Design and Empirical Validation of a LoRaWAN IoT Smart Irrigation System †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design of the System
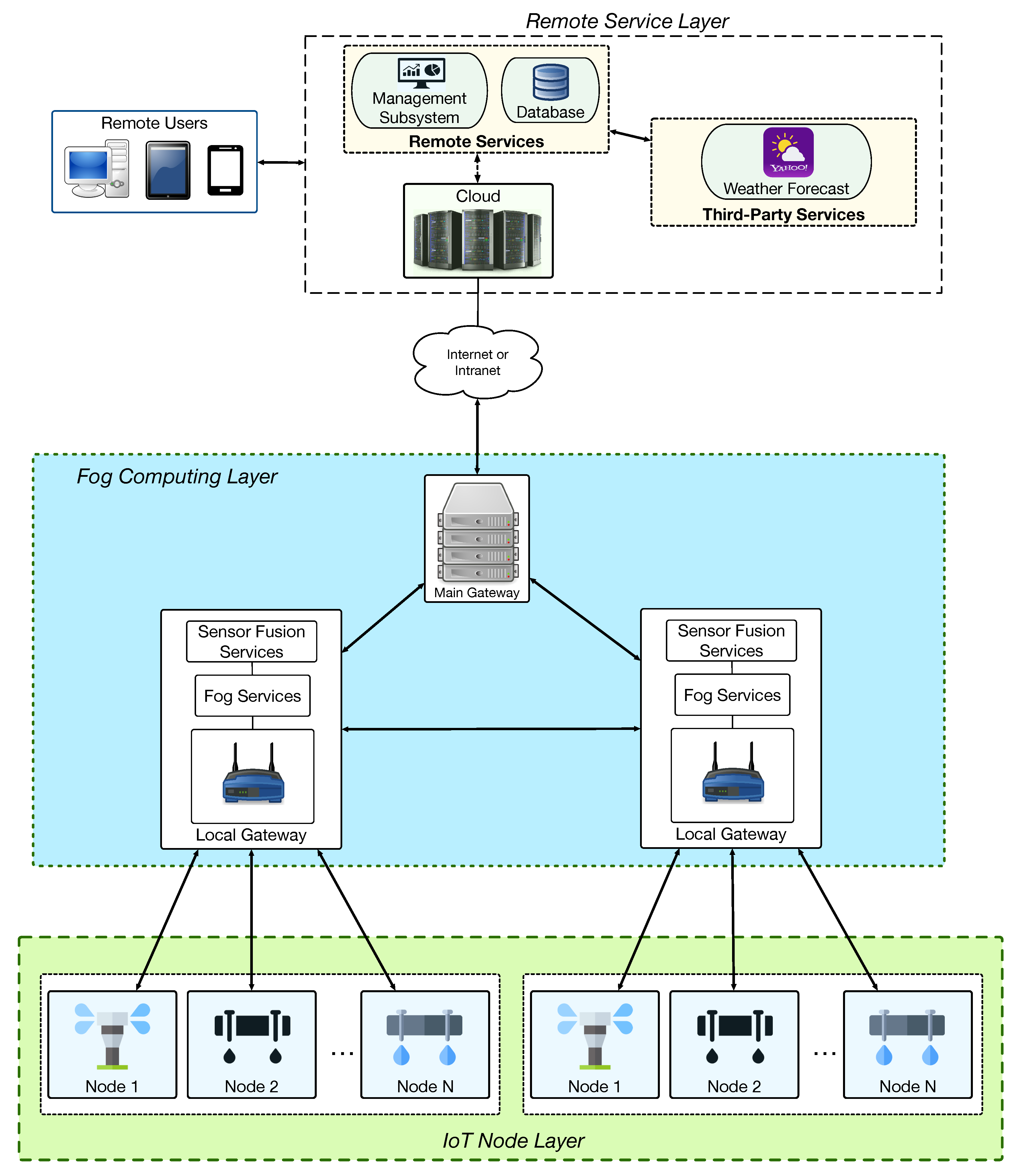
2.1. Communications Architecture
- IoT Layer. It consists of smart irrigation IoT nodes that exchange information with local gateways of the fog computing layer. IoT nodes essentially send information obtained by their sensors and receive remote irrigation commands from either fog computing gateways or the cloud.
- Fog Computing Layer. Its fog computing gateways provide the deployed IoT nodes with fog and sensor fusion services, which are location-aware, reduce latency response, and decrease the cloud communications load [9].
- Remote Service Layer. It collects the data of the system through the cloud, which stores them in a database and processes them to be shown in a user-friendly way to remote users. In addition, the remote services of this layer can make use of third-party services such as weather forecasts when deciding irrigation schedules.
3. Campus Radio Channel Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN Water 2014. Available online: https://www.unccd.int/issues/land-and-drought (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Ayaz, M.; Ammad-Uddin, M.; Sharif, Z.; Mansour, A.; Aggoune, E.H.M. Internet-of-Things (IoT)-Based Smart Agriculture: Toward Making the Fields Talk. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129551–129583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ali, I.; Zakarya, M.; Ahmad, M.; Imran, M.; Shoaib, M. Technology-Assisted Decision Support System for Efficient Water Utilization: A Real-Time Testbed for Irrigation Using Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 25686–25697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Expósito, J.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Castedo, L. VineSens: An Eco-Smart Decision-Support Viticulture System. Sensors 2017, 17, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloria, A.; Dionisio, C.; Simões, G.; Sebastião, P.; Souto, N. WSN Application for Sustainable Water Management in Irrigation Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Limerick, Ireland, 15–18 April 2019; pp. 833–836. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Celaya-Echarri, M.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Castedo, L.; Azpilicueta, L.; Aguirre, E.; Suárez-Albela, M.; Falcone, F.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Design and Experimental Validation of a LoRaWAN Fog Computing Based Architecture for IoT Enabled Smart Campus Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmonov, M.; Gregoretti, F. Design and implementation of a LoRa based wireless control for drip irrigation systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Automation Engineering (ICRAE), Shanghai, China, 29–31 December 2017; pp. 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Lin, S.; Han, J.; Xu, R.; Hou, L. Design and Implementation of Smart Irrigation System Based on LoRa. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Suárez-Albela, M.; Vilar-Montesinos, M. A Fog Computing and Cloudlet Based Augmented Reality System for the Industry 4.0 Shipyard. Sensors 2018, 18, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azpilicueta, L.; Rawat, M.; Rawat, K.; Ghannouchi, F.; Falcone, F. Convergence Analysis in Deterministic 3D Ray Launching Radio Channel Estimation in Complex Environments. ACES J. 2014, 29, 256–271. [Google Scholar]
- Azpilicueta, L.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Aguirre, E.; Vargas-Rosales, C.; León, A.; Falcone, F. Influence of Meshing Adaption in Convergence Performance of Deterministic Ray Launching Estimation in Indoor Scenarios. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2017, 31, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
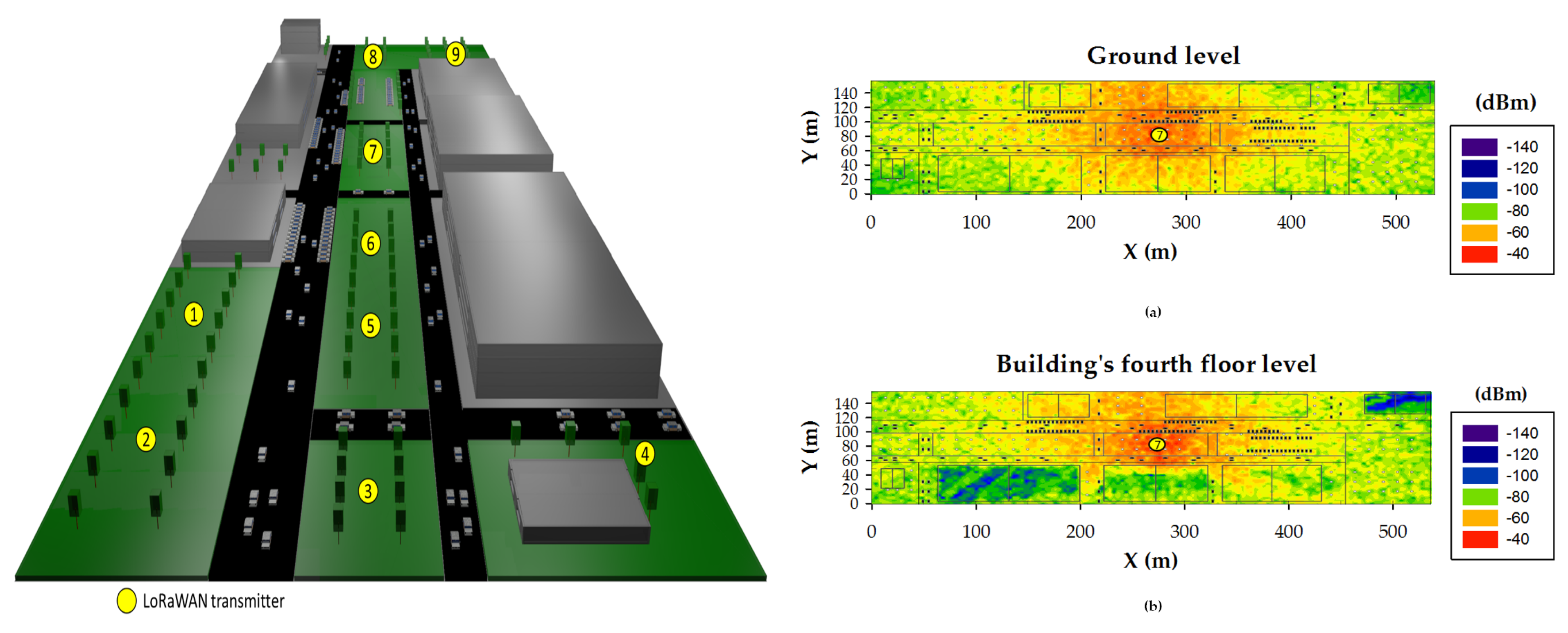
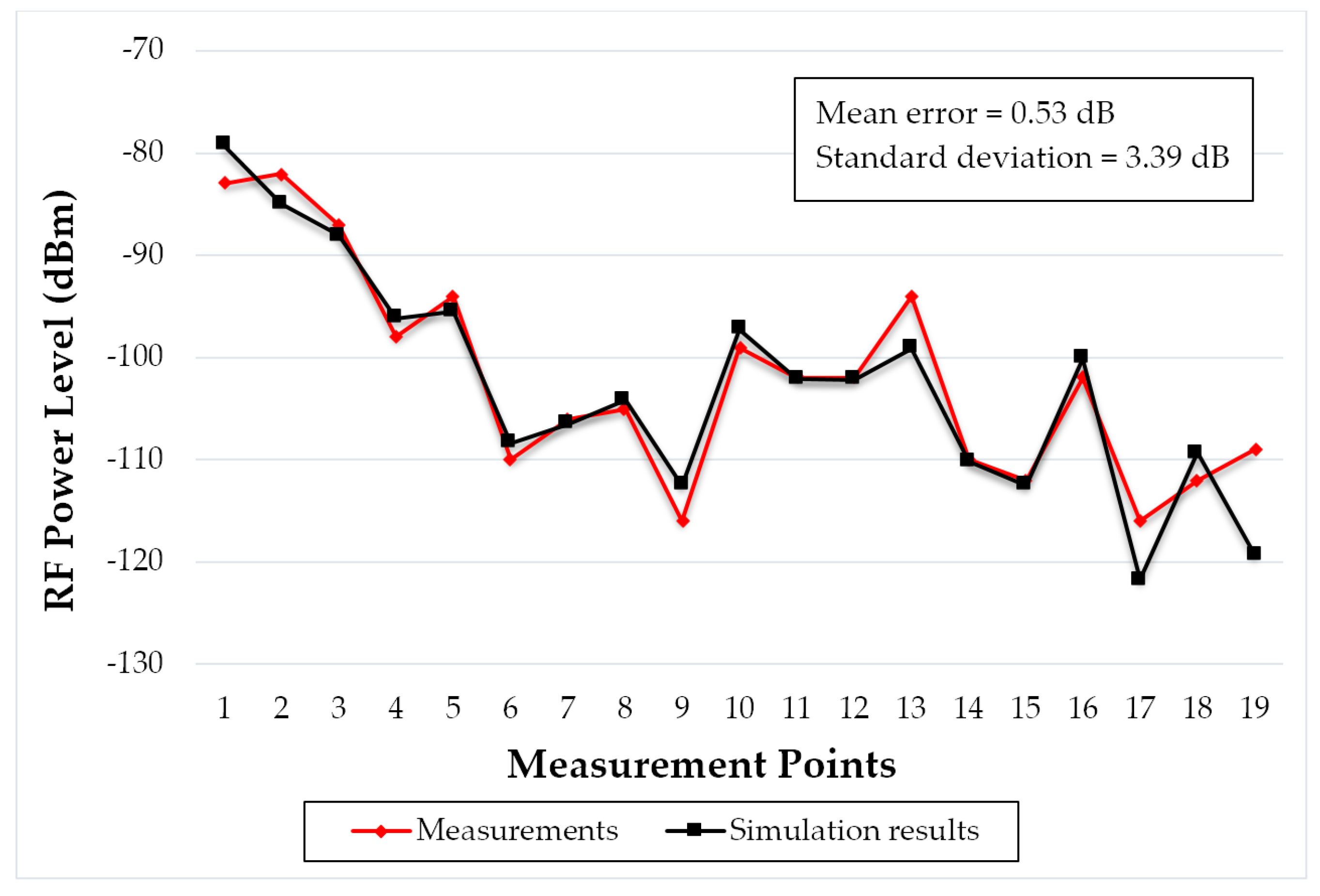
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operation frequency | 868.3 MHz |
| Output power level | 14 dBm |
| Permitted reflections | 6 |
| Cuboid resolution | 4 m × 4 m × 4 m |
| Launched ray resolution | 1¼ |
| Antenna type and gain | Monopole, 0 dBi |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fraga-Lamas, P.; Celaya-Echarri, M.; Azpilicueta, L.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Falcone, F.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Design and Empirical Validation of a LoRaWAN IoT Smart Irrigation System. Proceedings 2020, 42, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-6-06540
Fraga-Lamas P, Celaya-Echarri M, Azpilicueta L, Lopez-Iturri P, Falcone F, Fernández-Caramés TM. Design and Empirical Validation of a LoRaWAN IoT Smart Irrigation System. Proceedings. 2020; 42(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-6-06540
Chicago/Turabian StyleFraga-Lamas, Paula, Mikel Celaya-Echarri, Leyre Azpilicueta, Peio Lopez-Iturri, Francisco Falcone, and Tiago M. Fernández-Caramés. 2020. "Design and Empirical Validation of a LoRaWAN IoT Smart Irrigation System" Proceedings 42, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-6-06540
APA StyleFraga-Lamas, P., Celaya-Echarri, M., Azpilicueta, L., Lopez-Iturri, P., Falcone, F., & Fernández-Caramés, T. M. (2020). Design and Empirical Validation of a LoRaWAN IoT Smart Irrigation System. Proceedings, 42(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-6-06540










