Spin Rate Measurements in Cricket Bowling Using Magnetometers †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
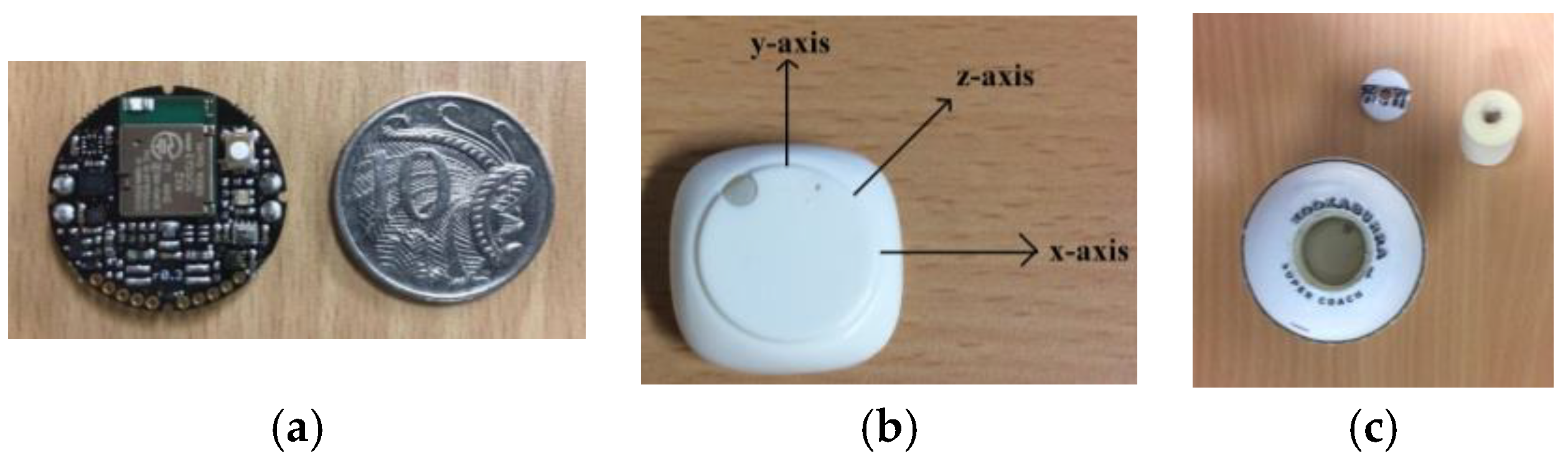
2.1. Instrumented Ball
2.2. IMU and Motion Capture
2.3. Sensor Calibration
3. Results
3.1. Spin Rate Measurement
3.2. Characteristics of the Spin Bowler
3.3. Spin Type Classification
3.4. Biomechanical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, R.D. An overview of cricket ball swing. Sports Eng. 2005, 8, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, H.G.; Shepherd, J.B.; Thiel, D.V.; Worsey, M.T.O. Anytime, anywhere! Inertial sensors monitor sports performance. IEEE Potentials 2019, 38, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, D.; James, D.A.; Thiel, D.V. Bowler analysis in cricket using centre of mass inertial monitoring. Sports Technol. 2009, 2, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doljin, B.; Fuss, F.K. Development of a smart cricket ball for advanced performance analysis of bowling. Procedia Technol. 2015, 20, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MbientLab–Wearable Bluetooth 9-axis IMUs & environmental Sensors. Available online: https://mbientlab.com/ (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Fuss, F.K.; Smith, R.M.; Subic, A. Determination of spin rate and axes with an instrumented cricket ball. Procedia Eng. 2012, 34, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersfield, B. Smart Ball, Locator System and Method Therefor. U.S. Patent US20190168081A1, 6 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jinji, T.; Sakurai, S. Direction of spin axis and spin rate of the pitched baseball. Sports Biomech. 2006, 5, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.; Elliott, B.; Alderson, B.; Lloyd, D.; Foster, D. The off-break and “doosra”: Kinematic variations of elite and sub-elite bowlers in creating ball spin in cricket bowling. Sports Biomech. 2009, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cork, A.; Justham, L.; West, A. Three-dimensional vision analysis to measure the release characteristics of elite bowlers in cricket. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part P J. Sports Eng. Tech. 2013, 227, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, A.J.; Ferdinands, R.E.D.; Sinclair, P.J. The kinematic differences between off-spin and leg-spin bowling in cricket. Sports Biomech. 2016, 15, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C. A unified framework for the prediction of cricket ball trajectories in spin and swing bowling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part P J. Sports Eng. Tech. 2013, 227, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, H.G.; Ӧchsner, A.; Mirnajafizadeh, A.; James, D.A. On the preliminary design of an instrumented ball for sports applications. Hum. Technol. 2016, 1, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa, H.G.; Lee, J.; James, D.A. The inertial sensor: A base platform for wider adoption in sports science applications. J. Fitness Res. 2015, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]







| Type of Spin | Average Peak Central Frequency (Hz) | Average Frequency Range (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| Off-spin | 7.22 | 05–10 |
| Leg-spin | 11.31 | 10–13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, A.; Espinosa, H.G.; Worsey, M.; Thiel, D.V. Spin Rate Measurements in Cricket Bowling Using Magnetometers. Proceedings 2020, 49, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049011
Kumar A, Espinosa HG, Worsey M, Thiel DV. Spin Rate Measurements in Cricket Bowling Using Magnetometers. Proceedings. 2020; 49(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049011
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Aswath, Hugo G. Espinosa, Matthew Worsey, and David V. Thiel. 2020. "Spin Rate Measurements in Cricket Bowling Using Magnetometers" Proceedings 49, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049011
APA StyleKumar, A., Espinosa, H. G., Worsey, M., & Thiel, D. V. (2020). Spin Rate Measurements in Cricket Bowling Using Magnetometers. Proceedings, 49(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049011








