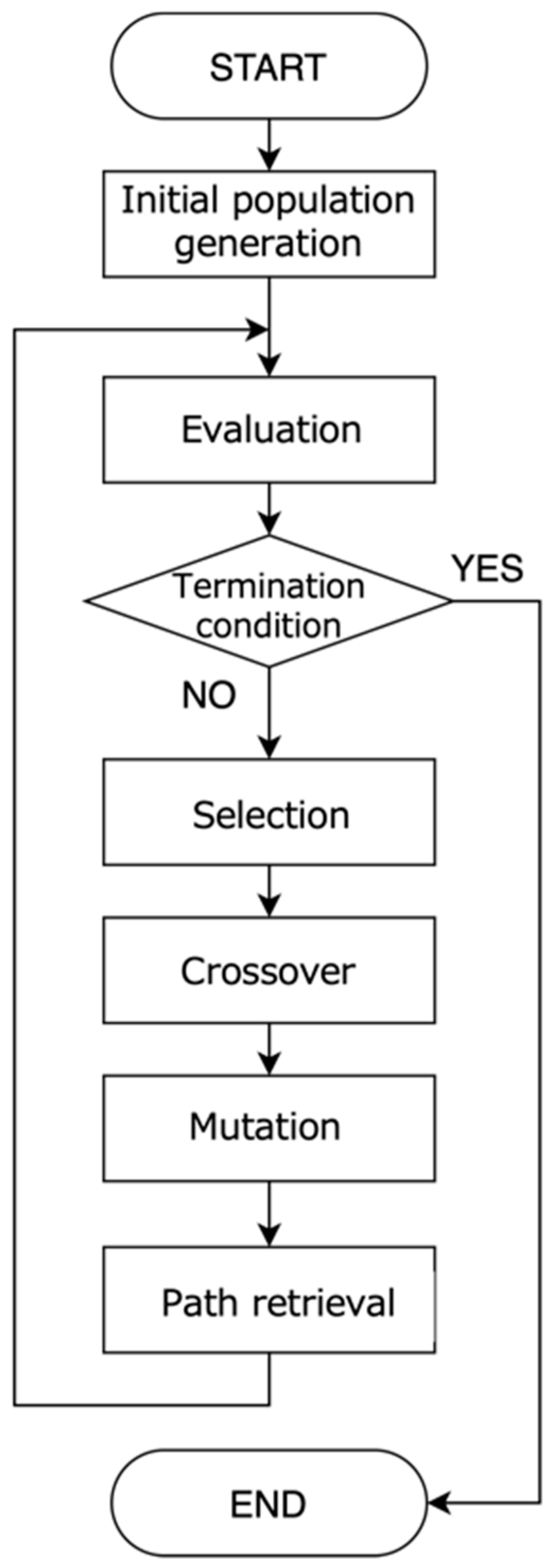
In the present study, the process of path optimization using IGA is based on the gene information expressed by . To such extent, the learner first rates some paths presented to them by the system in terms of relevance with their interests. Here, it seems important to bear in mind that learners are not prompted to evaluate each edge or node, but the whole path with a focus on the connection between starting nodes and ending nodes. The intention here is to make the system capture how interesting the learner finds the connection between several related events across various scientific disciplines and eras. Based on the obtained evaluation values, the path is optimized by Genetic Algorithm processing, and the next-generation solution candidate (i.e., learning path) is presented to the learner. The path is optimized by repeating this process for a certain number of generations. The flowchart of the IGA used in our study is shown in Figure 3. Note that here the path optimization differs from the usual implementation of the IGA as it requires an additional process during Path retrieval. When generating the next generation of solutions, in most cases, Crossover or Mutation will cause the generation of candidate solutions (i.e., paths) that do not exist in the path database RDB. Therefore, for example, a non-existent path needs to be “replaced” by an existing path with the constraint that both paths are similar enough (i.e., ≅ ). When calculating the degree of similarity between two paths, we adopted the Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) algorithm, which is a well-known technique to find an optimal alignment between two given (time-dependent) sequences under certain restrictions [57]. It seems important to bear in mind that we consider that paths generated by the IGA as well as paths in the database can be seen as time series data, which can be transformed as linear sequence of features (i.e., nodes and edges). The DTW distance which indicates the degree of similarity of two different paths and , can be recursively calculated using the following equation:
where denotes the distance between respective edges of and , calculated as follows:
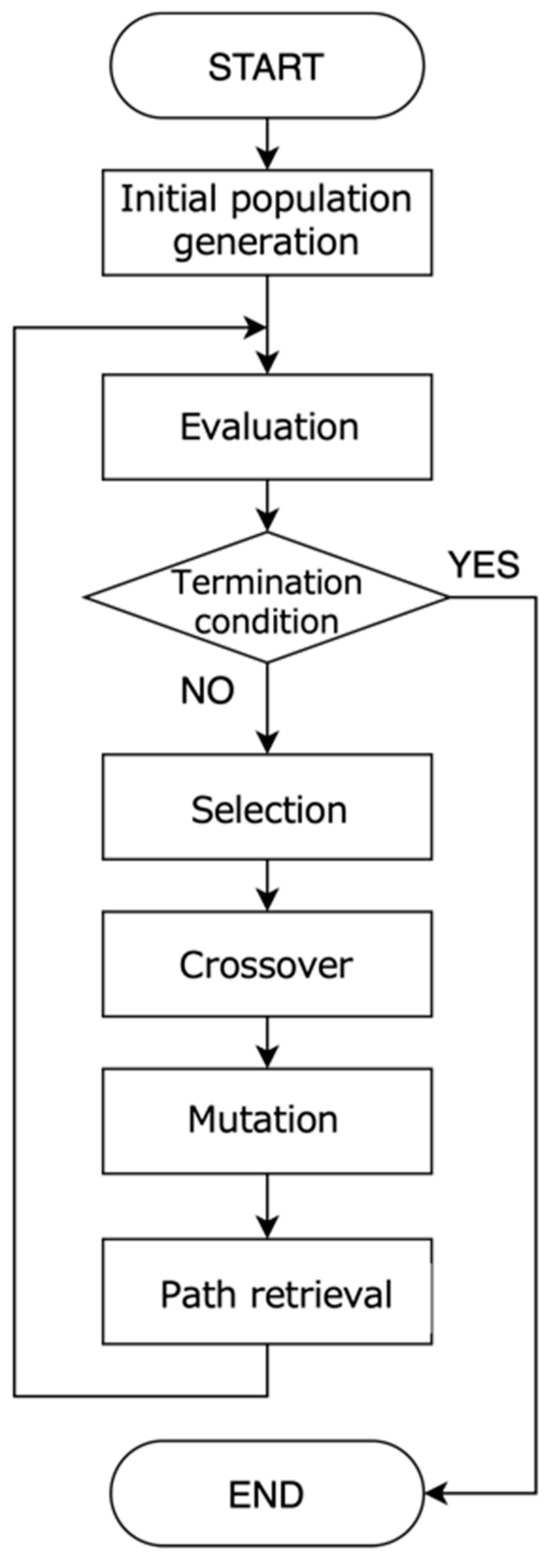
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the Interactive Genetic Algorithm.
It is also worth mentioning that in this study, a Python implementation of the DTW algorithm (dtw-python) [58,59] was used for similarity score calculation.
3.6. Illustrative Examples of Novel and Unexpected Paths
To better understand how the proposed system recommends novel and unexpected paths, let us consider two illustrative examples.
Example 1:
Path: Invention of the telescope (Astronomy, 1608) → Discovery of Jupiter’s moons (Astronomy, 1610) → Development of calculus (Mathematics, 1670s) → Formulation of laws of planetary motion (Astronomy/Physics, 1600s).
This path connects developments in astronomy, mathematics, and physics across the 17th century in an unusual way. While the first two and last nodes are more typically associated, linking them through the development of calculus is unexpected. This novel connection highlights the interdisciplinary nature of scientific advances in that era, showcasing how breakthroughs in one field (mathematics) can lead to significant discoveries in others (astronomy and physics).
Example 2:
Path: Invention of photography (Others, 1830s) → Germ theory of disease (Biology, 1860s) → Discovery of radioactivity (Physics, 1890s) → Formulation of special relativity (Physics, 1900s)
This path spans multiple disciplines and eras in an atypical way. Connecting the invention of photography to later developments in biology and physics is unlikely to be expected by most users. The novel combination of topics can spark new insights into how technologies like photography have enabled scientific discoveries across fields over time. By presenting such unexpected connections, the system encourages users to explore the interdependence of seemingly unrelated scientific advancements.
These examples demonstrate how the recommended paths can provide unexpected disciplinary and temporal connections while still relating to the user’s interests. By leveraging the IGA’s combination of user preferences with stochastic variations, the system generates paths that balance relevance and novelty, promoting serendipitous learning experiences.
4. Simulation Study
4.1. Simulation Outline
Careful testing and parameterization must be carried out before a recommender system is finally deployed in a real setting because the performance of recommendation algorithms seems to be dependent on the particularities of the application context. Therefore, it is advised to experimentally analyze various design choices for a recommender system before its actual deployment. In this section, we present the results of a numerical simulation that was conducted to verify under which settings our learning content optimization algorithm performs the best. For instance, in this simulation, we investigated whether the content optimization algorithm could learn and present information of interest to a pseudo-user. The content optimization algorithm assumes that the user evaluates the paths presented by the system, but in this simulation, we used a pseudo-user created on the computer instead of a real user. The pseudo-user evaluated each path using a pseudo-evaluation function, which is an evaluation function that mimics the user’s evaluation. To do so, we set a path called the target path that best fit the pseudo-user’s latent interest. Then, we evaluated each generated path based on its similarity to the target path by calculating the DTW distance between both paths, using (17) and (18). Note that a smaller DTW value here indicates a higher degree of similarity between the target path and a generated one.
Table 3 shows the Genetic Algorithm parameters used in this simulation, while the total number of paths in the path database RDB and the total number of paths available for each era are shown in Table 4.

Table 3.
IGA parameters of the simulation.

Table 4.
Number of available paths per era.
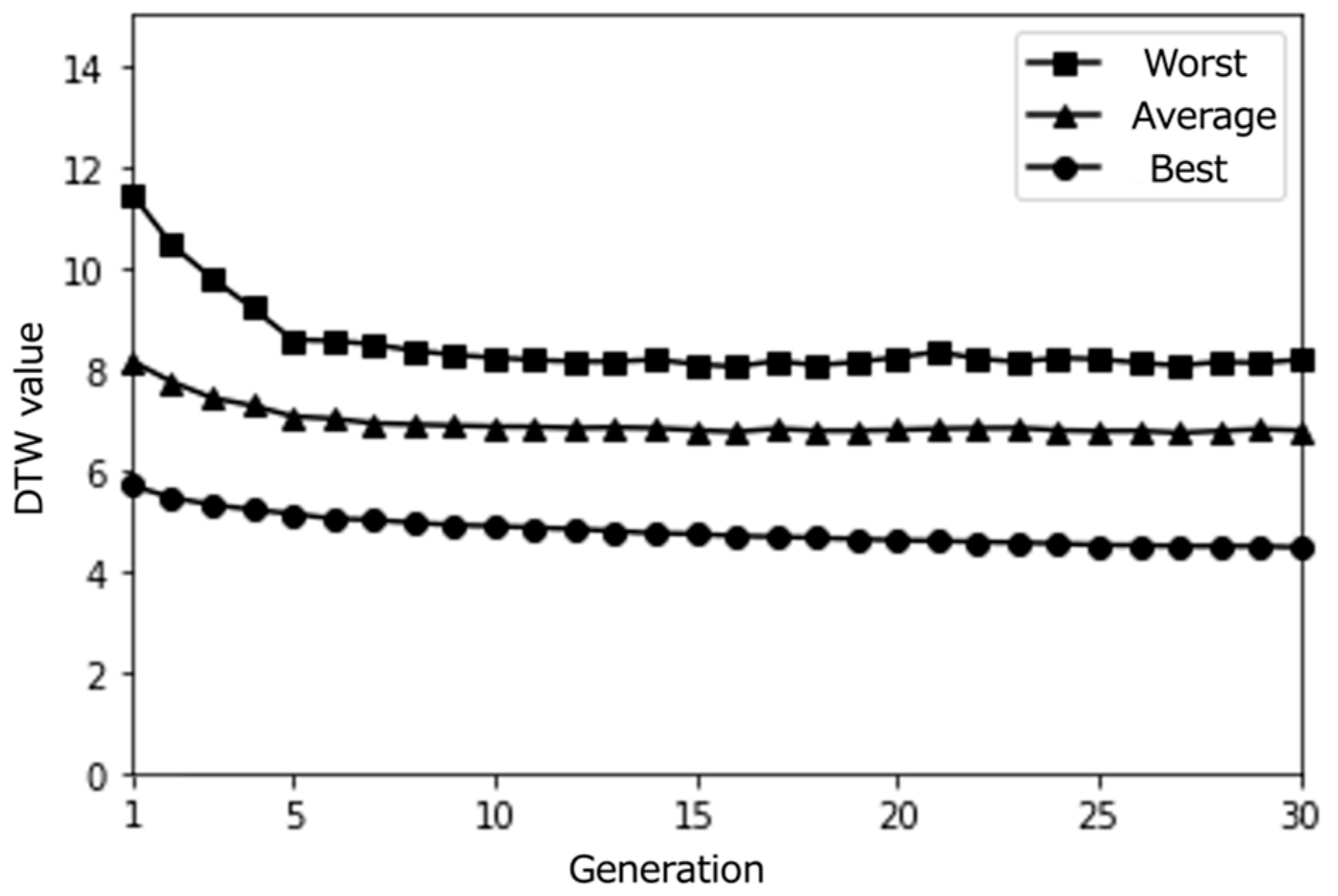
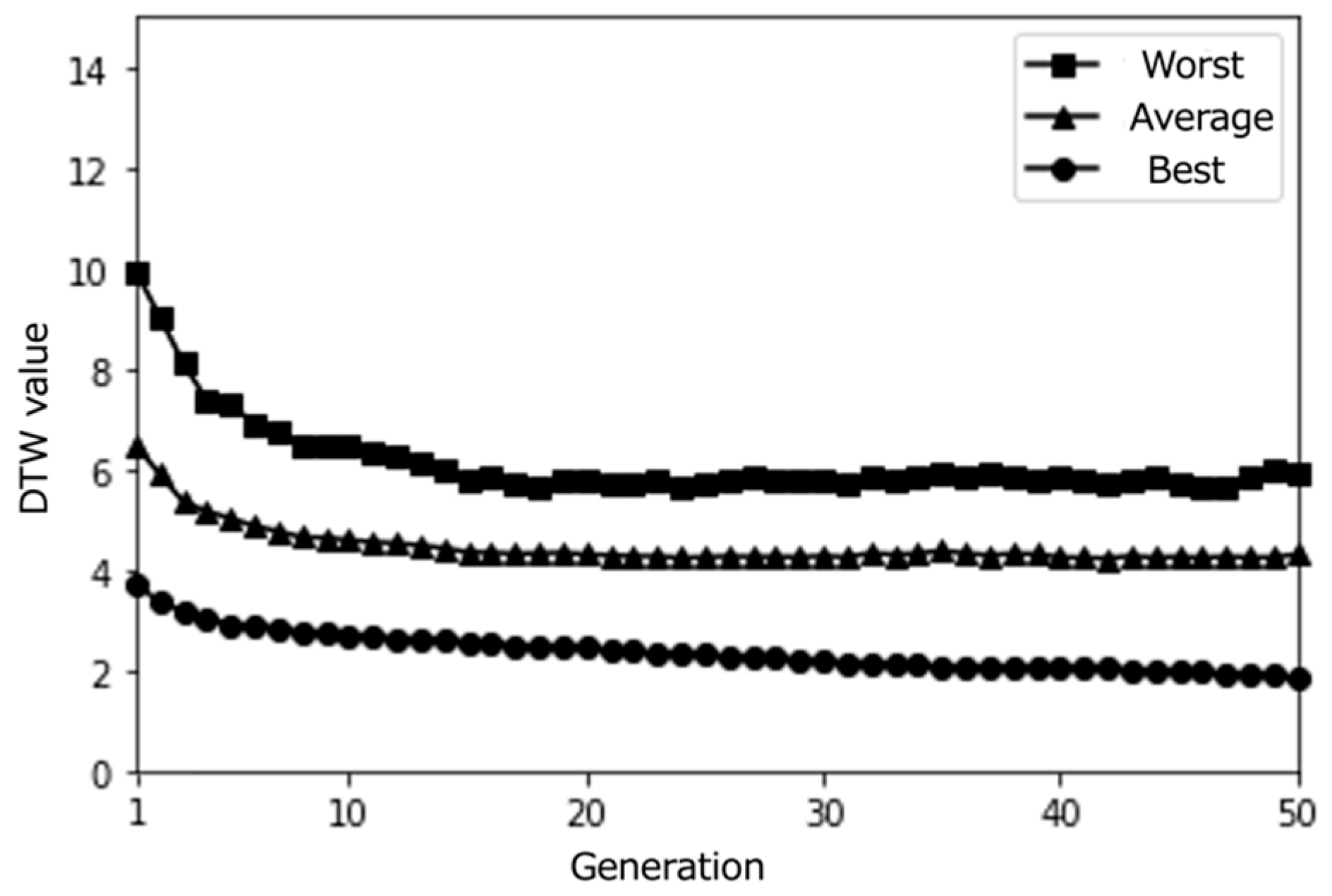
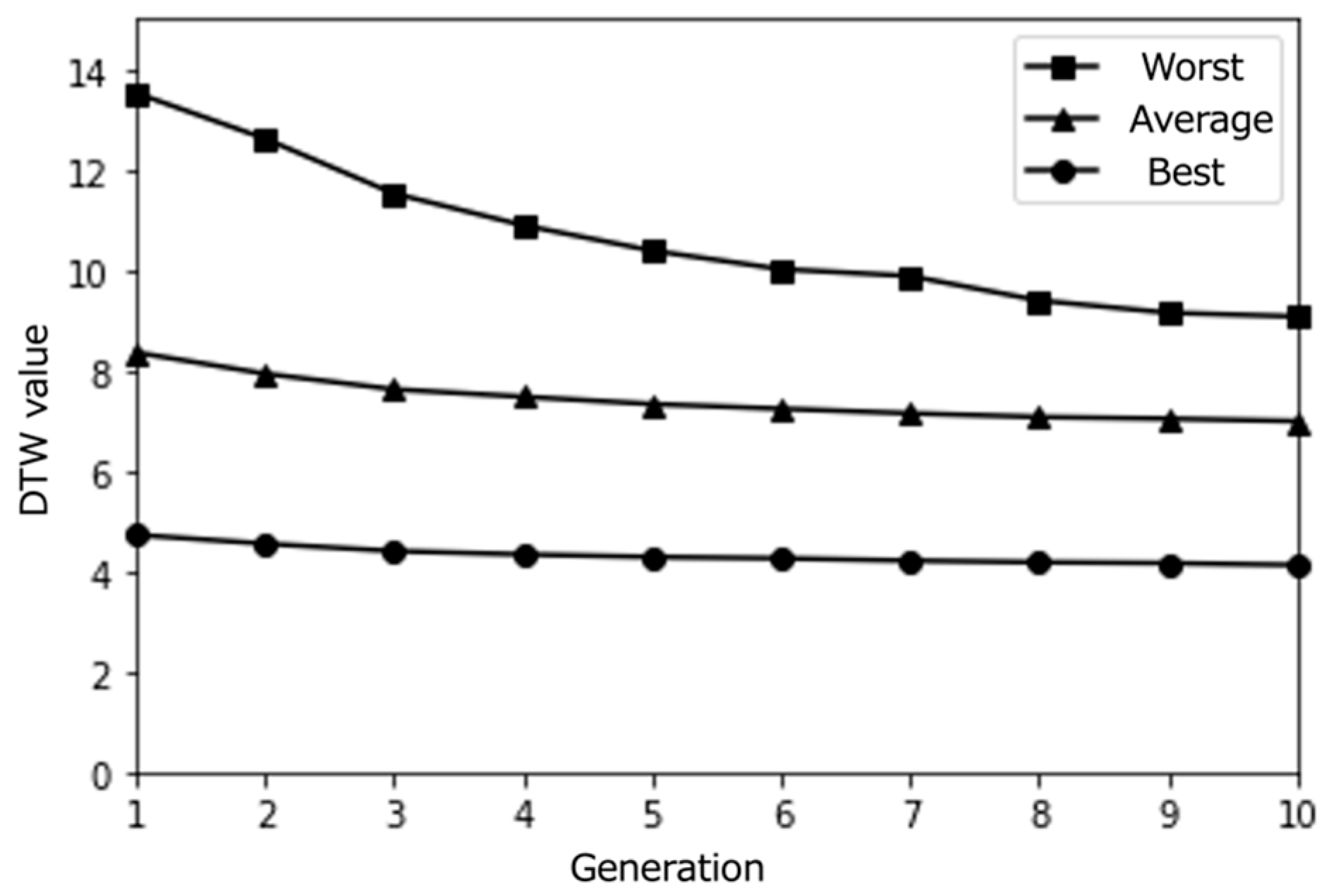
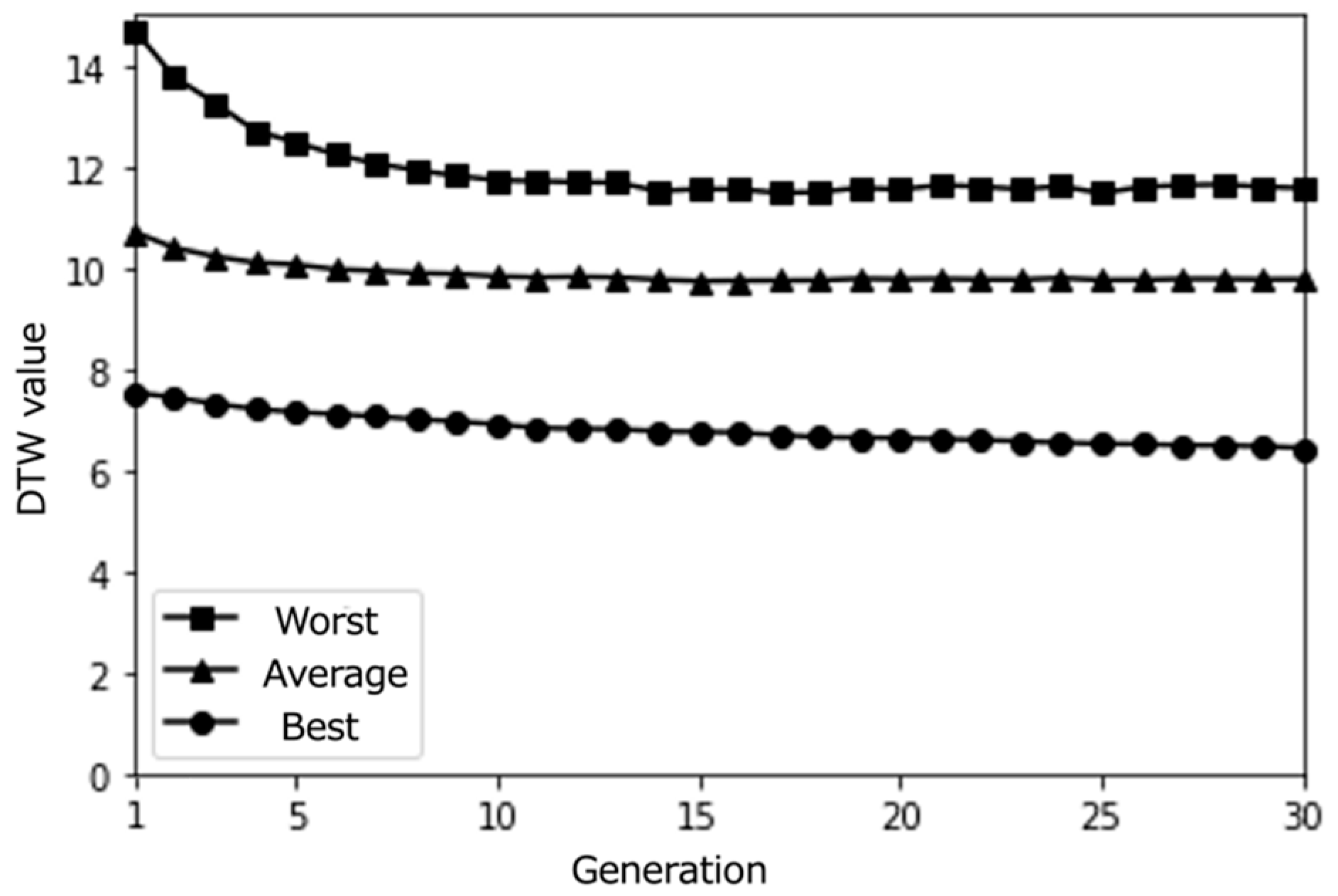
4.2. Simulation Results
Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 show the results of the different simulations that were conducted to investigate the meaningfulness of the proposed algorithm when varying the number of individuals (i.e., paths) and the number of epochs.
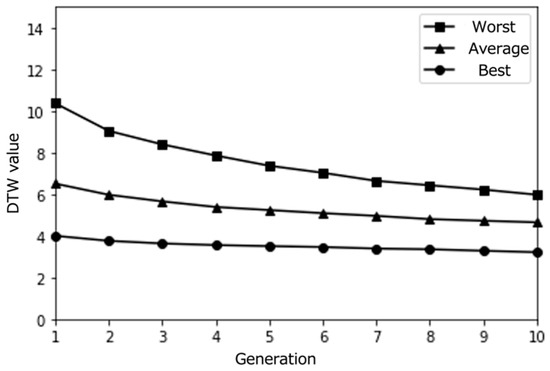
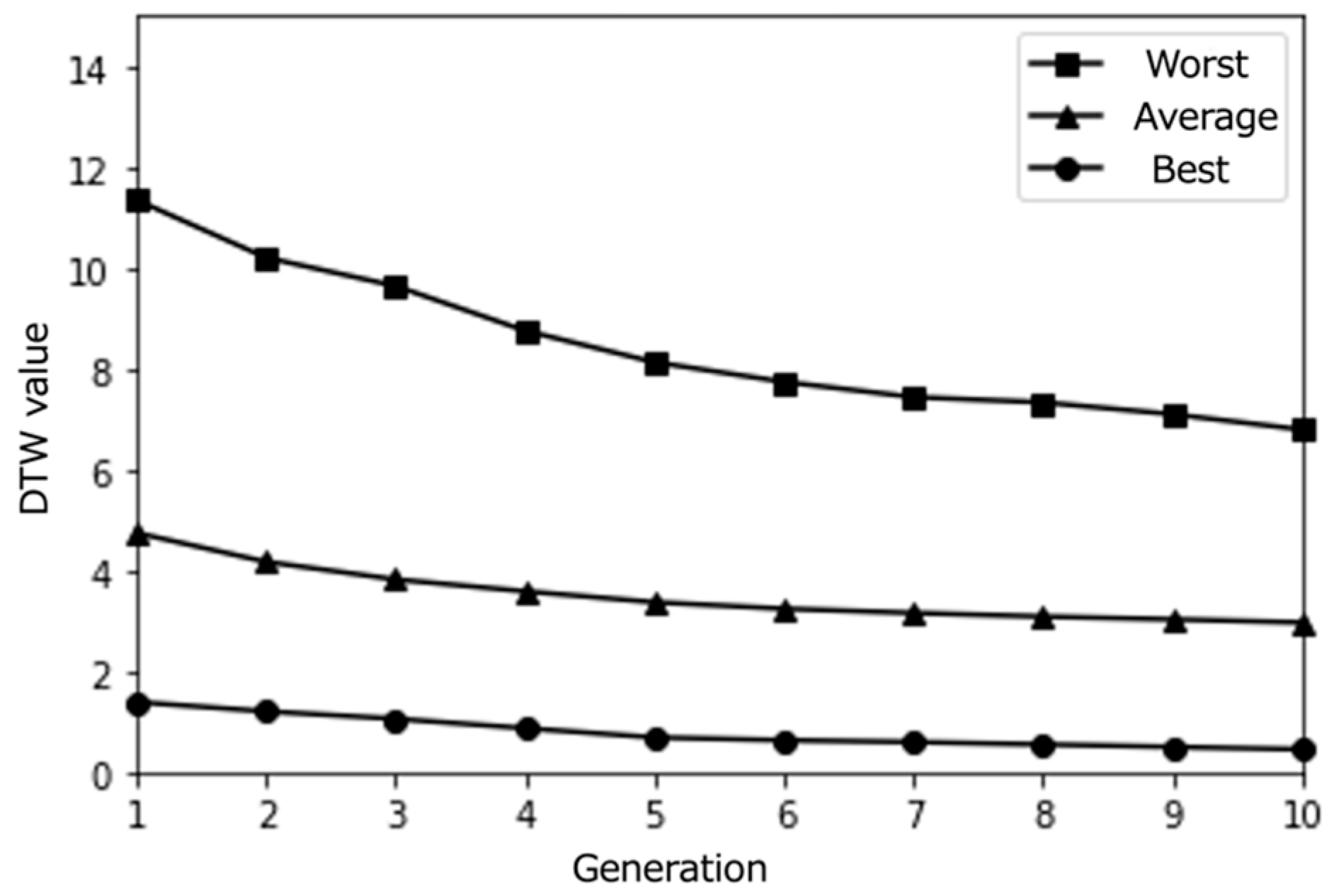
Figure 4.
Simulation results with a small population size (10) over 10 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
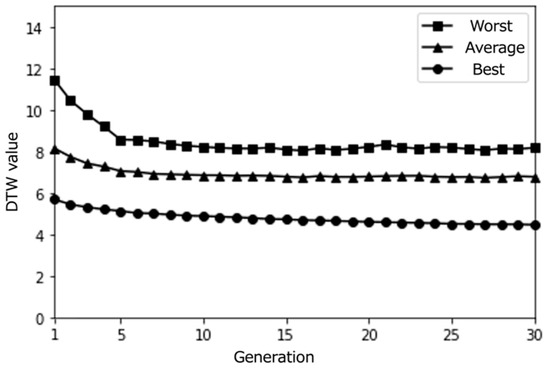
Figure 5.
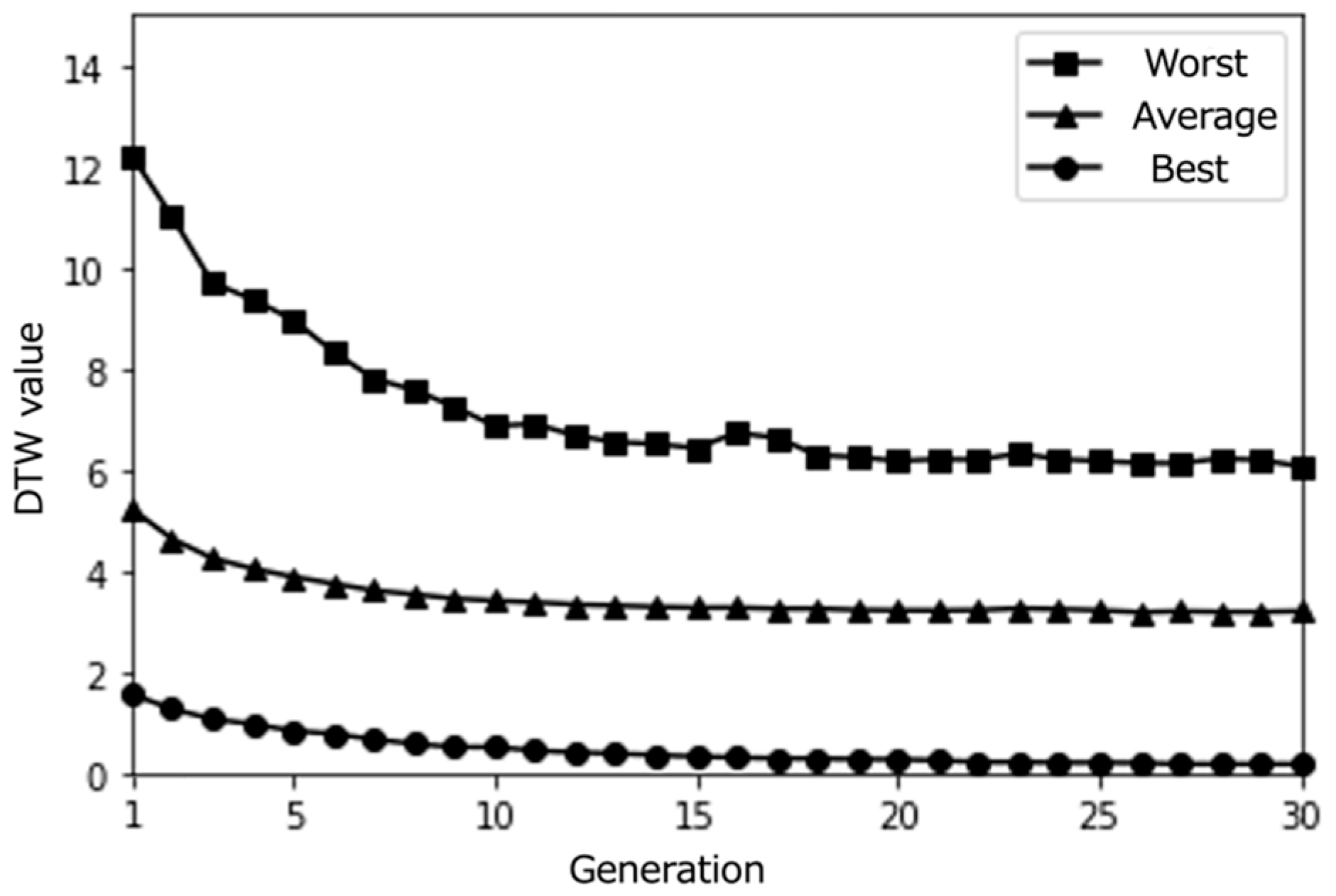
Simulation results with a small population size (10) over 30 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
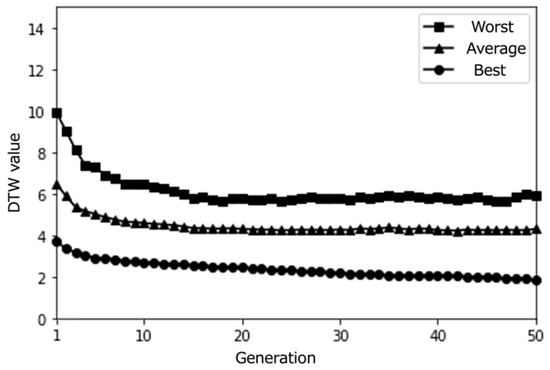
Figure 6.
Simulation results with a small population size (10) over 50 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
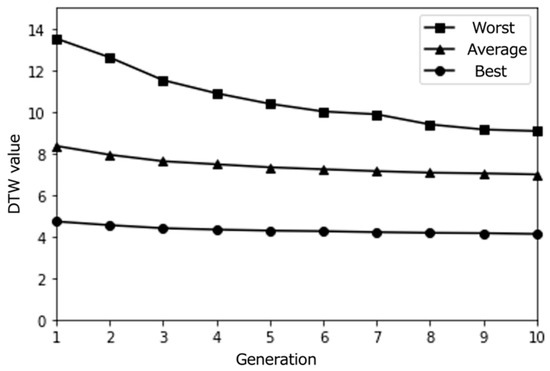
Figure 7.
Simulation results with a medium population size (30) over 10 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
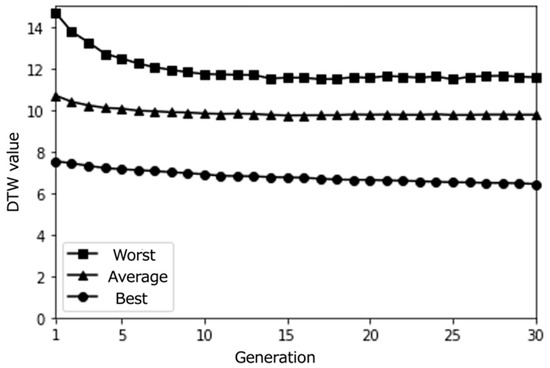
Figure 8.
Simulation results with a medium population size (30) over 30 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
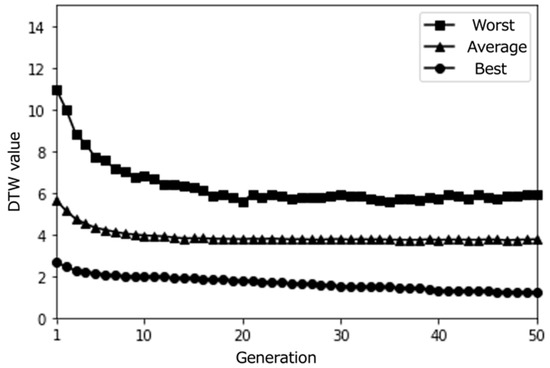
Figure 9.
Simulation results with a medium population size (30) over 50 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
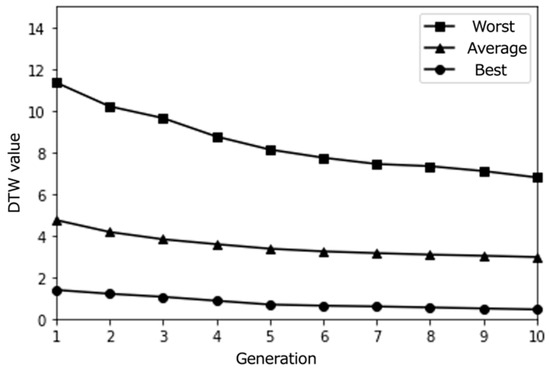
Figure 10.
Simulation results with a larger population size (50) over 10 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
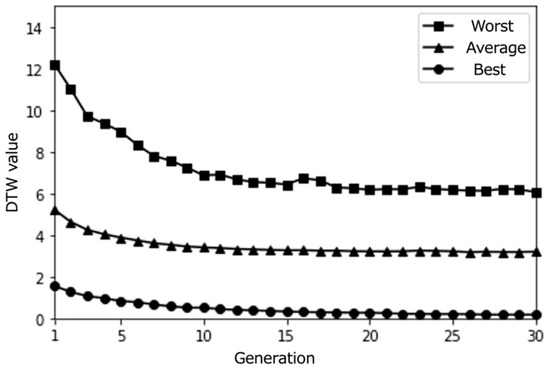
Figure 11.
Simulation results with a larger population size (50) over 30 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
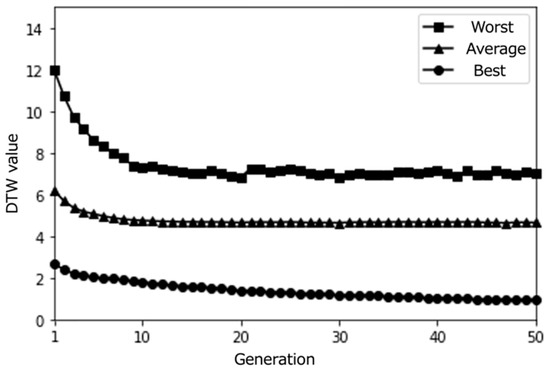
Figure 12.
Simulation results with a larger population size (50) over 50 epochs (average results for 100 trials).
The initial path database used in the simulation study is populated with paths extracted from the Knowledge Graph, providing a diverse starting set before any simulated user interaction occurs. The IGA then iteratively optimizes the paths over multiple generations, also known as epochs, based on the simulated user’s preferences. In the context of the IGA, an epoch represents a complete iteration of the evolutionary process, which includes selection, crossover, and mutation operations.
During each epoch, the IGA selects the best-performing paths based on the simulated user’s ratings, applies crossover to combine features from these paths, and introduces random mutations to maintain diversity in the path population. The resulting set of paths is then evaluated by the simulated user, and the process repeats for the specified number of epochs.
The number of epochs determines the extent of path refinement and optimization. A higher number of epochs allows the IGA to perform more iterations of the evolutionary process, progressively fine-tuning the paths to better align with the simulated user’s preferences. With each additional epoch, the IGA has more opportunities to explore the search space, discover novel path combinations, and converge towards paths that are more likely to be of interest to the user.
However, it is important to note that the optimal number of epochs may vary depending on factors such as the size and complexity of the path database, the diversity of user preferences, and the desired balance between exploration and exploitation in the optimization process. Setting the number of epochs too low may result in suboptimal path recommendations, while setting it too high may lead to diminishing returns in terms of path quality and computational efficiency. Therefore, in the simulation study, we systematically varied the number of epochs to investigate its impact on the IGA’s performance in generating personalized and serendipitous path recommendations. By examining the results across different epoch settings, we could gain insights into the trade-offs involved and determine a suitable range of epochs for the proposed system.
4.3. Discussion
From the obtained results, we can observe that individuals close to the best solution were found quite early, in the vicinity of the initial generation, independently of the simulation conditions. When viewing this through the lens of March’s organizational learning theory [60], this quick convergence raises important questions about the exploration–exploitation balance in our system. While efficient optimization is generally desirable, such rapid convergence to locally optimal solutions might limit the system’s capacity to support serendipitous discoveries.
This tendency to fall into locally optimal solutions under all simulation conditions suggests a characteristic of our search space that aligns with Kaufmann’s theory of search landscapes [61]. The prevalence of similar individuals that might have been calculated as the (locally) optimal solution indicates that our Knowledge Graph might represent a relatively smooth search landscape. While this promotes efficient optimization, it raises questions about whether a more rugged search landscape might better support serendipitous discovery.
Interestingly, we notice that as the number of generations increases, more individuals with DTW values close to 0 are generated. This suggests that our proposed content optimization algorithm successfully finds individuals that almost perfectly match the pseudo-user’s latent interest. However, this observation must be considered critically: while algorithmic convergence is achieved, the educational value of such precise matching requires careful examination, particularly in the context of supporting serendipitous learning.
The limited size of the path database used for this initial simulation emerges as a significant constraint when viewed through the lens of constructivist learning theory. The similarity among candidate solutions not only indicates a technical limitation but also raises theoretical questions about the diversity needed to support genuine knowledge construction through unexpected discoveries. This insight suggests that using a larger path database would be necessary when conducting evaluations with real users, not just for technical robustness but to provide the rich environment needed for meaningful learning experiences.
Although this simulation study seems to validate our algorithm’s technical performance, examining serendipitous learning requires human participation. Therefore, we conducted experimental evaluation with real users to assess how effectively our system balances relevant content with unexpected discoveries in authentic learning scenarios.
5. Experimental Evaluation
5.1. Proposed System and Interaction Design
As mentioned earlier in this paper, the aim of this work was to propose an Interactive Genetic Algorithm-driven recommender interface that could induce serendipity in informal learning settings. Figure 13 shows a schematic diagram of the proposed system. The system presents information related to various discoveries in science and technology, using a knowledge database built with the contents of the book Science: The Definitive Visual Guide, by Adam Hart-Davis (Ed.) [55], as mentioned earlier. We implemented a content optimization algorithm that enables the system to account for learners’ interests and preferences when presenting new paths of interest to learners according to the methods detailed in Section 3. The learning environment thereby achieved aimed at providing learners with an informal learning opportunity in the context of history learning, more specifically in the domain of scientific discoveries.
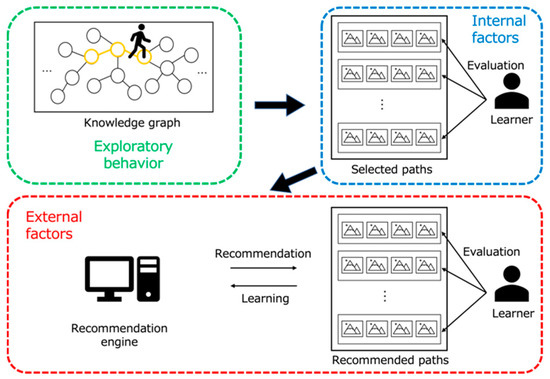
Figure 13.
Overview of interactions between the learner and the system.
Furthermore, the proposed system is equipped with functions to support the three key elements (i.e., internal factor, external factor, exploratory behavior) necessary to induce serendipity within learners, as described in Section 3. First, the exploratory behavior is supported by a function that allows users to explore the system’s Knowledge Graph according to their own interests during the exploration phase (see details in the next section). For example, the learner can explore the learning contents by browsing hints about the nodes of the presented path using the HINT feature, which is shown on the top-left hand side of the interface in Figure 14 The learner may also move to an older or newer event node related to the current one by clicking on the BEFORE or AFTER buttons.

Figure 14.
System interface showing the path navigation window.
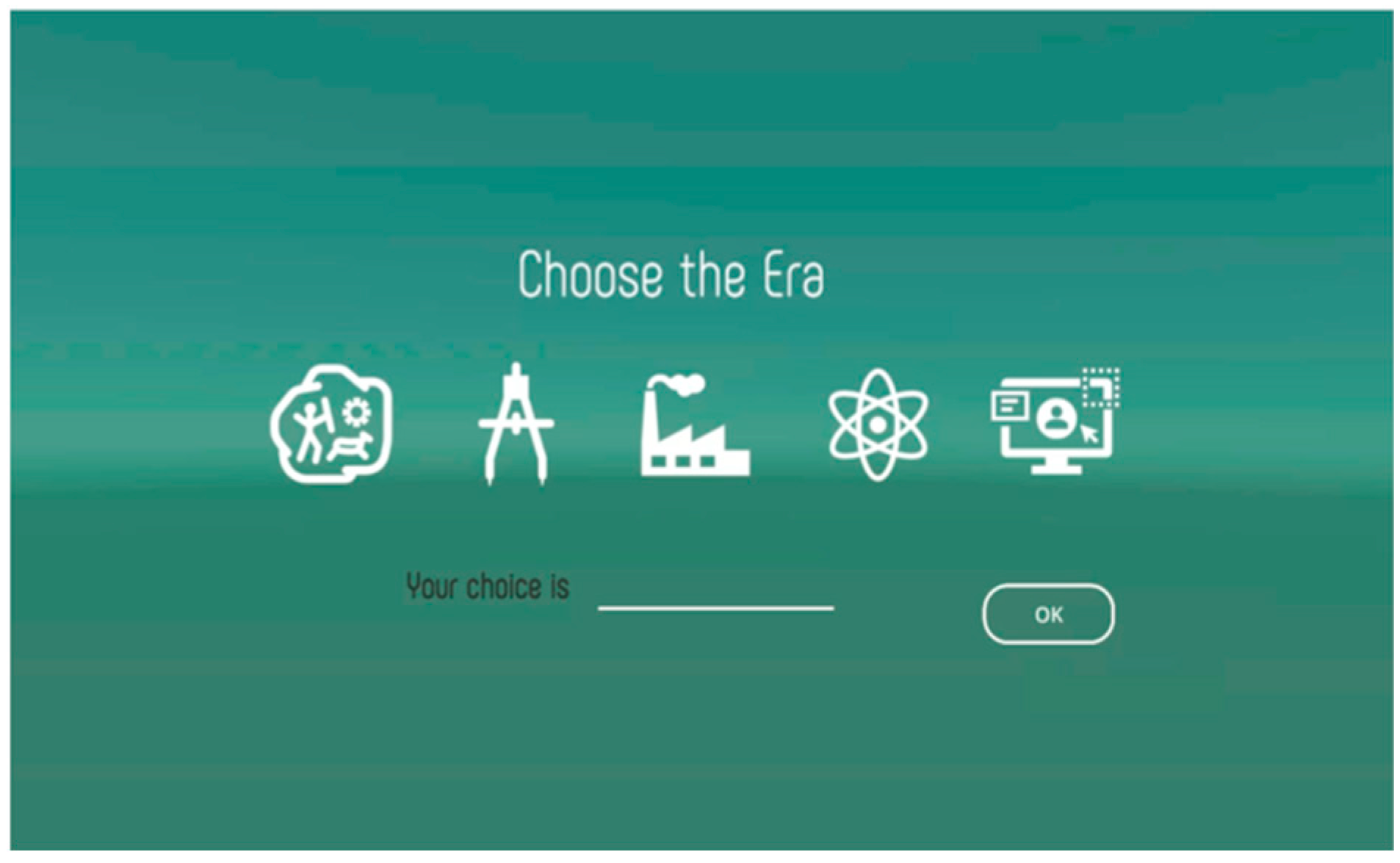
Next, the internal factor is realized by a function that allows the user to select information of interest. For instance, the user can select an era of interest from any of the eras covered in the book using a dedicated window, as shown in Figure 15. The system then presents paths containing nodes of the selected era to the learner.
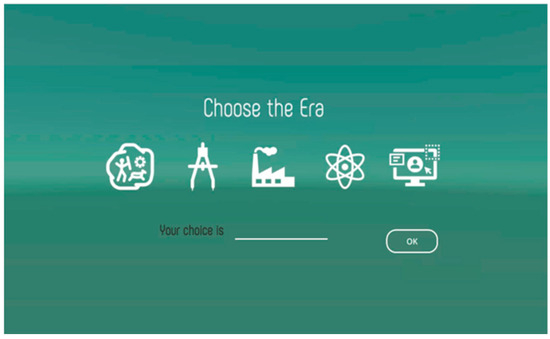
Figure 15.
System interface showing the era selection window.
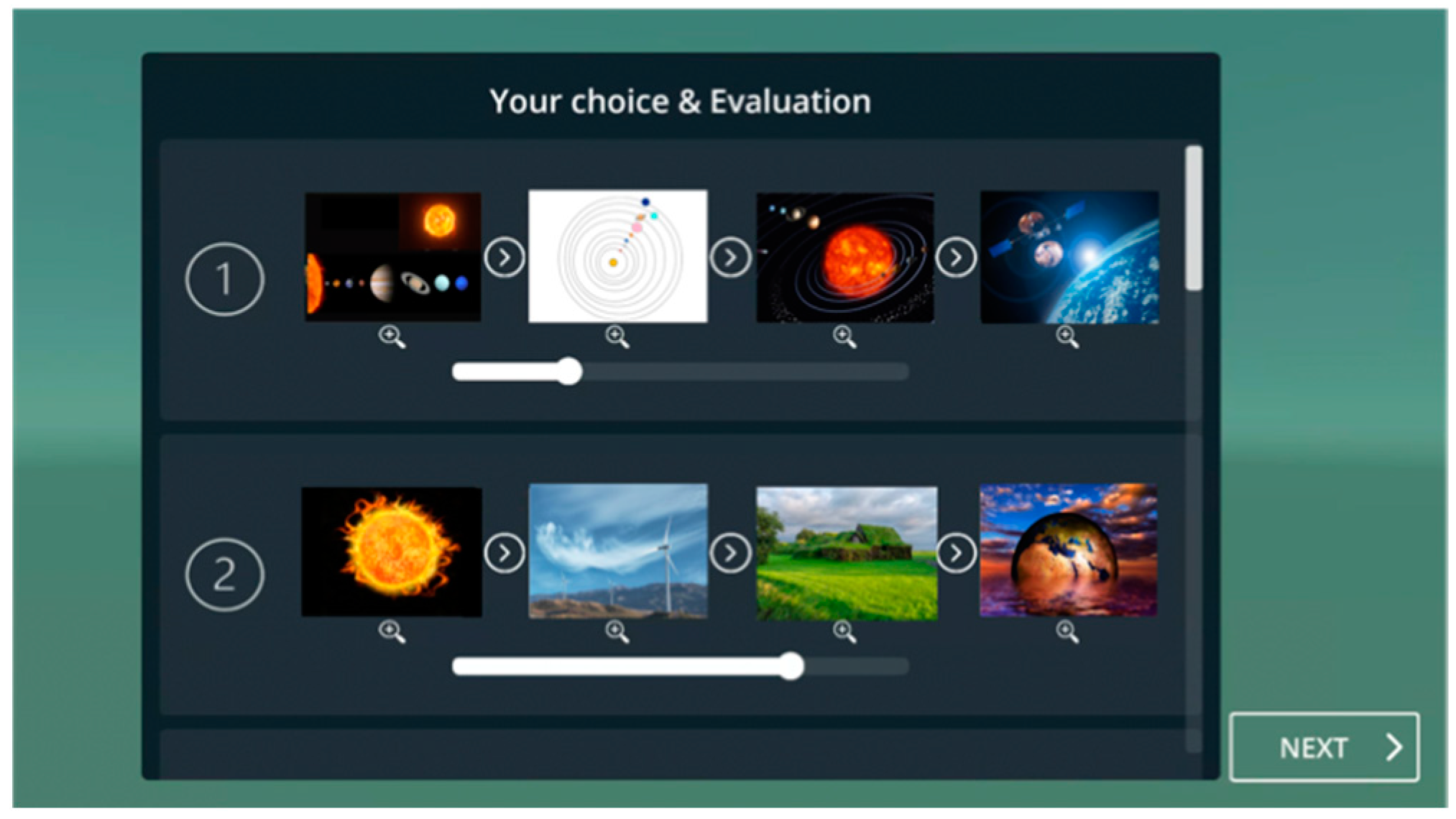
Finally, the external factor is supported by implementing a path presentation feature in the proposed system. The paths presented are first randomly retrieved from the path database and then optimized progressively based on the learner’s evaluation data. A given path consists of four related nodes, each of which depicts a major scientific discovery or invention, and is represented by an image, as shown in Figure 16.
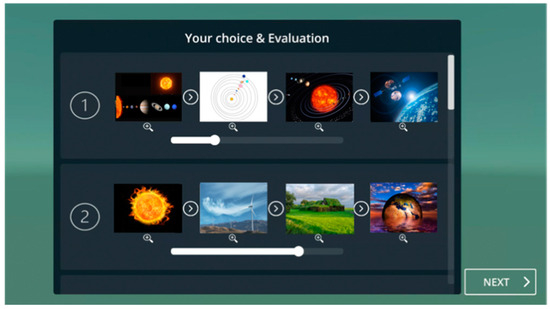
Figure 16.
System interface showing the path evaluation window.
Moreover, the user can also create a path of interest using the browsing history of explored nodes. After exploring and creating a path, the learner can evaluate its degree of interest. Such information is used by the system to propose paths that better fit the interest of the learner during the recommendation phase.
In sum, by targeting each of the three elements above-mentioned, the proposed system is expected to not only recommend information of interest to each learner but also contribute to inducing serendipity by presenting information that is both novel and unexpected to each learner.
5.2. Experiment Outline and Flow
We conducted an experimental evaluation to investigate whether the proposed system could present information of interest but yet unexpected enough to induce serendipity within participants. The subjects in the experiment were 25 university students majoring in science-related fields. Interaction with the system was carried out in two phases: Phase 1 (Exploration Phase) and Phase 2 (Recommendation Phase).
In order to collect learners’ preference data, we adopted an explicit approach and employed a 6-point (0–5) Likert scale. In general, preferences may be expressed either explicitly or implicitly. Implicit preferences are gathered through the user’s actions. These actions can be telling about the user’s preferences, even if they are unaware of it: clicking on a link (advertisement, search result, or cross-reference), spending time watching content, etc. For explicit preferences, the system asks the user to rate an item. This can be completed using a variety of paradigms, such as a scale of 0–5 points, positive or negative votes, or only upvotes. These data are harder to collect since they require user action and thus more effort compared to implicit data. However, in our study, we opted for the latter method (explicit preferences) in order to make sure that data used for content generation actually reflected learners’ opinions and preferences. In addition, such an approach is in line with the idea of involving the learners in the design process of learning contents, as suggested in the literature [62,63].
First, in phase 1, subjects were prompted to select an era in which they were interested for learning about scientific discoveries. Figure 16 shows the UI used by the learner to select the desired era. Then, based on the learner’s selection, the system presented nodes corresponding to the selected era. After viewing the contents of a given node, learners could freely navigate through related nodes by selecting other nodes of interest from the ones displayed on the interface via the “BEFORE” and “AFTER” buttons. Note that when clicking on a given node, subjects were presented with a window showing the contents of a given page in the Science: The Definitive Visual Guide book, in addition to information such as the era and scientific field of the scientific event depicted, as well as links to related nodes. Each time a total of four nodes (i.e., length of a path) were explored by the subject, the corresponding sequence of nodes and edges was saved as a learning path. After 10 paths were created, subjects were prompted with an evaluation window to evaluate the interestingness of the visited paths, on a scale of 0 to 5.
Then, in phase 2, based on the evaluation data collected from phase 1, the system automatically generated several paths using the proposed algorithm. Here, subjects were asked to visit and then evaluate the paths proposed by the system in terms of preference level on the scale of 0 to 5. Based on their ratings, the system generated new paths and the same operation was repeated until the ending condition (i.e., 10 generation rounds) was met. Table 5 shows the parameters of the implemented Genetic Algorithm-based optimization technique used to achieve this. As suggested in the discussion section of the simulation study (i.e., Section 4.3), we found that our proposed content optimization algorithm could successfully generate paths that matched the pseudo-user’s latent interest no matter the simulation conditions. In this experiment, considering the evaluation burden on real users, we limited the number of path generation rounds to 10 iterations. Moreover, if paths generated by the Genetic Algorithm did not actually exist in the database, the generated paths were replaced by the most similar ones in the database using DTW values. The similarity score between two paths was calculated using Equations (15) and (16).

Table 5.
IGA parameters of this experimental study.
After phase 2, we administrated a questionnaire survey, whose contents are shown in Table 6, to collect participants’ subjective opinions on the meaningfulness of their interaction with the system.

Table 6.
Contents of the questionnaire.
5.3. Results
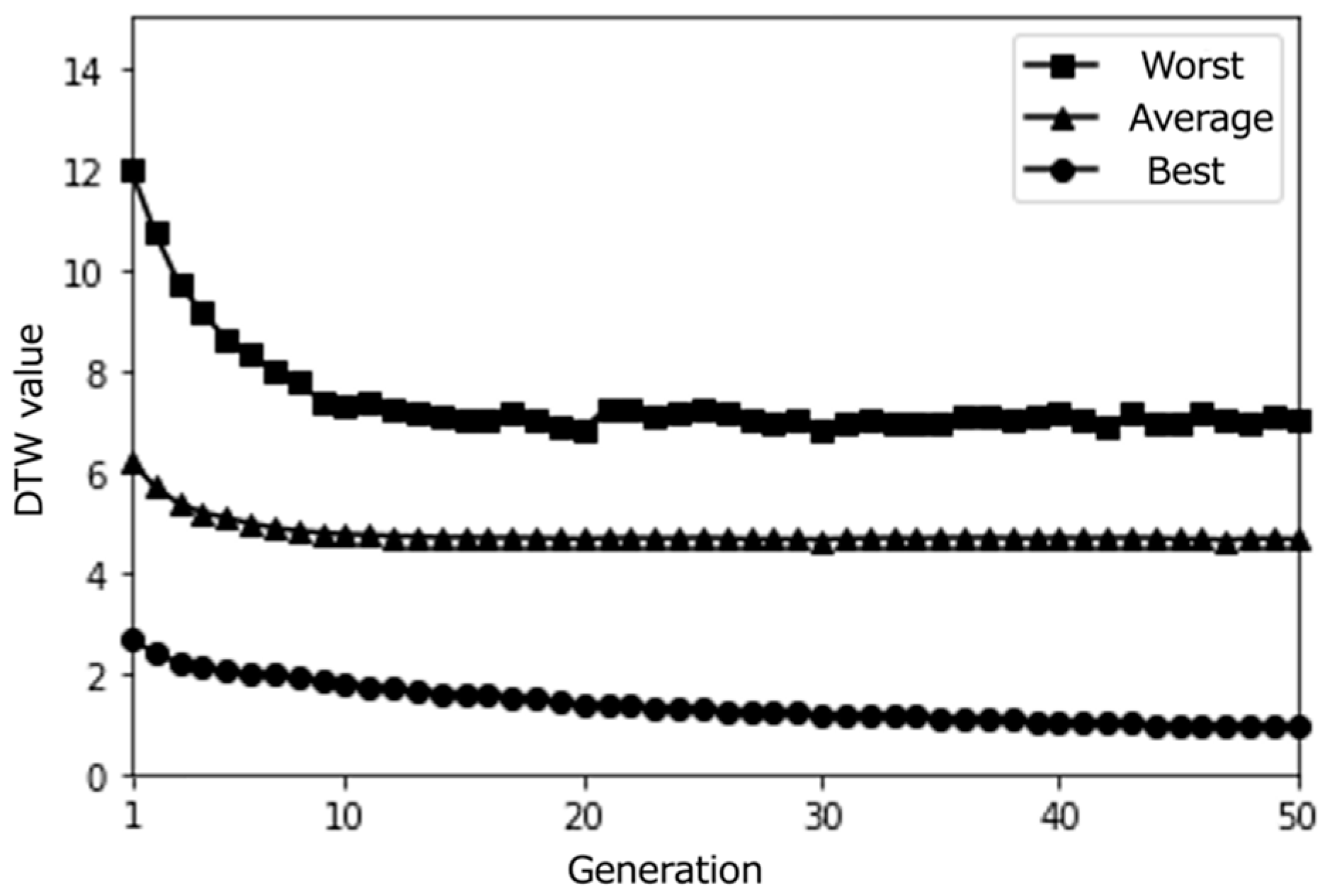
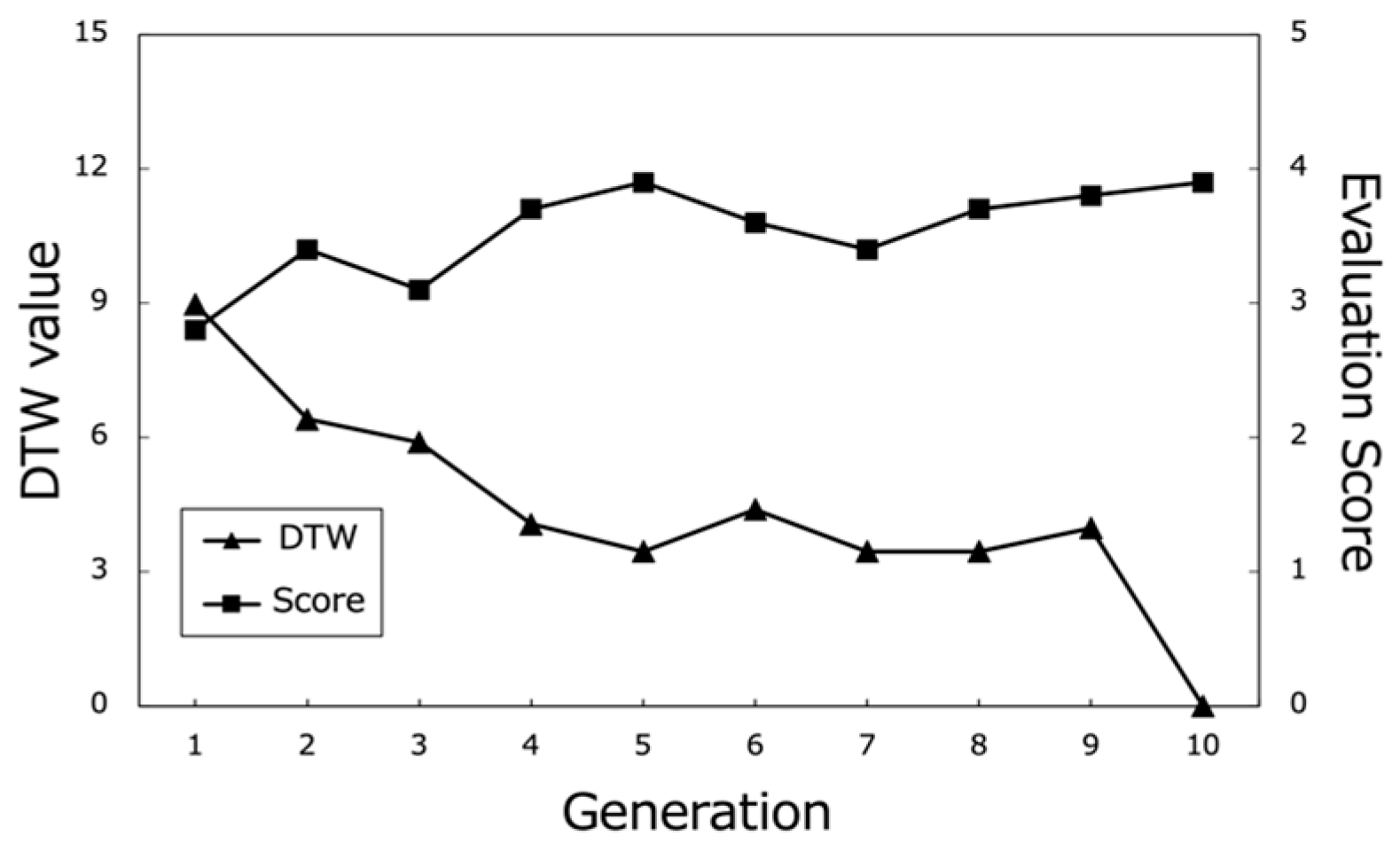
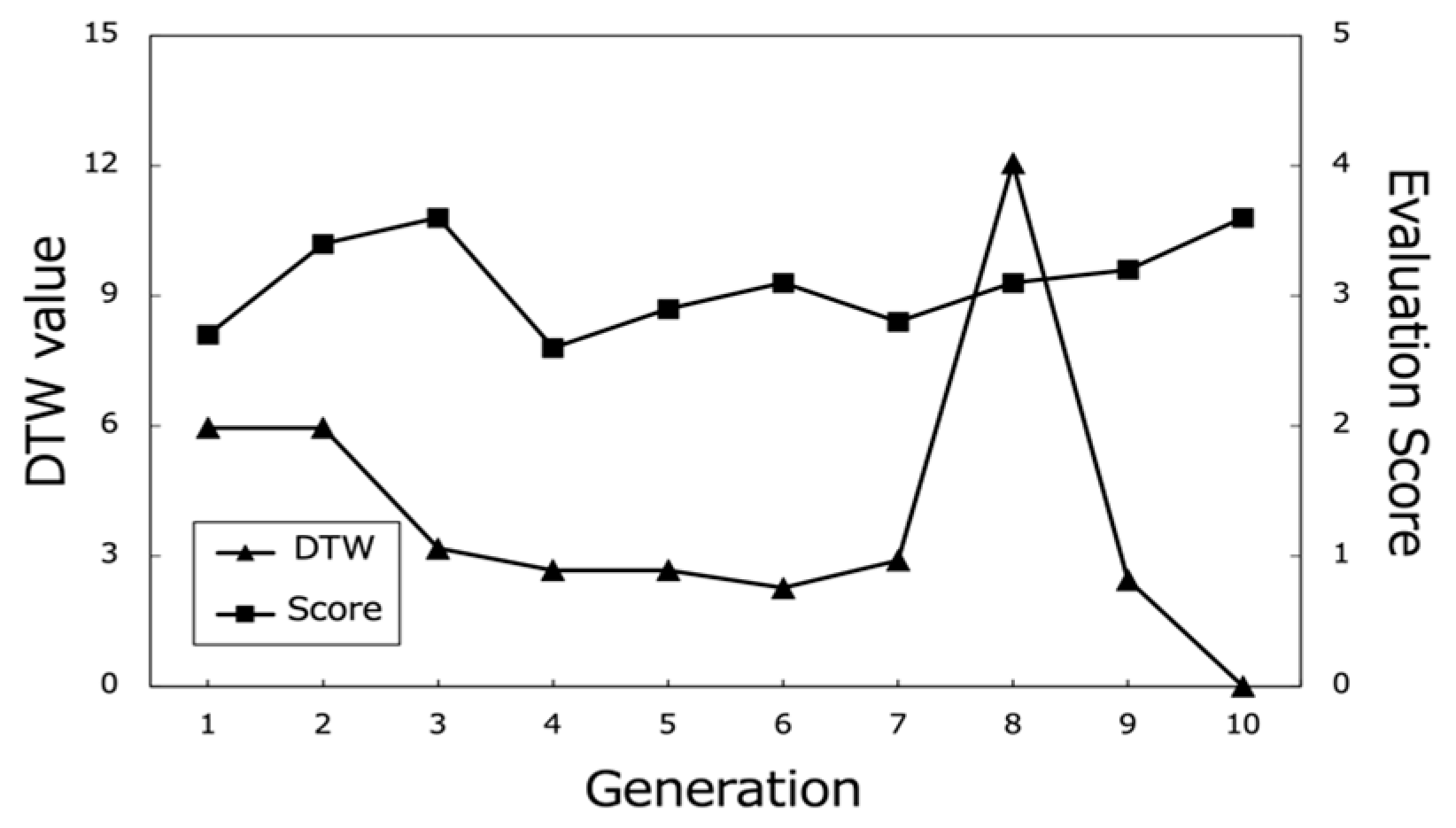
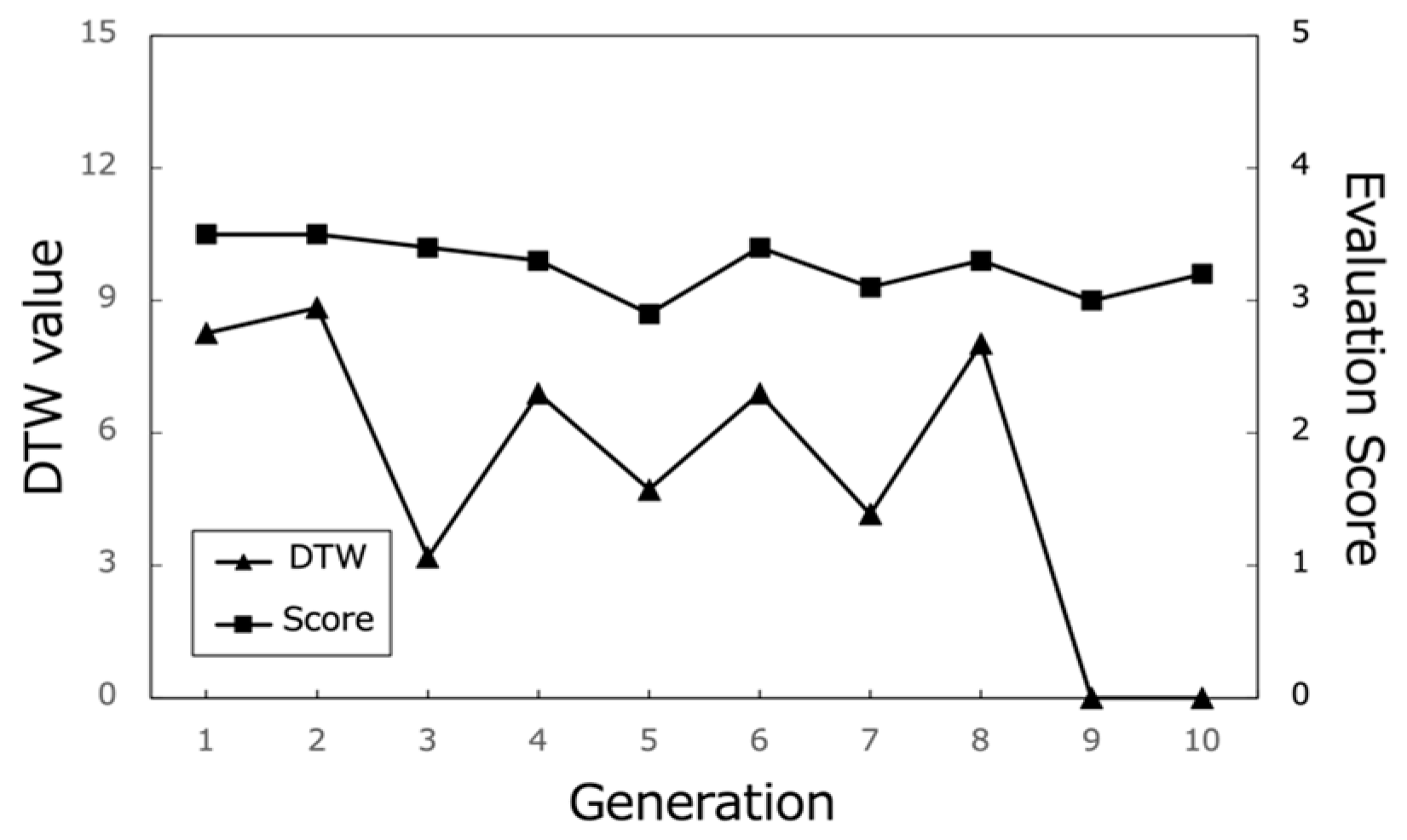
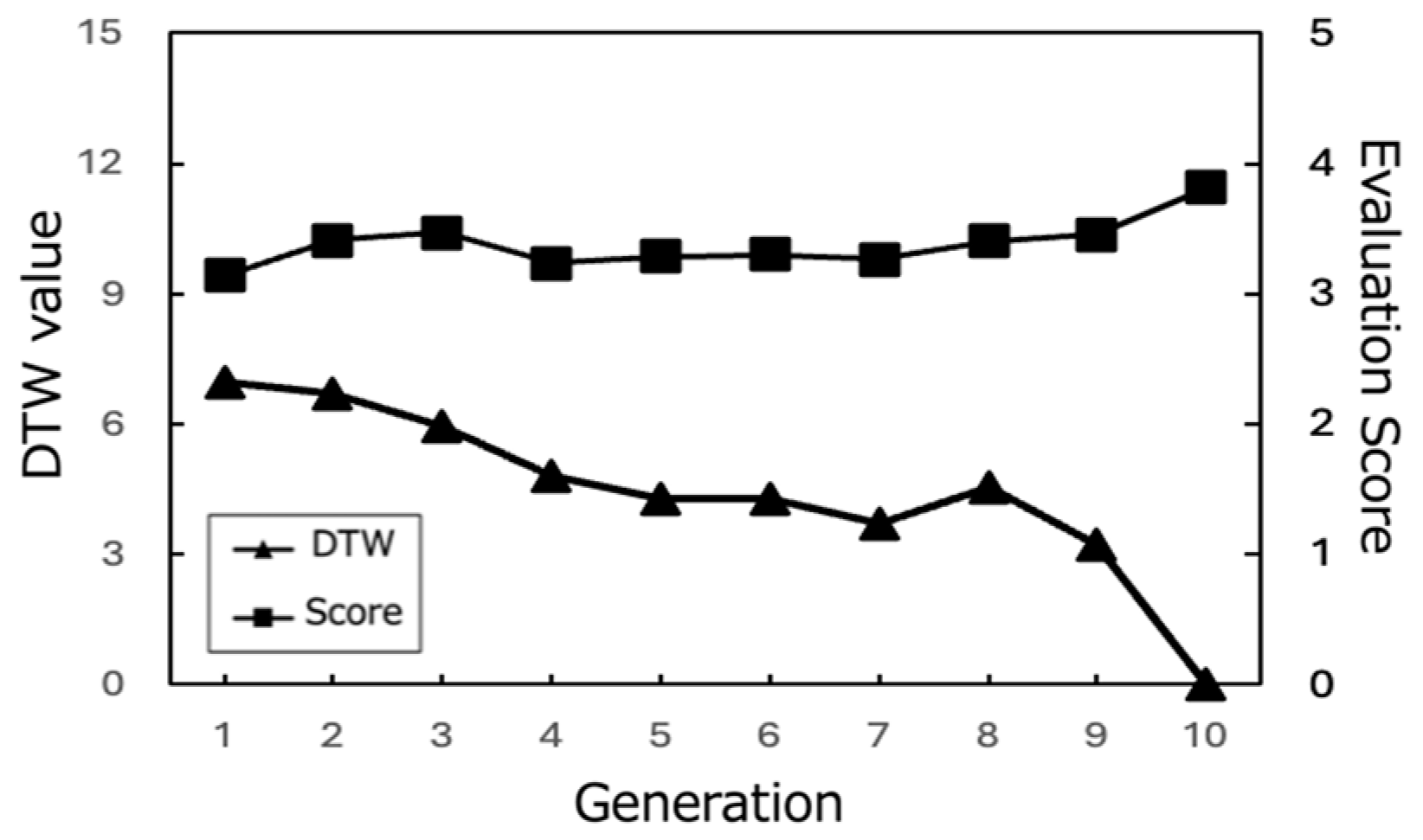
Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19 show the changes in the DTW values and evaluation scores of three representative participants (Subjects A, B, and C) across all generations. These changes refer to the differences in DTW values between the path that each subject rated highest in each generation and the path they rated highest in the final (10th) generation. Figure 20 presents the average evaluation scores and DTW values for all 25 participants, providing an overall view of the system’s performance.
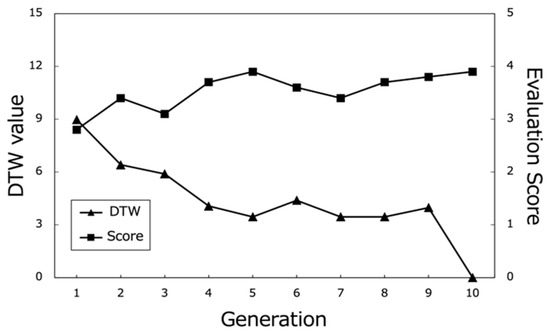
Figure 17.
Evaluation scores of the best paths and corresponding DTW values (Subject A).
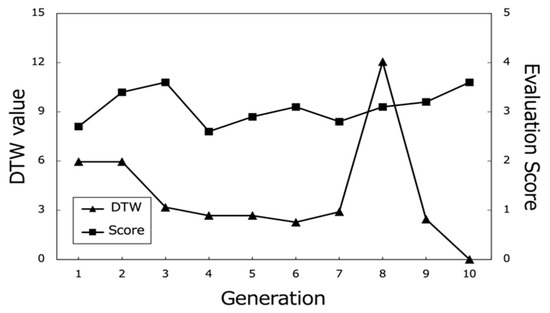
Figure 18.
Evaluation scores of the best paths and corresponding DTW values (Subject B).
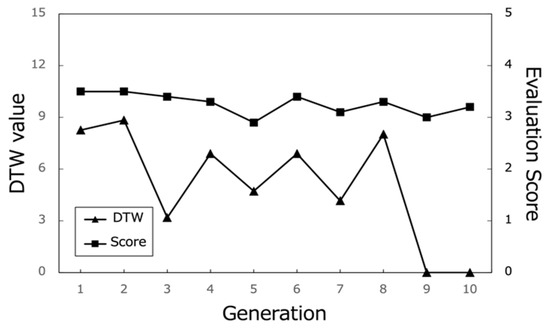
Figure 19.
Evaluation scores of the best paths and corresponding DTW values (Subject C).
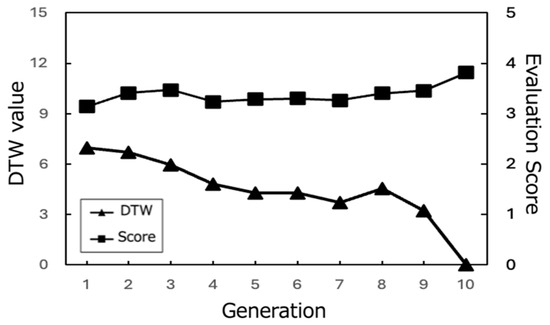
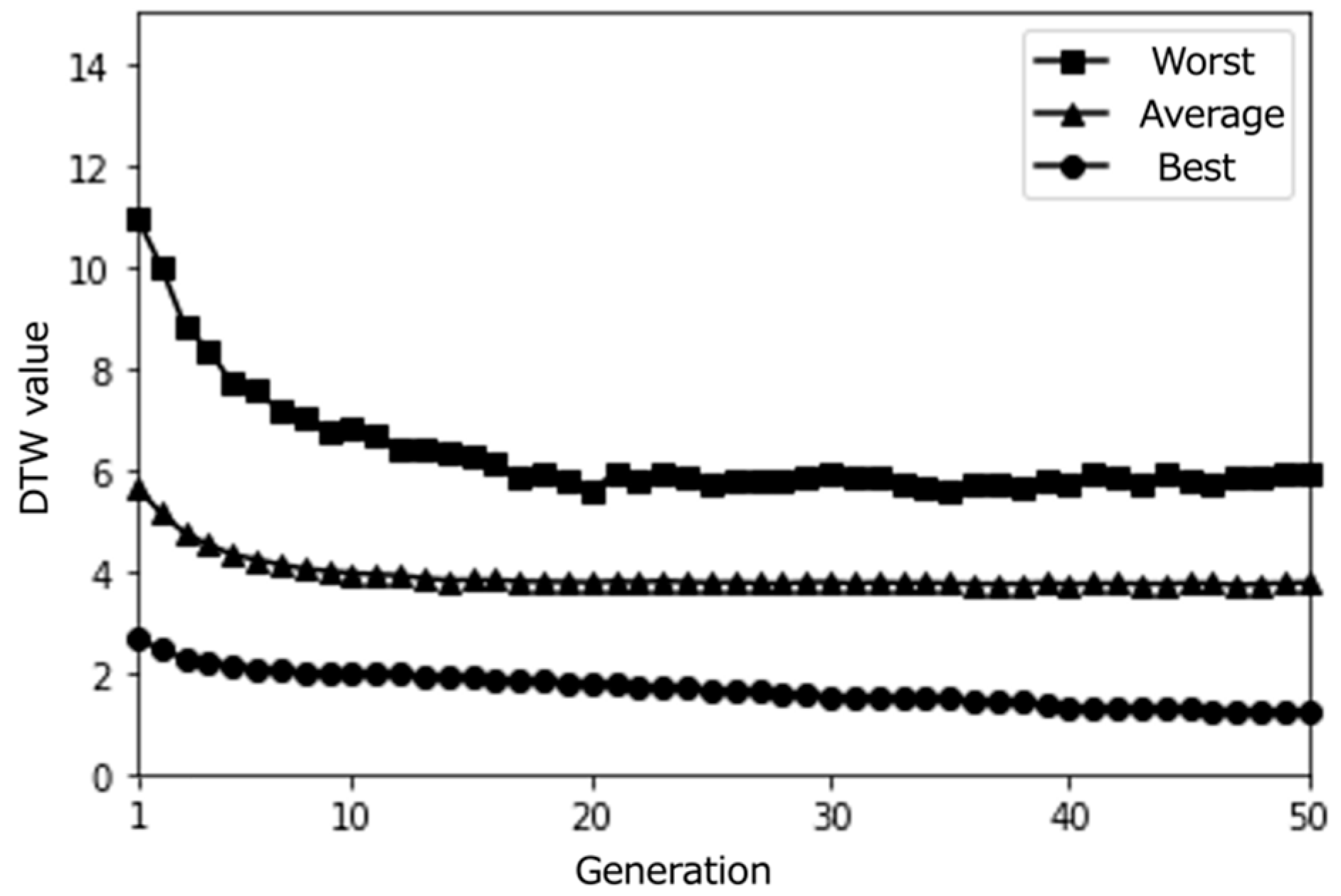
Figure 20.
Evaluation scores of the best paths and corresponding DTW values (All Subjects).
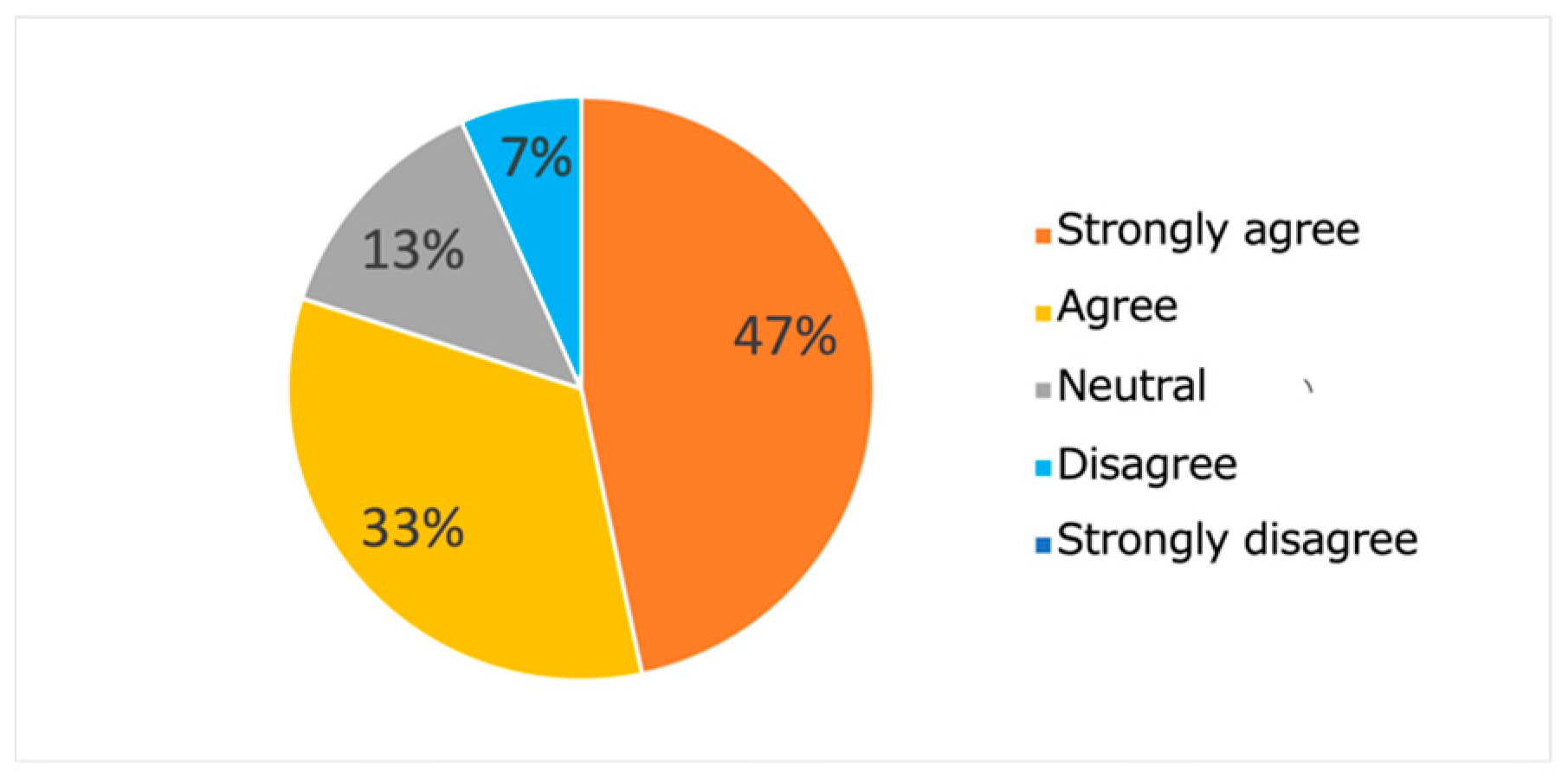
From these results, it can be observed that the proposed system effectively optimized the learning paths according to each user’s preferences. The highest evaluation scores from participants stabilize around the last generations, indicating that the system gradually converged towards presenting subjects with highly rated learning contents. As shown in Figure 20, the average evaluation score of the learning paths presented in the final generation across all participants was relatively high (M = 3.9, SD = 0.92), demonstrating the system’s ability to generate recommendations that align with users’ interests.
Moreover, the DTW values, which measure the similarity between the generated paths and the paths stored in the database, tend to converge towards 0 in the later generations. This trend suggests that the proposed system successfully generated paths that closely matched the users’ preferred paths, even if the exact paths were not present in the database. The convergence of DTW values towards 0 is evident in the individual participant results (Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19) and the overall average results (Figure 20), indicating the effectiveness of the path optimization process.
However, when analyzing the transition of DTW values for some subjects, there were cases in which DTW values rose rapidly even near the last generation or did not show a decreasing trend despite the number of generations increased, such as in the case of Subject B (Figure 18). Therefore, we cannot rule out the hypothesis that using a method other than DTW distance as a method for calculating path similarity may lead to a higher performance for path optimization.
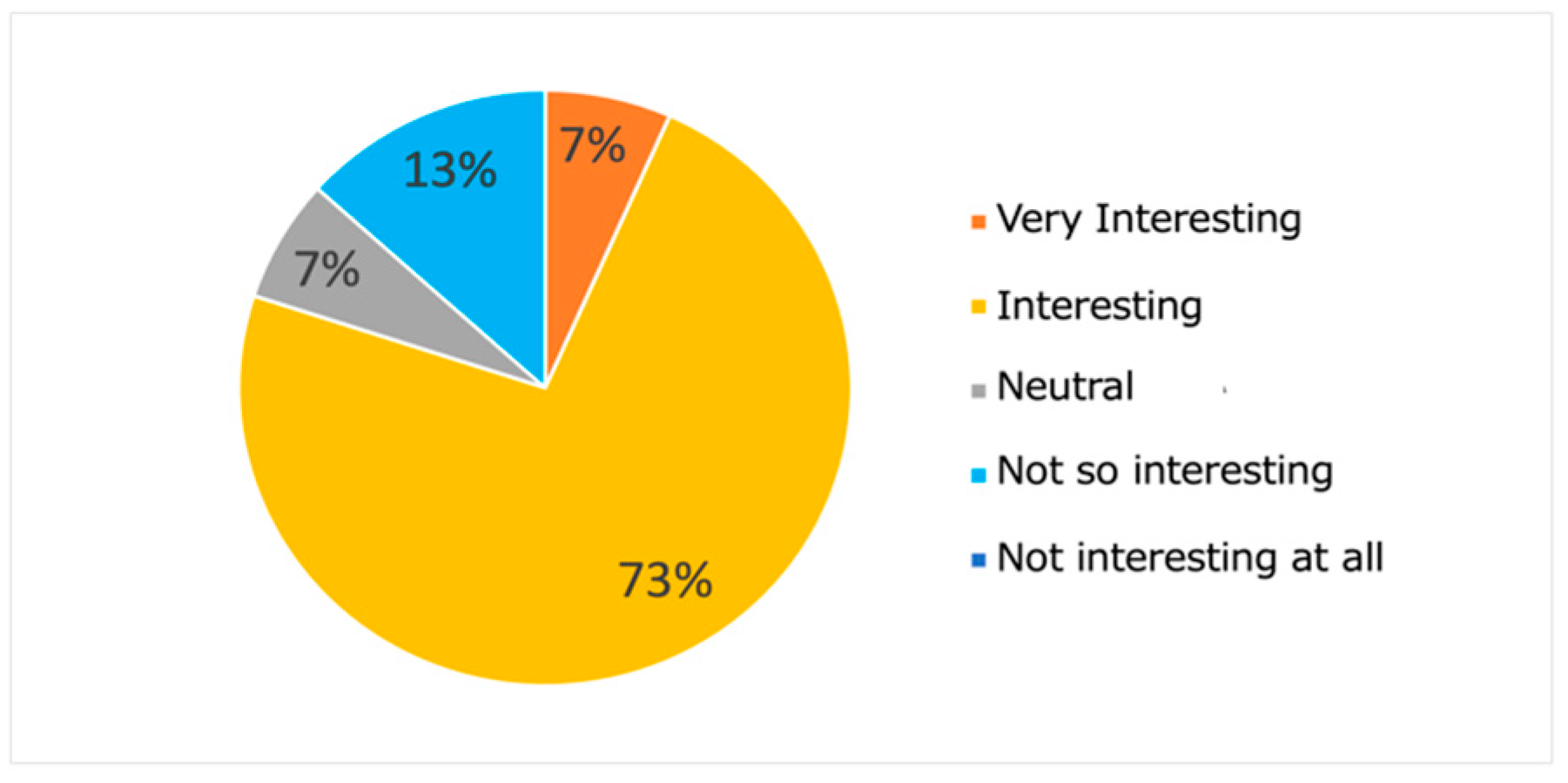
Figure 20 and Figure 21 show the results of the questionnaire administrated to the subjects. From the results presented in Figure 21, we note that the proposed system was able to present interesting and surprising learning contents to most (80%) subjects. Such results seem to suggest the meaningfulness of the proposed approach, which makes it possible to learn the features of contents that match each learner’s interests. Moreover, the results presented in Figure 22 show that most subjects (80%) declared that they were able to experience serendipity through their interaction with the system.
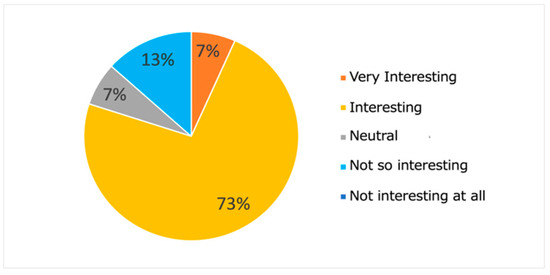
Figure 21.
Results of Q1.
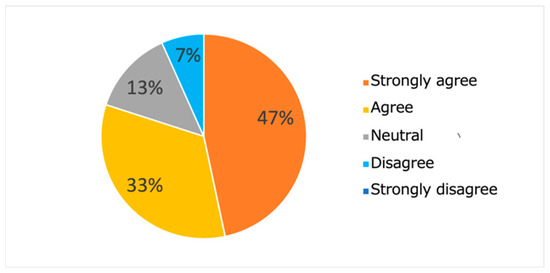
Figure 22.
Results of Q2.
5.4. Discussion
The outcomes detailed above offer valuable insights while raising important theoretical considerations. From an algorithmic perspective, our observations indicate that the proposed learning path optimization method exhibited a promising performance, evidenced by decreasing DTW values throughout the learning journey. However, viewing this through Self-Determination Theory (SDT) [28], we must critically examine whether such algorithmic optimization truly supports or potentially constrains learner autonomy, a key component of SDT’s psychological needs framework.
Crucially, the majority of participants reported finding system-recommended paths intriguing and surprising. These results are in line with the pilot study reported in a prior short paper [64]. While this positive reception appears linked to our system’s comprehensive support for the three serendipity-inducing factors delineated in Section 3, constructivist learning theory suggests we should question whether these surprising discoveries led to meaningful knowledge construction [65]. The expanded sample size and consistent results across participants underscore the system’s potential for promoting serendipitous learning experiences, though questions remain about the depth and permanence of such learning outcomes.
The convergence of DTW values near 0 around the last generation demonstrates technical success in generating paths similar to database entries. However, through the lens of Kaufmann’s search space theory, this convergence raises critical questions about whether optimal algorithmic performance necessarily translates to optimal learning experiences. Are we potentially limiting the diversity of discoveries in pursuit of mathematical optimization?
Gritton’s work on serendipitous discovery [54] suggests that unveiling hidden connections between ideas can stimulate ‘out-of-the-box’ thinking and challenge existing mental models. Building on this theoretical foundation, our results indicate that the system enhanced learners’ capacity to recognize seemingly unrelated connections within scientific discoveries. Yet, we must critically consider whether system-mediated serendipity differs qualitatively from natural serendipitous discoveries.
Our approach to supporting learners’ agency through interactive Genetic Algorithms aligns with Brennan’s theoretical framework of resource accessibility [22]. The two-phase design (exploration followed by recommendation) reflects Vygotsky’s scaffolding principle, where initial exploration builds the foundation for guided discovery [66]. However, this raises important questions about the balance between algorithmic guidance and genuine learner autonomy. The system’s success in stimulating curiosity and exploratory behavior must be weighed against the potential for algorithmic determinism.
In the broader context of lifelong learning theory, our work demonstrates the feasibility of recommender systems that balance learner preferences with serendipitous discovery [2]. Yet, critical questions emerge about long-term learning impacts and the role of prior knowledge in shaping serendipitous experiences. The system serves as a proof of concept while highlighting the need for longitudinal studies of learning outcomes.
In summary, while our evaluation results are generally positive, they prompt important theoretical considerations. Through the lens of SDT and constructivist learning theory, we can see that IEC-driven recommender systems can support learner agency while facilitating serendipitous discovery. The favorable user satisfaction findings validate our core hypothesis while raising questions about the nature of system-mediated serendipity. Our qualitative approach aligns with recommendations from learning-support-oriented recommender systems research [26,42], emphasizing user-centered metrics for understanding social, affective, and conceptual dimensions. However, future work must address how such systems influence long-term learning trajectories and knowledge construction processes.
5.5. Limitations and Future Works
While this study has met its objectives, it is not without limitations, which we acknowledge. Constructing recommender systems aimed at suggesting serendipitous items presents inherent challenges, as what constitutes serendipity for a user and how to generalize this across diverse learning activities remain open questions.
In this study, to assess the effectiveness of the proposed system in promoting serendipitous learning experiences, we explicitly asked users to rate the interestingness of the presented paths on a scale of 0 to 5 during their interaction with the system. This approach allowed us to directly track users’ perceptions of the quality and relevance of the recommended contents. However, the evaluation primarily focused on user interest and overall perceptions of serendipity, leaving room for a more granular assessment of the novelty and unexpectedness of individual recommended paths in future studies. While user interest is a crucial factor in assessing the system’s performance, it does not fully capture the nuances of serendipity, such as the degree of surprise or the extent to which the recommended paths deviate from users’ expectations.
Moreover, serendipity was measured using only two post-task questions, providing only a high-level indicator of users’ overall serendipitous experiences. We acknowledge that this approach, while informative, may not fully capture the complex and multifaceted nature of serendipity in learning contexts.
To address these limitations, future research should conduct more extensive evaluations that separately probe the novelty, unexpectedness, and serendipity of specific paths. This could involve asking users to rate each recommended path along these distinct dimensions, enabling a more fine-grained analysis of the system’s serendipity-inducing capabilities. Additionally, gathering qualitative user feedback through interviews or open-ended survey questions could provide deeper insights into how users perceive and experience the system’s recommendations.
By combining quantitative ratings with qualitative feedback, future studies can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how the system’s recommendations are experienced and identify specific aspects that contribute to or hinder serendipitous learning experiences. This knowledge can then inform further enhancements to the system’s algorithms and user interface, ultimately improving its ability to promote serendipity in informal learning contexts. Additionally, the relatively modest number of participants in the experimental evaluation and the size of the path database may be perceived as limitations, although we contend that these factors do not fundamentally undermine the core findings of this study.
Furthermore, the participants in our experimental evaluation were university students majoring in science-related fields, including computer science, and electrical engineering. While this sample provides a relevant target audience for evaluating a system designed to recommend scientific content, we acknowledge that the participants’ prior knowledge and familiarity with the domain may influence their perceptions of novelty and serendipity. Future studies should investigate the system’s effectiveness with learners from diverse educational backgrounds and expertise levels to assess its generalizability and potential for promoting serendipitous discovery across a wider spectrum of learners.
Our future endeavors will also focus on further substantiating the observed trends through comprehensive research efforts. One of the key challenges in implementing and sustaining a serendipity-oriented recommendation system for informal learning is the maintainability of the content Knowledge Graph. As scientific knowledge continues to evolve and expand, it is crucial to ensure that the system’s content remains up-to-date and comprehensive. This requires ongoing efforts to identify and integrate new sources of information, as well as to validate and update existing knowledge representations. To this end, expanding the scale of the knowledge database to encompass a broader spectrum of learning content will be a priority. For instance, we could explore the integration of additional authoritative sources, such as academic publications and expert-curated online resources, to expand the scope and depth of the Knowledge Graph. Additionally, the use of collaborative content curation approaches, where learners actively contribute to the creation and refinement of the Knowledge Graph, can be promising. This could involve the development of user-friendly interfaces and incentive mechanisms to encourage user participation and ensure the quality and reliability of user-generated content. Moreover, the development of semi-automated techniques for knowledge extraction and graph construction, such as natural language processing and machine learning, could help to streamline the process of updating and maintaining the Knowledge Graph as new scientific discoveries emerge. This expansion will enable the proposed system to recommend more diverse content, thereby enhancing the prospects of inducing serendipity. Achieving this involves importing learning content in machine-readable formats, ideally structured as Knowledge Graphs.
Another promising direction for enhancing the effectiveness and personalization of the proposed recommendation system is the incorporation of a learner/user model. By capturing and leveraging information about individual learners’ background knowledge, interests, learning preferences, and interaction history, the system could generate more targeted and relevant learning path recommendations. However, the implementation of a learner/user model also raises important technical and ethical considerations. From a technical perspective, the system must be able to efficiently store, update, and protect user data, while ensuring the scalability and robustness of the user modeling algorithms. From an ethical perspective, it is crucial to obtain learners’ informed consent, protect their privacy, and provide them with control over their personal data.
6. Conclusions
The process of gaining fresh insights or discovering intriguing connections between seemingly disparate pieces of information represents a rewarding facet of the learning journey. Such experiences have the potential to transform learners’ existing assumptions, fuel exploration, and inspire investigations that lead to the construction of new knowledge [17].
In this paper, we have introduced and rigorously evaluated a serendipity-oriented learning content recommendation system. This system was meticulously designed to propose learning content that not only captures learners’ interest but also introduces elements of novelty and unexpectedness within an informal learning environment. At its core, our proposed system features a content optimization algorithm that harnesses the power of Interactive Genetic Algorithms and Knowledge Graphs to discern the characteristics of historical discoveries and inventions likely to intrigue, surprise, and captivate each individual learner.
Our research journey encompassed both numerical simulations, affirming the effectiveness of the content optimization algorithm, and an experimental evaluation involving real users. The results of our experiments hint at the significance of our approach in fostering serendipitous moments within learners. Notably, the majority of participants reported finding certain learning content recommended by the system to be both interesting and unexpected. This outcome substantiates our hypothesis that the proposed system possesses the capacity to suggest valuable items, thus facilitating serendipity within learners in informal learning settings.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that the unpredictable nature of serendipitous learning renders the conceptualization and measurement of its influencing factors, processes, and outcomes a complex endeavor. Thus, our future efforts will be dedicated to further substantiating the trends and findings presented in this paper.
The development of learning support systems capable of kindling learners’ intrinsic motivation to proactively explore the learning environment by presenting captivating and inspiring content represents a promising avenue for research and development within the realm of technology-enhanced education. We aspire that this work will serve as a stepping stone toward the realization of technology-mediated learning support that transcends predefined and pre-designed instruction, fostering an environment where learners embark on journeys of self-directed discovery and knowledge construction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, S.I.; writing—review and editing, data curation, funding acquisition, E.A.; conceptualization, methodology, H.T.; supervision, review and editing, M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers #21K12099 and #22K18011.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional Review Board Statement: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Review Committee of the Organization for Research and Development of Innovative Science and Technology (ORDIST) in Kansai University, with the date of approval 24 January 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
All of the data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ricci, F.; Rokach, L.; Shapira, B. Recommender systems: Introduction and challenges. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drachsler, H.; Verbert, K.; Santos, O.C.; Manouselis, N. Panorama of recommender systems to support learning. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 421–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, M.D. Collaborative Filtering Recommender Systems; Foundations and Trends® in Human–Computer Interaction: Hanover, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 81–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lops, P.; De Gemmis, M.; Semeraro, G. Content-based recommender systems: State of the art and trends. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, K.; Hattori, F. Fusion-based recommender system for serendipity-oriented recommendations. J. Jpn. Soc. Fuzzy Theory Intell. Inform. 2013, 25, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaquinta, L.; de Gemmis, M.; Lops, P.; Semeraro, G.; Filannino, M.; Molino, P. Introducing serendipity in a content-based recommender system. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 10–12 September 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Gup, T. Technology and the end of serendipity. Educ. Dig. 1997, 66, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pardos, Z.A.; Jiang, W. Designing for serendipity in a university course recommendation system. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Analytics & Knowledge, Frankfurt, Germany, 23–27 March 2020; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Lenox, R.S. Educating for the serendipitous discovery. J. Chem. Educ. 1985, 62, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiane, O.R. Building a recommender agent for e-learning systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computers in Education, Auckland, New Zealand, 3–6 December 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra, M.J.; Serrano, C.; Navarro, A.F. Recommender system to identify students with learning deficiencies in assessments. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Computers in Education (SIIE), Salamanca, Spain, 13–15 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rismanto, R.; Syulistyo, A.R.; Agusta, B.P.C. Research supervisor recommendation system based on topic conformity. Int. J. Mod. Educ. Comput. Sci. 2020, 12, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.S. Three princes of Serendip. Science 1963, 141, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotkov, D.; Konstan, J.A.; Zhao, Q.; Veijalainen, J. Investigating serendipity in recommender systems based on real user feedback. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Pau, France, 9–13 April 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1341–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, T.S. Historical structure of scientific discovery: To the historian discovery is seldom a unit event attributable to some particular man, time, and place. Science 1962, 136, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoskopf, M.K. Observation and cogitation: How serendipity provides the building blocks of scientific discovery. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Séaghdha, D.Ó.; Quercia, D.; Jambor, T. Auralist: Introducing serendipity into music recommendation. In Proceedings of the Fifth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 February 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Adamopoulos, P.; Tuzhilin, A. On unexpectedness in recommender systems: Or how to better expect the unexpected. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2014, 5, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchem, I. Serendipitous learning: Recognizing and fostering the potential of microblogging. Form@Re Open J. Form. Rete 2013, 11, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, A.; Deegan, J.G. Three principles of Serendip: Insight, chance, and discovery in qualitative research. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Educ. 1996, 9, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, O. Serendipity: Towards a taxonomy and a theory. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, K. Best of Both Worlds: Issues of Structure and Agency in Computational Creation, in and Out of School. Doctoral Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, M.S. Glasgow Caledonian University. Self-Directed Learning: A Guide for Learners and Teachers; Granary Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jézégou, A.; Carré, P.; Kaplan, J.; Cyrot, P.; Noel, D. L’autoformation: The state of research on self-directed learning in France. Int. J. Self-Dir. Learn. 2011, 8, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, L.M. Self-determined learning (heutagogy) and digital media creating integrated educational environments for developing lifelong learning skills. In The digital Turn in Higher Education; Kergel, D., Heidkamp, B., Telléus, P., Rachwal, T., Nowakowski, S., Eds.; Springer VS: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemenčič, M. From student engagement to student agency: Conceptual considerations of European policies on student-centered learning in higher education. High. Educ. Policy 2017, 30, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Hew, K.F. Examining learning engagement in MOOCs: A self-determination theoretical perspective using mixed method. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2020, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation from a self-determination theory perspective: Definitions, theory, practices, and future directions. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 61, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajda, J.; Zajda, J. Constructivist learning theory and creating effective learning environments. In Globalisation and Education Reforms: Creating Effective Learning Environments; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Aladjem, R.; Nachmias, R. The mobile as an ad hoc PLE: Learning serendipitously in urban contexts. In Learning and Diversity in the Cities of the Future; Logos: Berlin, Germany, 2014; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Vygotsky, L.S.; Cole, M. Mind in Society: Development of Higher Psychological Processes; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Konstan, J.A.; Riedl, J. Recommender systems: From algorithms to user experience. User Model. User Adapt. Interact. 2012, 22, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, O.C.; Boticario, J.G. Practical guidelines for designing and evaluating educationally oriented recommendations. Comput. Educ. 2015, 81, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.L.; Slodkowski, B.K.; da Silva, K.K.A.; Cazella, S.C. A systematic literature review on educational recommender systems for teaching and learning: Research trends, limitations and opportunities. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 3289–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, S.; Sheldon, F. Systematic review of recommendation systems for course selection. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 560–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, N.W.; Ferdiana, R.; Kusumawardani, S.S. A systematic review of learning path recommender systems. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 7437–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, D.; Maclachlan, A. Slope one predictors for online rating-based collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 2005 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 21–23 April 2005; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Aucancela, M.; Briones, A.; Chamoso, P. Educational recommender systems: A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the Barcelona Conference on Education 2023: Official Conference Proceedings, Barcelona, Spain, 19–23 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, F.L. The research trends in recommender systems for e-learning: A systematic review of SSCI journal articles from 2014 to 2018. Asian Assoc. Open Univ. J. 2019, 14, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschênes, M. Recommender systems to support learners’ agency in a learning context: A systematic review. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2020, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drachsler, H.; Hummel, H.G.K.; Koper, R. Personal recommender systems for learners in lifelong learning networks: The requirements, techniques and model. Int. J. Learn. Technol. 2008, 3, 404–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, S.; Loni, B.; Drachsler, H.; Sloep, P. Which recommender system can best fit social learning platforms? In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning, Graz, Austria, 16–19 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 84–97. [Google Scholar]
- Fazeli, S.; Drachsler, H.; Bitter-Rijpkema, M.; Brouns, F.; van der Vegt, W.; Sloep, P.B. User-centric evaluation of recommender systems in social learning platforms: Accuracy is just the tip of the iceberg. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2018, 11, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H. Interactive evolutionary computation: Fusion of the capabilities of EC optimization and human evaluation. Proc. IEEE 2001, 89, 1275–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gong, D. Surrogate model-assisted interactive genetic algorithms with individual’s fuzzy and stochastic fitness. J. Control Theory Appl. 2010, 8, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, C.; Johnston, V.S. Tracking a criminal suspect through “face-space” with a genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Genetic Algorithms, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–16 July 1991; pp. 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, S.B. Accelerating evolution by direct manipulation for interactive fashion design. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Applications (ICCIMA), Yokusika, Japan, 30 October–1 November 2001; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Tokui, N.; Iba, H. Music composition with interactive evolutionary computation. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Generative Art, Milan, Italy, 14–16 December 2000; Volume 17, pp. 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, H.; Ohsaki, M. Interactive evolutionary computation-based hearing aid fitting. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2007, 11, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, M.; Inoue, M.; Imai, J. User’s favorite scent design using paired comparison-based interactive differential evolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibuchi, H.; Sudo, T.; Nojima, Y. Interactive evolutionary computation with minimum fitness evaluation requirement and offline algorithm design. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, R.G.; Hiemstra, R. Self-Direction in Adult Learning: Perspectives on Theory, Research and Practice; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Olshannikova, E.; Olsson, T.; Huhtamäki, J.; Paasovaara, S.; Kärkkäinen, H. From chance to serendipity: Knowledge workers’ experiences of serendipitous social encounters. Adv. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2020, 2020, 1827107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritton, J. Can Serendipitous Browsing Lead to Serendipitous Learning? 2007. Available online: http://www.futurelab.org.uk/resources/publications-reports-articles/web-articles/Web-Article795 (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Hart-Davis, A. (Ed.) Science: The Definitive Visual Guide; Dorling Kindersley Ltd.: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, A.; Barbosa, D.; Firmani, D.; Matinata, A.; Merialdo, P. Knowledge graph embedding for link prediction: A comparative analysis. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2021, 15, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoe, H.; Chiba, S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1978, 26, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgino, T. Computing and visualizing dynamic time warping alignments in R: The dtw package. J. Stat. Softw. 2009, 31, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynamic Time Warp Algorithm Package. Available online: https://github.com/DynamicTimeWarping/dtw-python (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- March, J.G. Exploration and exploitation in organizational learning. Organ. Sci. 1991, 2, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, S.; Levin, S. Towards a general theory of adaptive walks on rugged landscapes. J. Theor. Biol. 1987, 128, 11–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, S.; Kay, J. SMILI☺: A framework for interfaces to learning data in open learner models, learning analytics and related fields. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2016, 26, 293–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J. Learner know thyself: Student models to give learner control and responsibility. In International Conference on Computers in Education; Halim, Z., Ottomann, T., Razak, Z., Eds.; AACE: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1997; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ayedoun, E.; Inoue, S.; Takenouchi, H.; Tokumaru, M. Combining IGA and KG for serendipitous learning contents recommendation. In Proceedings of the Fourth Knowledge-Aware and Conversational Recommender Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 22 September 2022; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hmelo-Silver, C.E.; Duncan, R.G.; Chinn, C.A. Scaffolding and achievement in problem-based and inquiry learning: A response to Kirschner, Sweller, and Clark (2006). Educ. Psychol. 2007, 42, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.; Bruner, J.S.; Ross, G. The role of tutoring in problem solving. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1976, 17, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).