Standardized Questionnaires for User Experience Evaluation: A Systematic Literature Review †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Systematic Literature Review
3.1. Planning the Review
3.1.1. Research Question
3.1.2. Search Strategy
3.1.3. Study Selection
3.2. Conducting the Review
3.2.1. Identification
3.2.2. Screening
3.2.3. Eligibility
3.2.4. Included
4. Discussion and Results
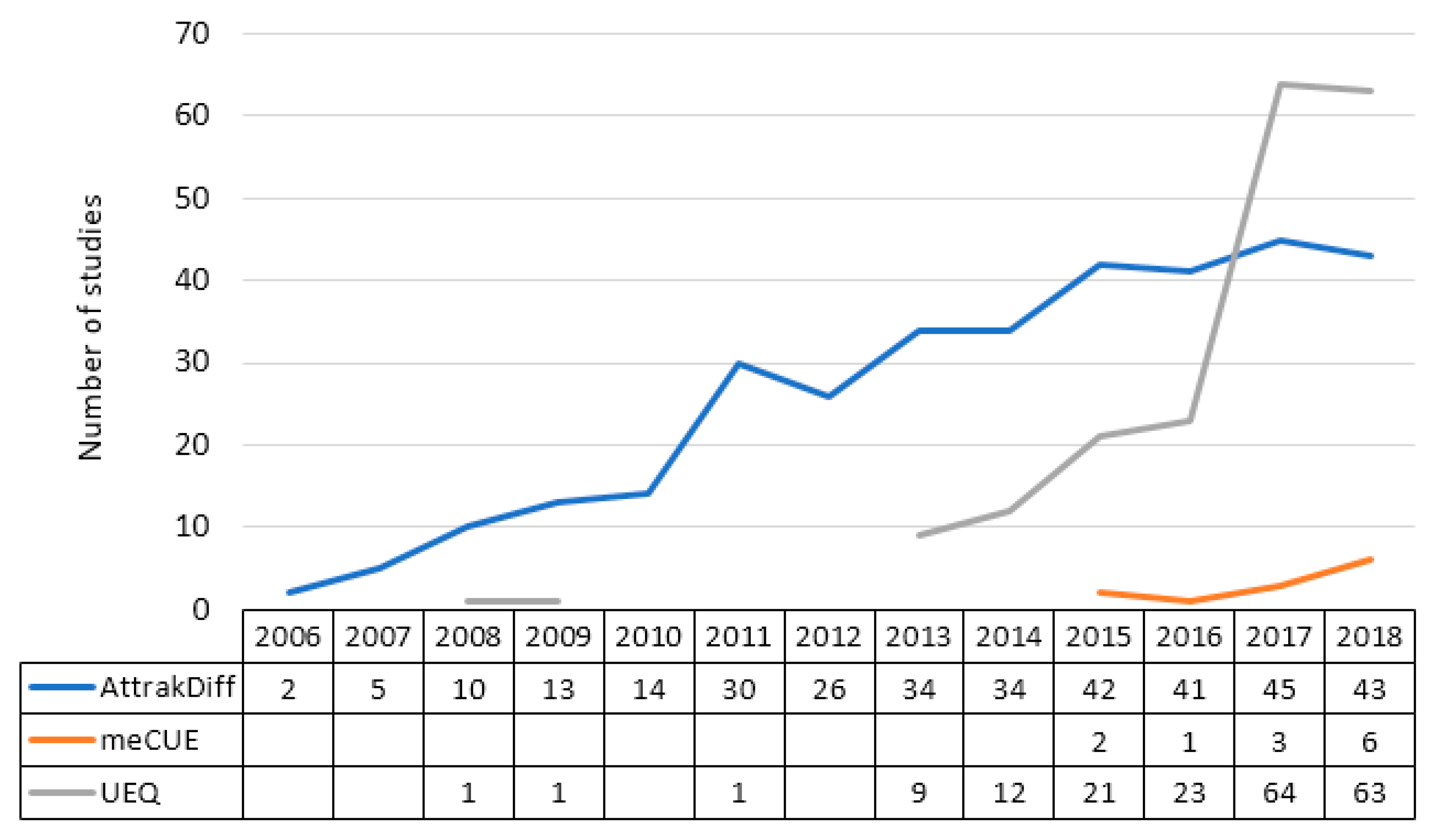
4.1. Most Used Standardized Evaluation Questionnaires
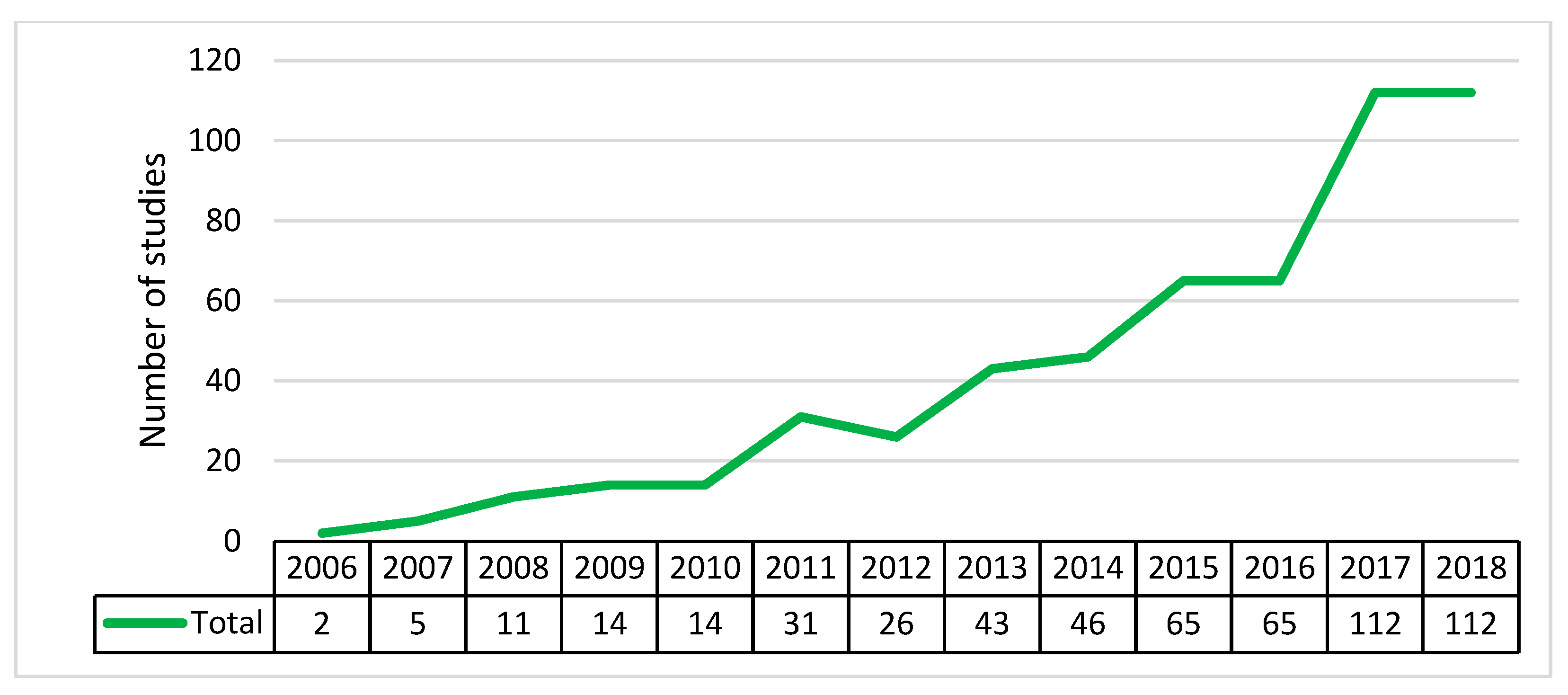
4.2. Uses by Year
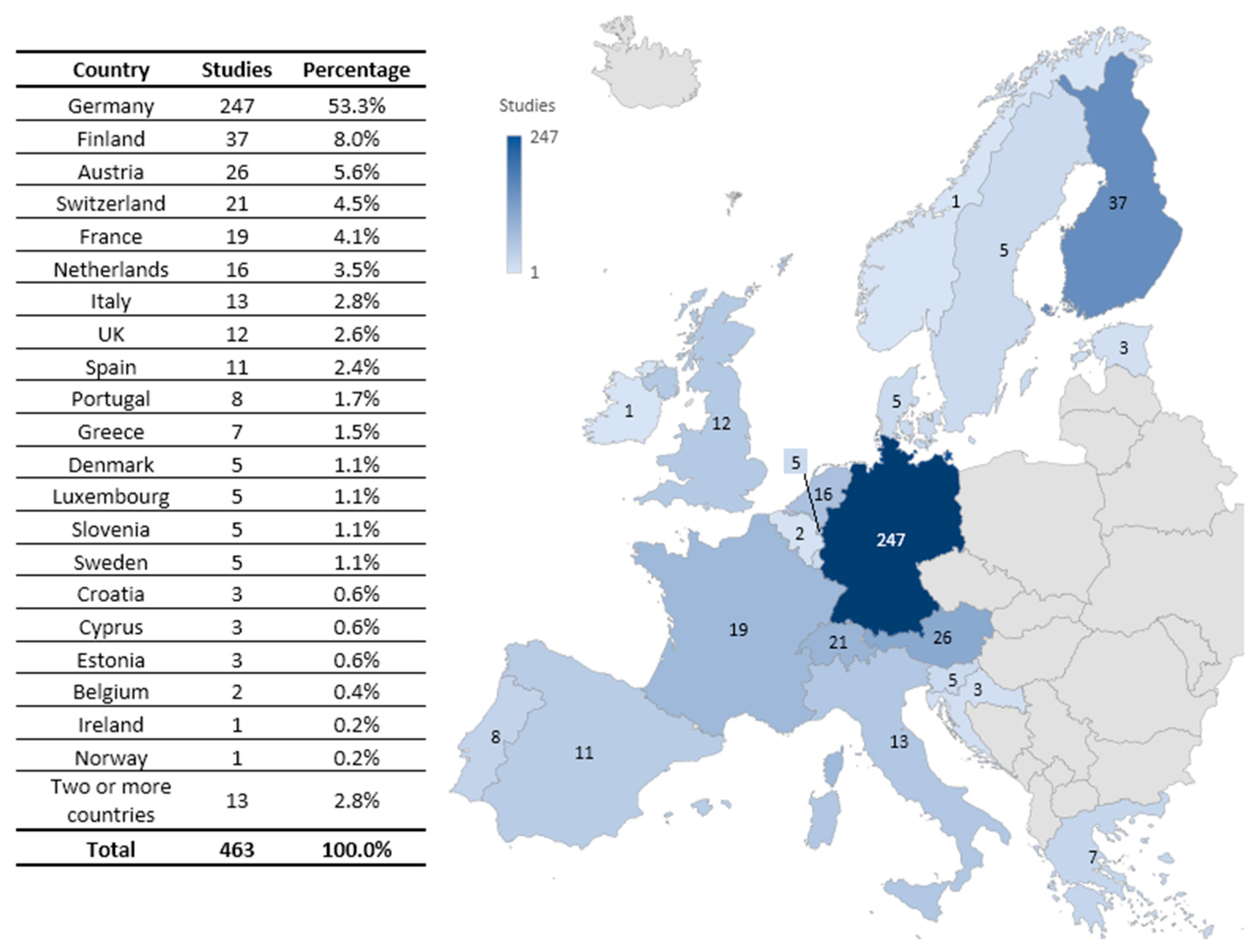
4.3. Geographical Distribution of the Use of Questionnaires
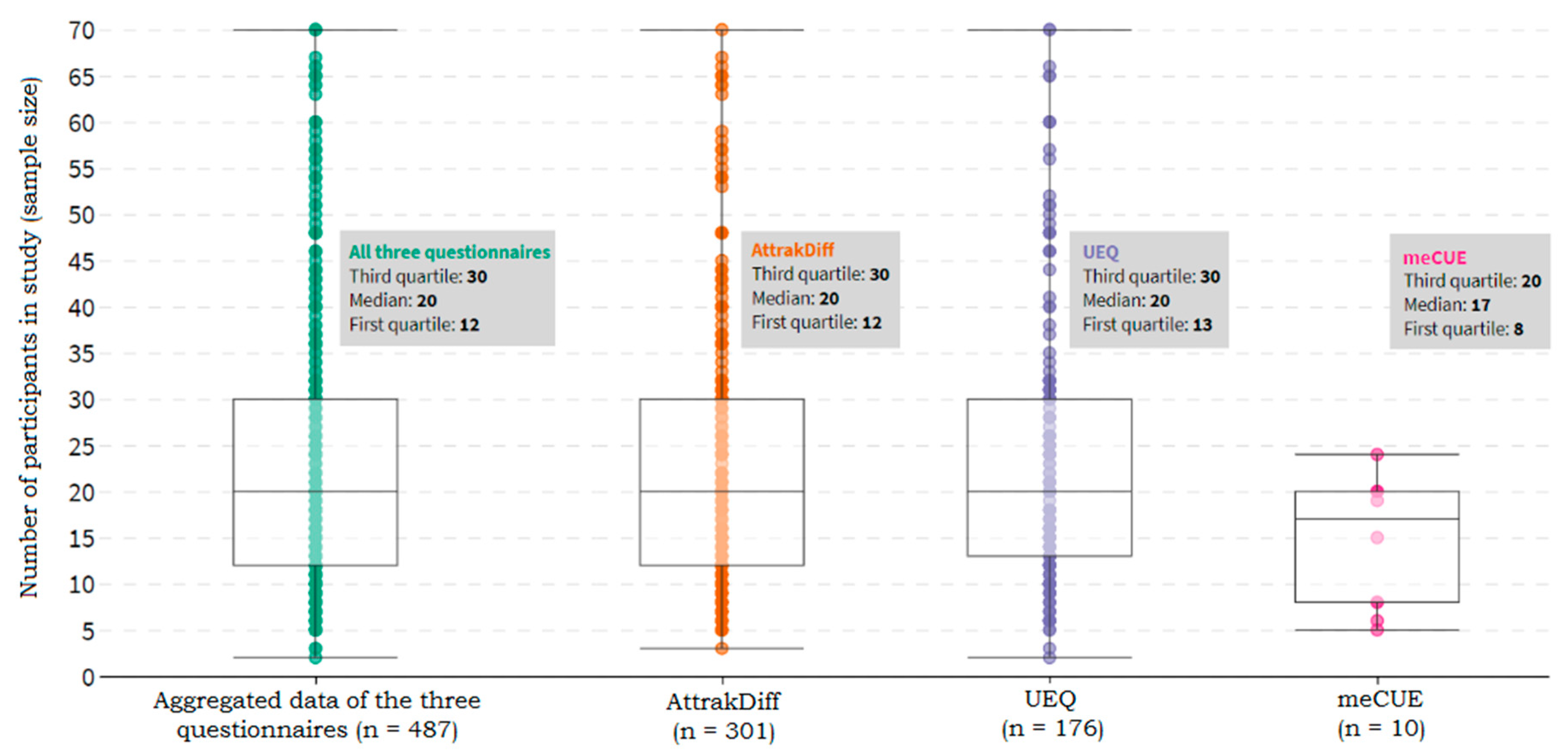
4.4. Sample Size
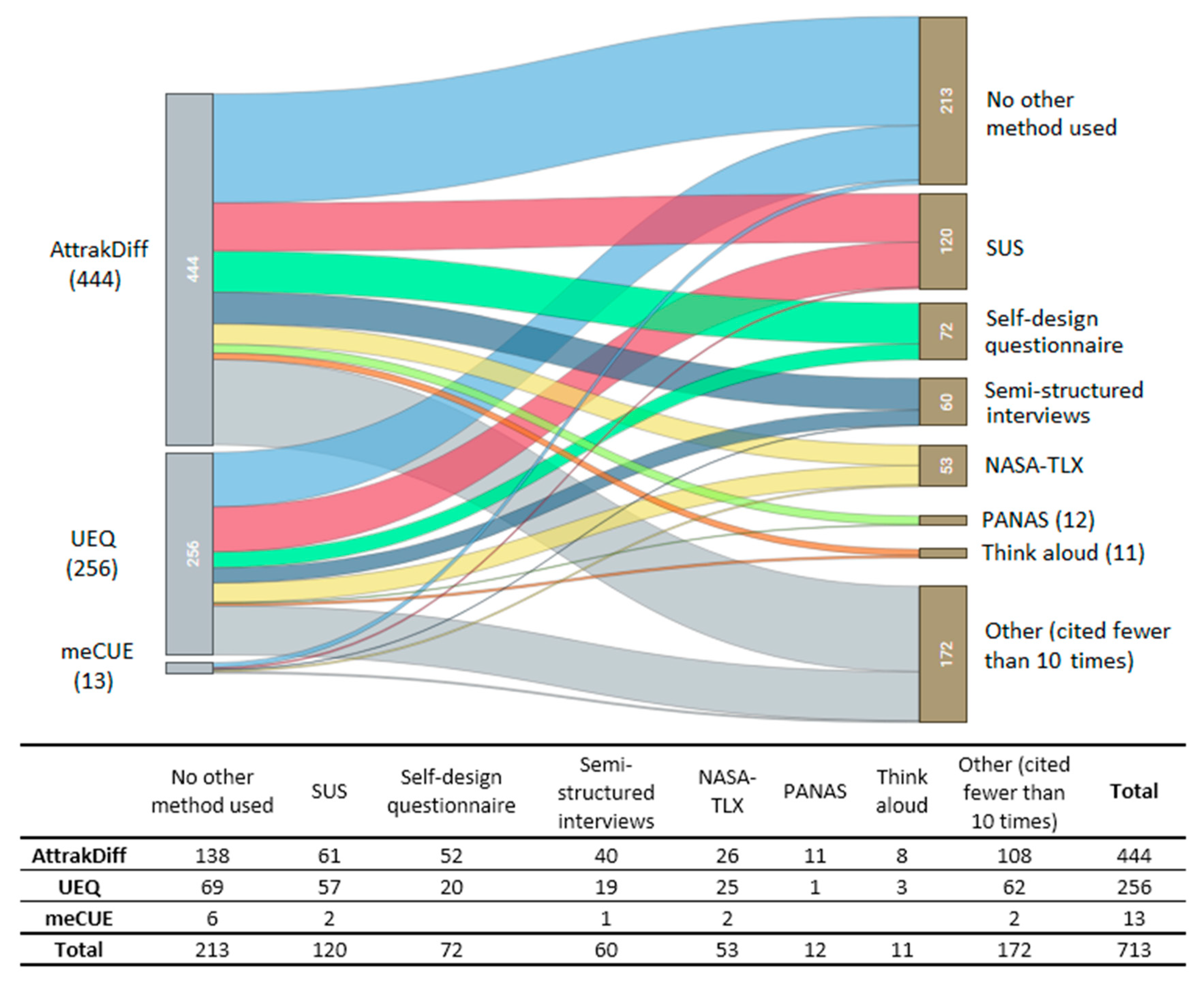
4.5. Association with Other Evaluation Mechanisms
5. Threats to Validity
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schrepp, M.; Hinderks, A.; Thomaschewski, J. Applying the user experience questionnaire (UEQ) in different evaluation scenarios. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer International Publishing: Crete, Greece, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeeren, A.P.O.S.; Law, E.L.-C.; Roto, V.; Obrist, M.; Hoonhout, J.; Väänänen-Vainio-Mattila, K. User experience evaluation methods. In Proceedings of the 6th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction Extending Boundaries - NordiCHI ’10, Reykjavik, Iceland, 16–20 October 2010; p. 521. [Google Scholar]
- Wallach, D.; Conrad, J.; Steimle, T. The UX metrics table: A missing artifact. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer International Publishing: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ISO DIS 9241-210:2010; Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction. International Standardization Organization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Lallemand, C.; Koenig, V. How Could an Intranet be Like a Friend to Me? In Proceedings of the European Conference on Cognitive Ergonomics 2017 - ECCE 2017, Umeå, Sweden, 19–22 September 2017.
- Baumgartner, J.; Sonderegger, A.; Sauer, J. No need to read: Developing a pictorial single-item scale for measuring perceived usability. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2019, 122, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, Y.; Hergeth, S.; Naujoks, F.; Krems, J.F. How Usability Can Save the Day - Methodological Considerations for Making Automated Driving a Success Story. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 23–25 September 2018; pp. 278–290. [Google Scholar]
- Klammer, J.; van den Anker, F.W.G. Design, User Experience, and Usability: Users, Contexts and Case Studies; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 10920. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, C.L.B.; Furtado, E.S. A systematic review about user experience evaluation. In Design, User Experience, and Usability: Design Thinking and Methods; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9746, pp. 445–455. [Google Scholar]
- Ten, A.C.; Paz, F. A systematic review of user experience evaluation methods in information driven websites. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer International Publishing: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017; Volume 10288, LNCS; pp. 492–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lallemand, C.; Koenig, V. How Could an Intranet Be Like a Friend to Me?: Why Standardized UX Scales Don’T Always Fit. In In Proceedings of the European Conference on Cognitive Ergonomics 2017, Umea, Sweden, 19–22 September 2017; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Likert, R. A Technique For The Measurement of Attitude; Archieves of Psychology: New York, NY, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Osgood, E.C. The Nature and measurement of meaning. Psychol. Bull. 1952, 49, 197–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronier, G.; Lallemand, C.; Chauvet, A. Mesurer la formation de la première impression d’une interface à l’aide du test des 5 secondes; Huitième Colloque de Psychologie Ergonomique (EPIQUE): Aix-en-Provence, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hassenzahl, M.; Burmester, M.; Koller, F. AttrakDiff: Ein Fragebogen zur Messung wahrgenommener hedonischer und pragmatischer Qualität. In Mensch & Computer 2003: Interaktion in Bewegung; B. G. Teubner: Stuttgart, Germany, 2003; pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz, B.; Held, T.; Schrepp, M. Construction and Evaluation of a User Experience Questionnaire. Comput. Sci. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minge, M.; Riedel, L. meCUE – Ein modularer Fragebogen zur Erfassung des Nutzungserlebens [meCUE - A modular questionnaire for capturing the user experience]. Mensch und Comput. 2013, 9, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies that Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar]
- Minge, M.; Thüring, M.; Wagner, I.; Kuhr, C.V. The meCUE Questionnaire: A Modular Tool for Measuring User Experience; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Minge, M.; Thüring, M. The MeCUE Questionnaire (2.0): Meeting Five Basic Requirements for Lean and Standardized UX Assessment. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2018, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–20 July 2018; Volume 10918, pp. 451–469. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, I.; Minge, M. The gods play dice together: The influence of social elements of gamification on seniors’ user experience. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer International Publishing: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pollmann, K.; Sinram, V.; Fronemann, N. Design. Can We Distinguish Pragmatic from Hedonic User Experience Qualities with Implicit Measures? In Proceedings of the HCI International 2018, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–20 July 2018; Volume 10918, pp. 509–527. [Google Scholar]
- Mõttus, M.; Lamas, D.; Kukk, L. Aesthetic Categories of Interaction: Aesthetic Perceptions on Smartphone and Computer. In Proceedings of the 2017 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, Prague, Czech Republic, 3–6 September 2017; Volume 11, pp. 1249–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M. A Data-Driven Knowledge Acquisition System: An End-to-End Knowledge Engineering Process for Generating Production Rules. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 15587–15607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, S. An Evaluation of a Smart-Phone-Based Menu System for Immersive Virtual Environments. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Symp. 3D User Interfaces, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 29–30 March 2014; pp. 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt, S.; Pick, S.; Leithold, F.; Hentschel, B.; Kuhlen, T. Extended Pie Menus for Immersive Virtual Environments. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2013, 19, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
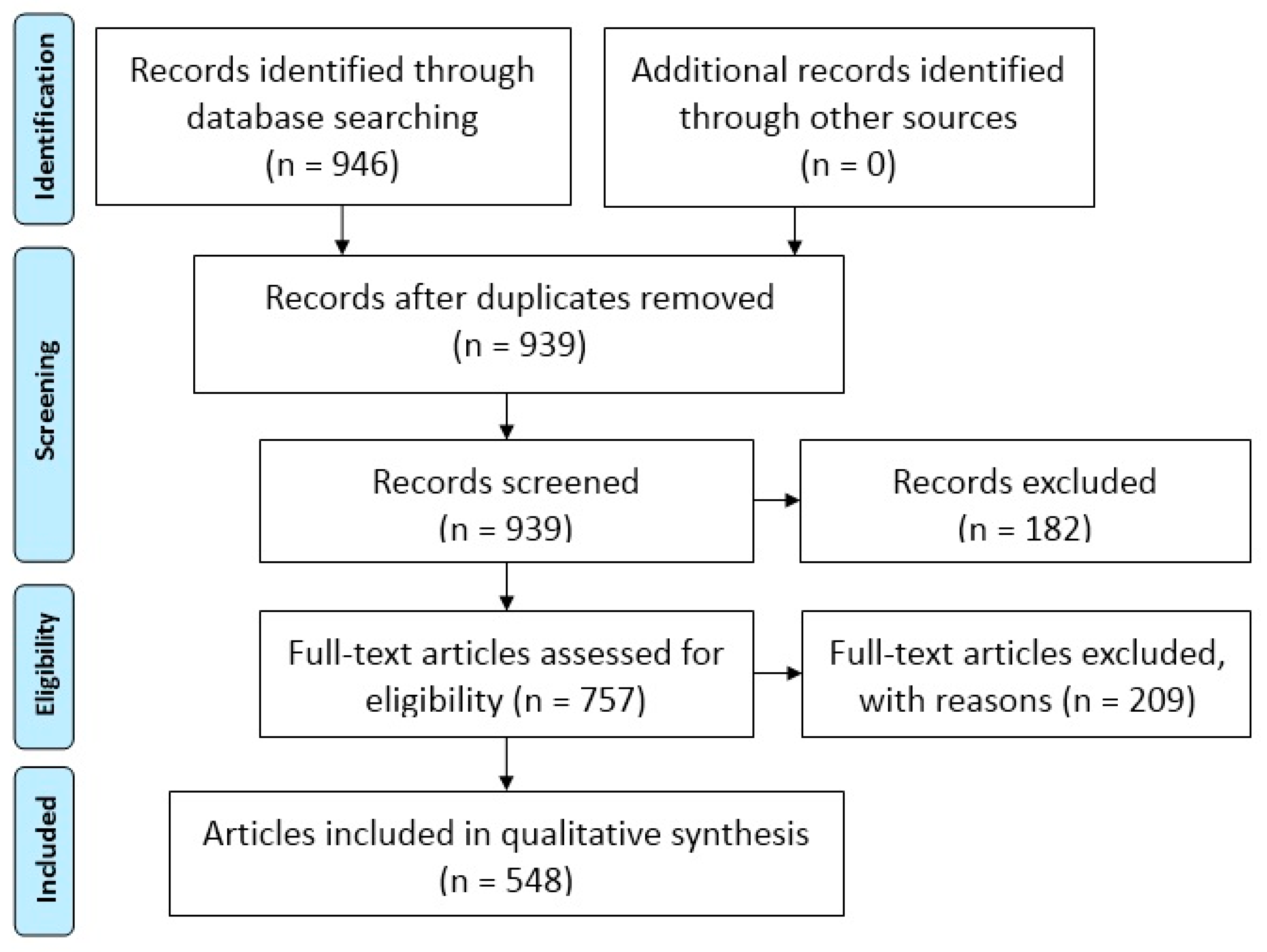
| Source | Query Result | Title and Abstract Reviewed | Title and Abstract Included | Full Paper Reviewed | Full Paper Included (*) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM | 351 | 348 | 304 | 304 | 234 a | |
| IEEE Xplore | 145 | 144 | 132 | 132 | 94 b | |
| Springer Link | 343 | 340 | 250 | 250 | 166 c | |
| Science Direct | 107 | 107 | 71 | 71 | 54 d | |
| Total | 946 | 939 | 757 | 757 | 548 | |
| Percentage | 100.0% | 99.3% | 80.0% | 80.0% | 57.9% | |
| Questionnaire | AttrakDiff | UEQ | meCUE | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uses | 341 | 200 | 12 | 553 |
| Percentage | 61.6% | 36.2% | 2.2% | 100% |
| Questionnaire | Europe | Asia | North America | South America | Oceania | More than one Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AttrakDiff | 303 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 7 |
| UEQ | 150 | 25 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| meCUE | 10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total | 463 | 33 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 10 |
| Percentage | 84.0% | 6.0% | 3.6% | 2.7% | 1.8% | 1.8% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Oreiro, I.; López, G.; Quesada, L.; Guerrero, L.A. Standardized Questionnaires for User Experience Evaluation: A Systematic Literature Review. Proceedings 2019, 31, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031014
Díaz-Oreiro I, López G, Quesada L, Guerrero LA. Standardized Questionnaires for User Experience Evaluation: A Systematic Literature Review. Proceedings. 2019; 31(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031014
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Oreiro, Ignacio, Gustavo López, Luis Quesada, and Luis A. Guerrero. 2019. "Standardized Questionnaires for User Experience Evaluation: A Systematic Literature Review" Proceedings 31, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031014
APA StyleDíaz-Oreiro, I., López, G., Quesada, L., & Guerrero, L. A. (2019). Standardized Questionnaires for User Experience Evaluation: A Systematic Literature Review. Proceedings, 31(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031014




