Ontology-Based Categorisation of Medical Texts for Health Professionals †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Works
3. Method
- Recording information generated by health professionals: First, the information generated by health professionals is collected in order to process it.
- Text analysis: Second, the medical text is analysed by splitting it into tokens.
- Diagnosis extraction: Third, medical vocabulary concepts included in the processed text are extracted.
- Coding by medical vocabularies: Fourth, the text is encoded by relating it to the list of tags proposed by the medical vocabularies.
- Returning resulted tags: Finally, the tags are returned so that external systems can use them to support health professionals tagging.
4. Evaluation
4.1. Method Deployment
4.2. Analysis of Results
- Total match: The keyword proposed by the author appears in the result provided by Apache Stanbol.
- Partial match: The keyword proposed by the author is a compound word and it partially appears in the result provided by Apache Stanbol.
- No match: The keyword proposed by the author does not appear in the result provided by Apache Stanbol.
- The keywords choice of an article is a subjective task. Different authors can choose different keywords for the same article.
- Apache Stanbol returns the related keywords to the words that appear in the abstract of each article only if they are also part of the ontology.
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Funding
References
- Lee, D.; de Keizer, N.; Lau, F.; Cornet, R. Literature review of SNOMED CT use. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2013, 21, e11–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, T. Principles of Health Interoperability HL7 and SNOMED; Springer: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb, C.E. Medical subject headings (MeSH). Bull. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2000, 88, 265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kreuzthaler, M.; Pfeifer, B.; Vera, J.R.; Kramer, D.; Grogger, V.; Bredenfeldt, S.; Pedevilla, M.; Krisper, P.; Schulz, S. EHR Text Categorization for Enhanced Patient-Based Document Navigation. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2018, 248, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunter, T.D.; Terry, N.P. The emergence of national electronic health record architectures in the United States and Australia: models, costs, and questions. J. Med. Internet Res. 2005, 7, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuzthaler, M.; Schulz, S.; Berghold, A. Secondary use of electronic health records for building cohort studies through top-down information extraction. J. Biomed. Inform. 2015, 53, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McCracken, S.S.; Edwards, J.S. Implementing a knowledge management system within an NHS hospital: a case study exploring the roll-out of an electronic patient record (EPR). Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2017, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.L.T.; Siu, K.Y.P.; Ho, T.S.G.; Wu, C.; Lam, H.Y.; Tang, V.; Tsang, Y.P. An intelligent case-based knowledge management system for quality improvement in nursing homes. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2018, 48, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeshan, F.; Mohamad, R. Medical ontology in the dynamic healthcare environment. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2012, 10, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Solano, C.; Cáceres, J.; Sicilia, M.Á. Generating SNOMED CT subsets from clinical glossaries: An exploration using clinical guidelines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on ENTERprise Information Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 5–7 October 2011; pp. 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kassahun, Y.; Perrone, R.; De Momi, E.; Berghöfer, E.; Tassi, L.; Canevini, M.P.; Spreafico, R.; Ferrigno, G.; Kirchner, F. Automatic classification of epilepsy types using ontology-based and genetics-based machine learning. Artif. Intell. Med. 2014, 61, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopman, B.; Zuccon, G.; Nguyen, A.; Bergheim, A.; Grayson, N. Automatic ICD-10 classification of cancers from free-text death certificates. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2015, 84, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Mar Roldán-García, M.; García-Godoy, M.J.; Aldana-Montes, J.F. Dione: An OWL representation of ICD-10-CM for classifying patients’ diseases. J. Biomed. Semant. 2016, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, B. Design and Creation. Researching Information Systems and Computing; Sage: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2005; pp. 108–124. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, F. Has the revolution arrived? Nature 2010, 464, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høst, A.; Halken, S. A prospective study of cow milk allergy in Danish infants during the first 3 years of life. Allergy 1990, 45, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvia, L.; H., A.A. Posttraumatic Headache: Classification by Symptom—Based Clinical Profiles. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2018, 58, 873–882. [Google Scholar]
- Urke, H.B.; Mittelmark, M.B.; Amugsi, D.A.; Matanda, D.J. Resources for nurturing childcare practices in urban and rural settings: Findings from the Colombia 2010 Demographic and Health Survey. Child Care Health Dev. 2018, 44, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
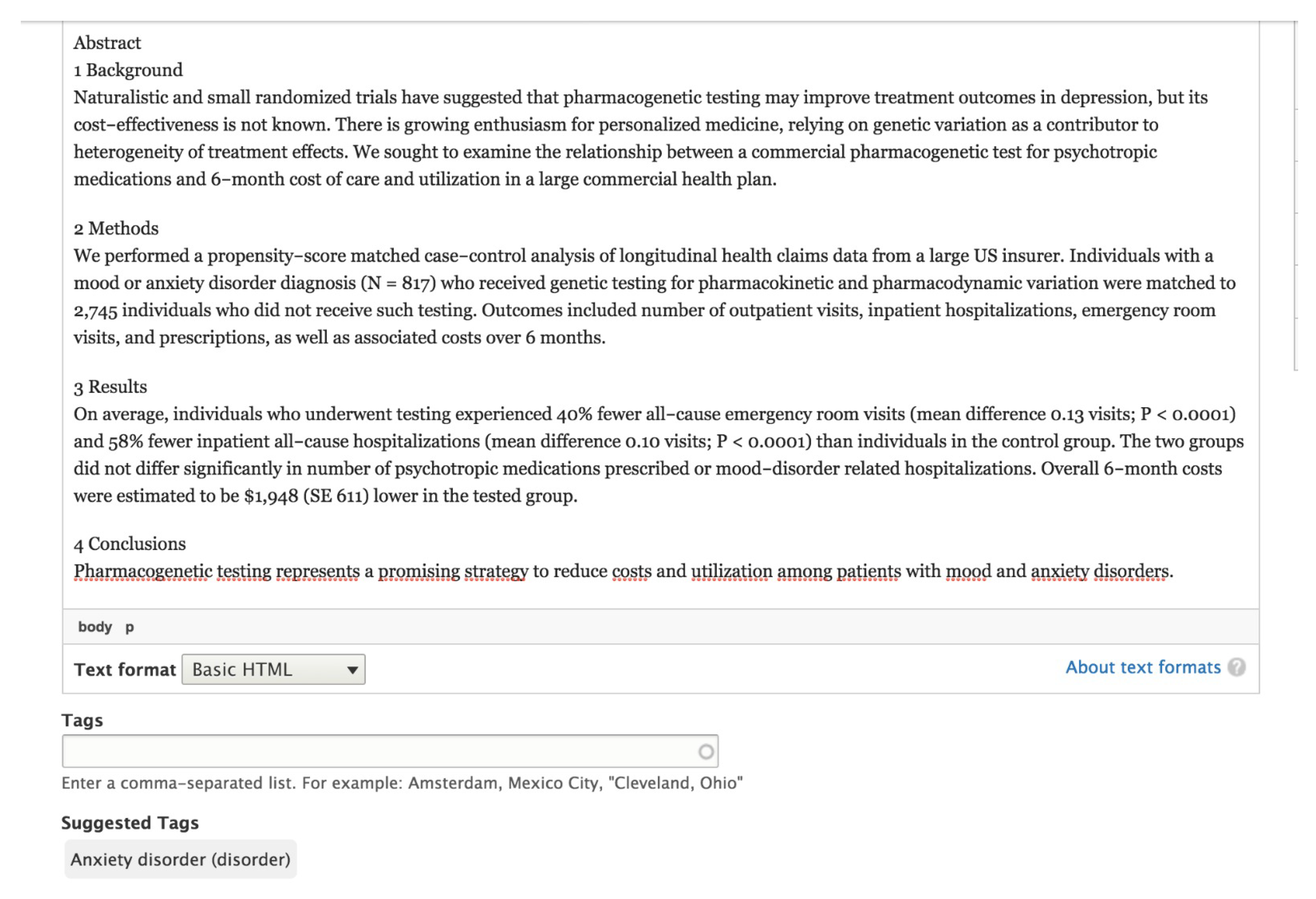
- Perlis, R.H.; Mehta, R.; Edwards, A.M.; Tiwari, A.; Imbens, G.W. Pharmacogenetic testing among patients with mood and anxiety disorders is associated with decreased utilization and cost: A propensity—Score matched study. Depress. Anxiety 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, G.L.; Liu, Y.; Isaacs, Y.E.; Ayoub, A.M.; Brosius, A.; Salander, Z.; Arnold, P.D. Error-related brain activity in adolescents with obsessive—Compulsive disorder and major depressive disorder. Depress. Anxiety 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lars, E. Future Preventive Therapy: Are There Promising Drug Targets? Headache Curr. 2006, 3, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, S.A.; Tajiri, N.; Bickford, P.C.; Borlongan, C.V. Cell Proliferation in the Brains of Adult Rats Exposed to Traumatic Brain Injury. In Neurostereology; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Chapter 2; pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maternal medication and the baby. In Neonatal Formulary 7; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Chapter 18; pp. 560–607.
- Wildhaber, J.; Carroll, W.D.; Brand, P.L. Global impact of asthma on children and adolescents’ daily lives: The room to breathe survey. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2012, 47, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanaporn, A.; Surachai, K.; Somchai, S. Natural history of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea in Thai school-age children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2005, 39, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Paper | Keywords | Apache Stanbol Proposed MeSH Keywords | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | food allergy; incidence; inhalant allergy; milk allergy | allergens; development; diagnosis; food; infant; milk proteins; municipalities; risk; sensitivity; symptoms; time | 0.25 | 0.625 |
| [17] | posttraumatic headache; traumatic brain injury; International Classification of Headache Disorders; secondary headache disorders | classification; headache; headache disorders; needs; patients | 0.25 | 0.375 |
| [18] | childcare; Colombia; education; household wealth; maternal decision latitude; nurturing childcare; urban-rural residence | age groups; attention; caregivers; child; child health; Colombia; demographic and health surveys; findings; hygiene; immunization; methods; mothers; regression analysis; research; resources; socialization | 0.219 | 0.437 |
| [19] | antidepressant; anxiety disorder; biomarker; cytochrome P450; genetic; major depressive disorder; propensity score | anxiety disorders; anxiety disorders/diagnosis; control groups; cost; depression; genetic testing; genetic variation; hospitalization; medicine; methods; patients; pharmacogenomic testing; prescriptions; treatment outcome; utilization | 0.23 | 0.5 |
| [20] | adolescence; anxiety; biomarker; child behavior checklist; depression; error-related negativity; event-related potentials; research domain criteria | adolescent; control; history; methods; patients; risk; trends | 0.143 | 0.125 |
| [21] | migraine; prophylaxis; CGRP; VIP; trigeminovascular reflex | association; blood vessels; Europe; headache; neurotransmitters; population; review; role | 0.125 | 0.2 |
| [22] | adult rats; brain; cell proliferation; gray matter; traumatic brain injury (TBI) | cell death; cell proliferation; cerebral peduncle; disease/pathology; findings; injuries; neurogenesis | 0.286 | 0.4 |
| [23] | baby; maternal medications | abnormalities; acebutolol; bradycardia; malformations; mothers; ofloxacin; pantoprazole; placenta; quetiapine; risperidone; salmeterol | 0.045 | 0.25 |
| [24] | asthma; children; adolescent; pediatric; room; breathe; survey | ability; asthma; bullying; Canada; control; Greece; health; Hungary; quality of life; South Africa; sports; symptoms; United Kingdom | 0.077 | 0.143 |
| [25] | snoring; sleep; obstructive sleep apnea; polysomnography; children; natural history | aged; disease; natural history; parents; polysomnography; prevalence; questionnaires; research; sleep; Sleep Apnea Syndromes; snoring; symptoms | 0.375 | 0.75 |
| Average results | 0.2 | 0.38 | ||
| Paper | Keywords | Apache Stanbol proposed SNOMED-CT Keywords | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | food allergy; incidence; inhalant allergy; milk allergy | milk protein (substance), prick test (procedure) | 0.5 | 0.125 |
| [17] | posttraumatic headache; traumatic brain injury; International Classification of Headache Disorders; secondary headache disorders | headache disorder (disorder) | 0.5 | 0.125 |
| [18] | childcare; Colombia; education; household wealth; maternal decision latitude; nurturing childcare; urban-rural residence | symptom management (procedure) | 0 | 0 |
| [19] | antidepressant; anxiety disorder; biomarker; cytochrome P450; genetic; major depressive disorder; propensity score | anxiety disorder (disorder) | 1 | 0.14 |
| [20] | adolescence; anxiety; biomarker; child behavior checklist; depression; error-related negativity; event-related potentials; research domain criteria | 0 | 0 | |
| [21] | migraine; prophylaxis; CGRP; VIP; trigeminovascular reflex | calcitonin gene-related peptide (substance) | 1 | 0.2 |
| [22] | adult rats; brain; cell proliferation; gray matter; traumatic brain injury (TBI) | traumatic brain injury (disorder) | 1 | 0.2 |
| [23] | baby; maternal medications | 0 | 0 | |
| [24] | asthma; children; adolescent; pediatric; room; breathe; survey | 0 | 0 | |
| [25] | snoring; sleep; obstructive sleep apnea; polysomnography; children; natural history | sleep apnea (disorder) | 0.5 | 0.083 |
| Average results | 0.45 | 0.0873 | ||
| Approach | Issues |
|---|---|
| Manual categorisation | Time consuming task and transcription errors |
| clustering | Terms used to classify documents usually are not the right terms |
| Terms of a specific field | Computer-based methods that only work with a subset of terms |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balderas, A.; Person, T.; Baena-Pérez, R.; Dodero, J.M.; Ruiz-Rube, I.; De-Diego-González, J.L. Ontology-Based Categorisation of Medical Texts for Health Professionals. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2191203
Balderas A, Person T, Baena-Pérez R, Dodero JM, Ruiz-Rube I, De-Diego-González JL. Ontology-Based Categorisation of Medical Texts for Health Professionals. Proceedings. 2018; 2(19):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2191203
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalderas, Antonio, Tatiana Person, Rubén Baena-Pérez, Juan Manuel Dodero, Iván Ruiz-Rube, and José Luís De-Diego-González. 2018. "Ontology-Based Categorisation of Medical Texts for Health Professionals" Proceedings 2, no. 19: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2191203
APA StyleBalderas, A., Person, T., Baena-Pérez, R., Dodero, J. M., Ruiz-Rube, I., & De-Diego-González, J. L. (2018). Ontology-Based Categorisation of Medical Texts for Health Professionals. Proceedings, 2(19), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2191203






