1. Introduction
The authors have developed an intensive open field heated agriculture system using geothermal steam and steam condensate that extends growing seasons and enables out of region crops [
1]. It has an underground piping system in Iceland that is similar to heated sidewalks in New York City and how waste heat from combined heat and power (CHP) systems warms green roofs [
2].
The authors developed a sustainable monitoring system using the same heat source as the underground pipes to power thermoelectric generators.
The authors have patented the Thermoelectric Power Generation Device [
3], a standalone unit that has generated 6 W of steady state power in a test bed location with a delta T of about 130 °C.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Thermoelectric Power Generation Device
The Thermoelectric Power Generation Device uses the ambient air for cooling. It has no moving parts and can be easily retrofitted on to an existing steam or hot water pipe.
Depicted in
Figure 1, the generator assembly consists of mirrored generators mounted directly opposite each other on the pipe. Steel hot blocks conform to the surface of the hot pipe and provide a transition surface for the flat thermoelectric modules. Thermal grease interfaces enhance the heat transfer and provide some protection against galvanic corrosion due to the dissimilar materials. Three thermoelectric modules (TEMs) are wired in series. The cooling is enhanced by a copper heat pipe that creates the cold block.
The authors used Laird PB23 Series thermoelectric modules (TEMs) that are commercially marketed as solid-state heat pumps. A temperature difference on opposite sides of the modules produces electricity [
2,
4]. Thermoelectric modules are voltage sources like photovoltaic cells. Therefore, the voltage is additive, but the amperage remains fixed when wired in series. When wired in parallel the amperage increases while the voltage is approximately the average of the units [
2,
5,
6]. Carnot efficiency in this temperature range is 30%. Using Laird Tech TEG Modeling Software the efficiency of the thermoelectric system was 2.6% using these measurements [
6]. The second law efficiency (actual over Carnot) is therefore 8.6%. The average Seebeck Coefficient was 0.42 V/°C for six TEMs in series.
For comparison purposes, each TEM produces 1 W of useable power at these temperatures. Thermoelectric power measurements will be in watts for this paper.
The author’s steam pipe test bed, produces steam temperatures up to 160 °C. The ambient is conservatively measured at 30 °C for data collection purposes. The resultant delta T of 130 °C produces 31.2 V open circuit and 0.89 A, using a pair of mirrored generators that are attached to a new 3 inch steam pipe
The authors successfully powered two microcontroller based security cameras, using both cellular connectivity and wireless LAN [
7]. A Calliope2SP robot was charged by a 12
V 7
Ah lead acid battery that was trickle charged by the thermoelectric generator [
8]. The system also simultaneously recharged a previously drained second identical battery.
2.2. Iceland Test Bed
In Iceland the thermoelectric generators were attached outdoors to an old galvanized pipe with a surface temperature of up to 140 °C from a geothermal steam borehole line at the Agricultural University of Iceland in Hveragerdi.
The generators were placed in adjoining protective sheds and attached to the outside wall of an existing green house as shown in
Figure 2. The open areas of these sheds were covered by 2 cm wire mesh to prevent vandalism and vermin. Twin wall clear Polycarbonate Sheet roofs also shielded the generators from precipitation. The authors’ open field heated agricultural test beds were 10 m distant. They were approximately one meter lower in elevation.
The total voltage of the three units in series after 9 months of exterior exposure was 39.2 (open circuit) and the amperage was 0.64 (short circuit). The output in parallel was 13.4 V (open circuit) and 1.81 A (short circuit). The camera was mounted on a wood beam that is attached to the protective sheds at a height of 3 m.
2.3. Thermoelectric Power Production in Iceland
The power produced was approximately 6 W using the calculations established in the authors’ previous papers [
2,
5,
6].
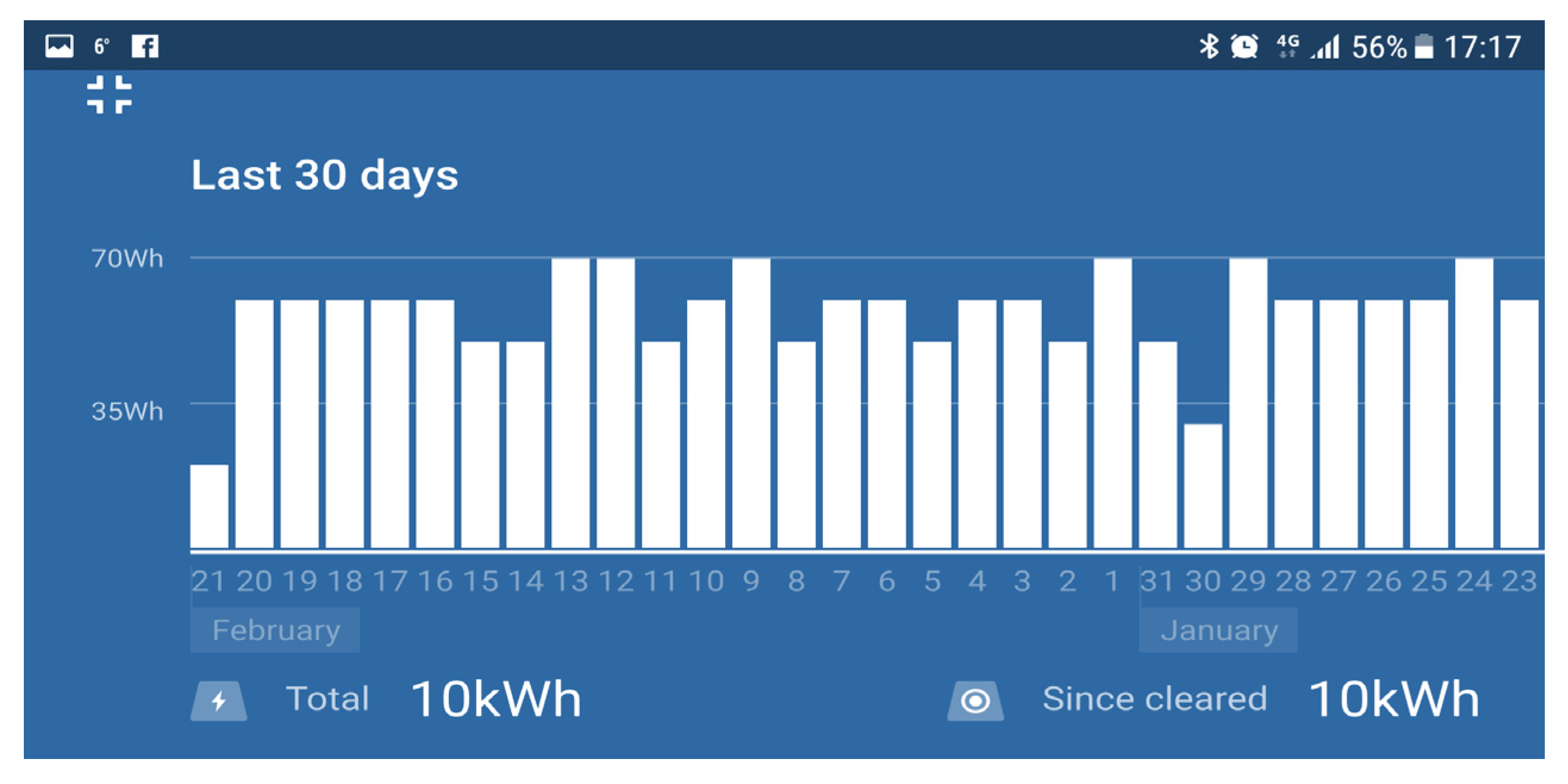
Figure 3 shows the steady state performance of the generators over 30 days. The dips in power production could relate to higher ambient temperatures or periods when the steam was turned off.
2.4. Router, Charge Controller, and Camera Selection
A Sierra Wireless, Richmond, Canada, AirLink RV50 Industrial LTE Gateway router uses approximately 1 W in standby mode and a low voltage disconnect that prevents battery depletion. The system used the surplus power produced by the thermoelectric generator for trickle charging a BIGBAT 12 V, 3.2 Ah lead-acid battery with a Phocos, Ulm, Germany, CA14-2.2. Solar Charge Controller [
9]. This battery power can be used as a backup, or be discharged in series to increase the voltage [
7]. This also enables amperage increases for peak power levels.
The battery was connected to the charge controller as shown in
Figure 4. The RV50 and the Vivotek IB8369 IP-camera were wired in parallel. The Vivotek IB8369 Network Camera (
www.vivotek.com) operates between −20 °C and 50 °C, has a 2 Megapixel image sensor, a fixed 3.6 mm lens, and a 0.72 kg 74 × 211 × 77 mm ceiling mountable housing. It claims low-light functionality up to 20 m with infrared LEDs. Infrared was disabled on the Vivotek to save additional power. The system trickle charged the battery while the camera was powered and connected by 3G to the web.
Other considerations included image sensor resolution, lens type and adjustability, housing and mounting configuration, and infrared night and low-light functionality.
An Ethernet cable connected the camera to the RV50. A Micro-USB to USB cable was used to access the web application for configuring the RV50 (ACE manager version 4.8.0) on a laptop computer that was running the firmware. DHCP reservation was used to assign a specific IP address to the camera. This ensures that the router assigns the same IP address to the camera every time the camera is detected in the local area network (LAN). The camera IP is of the form 192.168.13.XX as required by the RV50’s interface for Ethernet connected devices. The last two digits are chosen arbitrarily. The Ethernet port on the RV50 was then configured to function as a LAN connection. Port forwarding was enabled. This allows devices from outside the local (router-camera) network to access the camera. Ports can be modified to accommodate more devices on the network, and allow access to those devices if desired. The public and private start ports were set to 80, and the host IP was set to the camera’s IP address. By default, the camera is on port 80.
A computer from another network is then able to remotely view the camera’s live feed by initiating a connection with the RV50 through the RV50’s active WAN IP address.
3. Results
The first successful 3G Thermoelectric powered time coded image was received using a Vodaphone 4G stick. The quality of the system can be seen in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6.
4. Conclusions
The thermoelectric generator can power a 3G webcam surveillance system. Unlike batteries, the thermoelectric generator’s performance benefits from a decreasing ambient temperature. This is an advantage in colder climates such as Iceland.
The video signal could be sent to a server for streaming from a website to prevent numerous simultaneous clients from increasing the power draw.
Optional telemetry capacity for controlling the irrigation and other systems is an option if additional thermoelectric generators are added to the system. Additional generators will permit webcams a lower delta T.
This relatively low power system is a viable option in unique environments where traditional access to the electrical grid is problematic.
The robustness can be increased to eliminate the protective sheds. Additional low power monitoring and control systems that are currently being designed for photovoltaic systems should be investigated as they appear in the marketplace.
Author Contributions
R.D. conceived and designed the experiments; R.D. and G.G. performed the experiments; R.D., M.T.P., C.S.W., and R.U. analyzed the data; R.U. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; R.D., R.U., C.S.W., G.G., and M.T.P. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support extended by the following organizations and corporations: The Cooper Union for the Advancement of Science and Art, Center for Innovation and Applied Technology, C.V. Starr Research Foundation, Keilir Institute of Technology. Special thanks to: Richard Stock, Anita Raja, Yash Risbud, Melody Baglione, Ashish Pokharel, Mark Epstein, Ruth Nerken, Gudridur Helgadottir, Sverrir Gudmundsson, Elias Oskarsson, Borkur Hrafnkelsson, Mar Gudmundsson, Fridrik Brekkan, Stefan Sigurdsson, Gísli Páll Pálsson and Aladino Melendez, The authors appreciate the contributions of Center for Innovation and Applied Technology Research Assistants: Christopher E, Jing Jin, SanjevMenon, Di Yi Liu, Daniel Feyman, Alinur Rahim, Justin Jose, James Ngai, Hou Chong Chan, Issei Abraham Yamada, Wei Yan Tin, Chengyin Jiang, Yueyue Li, TaeKoung Lee, Harrison Milne, Romaniya Voloshchuk, Monica Chen, Jordan Selig, and Matthew Cavallaro.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Dell, R.; Wei, C.S.; Foley, W. Enhanced Agricultural Production from an Intensive Bottom Heat System using Waste Geothermal Hot Water and Steam Condensate. Geotherm. Resour. Counc. (GRC) Trans. 2014, 38, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, R.; Unnthorsson, R.; Wei, C.S.; Foley, W. Repurposing Waste Steam and Hot Water to Accelerate Plant Growth in Heated Green Roofs. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–21 November 2013. IMECE2013-65200. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, R.; Wei, C.S.; Sidebotham, G. Thermoelectric Power Generation Device. European Patent No. EP 2,095,440 B1, U.S. Patent No. US 8,829,326 B2, and 9,590,160, Canadian Patent No. CA 2,671,995. 7 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, D.D. Thermocouples: Theory and Properties; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, R.; Wei, C.S.; Sidebotham, G.; Jonsson, M.T.; Unnþórsson, R. A Thermoelectric-Based Point of Use Power Generator for Steam Pipes. In Proceedings of the GRC 35th Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–26 October 2011; pp. 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, R.; Unnthrosson, R.; Wei, C.S.; Sidebotham, G.; Jonsson, M.; Foley, W.; Ginzburg, E.; Paul, S.; Kim, S.; Morris, A. Thermo-Electric-Based Power Generator for Powering Microcontroller Base Security Camera. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Houston, TX, USA, 9–15 November 2012; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012. IMECE2012-89611. pp. 635–642. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, R.; Unnthorsson, R.; Wei, C.S.; Foley, W. Supercapacitors and Battery Configuration for Utilizing a Thermoelectric Generator to Power a Web-Accessible Robotics Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–20 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, R.; Unnthorsson, R.; Wei, C.S.; Foley, W. A Web-accessible Robotics Monitoring System Powered by a Thermoelectric Generator Connected to a Battery. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–20 November 2014. IMECE2014-39077. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, R.; Unnthorsson, R.; Wei, C.S.; Foley, W.; Cady, M.; Dell, M. Web Accessible Security Camera System Independently Powered by a Point of Use Thermoelectric Generator Using Geothermal Pipes as a Heat Source. In Proceedings of the GRC Annual Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 28 September–1 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
| Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).