Serosurvey of IgG Antibodies against Bartonella henselae and Rickettsia typhi in the Population of Attica, Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
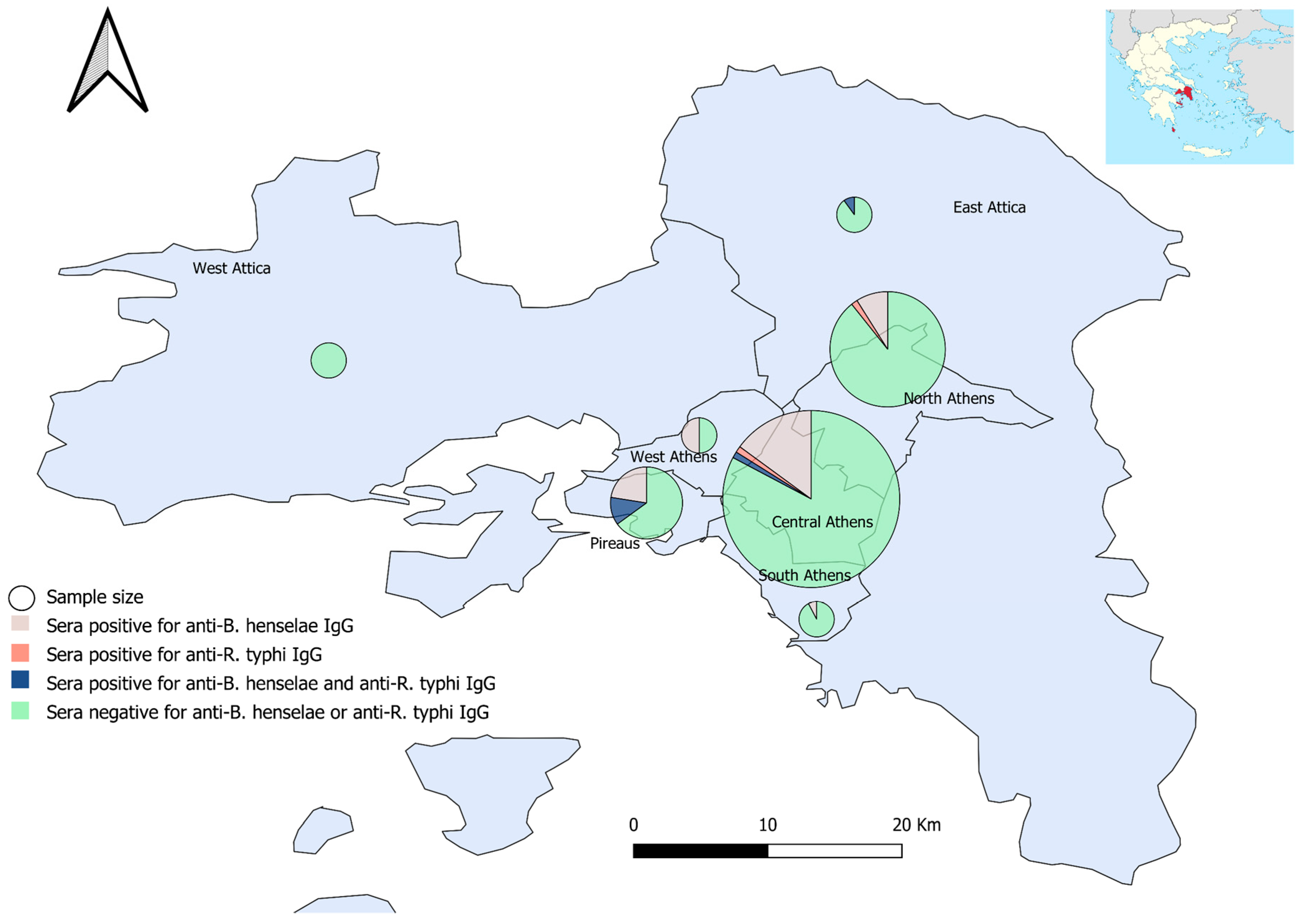
3.1. Study Subjects
3.2. IgG Antibodies Prevalence Rates
3.3. Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Álvarez-Fernández, A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Solano-Gallego, L. Bartonella infections in cats and dogs including zoonotic aspects. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsioutis, C.; Zafeiri, M.; Avramopoulos, A.; Prousali, E.; Miligkos, M.; Karageorgos, S.A. Clinical and laboratory characteristics, epidemiology, and outcomes of murine typhus: A systematic review. Acta Trop 2017, 166, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouffok, N.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Murine typhus, Algeria. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Warashina, W.R.; Sturgeon, M.M.; Buchholz, A.E.; Olmsted, G.K.; Park, S.Y.; Effler, P.V.; Karpathy, S.E. Rickettsia typhiand R.felis in Rat Fleas (Xenopsylla cheopis), Oahu, Hawaii. Emerg Infect. Dis 2008, 14, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civen, R.; Ngo, V. Murine Typhus: An Unrecognized Suburban Vectorborne Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheslock, M.A.; Embers, M.E. Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, S.; Andrade, G.C.D.; Cavalcanti, C.; Nascimento, H. Cat Scratch Disease: Not a Benign Condition. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2017, 26, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbacher, M.E.; Klotz, S.; Klotz, J.; Pinnas, J.L. Bartonella henselae and the Potential for Arthropod Vector-Borne Transmission. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhsira, E.; Ferrandez, Y.; Liu, M.; Franc, M.; Boulouis, H.J.; Biville, F. Ctenocephalides felis an in vitro potential vector for five Bartonella species. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Boulouis, H.J.; Breitschwerdt., E.B. Cat scratch disease and other zoonotic Bartonella infections. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Stuckey, M.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Henn, J.B.; Koehler, J.E.; Chang, C.C. Experimental infection of cats with Afipia felis and various Bartonella species or subspecies. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, P.P.; Maggi, R.G.; Schwartz, D.S.; Cadenas, M.B.; Bradley, J.M.; Hegarty, B.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Canine bartonellosis: Serological and molecular prevalence in Brazil and evidence of co-infection with Bartonella henselae and Bartonella vinsonii subsp.berkhoffii. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tea, A.; Arvanitidou, M.; Antoniadis, A.; Diza, E.; Alexiou-Daniel, S. Occurrence of Bartonella Henselae And Bartonella Quintana In A Healthy Greek Population. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, H.Y.; Im, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Baek, J.H.; Durey, A.; Park, S.G.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, J.S. The seroprevalence of Bartonella henselae in healthy adults in Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Łysakowska, M.E.; Brzezińska, O.; Szybka, M.; Konieczka, M.; Moskwa, S.; Brauncajs, M.; Makowska, J.; Pastuszak-Lewandoska, D.; Grzegorczyk, J. The seroprevalence of Bartonella spp. in the blood of patients with musculoskeletal complaints and blood donors, Poland: A pilot study. Clin. Rheumatol 2019, 38, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Li, D. Bartonella and Bartonella infections in China: From the clinic to the laboratory. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, I.; Sanfeliu, I.; Cardeñosa, N.; Nogueras, M.M.; Font, B.; Segura, F. Serological evidence of Bartonella henselaeinfection in healthy people in Catalonia, Spain. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.A.; Manika, K.; Arvanmdou, M.; Antoniadis, A. Prevalence of Rickettsia conorii and Rickettsia typhi infections in the population of northern Greece. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños-Rivero, M.; Santana-Rodriguez, É.; Ángel-Moreno, A.; Hernández-Cabrera, M.; Limiñana-Canal, J.M.; Carranza-Rodríguez, C.; Antonio-Manuel Martín-Sánchez, A.M.; Pérez-Arellano, J.L. Seroprevalence of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia conorii infections in the Canary Islands. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e481–e485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, M.Y.; Weinstein, P.; Bell, A.; Hambling, T.; Tompkins, D.M.; Slaney, D. Seroprevalence of antibodies to Rickettsia typhi in the Waikato region of New Zealand. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Shan, A.; Mathew, B.; Yin, J.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.; Xu, J.; Dumler, J.S. Rickettsial Seroepidemiology among Farm Workers, Tianjin, People’s Republic of China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 938–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosoy, M.; Bai, Y. Bartonella Bacteria in Urban Rats: A Movement from the Jungles of Southeast Asia to Metropoles Around the Globe. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billeter, S.A.; Gundi, V.A.; Rood, M.P.; Kosoy, M.Y. Molecular Detection and Identification of Bartonella Species in Xenopsylla cheopis Fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) Collected from Rattus norvegicus Rats in Los Angeles, California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7850–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Psaroulaki, A.; Papaeustathiou, A.; Loukaides, F.; Tselentis, Y.; Antoniou, M.; Toumazos, P. First Detection of Rickettsia Felis In Ctenocephalides Felis Fleas Parasitizing Rats in Cyprus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R.; Krasnov, B.; Morick, D.; Gottlieb, Y.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Harrus, S. Bartonella infection in rodents and their flea ectoparasites: An overview. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Wardrop, N.; Chang, C.-T.; Wang, H.-C.; Atkinson, P.M. Significance of major international seaports in the distribution of murine typhus in Taiwan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005589. [Google Scholar]
- Mane, A.; Kamble, S.; Singh, M.K.; Ratnaparakhi, M.; Nirmalkar, A.; Gangakhedkar, R. Seroprevalence of spotted fever group and typhus group rickettsiae in individuals with acute febrile illness from Gorakhpur, India. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 79, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeulen, M.J.; Verbakel, H.; Notermans, D.W.; Reimerink, J.H.J.; Peeters, M.F. Evaluation of sensitivity, specificity and cross-reactivity in Bartonella henselae serology. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, P.S.G.D.; Brigatte, M.E.; Greco, D.B. Antibodies to Rickettsia rickettsii, Rickettsia typhi, Coxiella burnetii, Bartonella henselae, Bartonella quintana, and Ehrlichia chaffeensis among healthy population in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2005, 100, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, Y.T.; Hii, S.F.; Stevenson, M.A.; Graves, S.; Rees, R.; Stenos, J.; Traub, R.J. Serological evidence of exposure to Rickettsia felis and Rickettsia typhi in Australian veterinarians. Parasit Vectors 2017, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maina, A.N.; Fogarty, C.; Krueger, L.; Macaluso, K.R.; Odhiambo, A.; Nguyen, K.; Farris, C.M.; Luce-Fedrow, A.; Bennett, S.; Ju, J.J.; et al. Rickettsial Infections among Ctenocephalides felis and Host Animals during a Flea-Borne Rickettsioses Outbreak in Orange County, California. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Persichetti, M.; Solano-Gallego, L.; Serrano, L.; Altet, L.; Reale, S.; Masucci, M.; Pennisi, M. Detection of vector-borne pathogens in cats and their ectoparasites in southern Italy. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nogueras, M.; Pons, I.; Ortuño, A.; Lario, S.; Segura, F. Rickettsia felis in Fleas from Catalonia (Northeast Spain). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edouard, S.; Nabet, C.; Lepidi, H.; Fournier, P.; Raoult, D. Bartonella, a Common Cause of Endocarditis: A Report on 106 Cases and Review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 53, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Anti-B. henselae IgG | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titre | No (%) | ||||||
| <1/64 | 1/64 | 1/128 | 1/256 | 1/512 | 1/1024 | ||
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 64 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 15 (7.4) |
| Female | 102 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 21 (10.4) |
| Age group | |||||||
| ≤14 years | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (1.0) |
| 15–29 years | 16 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 (2.0) |
| 30–50 years | 50 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 17 (8.4) |
| >50 years | 96 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 13 (6.4) |
| Contact with cats | |||||||
| Yes | 59 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 11 (5.4) |
| No | 107 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 25 (12.4) |
| Contact with dogs | |||||||
| Yes | 87 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 13 (6.4) |
| No | 79 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 23 (11.4) |
| Total No (%) | 166 (82.2) | 13 (6.4) | 9 (4.5) | 9 (4.5) | 5 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 202 (100.0) |
| Anti-R. typhiIgG | |||||||
| Titre | No (%) | ||||||
| <1/40 | 1/40 | 1/80 | 1/160 | 1/320 | 1/640 | ||
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 77 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (1.0) |
| Female | 116 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 (3.5) |
| Age group | |||||||
| ≤14 years | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0.0) |
| 15–29 years | 19 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.5) |
| 30–50 years | 62 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (2.5) |
| >50 years | 106 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (1.5) |
| Contact with cats | |||||||
| Yes | 67 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (1.5) |
| No | 126 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 (3.0) |
| Contact with dogs | |||||||
| Yes | 96 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 (2.0) |
| No | 97 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (2.5) |
| Total No (%) | 193 (95.5) | 8 (4.0) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 202 (100.0) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dougas, G.; Mavrouli, M.; Tsakris, A.; Billinis, C.; Papaparaskevas, J. Serosurvey of IgG Antibodies against Bartonella henselae and Rickettsia typhi in the Population of Attica, Greece. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030145
Dougas G, Mavrouli M, Tsakris A, Billinis C, Papaparaskevas J. Serosurvey of IgG Antibodies against Bartonella henselae and Rickettsia typhi in the Population of Attica, Greece. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(3):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030145
Chicago/Turabian StyleDougas, Georgios, Maria Mavrouli, Athanassios Tsakris, Charalambos Billinis, and Joseph Papaparaskevas. 2020. "Serosurvey of IgG Antibodies against Bartonella henselae and Rickettsia typhi in the Population of Attica, Greece" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 3: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030145
APA StyleDougas, G., Mavrouli, M., Tsakris, A., Billinis, C., & Papaparaskevas, J. (2020). Serosurvey of IgG Antibodies against Bartonella henselae and Rickettsia typhi in the Population of Attica, Greece. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(3), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030145








