Self-Supervised Foundation Model for Template Matching
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The high degree of generalization eliminates the need to retrain the model with real data;
- If further training (fine-tuning) is still necessary, very few images of the real data are needed until the desired accuracy is reached;
- The specially designed encoder is trained on the task of locating a searched object, which differs from the standard approaches of using a network trained on some other tasks, most often classification or a more general one;
- The integrated correlation operator we use provides real information about the location of the searched object, rather than being a separate layer of the network [15,16] which has to be further trained and decoded by one or more neural networks. This approach has not been found in the literature so far;
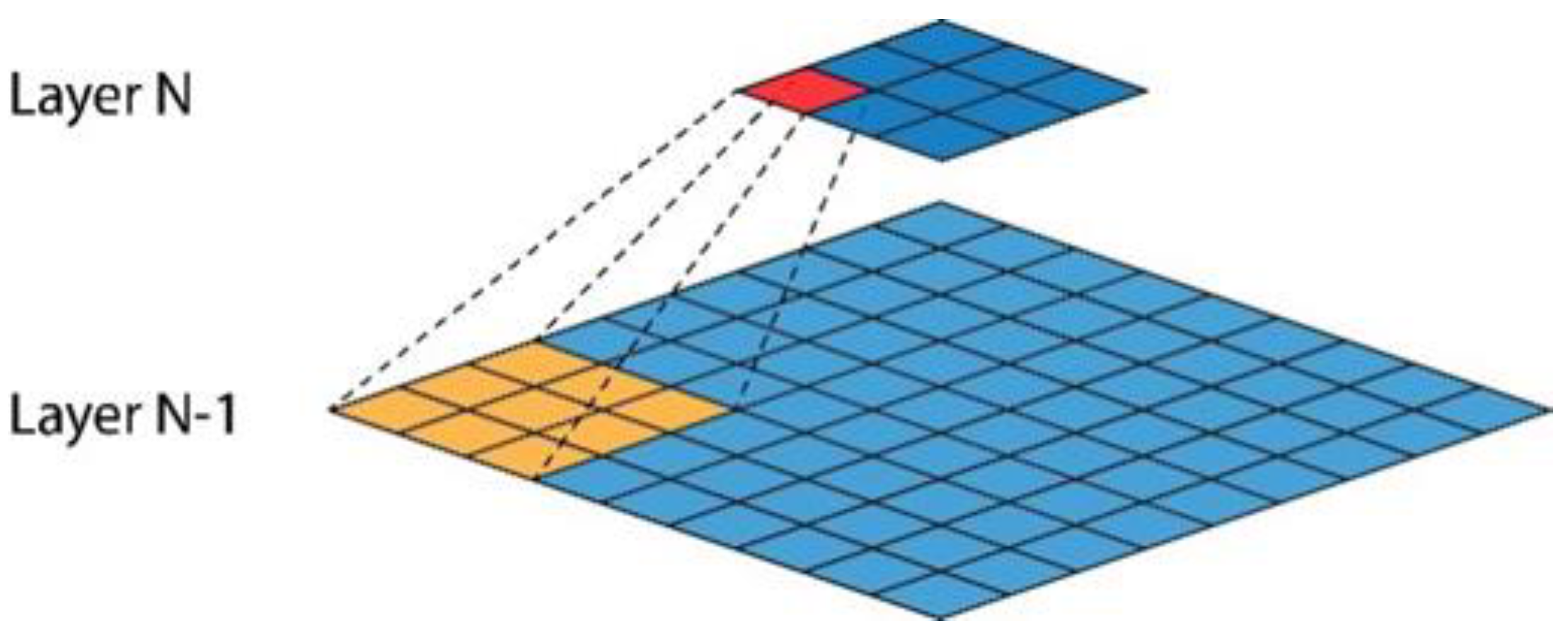
- Hierarchical propagation of activations from the last to the first layer leads to precise localization while precluding the need to use an additional decoder that needs to be trained. The result is an extremely simplified and lightweight architecture, while providing high accuracy. This approach has not been found in the literature so far;
- Two-step self-supervised training, involving two types of data augmentations: color augmentation and color and geometric augmentations;
- Self-TM is rotationally invariant. In this work, the Self-TM models’ family is trained over the entire interval from −90 to +90 degrees.
2. Related Work
2.1. Hand-Crafted Methods
2.2. Learnable Methods
2.3. Foundation Models
3. Theoretical Formulation of the Proposed Method
3.1. Model
3.2. Data
3.3. Training
- An input image I is taken from an unannotated image database, to which a random crop is applied, and then resized by to 189 × 189 pixels, yielding a “query” image, (see Figure 1);
- Another random crop is performed on , and then, random image augmentations (color and/or geometric) modifies the input image to obtain a “template” image, (see Figure 1). This step can produce one or many different templates. In the Self-TM training, only two “template” numbers are used;
- The position (ground truth position) of the resulting “template” on the “query” image is stored (the coordinates of the red rectangle’s center on “query” (see Figure 1);
- “Query” and the two templates are fed as inputs to the Self-TM network, , and the resulting feature maps from all layers are stored, , , where is the number of the network’s layers. In the current architecture, the number of layers is 3, denoted above by first, mid, and last;
- A correlation operator is applied to every two corresponding feature maps sequentially starting from the deepest layer. Then, the position of the maximum value (predicted position), , is found on its output (see “hierarchical activations propagation” in Figure 1);
- A mean squared error is calculated on every two corresponding feature maps, , where is the region of summation, i.e., the intersection of the two definition domains of the “template” feature map and the “query” feature map , . Multiplication is scalar, i.e., elementwise in ;
- Parameter optimization (gradient descent) is performed by minimizing the errors obtained from and the offset of the positions of , relative to the real positions of the template , which is possible due to compatibility of positions (in pixels).
3.4. Augmentation
3.4.1. Color Augmentations
- To obtain the “query” image, the following steps are applied sequentially:
- ○
- Random crop: scale from 0.1 to 0.9;
- ○
- Rescale: 189 × 189 pixels;
- ○
- Normalization: mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std = [0.228, 0.224, 0.225], computed on ImageNet;
- To obtain the two “templates” on the “query”, the following steps are applied sequentially:
- ○
- Random color jitter with an independent probability * of 80%: brightness = 0.4, contrast = 0.4, saturation = 0.2, and hue = 0.1;
- ○
- Random grayscale with an independent probability * of 20%;
- ○
- For “template” 1:
- ▪
- Random Gaussian blur: radius from 0.1 to 0.2;
- ○
- For “template” 2:
- ▪
- Random Gaussian blur with an independent probability * of 10%: radius from 0.1 to 2.0;
- ▪
- Random invert of all pixel values above a given threshold (solarization) with an independent probability * of 20%: threshold = 128;
- ○
- Normalization: the same as in “query”;
- ○
- Random crop: scale from 0.14 to 0.85; ratio from 0.2 to 5.0.
3.4.2. Geometric Augmentations
- Random square crop: scale from 0.14 to 0.45;
- A randomly selected geometric augmentation is applied with a 50% probability:
- ○
- Random perspective transformation: distortion scale = 0.5;
- ○
- Random rotation: degrees from −90 to +90;
- ○
- Random rescale: factor from −0.7 to 1.3.
3.5. Hierarchical Activations Propagation
3.6. Correlation
3.7. Loss
3.8. Hyperparameters/Optimization
3.9. Prediction
4. Experiments
- ImageNet-1K Test [56] showing the accuracy of template localization on data having the same modality as the training data;
- HPatches [46] evaluating the properties of feature maps as local descriptors for finding matches between different image patches in corresponding images;
- MegaDepth [47] evaluating image matching accuracy on outdoor scenes having different modality from the training data;
- ScanNet [48] evaluating image matching accuracy on indoor scenes having different modality from the training data.
4.1. ImageNet-1K Test
- An input image is taken from an unannotated dataset (ImageNet-1K test), from which a “template” is obtained. The positions of the maximum values of the correlation operator’s result are then calculated for each corresponding feature map (see training steps 1 to 5 in Section 3.3).
- For each corresponding feature map (i.e., for each layer), the position displacement measured in pixels () of is computed, relative to the actual template positions , using the Euclidean distance:where is the number of images in the dataset, and are the two-dimensional vectors of each image , and is the currently selected layer of the network ; in this case, , and for clarity, instead of , we use indexations; or is the average Euclidean distance for the deepest layer.
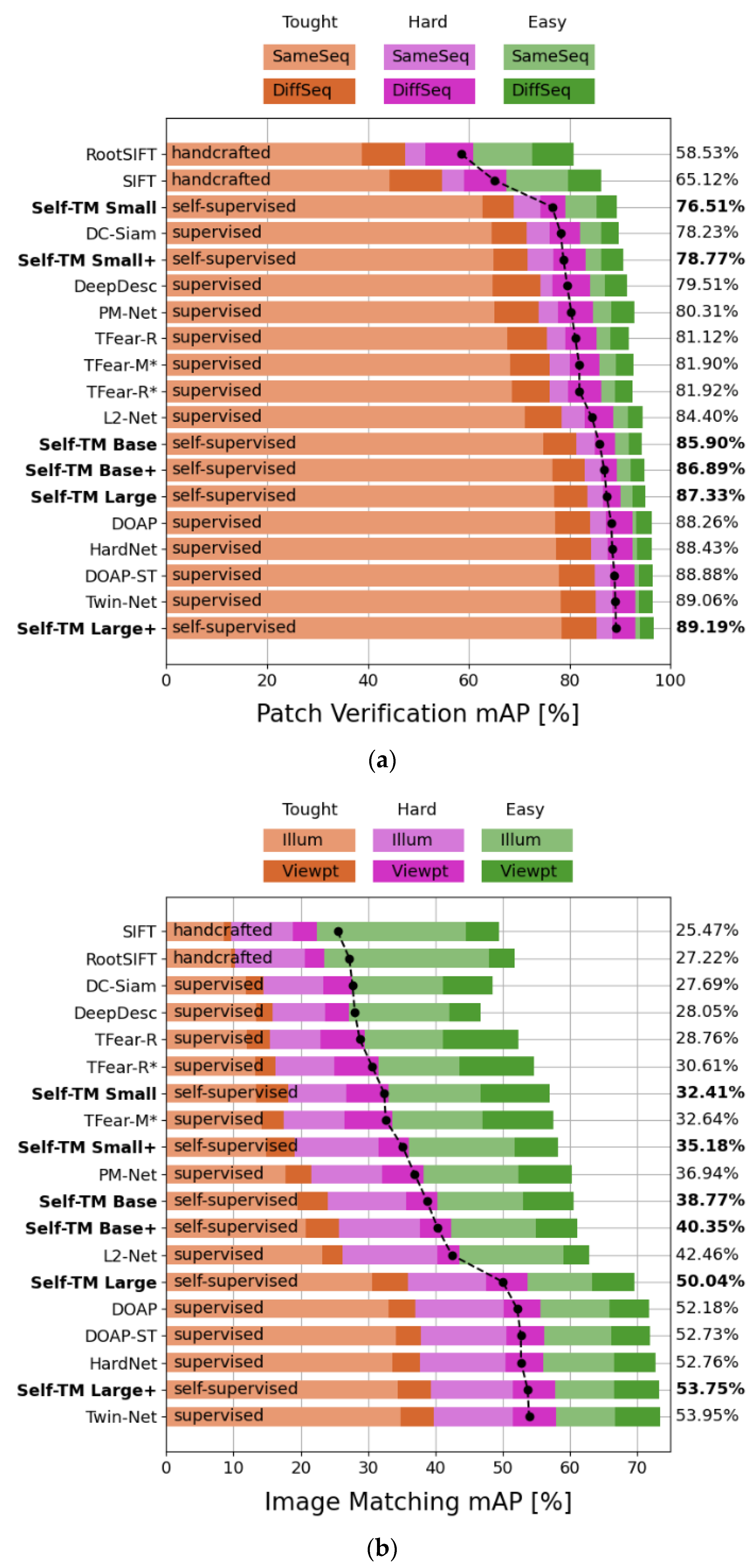
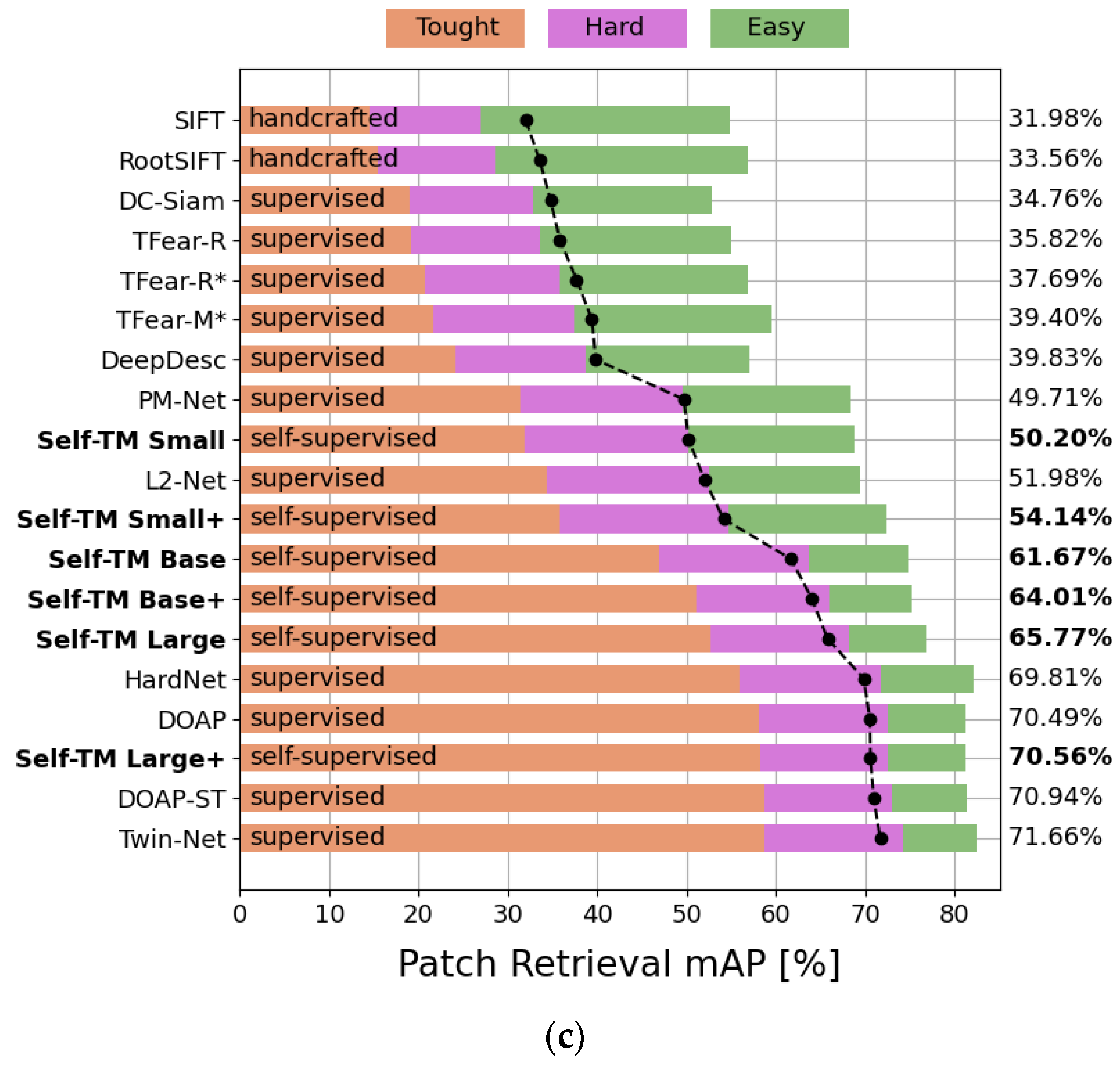
4.2. HPatches
4.3. Image Matching
5. Implementation Details
5.1. Two-Step Training
- ImageNet training (row 5 vs. row 4 in Table 9) results on the increased model accuracy: +31.77% for patch verification; +81.76% for image matching; +66.63% for patch retrieval;
- HPatches training (row 3 vs. row 1 in Table 9) results on the increased model accuracy: +9.23% for patch verification; +33.89% for image matching; +18.18% for patch retrieval.
5.2. Model Architecture
- Standard two-dimensional convolution (Conv2D) using a certain number of filters performing scalar multiplication on their input data;
- Linear layer (Linear), representing a fully connected layer where each neuron is connected to each neuron from the previous layer;
- Non-linear activation function GELU [50], used in all modern transformers.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 2020, 1, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2022, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Kim, S.; Yoo, K.; Kong, C.; Kim, J.; Kwak, N. Self-Distilled Self-Supervised Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 2828–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapos, A.; Gyires-Tóth, B. CNN-JEPA: Self-Supervised Pretraining Convolutional Neural Networks Using Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, L.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Chen, K.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. RingMo-Lite: A remote sensing lightweight network with CNN-Transformer hybrid framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H.S. Fully-Convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016 Workshops. ECCV 2016; Lecture notes in computer science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yan, J.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X. High performance visual tracking with Siamese Region Proposal network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Luo, C.; Tian, X.; Zeng, W. A twofold siamese network for real-time object tracking. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valmadre, J.; Bertinetto, L.; Henriques, J.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H.S. End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xing, J.; Yan, J. SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese Visual Tracking with Very Deep Networks. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Wu, W.; Yan, J.; Hu, W. Distractor-Aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018. ECCV 2018; Lecture notes in computer science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Ling, H. Siamese cascaded region proposal networks for real-time visual tracking. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ma, C.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J.; Lau, R.; Yang, M.-H. CREST: Convolutional Residual Learning for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S. SIAMCAR: Siamese Fully Convolutional Classification and Regression for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Bertinetto, L.; Torr, P.H.S. SiamMask: A framework for fast online object tracking and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 3072–3089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Zhai, X.; Wightman, R.; Uszkoreit, J.; Beyer, L. How to train your ViT? Data, Augmentation, and Regularization in Vision Transformers. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30, pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning 2020, Virtual Event, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisham, M.B.; Yaakob, S.N.; Raof, R.A.A.; Nazren, A.B.A.; Wafi, N.M. Template matching using sum of squared difference and normalized cross correlation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD) 2015, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 December 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niitsuma, H.; Maruyama, T. Sum of absolute difference implementations for image processing on FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Milan, Italy, 31 August–2 September 2010; Volume 33, pp. 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, C.P.; Oren, M.; Poggio, T. A general framework for object detection. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision (IEEE Cat. No. 98CH36271), Bombay, India, 7 January 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, L.; Mattoccia, S.; Tombari, F. ZNCC-based template matching using bounded partial correlation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2005, 26, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. SURF: Speeded up robust features. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2006. ECCV 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision 2011, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTone, D.; Malisiewicz, T.; Rabinovich, A. SuperPoint: Self-supervised interest point detection and description. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlin, P.-E.; DeTone, D.; Malisiewicz, T.; Rabinovich, A. SuperGlue: Learning feature matching with graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuturi, M. Sinkhorn Distances: Lightspeed computation of optimal transport. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 2292–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenberger, P.; Sarlin, P.-E.; Pollefeys, M. LightGlue: Local feature matching at light speed. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision 2023, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Karpur, A.; Cao, B.; Huang, Q.; Araujo, A. OmniGlue: Generalizable feature matching with foundation model guidance. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2024, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 19865–19875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Touvron, H.; Misra, I.; Jegou, H.; Mairal, J.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A. Emerging Properties in Self-Supervised Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhen, M.; Fang, T.; McKinnon, D.; Tsin, Y.; Quan, L. ASpanFormer: Detector-Free Image Matching with Adaptive Span Transformer. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Lecture notes in computer science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhou, X. LOFTR: Detector-Free local feature matching with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2021, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edstedt, J.; Athanasiadis, I.; Wadenbäck, M.; Felsberg, M. DKM: Dense Kernelized Feature Matching for geometry estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2023, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, P.; Danelljan, M.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. PDC-NET+: Enhanced Probabilistic Dense Correspondence Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 10247–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oquab, M.; Darcet, T.; Moutakanni, T.; Vo, H.; Szafraniec, M.; Khalidov, V.; Fernandez, P.; Haziza, D.; Massa, F.; El-Nouby, A.; et al. DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Oord, A.; Li, Y.; Vinyals, O. Representation Learning with Contrastive Predictive Coding. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y.; et al. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the EEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 2023, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, N.; Gabeur, V.; Hu, Y.-T.; Hu, R.; Ryali, C.; Ma, T.; Khedr, H.; Rädle, R.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; et al. SAM 2: Segment anything in images and videos. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.; Shen, C.; Huang, T. SegGPT: Towards segmenting everything in context. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 2023, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; Shen, C.; Huang, T. Images speak in images: A generalist painter for in-context visual Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2023, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balntas, V.; Lenc, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Mikolajczyk, K. HPatches: A benchmark and evaluation of handcrafted and learned local descriptors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Snavely, N. MegaDepth: Learning single-view depth prediction from internet photos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Chang, A.X.; Savva, M.; Halber, M.; Funkhouser, T.; Niessner, M. ScanNet: Richly-annotated 3D reconstructions of indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer normalization. arXiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavovic, I.; Kosaraju, R.P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Designing network design spaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning 2021, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikov, A.; Beyer, L.; Zhai, X.; Puigcerver, J.; Yung, J.; Gelly, S.; Houlsby, N. Big Transfer (BIT): General visual representation learning. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, N.K.; Fei-Fei, N.L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assran, M.; Duval, Q.; Misra, I.; Bojanowski, P.; Vincent, P.; Rabbat, M.; LeCun, Y.; Ballas, N. Self-Supervised learning from images with a joint-embedding predictive architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2023, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardes, A.; Ponce, J.; Lecun, Y. VICRegL: Self-supervised learning of local visual features. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 8799–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridle, J.S. Training stochastic model recognition algorithms as networks can lead to maximum mutual information estimation of parameters. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1989, 2, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, A.; Hafiz, R.; Ali, M.; Faisal, M.; Cho, Y.; Seo, J. Twin-Net descriptor: Twin negative mining with quad loss for Patch-Based matching. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 136062–136072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.-M. Structure-from-motion revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography. In Readings in Computer Vision; Elsevier eBooks; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S. Batch renormalization: Towards reducing minibatch dependence in Batch-Normalized models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, N.; Orfaig, R.; Bobrovsky, B.-Z. BOT-SORT: Robust Associations Multi-Pedestrian Tracking. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. ByteTrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Miura, Y.; Manning, C.D.; Langlotz, C. Contrastive Learning of Medical Visual Representations from Paired Images and Text. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-C.; Shen, L.; Lungren, M.P.; Yeung, S. GLORIA: A multimodal Global-Local Representation learning framework for label-efficient medical image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3922–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Vardhanabhuti, V.; Yu, L. Multi-Granularity cross-modal alignment for generalized medical visual representation learning. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ouyang, C.; Cheng, S.; Shah, A.; Bai, W.; Arcucci, R. G2D: From global to Dense Radiography Representation Learning via Vision-Language Pre-training. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, S.; Shi, M.; Shah, A.; Bai, W.; Arcucci, R. IMITATE: Clinical Prior Guided Hierarchical Vision-Language Pre-Training. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2025, 44, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| (a) | ||||
| Size | Number of Parameters | |||
| Self-TM Small | 128 | 256 | 512 | 13 M |
| Self-TM Base | 128 | 384 | 1024 | 40 M |
| Self-TM Large | 128 | 512 | 2048 | 130 M |
| (b) | ||||
| Input Size | Layer Name | Layer Components | Output Size | |
| 3 × 189 × 189 | Down sampling | × 63 × 63 | ||
| × 63 × 63 | ConvNeXt block | × 3 | × 63 × 63 | |
| × 63 × 63 | Normalization | × 63 × 63 | ||
| × 63 × 63 | Down sampling | × 21 × 21 | ||
| × 21 × 21 | ConvNeXt block | × 9 | × 21 × 21 | |
| × 21 × 21 | Normalization | × 21 × 21 | ||
| × 21 × 21 | Down sampling | × 7 × 7 | ||
| × 7 × 7 | ConvNeXt block | × 3 | × 7 × 7 | |
| × 7 × 7 | Normalization | × 7 × 7 | ||
| Model | Number of Parameters |
|---|---|
| Self-TM Small | 13 M |
| DeiT-S [22], ViT-S [18], and Swin-T [51] | 22–28 M |
| ConvNeXt-T [17] | 29 M |
| Self-TM Base | 40 M |
| ConvNeXt-S [17], Swin-S [51] | 50 M |
| EffNet-B7 [52], RegNetY-16G [53], DeiT-B [22], ViT-B [18], and Swin-B [51] | 66–88 M |
| ConvNeXt-B [17] | 89 M |
| EffNetV2-L [54] | 120 M |
| Self-TM Large | 130 M |
| ConvNeXt-L [17] | 198 M |
| ViT-L [18] | 304 M |
| ConvNeXt-XL [17] | 350 M |
| R-101x3 [55] and R-152x4 [55] | 388–937 M |
| Image Crop | Color Augmentation |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
| Image Crop | Color and Geometric Augmentation |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
| Model Size | Applied Augmentation | Pixels | Pixels | Pixels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-TM Small | color | 0.579 | 0.176 | 0.156 |
| Self-TM Base | color | 0.577 | 0.173 | 0.156 |
| Self-TM Large | color | 0.572 | 0.171 | 0.153 |
| Self-TM Small | color and geometric | 2.214 | 0.767 | 0.409 |
| Self-TM Base | color and geometric | 1.752 | 0.602 | 0.338 |
| Self-TM Large | color and geometric | 1.331 | 0.452 | 0.273 |
| Template | Result |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
| Method | MegaDepth-1500 | ScanNet | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC@5°/10°/20° | AUC@5°/10°/20° | ||
| Descriptors with hand-crafter rules | SIFT [27] + MNN | 25.8/41.5/54.2 | 1.7/4.8/10.3 |
| SuperPoint [30] + MNN | 31.7/46.8/60.1 | 7.7/17.8/30.6 | |
| Sparse methods | SuperGlue [31] | 42.2/61.2/76.0 | 10.4/22.9/37.2 |
| LightGlue [33] | 47.6/64.8/77.9 | 15.1/32.6/50.3 | |
| OmniGlue [34] | 47.4/65.0/77.8 | 14.0/28.9/44.3 | |
| OmniGlue + Self-TM Small Relative gain (in %) over OmniGlue | 48.2/64.7/73.8 +1.8/−0.4/−5.1 | 15.8/29.4/43.4 +13.0/+1.8/−2.0 | |
| OmniGlue + Self-TM Base Relative gain (in %) over OmniGlue | 56.7/69.4/78.1 +19.6/+6.7/+0.3 | 22.0/34.8/47.0 +57.1/+20.5/+6.2 | |
| OmniGlue + Self-TM Large Relative gain (in %) over OmniGlue | 59.8/70.6/78.4 +26.2/+8.7/+0.8 | 26.6/37.7/48.4 +90.1/+30.3/+9.2 |
| Model | Number of Parameters | Inference Speed at Various Input Resolution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| × 238 Pixels | × 490 Pixels | × 994 Pixels | ||
| Self-TM (Small) | 13 M | 212 ms | 659 ms | 2481 ms |
| Self-TM (Base) | 40 M | 244 ms | 914 ms | 3432 ms |
| DINOv2 (ViT-14-base) | 87 M | 445 ms | 3065 ms | 38,709 ms |
| Self-TM (Large) | 130 M | 377 ms | 1268 ms | 4706 ms |
| Model | Exp. No | Initial Weights | Dataset | Augmentations | Patch Verification mAP % | Image Matching mAP % | Patch Retrieval mAP % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-TM Base | 1 | Random init | HPatches | color | 64.15 | 8.32 | 25.74 |
| 2 | Random init | HPatches | color and geometric | 65.04 | 9.95 | 28.86 | |
| 3 | HPatches (color) | HPatches | color and geometric | 70.07 | 11.14 | 30.42 | |
| 4 | Random init | ImageNet | color | 65.19 | 21.33 | 37.01 | |
| 5 | ImageNet (color) | ImageNet | color and geometric | 85.90 | 38.77 | 61.67 | |
| 6 | ImageNet (color) | HPatches | color | 66.09 | 21.97 | 37.79 | |
| 7 | ImageNet (color) | HPatches | color and geometric | 78.97 | 29.85 | 50.30 | |
| 8 | ImageNet (color and geometric) | HPatches | color and geometric | 86.89 | 40.35 | 64.01 |
| Model | Number of Parameters | Dataset | Augmentations | Pixels | Pixels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConvNeXt-S [17] | 50 M | ImageNet | color | 1.119 | 0.418 |
| color and geometric | 2.515 | 0.542 | |||
| Self-TM Base Relative gain over ConvNeXt-S [17] | 40 M −20.00% | ImageNet | color | 0.577 −48.44% | 0.156 −62.68% |
| color and geometric | 1.752 −30.39% | 0.338 −37.64% |
| Model | Initial Weights | Dataset | Augmentations | Patch Verification mAP % | Image Matching mAP % | Patch Retrieval mAP % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConvNeXt-S [17] | Random init | ImageNet | color | 63.00 | 16.99 | 33.49 |
| ImageNet (color) | ImageNet | color and geometric | 83.31 | 32.94 | 58.42 | |
| ImageNet (color and geometric) | HPatches | color and geometric | 84.39 | 34.88 | 60.61 | |
| Self-TM Base Relative gain over ConvNeXt-S [17] | Random init | ImageNet | color | 65.19 +3.48% | 21.33 +25.54% | 37.01 +10.51% |
| ImageNet (color) | ImageNet | color and geometric | 85.90 +3.11% | 38.77 +17.70% | 61.67 +5.56% | |
| ImageNet (color and geometric) | HPatches | color and geometric | 86.89 +2.96% | 40.35 +15.68% | 64.01 +5.61% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hristov, A.; Dimov, D.; Nisheva-Pavlova, M. Self-Supervised Foundation Model for Template Matching. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020038
Hristov A, Dimov D, Nisheva-Pavlova M. Self-Supervised Foundation Model for Template Matching. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2025; 9(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleHristov, Anton, Dimo Dimov, and Maria Nisheva-Pavlova. 2025. "Self-Supervised Foundation Model for Template Matching" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 9, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020038
APA StyleHristov, A., Dimov, D., & Nisheva-Pavlova, M. (2025). Self-Supervised Foundation Model for Template Matching. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 9(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020038








