Explainable Deep Learning for COVID-19 Vaccine Sentiment in Arabic Tweets Using Multi-Self-Attention BiLSTM with XLNet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Designing an explainable DL approach for sentiment analysis of Arabic tweets by utilizing MSA-BiLSTM and XLNet embeddings.
- Developing a robust model, which is capable of accurately classifying the sentiment of Arabic tweets related to COVID-19 vaccines.
- Generating interpretability of decisions within the proposed sentiment analysis approach to provide transparency into the factors influencing its predictions.
2. Related Work
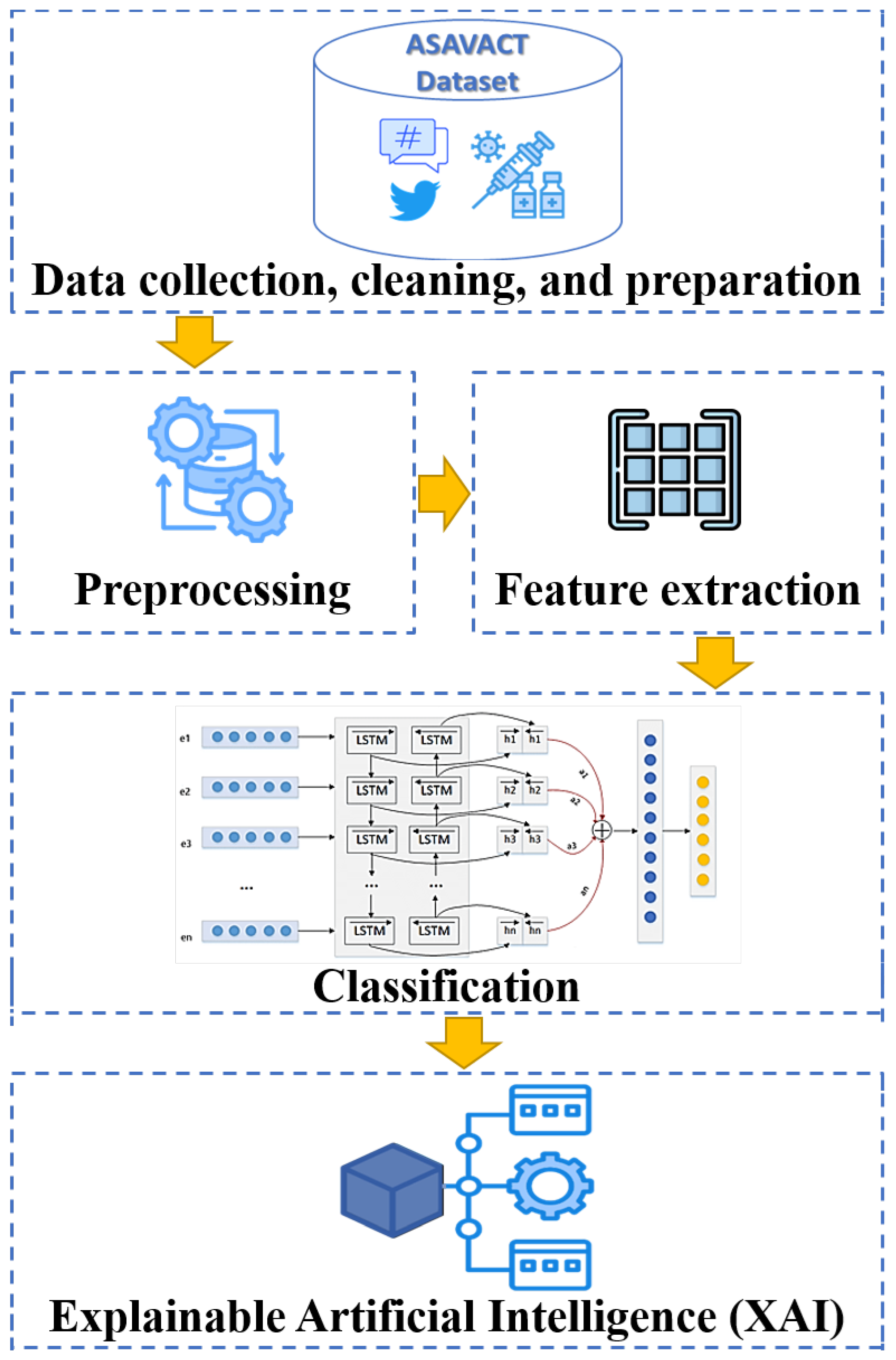
3. Proposed Approach
3.1. Dataset Preparation
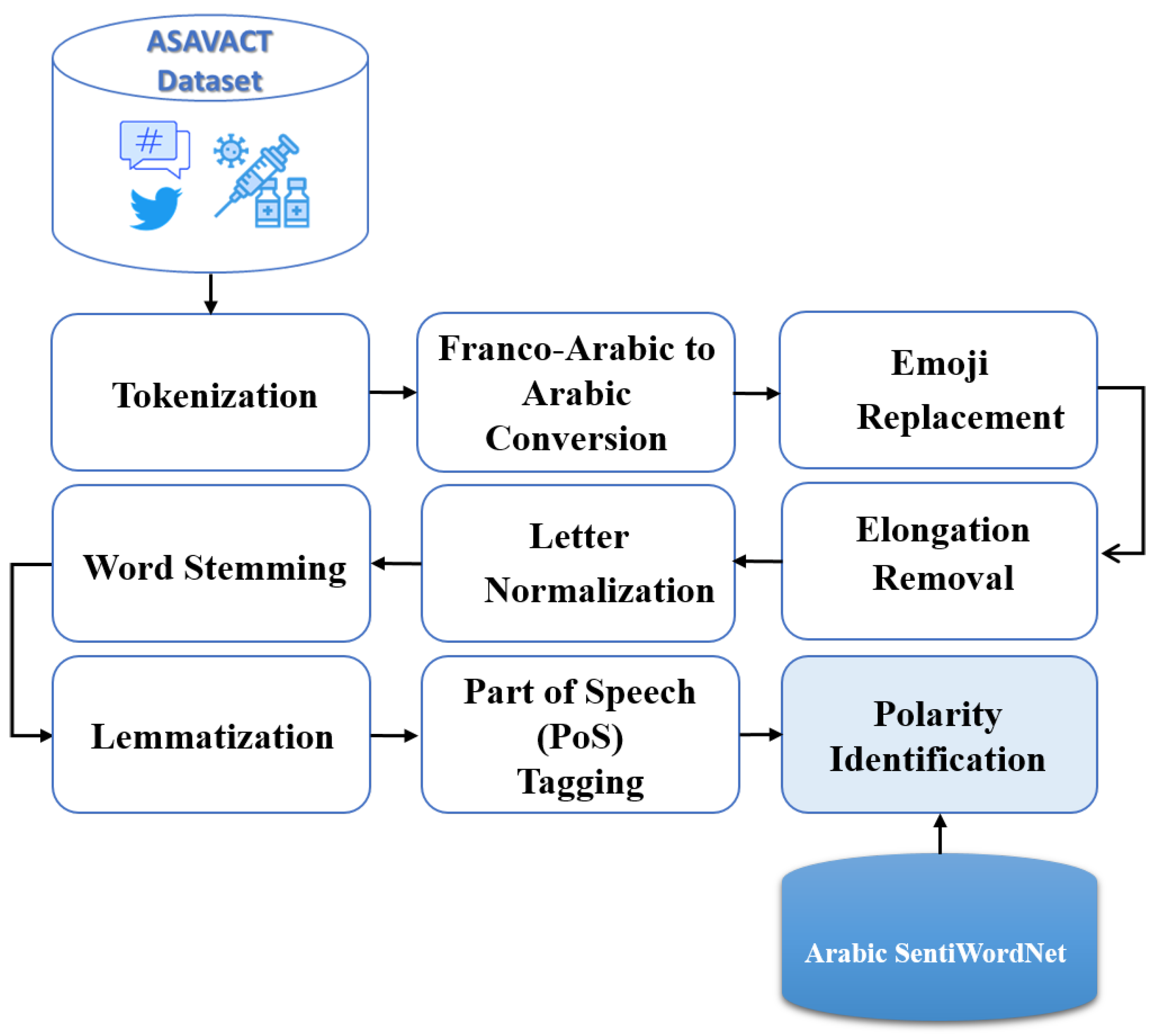
3.2. Preprocessing
- Tokenizing social input text: Present each word in the input social text as a token that could be further divided into several sub-words [21].
- Converting Franco-Arabic text into Arabic: Check Google’s API and match the Franco-Arabic words, which are Arabic words created using a combination of Latin characters, with their corresponding original Arabic words, such as writing the word (تطعيم) (Vaccination) as “tat3eem” [22].
- Removing elongation: Remove repeated letters used for emphasizing/expressing strong emotions, such as writing the word as (!أخبااار رااائعة) (Great News!), to reduce words to their standard form. In the proposed approach, at most two repeated consecutive letters are kept. Also, elongation (also known as تطويل “Tatweel”), which means stretching/lengthening words by increasing the length of some characters (by using the “kashida” character “-”), is adjusted to unify the letters that can appear in different forms [23].
- Letter normalization: Use the normalization procedure to eliminate punctuation and diacritics “Tashkeel”, such as (ضمة “damma” or ُ in the word كُورونا (Corona)).
- Word stemming: Break Arabic words down to their word root form or stem using the Information Science Research Institute (ISRI) rule-based stemmer, such as stemming the text [24]: ( للجميع الآن متاح كورونا لقاح رائعة! أخبار) (Great News! The COVID-19 vaccine is now available for everyone) to be ( متاح، آن، جميع كورونا، لقاح، رائع، خبر،) (news, great, vaccine, corona, available, now, everyone).
- Lemmatization: Use morphological analysis of words by removing inflectional endings (suffixes, prefixes, etc.), such as mapping the word (أخبار ) (news) to the lemma (خبر ) (news) and the word (اجراءات) (procedures) to the lemma (اجراء) (procedure). It is used to reduce morphological variations.
- Part of Speech (PoS) Tagging: The proposed method develops a PoS tagger using a rule-based linguistic approach. Words in a given text are annotated according to their definitions and contextual usage. For instance, the word (الملتزمين) (adhering ones) is assigned the tag (NNS: Noun Phrase Plural) because it represents the plural form of the noun (الملتزم) (adhering one) and is preceded by the preposition (من) (of). The complete set of tags and their conventional meanings follow the International Corpus of Arabic (ICA) tagset, employing a rule-based tagging approach.
- Polarity Identification: PoS tagging is used to reduce the dimensionality of the matrix and consequently enhance model performance. The Stanford PoS tagging tool is utilized to assign polarity tags to words, such as tagging the PoS (الاحترازية) (precautionary) as negative.This paper uses ArSenL, a supervised Arabic sentiment analysis tool, for PoS tagging.
3.3. Feature Extraction
3.4. Classification
3.5. XAI Mechanisms
| Algorithm 1 LIME: Generating Explanations for Arabic Text Sentiment |
|
| Algorithm 2 SHAP: Generating Explanations for Arabic Text Sentiment |
|
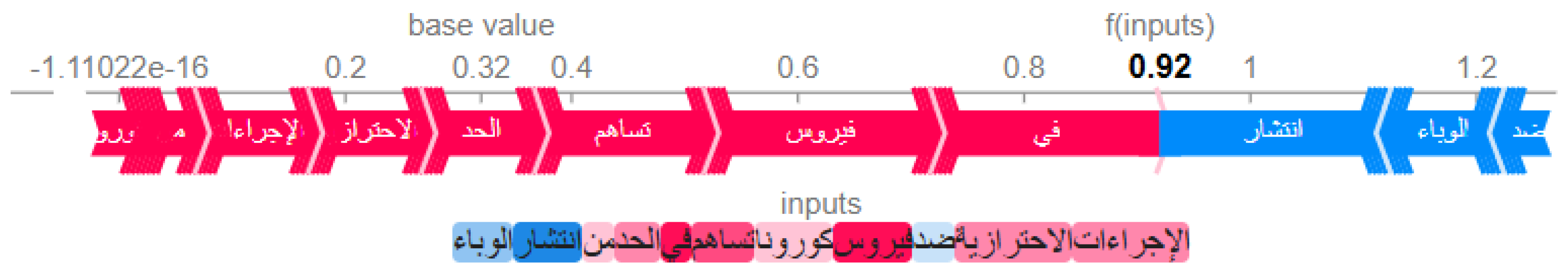
- “الوضع الوبائي خطير جدا” (The epidemiological situation is very serious);
- “الوضع الوبائي الحالي خطير” (The current epidemiological situation is serious);
- “الوبائي الحالي خطير جدا” (The current epidemic is very serious).
- “خطير” (serious) → High negative coefficient;
- “جدا” (very) → High negative coefficient;
- “الوضع” (situation) → Medium negative coefficient.
- “فعال” (effective) → Positive SHAP value;
- “آمن” (safe) → Positive SHAP value;
- “اللقاح”(vaccine) → Neutral SHAP value.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
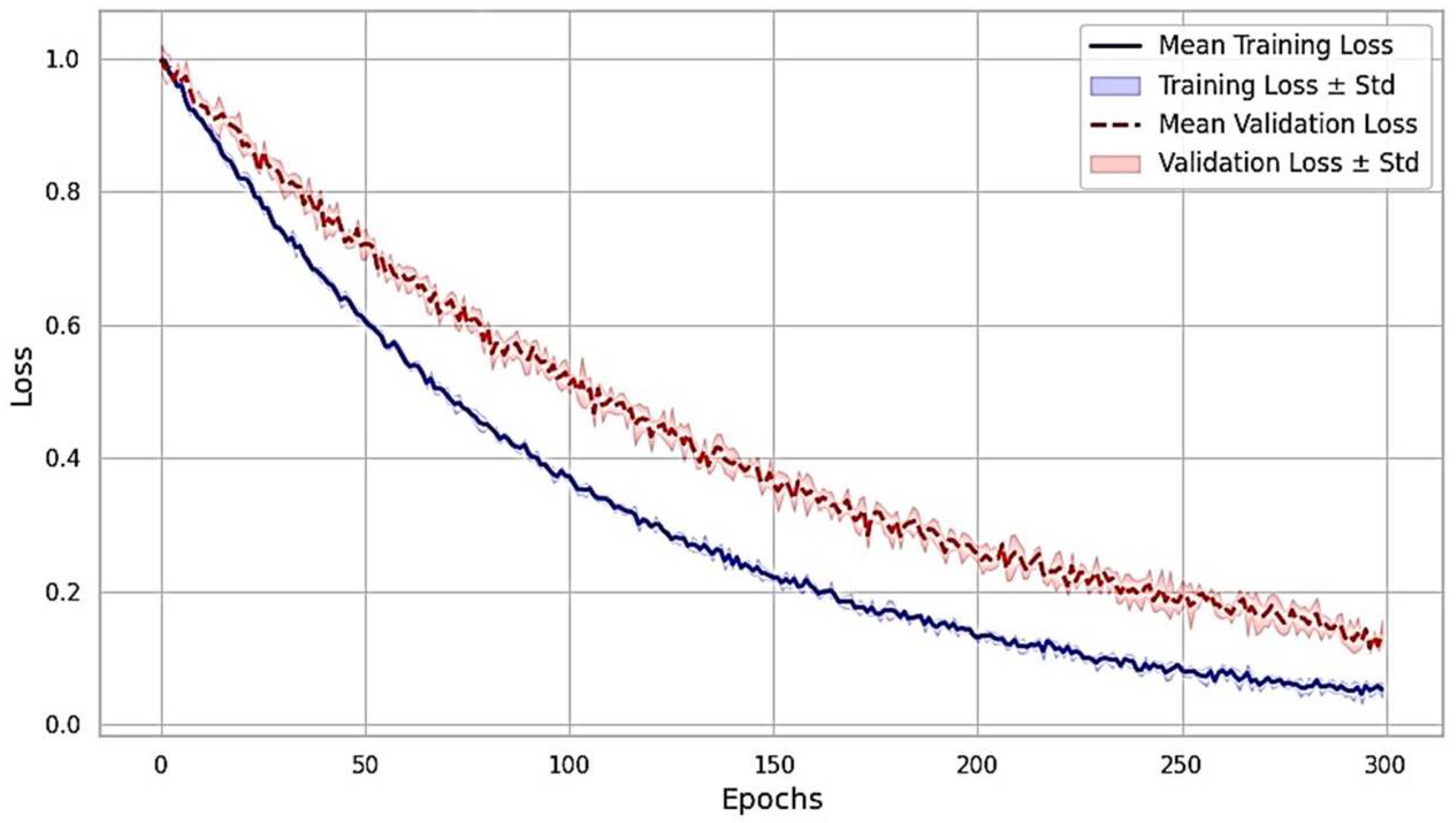
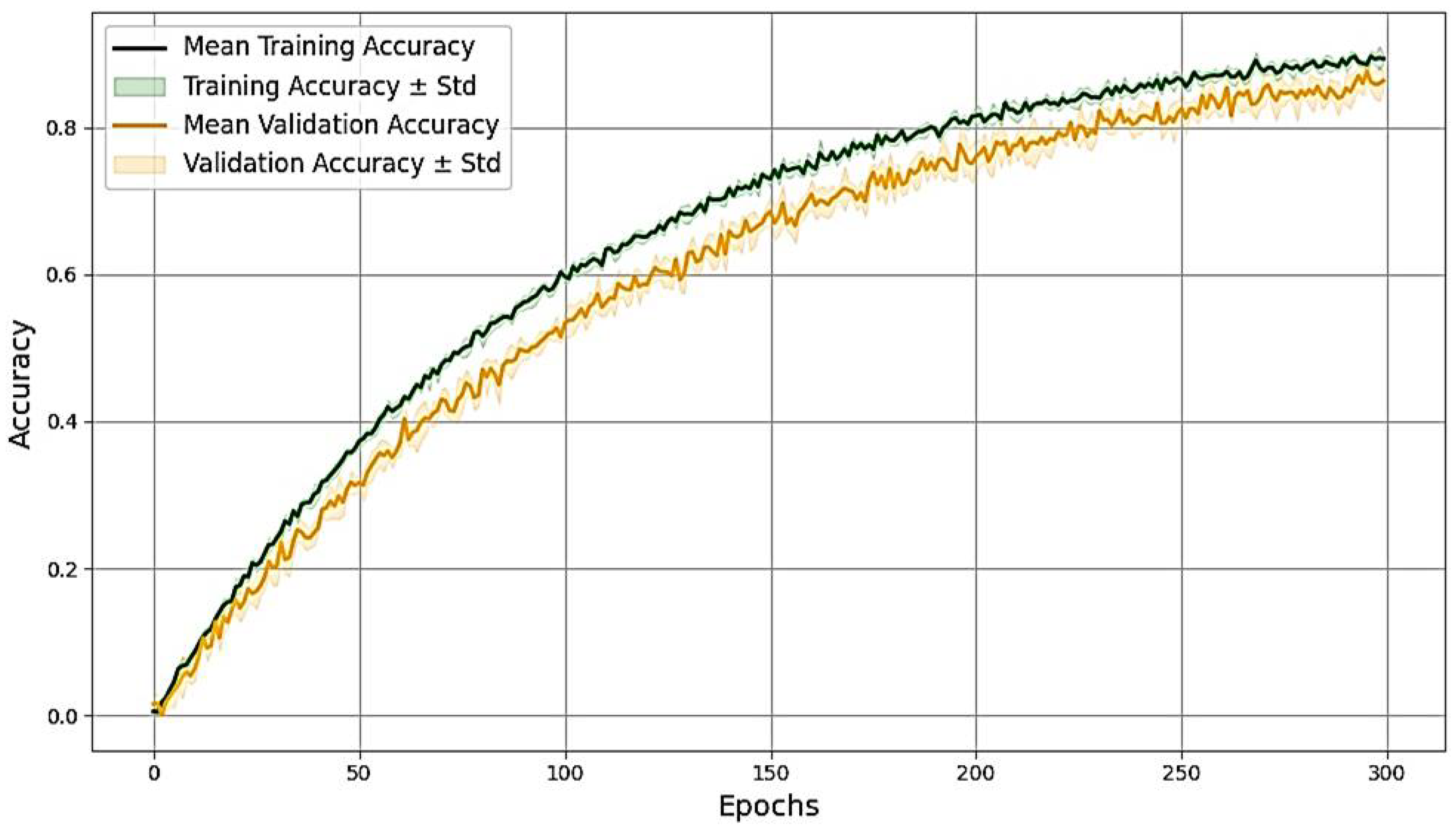
4.2. Experimental Analysis
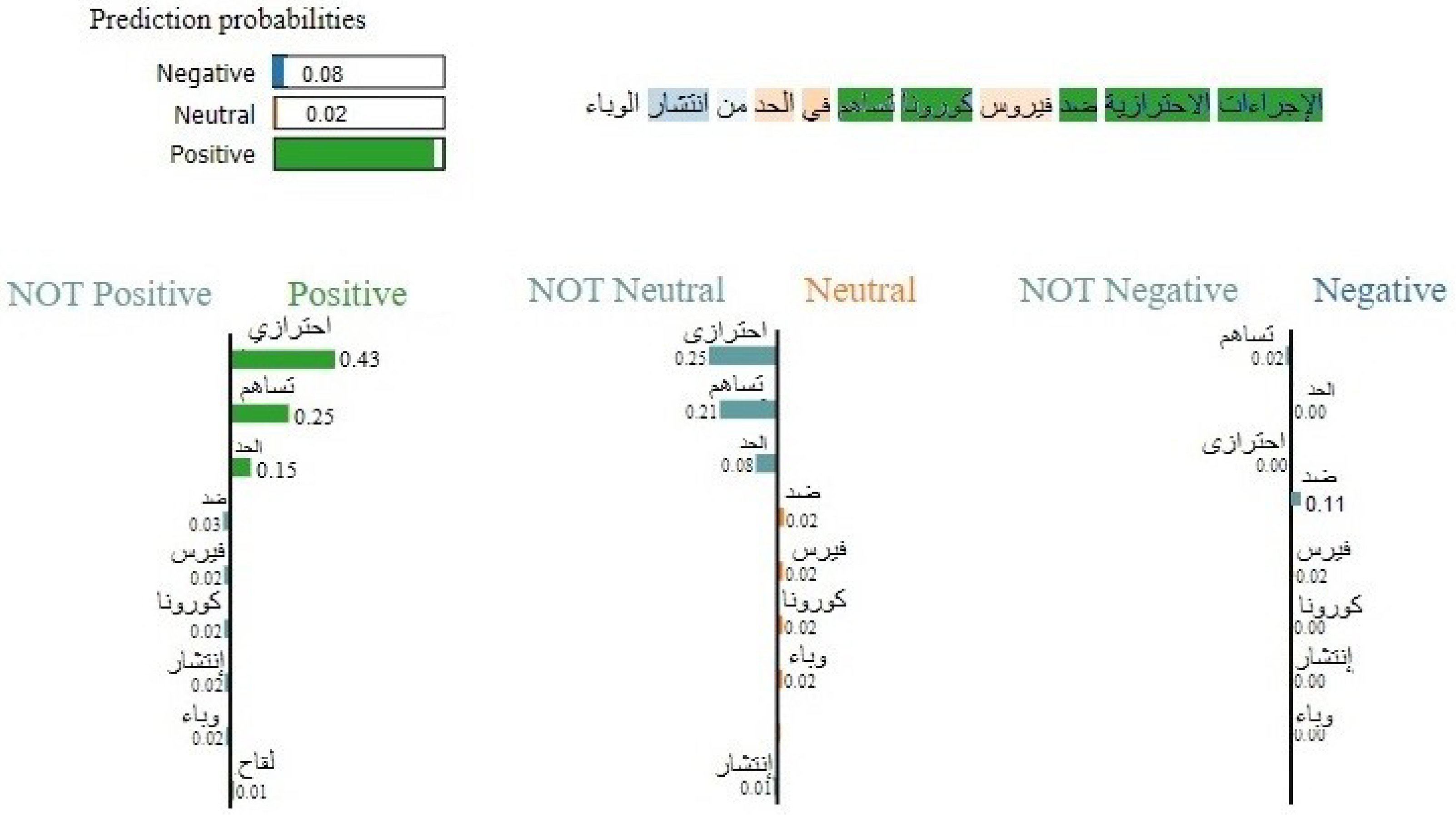
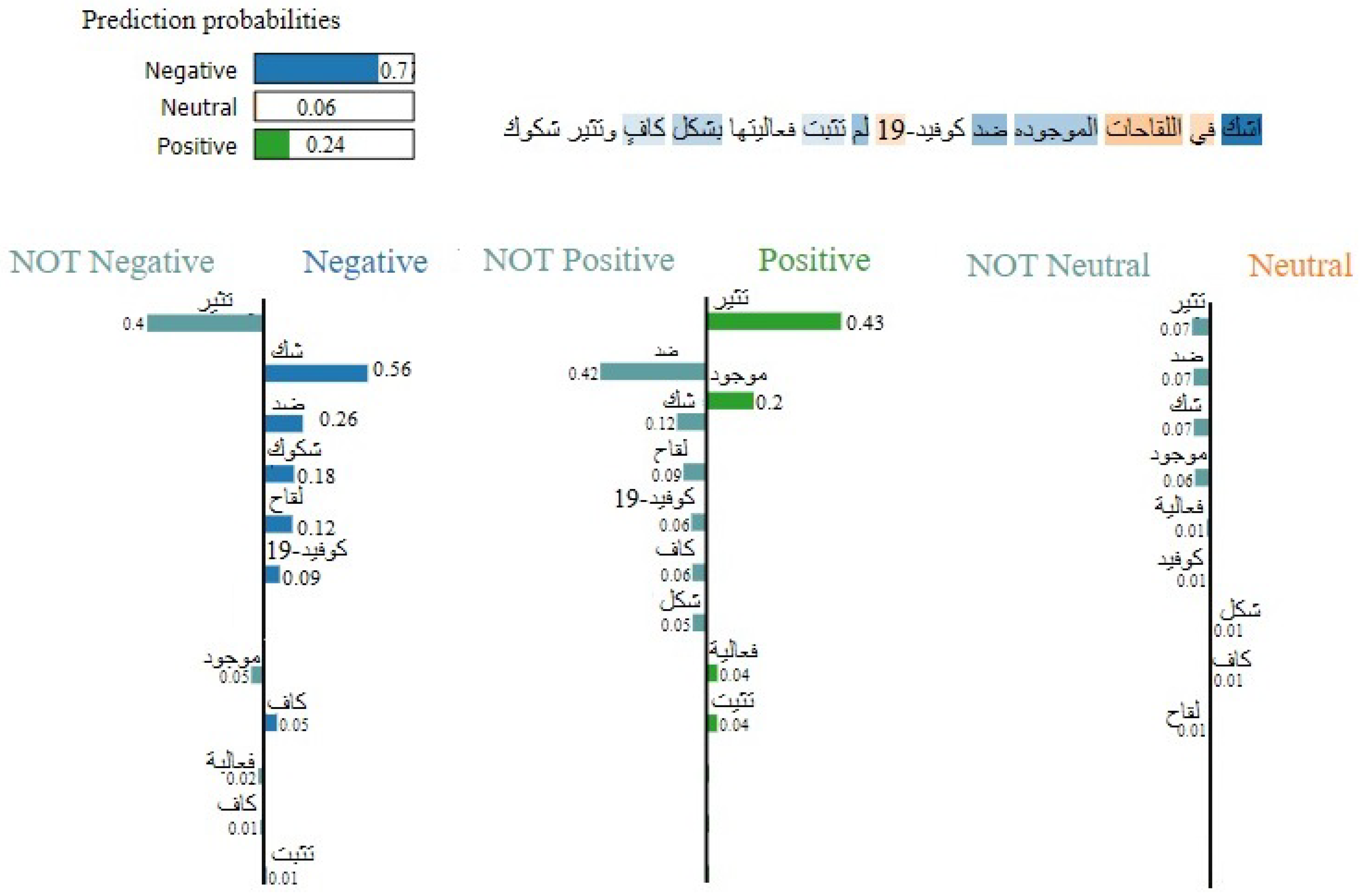
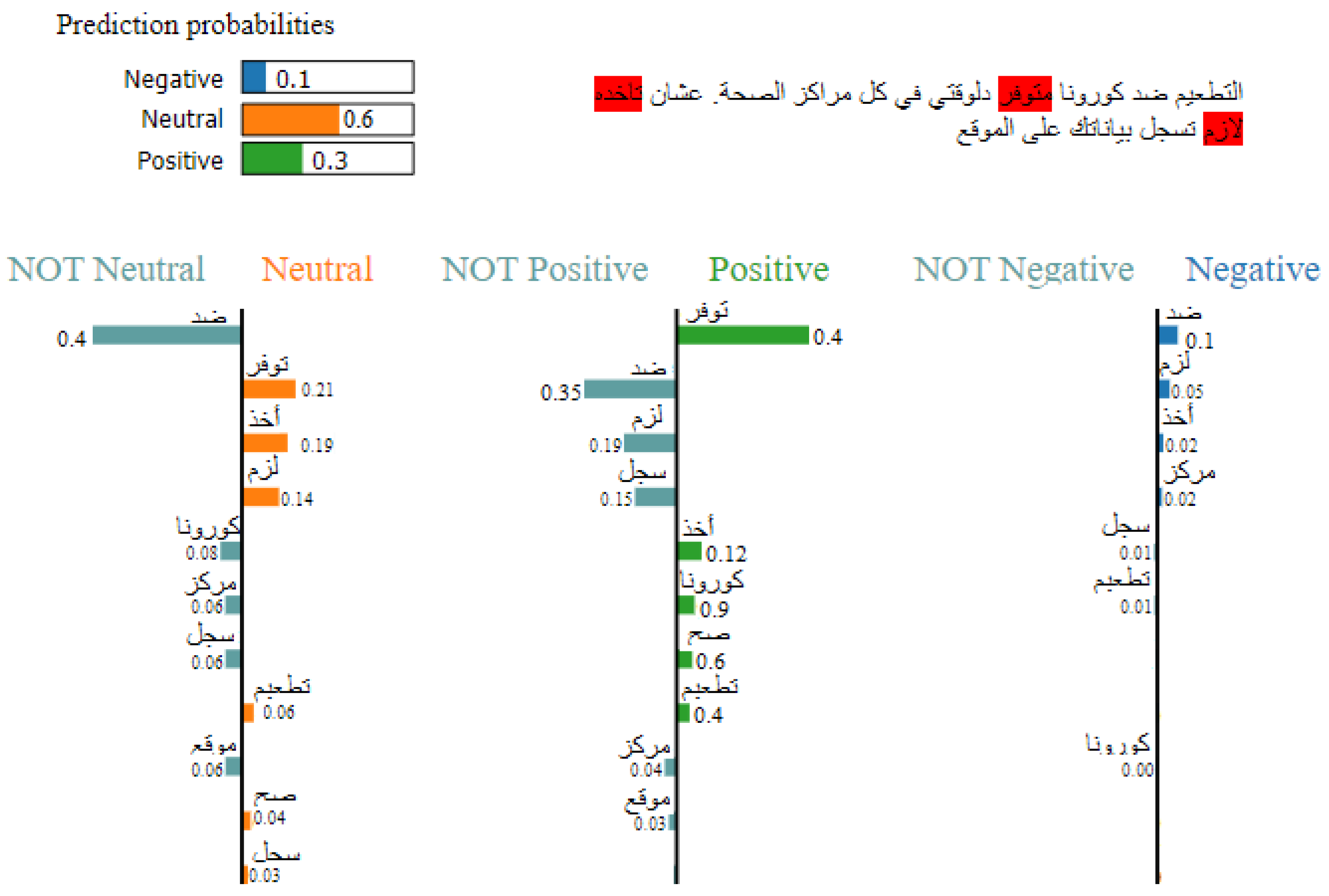
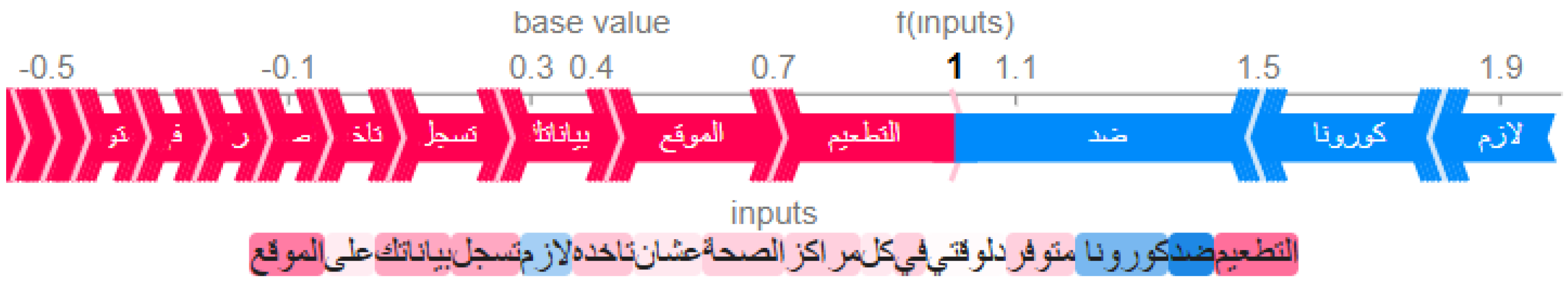
4.3. LIME-Based Model Analysis
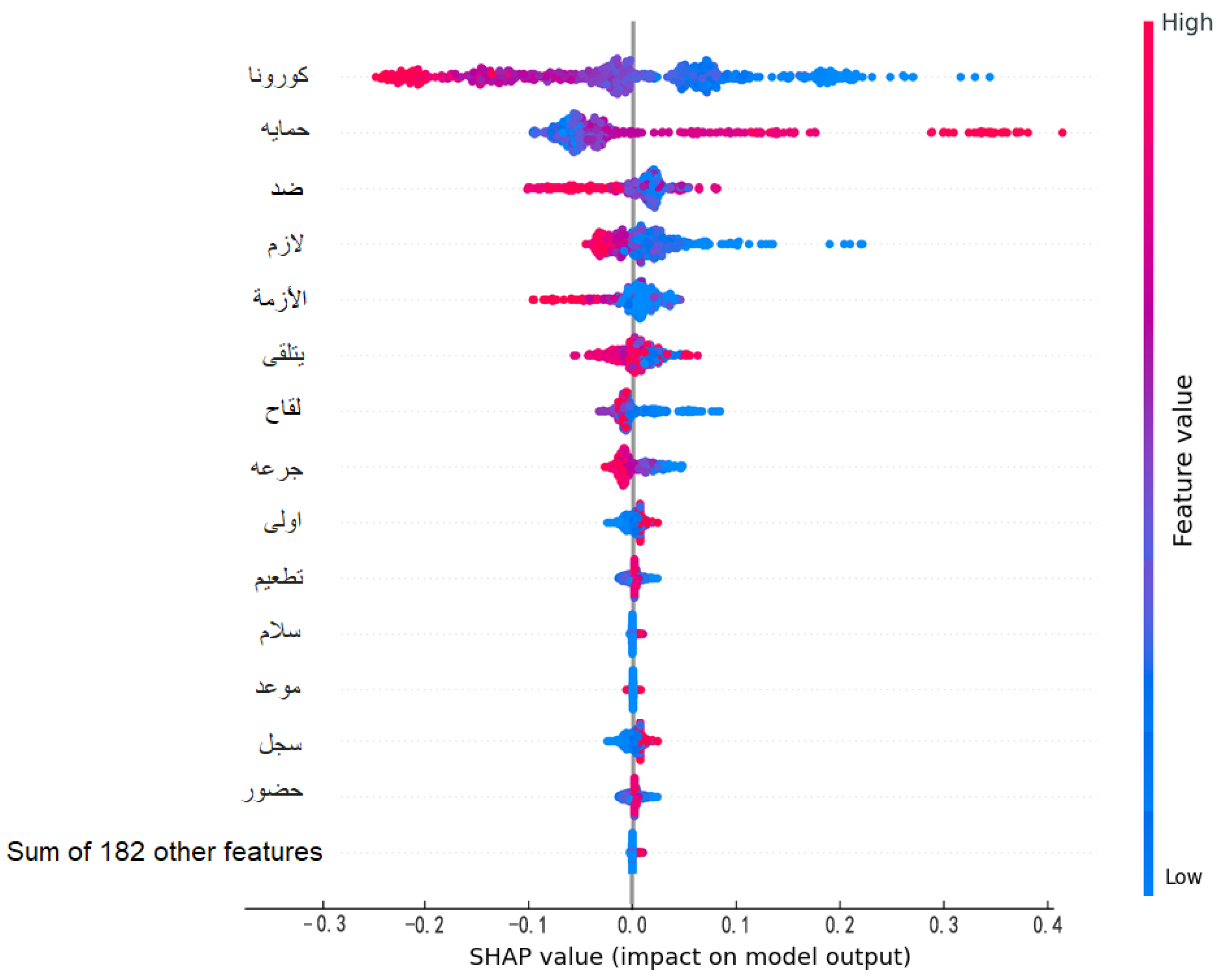
4.4. SHAP-Based Model Analysis
4.5. Comparative Analysis Discussion
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aljedaani, W.; Abuhaimed, I.; Rustam, F.; Mkaouer, M.W.; Ouni, A.; Jenhani, I. Automatically detecting and understanding the perception of COVID-19 vaccination: A middle east case study. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumoud, S.; Al Wazrah, A.; Alhussain, L.; Alrushud, L.; Aldosari, A.; Altammami, R.N.; Almukirsh, N.; Alharbi, H.; Alshahrani, W. ASAVACT: Arabic sentiment analysis for vaccine-related COVID-19 tweets using deep learning. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeid, N.; Tang, L.; Amith, M.T. The spread of COVID-19 vaccine information in Arabic on YouTube: A network exposure study. Digit. Health 2023, 9, 20552076231205714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wankhade, M.; Annavarapu, C.S.R.; Abraham, A. CBMAFM: CNN-BiLSTM Multi-Attention Fusion Mechanism for Sentiment Classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 51755–51786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Meng, X. Sentiment Analysis with an Integrated Model of BERT and Bi-LSTM Based on Multi-Head Attention Mechanism. Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 50, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.G.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Le, Q.V. XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’16), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Shrikumar, A.; Greenside, P.; Shcherbina, A.; Kundaje, A. Not Just a Black Box: Learning Important Features Through Propagating Activation Differences. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1605.01713. [Google Scholar]
- Aljameel, S.S.; Alabbad, D.A.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Alqarni, S.M.; Alamoudi, F.A.; Babili, L.M.; Aljaafary, S.K.; Alshamrani, F.M. A Sentiment Analysis Approach to Predict an Individual’s Awareness of the Precautionary Procedures to Prevent COVID-19 Outbreaks in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubarak, H.; Hassan, S.; Chowdhury, S.A.; Alam, F. ArCovidVac: Analyzing Arabic Tweets About COVID-19 Vaccination. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 20–25 June 2022; Calzolari, N., Béchet, F., Blache, P., Choukri, K., Cieri, C., Declerck, T., Goggi, S., Isahara, H., Maegaard, B., Mariani, J., et al., Eds.; European Language Resources Association: Paris, France, 2022; pp. 3220–3230. [Google Scholar]
- Alhazmi, H. Arabic Twitter conversation dataset about the COVID-19 vaccine. Data 2022, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Salathé, M.; Kummervold, P. COVID-Twitter-BERT: A natural language processing model to analyse COVID-19 content on Twitter. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1023281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhady, N.; Hassan, A.; Soliman, T.; F. Farghally, M. Stacked-CNN-BiLSTM-COVID: An effective stacked ensemble deep learning framework for sentiment analysis of Arabic COVID-19 tweets. J. Cloud Comput. 2024, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumayani, M.K.; Alhazmi, H.N. Detecting reported side effects of COVID-19 vaccines from Arabic twitter (X) data. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 55367–55388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Roy, P.K.; Singh, J.P. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers for the COVID-19 vaccine stance classification. In Proceedings of the Working Notes of FIRE 2021—Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation, Gandhinagar, India, 13–17 December 2021; Mehta, P., Mandl, T., Majumder, P., Mitra, M., Eds.; CEUR Workshop Proceedings: Aachen, Germany, 2021; Volume 3159, pp. 1216–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, M.; Poddar, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, K. Overview of the FIRE 2021 track: Information Retrieval from Microblogs during Disasters (IRMiDis). In Proceedings of the FIRE’21: Proceedings of the 13th Annual Meeting of the Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation, Virtual, 13–17 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, J.P.; Singh, A.K. Explainable BERT-LSTM Stacking for Sentiment Analysis of COVID-19 Vaccination. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Vijay, A.A. A multi-aspect framework for explainable sentiment analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2024, 178, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sweidan, A.H.; El-Bendary, N.; Elhariri, E. Autoregressive Feature Extraction with Topic Modeling for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis of Arabic as a Low-resource Language. In ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, I.; Vu, N.T.; Abdennadher, S. Arzen: A speech corpus for code-switched egyptian arabic-english. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 4237–4246. [Google Scholar]
- Bouamor, H.; Habash, N.; Oflazer, K. A Multidialectal Parallel Corpus of Arabic. In Proceedings of the LREC, 2014, Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; pp. 1240–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Taghva, K.; Elkhoury, R.; Coombs, J. Arabic stemming without a root dictionary. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technology: Coding and Computing (ITCC’05)-Volume II, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–6 April 2005; Volume 1, pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Abuhmed, T.; El-Sappagh, S.; Muhammad, K.; Alonso-Moral, J.M.; Confalonieri, R.; Guidotti, R.; Del Ser, J.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Herrera, F. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): What we know and what is left to attain Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, U. Explainable AI lacks regulative reasons: Why AI and human decision-making are not equally opaque. AI Ethics 2023, 3, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, D.; Silva, P.; Silva, C. Explainable AI for Intrusion Detection Systems: LIME and SHAP Applicability on Multi-Layer Perceptron. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 30164–30175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazmi, H. Arabic Twitter Conversation Dataset about COVID-19 Vaccine. 2022. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/zmwfnsms9n/1 (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- Mubarak, H.; Hassan, S.; Chowdhury, S.A.; Alam, F. ArCovidVac: Arabic COVID-19 Vaccine Sentiment Dataset. 2022. Available online: https://huggingface.co/datasets/arbml/ArCovidVac (accessed on 20 July 2024).


| Study | Task | Methods | Dataset | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] (2021) | Prediction of individual COVID-19 precautionary awareness | SVM, NB, KNN | collected dataset of Arabic COVID-19-related tweets | Accuracy = 85% (SVM with bigrams TF-IDF) |
| [11] (2022) | Stance detection in Arabic tweets | Transformer architectures | ArCovidVac (10K Arabic tweets) | F1-score = 80% |
| [12] (2022) | Analysis of Arabic tweets related to vaccine | Text analysis | 1M+ Arabic COVID-19 tweets | – |
| [2] (2023) | Sentiment polarity analysis of Arabic tweets | SGRU, SBi-GRU, ensemble, AraBERT | ASAVACT (32,476 Arabic tweets) | Accuracy = 81.67% |
| [13] (2023) | COVID-19 vaccination sentiment classification | COVID-Twitter-BERT (CT-BERT) transformer-based model | Training: collected corpus of 160 M COVID-19 tweets Testing: Twitter-related data. | F1-score: 0.833 |
| [15] (2024) | Tweet classification on COVID-19 vaccines | hybrid CNN-BiLSTM | SenWave, AraCOVID19-SSD and ArCovidVac | F-measures of 76.76%, 87%, and 80.5% on the datasets, respectively. |
| [16] (2024) | detect side effect for Vaccine | BTM, SVM | 65,387 Arabic tweets | Accuracy = 90.9%, F1-score = 0.876 |
| [17] (2021) | COVID-19 vaccination stance classification | ensemble-based CT-BERT model | validated by the FIRE-2021 shared task [18] | validation F1-score = 0.86 testing F1-score = 0.532 |
| [19] (2023) | XAI based sentiment analysis of COVID-19 vaccination tweets | CT-BERT-LSTM | Tested by the FIRE-2021 shared task [18] | F1-score = 0.88 |
| [20] (2024) | XAI based Multi-aspect sentiment analysis | Hierarchical neural network | Benchmark datasets of reviews, tweets | Accuracy = 93.17%, F1-score = 0.9318 |
| Raw Tweet | Pre-Processed | Sentiment | Word Polarity | Total | Sentiment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tweet | Words | Score | Score | ||
الآن
متاح
كورونا
لقاح
رائعة
أخبار  | لقاح، رائع، خبر، | رائعة | 0.6 | ||
| على للحصول سجل ۱۸. سن فوق للجميع | الان، متاح، كورونا، | متاح | 0.2 | 0.9 | Positive |
| الحل! من جزءًا وكن اليوم موعدك | سن، فوق، جميع، | سجل | 0.1 | ||
| ۱۹ #الصحة_العامة #اللقاح_فعال #كوفيد - | موعد، سجل، حصل، | ||||
| يوم، كن، جزء، حل | |||||
 Great news! The COVID-19 vaccine is now Great news! The COVID-19 vaccine is now | news, great, vaccine, | ||||
| available to everyone over the age of 18. Register | Corona, Available, Now, | Greats | |||
| for your appointment today and be part of the | all, above, age, | available | |||
| solution! #VaccineWorks #COVID-19 #PublicHealth | Register, get, appointment, | register | |||
| day, be, part, solution | |||||
| في دلوقتي متوفر كورونا ضد التطعيم | تطعيم، ضد، | ضد | −0.60 | ||
| لازم تاخده عشان الصحة. مراكز كل | مركز، توفر، كورونا، | توفر | 0.4 | 0 | Neutral |
| الموقع على بياناتك تسجل | لزم، أخذ، صح، | أخذ | 0.15 | ||
| سجل، بيان، موقع | لزم | 0.05 | |||
| Corona vaccination is now available | Vaccination, against, Corona, | against | |||
| in health centers. To get it, | availability, Center, correct, take, | provide | |||
| you must register your data on the website | necessary, record, statement, | get | |||
| location | must | ||||
| - ۱۹ كوفيد ضد الموجوده اللقاحات في اشك | شك، لقاح، موجود، | اشك | −0.54 | ||
| شكوك وتثير كافٍ بشكل فعاليتها تثبت لم | ضد، كوفيد - ۱۹، | تثير | 0.27 | −0.9 | Negative |
| ثبت، فعالية، كاف، | شكوك | −0.63 | |||
| ثار، شك | |||||
| I doubt that the existing vaccines | Doubt, vaccine, exist, | doubt | |||
| against COVID-19 have not been proven | against, COVID-19, proved | raise | |||
| to be effective enough and raise doubts. | effectiveness, enough, raise, doubt | doubts |
| Dataset | Number of Tweets | Class Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset-I (An Arabic Twitter dataset) [28] | 1.1 M Arabic tweets | Positive: 400,000 Neutral: 300,000 Negative: 400,000 |
| Dataset-II (ArCovidVac dataset) [29] | 10,002 Arabic tweets | Positive: 4000 Neutral: 3000 Negative: 3002 |
| Metric | XLNet | BERT |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 93.2% | 85.0% |
| Recall (Sensitivity) | 92.3% | 85.2% |
| Precision | 92.0% | 82.1% |
| F-measure | 92.0% | 81.0 % |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sweidan, A.H.; El-Bendary, N.; Taie, S.A.; Idrees, A.M.; Elhariri, E. Explainable Deep Learning for COVID-19 Vaccine Sentiment in Arabic Tweets Using Multi-Self-Attention BiLSTM with XLNet. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020037
Sweidan AH, El-Bendary N, Taie SA, Idrees AM, Elhariri E. Explainable Deep Learning for COVID-19 Vaccine Sentiment in Arabic Tweets Using Multi-Self-Attention BiLSTM with XLNet. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2025; 9(2):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleSweidan, Asmaa Hashem, Nashwa El-Bendary, Shereen A. Taie, Amira M. Idrees, and Esraa Elhariri. 2025. "Explainable Deep Learning for COVID-19 Vaccine Sentiment in Arabic Tweets Using Multi-Self-Attention BiLSTM with XLNet" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 9, no. 2: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020037
APA StyleSweidan, A. H., El-Bendary, N., Taie, S. A., Idrees, A. M., & Elhariri, E. (2025). Explainable Deep Learning for COVID-19 Vaccine Sentiment in Arabic Tweets Using Multi-Self-Attention BiLSTM with XLNet. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 9(2), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9020037







