Non-Ideal X-Gate and Z-Gate in Semiconducting Spin Qubit Implementations †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantum Dot and Donor Spin Qubits Effective Hamiltonian Models
- SQ: is the Zeeman frequency associated to the DC applied magnetic field, is the angular frequency of the AC local magnetic field and is the angular frequency that depends on the amplitude of that field.
- STQ: is the magnetic field gradient between the QDs and J is the exchange coupling between the two spins.
- HQ: is the Zeeman energy associated to the constant applied magnetic field and are the exchange couplings among couple of spins.
- DQ: the same as for the SQ, where is the analogous of and is equal to , with and . The parameters and are respectively the electron and nuclear gyromagnetic ratio, is the external DC magnetic field and A is the hyperfine coupling. The donor nuclear spin is supposed equal to .
- SDQ: J is the exchange coupling between the electron spins of the donor and of the dot, A is the hyperfine coupling between the electron spin and the nuclear spin of the donor and is the applied DC magnetic field. The donor nuclear spin is supposed equal to .
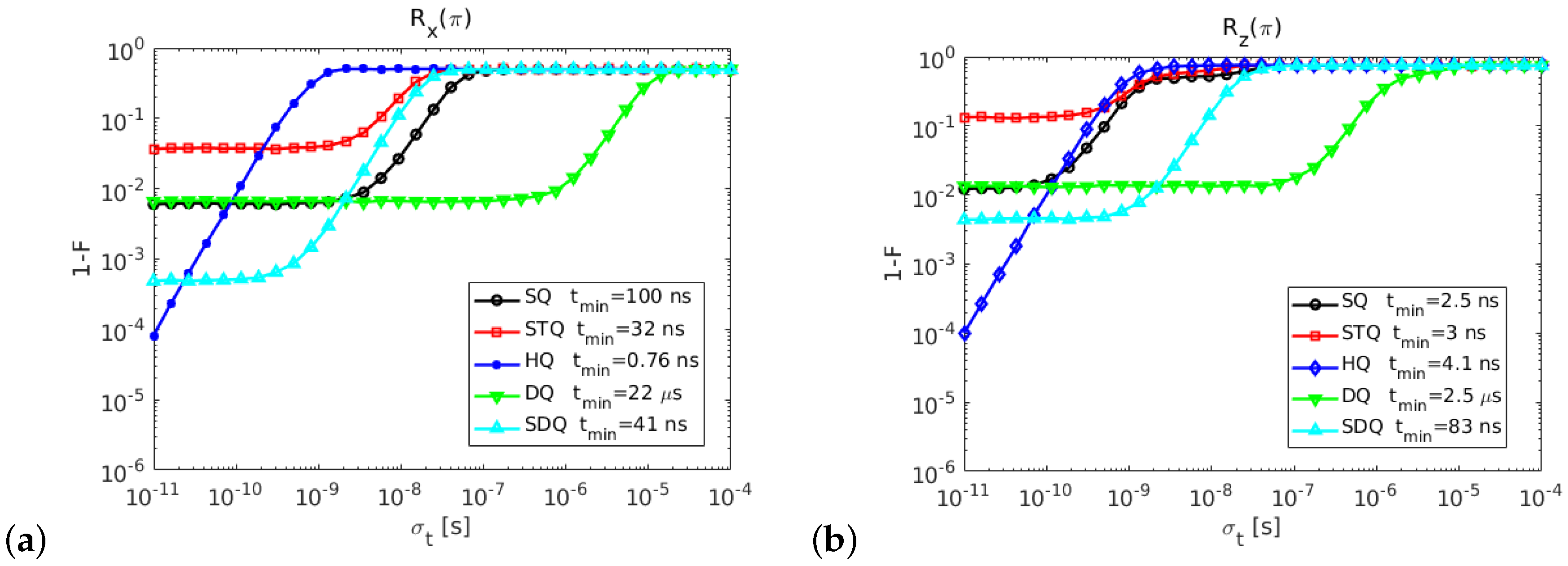
2.2. Comparison of Gate Fidelities among Qubit Types
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawakami, E.; Scarlino, P.; Ward, D.R.; Braakman, F.R.; Savage, D.E.; Lagally, M.G.; Friesen, M.; Coppersmith, S.N.; Eriksson, M.A.; Vandersypen, L.M.K. Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a Si/SiGe quantum dot. Nat. Nanotchnol. 2014, 9, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, J.J.; Tan, K.Y.; Dehollain, J.P.; Lim, W.H.; Morton, J.J.; Jamieson, D.N.; Dzurak, A.S.; Morello, A. A single-atom electron spin qubit in silicon. Nature 2012, 489, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, L.; Xuedong, H.; You, J.Q. Controllable exchange coupling between two singlet-triplet qubits. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 205306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coish, W.A.; Loss, D. Singlet-triplet decoherence due to nuclear spins in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 125337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ward, D.R.; Prance, J.R.; Kim, D.; Gamble, J.K.; Mohr, R.T.; Shi, Z.; Savage, D.E.; Lagally, M.G.; Friesen, M.; et al. Two-axis control of a singlet–triplet qubit with an integrated micromagnet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11938–11942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorgrimsson, B.; Kim, D.; Yang, Y.C.; Smith, L.W.; Simmons, C.B.; Ward, D.R.; Foote, R.H.; Corrigan, J.; Savage, D.E.; Lagally, M.G.; et al. Extending the coherence of a quantum dot hybrid qubit. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2017, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucht, A.; Muhonen, J.T.; Mohiyaddin, F.A.; Kalra, R.; Dehollain, J.P.; Freer, S.; Hudson, F.E.; Veldhorst, M.; Rahman, R.; Klimeck, G.; et al. Electrically controlling single-spin qubits in a continuous microwave field. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey-Collard, P.; Jacobson, N.T.; Rudolph, M.; Dominguez, J.; Ten Eyck, G.A.; Wendt, J.R.; Pluym, T.; Gamble, J.K.; Lilly, M.P.; Pioro-Ladrière, M.; et al. Coherent coupling between a quantum dot and a donor in silicon. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, E.; De Michielis, M.; Mazzeo, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Prati, E. Effective Hamiltonian for the hybrid double quantum dot qubit. Quantum Inf. Process. 2014, 13, 1155–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, E.; De Michielis, M.; Fanciulli, M.; Prati, E. Effective Hamiltonian for two interacting double-dot exchange-only qubits and their controlled-NOT operations. Quantum Inf. Process. 2015, 14, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Michielis, M.; Ferraro, E.; Fanciulli, M.; Prati, E. Universal set of quantum gates for double-dot exchange-only spin qubits with intradot coupling. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2015, 48, 065304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, E.; Fanciulli, M.; De Michielis, M. Gate fidelity comparison in semiconducting spin qubit implementations affected by control noises. J. Phys. Commun. 2018, 2, 115022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technologies Keysight. Keysight Technologies E8257D PSG Microwave Analog Signal Generator; Technologies Keysight: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Qubit | {, } | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQ (rot. frame) | 0 | |||
| STQ | ||||
| HQ | ||||
| DQ (rot. frame) | 0 | |||
| SDQ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferraro, E.; Fanciulli, M.; Michielis, M.D. Non-Ideal X-Gate and Z-Gate in Semiconducting Spin Qubit Implementations. Proceedings 2019, 12, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019012053
Ferraro E, Fanciulli M, Michielis MD. Non-Ideal X-Gate and Z-Gate in Semiconducting Spin Qubit Implementations. Proceedings. 2019; 12(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019012053
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerraro, Elena, Marco Fanciulli, and Marco De Michielis. 2019. "Non-Ideal X-Gate and Z-Gate in Semiconducting Spin Qubit Implementations" Proceedings 12, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019012053
APA StyleFerraro, E., Fanciulli, M., & Michielis, M. D. (2019). Non-Ideal X-Gate and Z-Gate in Semiconducting Spin Qubit Implementations. Proceedings, 12(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019012053





