Abstract
Accurate identification of COVID-19 is now a critical task since it has seriously damaged daily life, public health, and the economy. It is essential to identify the infected people to prevent the further spread of the pandemic and to treat infected patients quickly. Machine learning techniques have a significant role in predicting of COVID-19. In this study, we performed binary classification (COVID-19 vs. other types of coronavirus) by extracting features from genome sequences. Support vector machines, naive Bayes, K-nearest neighbor, and random forest methods were used for classification. We used viral gene sequences from the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Resource Database. Experimental results presented show that a decision tree method achieved 93% accuracy.
1. Introduction
Coronaviruses, known to include some of the largest viral genomes (about 30,000 bps in length), are single stranded positive sense RNA viruses [1]. The family of coronaviruses contains four genera, which are alphacoronavirus, betacoronavitus, gammacoronavirus, and recently defined deltacoronavirus. Although alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus are able to infect mammalian hosts, gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus mainly infect avian species [2]. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), which belong to betacoronavirus, are human coronaviruses causing highly patogenic aoutcomes. Both coronaviruses can be transmitted to humans due to their zoonotic nature, and cause symptoms of viral pneumonia, fever, breathing difficulties, etc. [3]. An unrecognized pneumonia disease, which is thought to have originated from a local seafood market in December 2019, caused an outbreak in Wuhan, China. The disease sufficiently diverged from SARS-CoV to be considered a new human-infecting betacoronavirus, and it was named COVID-19, which has been officially named SARS-CoV-2 [1].
Sequence alignment methods, such as BLAST [4] and FASTA [5], perform classification using viral sequencing techniques. These methods are based on the assumption that DNA sequences share common features [6]. Although alignment-based methods are successful in detecting similarities, their application can be challenging in most cases [7]. Analyzing thousands of complete genomes using alignment-based methods is too expensive. To overcome the difficulties of alignment-based methods, alignment-free methods have been introduced [8,9]. Recent studies revealed that machine learning techniques have been applied successfully for virus classification [10,11]. Reyes, Avino, and Kari [10] proposed an open-source supervised alignment-free method operating k-mer frequencies in HIV-1 sequences. They used support vector machines, multilayer perceptron, and logistic regression for classification. They demonstrated classification accuracies over 90% in all cases for full length genome datasets of hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and influenza A viruses. Randhawa, Hill, and Kari [3] proposed a combination of supervised machine learning with digital signal processing for accurate and scalable genome annotation. They mapped genomic sequences into discrete values for applying digital signal processing techniques. They classified plastic genomes of viruses such as dengue and influenza accurately. Reyes et. al. [12] proposed an alignment-free method based on intrinsic genomic signatures delivering highly accurate real-time taxonomic predictions. They used a decision tree method and confirmed this with Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient analyses.
Wang et al. [13] reported that COVID-19 has extremely low CG abundance in its open reading frame. They found that CG reduction in COVID-19 can be achieved by mutating C/G into A/T. Based on this idea, in this study, we used CpG island features to predict the COVID-19 virus. We applied four machine learning techniques—support vector machines, naive Bayes, k-nearest neighbor, and random forest. Results were evaluated on the 2019 New Coronavirus Resource (2019nCoVR) repository [14].
2. Material and Method
In this section, first, we explain how genome sequences were retrieved. Second, we explain how distinguishing features were extracted. Finally, we overview the machine learning algorithms that we used for prediction of COVID-19.
2.1. Dataset
The 2019 Novel Coronavirus Resource (2019nCoVR) by China’s National Center for Bioinformation [14] collects public coronavirus sequences from various databases, including NCBI, NMDC, GISAID, and CNCB/NGDC. We downloaded 1000 available COVID-19 sequences on August 2020. For non-COVID-19 sequences, 2019nCoVR includes alphacoronavirus, betacoronavirus-1, human coronavirus 229E, human coronavirus HKU1, and human coronavirus NL63 species. We downloaded all available 334 human coronavirus sequences not including COVID-19 on August 2020. Properties of the sequences are also given in Table 1. All sequences were complete genome sequences that were about 30 kbp, and host was chosen as Homo sapiens.

Table 1.
Sequence properties. The 2019 Novel Coronavirus Resource (2019nCoVR) naming convention was used.
2.2. Feature Extraction
The choice of the differentiable features is a critical step to improve recognition performance depending on the characteristics of the COVID-19 virus. By using the assumption that SARS-CoV-2 exhibits a strong absence of CpG [13,15], we proposed the use of CpG island features [16,17], extracted by using Equations (1) and (2).
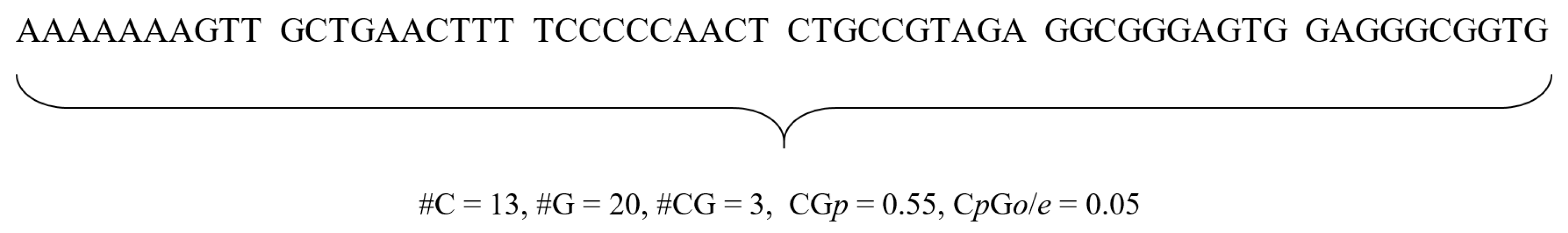
where p(C), p(G), and p(CG) are percentages of C, G, and CG in a sequence. Thus, for a given sequence, we presented the two CpG island features. Figure 1 illustrates an example of computing the features from a sequence.
CGp = p(C) + P(G)
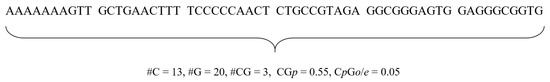
Figure 1.
CpG island features. The values of C, G, and CG are 13, 20, and 3, respectively. Thus, CGp = p(C)+ p(G) = 0.55, and CpGo = p(CG)/(p(C)p(G)) = 0.05.
2.3. Machine Learning Algorithms
The classification was performed to classify the given human genome sequences into COVID-19 or not. Various machine learning techniques can be used to achieve classification. Support vector machines, naive Bayes, K-nearest neighbor, and random forest were used for performing this task.
2.3.1. Support Vector Machines
The support vector machine (SVM) method is a supervised nonparametric statistical learning technique. Therefore, it does not make any assumption on the underlying data distribution. It has various advantages, such as the sparsity of the solution, global optimization, solid theoretical foundation, generalization, and nonlinearity. In the original formulation of SVMs, the method finds an optimal separating hyperplane using a broad set of observations with known labels (i.e., training set) by maximizing the margin between two classes. The term optimal separating hyperplane refers to the decision boundary minimizing misclassifications. The subset of data that lie on the margin is called a support vector. New unlabeled data are allocated to a class based on their geometric position relative to the classifier function. In practice, data points belonging to different class members may overlap one another, which makes linear separability difficult. The soft margin method and the kernel trick are used by adding slack variables to solve the inseparability problem [18].
2.3.2. Naive Bayes
Naive Bayes (NB) is a frequently used machine learning classification algorithm based on Bayes’ theorem, which provides evaluation of explicit probabilities for any hypothesis. The theorem states that:
where P(h) denotes prior probability of hypothesis h, P(T) is prior probability of training data T, P(T|h) is probability of T given h, and P(h|T) is probability of h given T. In order to choose the acceptable hypothesis the most probable one is selected.
2.3.3. K-Nearest Neighbor
K-nearest neighbor (KNN) is known as one of the simplest nonparametric classifiers. It is a lazy learning algorithm and it does not require any learning process. KNN assigns a new observation into a class with the majority of votes based on k-nearest neighbors [19]. In this step, a Euclidean-like distance is used. Optimum amounts of k-values can be defined using a cross-validation technique.
2.3.4. Random Forest
Random forest (RF) classifier is an ensemble machine learning algorithm that is used for classification and works similarly to a decision tree. It uses the bootstrap aggregating method for training. The overall prediction can be done by averaging predictions of all the individual trees. When feature vectors are given as an input, random forest algorithm creates a forest from a subset of randomly selected data with the help of various decision trees. Next, the algorithm sums up the votes of the decision trees to determine the prediction of COVID-19 or not.
3. Results
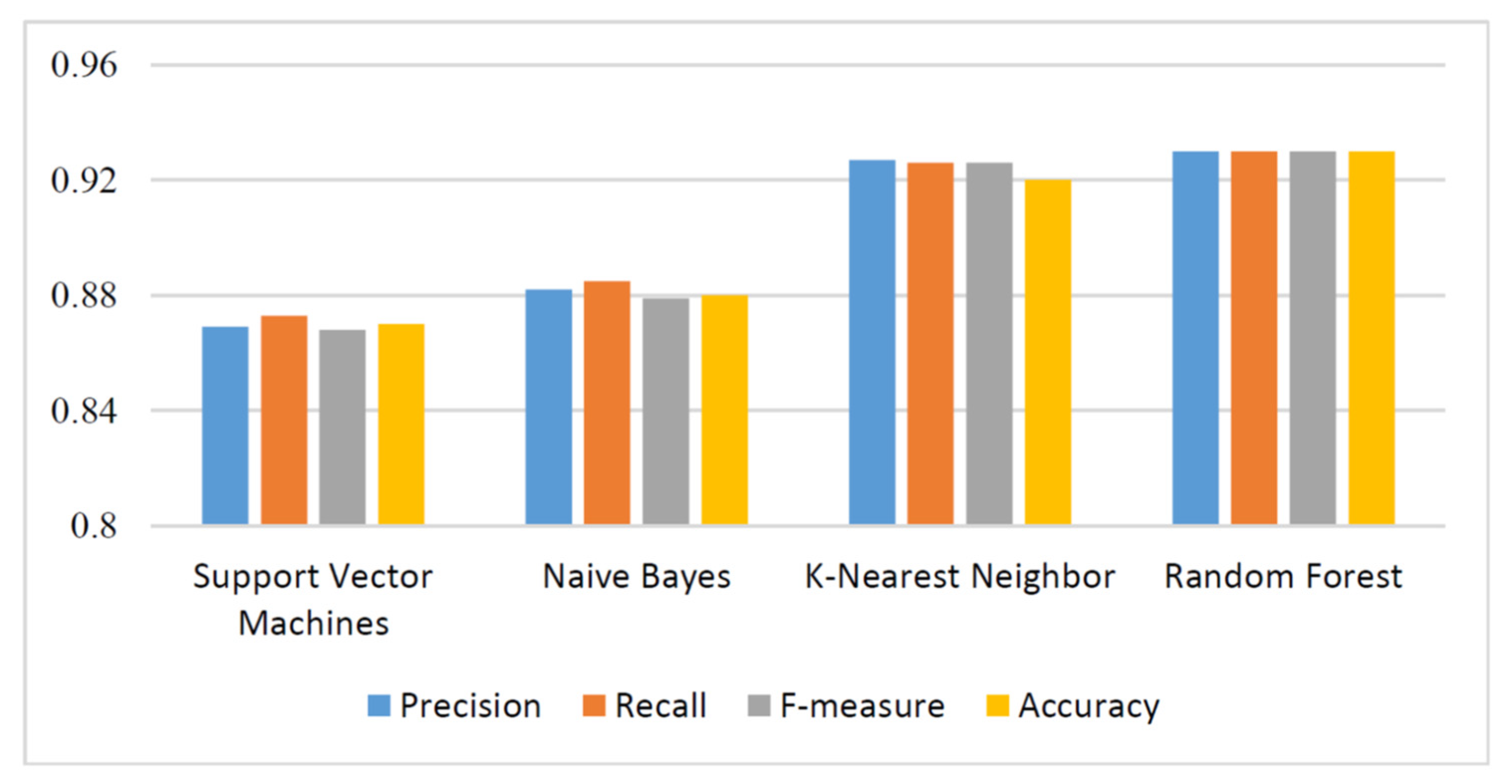
We were interested in the effectiveness of CpG island features in COVID-19 classification. After CpG island features were extracted using Equation 1 and Equation 2, they were classified by using the machine learning techniques, which were support vector machines, naive Bayes, k-nearest neighbor, and random forest. Weka-3-8-4 tool [20] was used to perform machine learning classifications. The numerical results were obtained by using a computer with Linux operating system, 16 GB RAM, and 2.7 GHz processor. Performance of each classifier was measured in terms of precision, recall, F-measure, and accuracy. The tenfold cross-validation strategy was applied and results are reported in Table 2. Moreover, Figure 2 visualizes precision, recall, F-measure, and accuracy values. The maximum classification accuracy was 93%, which was obtained using random forest with CpG island-based features. The machine learning models used in this study with the proposed features predicted COVID-19 sequences in high accuracy. This underlines the efficiency of the proposed method.

Table 2.
COVID-19 classification results (10-fold cross-validation).
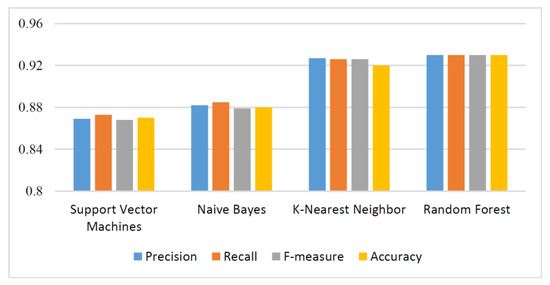
Figure 2.
Evaluation of machine learning methods.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we classified COVID-19 cases from human genome sequences using four machine learning methods—support vector machines, naive Bayes, k-nearest neighbor, and random forest. Experimental results showed k-nearest neighbor and random forest methods with genome-based features gave remarkable results by reaching 92% and 93% accuracy, respectively. In future studies, we will compare COVID-19 sequences coming from humans to other types of coronavirus sequences, such as those coming from musculus, and propose a similarity-based feature.
Funding
These research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was generated by using the publicly available dataset and was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by China National Center for Bioinformation, China.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study that the publicly available dataset was generated.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available dataset was analyzed in this study. This data can be found here (2019nCoVR) https://bigd.big.ac.cn/ncov/?lang=en.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Zheng, B.J.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Zhuang, Z.X.; Cheung, C.L.; Luo, S.W.; Li, P.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Guan, Y.J.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Viruses Related to the SARS Coronavirus from Animals in Southern China. Science 2003, 302, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, W.R. Rapid and Sensitive Sequence Comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 183, 63–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinello, L.; Lo Bosco, G.; Yuan, G.C. Applications of alignment-free methods in epigenomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 15, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinga, S.; Almeida, J. Alignment-free sequence comparison—A review. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kari, L.; Hill, K.A.; Sayem, A.S.; Karamichalis, R.; Bryans, N.; Davis, K.; Dattani, N.S. Mapping the Space of Genomic Signatures. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamichalis, R.; Kari, L.; Konstantinidis, S.; Kopecki, S. An investigation into inter- and intragenomic variations of graphic genomic signatures. Bmc Bioinform. 2015, 16, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis-Reyes, S.; Avino, M.; Poon, A.; Kari, L. An open-source k-mer based machine learning tool for fast and accurate subtyping of HIV-1 genomes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, G.; Hill, K.; Kari, L. ML-DSP: Machine Learning with Digital Signal Processing for ultrafast, accurate, and scalable genome classification at all taxonomic levels. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, G.S.; Soltysiak, M.P.M.; El Roz, H.; de Souza, C.P.E.; Hill, K.A.; Kari, L. Machine learning using intrinsic genomic signatures for rapid classification of novel pathogens: COVID-19 case study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, J.M.; Wang, G.D.; Luo, Z.P.; Yang, L.; Yao, Q.; Chen, K.P. Human SARS-CoV-2 has evolved to reduce CG dinucleotide in its open reading frames. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5165–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-M.; Song, S.-H.; Chen, M.-L.; Zou, D.; Ma, L.-N.; Ma, Y.-K.; Li, R.-J.; Hao, L.-L.; Li, C.-P.; Tian, D.-M.; et al. The 2019 novel coronavirus resource. Yi Chuan 2020, 42, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinka, H.; Milkesa1, A. Unfolding SARS-CoV-2 viral genome to understand its gene expression regulation. Infect Genet Evol. 2020, 84, 104386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponger, L.; Mouchiroud, D. CpGProD: Identifying CpG islands associated with transcription start sites in large genomic mammalian sequences. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, H. A New Promoter Prediction Method using Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Sivas, Turkey, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, D.; Chai, Z.; Yang, L.T.; Liu, X.; Gong, F.; Yang, S. Deep Learning and SVM-Based Emotion Recognition from Chinese Speech for Smart Affective Services. Softw. Pract. Exper. 2017, 47, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, I.; Mues, C. An experimental comparison of classification algorithms for imbalanced credit scoring data sets. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA Workbench. In Online Appendix for “Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques”, 4th ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).