Increasing Wheat Protein and Yield through Sulfur Fertilization and Its Relationship with Nitrogen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
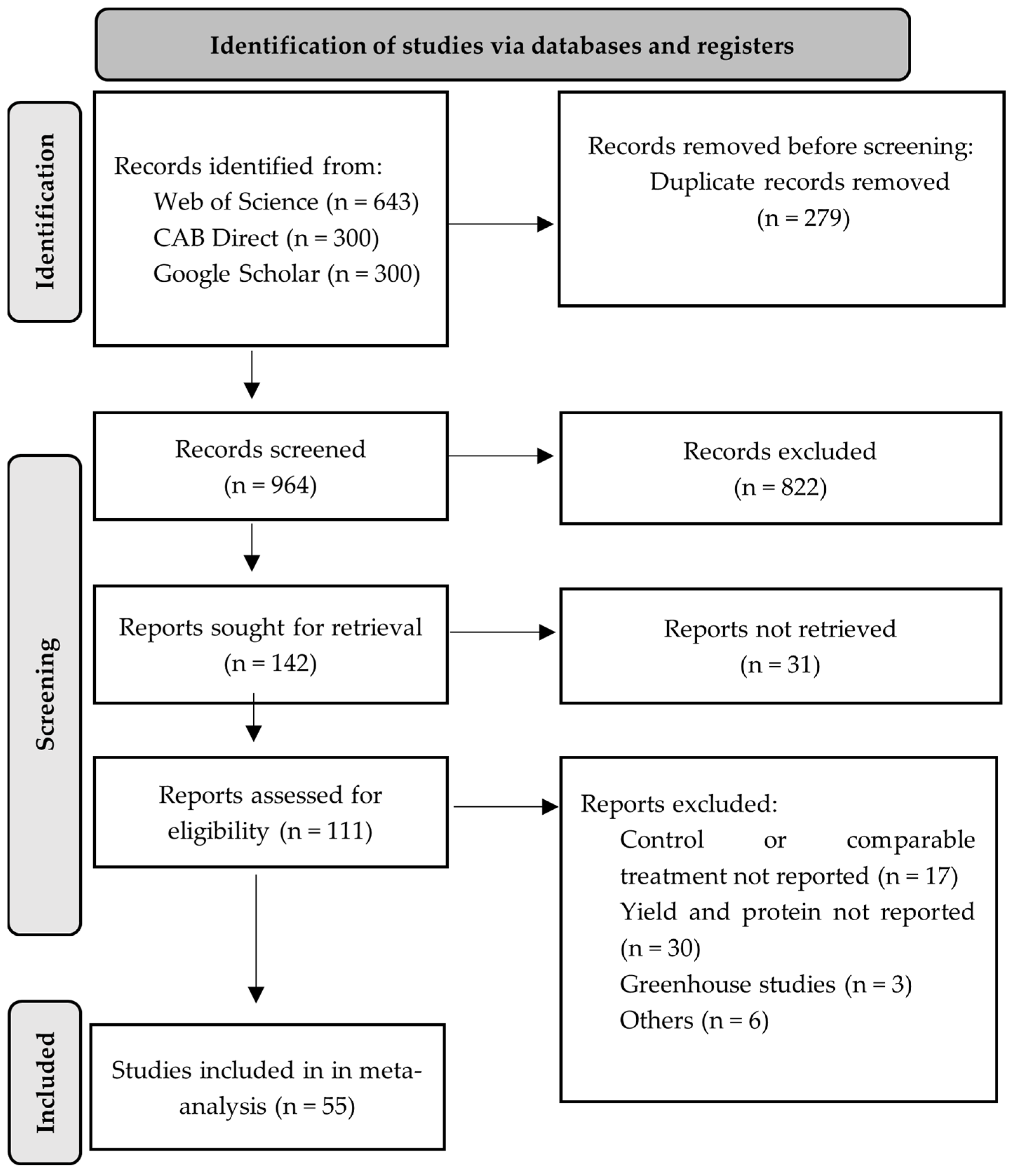
2.1. Meta-Analysis
Data Collection and Selection Criteria
- (I)
- Studies that included comparisons between a treatment without sulfur and another with sulfur, with the same amounts of other nutrients such as N, P, K, etc. All data were adopted if studies were conducted over multiple years, at multiple sites, or combinations thereof.
- (II)
- Studies that reported at least the grain yield and grain protein concentration. In cases where the grain N content was reported, the protein concentration was calculated by multiplying the N content by 5.49 [32].
- (III)
- Studies that contained the mean (M), the number of samples or replications (NS), and the standard deviation (SD), standard error (SE), or the coefficient of variation (CV) for the control and treatment groups. If a study did not report SD, SE, or CV values, the average CV was calculated within each dataset and then the SD was recalculated.
- (IV)
2.2. Greenhouse Study
2.2.1. Site and Experimental Design
2.2.2. Data Collection and Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Meta-Analysis
2.3.2. Greenhouse Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Meta-Analysis: Effects of Sulfur Application on Protein and Yield
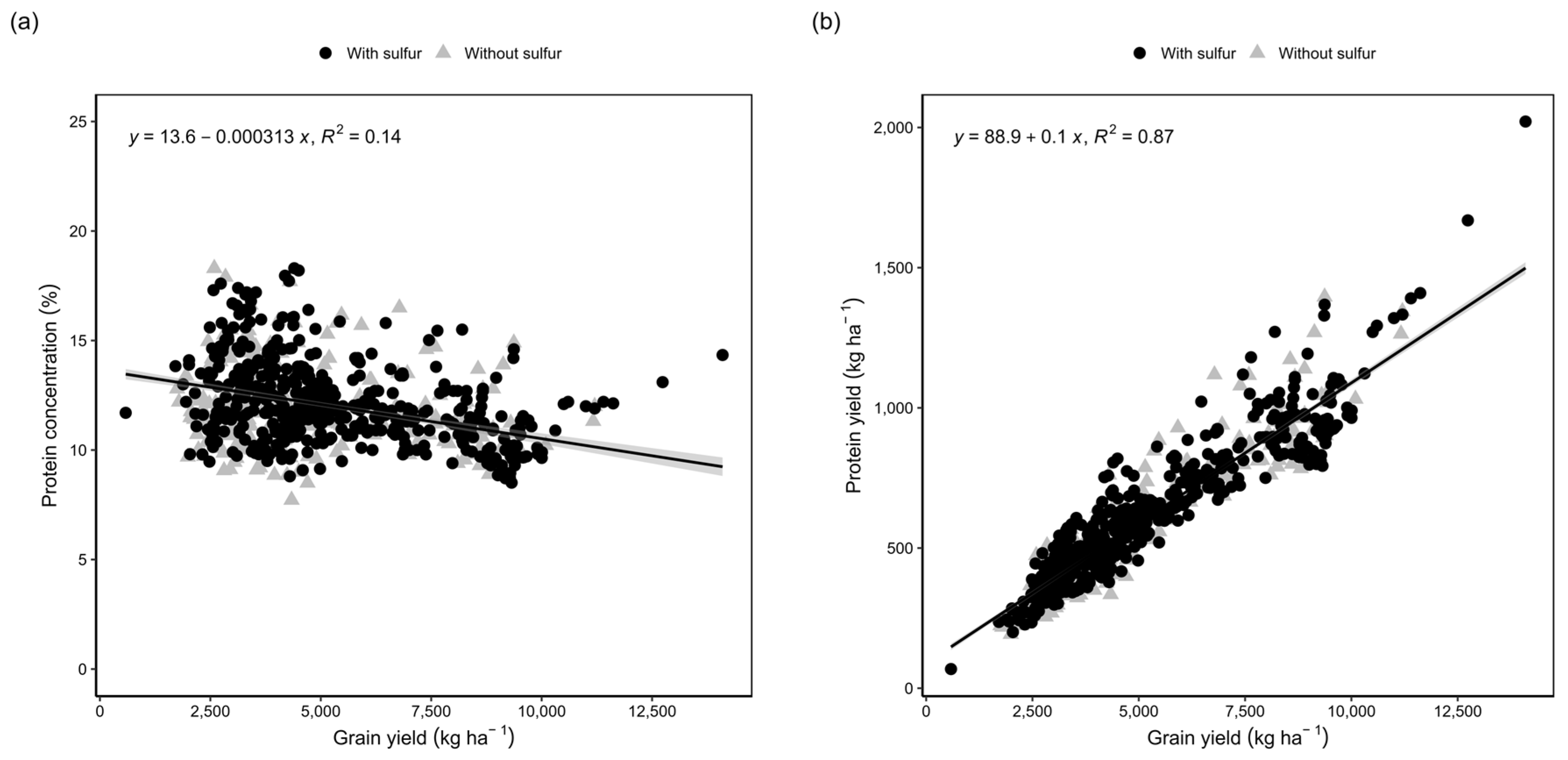
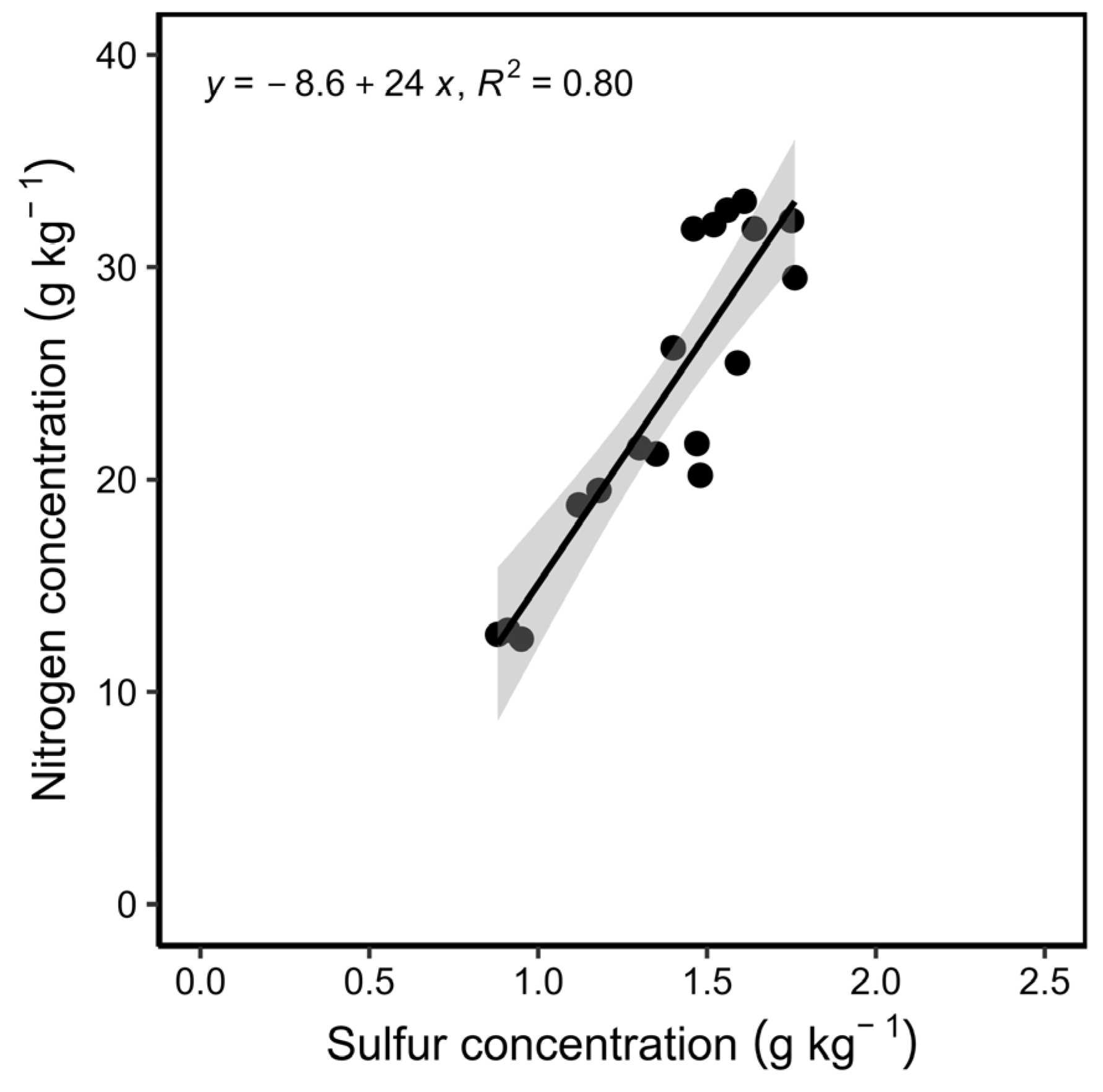
3.2. Meta-Analysis: Relationship between Protein and Yield
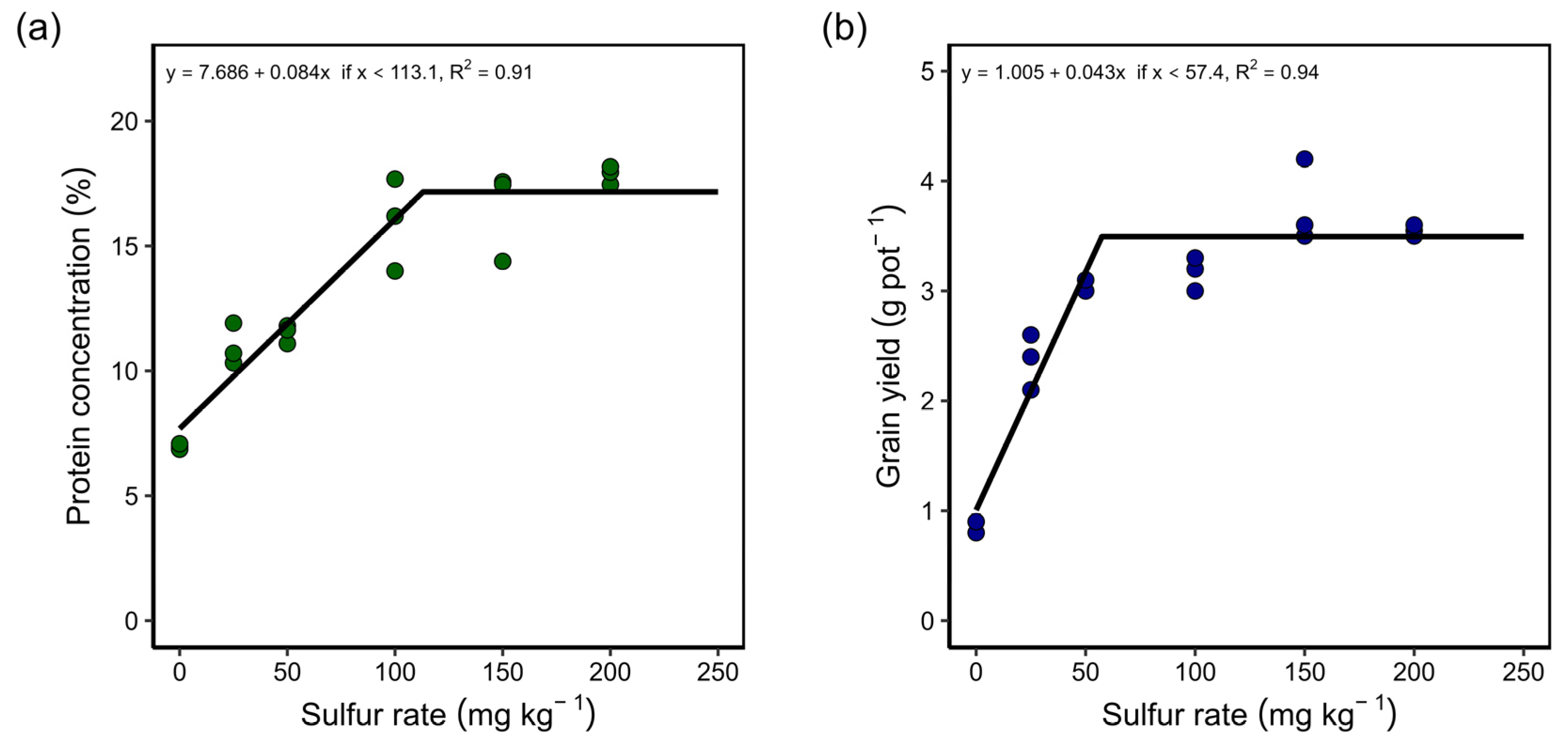
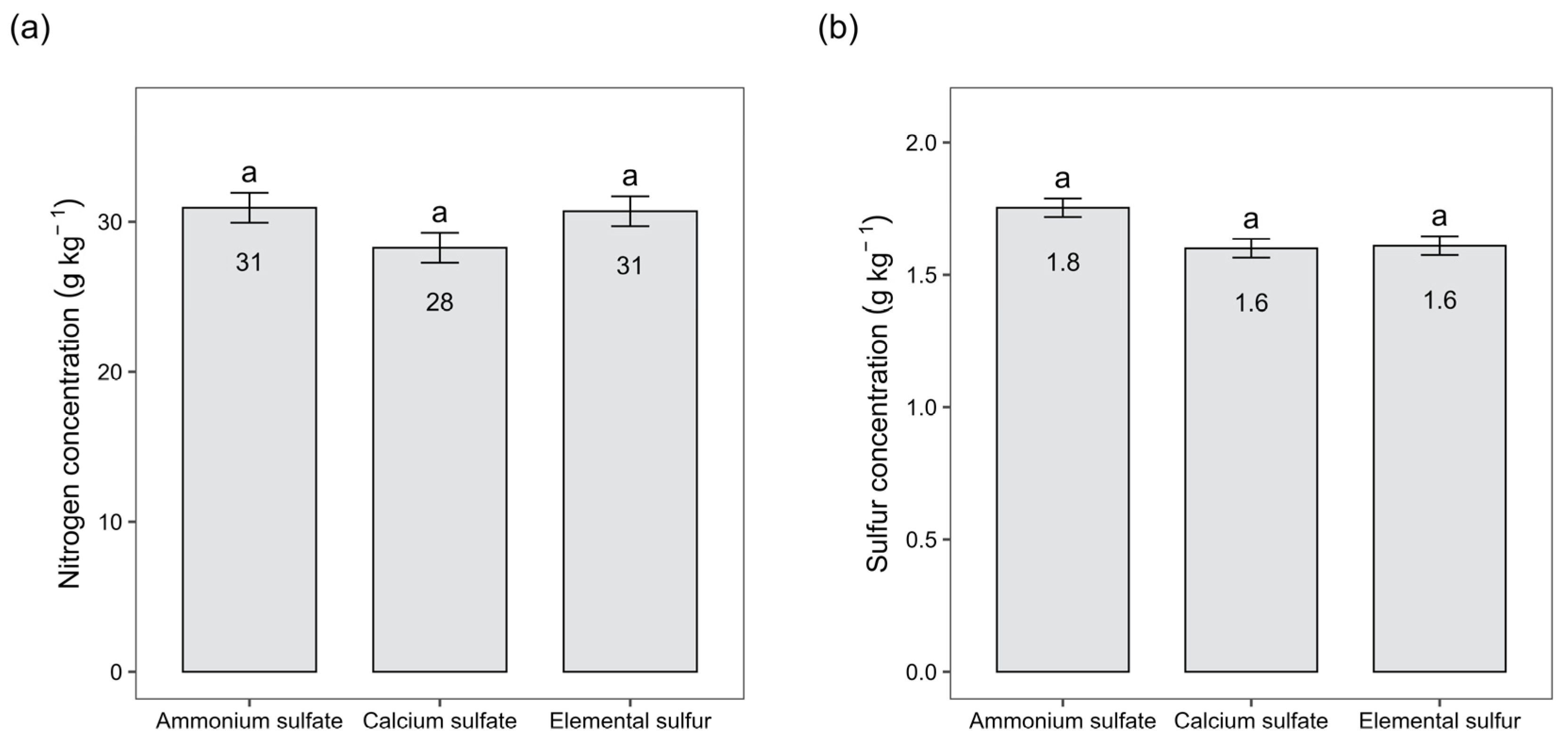
3.3. Greenhouse: Study with Different Sulfur Rates and Sources
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Mottaleb, K.A.; Sonder, K.; Donovan, J.; Braun, H.-J. Global Trends in Wheat Production, Consumption and Trade. In Wheat Improvement: Food Security in a Changing Climate; Reynolds, M.P., Braun, H.-J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 47–66. ISBN 978-3-030-90673-3. [Google Scholar]
- Shiferaw, B.; Smale, M.; Braun, H.-J.; Duveiller, E.; Reynolds, M.; Muricho, G. Crops That Feed the World 10. Past Successes and Future Challenges to the Role Played by Wheat in Global Food Security. Food Sec. 2013, 5, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Ludewig, U.; Hawkesford, M.J. Perspective on Wheat Yield and Quality with Reduced Nitrogen Supply. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkesford, M.J. Plant Responses to Sulphur Deficiency and the Genetic Manipulation of Sulphate Transporters to Improve S-utilization Efficiency. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Hawkesford, M.; McGrath, S. Sulphur Assimilation and Effects on Yield and Quality of Wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 1999, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, H.W. Sulphur in Crop Production—Invited Paper. Eur. J. Agron. 2001, 14, 81–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Cox, M.S.; Oglesby, C.; Dhillon, J.S. Revisiting the Role of Sulfur in Crop Production: A Narrative Review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 15, 101013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberato, J.; Shaun, S. Sulfur Deficiency. In Soil Fertility Update; Purdue University Department of Agronomy: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Branlard, G.; Griffin, W.; McNeil, D. The Effect of Nitrogen and Sulphur Fertilisation and Their Interaction with Genotype on Wheat Glutenins and Quality Parameters. Cereal Sci. 2000, 31, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M.J.; De Kok, L.J. Managing Sulphur Metabolism in Plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvagiotti, F.; Castellarín, J.M.; Miralles, D.J.; Pedrol, H.M. Sulfur Fertilization Improves Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Wheat by Increasing Nitrogen Uptake. Field Crops Res. 2009, 113, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, E.; Haneklaus, S.; Schnug, E. Influence of Nitrogen and Sulfur Fertilization on the Alliin Content of Onions and Garlic. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 27, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, T.; Wachter, A. Sulfur Metabolism: A Versatile Platform for Launching Defence Operations. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, E.K.; Tosi, M.; Obregón, D.; Dunfield, K.E.; Germida, J.J. Rethinking Crop Nutrition in Times of Modern Microbiology: Innovative Biofertilizer Technologies. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 606815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, O.P.; Kumar, P.; Yadav, B.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Sulfur Nutrition and Its Role in Plant Growth and Development. Plant Signal. Behav. 2022, 0, 2030082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tea, I.; Genter, T.; Naulet, N.; Boyer, V.; Lummerzheim, M.; Kleiber, D. Effect of Foliar Sulfur and Nitrogen Fertilization on Wheat Storage Protein Composition and Dough Mixing Properties. Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Grover, C.; Steinfurth, D.; Hermann Mühling, K. Quantitative Proteome Analysis of Wheat Gluten as Influenced by N and S Nutrition. Plant Soil 2010, 327, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flæte, N.E.S.; Hollung, K.; Ruud, L.; Sogn, T.; Færgestad, E.M.; Skarpeid, H.J.; Magnus, E.M.; Uhlen, A.K. Combined Nitrogen and Sulphur Fertilisation and Its Effect on Wheat Quality and Protein Composition Measured by SE-FPLC and Proteomics. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 41, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryant, P.; Hřivna, L. The Effect of Sulphur Fertilisation on Yield and Technological Parameters of Spring Wheat Grain. Agron. Sci. 2004, 59, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Salmon, S.; Withers, P.; Monaghan, J.; Evans, E.; Shewry, P.; McGrath, S. Variation in the Breadmaking Quality and Rheological Properties of Wheat in Relation to Sulphur Nutrition under Field Conditions. J. Cereal Sci. 1999, 30, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, D.; Franzen, D.W.; Chatterjee, A. Do Crops’ Responses to Sulfur Vary with Its Forms? Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2021, 4, e20201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dick, W.A. Gypsum as an Agricultural Amendment: General Use Guidelines; The Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, J. Soil Sulfur Cycling in Temperate Agricultural Systems. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Chapter 2; Volume 102, pp. 55–89. ISBN 978-0-12-374818-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bargaz, A.; Lyamlouli, K.; Chtouki, M.; Zeroual, Y.; Dhiba, D. Soil Microbial Resources for Improving Fertilizers Efficiency in an Integrated Plant Nutrient Management System. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, J.R.; Hinckley, E.-L.S. It Is Time to Develop Sustainable Management of Agricultural Sulfur. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Web of Science Research Database. Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- CAB Direct Research Database. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Google Scholar Academic Search Engine. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Ritchie, S.; Banyas, K.; Sevin, C.A. Comparison of Selected Bibliographic Database Search Retrieval for Agricultural Information. Issues Sci. Technol. Librariansh. 2019, 93, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayyan Systematic Review Management Tool. Available online: https://www.rayyan.ai/ (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Mariotti, F.; Tomé, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting Nitrogen into Protein—Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ Factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, S. GetData Graph Digitizer 2.26 2017. Available online: https://getdata-graph-digitizer.software.informer.com/ (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Extract Table Data Extraction Tool. Available online: https://www.extracttable.com/ (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Waksman, S.A.; Stevens, K.R. A Critical Study of the Methods for Determining the Nature and Abundance of Soil Organic Matter. Soil Sci. 1930, 30, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.A.; Wilks, A.R.; Brownrigg, R.; Minka, T.P.; Deckmyn, A. Maps: Draw Geographical Maps. R Package Version 3.4.2. 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.maps (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Randall, P.; Freney, J.; Smith, C.; Moss, H.; Wrigley, C.; Galbally, I. Effect of Additions of Nitrogen and Sulfur to Irrigated Wheat at Heading on Grain Yield, Composition and Milling and Baking Quality. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1990, 30, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.P.; Ram, P.C.; Warsi, A.S. Effect of Sulphur on Growth, Yield and Quality of Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Indian J. Agron. 1991, 36, 258. [Google Scholar]
- Feyh, R.L.; Lamond, R.E. Sulfur and Nitrogen Fertilization of Winter Wheat. J. Prod. Agric. 1992, 5, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.H.; Modhwadia, M.M.; Khanpara, V.D. Integrated Nutrient Management in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Gujarat Agric. Univ. Res. J. 1997, 23, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.J.; Withers, P.J.A.; Evans, E.J.; Monaghan, J.M.; Salmon, S.E.; Shewry, P.R. Yield and Breadmaking Quality Responses of Winter Wheat to Sulphur Fertiliser; HGCA Project Report; Home-Grown Cereals Authority: London, UK, 1999; 85p. [Google Scholar]
- Sakal, R.; Singh, A.P.; Sinha, R.B.; Bhogal, N.S.; Ismail, M. Impact of Sulphur Fertilisation in Sustaining the Productivity of Rice-Wheat Cropping System. Fert. News 1999, 44, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, B.A.; Haq, I.; Ahmad, E. Wheat Response to Sulphur Application. SJA 2003, 19, 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, M.M.; Bahar, A.A.; Kabesh, M.O. Role of Sulphur in Increasing Nutrient Use Efficiency by Wheat and Faba Bean. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. (Cairo) 2003, 28, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido-Lestache, E.; Lopez-Bellido, R.; Lopez-Bellido, L. Durum Wheat Quality under Mediterranean Conditions as Affected by N Rate, Timing and Splitting, N Form and S Fertilization. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 23, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.; Bernier, R.; Iraira, S. Efecto de Fuentes de Azufre Sobre El Rendimiento y Calidad de Trigo y Pradera En Dos Andisoles. Agric. Téc. 2006, 66, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, G.Y.; Couretot, L. Trigo: Efectos de La Interaccion Nitrogeno x Azufre y La Aplicación Complementaria de Nitrógeno Foliar Sobre El Rendimiento y La Calidad; Publicación Miscelánea No 107; INTA—Estación Experimental Agropecuaria Rafaela: Rafaela, Argentina, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kharub, A.S.; Dhillon, O.P. Effect of Sulphur Application on Productivity and Quality of Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 77, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pasha, A.; Chittapur, B.M.; Patil, B.N.; Hiremath, S.M. Effect of Prolonged Nitrogen Application and Sulphur Nutrition on Grain Quality and Nutrient Uptake of Wheat and Soil Available Nutrient Dynamics. Karnataka J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 20, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Shirpurkar, G.N.; Bhoite, S.V.; Wagh, M.P. Effect of Nitrogen and Sulphur Levels on Yield and Quality of Wheat. Agric. Sci. Dig. 2007, 27, 150–151. [Google Scholar]
- Tea, I.; Genter, T.; Naulet, N.; Marie, L.M.; Kleiber, D. Interaction between Nitrogen and Sulfur by Foliar Application and Its Effects on Flour Bread-Making Quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 2853–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, W.E.; Phillips, S.B.; Pridgen, T.H.; Kenner, J.C.; Griffey, C.A.; Beahm, B.R.; Seabourn, B.W. Managing Nitrogen and Sulfur Fertilization for Improved Bread Wheat Quality in Humid Environments. Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanetto, H.; Keller, O.; Albrecht, J.; Negro, C.; Belotti, L.; Giailevra, D. Efecto de Fuentes y Dosis de Nitrógeno Combinados Con Azufre Sobre Los Rendimientos y La Calidad Panadera Del Trigo En La Región Central de Santa Fe; Publicación Miscelánea No 109; INTA—Estación Experimental Agropecuaria Rafaela: Rafaela, Argentina, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Järvan, M.; Edesi, L.; Adamson, A.; Lukme, L.; Akk, A. The Effect of Sulphur Fertilization on Yield, Quality of Protein and Baking Properties of Winter Wheat. Agron. Res. 2008, 6, 459–469. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf, A.I. Effect of Phosphorus, Zinc and Sulphur Application on the Growth Characters, p and Zn Uptake, Yield Components of Wheat Plant Grown on Calcareous Soil. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2008, 33, 6265–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.A.; Koller, W.D.; Graeff, S.; Hermann, W.; Merkt, N.; Claupein, W. Impact of Different Nitrogen Fertilizers and an Additional Sulfur Supply on Grain Yield, Quality, and the Potential of Acrylamide Formation in Winter Wheat. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2008, 171, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.S.; Schoenau, J.J.; Vera, C.L. Influence of Six Successive Annual Applications of Sulphur Fertilizers on Wheat in a Wheat-Canola Rotation on a Sulphur Deficient Soil. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2009, 89, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, D.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Powers, S.J.; Millar, S.; Shewry, P.R. Effects of Crop Nutrition on Wheat Grain Composition and End Use Quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoel, B.O. Effects of Sulphur Application on Grain Yield and Quality, and Assessment of Sulphur Status in Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Plant Soil Sci. 2011, 61, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.M.; Shehata, H.S.; Shaban, K.A. Impact of Biofertilizer and Elemental Sulphur on Growth and Yield of Wheat (Triticum aestivum Var.) Grown in Saline Sodic Soil. Egypt. J. Microbiol. 2010, SI, 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Coventry, D.R.; Poswal, R.S.; Yadav, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Gill, S.C.; Chhokar, R.S.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Mehta, A.; et al. Effect of Tillage and Nutrient Management on Wheat Productivity and Quality in Haryana, India. Field Crops Res. 2011, 123, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L.E.; Pinilla, H.; Sanhueza, H. Effects of Sulfur Fertilization on Wheat Production and Industrial Quality (Triticum aestivum). Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2012, 39, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Ullah, H.; Ahmad, B.; Inamullah; Malik, M.F.A. Effect of Incremental Dose of Phosphorous and Sulphur upon Yield and Protein Content of Wheat. BioDiCon 2012, 5, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Järvan, M.; Edesi, L.; Adamson, A. The Content and Quality of Protein in Winter Wheat Grains Depending on Sulphur Fertilization. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2012, 62, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondek, K. Contents of Sulphur, Total Protein, Methionine and Cysteine in Spring Wheat Biomass after Fertilization with Sewage Sludge. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2012, 19, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrivna, L.; Kotkova, B.; Buresova, I. Effect of Sulphur Fertilization on Yield and Quality of Wheat Grain. Cereal Res. Commun. 2015, 43, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, S.; Singh, J.; Singh, S.P. Influence of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Fertility and Productivity of Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 85, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivoto, T.; Carvalho, I.R.; Nardino, M.; Ferrari, M.; de Pelegrin, A.J.; Follmann, D.N.; Gutkoski, L.C.; Souza, V.Q. de Efeitos de Enxofre e Nitrogênio Na Qualidade Industrial e No Rendimento de Grãos de Trigo. Rev. Ciênc. Agroveterinárias 2016, 15, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klikocka, H.; Cybulska, M.; Barczak, B.; Narolski, B.; Szostak, B.; Kobiałka, A.; Nowak, A.; Wójcik, E. The Effect of Sulphur and Nitrogen Fertilization on Grain Yield and Technological Quality of Spring Wheat. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Shukla, R.; Verma, S.; Pathak, R. Yield and Quality of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Influenced by NPK Levels, Sulphur Levels and FYM. IJCS 2017, 5, 806–808. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, F.; Fathallah Rehab, I.; Khalil ElSakhawy, G.A.; Ibrahim, M.E. Impact of Sulfur, Nitrogen Application Methods and Biofertilization on Productivity and Quality of Wheat Crop. Adv. Agric. Res. 2017, 22, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Karaman, R.; Șener, A. Effects of Nano Sulfur (S) Applications on Yield and Some Yield Properties of Bread Wheat. Sci. Pap.–Ser. A Agron. 2018, 61, 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Stockmann, F.; Weber, E.A.; Schreiter, P.; Merkt, N.; Claupein, W.; Graeff-Hönninger, S. Impact of Nitrogen and Sulfur Supply on the Potential of Acrylamide Formation in Organically and Conventionally Grown Winter Wheat. Agronomy 2018, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A. Additions of Ammonium Sulfate and Urease Inhibitor with Urea to Improve Spring Wheat and Sugar Beet Yield. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A. Spring Wheat Response to Supplemental Nutrient Additions under Silty Clay Loam Soils of Minnesota. Crop Forage Turfgrass Manag. 2018, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, B.R.; Lollato, R.P. Wheat Grain Yield and Protein Response to Nitrogen and Sulfur Rates. Kans. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, D.E.; Sutradhar, A.K.; Wiersma, J.J. Do Hard Red Spring Wheat Varieties Vary in Their Response to Sulfur? Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, M.; Lepiarczyk, A.; Bachara, B.F.M. Ammonium Nitrate Enriched with Sulfur Influences Wheat Yield and Soil Properties. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventimiglia, L.; Torrens Baudrix, L. Trigo: Mejorando El Rendimiento Con Azufre. Profesionales AER 9 de Julio; INTA—Estación Experimental Agropecuaria Pergamino: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Santis, M.A.; Giuliani, M.M.; Flagella, Z.; Reyneri, A.; Blandino, M. Impact of Nitrogen Fertilisation Strategies on the Protein Content, Gluten Composition and Rheological Properties of Wheat for Biscuit Production. Field Crops Res. 2020, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, L.; Napoli, M.; Mancini, M.; Masella, P.; Cappelli, A.; Parenti, A.; Orlandini, S. Wheat Grain Composition, Dough Rheology and Bread Quality as Affected by Nitrogen and Sulfur Fertilization and Seeding Density. Agronomy 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, B.R.; Wilson, T.; Nelson, N.O.; Guttieri, M.; Lollato, R.P. Wheat Grain Yield and Protein Concentration Response to Nitrogen and Sulfur Rates. Kans. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 2020, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, V.K.; Raza, M.D.B.; Dimree, S.; Verma, A.K.; Pawar, A.B.; Upadhyay, D.P. Effect of Balanced Use of Nutrients on Yield Attributes, Yield and Protein Content of Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 90, 2369–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admasu, A. Effect of Sulphur on Quality and Nutrient Uptake of Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum) on Vertisols, Central Highlands, Ethiopia. Am. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 10, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, A.F.; Rogers, W.J.; Tranquilli, G.E.; Arrigoni, A.C.; Rondanini, D.P. Nitrogen-Sulfur Fertilisation Effects on Gluten Composition and Industrial Quality in Argentinean Bread Wheat Cultivars Differing in Apparent Sulfur Recovery. Crop Pasture Sci. 2021, 72, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carucci, F.; Gatta, G.; Gagliardi, A.; De Vita, P.; Bregaglio, S.; Giuliani, M.M. Agronomic Strategies to Improve N Efficiency Indices in Organic Durum Wheat Grown in Mediterranean Area. Plants 2021, 10, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibadullah; Muhammad, D. Enhancement in Maize-Wheat Productivity and N Use Efficiency through Sulfur Application in Two Diverse Climatic Conditions. Biosci. Res. 2021, 18, 1914–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch, B.R.; Wilson, T.; Nelson, N.; Guttieri, M.; Lollato, R.P. Wheat Variety Yield Response to Nitrogen and Sulfur Rates During the 2019–2020 Growing Season. Kans. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 2021, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Quality of Wheat (Triticum aestivum) under Nitrogen and Sulphur Nutrition in Alluvial Soil. Ann. Plant Soil Res. 2021, 23, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; She, M.; Zheng, T.; Diepeveen, D.; Islam, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Impact and Mechanism of Sulphur-Deficiency on Modern Wheat Farming Nitrogen-Related Sustainability and Gliadin Content. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soofizada, Q.; Pescatore, A.; Guerrini, L.; Fabbri, C.; Mancini, M.; Orlandini, S.; Napoli, M. Effects of Nitrogen plus Sulfur Fertilization and Seeding Density on Yield, Rheological Parameters, and Asparagine Content in Old Varieties of Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.B.; Nathan, M.V.; Laboski, C.A.M. pH and Lime Requirement. In Recommended Chemical Soil Test Procedures for the North Central Region; Nathan, M.V., Gelderman, R., Eds.; North Central Regional Research Publication No. 221 (Revised). SB 1001; Missouri Agricultural Experiment Station: Columbia, MO, USA, 2012; Chapter 4; pp. 4.1–4.7. [Google Scholar]
- Combs, S.M.; Nathan, M.V. Soil Organic Matter. In Recommended Chemical Soil Test Procedures for the North Central Region; Nathan, M.V., Gelderman, R., Eds.; North Central Regional Research Publication No. 221 (Revised). SB 1001; Missouri Agricultural Experiment Station: Columbia, MO, USA, 1998; Chapter 12; pp. 12.1–12.6. [Google Scholar]
- Warncke, D.; Brown, J.R. Potassium and Other Basic Cations. In Recommended Chemical Soil Test Procedures for the North Central Region; Nathan, M.V., Gelderman, R., Eds.; North Central Regional Research Publication No. 221 (Revised). SB 1001; Missouri Agricultural Experiment Station: Columbia, MO, USA, 1998; Chapter 7; pp. 7.1–7.3. [Google Scholar]
- Gieseking, J.E.; Snider, H.J.; Getz, C.A. Destruction of Organic Matter in Plant Material by the Use of Nitric and Perchloric Acids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1935, 7, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, R.C.; Harley, C.P. A Rapid Method for the Determination of Nitrogen in Plant Tissue. Science 1942, 96, 565–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.L.; Sheard, R.W.; Moyer, J.R. Comparison of Conventional and Automated Procedures for Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Analysis of Plant Material Using a Single Digestion. Agron. J. 1967, 59, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Sadras, V.O.; Lu, G.; Zhang, P.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Xie, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. A Global Meta-Analysis of Split Nitrogen Application for Improved Wheat Yield and Grain Protein Content. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The Meta-Analysis of Response Ratios in Experimental Ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.S.; Wang, X. A Meta-Analysis of Elevated CO2 Effects on Woody Plant Mass, Form, and Physiology. Oecologia 1998, 113, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Coulter, J.A.; Xie, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Deng, X.; Li, L. Winter Wheat Yield and Water Use Efficiency Response to Organic Fertilization in Northern China: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 229, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the Metafor Package. J. Stat. Soft. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrer, M.; Cuijpers, P.; Furukawa, T.A.; Ebert, D.D. Doing Meta-Analysis with R: A Hands-On Guide, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-0-367-61007-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, R.D. Detection of Influential Observation in Linear Regression. Technometrics 1977, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.D. Influential Observations in Linear Regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C.; Gurevitch, J.; Rosenberg, M.S. Resampling Tests for Meta-Analysis of Ecological Data. Ecology 1997, 78, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez, F.E. Nlraa: Nonlinear Regression for Agricultural Applications. R Package Version 1.9.7. 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.nlraa (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Anderson, R.L.; Nelson, L.A. A Family of Models Involving Intersecting Straight Lines and Concomitant Experimental Designs Useful in Evaluating Response to Fertilizer Nutrients. Biometrics 1975, 31, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciochi, W.D.; Wyngaard, N.; Divito, G.A.; Cabrera, M.L.; Reussi Calvo, N.I.; Echeverría, H.E. A Comparison of Indexes to Estimate Corn S Uptake and S Mineralization in the Field. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Soft. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2019; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Castellari, M.P.; Poffenbarger, H.J.; Van Sanford, D.A. Sulfur Fertilization Effects on Protein Concentration and Yield of Wheat: A Meta-Analysis. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdoff, F.; Van Es, H. Building Soils for Better Crops: Ecological Management for Healthy Soils; Handbook Series, 4th ed.; Sustainable Agriculture Research & Education: College Park, MD, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-888626-19-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, W.A.; Kost, D.; Chen, L. Availability of Sulfur to Crops from Soil and Other Sources. In Sulfur: A Missing Link between Soils, Crops, and Nutrition; Jez, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Chapter 5; Volume 50, pp. 59–82. ISBN 978-0-89118-186-6. [Google Scholar]
- Heckman, J. E365: Sulfur Nutrition and Soil Fertility Management for New Jersey Crops. Available online: https://njaes.rutgers.edu/e365/ (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Kertesz, M.A.; Mirleau, P. The Role of Soil Microbes in Plant Sulphur Nutrition. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churka, B.S.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Caires, E.F.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Sulfur Forms in Organic Substrates Affecting S Mineralization in Soil. Geoderma 2013, 200–201, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilom, G.; Rice, J.A. Organo-Clay Complexes in Soils and Sediments. In Biophysico-Chemical Processes Involving Natural Nonliving Organic Matter in Environmental Systems; Senesi, N., Xing, B., Huang, P.M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 111–145. ISBN 978-0-470-41300-5. [Google Scholar]
- White, C.; Spargo, J.; Wells, H.; Sanders, Z.; Rice, T.; Beegle, D. Sulfur Fertility Management for Grain and Forage Crops; Grain Crops—Agronomy Facts 80; The Pennsylvania State University: University Park, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, D. Evaluating the Need for Sulfur in High Organic Matter Soils; Minnesota Crop News—University of Minnesota Extension: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, N.W. The Relation between Yield and Protein in Cereal Grain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1995, 67, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreche, M.M.; Slafer, G.A. Variation of Grain Nitrogen Content in Relation with Grain Yield in Old and Modern Spanish Wheats Grown under a Wide Range of Agronomic Conditions in a Mediterranean Region. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 147, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.L.; Guttieri, M.J.; Nelson, N.O.; Fritz, A.; Tilley, M. Nitrogen and Sulfur Effects on Hard Winter Wheat Quality and Asparagine Concentration. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 93, 102969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, N.; Sadras, V.O.; Lollato, R.P. Late-Season Nitrogen Application Increases Grain Protein Concentration and Is Neutral for Yield in Wheat. A Global Meta-Analysis. Field Crops Res. 2023, 290, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ma, G.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Li, S.; Xie, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. Effect of Irrigation and Nitrogen Application on Grain Amino Acid Composition and Protein Quality in Winter Wheat. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomari, D.Z.; Schierenbeck, M.; Alqudah, A.M.; Alqahtani, M.D.; Wagner, S.; Rolletschek, H.; Borisjuk, L.; Röder, M.S. Wheat Grains as a Sustainable Source of Protein for Health. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid Iqbal, M.; Shams, N.; Fatima, K. Nutritional Quality of Wheat. In Wheat; Ansari, M.-R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-80355-522-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fukai, S.; Mitchell, J. Grain Yield and Protein Concentration Relationships in Rice. Crop Environ. 2024, 3, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, L.; He, P.; Pampolino, M.F.; Johnston, A.M.; Jin, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, W. Establishing a Scientific Basis for Fertilizer Recommendations for Wheat in China: Yield Response and Agronomic Efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2013, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, M.E.; Blackmer, A.M. Comparison of Models for Describing; Corn Yield Response to Nitrogen Fertilizer. Agron. J. 1990, 82, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Muhammad, D.; Mussarat, M. Effect of Various Nitrogen Sources at Various Sulfur Levels on Maize–Wheat Yield and N/S Uptake under Different Climatic Conditions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 2073–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, O.; Hewedy, O.A.; Abdelmoteleb, A.; Ali, M.; Youssef, M.S.; Roumia, A.F.; Seymour, D.; Yuan, Z.-C. Nitrogen Journey in Plants: From Uptake to Metabolism, Stress Response, and Microbe Interaction. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divito, G.A.; Echeverría, H.E.; Andrade, F.H.; Sadras, V.O. Diagnosis of S Deficiency in Soybean Crops: Performance of S and N:S Determinations in Leaf, Shoot and Seed. Field Crops Res. 2015, 180, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R.J.; Maples, R.L. Effect of Sulfur Additions on Soil and the Nutrition of Wheat. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1987, 18, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, S. Synergistic Impact of Co-Applied Micronized Sulfur and Nitrogen on Agronomical Traits of a Modern Spring Wheat Cultivars Grown in Alkaline Soil. Asian J. Res. Crop Sci. 2020, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
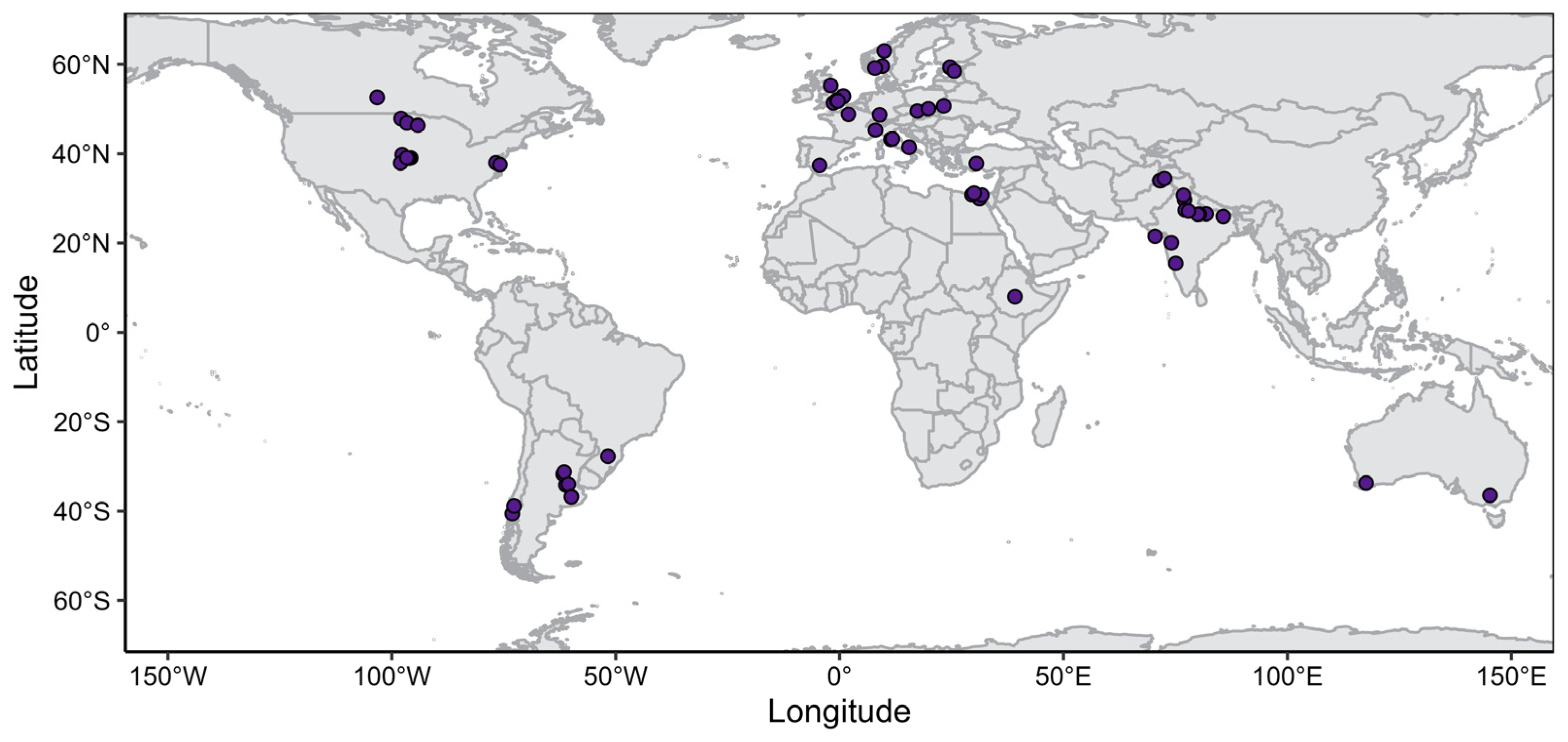



| Reference | Study ID | Country | Number of Comparisons | Concurrent Factors † | Experimental Design § | Number of Replications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | 1 | Australia | 2 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [38] | 2 | India | 5 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [39] | 3 | USA | 18 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [40] | 4 | India | 2 | SY, SS, SV | SP | 4 |
| [41] | 5 | UK | 139 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [42] | 6 | India | 9 | SY, SS, SV | NR | 6 |
| [43] | 7 | Pakistan | 15 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [44] | 8 | Egypt | 4 | MY, MS, SV | NR | 4 |
| [45] | 9 | Spain | 2 | MY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [46] | 10 | Chile | 4 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [47] | 11 | Argentina | 3 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [48] | 12 | India | 7 | MY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [49] | 13 | India | 10 | SY, SS, SV | SP | 3 |
| [50] | 14 | India | 3 | SY, SS, SV | SP | 3 |
| [51] | 15 | France | 1 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [52] | 16 | USA | 4 | SY, SS, MV | SP | 4 |
| [53] | 17 | Argentina | 10 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [54] | 18 | Estonia | 9 | SY, SS, SV | NR | 4 |
| [55] | 19 | Egypt | 18 | SY, SS, SV | SP | 4 |
| [56] | 20 | Germany | 2 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [57] | 21 | Canada | 16 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [58] | 22 | UK | 1 | MY, SS, SV | NR | 3 |
| [59] | 23 | Norway | 12 | MY, MS, MV | RCB | 3 |
| [60] | 24 | Egypt | 10 | MY, SS, SV | SP | 4 |
| [61] | 25 | India | 24 | SY, MS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [62] | 26 | Chile | 6 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [63] | 27 | Pakistan | 3 | SY, SS, SV | SP | 4 |
| [64] | 28 | Estonia | 6 | SY, SS, SV | NR | 4 |
| [65] | 29 | Poland | 1 | MY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [66] | 30 | Czech Republic | 10 | SY, SS, SV | NR | 4 |
| [67] | 31 | India | 1 | MY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [68] | 32 | Brazil | 1 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [69] | 33 | Poland | 4 | MY, SS, SV | SP | 4 |
| [70] | 34 | India | 4 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [71] | 35 | Egypt | 4 | SY, SS, SV | SP | 3 |
| [72] | 36 | Turkey | 4 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [73] | 37 | Germany | 2 | MY, MS, SV | NR | 3 |
| [74] | 38 | USA | 4 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [75] | 39 | USA | 3 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [76] | 40 | USA | 9 | SY, MS, MV | SP | 4 |
| [77] | 41 | USA | 2 | MY, MS, MV | SP | 4 |
| [78] | 42 | Poland | 9 | SY, SS, SV | NR | 4 |
| [79] | 43 | Argentina | 6 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 4 |
| [80] | 44 | Italy | 9 | SY, SS, MV | RCB | 4 |
| [81] | 45 | Italy | 1 | SY, SS, MV | SP | 3 |
| [82] | 46 | USA | 18 | SY, SS, MV | SP | 4 |
| [83] | 47 | India | 2 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [84] | 48 | Ethiopia | 5 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [85] | 49 | Argentina | 60 | SY, SS, SV | SP | 3 |
| [86] | 50 | Italy | 2 | SY, SS, MV | SP | 3 |
| [87] | 51 | Pakistan | 18 | SY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [88] | 52 | USA | 9 | SY, SS, MV | SP | 4 |
| [89] | 53 | India | 3 | MY, SS, SV | RCB | 3 |
| [90] | 54 | Australia | 8 | SY, SS, SV | NR | 3 |
| [91] | 55 | Italy | 1 | MY, SS, MV | SP | 3 |
| Component | Value |
|---|---|
| pH (1:1) | 5.8 |
| OM (g kg−1) | 9.0 |
| P—Mehlich 3 (mg kg−1) | 54 |
| K (mg kg−1) | 127 |
| S (mg kg−1) | 1.4 |
| CEC (cmol+ kg−1) | 6.8 |
| Texture | Sandy loam |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roa, G.A.; Quintana-Obregón, E.A.; González-Renteria, M.; Ruiz Diaz, D.A. Increasing Wheat Protein and Yield through Sulfur Fertilization and Its Relationship with Nitrogen. Nitrogen 2024, 5, 553-571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen5030037
Roa GA, Quintana-Obregón EA, González-Renteria M, Ruiz Diaz DA. Increasing Wheat Protein and Yield through Sulfur Fertilization and Its Relationship with Nitrogen. Nitrogen. 2024; 5(3):553-571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen5030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoa, Gustavo A., Eber Addí Quintana-Obregón, Mariela González-Renteria, and Dorivar A. Ruiz Diaz. 2024. "Increasing Wheat Protein and Yield through Sulfur Fertilization and Its Relationship with Nitrogen" Nitrogen 5, no. 3: 553-571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen5030037
APA StyleRoa, G. A., Quintana-Obregón, E. A., González-Renteria, M., & Ruiz Diaz, D. A. (2024). Increasing Wheat Protein and Yield through Sulfur Fertilization and Its Relationship with Nitrogen. Nitrogen, 5(3), 553-571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen5030037







