A Design Approach for Simultaneous Cooperative Interception Based on Area Coverage Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Reachable Area of an Interceptor
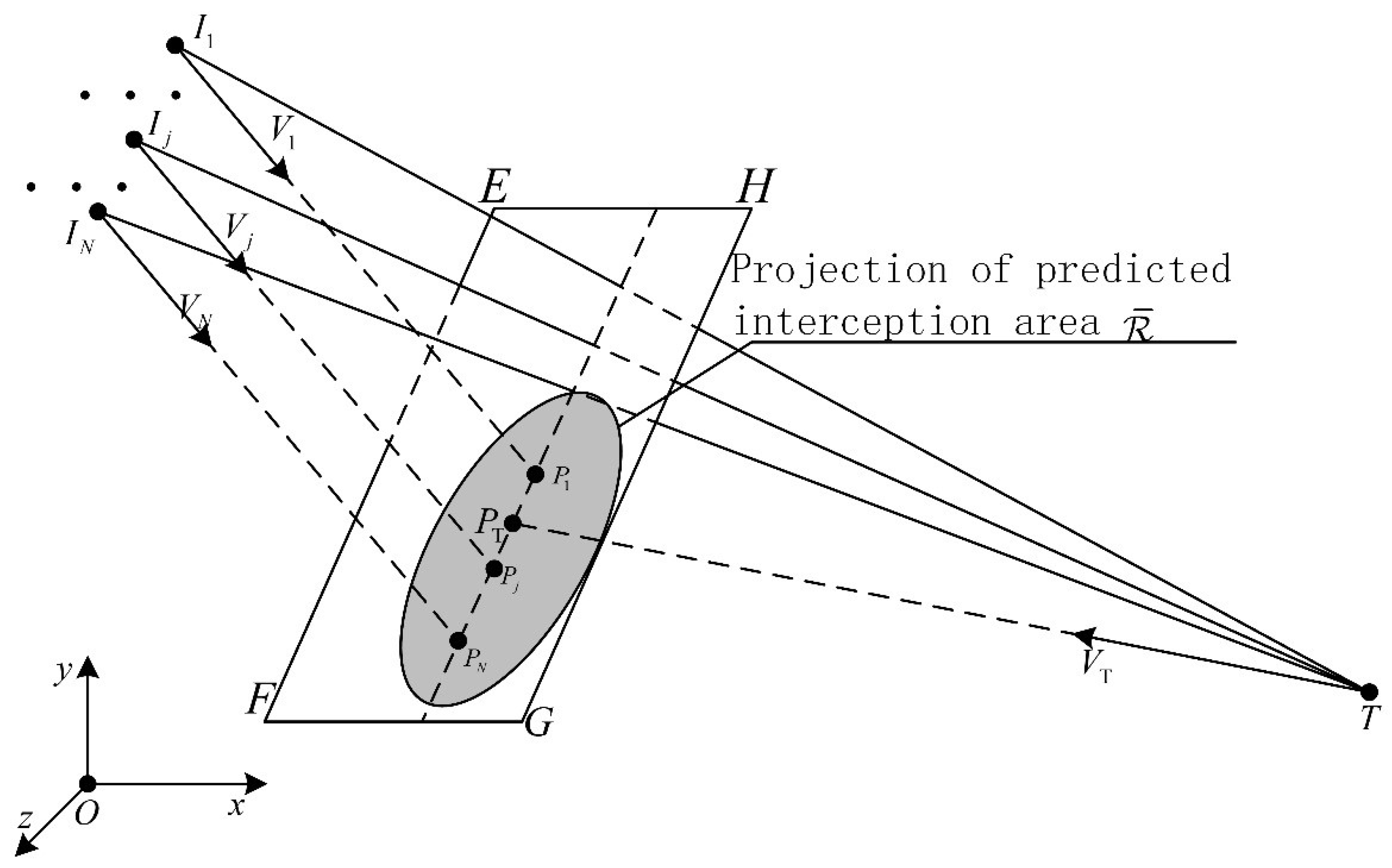
2.2. Predicted Interception Area
2.3. Problem Formulation of Simultaneous Cooperative Interception
3. Simultaneous Cooperative Interception Design Based on Area Coverage Optimization
3.1. Area Coverage Optimization Algorithm for Simultaneous Cooperative Interception
| Algorithm 1 Area coverage optimization algorithm |
|
3.2. Simultaneous Cooperative Interception Design
- Step 1: set the initial number of interceptors to be N0 and let i = k = l = 0;
- Step 2: let N = Ni, i = i + 1;
- Step 3: solve the TPZCs of Ni interceptors based on the area coverage optimization algorithm;
- Step 4: calculate the probability of a successful handover for Ni interceptors according to Equation (40);
- Step 5: if and , then k = Ni-1, and return to step 2; if and , then and stop iterating; if and k = 0, then Ni = 2 l and return to step 2; if and , then and return to step 2.
4. Simulation Experiments and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Projection of the Predicted Interception Area
Appendix B. Convergence Proof of the Area Coverage Optimization Algorithm
References
- Ulybyshev, Y. Terminal Guidance Law Based on Proportional Navigation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2005, 28, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryluk, R.; Shima, T.; Golan, O.M. Shoot-Shoot-Look for an Air Defense System. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Nan, L.; Hu, K.; Niu, B.; He, X. Solving Weapon-Target Assignment Problem using Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 6th Word Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Dalian, China, 21–23 June 2006; pp. 3562–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, G.; Marden, J.R.; Shamma, J.S. Autonomous Vehicle-target Assignment: A Game-theoretical Formulation. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2007, 129, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Ménec, S.; Shin, H.-S.; Markham, K.; Tsourdos, A.; Piet-Lahanier, H. Cooperative allocation and guidance for air defence application. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 32, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, A.; Savelsberg, R. Optimal mid-course doctrine for multiple missile deployment. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 13–16 August 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiyu, Z.; Rui, Z.; Chen, W.; Quanxin, D. Design of Time-constrained Guidance Laws via Virtual Leader Approach. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2010, 23, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, G.; Liu, A. Guidance law with impact time and impact angle constraints. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, X. Sliding mode control based guidance law with impact angle constraint. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oza, H.; Padhi, R. Impact-Angle-Constrained Suboptimal Model Predictive Static Programming Guidance of Air-to-Ground Missiles. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2012, 35, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Rao, S.; Ghose, D. Sliding-Mode Guidance and Control for All-Aspect Interceptors with Terminal Angle Constraints. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2012, 35, 1230–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Compound Cooperative Guidance for High Parabolic Trajectory in Three-Dimensional Space. Aero Weapon. 2021, 28, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Guo, Z.; Lü, M.; Wang, P.; Hanm, Z. Design of a New Guidance Law for Guided Multiple Missiles. Aero Weapon. 2020, 27, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Song, S. Multi-Missile Cooperative Guidance Law for Intercepting Maneuvering Target. Aero Weapon. 2021, 18, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, H.; Shen, X. Research on Cooperative Guidance Law of Multi-Missile Based on Trajectory Super-Real Time Simulation. Aero Weapon. 2021, 28, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A.; Kim, K.; Davis, J.W.; Machiraju, R.; Parent, R. Coverage optimization to support security monitoring. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2007, 31, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Hong, Y. Decentralized sweep coverage algorithm for multi-agent systems with workload uncertainties. Automatica 2013, 49, 2154–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, I.I.; Stipanovic, D.M. Effective Coverage Control for Mobile Sensor Networks with Guaranteed Collision Avoidance. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2007, 15, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polycarpou, M.M.; Yang, Y.; Passino, K.M. A Cooperative Search Framework for Distributed Agents. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control, Mexico City, Mexico, 4 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Pan, J.; Wu, T. Node Coverage Optimization Strategy Based on Ions Motion Optimization. J. Netw. Intell. 2019, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Tsai, P.; Tang, L.; Ji, X. A Coverage Loopholes Recovery Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Inf. Hiding Multimed. Signal Process. 2016, 7, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Dionne, D.; Michalska, H.; Rabbath, C.A. Predictive Guidance for Pursuit-Evsion Engagements Involving Multiple Decoys. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2007, 30, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalauskas, L.L. Nonlinear stochastic programming by Monte-Carlo estimators. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 137, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenberger, D.G.; Ye, Y. Linear and Nonlinear Programming; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 183–212. [Google Scholar]





| Interceptor/Target | Position (km) | Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| I1 | (−87.476, 50.208, 3.5) | (2097.8, −312.8, 100) |
| I2 | (−87.948, 44.812, 3.5) | (2097.8, −312.8, 100) |
| I3 | (−87.948, 44.812, −1.5) | (2097.8, −312.8, 100) |
| I4 | (−87.476, 50.208, −1.5) | (2097.8, −312.8, 100) |
| Target | (100, 30, 0) | (−2720, −0, 0) |
| Interception Cases | Error of Target Position (m) | Error of Target Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | (1000, 1000, 1000) | (100, 100, 100) |
| Case 2 | (−1000, −1000, 1000) | (−100, −100, 100) |
| Case 3 | (−1000, −1000, −1000) | (−100, −100, −100) |
| Case 4 | (1000, 1000, −1000) | (100, 100, −100) |
| Interception Cases | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 2673.2 m | 1534.9 m | 0.24 m | 2029.2 m |
| Case 2 | 1781.9 m | 2394.5 m | 1828.8 m | 0.27 m |
| Case 3 | 0.22 m | 1852.7 m | 2383.8 m | 1712.6 m |
| Case 4 | 2012.9 m | 0.19 m | 1511.7 m | 2625.4 m |
| Interception Cases | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 1665.2 m | 1251.5 m | 1168.7 m | 1427.3 m |
| Case 2 | 1539.1 m | 1273.5 m | 1195.4 m | 1263.1 m |
| Case 3 | 1428.2 m | 1280.2 m | 1214.4 m | 1373.9 m |
| Case 4 | 1569.7 m | 1256.2 m | 1190.7 m | 1521.1 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Liu, K.; Yao, Y.; He, F. A Design Approach for Simultaneous Cooperative Interception Based on Area Coverage Optimization. Drones 2022, 6, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6070156
Wang L, Liu K, Yao Y, He F. A Design Approach for Simultaneous Cooperative Interception Based on Area Coverage Optimization. Drones. 2022; 6(7):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6070156
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Long, Kai Liu, Yu Yao, and Fenghua He. 2022. "A Design Approach for Simultaneous Cooperative Interception Based on Area Coverage Optimization" Drones 6, no. 7: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6070156
APA StyleWang, L., Liu, K., Yao, Y., & He, F. (2022). A Design Approach for Simultaneous Cooperative Interception Based on Area Coverage Optimization. Drones, 6(7), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6070156






