New Strains of Bacteria that Degrade Aromatic Compounds Act as Antagonists of Highly Active Phytopathogens †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Cultivation Conditions
2.2. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of 16S rRNA Genes
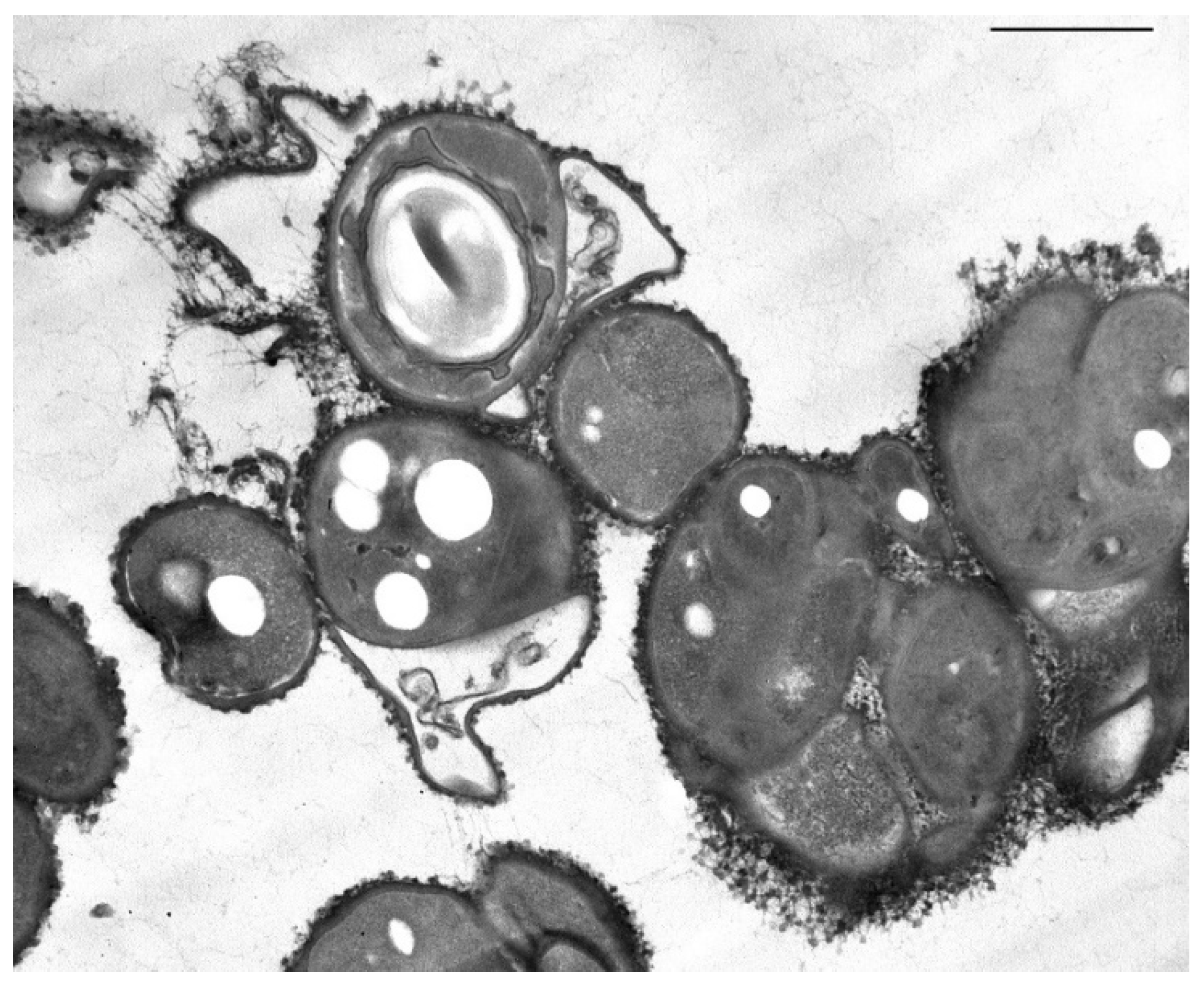
2.3. Microscopy
2.4. Determination of the Antagonistic Activity of Soil Strains against Phytopathogenic Fungi
2.5. Characterization of the Biochemical Properties of the Tested Strains
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antagonistic Activity
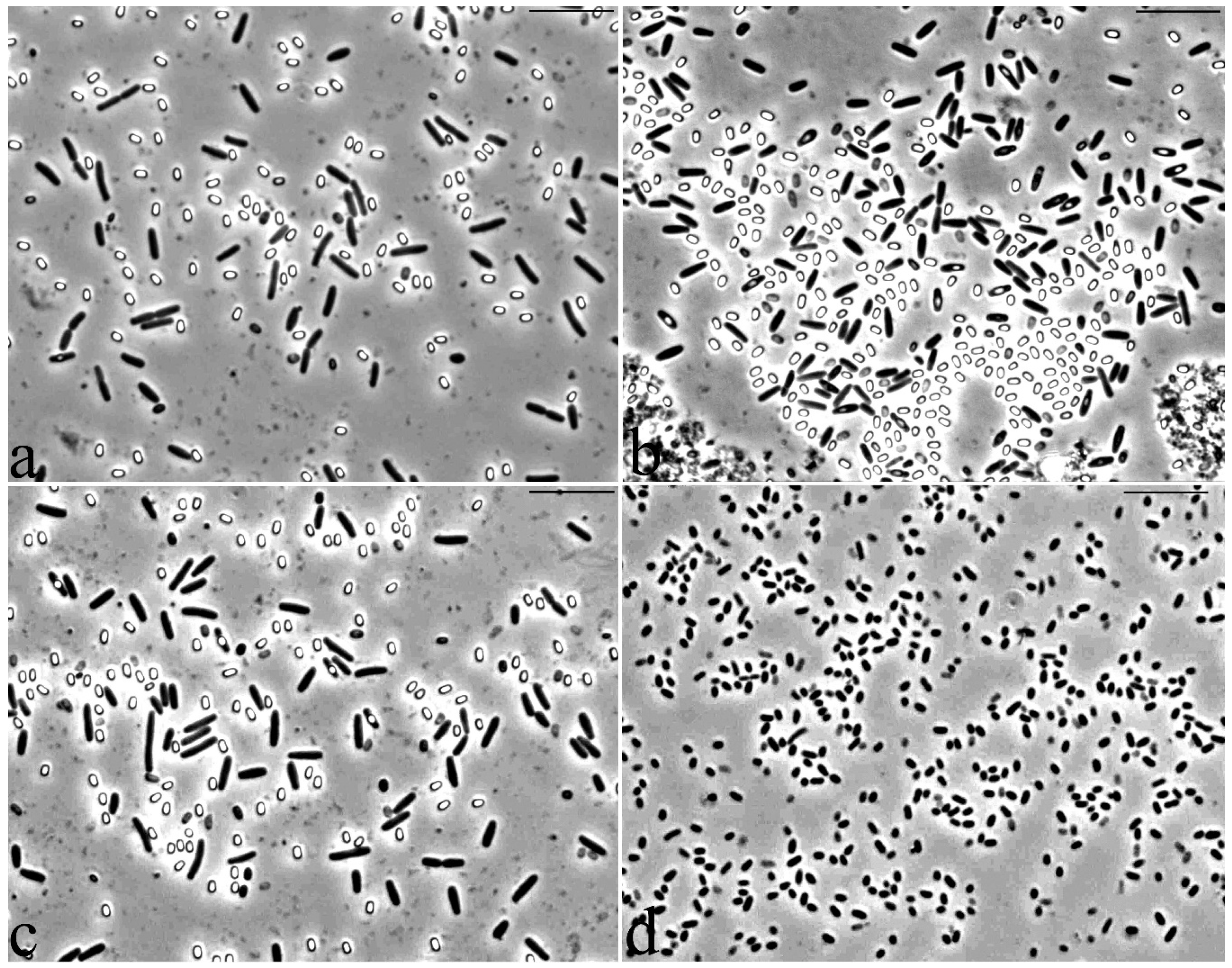
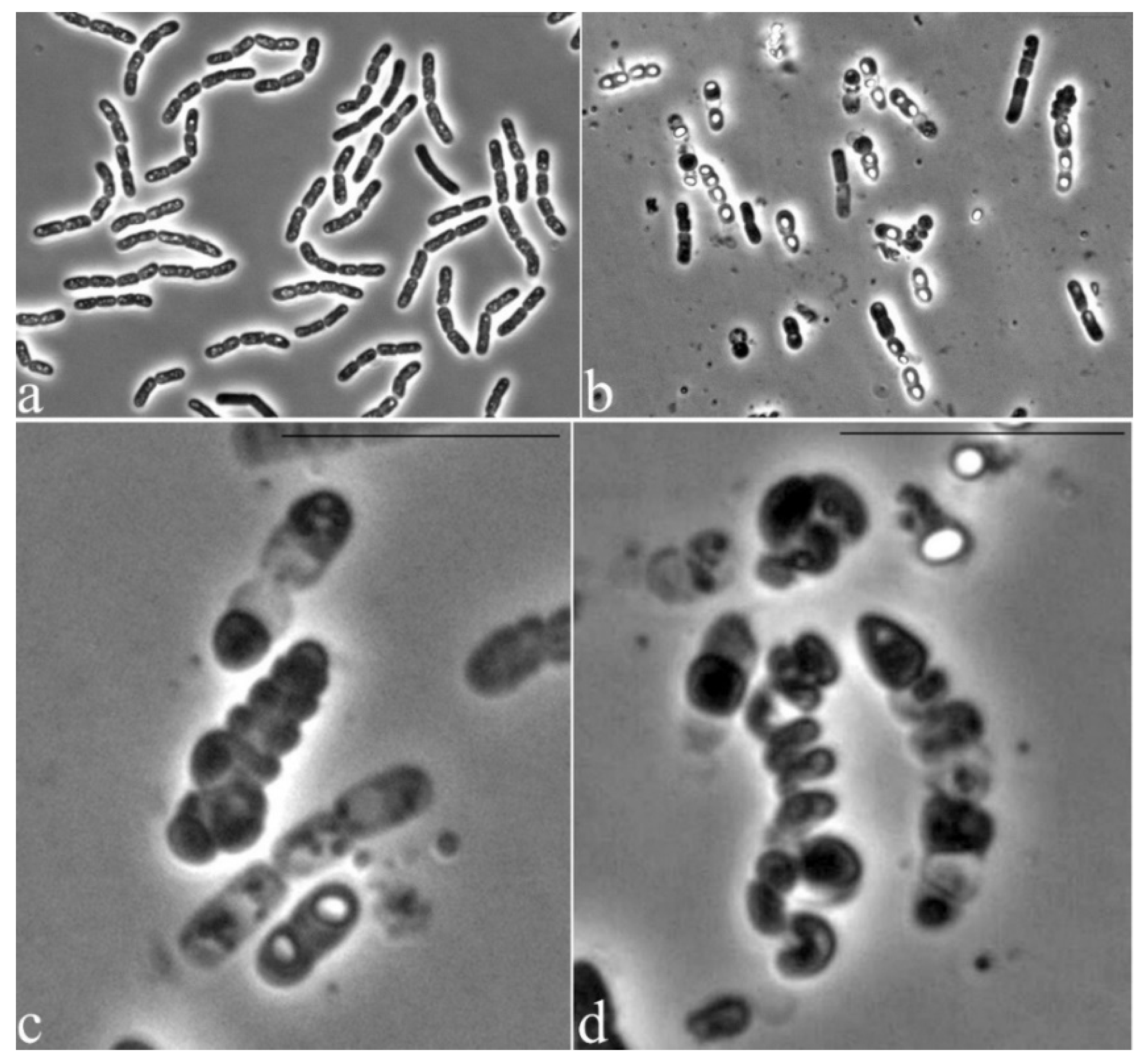
3.2. Microscopic Studies
3.3. Strains Identification
3.4. Biochemical Characteristics of Soil Strains
3.5. Features of the Morphology of Bacillus Aryabhattai 25
4. Conclusions
Ethical Approval
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, R. The metagenomics of soil. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegeye, E.K.; Brislawn, C.J.; Farris, Y.; Fansler, S.J.; Hofmockel, K.S.; Jansson, J.K.; Wright, A.T.; Graham, E.B.; Naylor, D.; McClure, R.S.; et al. Selection, succession, and stabilization of soil microbial consortia. mSystems 2019, 4, e00055–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, N.B.; Maphosa, F.; Morillo, J.A.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Langenhoff, A.A.M.; Grotenhuis, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Smidt, H. Impact of long-term diesel contamination on soil microbial community structure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balderas-Ruíz, K.A.; Bustos, P.; Santamaria, R.I.; González, V.; Cristiano-Fajardo, S.A.; Barrera-Ortíz, S.; Mezo-Villalobos, M.; Aranda-Ocampo, S.; Guevara-García, A.A.; Galindo, E.; et al. Bacillus velezensis 83 a bacterial strain from mango phyllosphere, useful for biological control and plant growth promotion. AMB Express 2020, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamalero, E.; Favale, N.; Bona, E.; Novello, G.; Cesaro, P.; Massa, N.; Glick, B.R.; del Carmen Orozco-Mosqueda, M.; Berta, G.; Lingua, G. Screening of bacterial endophytes able to promote plant growth and increase salinity tolerance. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.D.; Ambrosini, A.; Passaglia, L.M. Plant growth-promoting bacteria as inoculants in agricultural soils. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucy, M.; Reed, E.; Glick, B.R. Applications of free living plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2004, 86, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, S.; Kerry, R.G.; Das, G.; Paramithiotis, S.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Revitalization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for sustainable development in agriculture. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozhemyakov, A.P.; Belobrova, S.N.; Orlova, A.G. Creating and analyzing a database on the efficiency of microbial preparations of complex action. Agric. Biol. 2011, 3, 112–115. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zhukov, V.A.; Shtark, O.Y.; Borisov, A.Y.; Tikhonovich, I.A. Breeding to improve symbiotic effectiveness of legumes. In Plant Breeding from Laboratories to Fields; Andersen, S.B., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 167–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; p. 479. [Google Scholar]
- Ownley, B.H.; Weller, D.M.; Thomashow, L.S. Influence of in situ and in vitro pH on suppression of Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici by Pseudomonas fluorescens 2-79. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematic; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siunova, T.V.; Anokhina, T.O.; Sizova, O.I.; Sokolov, S.L.; Sazonova, O.I.; Kochetkov, V.V.; Boronin, A.M.; Patil, S.G.; Chaudhari, A.B. PGPR Pseudomonas strains promising for the development of bioformulations for plant protection and stimulation. Biotechnologia 2017, 33, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, C.; Bakshi, U.; Mallick, I.; Mukherji, S.; Bera, B.; Ghosh, A. Genome-guided insights into the plant growth promotion capabilities of the physiologically versatile Bacillus aryabhattai strain AB211. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strain | Identification According 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing | Phytopathogen Suppression Zone, mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F. graminearum | R. solani | G. g. tritici | ||
| 3 | P. chlororaphis | 3 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 |
| 18 | B. subtilis | ≤1 | – 1 | – |
| 27 | B. subtilis | ≤2 | – | – |
| 28 | B. subtilis | ≤2 | – | – |
| P. chlororaphis BS1393 | 2 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anokhina, T.O.; Esikova, T.Z.; Abashina, T.N.; Suzina, N.E.; Solyanikova, I.P. New Strains of Bacteria that Degrade Aromatic Compounds Act as Antagonists of Highly Active Phytopathogens. Proceedings 2020, 66, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066002
Anokhina TO, Esikova TZ, Abashina TN, Suzina NE, Solyanikova IP. New Strains of Bacteria that Degrade Aromatic Compounds Act as Antagonists of Highly Active Phytopathogens. Proceedings. 2020; 66(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066002
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnokhina, Tatiana O., Tatiana Z. Esikova, Tatiana N. Abashina, Nataliya E. Suzina, and Inna P. Solyanikova. 2020. "New Strains of Bacteria that Degrade Aromatic Compounds Act as Antagonists of Highly Active Phytopathogens" Proceedings 66, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066002
APA StyleAnokhina, T. O., Esikova, T. Z., Abashina, T. N., Suzina, N. E., & Solyanikova, I. P. (2020). New Strains of Bacteria that Degrade Aromatic Compounds Act as Antagonists of Highly Active Phytopathogens. Proceedings, 66(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066002






